Changes in Behavior and Brain Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Mosquito Fish, Gambusia affinis in Response to the Sub-Lethal Exposure to Chlorpyrifos
Abstract
:Introduction
Materials and Methods
Determination of Median Lethal Concentration (LC50)
Statistical Analysis
Results and Discussions
| Compound | Regression Equation | Acute Toxicity Range 98% Confidence Limit | Median LC50 (µg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
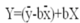 | Upper (µg/L) | Lower (µg/L) | ||
| Chlorpyrifos | -13.86 + 4.21X | 340.21 | 255.06 | 297.63 ± 21.72 |




| Exposure Period (Days) | Time After Initial Value (Hours) | Bio-Concentration Factors* in Different Parts of Fish | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscera | Head | Body | ||
| 4 | 0 | 0.197 (0.00) | 0.014 (0.00) | 0.005 (0.00) |
| 8 | 96 | 0.154 (21.83) | 0.011 (21.43) | 0.005 (0.00) |
| 12 | 192 | 0.100 (49.24) | 0.009 (35.71) | 0.004 (20.00) |
| 16 | 288 | 0.054 (72.59) | 0.006 (57.14) | 0.003 (40.00) |
| 20 | 384 | 0.038 (80.71) | 0.003 (78.57) | 0.002 (60.00) |
| Average bio concentration values ± SE | 0.109 | 0.009 | 0.004 | |
| ±0.029 | ±0.002 | ±0.001 | ||
Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Coppage, D.L.; Bradeich, E. River pollution by anti-cholinesterase agent. Water Research 1976, 10, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, Khan. Integrated Pest Management and Sustainable Agriculture. Farmer and Parliament 1996, 30, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, S. W. Changes in the toxicity of the three pesticides as a function of Environmental pH and temperature. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1991, 46, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmonds, C.R.; Dutta, H.M. Effect of malathion on the brain acetylcholinesterase activity of bluegill sunfish Lepomis macrochirus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1992, 49, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswara Rao, J. Effects of monocrotophos and its analogs in acetylcholinesterase activity’s inhibition and its pattern of recovery on euryhaline fish, Oreochromis mossambicus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, R. A.; Russom, C. L. Behavioral toxicity syndromes, a promising tool for assessing toxicity mechanisms in juvenile fat-head minnows. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1990, 9, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, E. Behavioral responses as indicator of environmental alterations: approaches, results, developments. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 1992, 8, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, J.; MacPhail, R. C. Ethological and experimental approaches to behavior analysis: implications for ecotoxicology. Environ. Health Persp. 1996, 104, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadehl, H.; Häder, D. P. Automated biomonitoring using real time movement analysis of Euglena gracilis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2001, 48, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J. A portrait of locomotor behavior in Drosophila determined by a video-tracking paradigm. Behaviour. Proc. 2003, 67(2), 207–219. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswara Rao, J.; Parvathi, K.; Kavitha, P.; Jakka, N.M.; Pallela, R. Effect of chlorpyrifos and monocrotophos on locomotor behaviour and acetylcholinesterase activity of subterranean termites, Odontotermes obesus. Pest Management Science 2004, 60, 000–000, (Published Online: 10 Nov 2004; DOI: 10.1002/ps.986). [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J. A.; Marr, J. C. A.; Lipton, J.; Cacela, D.; Bergman, H. L. Difference in neurobehavioural response of Chinook salmon, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha, and rainbow trout, Oncorynchus mykiss exposed to copper and cobalt, behavioural avoidance. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’Omo, G.; Bryenton, R.; Shore, R.F. Effects of exposure to an organophosphate pesticide on behavior and acetylcholinesterase activity in the common shrew, Sorex araneus. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, E. E.; Finger, S. E. Swimming behavior as an indicator of sublethal toxicity in fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1990, 9, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotz, K. G. Visual guidance in Drosophila. In: Development and Neurobiology of Drosophila. Siddiqui, O., Babu, P., Hall, L.M., Hall, J.C., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, 1980; pp. 391–407. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, S. K.; Little, E. E.; DeLonay, A. J.; Beauvais, S. L.; Jones, S. B.; Ellersieck, M. R. Behavioral Dysfunctions Correlate to Altered Physiology in Rainbow Trout (Oncorynchus mykiss) Exposed to Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Chemicals. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 40, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Healing, G.; Harvey, P. W.; Mc Farlane, M.; Buss, N. A. P. S.; Mallyon, B. A.; Cockburn, A. Assessment of motor activity in regulatory neurotoxicity studies, Validation of the EthoVision video tracking system in rats treated with amphetamine and chlorpromazine. Toxicol. Methods 1997, 7, 279–287. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, P.; Noldus, J. J.; Andrew, S.; Ruud, A.; Tegelenbosh, J. Computerized video tracking, movement analysis and behavior recognition in insects. Com. Electron. Agri. 2002, 35(2-3), 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, E. I.; Unlu, E.; Balci, K. The histopathological effects of thiodan on the liver and gut of mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis. J. Environ. Sci. Health B. 2001, 36(1), 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, E. I.; Unlu, E. Histopathological changes in the gills of mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis exposed to endosulfan. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 68(2), 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanein, H. M. Toxicological effects of the herbicide oxyfluorfen on acetylcholinesterase in two fish species, Oreochromis niloticus and Gambusia affinis. J. Environ. Sci. Health. Part A. Tox. 2002, 37(4), 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Clesceri, L. S., Greenberg, A. E., Eaton, A. D., Eds.; 20th editionAmerican Public Health Association: Washington, DC, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP/FAO/IAEA. Estimation of the Acute Lethal Toxicity of Pollutants to Marine Fish and Invertebrates. In Reference methods for marine pollution studies; No. 43.; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Finney, D.J. Probit analysis 2nd edition. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, O. H.; Rosebrough, N. J.; Farr, A. L.; Randall, R. J. Protein measurement with Folin Phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Ellman, G. L.; Courtney, K. D.; Andres Jr, V. V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmocol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S. C.; Tannan, S. K. Future of Indian pesticides industry in the next millennium. Pest. Inform. 1999, 24, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswara Rao, J.; Shilpanjali, D.; Kavitha, P.; Madhavendra, S. S. Toxic effects of profenofos on tissue acetylcholinesterase and gill morphology in a euryhaline fish, Oreochromis mossambicus. Arch. Toxicol. 2003, 77(4), 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, M. R.; Fanta, E. Effects of the organophosphorous methyl parathion on the branchial epithelium of a freshwater fish Metynnis roosevelti. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2003, 46(3), 361–372. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswara Rao, J.; Shoba Rani, C. H.; Kavitha, P.; Nageswara Rao, R.; Madhavendra, S. S. Toxic effects of chlorpyrifos on Oreochromis mossambicus. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 70(5), 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerterp, K. How rats economize–energy loss in starvation. Physiol. Zoo. 1977, 50, 331–362. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, G. E.; Rosen, P.; Johansson, D. Anoxic depression of spontaneous locomotor activity in crucian carp quantified by a computerized imaging technique. J. Exp. Biol. 1993, 180, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Bayley, M.; Baatrup, E.; Heimbach, U.; Bjerregaard, P. Elevated copper levels during larval development cause altered locomotor behaviour in the adult Carabid Beetle, Pterostichus cupreus L. (Coleooptera: Carabidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1995, 32, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Omo, G.; Pleskacheva, M. G.; Wolfer, D. P.; Lipp, H. P.; Shore, R. F. Comparative effects of exposure to an organophosphate pesticide on locomotor activity of laboratory mice and five species of wild rodents. Bull. Environ. Cont. Toxicol. 2003, 70(1), 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chapman, J. C. Profenofos residues in wild fish from cotton-growing areas of New South Wales, Australia. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K. J.; Cha, C. G. etermination of the bioconcentration of phosphamidon and profenofos in zebra fish, Brachydanio rerio. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 65, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S. R.; Bansal, S. K.; Dalela, R. C. Quantitative estimation of biocide residues in a few tissues of Labio rohita and Saccobrachus fossilis. Ind. J. Environ. Health. 1977, 19, 189–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, N.; Venugopalan, V. K. Bioconcentration of endosulfan in different body tissues of estuarine organisms under sublethal exposure. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1991, 46, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghousia, Begum.; Shanta, Vijayaraghavan.; Nageswara Sharma, P. Sajid Husain: Study of dimethoate bioaccumulation in liver and muscle tissues of Clarias batrachus and its elimination following cessation of exposure. Pest. Sci. 1994, 40, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn Sipes, I.; Gandolfi, J. Biotransformation of Toxicants. In The Basic Science of poisonsKlaassen, Curtis D, Amdur., Mary O, Doull., John, Eds.; 3rd edition; Macmillan Publishing Company: New York, 1986; pp. 64–98. [Google Scholar]
- Jimener, B. D.; Stegman, S. S. American Fisheries Society Symposium. 1990; pp. 867–879. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Oost, R.; Heida, H.; Opperhuizen, A.; Vermeulen, N. P. Interrelationships between bioaccumulation of organic trace pollutants (PCBs, organochlorine pesticides and PAHs), and MFO-induction in fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1991, 100, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
© 2005 MDPI. All rights reserved.
Share and Cite
Rao, J.V.; Begum, G.; Pallela, R.; Usman, P.K.; Rao, R.N. Changes in Behavior and Brain Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Mosquito Fish, Gambusia affinis in Response to the Sub-Lethal Exposure to Chlorpyrifos. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 478-483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2005030013
Rao JV, Begum G, Pallela R, Usman PK, Rao RN. Changes in Behavior and Brain Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Mosquito Fish, Gambusia affinis in Response to the Sub-Lethal Exposure to Chlorpyrifos. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2005; 2(3):478-483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2005030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, J. Venkateswara, Ghousia Begum, R. Pallela, P. K. Usman, and R. Nageswara Rao. 2005. "Changes in Behavior and Brain Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Mosquito Fish, Gambusia affinis in Response to the Sub-Lethal Exposure to Chlorpyrifos" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2, no. 3: 478-483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2005030013
APA StyleRao, J. V., Begum, G., Pallela, R., Usman, P. K., & Rao, R. N. (2005). Changes in Behavior and Brain Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Mosquito Fish, Gambusia affinis in Response to the Sub-Lethal Exposure to Chlorpyrifos. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2(3), 478-483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2005030013




