Geospatial Distributions of Groundwater Quality in Gedaref State Using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Drinking Water Quality Index (DWQI)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geology
2.2. Hydrogeological Setting
2.3. Spatial Interpolation and Groundwater Quality Mapping
2.4. Drinking Water Quality Index DWQI
3. Results
3.1. Interpolation and Elements Distribution Maps
3.2. Correlation Matrix
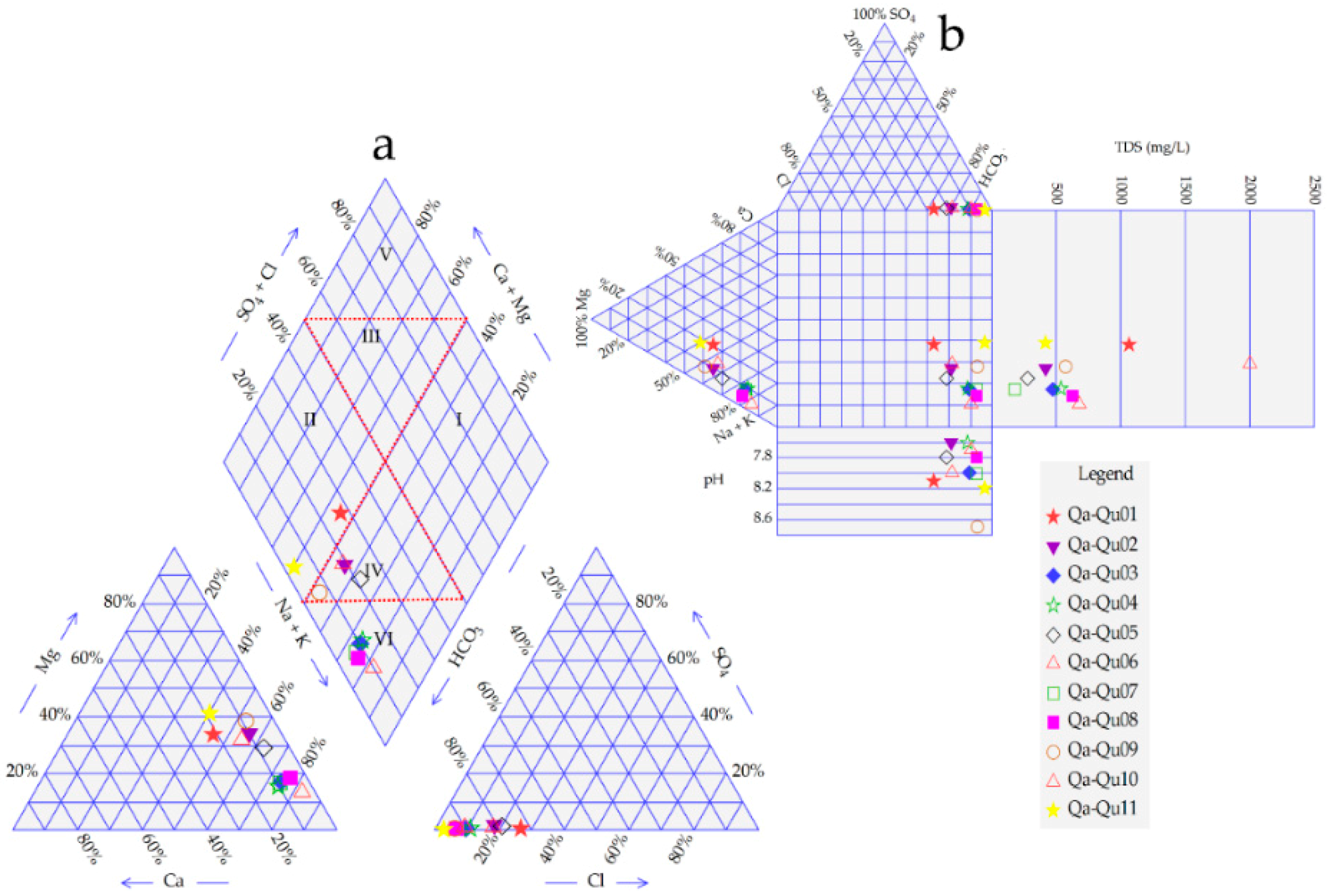
3.3. Groundwater Facies
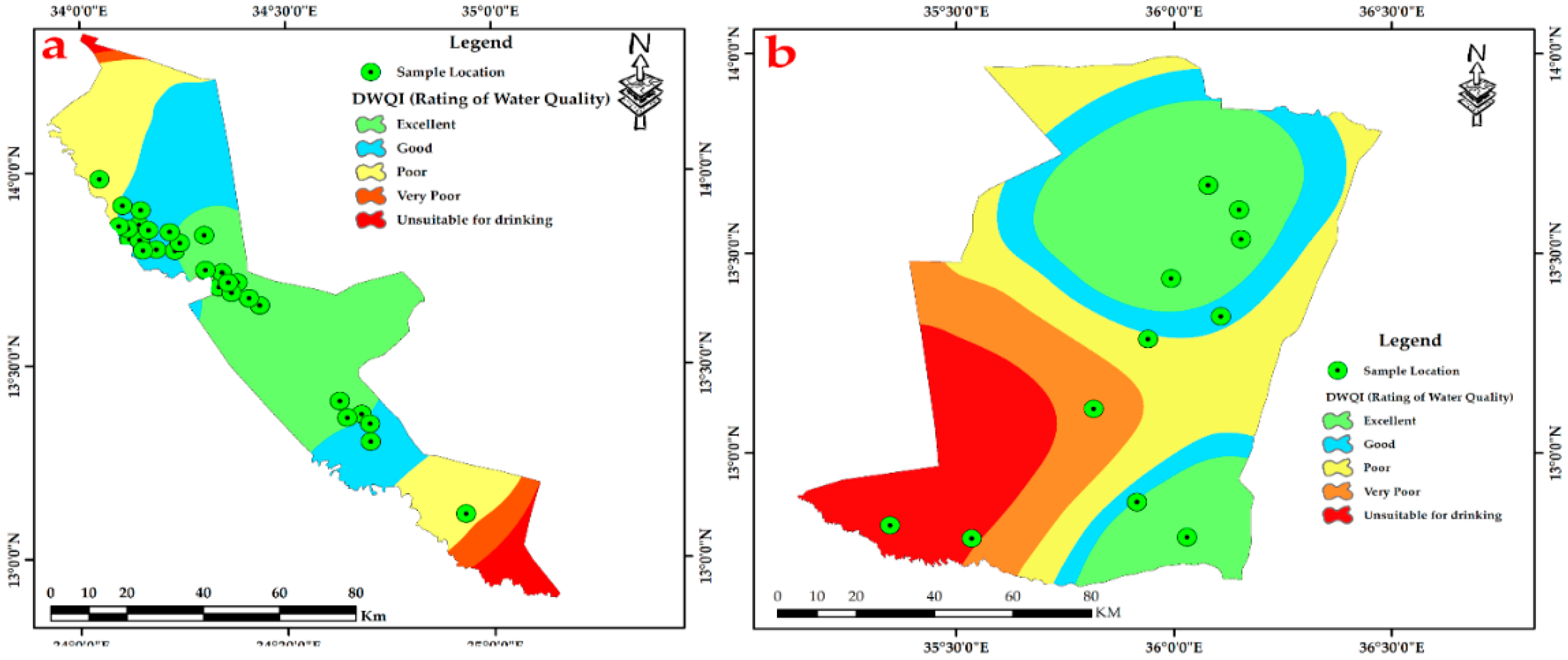
3.4. Drinking Water Quality Index (DWQI)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Tian, R.; He, S.; He, X.; Xue, C.; Zhang, K. Geochemistry, hydraulic connectivity and quality appraisal of multilayered groundwater in the Hongdunzi coal mine, northwest China. Mine Water Environ. 2018, 37, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferchichi, H.; Hamouda, M.B.; Farhat, B.; Mammou, A.B. Assessment of groundwater salinity using GIS and multivariate statistics in a coastal Mediterranean aquifer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 2473–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Ghione, R.; De Maio, M.; Lavy, M. Evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality for suitability of drinking and irrigation purposes: A case study in the Aosta Valley region, Italy. Arabian J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kura, N.U.; Ramli, M.F.; Sulaiman, W.N.A.; Ibrahim, S.; Aris, A.Z.; Mustapha, A. Evaluation of factors influencing the groundwater chemistry in a small tropical island of Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 1861–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhusari, V.; Katpatal, Y.; Kundal, P. Performance evaluation of a reverse-gradient artificial recharge system in basalt aquifers of Maharashtra, India. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesali Naseh, M.R.; Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Adamowski, J.; Sadatipour, E. Groundwater Pollution Sources Apportionment in the Ghaen Plain, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; CRC Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; p. 647. [Google Scholar]
