Investigating Effect of Service Encounter, Value, and Satisfaction on Word of Mouth: An Outpatient Service Context
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Model, Literature, and Hypotheses
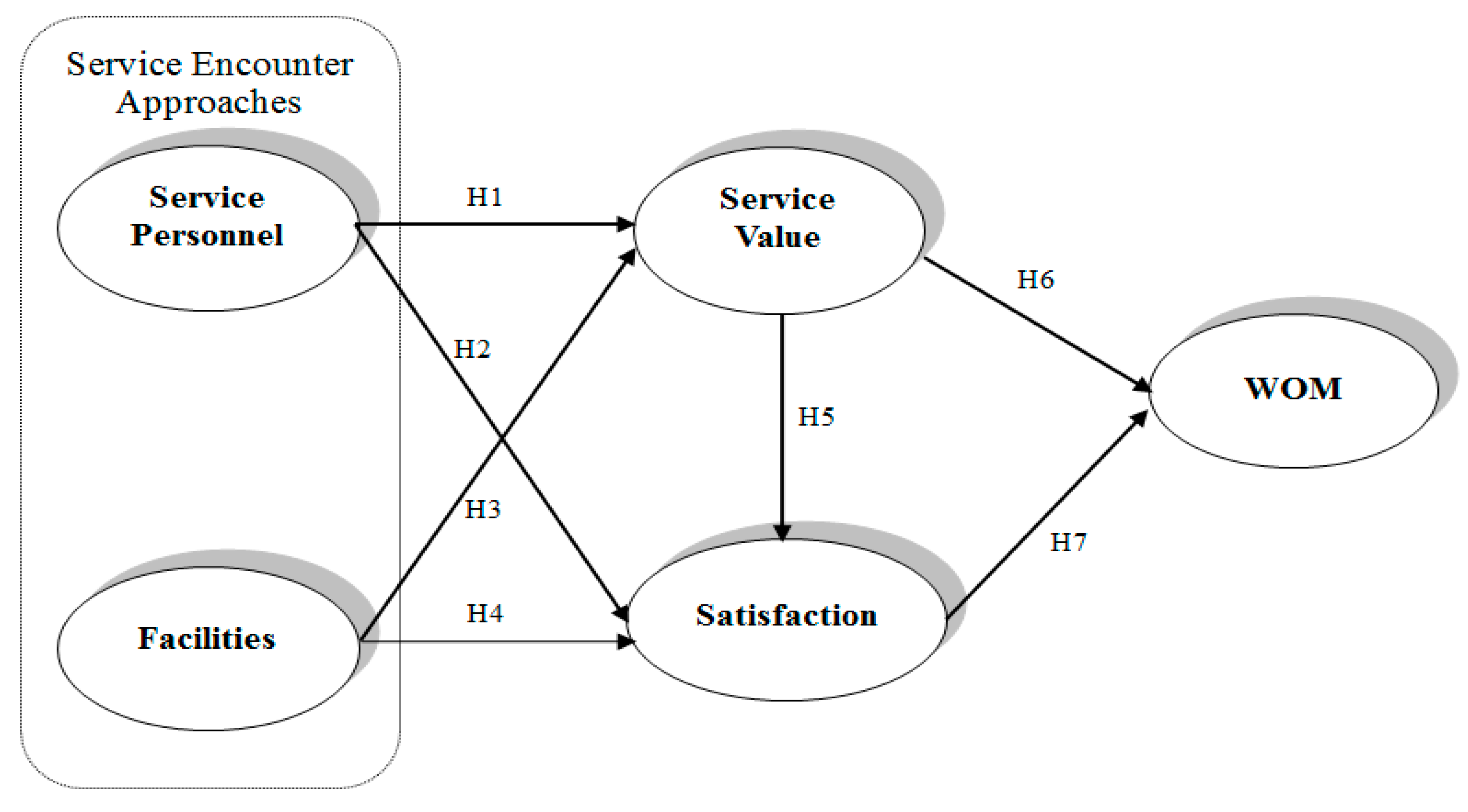
2.1. Research Model
2.2. Service Encounters
2.3. Service Value
2.4. Satisfaction
2.5. WOM
2.6. Research Hypotheses
3. Methodology
3.1. Sample and Data Collection
3.2. Measurement Development
4. Results
4.1. Demographic Characteristics
4.2. Data Analysis
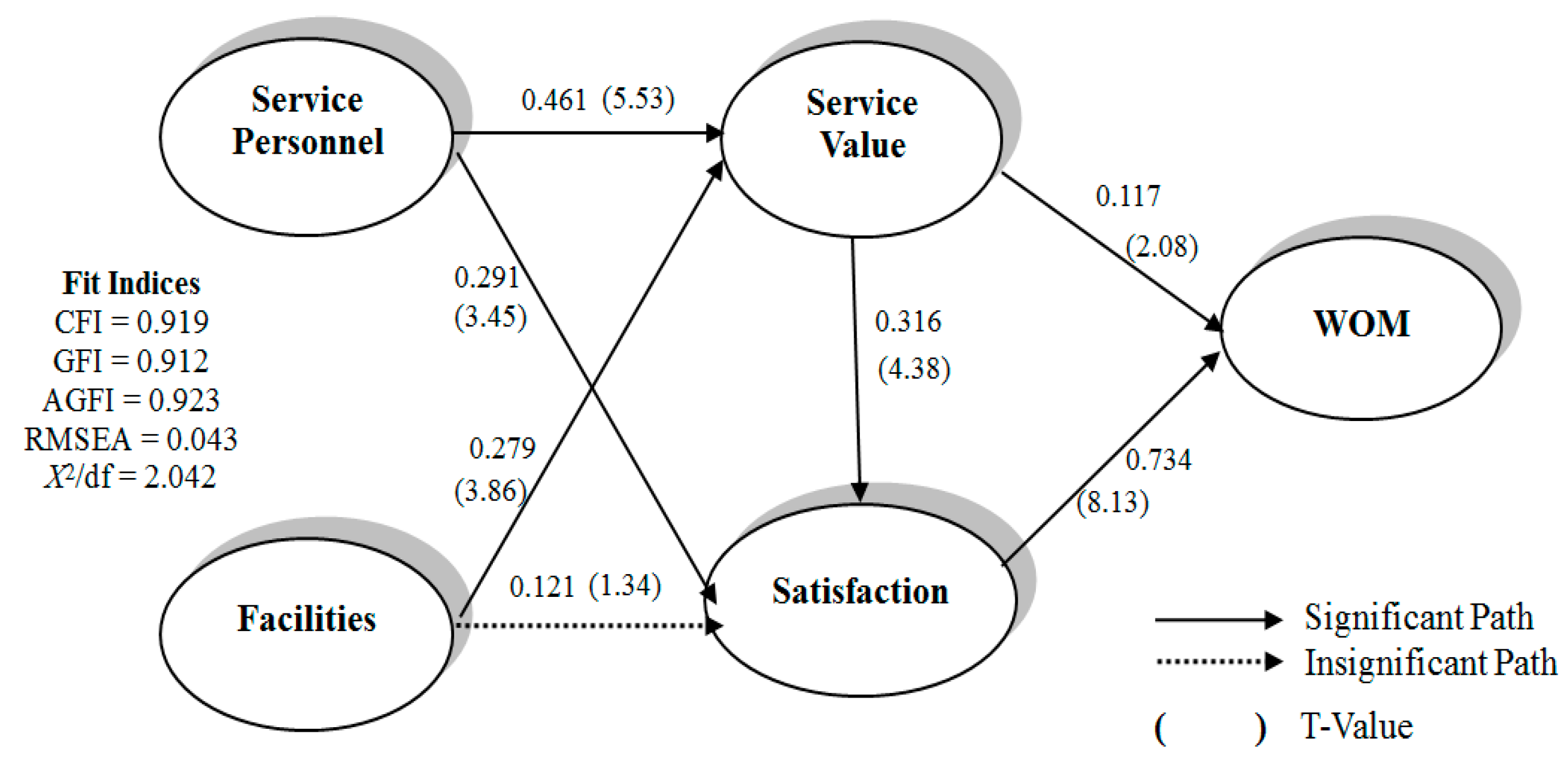
4.3. Model Estimate and Modification Indices
5. Discussion
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Managerial Implications
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meesala, A.; Paul, J. Service quality, consumer satisfaction and loyalty in hospitals: Thinking for the future. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2018, 40, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, S.F.; Narver, J.C. Customer-led and market oriented: Let’s not confuse the two. Strateg. Manag. J. 1998, 19, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Yuan, C.H. Analysis of social capital accumulation and competitive advantages of hospital. Chin. Health. Serv. Manag. 2005, 21, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dolen, W.; Lemmink, J.; de Ruyter, K.; de Jong, A. Customer-sales employee encounters: A dyadic perspective. J. Retail. 2002, 78, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.R.; Surprenant, C.S.; Czepiel, J.A.; Gutman, E.G. A role theory perspective on dyadic interactions: The service encounter. J. Mark. 1985, 49, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shostack, G.L. Planning the Service Encounter; Lexington Books: Lanham, MD, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Czepiel, A.; Solomon, M.R.; Surprenant, C.F.; Gutman, E.G. The Service Encounter: Managing Employee/Customer Interaction in Service Business; Lexington Books: Lanham, MD, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees, C.M.; Fombelle, P.W.; Gregoire, Y.; Bone, S.; Gustafsson, A.; Sousa, R.; Walkowiak, T. Service encounters, experiences and the customer journey: Defining the field and a call to expand our lens. J. Bus Res. 2017, 79, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J. The Role of the Environment in Marketing Service: The Customer Perspective. In The Service Challenge: Integrating for Competing Advantage; Czepie, J.A., Carole, A.C., Shanahan, J., Eds.; American Marketing Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 1986; pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Booms, B.H.; Bitner, M.J. Marketing strategies and organization structures for service firms. In Marketing of Services; Donnelly, J., George, W.R., Eds.; American Marketing Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 1981; Volume 32, pp. 