Respiratory Health Symptoms among Students Exposed to Different Levels of Air Pollution in a Turkish City
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- - Preliminary assessment of the air pollution was made by using passive samplers.
- - Schools were selected based on prepared distribution maps for NO2 and ozone with the help of ArcGIS software.
- - A questionnaire was prepared and filled out via interviews with children.
- - Questionnaire responses were evaluated together with outdoor and indoor pollutant concentrations.
2.1. Air Quality Parameters Analysis
2.2. Questionnaires
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
References
- Curtis, LK; Rea, W; Smith-Willis, P; Fenyves, E; Pan, Y. Adverse health effects of outdoor air pollutants. Environ. Int 2006, 32, 815–830. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, JA; Alexis, N; Barnes, C; Bernstein, IL; Bernstein, JA; Nel, A; Peden, D; Diaz-Sanchez, D; Tarlo, SM; Williams, PB. Health effects of air pollution. J. Allergy Clin. Immun 2004, 114, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, AJ; Ross, AH; Ostro, B; Pandey, KD; Krzyzanowski, M; Kunzli, N; Gutschmidt, K; Pope, A; Romieu, I; Samet, JM; Smith, K. The global burden of disease due to outdoor air pollution. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2005, A68, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar]
- De Marini, DM; Claxton, LD. Outdoor air pollution and DNA damage. Occup. Environ. Med 2006, 63, 227–228. [Google Scholar]
- Vineis, P; Forastere, F; Hoek, G; Lipsett, M. Outdoor air pollution and lung cancer: Recent epidemiologic evidence. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 111, 647–657. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, TJ; Parker, JD; Adams, K; Bell, ML; Gehring, U; Glinianaia, S; Ha, EH; Jalaludin, B; Slama, R. International collaboration on air pollution and pregnancy outcomes (ICAPPO). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2638–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Rocklöv, J; Forsberg, B. The effect of high ambient temperature on the elderly population in three regions of Sweden. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar]
- Salvi, S. Health effects of ambient air pollution in students. Pediatr. Respir. Rev 2007, 8, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ness, O; Piro, FN; Nafstad, P; Smith, GD; Leyland, AH. Air pollution, social deprivation, and mortality a multilevel cohort study. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 686–694. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, NAH; Viliet, PHN; Aarts, F; Harssema, H; Brunekreef, B. Assessment of exposure to traffic related air pollution of students attending schools near motorways. Atmos. Environ 2001, 35, 3875–3884. [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore, MR; Dimitroulopoulou, C. Personal exposure of students to air pollution. Atmos. Environ 2009, 43, 128–141. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, SC; Wang, M. Indoor and outdoor air quality investigation at schools in Hong Kong. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Godwin, C; Batterman, S. Indoor air quality in Michigan schools. Indoor Air 2007, 17, 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, CYH. Comparison between indoor and outdoor air contaminant levels in residential buildings from passive sampler study. Build. Environ 2001, 36, 999–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Kousa, A; Monn, C; Rotko, T; Alm, S; Oglesby, L; Jantunen, MJ. Personal exposures to NO2 in the EXPOLIS-study: Relation to residential indoor, outdoor and workplace concentrations in Basel, Helsinki and Prague. Atmos. Environ 2001, 35, 3405–3412. [Google Scholar]
- TUİK. Address Based Population Registration System Population Census 2009; Turkish Statistical Institute, Printing Division: Ankara, Turkey, March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, MI; Keil, U; Anderson, HR; Beasley, R; Crane, J; Martinez, F; Mitchell, EA; Pearce, N; Sibbald, B; Stewart, AW; Strachan, D; Weiland, SK; Williams, HC. International study of asthma and allergies in childhood (ISAAC): Rationale and methods. Eur. Respir. J 1995, 8, 483–491. [Google Scholar]
- Keleş, N; Ilicali, C. The impact of outdoor pollution on upper respiratory diseases. Rhinology 1998, 36, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kilpelainen, M; Terho, BO; Helenius, H; Koskenvuo, M. Validation of a new questionnaire on asthma, allergic rhinitis, and conjunctivitis in young adults. Allergy 2001, 56, 377–384. [Google Scholar]
- Van Roosbroeck, S; Wichmann, J; Janssen, NAH; Hoek, G; van Wijnen, JH; Lebret, E; Brunekreef, B. Long-term personal exposure to traffic-related air pollution among school students, a validation study. Sci. Total Environ 2006, 368, 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Van Roosbroeck, S; Li, R; Hoek, G; Lebret, E; Brunekreef, B; Spiegelman, D. Traffic-Related outdoor air pollution and respiratory symptoms in students: The impact of adjustment for exposure measurement error. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Gauderman, WJ; Avol, E; Gilliland, F; Vora, H; Thomas, D; Berhane, K; McConnell, R; Kuenzli, N; Lurmann, F; Rappaport, E; Margolis, H; Bates, D; Peters, J. The effect of air pollution on lung development from 10 to 18 years of age. N. Engl. J. Med 2004, 351, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, J. Air pollution and children’s health. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Diapouli, E; Chaloulakou, A; Spyrellis, N. Indoor and outdoor particulate matter concentrations at schools in the Athens area. Indoor Built. Environ 2007, 16, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z; Chapman, RS; Hu, W; Wei, F; Korn, LR; Zhang, J. Using air pollution based community clusters to explore air pollution health effects in children. Environ. Int 2004, 30, 611–620. [Google Scholar]