- Chacha, N.; Njau, K.N.; Lugomela, G.V.; Muzuka, A.N. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and spatial distribution of groundwater quality in Arusha well fields, Northern Tanzania. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelly, K.C.; Mutua, F. Ground Water Quality Assessment Using GIS and Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Juja Location, Kenya. Am. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2016, 5, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R. Principal component analysis and hydrochemical facies characterization to evaluate groundwater quality in Varahi river basin, Karnataka state, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, S.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of the groundwater quality with WQI (Water Quality Index) and multivariate analysis: A case study of the Tefenni plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1725–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eang, K.E.; Igarashi, T.; Kondo, M.; Nakatani, T.; Tabelin, C.B.; Fujinaga, R. Groundwater monitoring of an open-pit limestone quarry: Water-rock interaction and mixing estimation within the rock layers by geochemical and statistical analyses. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Clark, I. Groundwater flow and geochemical evolution in the Central Flinders Ranges, South Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, J. Groundwater as a geologic agent: An overview of the causes, processes, and manifestations. Hydrogeol. J. 1999, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, S.R.; Redwan, M.; Masoud, A.M.; Moneim, A.A.A. Chemical characteristics and assessment of groundwater quality in Halayieb area, southeastern part of the Eastern Desert, Egypt. Geosci. J. 2018, 23, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidey, A. Geospatial distribution modeling and determining suitability of groundwater quality for irrigation purpose using geospatial methods and water quality index (WQI) in Northern Ethiopia. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, A.; Gooddy, D.; Kanatharana, P.; Meesilp, W.; Ramnarong, V. Groundwater evolution beneath Hat Yai, a rapidly developing city in Thailand. Hydrogeol. J. 2000, 8, 564–575. [Google Scholar]