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, L.L.; Yadav, M.S. El papel del valor en la determinación del precio de los ser-vicios. Harv. Deusto Bus. Rev. 1997, 78, 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, D.J.; Woodruff, R.B.; Gardial, S.F. Exploring the phenomenon of customers’ desired value change in a business-to-business context. J. Mark. 2002, 66, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, I.; Berenguer, G.; Cervera, A. The roles of service encounters, service value, and job satisfaction in achieving customer satisfaction in business relationships. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2008, 37, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, K.B. Política de Precios: Para Hacer Más Rentables Las Decisiones; McGraw-Hill: Madrid, Spain, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, R.B. Customer value: The next source for competitive advantage. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1997, 25, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, R.N. An experimental study of customer effort, expectation, and satisfaction. J. Mark Res. 1965, 3, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Pain Society Quality of Care Committee. Quality improvement guidelines for the treatment of acute pain & cancer pain. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1995, 274, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesh, J.; Arnold, M.J.; Reynolds, K.E. Understanding the customer base of service providers: An examination of the differences between switchers and stayers. J. Mark. 2000, 64, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, K.N.; White, T.B.; Winer, R.S. Dynamic customer relationship management: Incorporating future considerations into the service retention decision. J. Mark. 2002, 66, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. Whence consumer loyalty. J. Mark. 1999, 63, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzellis, L.; D’Uggento, A.M.; Romanazzi, S. Student satisfaction and quality of service in Italian universities. Manag. Serv. Qual. 2006, 16, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, J. Word of Mouth Advertising: A Review of the Literature; Advertising Research Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, W.C.; Lueg, J.E. Modeling word-of-mouth usage. J. Bus. Res. 2013, 66, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.C.; Chih, W.H.; Liou, D.K. Investigating community members’ eWOM effects in Facebook fan page. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2016, 116, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higie, R.A.; Feick, L.F.; Price, L.L. Types and amount of word-of-mouth communications about retailers. J. Retail. 1987, 63, 260–278. [Google Scholar]
- Eisingerich, A.B.; Chun, H.E.H.; Liu, Y.; Jia, H.; Bell, S.J. Why recommend a brand face-to-face but not on Facebook? How word-of-mouth on online social sites differs from traditional word-of-mouth. J. Consum. Psychol. 2015, 25, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.R. Consumer Behavior-Buying, Having, and Being, 8th ed.; Prentice-Hall International Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, L.C. An integrated research of benefits sought, service quality to overall satisfaction & repeat visits: An example of international tourism hotel in Taiwan area. Far East J. 2006, 23, 177–200. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.S.; Weng, H.C.; Chang, H.H.; Hsu, T.H. Customer satisfaction in medical service encounters: A comparison between obstetrics and gynecology patients & general medical patients. J. Nurs. Res. 2006, 14, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Argenton, C.; Prüfer, J. Search engine competition with network externalities. J. Compet. Law Econ. 2012, 8, 73–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Yang, C.G.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, J.B. A study on the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction and dissatisfaction in web portal usage. Serv. Bus. 2015, 9, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Johnson, M.D.; Anderson, E.W.; Cha, J.; Bryant, B.E. The American customer satisfaction index: Nature, purpose, and findings. J. Mark. 1996, 60, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.J., Jr.; Brady, M.K.; Hult, G.T.M. Assessing the effect of quality, value and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioral intention in service environment. J. Retail. 2000, 76, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H. Service quality, customer satisfaction, and customer value: A holistic perspective. Hosp. Manag. 1999, 18, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H. Price fairness and its asymmetric effects on overall price, quality, and value judgements: The case of an upscale hotel. Tour. Manag. 2003, 24, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, A.; Money, A.H.; Berthon, P.R. Service quality and satisfaction—The moderating role of value. Eur. J. Mark. 2000, 34, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, B.J.; Kim, K. International students travel behavior: A model of the travel-related consumer/dissatisfaction process. J. Travel Touris. Mark. 2001, 10, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallarza, M.; Gil, I. Value dimensions, perceived value, satisfaction and loyalty: An investigation of university students’ travel behavior. Touris. Manag. 2006, 27, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandon, J.L.; Leo, P.Y.; Philippe, J. Service encounter dimensions—A dyadic perspective: Measuring the dimensions of service encounters as perceived by customers & personnel. Int. J. Serv. Ind. Manag. 1997, 8, 65–86. [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino, E.; Johnson, M.S. The different roles of satisfaction, trust, & commitment in customer relationships. J. Mark. 1999, 63, 70–87. [Google Scholar]
- Athanassopoulos, A.D. Customer satisfaction cues to support market segmentation & explain switching behavior. J. Bus. Res. 2000, 47, 191–207. [Google Scholar]
- Blodgett, J.; Hill, D.; Tax, S. The effects of distributive, procedural, and interactional justice on complaint behavior. J. Retail. 1997, 73, 185–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreng, R.A.; Harrell, G.D.; Mackoy, R.D. Service recovery: Impact on satisfaction and intentions. J. Serv. Mark. 1995, 9, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.H.; Yang, Y.J. The satisfaction, repurchase intention and word-of-mouth effects of movies. In Proceedings of the 2009 Service Marketing Conference, Taichung, Taiwan, 15 May 2009; National Chung Hsing University; pp. 131–153. [Google Scholar]