- de Marco, R; Marcon, A; Rava, M; Cazzoletti, L; Pironi, V; Silocchi, C; Ricci, P. Proximity to chipboard industries increases the risk of respiratory and irritation symptoms in children: The Viadana study. Sci. Total Environ 2010, 408, 511–517. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D; Takahashi, K; Pan, G; Chan, CC; Zhang, Z; Feng, Y; Hoshuyama, T; Chuang, KJ; Lin, RT; Hwang, JS. Respiratory symptoms among residents of a heavy-industry province in China: Prevalence and risk factors. Resp. Med 2008, 102, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2008: The MPOWER Package; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Morgenstern, V; Zutavern, A; Cyrys, J; Brockow, I; Gehring, U; Koletzko, S; Bauer, CP; Reinhardt, D; Wichmann, HE; Heinrich, J. Respiratory health and individual estimated exposure to traffic-related air pollutants in a cohort of young students. Occup. Environ. Med 2007, 64, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, PC; Lai, YM; Wang, JD; Yang, CY; Hwang, JS; Kuo, HW; Hwang, SL; Chan, CC. Adverse Effect of air pollution on respiratory health of primary school children in Taiwan. Environ. Health Perspect 1998, 106, 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Langkulsen, U; Jinsart, W; Karita, K; Eiji, YE. Respiratory symptoms and lung function in Bangkok school children. Eur. J. Public Health 2006, 16, 676–681. [Google Scholar]
- Epton, MJ; Dawson, RD; Brooks, WM; Kingham, S; Aberkane, T; Cavanagh, JA; Frampton, CM; Hewitt, T; Cook, JM; McLeod, S; McCartin, F; Trought, K; Brown, L. The effect of ambient air pollution on respiratory health of school children: A panel study. Environ. Health 2008, 7, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Carbajal-Arroyo, L; Barraza-Villarreal, A; Durand-Pardo, R; Moreno-Macias, H; Espinoza-Lain, R; Chiarella-Ortigosa, P; Romieu, I. Impact of traffic flow on the asthma prevalence among school children in Lima, Peru. J. Asthma 2007, 44, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Castillejos, M; Gold, D; Dockery, D; Tosteson, T; Baum, T; Speizer, F. Effects of ambient ozone on respiratory function and symptoms in Mexico school students. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis 1992, 145, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- Romieu, I; Meneses, F; Ruiz Velasco, S; Sienra-Monge, JJ; Huerta, J; White, MC; Etzel, RA; Hernandez, M. Effects of intermittent ozone exposure on respiratory health of asthmatic students in Mexico City. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis 1994, 149, A659. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, R; Berhane, K; Gilliland, F; London, SJ; Islam, T; Gauderman, WJ; Avol, E; Margolis, HG; Peters, JM. Asthma in exercising children exposed to ozone: A cohort study. Lancet 2002, 359, 386–391. [Google Scholar]
- Pershagen, G; Rylander, E; Norberg, S; Eriksson, M; Nordvall, SL. Air pollution involving nitrogen dioxide and wheezing bronchitis in children. Int. J. Epidemiol 1995, 24, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar]
