Spatiotemporal Variations in Gastric Cancer Mortality and Their Relations to Influencing Factors in S County, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
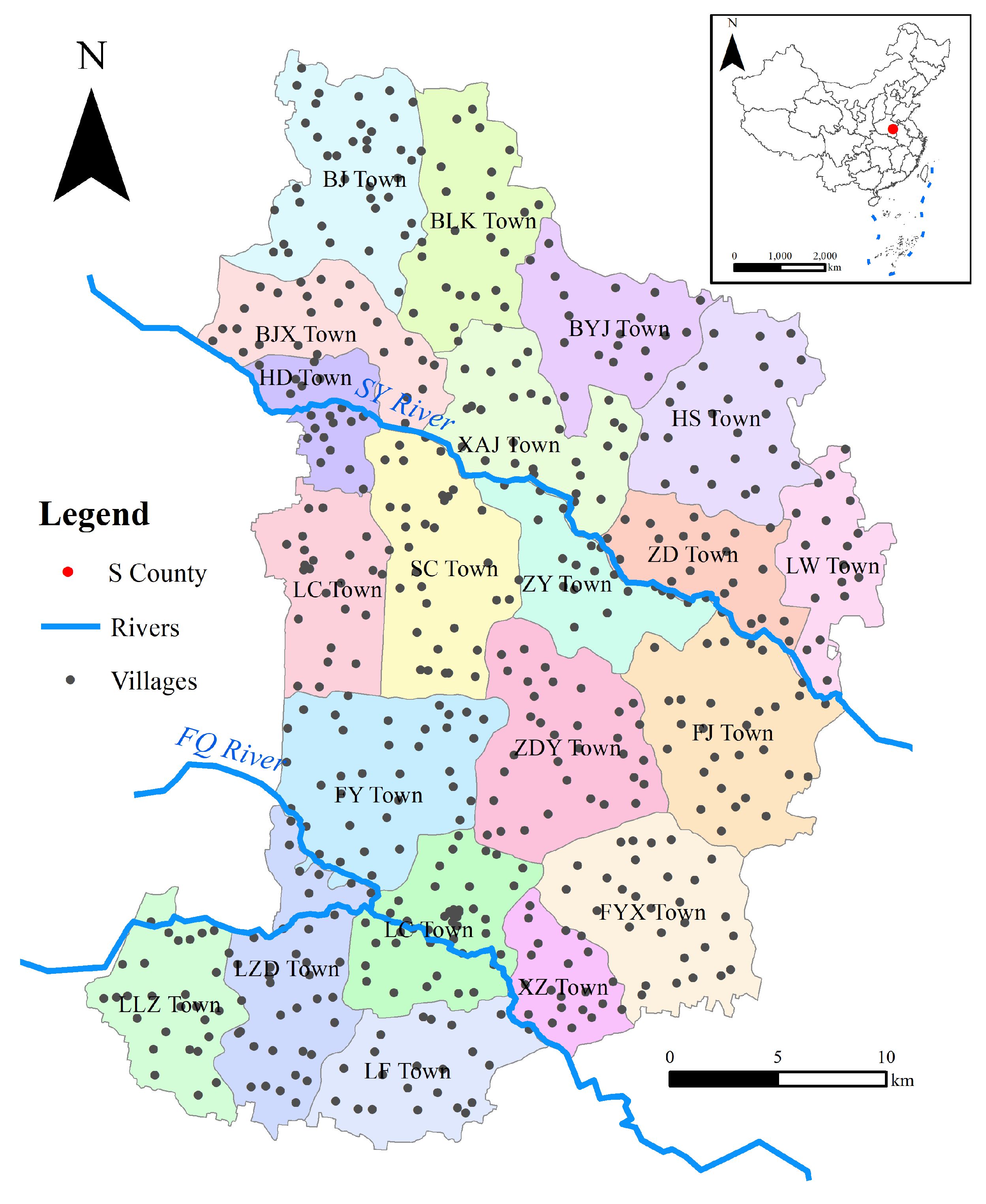
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Spatial Analysis Methods
2.3.1. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
2.3.2. Hot Spot Analysis
2.3.3. GeoDetector
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemproal Variations of Influencing Factors
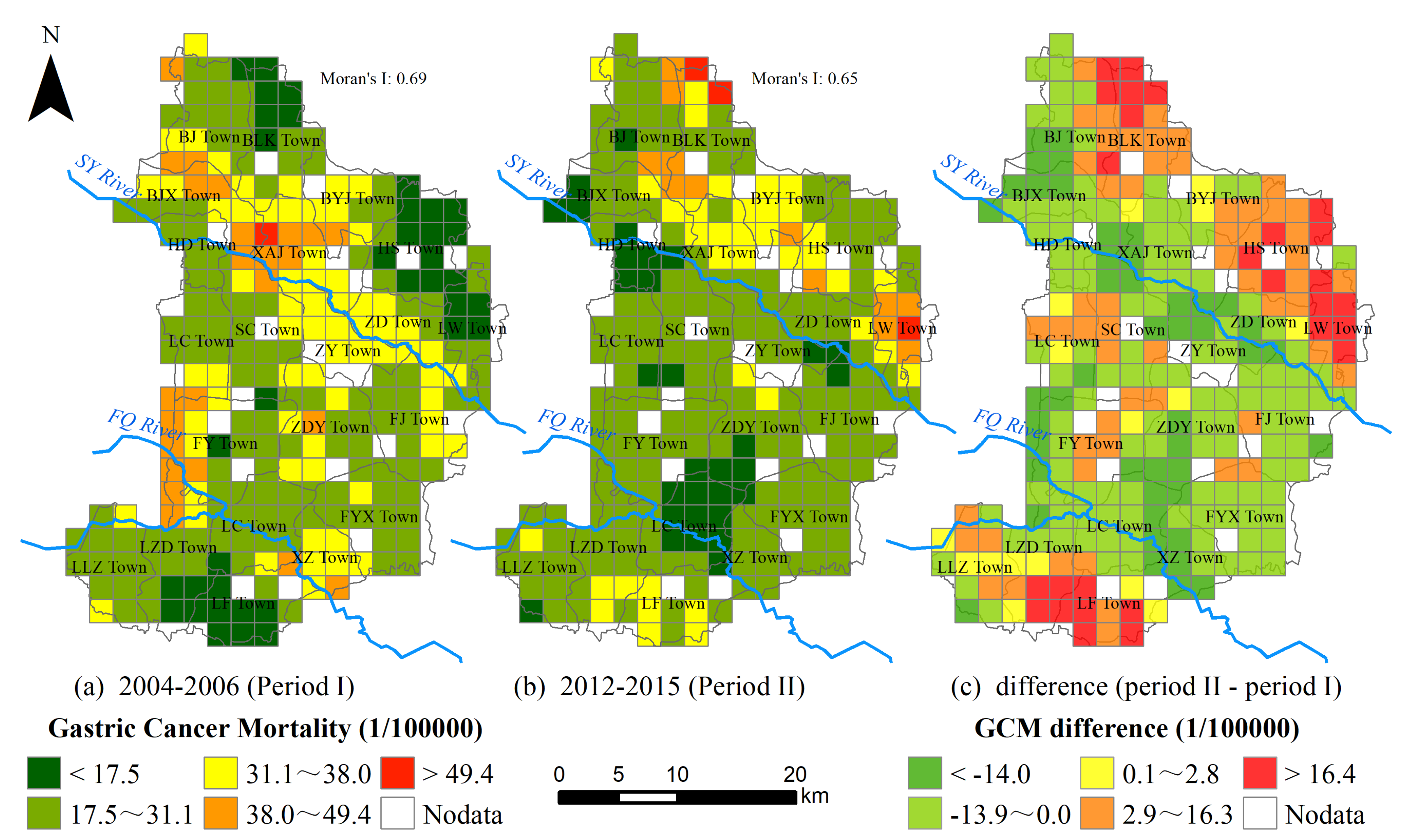
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations of GCM
3.3. Relationships between GCM and Influencing Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Shi, J.-F.; Guo, L.-W.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Wang, L.; Liao, X.-Z.; Liu, G.-X.; Bai, Y.-N.; Mao, A.-Y.; Ren, J.-S. Expenditure and financial burden for common cancers in China: a hospital-based multicentre cross-sectional study. Lancet 2016, 388, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Meta-analysis of the relationship between dietary habits and gastric cancer of Chinese residents. Mod. Prev. Med. 2008, 35, 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Wei, J.; He, X.; An, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Shao, D.; Liang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. Landscape of dietary factors associated with risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2820–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rota, M.; Pelucchi, C.; Bertuccio, P.; Matsuo, K.; Zhang, Z.F.; Ito, H.; Hu, J.; Johnson, K.C.; Palli, D.; Ferraroni, M.; et al. Alcohol consumption and gastric cancer risk-A pooled analysis within the StoP project consortium. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1950–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsugane, S. Salt, salted food intake, and risk of gastric cancer: epidemiologic evidence. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.H.; Zhuang, D.F. Atlas of the Huai River Basin Water Environment: Digestive Cancer Mortality; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.Y.; Wan, X.; Yang, F.; Shi, X.; Xu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Yang, G. Association between changing mortality of digestive tract cancers and water pollution: a case study in the Huai River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 12, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, A.; Ren, M.; Ge, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wan, S.; Hu, A.; Bo, Q.; et al. Potential health risks of heavy metals in cultivated topsoil and grain, including correlations with human primary liver, lung and gastric cancer, in Anhui province, Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, M.; Franceschi, S.; Vignat, J.; Forman, D.; de Martel, C. Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fock, K.M.; Talley, N.; Moayyedi, P.; Hunt, R.; Azuma, T.; Sugano, K.; Xiao, S.D.; Lam, S.K.; Goh, K.L.; Chiba, T. Asia–Pacific consensus guidelines on gastric cancer prevention. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Chengdong, X.U. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, W.R. A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Q.; Ren, Y.; Lou, Z. Spatiotemporal analysis and risk assessment of thyroid cancer in Hangzhou, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 30, 2155–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Bo, Y.; Xu, C.; Hu, M.; Huang, D. Identification of health risks of hand, foot and mouth disease in China using the geographical detector technique. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3407–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Christakos, G.; Sun, J.L.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Fu, X.Q.; Shi, Y.Q.; Li, X.M. Spatiotemporal transmission and determinants of typhoid and paratyphoid fever in Hongta District, Yunnan Province, China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Miao, C. Spatial Assessment of Cancer Incidences and the Risks of Industrial Wastewater Emission in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. Made in China: Cancer Villages. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 2010, 52, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.M.; Wen, Z.G. Review and challenges of policies of environmental protection and sustainable development in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Liao, W. Legislation, plans, and policies for prevention and control of air pollution in China: achievements, challenges, and improvements. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, S.; Han, X.; Liu, W.; Song, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Yang, F.; Tan, X.; Chen, X. Cancer mortality trends in an industrial district of Shanghai, China, from 1974 to 2014, and projections to 2029. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, W.; Xu, Z. Legal control of water pollution in Huai river, China: A case study. In Proceedings of the Conference Paper for Sixth International Conference on Environmental Compliance and Enforcement, San Jose, Costa Rica, 15–19 April 2002; International Network for Environmental Compliance and Enforcement: San Jose, Costa Rica, 2002; pp. 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Xu, D.; Shi, X.; Xu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Yang, G. Characterisation of gastric cancer and its relation to environmental factors: A case study in Shenqiu County, China. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2016, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M. Evaluation of the implementation of water pollution prevention and control plans in China: The case of Huai River Basin. In Background Paper, World Bank Policy Analytical and Advisory Assistance Program; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Henan Province Arranges Special Funds to Solve Drinking Water Safety Problems in Heavily Polluted Areas. Available online: http://www.people.com.cn/GB/huanbao/1073/3192409.html (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- Zhou, L.; Jiangang, X.U.; Jiang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, D. Spatial diversity characteristics of comprehensive control ability for water environmental pollution in the Huaihe River Basin. Prog. Geogr. 2013, 32, 560–569. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Zhou, M.; Tao, Z.; Ding, D.; Yang, G. Epidemiologic application of verbal autopsy to investigate the high occurrence of cancer along Huai River Basin, China. Popul. Health Metr. 2011, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Public Security. Demographic Statistics of Counties and Cities in People’s Republic of China (2012); Mass Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Richardson, S.; Thomson, A.; Best, N.; Elliott, P. Interpreting Posterior Relative Risk Estimates in Disease-Mapping Studies. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical analysis of disease data: estimation of cancer mortality risk from empirical frequencies using Poisson kriging. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2005, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, D.; Kaldor, J. Empirical Bayes estimates of age-standardized relative risks for use in disease mapping. Biometrics 1987, 43, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Ji, W.; Ren, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yang, G.; Zhuang, D. Model Analysis of Upper Digestive Tract Cancer and Environmental Pollution in Huaihe River Watershed. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2012, 14, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, J.N.; Catt, J.A. Enrichment of heavy metals in sediment resulting from soil erosion on agricultural fields. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3495–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.A.; Farley, T.A.; Mason, K. Why is poverty unhealthy? Social and physical mediators. Soc. Sci. Med. 2003, 57, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosadeghrad, A.M. Factors affecting medical service quality. Iran J. Public Health 2014, 43, 210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- FU, J.; JIANG, D.; HUANG, Y. 1 km grid population dataset of China (2005, 2010). Acta Geogr. Sini. 2014, 69, 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Fu, J. 1 km grid GDP dataset of China (2005, 2010). Acta Geogr. Sin. 2014, 69, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Selinus, O.; Alloway, B.J.; Centeno, J.A.; Finkelman, R.B.; Fuge, R.; Lindh, U.; Smedley, P. Essentials of Medical Geology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L.; Getis, A. Perspectives on spatial data analysis. In Perspectives on Spatial Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Liwei, W.; Changchun, F.; Shuncai, X. Return intention of migrant workers in a traditional agricultural area and planning response: Based on a questionnaire survey in Zhoukou, Henan Province. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 990–999. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Dafang, Z.; Hongyan, R.; Dong, J.; Yaohuan, H.; Xinliang, X.; Wei, C.; Xiaosan, J. Spatiotemporal variation of surface water quality for decades: a case study of Huai River System, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 1233. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Liu, C.; Li, L. Discussion and countermeasures on safe drinking water in the rural areas of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 62, 907. [Google Scholar]
- “Thirteenth Five-Year Plan” for Poverty alleviation in S County. Available online: http://www.shenqiu.gov.cn/news_xx.asp?msg=52393 (accessed on 9 January 2019).