- Edmunds, W.; Ma, J.; Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Kipfer, R.; Darbyshire, D. Groundwater recharge history and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Minqin Basin, North West China. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 2148–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Hernández, P.; del Rocío Torres-Alvarado, M.; Herrera-San Luis, J.A.; Cruz-López, N. Water quality of a reservoir and its major tributary located in east-central Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 6119–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, C.B.; Moharir, K. Spatial analysis of groundwater quality mapping in hard rock area in the Akola and Buldhana districts of Maharashtra, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Behera, S.; Kar, A.; Narendra, P.; Guha, S. Hydrogeomorphological mapping in ground water exploration using remotely sensed data—A case study in keonjhar district, orissa. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 1997, 25, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, F. Mapping of groundwater prospective zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques: A case study from the Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2012, 70, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moubark, K.; Abdelkareem, M. Characterization and assessment of groundwater resources using hydrogeochemical analysis, GIS, and field data in southern Wadi Qena, Egypt. Arabian J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, Ş.; Şener, E.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, P.; Sikdar, P.J.E.G. Hydrochemical framework of the aquifer in and around East Kolkata Wetlands, West Bengal, India. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Arias, H.; Contreras-Caraveo, M.; Quintana, R.M.; Saucedo-Teran, R.A.; Pinales-Munguia, A. An overall water quality index (WQI) for a man-made aquatic reservoir in Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Mora-Orozco, C.; Flores-Lopez, H.; Rubio-Arias, H.; Chavez-Duran, A.; Ochoa-Rivero, J. Developing a water quality index (WQI) for an irrigation dam. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.; Shoaib, M.; Farid, H.; Lee, J. Assessment of Water Quality Profile Using Numerical Modeling Approach in Major Climate Classes of Asia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R.; Prakash, K. A comparative study on usage of Durov and Piper diagrams to interpret hydrochemical processes in groundwater from SRLIS river basin, Karnataka, India. Elixir Earth Sci. 2015, 80, 31073–31077. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Deng, J. Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misaghi, F.; Delgosha, F.; Razzaghmanesh, M.; Myers, B. Introducing a water quality index for assessing water for irrigation purposes: A case study of the Ghezel Ozan River. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tameim, O.; Zakaria, Z.; Hussein, H.; el Gaddal, A.A.; Jobin, W.R. Control of schistosomiasis in the new Rahad Irrigation Scheme of Central Sudan. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 88, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for drinking-water quality: First addendum to the fourth edition; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 631. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, K.; Hussein, M.; Giddo, I. Application of combined geophysical and hydrogeological techniques to groundwater exploration: A case study of Showak-Wad Elhelew area, Eastern Sudan. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 1992, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisawi, A.; Schrank, E. Terrestrial palynology and age assessment of the Gedaref Formation (eastern Sudan). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2009, 54, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipki, M.; Germann, K.; Schwarz, T. Alunitic kaolins of the Gedaref region (NE-Sudan). In Geoscientific Research in Northeast Africa; CRC Press: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Dawelbeit, M.I.; Babiker, E.J.S. Effect of tillage and method of sowing on wheat yield in irrigated Vertisols of Rahad, Sudan. Soil Tillage Res. 1997, 42, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, D.A. Wheat in Heat-stressed Environments: Irrigated, Dry Areas, and Rice-wheat Farming Systems: Proceedings of the International Conferences: Wheat in Hot, Dry, Irrigated Environments, Wad Medani, Sudan, 1-4 February 1993, Wheat in Warm Area, Rice-wheat Farming Systems, Dinajpur, Bangladesh, 13-15 Feburary [sic] 1993; CIMMYT: Wad Medani, Sudan, 1994; p. 415. [Google Scholar]
- Mozafar, A. Nitrogen fertilizers and the amount of vitamins in plants: A review. J. Plant Nutr. 1993, 16, 2479–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






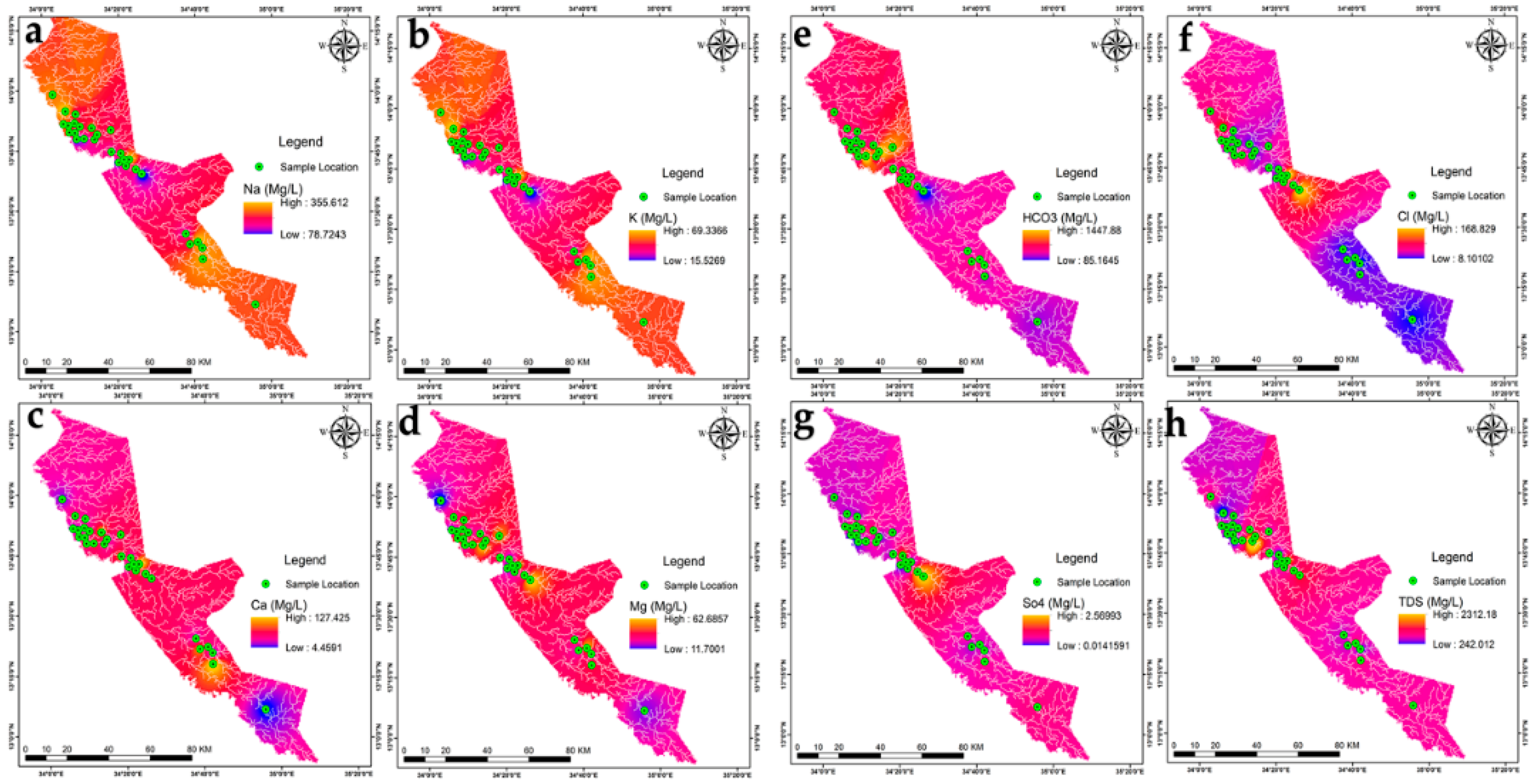