- WHO (World Health organization). Air Quality Guidelines—Global Update 2005; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Penard-Morand, C; Charpin, D; Raherison, C; Kopferschmitt, C; Caillaud, D; Lavaud, F. Long-term exposure to background air pollution related to respiratory and allergic health in school students. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2005, 35, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z; Zhang, Z; Wang, Z; Ferm, M; Liang, Y; Norbäck, D. Asthmatic symptoms among pupils in relation to winter indoor and outdoor air pollution in schools in Taiyuan, China. Environ. Health Perspect 2008, 116, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Blondeau, P; Iordache, V; Poupard, O; Genin, D; Allard, F. Relation between outdoor and indoor air quality in eight French schools. Indoor Air 2005, 15, 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Poupard, O; Blondeau, P; Iordache, V; Allard, F. Statistical analysis of parameters influencing the relationship between outdoor and indoor air quality in schools. Atmos. Environ 2005, 39, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar]
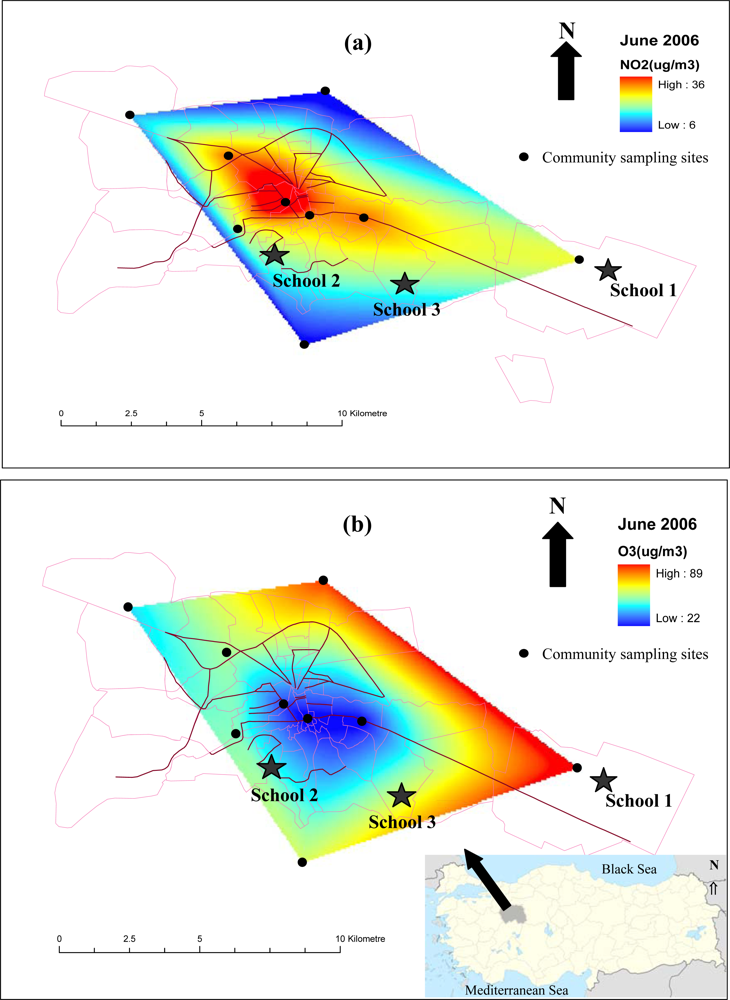
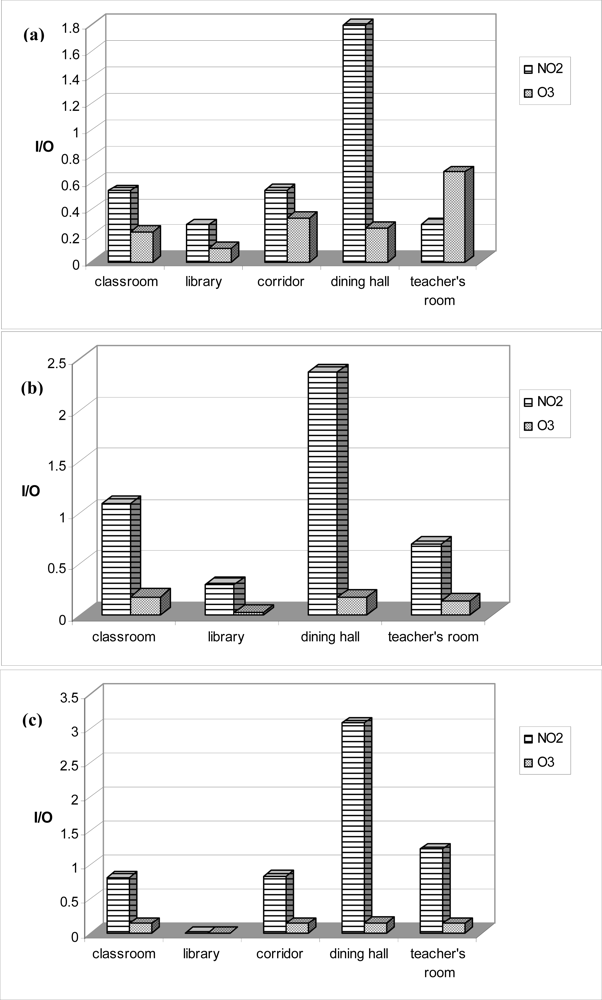
| Variable | Total | School 1 (n = 249) | School 2 (n = 254) | School 3 (n = 164) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| Gender | |||||||||
| Male | 455 | 68.2 | 192 | 77.1 | 169 | 66.5 | 94 | 57.3 | |
| Female | 212 | 31.8 | 57 | 22.9 | 85 | 33.5 | 70 | 42.7 | |
| Age (year) | |||||||||
| 15 | 215 | 32.2 | 81 | 32.5 | 74 | 29.1 | 60 | 36.6 | |
| 16 | 239 | 35.8 | 92 | 36.9 | 81 | 31.9 | 66 | 40.2 | |
| 17 | 188 | 28.2 | 70 | 28.1 | 83 | 32.7 | 35 | 21.3 | |
| 18 | 25 | 3.7 | 6 | 2.4 | 16 | 6.3 | 3 | 1.8 | |
| Living at current address (year) | |||||||||
| 3–5 | 420 | 62.9 | 169 | 67.9 | 190 | 74.8 | 61 | 37.2 | |
| 6–10 | 98 | 14.7 | 28 | 11.2 | 30 | 11.8 | 40 | 24.4 | |
| 11–15 | 121 | 18.2 | 36 | 14.5 | 32 | 12.6 | 53 | 32.3 | |
| ≥16 | 28 | 4.2 | 16 | 6 | 2 | 0.8 | 10 | 6.1 | |
| Mother’s education | |||||||||
| ≤Primary school | 250 | 37.5 | 134 | 53.8 | 60 | 23.6 | 56 | 34.1 | |
| Middle school | 103 | 15.4 | 55 | 22.1 | 24 | 9.5 | 24 | 14.6 | |
| High school | 162 | 24.3 | 42 | 16.9 | 68 | 26.8 | 52 | 31.7 | |
| University | 152 | 22.8 | 18 | 7.2 | 102 | 40.1 | 32 | 19.6 | |
| Father’s education | |||||||||
| ≤Primary school | 118 | 17.7 | 75 | 30.1 | 14 | 5.5 | 29 | 17.6 | |
| Middle school | 82 | 12.3 | 57 | 22.9 | 13 | 5.1 | 12 | 7.3 | |
| High school | 204 | 30.6 | 82 | 32.9 | 65 | 25.6 | 57 | 34.8 | |
| University | 263 | 39.4 | 35 | 14.1 | 162 | 63.8 | 66 | 40.3 | |
| Mother’s job | |||||||||
| Housewife | 473 | 70.9 | 221 | 88.8 | 136 | 53.5 | 116 | 70.7 | |
| Retired | 52 | 7.8 | 7 | 2.8 | 32 | 12.6 | 13 | 7.9 | |
| Blue collar worker | 14 | 2.1 | 7 | 2.8 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 4.3 | |
| White collar worker | 112 | 16.8 | 14 | 5.6 | 81 | 31.9 | 17 | 10.4 | |
| Other | 16 | 2.4 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 2.0 | 11 | 6.7 | |
| Father’s job | |||||||||
| Retired | 126 | 18.9 | 39 | 15.7 | 48 | 18.9 | 39 | 23.8 | |
| Blue collar worker | 128 | 19.2 | 83 | 33.3 | 19 | 7.5 | 26 | 15.9 | |
| White collar worker | 98 | 14.7 | 51 | 20.5 | 27 | 10.6 | 20 | 12.2 | |
