Evaluation of Benzo[a]pyrene in Food from China by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Sample Treatment
2.4. DLLME-SFO Procedures
2.5. HPLC Analysis
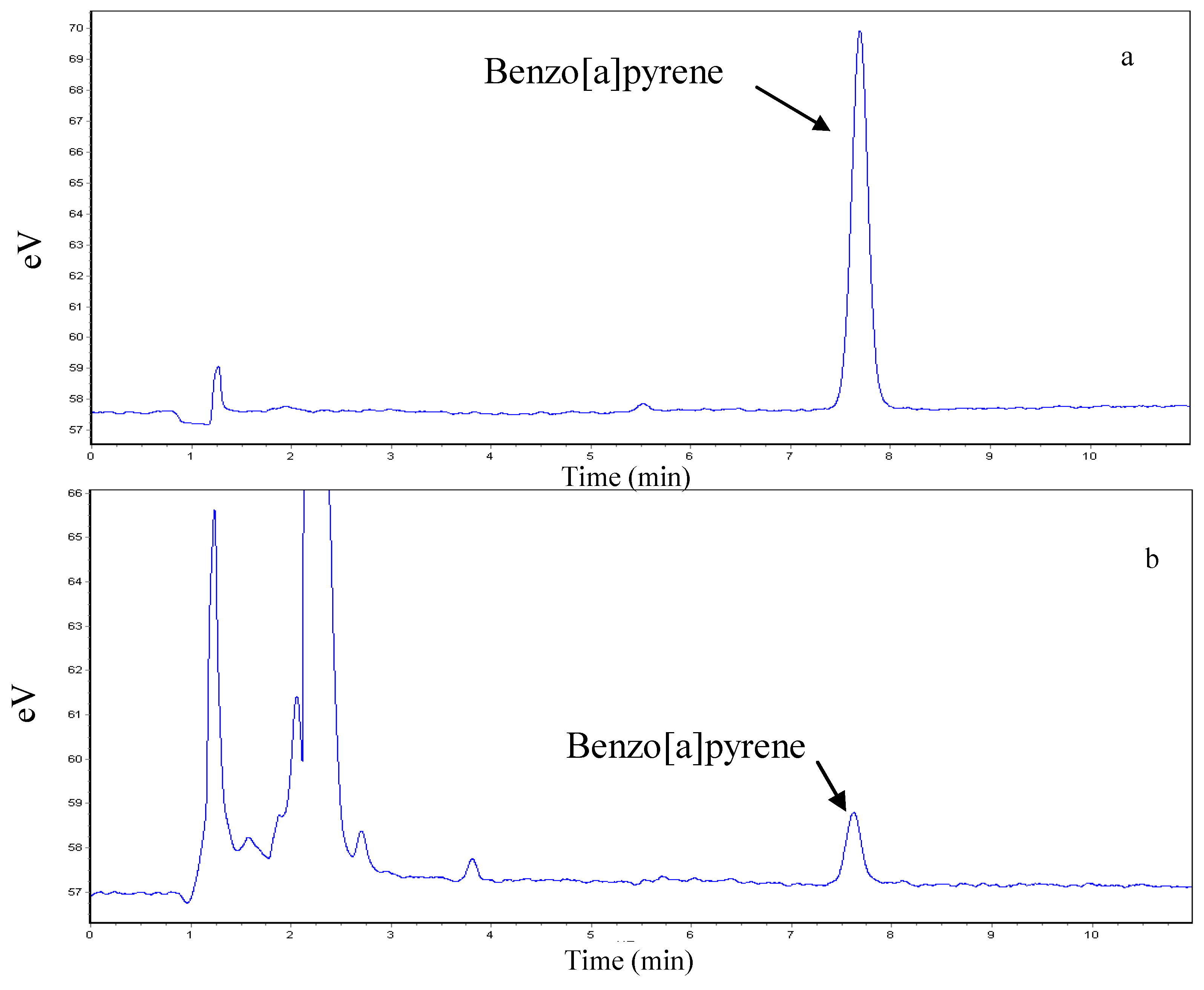
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of the Analytical Method
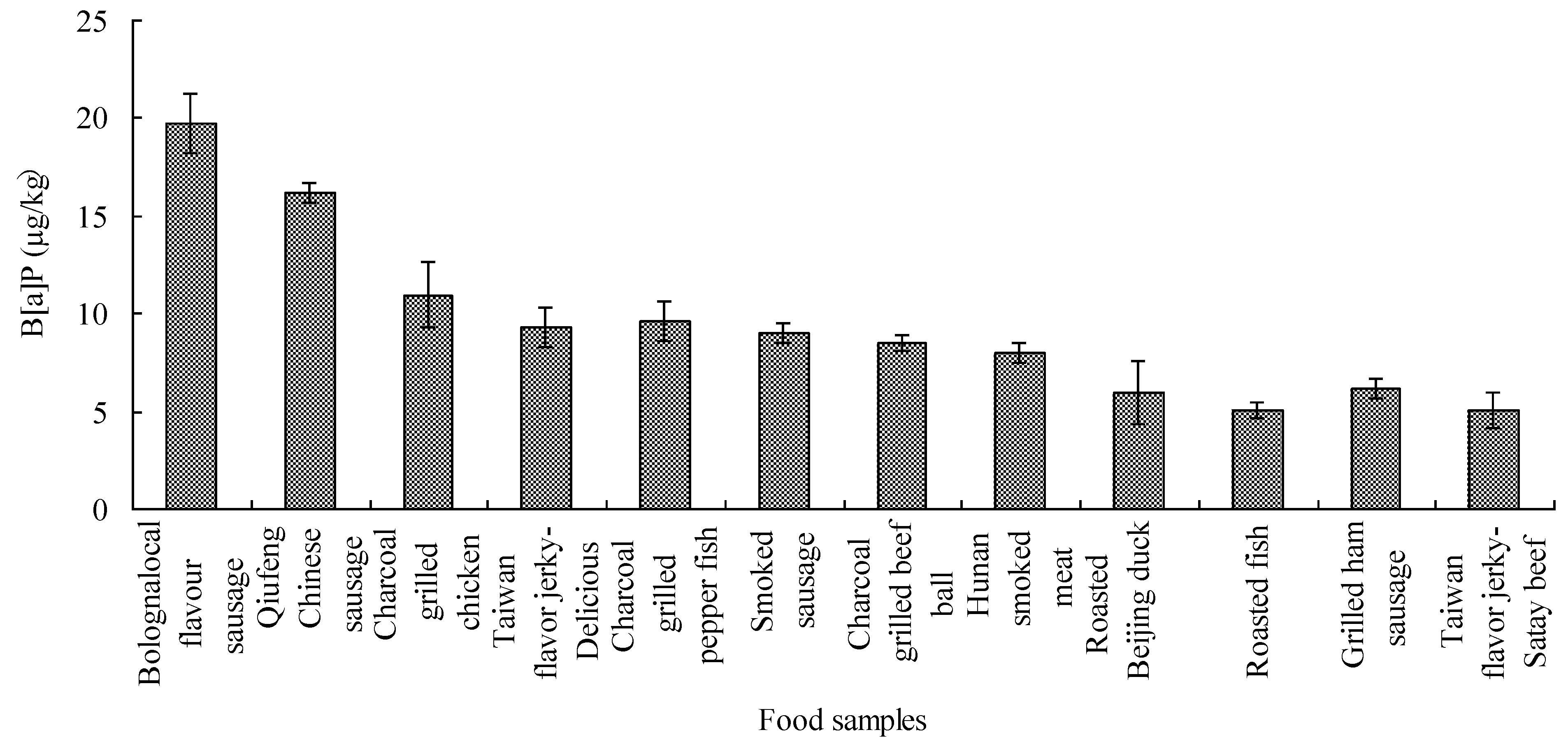
3.2. The Occurrence and Levels of B[a]P in Foods
| Category of charcoal grilled samples | Samples tested | Sample positive | The level of B[a]P (µg/kg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Min | Max | |||
| Vegetable | 8 | 8 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.86 |
| Bean curd | 7 | 5 | 0.92 | 1.04 | 0.52 | 3.27 |
| Dried fruit | 6 | 2 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.1 | 0.58 |
| Cake dessert | 9 | 6 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.13 |
| Pork | 11 | 11 | 2.01 | 2.34 | 0.24 | 7.97 |
| Fish and shrimp | 22 | 20 | 1.97 | 2.11 | 0.32 | 9.97 |
| Sausage | 15 | 15 | 4.25 | 5.8 | 0.23 | 19.75 |
| Beef | 10 | 10 | 2.66 | 3.59 | 0.19 | 9.29 |
| Chicken | 17 | 16 | 1.85 | 2.54 | 0.2 | 10.96 |
| Mutton | 4 | 4 | 0.62 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 1.61 |
| Duck | 7 | 5 | 1.68 | 2.03 | 0.91 | 5.97 |
| Rabbit meat | 1 | 1 | 1.64 | - | - | - |
| Total | 119 | 105 | 1.84 | 3.00 | 0.03 | 19.75 |

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Gamboa, R.T.; Gamboa, A.R.; Bravo, A.H.; Ostrosky, W.P. Genotoxicity in child populations exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the air from Tabasco, Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2008, 5, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G. Methylmercury exposure and health effects from rice and fish consumption: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2666–2691. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, E.Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Xu, X.R.; Li, S.; Deng, G.F.; Li, H.B. Analytical methods and contents of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food. Int. J. Food Nutr. Saf. 2012, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, E.Q.; Xu, X.R.; Chen, Y.H.; Wu, S.; Deng, G.F.; Zou, Z.F.; Li, S.; Li, H.B. Occurrence and analytical methods of acrylamide in food. Int. J. Food Nutr. Saf. 2012, 1, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.H.; Xu, X.R.; Deng, G.F.; Xia, E.Q.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.B. Source and analytical methods of chloropropanols in food. Int. J. Food Nutr. Saf. 2012, 1, 107–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Nakagoshi, N.; Lu, X.; Xu, H. Sources, toxicity, potential cancer risk assessment and analytical methods for monitoring of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 524-527, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar]
- García-Falcón, M.S.; Soto-González, B.; Simal-Gándara, J. Evolution of the concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in burnt woodland soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Falcon, M.S.; Simal-Gándara, J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in smoke from different woods and their transfer during traditional smoking into chorizo sausages with collagen and tripe casings. Food Add. Contam. 2005, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Salgueiro, L.; Martinez-Carballo, E.; Garcia-Falcon, M.S.; Simal-Gandara, J. Effects of a chemical company fire on the occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in plant foods. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Salgueiro, L.; Martínez-Carballo, E.; García-Falcón, M.S.; González-Barreiro, C.; Simal-Gándara, J. Occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their hydroxylated metabolites in infant foods. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Salgueiro, L.; Martínez-Carballo, E.; García-Falcón, M.S.; Simal-Gándara, J. Survey of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in canned bivalves and investigation of their potential sources. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gregorio, M.R.; García-Falcón, M.S.; Martínez-Carballo, E.; Simal-Gándara, J. Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from organic solvents by ashes wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Ni, H.; Zeng, H. Parent and halogenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rice and implications for human health in China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 168, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Cao, Q. Human health risk due to consumption of vegetables contaminated with carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Soils Sed. 2012, 12, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, D.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Wu, M.; Fu, J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in animal-based foods from Shanghai: Bioaccessibility and dietary exposure. Food Add. Contam. 2012, 29, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanhai, L.D.K.; Gobin, J.; Beckles, D.M.; Mohammed, A. A risk assessment of metal and PAH contamination in the Caroni Swamp, Trinidad. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2010, 408, 5331–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.; Cai, Q.; Tang, S.; Zeng, Q.; Wu, Q. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in vegetables from nine farms of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 56, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, W.J.; Feist, S.W.; Jones, G.J.; Lyons, B.P.; Sheahan, D.A.; Stentiford, G.D. Comparison of biomarker and pathological responses in flounder (Platichthys flesus L.) induced by ingested polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) contamination. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorinen, P.J.; Keinanen, M.; Vuontisjarvi, H.; Barsiene, J.; Broeg, K.; Förlin, L.; Gercken, J.; Kopecka, J.; Köhler, A.; Parkkonen, J.; Pempkowiak, J.; Schiedek, D. Use of biliary PAH metabolites as a biomarker of pollution in fish from the Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 53, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherbiny, M.E.; Brocks, D.R. The ability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to alter physiological factors underlying drug disposition. Drug Metab. Rev. 2011, 43, 457–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayi-Fanou, L.; Avogbe, P.H.; Fayomi, B.; Keith, G.; Hountondji, C.; Creppy, E.E.; Autrup, H.; Rihn, B.H.; Sanni, A. DNA-adducts in subjects exposed to urban air pollution by benzene and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Cotonou. Benin. Environ. Toxicol. 2011, 26, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, H. Developmental brain and behavior toxicity of air pollutants: A focus on the effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tec. 2011, 41, 2026–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-acuna, R.; Perez-Camino, M.D.C.; Cert, A.; Moreda, W. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Spanish olive oils: Relationship between benzo(a)pyrene and total polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10428–10432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, V.; Lodovici, M.; Dolara, P. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fresh and smoked fish samples from three Nigerian cities. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 53, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky, W.; Shubik, P. Benzo[a]pyrene and other polynuclear hydrocarbons in charcoal-broiled meat. Science 1964, 88, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Salgueiro, L.; Garcia-Falcon, M.S.; Martínez-Carballo, E.; Simal-Gandara, J. Effects of toasting procedures on the levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in toasted bread. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Salgueiro, L.; Pontevedra-Pombal, X.; Álvarez-Casas, M.; Martínez-Carballo, E.; García-Falcón, M.S.; Simal-Gándara, J. Comparative performance of extraction strategies for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in peats. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 5235–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcı́a-Falcón, M.S.; Pérez-Lamela, C.; Simal-Gándara, J. Strategies for the extraction of free and bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in run-off waters rich in organic matter. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 508, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcı́a-Falcón, M.S.; Cancho-Grande, B.; Simal-Gándara, J. Minimal clean-up and rapid determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in instant coffee. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Falcón, M.S.; Simal-Gándara, J. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in alcoholic drinks and identification of their potential sources. Food Add. Contam. 2005, 22, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germán-Hernández, M.; Pino, V.; Anderson, J.L.; Afonso, A.M. Use of ionic liquid aggregates of 1-hexadecyl-3-butyl imidazolium bromide in a focused-microwaveassisted extraction method followed by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet and fluorescence detection to determine the 15+1 EU priority PAHs in toasted cereals (“gofios”). Talanta 2011, 2, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki, A.; Saito, K.; Hanioka, N.; Narimatsu, S.; Kataoka, H. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food samples by automated on-line in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5555–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danyi, S.; Brose, F.; Brasseur, C.; Schneider, Y.-J.; Larondelle, Y.; Pussemier, L.; Robbens, J.; De Saeger, S.; Maghuin-Rogister, G.; Scippo, M.-L. Analysis of EU priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food supplements using high performance liquid chromatography coupled to an ultraviolet, diode array or fluorescence detector. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 633, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Estévez, M.; Fernández-Gándara, D.; García-Falcón, M.S.; García-Río, L.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gándara, J. Sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to colloid dispersions of humic substances in water. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 251–254. [Google Scholar]