| Aquifer Type | Well Depth (m) | S.W.L (M) | Elevation (m) | Water Table (m) | Well Name |
| Alluvium | 23 | 16 | 425 | 409 | Ellewatah3 |
| Sandstone | 27 | 16 | 424 | 408 | Abu Kalbo |
| Sandstone | 64 | 37 | 423 | 386 | Um Rakuba |
| Sandstone | 48 | 27 | 425 | 398 | Um Tireaza |
| Sandstone | 21 | 11 | 444 | 432 | Um Tireaza 2 |
| Sandstone | 60 | 13 | 554 | 505 | Macancana |
| Sandstone | 48 | 11.94 | 426 | 414 | Wd Margi |
| Sandstone | 21 | 11 | 446 | 435 | Mohamed Ali |
| Alluvium | 14 | 7 | 424 | 417 | Um Gazaz |
| Sandstone | 64 | 12 | 425 | 413 | Wad Elkarar1 |
| Alluvium | 27 | 19 | 424 | 405 | Eldar Elbeida |
| Sandstone | 42 | 13 | 655 | 634 | Ellewatah2 |
| Alluvium | 27 | 16 | 486 | 470 | Halaly5 |
| Alluvium | 30 | 14 | 427 | 413 | Wad Elwosta |
| Alluvium | 57 | 34 | 424 | 383 | Wad Elkarar2 |
| Basaltic | 42 | 24 | 423 | 410 | Hilat Ali |
| Alluvium | 22.5 | 12 | 428 | 416 | Abu Saeed |
| Alluvium | 28 | 13 | 427 | 414 | Elyas |
| Alluvium | 26 | 12 | 648 | 634 | Elmeageerah |
| Sandstone | 25 | 7 | 598 | 591 | Dora |
| Well Code | Aquifer Type | Well Depth (m) | S.W.L (M) | Elevation (m) | Water Table (m) |
| Fw-Rh21 | Alluvium | 34 | 14 | 447 | 433 |
| Fw-Rh22 | Alluvium | 18 | 10 | 444 | 434 |
| Fw-Rh23 | Alluvium | 57 | 41 | 433 | 399 |
| Fw-Rh24 | Alluvium | 26 | 18 | 428 | 410 |
| Fw-Rh25 | Alluvium | 21 | 14 | 422 | 411 |
| Fw-Rh26 | Basaltic | 15 | 8 | 658 | 650 |
| Fw-Rh27 | Alluvium | 24 | 10 | 428 | 418 |
| Fw-Rh28 | Alluvium | 21 | 8 | 431 | 423 |
| Fw-Rh29 | Alluvium | 23 | 16 | 425 | 409 |
| Qa-Qu01 | Sandstone | 53 | 32 | 627 | 595 |
| Qa-Qu02 | Sandstone | 60 | 49 | 426 | 413 |
| Qa-Qu03 | Alluvium | 21 | 12 | 422 | 411 |
| Qa-Qu04 | Basaltic | 42 | 21 | 631 | 607 |
| Qa-Qu05 | Basaltic | 26 | 14 | 454 | 442 |
| Qa-Qu06 | Sandstone | 43 | 35 | 500 | 465 |
| Qa-Qu07 | Alluvium | 27 | 16 | 428 | 412 |
| Qa-Qu08 | Sandstone | 21 | 11 | 431 | 417 |
| Qa-Qu09 | Sandstone | 57 | 42 | 635 | 593 |
| Qa-Qu10 | Sandstone | 31 | 21 | 447 | 426 |
| Qa-Qu11 | Basaltic | 30 | 9 | 650 | 641 |
| Fw-Rh (N = 29) | Qa-Qu (N = 11) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | WHO | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. D. | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. D. |
| pH | 7.0–8.0 | 7.50 | 8.90 | 8.03 | 0.35 | 7.60 | 8.70 | 7.96 | 0.32 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 1000 | 242.00 | 2340.00 | 601.72 | 399.60 | 183.00 | 2007.00 | 663.18 | 502.41 |