| Own work | 25 | 3.7 | 12 | 4.8 | 11 | 4.3 | 2 | 1.2 | |
| Farmer | 175 | 26.2 | 48 | 19.3 | 95 | 37.4 | 32 | 19.5 | |
| Driver | 17 | 2.5 | 12 | 4.8 | 1 | 10.4 | 4 | 2.4 | |
| Other | 98 | 14.6 | 4 | 1.6 | 53 | 20.9 | 41 | 25.0 | |
| Student | |||||||||
| Yes works | 14 | 2.1 | 7 | 2.8 | 0 | 0.0 | 7 | 2.3 | |
| No doesn’t work | 653 | 97.9 | 242 | 97.2 | 254 | 100 | 157 | 95.7 | |
| Monthly income | |||||||||
| Low | 68 | 10.0 | 56 | 22.5 | 4 | 1.6 | 8 | 4.9 | |
| Medium | 494 | 74.2 | 186 | 74.7 | 178 | 70.1 | 130 | 79.3 | |
| High | 105 | 15.7 | 7 | 2.8 | 72 | 28.3 | 26 | 15.9 | |
| Own room | |||||||||
| There is | 521 | 78.1 | 198 | 79.5 | 181 | 71.3 | 142 | 86.6 | |
| There is not | 146 | 21.9 | 51 | 20.5 | 73 | 28.7 | 22 | 13.4 | |
| Smoking status | |||||||||
| Current smoker | 84 | 12.6 | 61 | 24.5 | 7 | 2.8 | 16 | 9.8 | |
| Never smoked | 545 | 81.7 | 168 | 67.5 | 233 | 91.7 | 144 | 87.8 | |
| Ex smoker | 38 | 5.7 | 20 | 8.0 | 14 | 5.5 | 4 | 2.4 | |
| Passive smoker | |||||||||
| Yes | 370 | 55.5 | 92 | 36.9 | 159 | 62.6 | 119 | 72.6 | |
| No | 297 | 44.5 | 157 | 63.1 | 95 | 37.4 | 45 | 27.4 | |
| Symptom | Total | School 1 (n = 249) | School 2 (n = 254) | School 3 (n = 164) | Chi-square | (p) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| Physician diagnosed chronic pulmonary disease | ||||||||||
| Yes | 105 | 15.7 | 54 | 21.7 | 30 | 11.8 | 21 | 12.8 | 10.660 | 0.005 * |
| No | 562 | 84.1 | 195 | 78.3 | 224 | 88.2 | 143 | 87.2 | ||
| Total | 667 | 100 | 249 | 100 | 254 | 100 | 164 | 100 | ||
| Wheezing | ||||||||||
| Yes | 126 | 19.0 | 57 | 22.9 | 43 | 16.9 | 26 | 15.9 | 4.226 | 0.121 |
| No | 541 | 81.0 | 192 | 77.1 | 211 | 83.1 | 138 | 84.1 | ||
| Total | 667 | 100 | 249 | 100 | 254 | 100 | 164 | 100 | ||
| Physician-diagnosed current asthma | ||||||||||
| Yes | 20 | 3.0 | 11 | 4.4 | 5 | 2.0 | 4 | 2.4 | 2.827 | 0.243 |
| No | 647 | 97.0 | 238 | 95.6 | 249 | 98.0 | 160 | 97.6 | ||
| Total | 667 | 100 | 249 | 100 | 254 | 100 | 164 | 100 | ||
| Tightness in the chest | ||||||||||
| Yes | 157 | 23.5 | 77 | 30.9 | 48 | 18.9 | 32 | 19.5 | 12.063 | 0.002 * |
| No | 510 | 76.5 | 172 | 69.1 | 206 | 81.1 | 132 | 80.5 | ||
| Total | 667 | 100 | 249 | 100 | 254 | 100 | 164 | 100 | ||
| Physician diagnosed bronchitis | ||||||||||
| Yes | 187 | 28.0 | 80 | 32.1 | 61 | 24.0 | 46 | 28.0 | 4.102 | 0.129 |
| No | 480 | 72.0 | 169 | 67.9 | 193 | 76.0 | 118 | 72.0 | ||
| Total | 667 | 100 | 249 | 100 | 254 | 100 | 164 | 100 | ||
| Persistent cough with phlegm | ||||||||||
| Yes | 336 | 50.4 | 114 | 45.8 | 128 | 50.4 | 94 | 57.3 | 5.262 | 0.072 |
| No | 331 | 49.6 | 135 | 54.2 | 126 | 49.6 | 70 | 42.7 | ||
| Total | 667 | 100 | 249 | 100 | 254 | 100 | 164 | 100 | ||
| Morning cough without infection | ||||||||||
| Yes | 62 | 9.3 | 36 | 14.5 | 15 | 5.9 | 11 | 6.7 | 12.635 | 0.002 * |
| No | 605 | 90.7 | 213 | 85.5 | 239 | 94.1 | 153 | 93.3 | ||
| Total | 667 | 100 | 249 | 100 | 254 | 100 | 164 | 100 | ||
| Morning phlegm without infection | ||||||||||
| Yes | 59 | 8.8 | 32 | 12.9 | 16 | 6.3 | 11 | 6.7 | 7.928 | 0.019 * |
| No | 608 | 91.2 | 217 | 87.1 | 238 | 93.7 | 153 | 93.3 | ||