- García-Falcón, M.S.; Simal-Gándara, J.; Carril-González-Barros, S.T. Analysis of benzo[a]pyrene in spiked fatty foods by second derivative synchronous spectrofluorimetry after microwave-assisted treatment of samples. Food Add. Contam. 2000, 17, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Falcón, M.S.; Pérez-Lamela, M.; Simal-Gándara, J. Comparison of strategies for extraction of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from drinking waters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6897–6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, S.R.; Ciolino, L.A.; Mohrhaus, A.S.; Gamble, B.M.; Gracie, J.M.; Jackson, D.S.; Roetting, J.P.; McCauley, H.A.; Heitkemper, D.T.; Fricke, F.L.; Krol, W.J.; Arsenault, T.L.; White, J.C.; Flottmeyer, M.M.; Johnson, Y.S. Screening and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in seafoods using quEChERS-based extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1601–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Salgueiro, L.; García-Falcón, M.S.; Soto-González, B.; Simal-Gándara, J. Procedure to measure the level of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in wood ashes used as fertilizer in agroforestry soils and their transfer from ashes to water. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3900–3904. [Google Scholar]
- Terzi, G.; Celik, T.H.; Nisbet, C. Determination of benzo[a]pyrene in Turkish doner kebab samples cooked with charcoal or gas fire. Irish J. Agric. Food Res. 2008, 47, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Aygun, S.F.; Kabadayi, F. Determination of benzo[a] pyrene in charcoal grilled meat samples by HPLC with fluorescence detection. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.Q.; Song, Y.; Ai, X.X.; Guo, Y.J.; Xu, X.R.; Li, H.B. A new high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination and distribution of linalool in Michelia alba. Molecules 2010, 15, 4890–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, A.; Jinap, S.; Hanifah, H.N.; Zaidul, I.S. Effects of meat preheating and wrapping on the levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in charcoal-grilled meat. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-H.; Xia, E.-Q.; Xu, X.-R.; Li, S.; Ling, W.-H.; Wu, S.; Deng, G.-F.; Zou, Z.-F.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.-B. Evaluation of Benzo[a]pyrene in Food from China by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 4159-4169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9114159
Chen Y-H, Xia E-Q, Xu X-R, Li S, Ling W-H, Wu S, Deng G-F, Zou Z-F, Zhou J, Li H-B. Evaluation of Benzo[a]pyrene in Food from China by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2012; 9(11):4159-4169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9114159
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yong-Hong, En-Qin Xia, Xiang-Rong Xu, Sha Li, Wen-Hua Ling, Shan Wu, Gui-Fang Deng, Zhi-Fei Zou, Jing Zhou, and Hua-Bin Li. 2012. "Evaluation of Benzo[a]pyrene in Food from China by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 9, no. 11: 4159-4169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9114159
APA StyleChen, Y.-H., Xia, E.-Q., Xu, X.-R., Li, S., Ling, W.-H., Wu, S., Deng, G.-F., Zou, Z.-F., Zhou, J., & Li, H.-B. (2012). Evaluation of Benzo[a]pyrene in Food from China by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 9(11), 4159-4169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9114159