- Streeter, J.L. Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Food Consumption and Nutrition in China: Empirical Evidence During the 1989–2009 Period. Chin. Econ. 2017, 50, 168–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, M. Natural history and epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 16, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Zheng, R.; Wang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Chen, W. Incidence and mortality of stomach cancer in China, 2014. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 30, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Wu, L.; Guan, W. Dietary Nitrates, Nitrites, and Nitrosamines Intake and the Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9872–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Environmental Factors | Proxy Variables | Dataset | Time | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human-made pollution | Distance from river | — | — | — | — |
| Percentage of farmlands | Land use data | 1995, 2005 * | 1 km | www.resdc.cn | |
| Physical environment | Elevation | Global Digital Elevation Model (V2) | 2009 | 30 m | www.gscloud.cn |
| Socioeconomic level | Population density | Gridded resident population density | 2005, 2015 | 1 km | www.resdc.cn |
| Gross domestic product (GDP) | Gridded GDP | 2005, 2015 | 1 km |
| Human-Made Pollution | Physical Environment | Socioeconomic Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| proxy variables | distance from river | the percentage of farmlands | elevation | population density | GDP |
| q statistic (Period I) | 0.15 *** | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| q statistic (Period II) | 0.11 *** | 0.03 *** | 0.00 | 0.02 *** | 0.03 *** |
| Interaction q statistic (Period II) | 0.14 *** | 0.00 | 0.04 *** | ||
| Proxy Variables | Distance from River (km) | Percentage of Farmlands (%) | Elevation (m) | Population Density (per/km²) | GDP (10,000 Yuan/km²) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strata | <3 | 3–10 | 10–15 | ≤median | >median | ≤median | >median | ≤median | >median | ≤median | >median |
| Mean GCM (Period I, 1/105) | 31.38 | 26.09 | 19.56 | Not significant | |||||||
| Mean GCM (Period II, 1/105) | 22.74 | 26.93 | 32.44 | 24.60 | 27.47 | Not significant | 27.17 | 24.72 | 27.46 | 24.51 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, C.; Wang, B.; Ren, H.; Wang, Z. Spatiotemporal Variations in Gastric Cancer Mortality and Their Relations to Influencing Factors in S County, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050784
Cui C, Wang B, Ren H, Wang Z. Spatiotemporal Variations in Gastric Cancer Mortality and Their Relations to Influencing Factors in S County, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(5):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050784
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Cheng, Baohua Wang, Hongyan Ren, and Zhen Wang. 2019. "Spatiotemporal Variations in Gastric Cancer Mortality and Their Relations to Influencing Factors in S County, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 5: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050784
APA StyleCui, C., Wang, B., Ren, H., & Wang, Z. (2019). Spatiotemporal Variations in Gastric Cancer Mortality and Their Relations to Influencing Factors in S County, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(5), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050784