- Cristiane, D.; Pizzutti, S.; Daniel, V.; der Heyde, F. Antecedents and consequences of consumer trust in the context of service. Brazil. Admin. Rev. 2008, 5, 225–244. [Google Scholar]
- Sirdeshmukh, D.; Singh, J.; Sabol, B. Consumer trust, value and loyalty in relational exchanges. J. Mark. 2002, 66, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöreskog, K.G.; Sörbom, D. LISREL 8: Structural Equation Modeling with the SIMPLIS Command Language; Lawrence Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. A conceptual model of service quality and implications for future research. J. Mark. 1985, 49, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsted, K.F. Service Encounter Dimensions: A Cross-Cultural Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Bitner, M.J. Evaluation service encounters: The effects of physical surroundings and employee responses. J. Mark. 1990, 54, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Choi, D.C.; Park, J.W. Service orientation: Its impact on business performance in the medical service industry. Serv. Ind. J. 2007, 27, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronholdt, L.; Martensen, A.; Kristensen, K. The relationship between customer satisfaction and loyalty: Cross-Industry differences. Total Qual. Manag. 2000, 11, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxham, J.G. Service recovery’s influence on consumer satisfaction, positive word-of-mouth, and purchase intentions. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 54, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brislin, R.W. Back translation for cross-cultural research. J. Cross-Cult. Psychol. 1970, 1, 185–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avolio, B.J.; Yammarino, F.J.; Bass, B.M. Identifying common methods variance with data collected from a single source: An unresolved sticky issue. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, H.H. Modern Factor Analysis; University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.C.; Gerbing, D.W. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review & recommended two-step approach. Psychol. Bull. 1988, 103, 411–423. [Google Scholar]
- Gaski, J.F.; Nevin, J.R. The differential effects of exercised and unexercised power sources in a marketing channel. J. Mark. Res. 1985, 22, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Yi, Y. On the evaluation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1988, 16, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, D.; Straub, D.W.; Boudreau, M. Structural equation modeling techniques and regression: Guidelines for research practice. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2000, 4, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice–Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.S.; Weng, H.C.A. Study of the relation between the service encounters and the medical treatment satisfaction—A sample of the gynecology clinics. In Proceedings of the 2004 Management Thinking and Practice Conference; Taipei, Taipei, Taiwan, 1 June 2004; Ming Chuan University, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, C.W.C.; Lai, J.Y.M.; Loi, R. Motivation of travel agents’ customer service behavior and organizational citizenship behavior: The role of leader-member exchange and internal marketing orientation. Tour. Manag. 2015, 48, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Song, H.J.; Lee, C.K. Effects of corporate social responsibility and internal marketing on organizational commitment and turnover intentions. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2016, 55, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherehiy, B.; Karwowski, W.; Layer, J.K. A review of enterprise agility: Concepts, frameworks and attributes. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2007, 37, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layer, J.K.; Karwowski, W.; Furr, A. The effect of cognitive demands and perceived quality of work life on human performance in manufacturing environments. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2009, 39, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genaidy, A.; Salem, S.; Karwowski, W.; Paez, O.; Tuncel, S. The work compatibility improvement framework: An integrated perspective of the human-at-work system. Ergonomics 2007, 50, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 129 | 36.9 |
| Female | 221 | 63.1 |
| Age | ||
| Under 20 | 66 | 18.9 |
| 2 to 29 | 86 | 24.6 |
| 30 to 39 | 101 | 28.9 |
| 40 to 49 | 51 | 14.6 |
| 50 to 59 | 26 | 7.4 |
| 60 and older | 20 | 5.6 |
| First Time for Medical Treatment | ||
| Yes | 59 | 16.9 |
| No | 291 | 83.1 |
| Division | ||
| General Internal Medicine | 71 | 20.3 |
| Gastrointestinal Medicine | 32 | 9.1 |
| Nephrology | 12 | 3.4 |
| Cardiovascular Medicine | 9 | 2.6 |
| Chest Medicine | 14 | 4.0 |
| Neurosurgery | 5 | 1.4 |
| Metabolism | 8 | 2.3 |
| Family Medicine | 33 | 9.4 |
| Rheumatology | 8 | 2.3 |
| Dermatology | 4 | 1.1 |
| Psychiatry | 6 | 1.7 |
| General Surgery | 32 | 9.1 |
| Chest Surgery | 6 | 1.7 |
| Colon and Rectum Surgery | 3 | 0.9 |
| Cardiovascular Surgery | 1 | 0.3 |
| Neurological Surgery | 2 | 0.6 |
| Ophthalmology | 5 | 1.4 |
| Ear, Nose, and Throat | 3 | 0.9 |
| Orthopedics | 10 | 2.9 |
| Dental Medicine | 3 | 0.9 |
| Urological department | 7 | 2.0 |
| Obstetrics and Gynecology | 31 | 8.9 |
| Pediatrics | 34 | 9.6 |
| Rehabilitation Medicine | 3 | 0.9 |
| Other Division | 8 | 2.3 |
| Outpatient Services Time | ||
| Morning | 117 | 33.4 |
| Afternoon | 168 | 48.0 |
| Night | 65 | 18.6 |
| Register Mode | ||
| Speech Sounds | 43 | 12.3 |
| Internet | 28 | 8.0 |
| Telephone | 35 | 10.0 |
| Locality | 82 | 23.4 |
| A Diagnosis Physician | 27 | 7.7 |
| Registers Locality on that Day | 129 | 36.9 |
| Nursing Stand | 1 | 0.3 |
| Other | 5 | 1.4 |
| Medical Treatment Factor | ||
| Relatives and Friends to Recommend | 70 | 15.1 |
| Traffic Convenient | 86 | 18.5 |
| Close to House | 136 | 29.2 |
| Good Facilities | 42 | 9.0 |
| Good Reputation | 33 | 7.1 |