| Ca | 75 | 4.45 | 130.00 | 37.47 | 30.06 | 10.44 | 53.00 | 22.21 | 12.43 |
| Mg | 30 | 11.66 | 120.53 | 34.28 | 23.86 | 11.56 | 72.00 | 36.20 | 18.23 |
| Na | 200 | 76.00 | 359.00 | 214.28 | 69.87 | 76.00 | 597.00 | 167.18 | 150.29 |
| K | - | 15.00 | 70.00 | 41.72 | 13.40 | 16.00 | 115.00 | 33.36 | 28.68 |
| Cl | 250 | 8.10 | 172.50 | 35.90 | 37.69 | 10.00 | 45.00 | 21.39 | 8.96 |
| HCO3 | - | 78.90 | 1450.00 | 499.35 | 311.78 | 118.60 | 930.00 | 355.40 | 247.40 |
| SO4 | 250 | 0.02 | 2.57 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 1.36 | 2.29 | 1.83 | 0.31 |
| F | 0.5–1 | 0.01 | 2.56 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 2.56 | 0.65 | 0.70 |
| NO3 | 50 | 0.20 | 15.00 | 3.88 | 3.96 | 1.50 | 11.10 | 5.05 | 3.11 |
| Fe | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 1.04 | 0.19 | 0.31 |
| E.C (µ.S/cm) | - | 345.00 | 3342.00 | 888.23 | 570.54 | 281.53 | 9692.00 | 1777.97 | 2721.19 |
| Area | Groundwater Parameters | Kriging Type | Transformation | Best Fitted Model | ME | RMSE | ASE | MSE | RMSSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fw-Rh | Na | Simple | None | Spherical | −1.5985 | 71.0051 | 73.1880 | −0.0226 | 0.9816 |
| K | Ordinary | None | Spherical | −0.2818 | 13.6108 | 14.0445 | −0.0207 | 0.9817 | |
| Ca | Ordinary | Log | Circular | 0.6579 | 32.1486 | 30.1062 | 0.0155 | 1.0624 | |
| Mg | Ordinary | Log | Gaussian | 0.5210 | 18.9853 | 22.6372 | −0.0224 | 0.8808 | |
| HCO3 | Ordinary | BoxCox | Stable | 19.5080 | 328.5189 | 367.5360 | 0.0498 | 0.9083 | |
| Cl | Ordinary | Log | Circular | −0.4151 | 38.0299 | 37.4075 | −0.0077 | 1.0432 | |
| SO4 | Ordinary | BoxCox | Stable | 0.0593 | 0.6693 | 0.6351 | 0.0892 | 1.0814 | |
| TDS | Ordinary | BoxCox | Stable | 12.4257 | 434.6693 | 453.4310 | 0.0294 | 1.0040 | |
| Qa-Qu | Na | Simple | None | Stable | 10.9458 | 143.4509 | 156.6227 | 0.0688 | 0.8907 |
| K | Simple | Log | Spherical | −0.1683 | 27.1142 | 19.2757 | −0.0102 | 1.4215 | |
| Ca | Simple | BoxCox | Stable | −0.3761 | 14.1042 | 11.5697 | −0.0176 | 1.1645 | |
| Mg | Ordinary | Log | Circular | 1.6593 | 20.6180 | 23.8640 | −0.0615 | 1.0218 | |
| HCO3 | Ordinary | BoxCox | Stable | 15.3778 | 261.7170 | 258.9817 | 0.0556 | 0.9939 | |
