Effects of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) Stress on Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (Bacillus sp. Strain MRP-3): Oxidative Stress and Bioaccumulation Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Heavy Metal Resistant PSB Strain
2.2. Bacterial Growth
2.3. Quantification of ROS
2.4. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) & Catalase (CAT) Activity Analyses
2.5. Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation Assays
2.6. Scanning Electron microscopy (SEM) and Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy-Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (STEM-EDS)
2.7. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) and X-ray Photoelectron Spectrometer (XPS) Analyses
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Effect of Pb and Cr Stress on PSB Growth
3.2. Effect of Pb and Cr on Oxidative Stress
3.3. Effect of Pb and Cr on Antioxidant Enzymes
3.4. Effect of Pb and Cr on Bioaccumulation
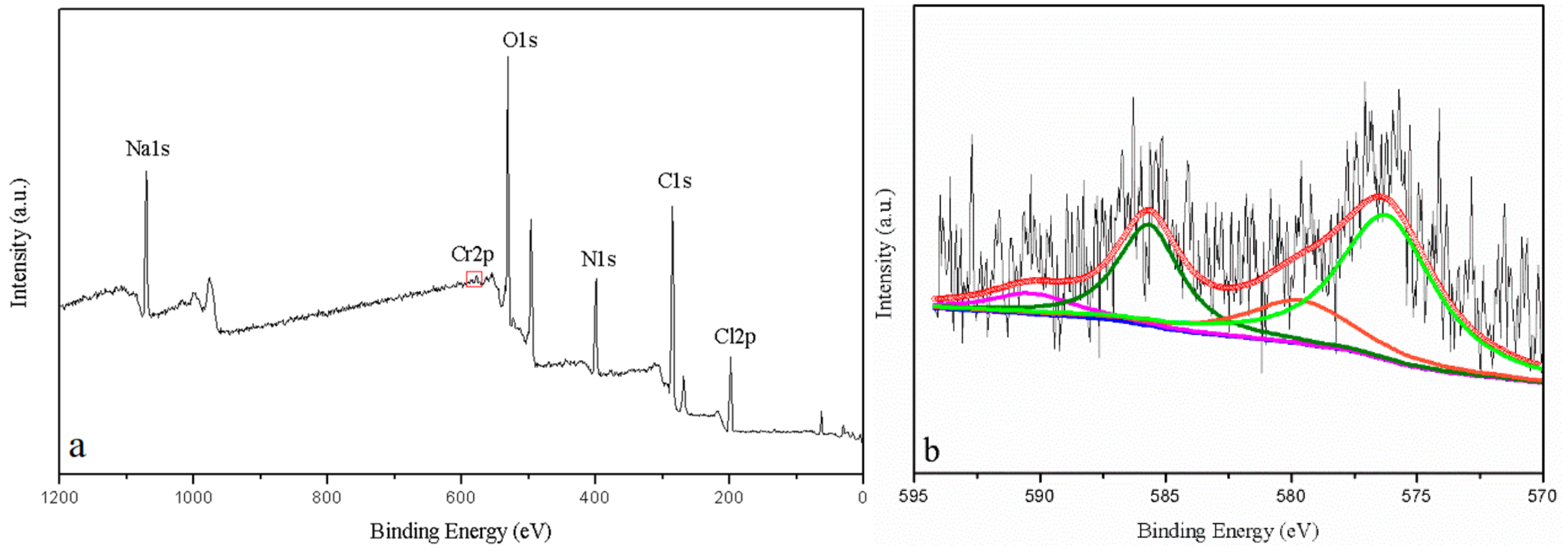
3.5. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and XPS Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kaur, G.; Reddy, M.S. Effects of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, rock phosphate and chemical fertilizers on maize-wheat cropping cycle and economics. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.C.; Singdevsachan, S.K.; Mishra, R.R.; Dutta, S.K.; Thatoi, H.N. Diversity, mechanism and biotechnology of phosphate solubilising microorganism in mangrove—A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2014, 3, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Bolan, N.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Concomitant rock phosphate dissolution and lead immobilization by phosphate solubilizing bacteria (Enterobacter sp.). J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranya, K.; Sundaramanickam, A.; Shekhar, S.; Meena, M.; Sathishkumar, R.S.; Balasubramanian, T. Biosorption of multi-heavy metals by coral associated phosphate solubilising bacteria Cronobacter muytjensii KSCAS2. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Moon, H.S.; Shin, D.; Nam, K. Survival of introduced phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) and their impact on microbial community structure during the phytoextraction of Cd-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Z.; Shao, W.; Zhang, K.; Huo, Y.; Li, M. Characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from heavy metal contaminated soils and their potential for lead immobilization. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, P.; Diwan, B. Bacterial Exopolysaccharide mediated heavy metal removal: A Review on biosynthesis, mechanism and remediation strategies. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 13, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joutey, N.T.; Sayel, H.; Bahafid, W.; El Ghachtouli, N. Mechanisms of hexavalent chromium resistance and removal by microorganisms. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 233, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Huang, J.; Tan, X.; Jian, H.; Hu, X.; Li, F.; Wang, D. Mechanism of Cr(VI) reduction by Aspergillus niger: Enzymatic characteristic, oxidative stress response, and reduction product. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6271–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fuego, D.; Keunen, E.; Cuypers, A.; Bertrand, A.; Gonzalez, A. Mycorrhization protects Betula pubescens Ehr. from metal-induced oxidative stress increasing its tolerance to grow in an industrial polluted soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 336, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkowski, A.; Szala, M.; Kowalczyk, P.; Cłapa, T.; Narożna, D.; Selwet, M. Oxidative stress in bacteria (Pseudomonas putida) exposed to nanostructures of silicon carbide. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakrashi, S.; Dalai, S.; Prathna, T.C.; Trivedi, S.; Myneni, R.; Raichur, A.M.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Cytotoxicity of aluminium oxide nanoparticles towards fresh water algal isolate at low exposure concentrations. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 132–133, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Jiao, S.; Wu, K.; La, G.