| Total | 667 | 100 | 249 | 100 | 254 | 100 | 164 | 100 | ||
| Dependent variables with only significant risk factors (p < 0.05) | Model coefficient (B) | Standard error | Statistical significance (p) | Odds Ratio (95%CI: lower-upper) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physician diagnosed chronic pulmonary disease | ||||
| Industrial zone (ref = school 3 ) | 0.396 | 0.150 | 0.008 | 1.49 (1.11–1.99) |
| In family asthma, allergy etc (ref = no ) | 0.927 | 0.239 | 0.0001 | 2.53 (1.58–4.04) |
| Gender (ref = female) | 0.569 | 0.260 | 0.029 | 1.77 (1.06–2.94) |
| Wheezing | ||||
| In family asthma, allergy etc (ref = no ) | 0.547 | 0.240 | 0.022 | 1.73 (1.08–2.76) |
| Mother’s job (ref = housewife) | –0.999 | 0.321 | 0.002 | 0.37 (1.01–3.16) |
| Smoking (ref = no) | 0.521 | 0.208 | 0.012 | 1.68 (1.12–2.53) |
| Physician –diagnosed current asthma | ||||
| In family asthma, allergy etc. (ref = no ) | 1.344 | 0.465 | 0.004 | 3.80 (1.53–9.45) |
| Working status of student (ref = no ) | 2.168 | 0.721 | 0.003 | 8.74 (2.13–35.92) |
| Tightness in the chest | ||||
| Industrial zone (ref = school 3 ) | 0.450 | 0.130 | 0.001 | 1.57 (1.22–2.02) |
| Physician –diagnosed bronchitis | ||||
| Passive smoker (ref = no ) | 0.465 | 0.188 | 0.013 | 1.59 (1.10–2.30) |
| Persistent cough with phlegm | ||||
| Father’s job (ref = retired) | 0.586 | 0.213 | 0.006 | 1.79 (1.18–2.72) |
| Morning cough without infection | ||||
| Industrial zone (ref = school 3 ) | 0.592 | 0.215 | 0.006 | 1.81 (1.19–2.75) |
| Mother’s education (ref = middle school) | –0.650 | 0.281 | 0.021 | 0.52 (0.30–0.90) |
| Morning phlegm without infection | ||||
| Smoking (ref = no) | 0.581 | 0.235 | 0.014 | 1.79 (1.13–2.83) |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gül, H.; Gaga, E.O.; Döğeroğlu, T.; Özden, Ö.; Ayvaz, Ö.; Özel, S.; Güngör, G. Respiratory Health Symptoms among Students Exposed to Different Levels of Air Pollution in a Turkish City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 1110-1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8041110
Gül H, Gaga EO, Döğeroğlu T, Özden Ö, Ayvaz Ö, Özel S, Güngör G. Respiratory Health Symptoms among Students Exposed to Different Levels of Air Pollution in a Turkish City. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2011; 8(4):1110-1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8041110
Chicago/Turabian StyleGül, Hülya, Eftade O. Gaga, Tuncay Döğeroğlu, Özlem Özden, Özkan Ayvaz, Sevda Özel, and Günay Güngör. 2011. "Respiratory Health Symptoms among Students Exposed to Different Levels of Air Pollution in a Turkish City" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 8, no. 4: 1110-1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8041110
APA StyleGül, H., Gaga, E. O., Döğeroğlu, T., Özden, Ö., Ayvaz, Ö., Özel, S., & Güngör, G. (2011). Respiratory Health Symptoms among Students Exposed to Different Levels of Air Pollution in a Turkish City. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 8(4), 1110-1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8041110