| Cl | Ordinary | Log | Stable | −0.3736 | 9.6335 | 7.1223 | −0.1165 | 1.2648 | |
| SO4 | Ordinary | None | Spherical | 0.0251 | 0.3209 | 0.3193 | 0.0654 | 1.0026 | |
| TDS | Simple | BoxCox | Gaussian | 6.7649 | 614.1923 | 453.6139 | −0.2829 | 1.8464 |
| Variables | pH | TDS | Ca | Mg | Na | K | Cl | HCO3 | SO4 | F | NO3 | Fe | E.C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||||||
| TDS | 0.20 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Ca | 0.11 | 0.26 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Mg | 0.10 | 0.53 | 0.31 | 1 | |||||||||
| Na | −0.30 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.07 | 1 | ||||||||
| K | −0.31 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.99 | 1 | |||||||
| Cl | −0.14 | 0.33 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 1 | ||||||
| HCO3 | −0.11 | −0.16 | −0.07 | 0.10 | −0.01 | 0.00 | −0.10 | 1 | |||||
| SO4 | 0.10 | 0.05 | −0.08 | 0.01 | −0.17 | −0.18 | 0.06 | −0.34 | 1 | ||||
| F | −0.26 | −0.17 | −0.35 | −0.21 | 0.14 | 0.13 | −0.18 | 0.09 | −0.26 | 1 | |||
| NO3 | 0.25 | 0.56 | 0.49 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.16 | −0.19 | 0.03 | −0.21 | 1 | ||
| Fe | −0.15 | −0.14 | −0.15 | −0.41 | −0.02 | −0.02 | −0.09 | −0.26 | −0.17 | 0.13 | −0.06 | 1 | |
| E.C | 0.19 | 0.99 | 0.24 | 0.55 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.34 | −0.16 | 0.05 | −0.16 | 0.55 | −0.15 | 1 |
| Variables | pH | TDS | Ca | Mg | Na | K | Cl | HCO3 | SO4 | F | NO3 | Fe | E.C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||||||
| TDS | 0.09 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Ca | 0.15 | 0.05 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Mg | 0.13 | −0.09 | 0.75 | 1 | |||||||||
| Na | −0.38 | −0.09 | 0.04 | 0.40 | 1 | ||||||||
| K | −0.38 | −0.09 | 0.04 | 0.41 | 0.99 | 1 | |||||||
| Cl | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.06 | −0.19 | −0.19 | 1 | ||||||
| HCO3 | 0.57 | −0.21 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.00 | 0.01 | −0.07 | 1 | |||||
| SO4 | 0.24 | −0.16 | 0.37 | 0.73 | 0.43 | 0.44 | −0.15 | 0.70 | 1 | ||||
| F | −0.27 | −0.22 | −0.35 | −0.18 | −0.09 | −0.09 | −0.16 | −0.42 | −0.30 | 1 | |||
| NO3 | −0.26 | 0.06 | −0.19 | −0.54 | −0.15 | −0.15 | −0.34 | −0.08 | −0.50 | −0.16 | 1 | ||
| Fe | 0.18 | −0.16 | −0.05 | −0.26 | −0.29 | −0.29 | −0.46 | 0.08 | −0.27 | −0.11 | 0.66 | 1 | |