| Service Attitude | 20 | 4.3 |
| Personal Habits | 32 | 6.9 |
| Medical Skill | 21 | 4.5 |
| Other | 25 | 5.4 |
| Factors | Mean | S.D. | Composite Reliability | Average Variance Extracted | Cronbach’s Alpha | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service Encounter | Service Personnel | 3.601 | 0.623 | 0.880 | 0.521 | 0.831 |
| Facilities | 3.571 | 0.616 | 0.940 | 0.724 | 0.797 | |
| Service Value | 3.369 | 0.740 | 0.934 | 0.718 | 0.904 | |
| Satisfaction | 3.542 | 0.503 | 0.933 | 0.602 | 0.871 | |
| WOM | 3.582 | 0.688 | 0.953 | 0.792 | 0.915 | |
| Constructs | SP | FAC | SV | SAT | WOM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service Personnel | 0.722 | ||||
| Facilities | 0.524 | 0.851 | |||
| Service Value | 0.555 | 0.534 | 0.847 | ||
| Satisfaction | 0.469 | 0.446 | 0.543 | 0.776 | |
| Word-of-mouth | 0.419 | 0.326 | 0.524 | 0.728 | 0.890 |
| Fit Indices | χ2/df * | CFI ** | GFI ** | AGFI ** | RMSEA *** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial research model | 3.756 | 0.870 | 0.878 | 0.840 | 0.088 |
| Modification research model | 2.042 | 0.919 | 0.912 | 0.923 | 0.043 |
| Level of acceptable fit | <3 | >0.9 | >0.9 | >0.9 | <0.08 |
| Acceptability | Acceptable | Acceptable | Acceptable | Acceptable | Acceptable |
| Latent Constructs Path | Hypothesized Model | Trimmed Model | T-Value | Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path Estimate | Standard Solutions | Path Estimate | Standard Solutions | |||
| Service Personnel→Service Value (H1) | 0.481 * | 0.423 | 0.578 * | 0.461 | 5.53 | Supported |
| Facilities→Service Value (H2) | 0.427 * | 0.304 | 0.390 * | 0.279 | 3.86 | Supported |
| Service Personnel→Satisfaction (H3) | 0.274 * | 0.299 | 0.294 * | 0.291 | 3.45 | Supported |
| Facilities→Satisfaction (H4) | 0.113 | 0.118 | - | - | 1.34 | Not Supported |
| Service Value→Satisfaction (H5) | 0.261 * | 0.323 | 0.255 * | 0.316 | 4.38 | Supported |
| Service Value→WOM (H6) | 0.129 * | 0.113 | 0.132 * | 0.117 | 2.08 | Supported |
| Satisfaction→WOM (H7) | 0.869 * | 0.734 | 0.871 * | 0.734 | 8.13 | Supported |
| Variable | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect | Ranking of Total Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA-SV-SA | 0.118 | 0.294 × 0.117 = 0.034 | 0.152 | 1 |
| FA-SV-WOM | - | 0.294 × 0.316 = 0.093 | 0.093 | 2 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, L.-C. Investigating Effect of Service Encounter, Value, and Satisfaction on Word of Mouth: An Outpatient Service Context. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010132
Hsu L-C. Investigating Effect of Service Encounter, Value, and Satisfaction on Word of Mouth: An Outpatient Service Context. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(1):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010132
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Li-Chun. 2018. "Investigating Effect of Service Encounter, Value, and Satisfaction on Word of Mouth: An Outpatient Service Context" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 1: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010132