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of Cd and Cr removal and tolerance by macrofungus Pleurotus ostreatus HAU-2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 330, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahl, C.D.; Behling, C.S.; Hackenhaar, F.S.; de Carvalho e Silva, M.N.; Putti, J.; Salomon, T.B.; Alves, S.H.; Fuentefria, A.; Benfato, M.S. Induction of ROS generation by fluconazole in Candida glabrata: Activation of antioxidant enzymes and oxidative DNA damage. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 82, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kováčik, J.; Rotková, G.; Bujdoš, M.; Babula, P.; Peterková, V.; Matúš, P. Ascorbic acid protects Coccomyxa subellipsoidea against metal toxicity through modulation of ROS/NO balance and metal uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Reduction of heavy metal (Pb2+) biosorption in zebrafish model using alginic acid purified from Ecklonia cava and two of its synthetic derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z.; Dong, Y. Activities of antioxidant enzymes in three bacteria exposed to bensulfuron-methyl. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1899–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Garg, S.K. Co-remediation of pentachlorophenol and Cr6+ by free and immobilized cells of native Bacillus cereus isolate: Spectrometric characterization of PCP dechlorination products, bioreactor trial and chromate reductase activity. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanella, P.; Cabral, L.; Costa, A.P.; de Oliveira Camargo, F.A.; Gianello, C.; Bento, F.M. Metal resistance mechanisms in Gram-negative bacteria and their potential to remove Hg in the presence of other metals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 140, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eboigbodin, K.E.; Biggs, C.A. Characterization of the extracellular polymeric substances produced by Escherichia coli using infrared Spectroscopic, Proteomic, and Aggregation Studies. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, S.; Huang, Q.; Cai, P. Bacterial cell surface properties: Role of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (LB-EPS). Colloids Surf. B 2015, 128, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Moon, H.S.; Nam, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, T.S. Application of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria for enhancing bioavailability and phytoextraction of cadmium (Cd) from polluted soil. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, V.; Guzmán-Moreno, J.; Rodríguez-González, V.; Flores-de la Torre, J.A.; Ramírez-Santoyo, R.M.; Vidales-Rodríguez, L.E. Biosorption of lead phosphates by lead-tolerant bacteria as a mechanism for lead immobilization. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joe, A.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, D.-J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Jhee, K.-H.; Sohn, Y.; Jang, E.-S. Antimicrobial activity of ZnO nanoplates and its Ag nanocomposites: Insight into an ROS-mediated antibacterial mechanism under UV light. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 267, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Dong, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, B. Effect of NaCl on the heavy metal tolerance and bioaccumulation of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.-N.; Shim, J.; You, Y.; Myung, H.; Bang, K.-S.; Cho, M.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Oh, B.-T. Characterization of lead resistant endophytic Bacillus sp. MN3-4 and its potential for promoting lead accumulation in metal hyperaccumulator Alnus firma. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 199–200, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, F.; Shahid, M.; Hussain, S.; Shahzad, T.; Tahir, M.; Ijaz, M.; Hussain, A.; Mahmood, K.; Imran, M.; Babar, S.A.K. Potential plant growth-promoting strain Bacillus sp. SR-2-1/1 decolorized azo dyes through NADH-ubiquinone:oxidoreductase activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 235, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehizadeh, H.; Shojaosadati, S.A. Removal of metal ions from aqueous solution by polysaccharide produced from Bacillus firmus. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4231–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shameer, S. Biosorption of lead, copper and cadmium using the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of Bacillus sp., from solar salterns. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, A.Z.; Cen, T.; Li, X.; He, M.; Li, D.; Chen, J. Sub-inhibitory concentrations of heavy metals facilitate the horizontal transfer of plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance genes in water environment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, U.N.; Singh, N.K.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Verma, S. Chromate tolerance and accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris L.: Role of antioxidant enzymes and biochemical changes in detoxification of metals. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Fan, X.; Patel, J.S.; Zhang, M. Characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from calcareous soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedeke, G.A.; Iwuchukwu, P.O.; Aladesida, A.A.; Afolabi, T.A.; Ayanda, I.O. Impact of heavy metal bioaccumulation on antioxidant activities and DNA profile in two earthworm species and freshwater prawn from Ogun River. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Huang, Q.; Yang, R.; Tie, B.; Lei, M. Cd sequestration by bacteria-aluminum hydroxide composites. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torger, B.; Müller, M. In situ-ATR–FTIR analysis on the uptake and release of streptomycin from polyelectrolyte complex layers. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2013, 104, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Li, J.; Sun, S.; Ding, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Qiu, G. Synergistic effect between sulfide mineral and acidophilic bacteria significantly promoted Cr(VI) reduction. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 219, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Hu, Q.; Yao, L.; Li, M.; Sun, D.; Shao, Q.; Qiu, B.; Guo, Z. Ultrasonic pretreated sludge derived stable magnetic active Carbon for Cr(VI) removal from wastewater. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7283–7291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Initial Metal Concentration (mmol·L−1) | Pb Accumulated (mmol·g−1 dry weight) | Cr Accumulated (mmol·g−1 dry weight) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intracellular | Extracellular | Intracellular | Extracellular | |
| 0.5 | 0.009 ± 0.002 c (4.1%) | 0.211 ± 0.031 b (95.9%) | 0.034 ± 0.002 c (98.7%) | <0.000 b (1.3%) |
| 1.0 | 0.134 ± 0.008 b (38.3%) | 0.216±0.005 b (61.7%) | 0.258 ± 0.026 b (97.0%) | 0.008 ± 0.002 b (3.0%) |
| 5.0 | 0.558 ± 0.035 a (29.7%) | 1.318±0.285 a (70.3%) | 0.565 ± 0.036 a (96.4%) | 0.021 ± 0.008 a (3.6%) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, W.; Li, M.; Teng, Z.; Qiu, B.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, K. Effects of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) Stress on Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (Bacillus sp. Strain MRP-3): Oxidative Stress and Bioaccumulation Potential. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122172
Shao W, Li M, Teng Z, Qiu B, Huo Y, Zhang K. Effects of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) Stress on Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (Bacillus sp. Strain MRP-3): Oxidative Stress and Bioaccumulation Potential. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(12):2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122172
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Wen, Min Li, Zedong Teng, Bin Qiu, Yaoqiang Huo, and Keyao Zhang. 2019. "Effects of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) Stress on Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (Bacillus sp. Strain MRP-3): Oxidative Stress and Bioaccumulation Potential" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 12: 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122172
APA StyleShao, W., Li, M., Teng, Z., Qiu, B., Huo, Y., & Zhang, K. (2019). Effects of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) Stress on Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria (Bacillus sp. Strain MRP-3): Oxidative Stress and Bioaccumulation Potential. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(12), 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122172