| E.C | −0.13 | 0.24 | −0.16 | −0.04 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.34 | −0.27 | 0.15 | −0.23 | 1 |
| Water Type | Fw-Rh | Qa-Qu | Water Type % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na-Mg-HCO3 | 10 | 6 | 16 (40%) |
| Na-HCO3 | 11 | 3 | 14 (35%) |
| Na-Ca-Mg-HCO3 | 3 | 0 | 3 (7.5%) |
| Na-Ca-HCO3 | 3 | 0 | 3 (7.5%) |
| Mg-Na-Ca-Cl | 1 | 0 | 1 (2.5%) |
| Mg-Na-HCO3 | 0 | 1 | 1 (2.5%) |
| Na-Ca-Mg-HCO3-Cl | 1 | 0 | 1 (2.5%) |
| Na-Mg-Ca-HCO3 | 0 | 1 | 1 (2.5%) |
| DWQI Value | Rating of Water Quality | Percent % | Fw-Rh Area | Qa-Qu Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–25 | Excellent | 8 (20%) | 5 | 3 |
| 25–50 | Good | 20 (50%) | 17 | 3 |
| 51–100 | Poor | 6 (15%) | 3 | 3 |
| 101–200 | Very Poor | 3 (7.5%) | 2 | 1 |
| >>200 | Unsuitable for drinking | 3 (7.5%) | 2 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
A. Elubid, B.; Huang, T.; H. Ahmed, E.; Zhao, J.; M. Elhag, K.; Abbass, W.; M. Babiker, M. Geospatial Distributions of Groundwater Quality in Gedaref State Using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Drinking Water Quality Index (DWQI). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050731
A. Elubid B, Huang T, H. Ahmed E, Zhao J, M. Elhag K, Abbass W, M. Babiker M. Geospatial Distributions of Groundwater Quality in Gedaref State Using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Drinking Water Quality Index (DWQI). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(5):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050731
Chicago/Turabian StyleA. Elubid, Basheer, Tao Huang, Ekhlas H. Ahmed, Jianfei Zhao, Khalid. M. Elhag, Waleed Abbass, and Mohammed M. Babiker. 2019. "Geospatial Distributions of Groundwater Quality in Gedaref State Using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Drinking Water Quality Index (DWQI)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 5: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050731
APA StyleA. Elubid, B., Huang, T., H. Ahmed, E., Zhao, J., M. Elhag, K., Abbass, W., & M. Babiker, M. (2019). Geospatial Distributions of Groundwater Quality in Gedaref State Using Geographic Information System (GIS) and Drinking Water Quality Index (DWQI). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(5), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050731






