Geological Factors and Reservoir Properties Affecting the Gas Content of Coal Seams in the Gujiao Area, Northwest Qinshui Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
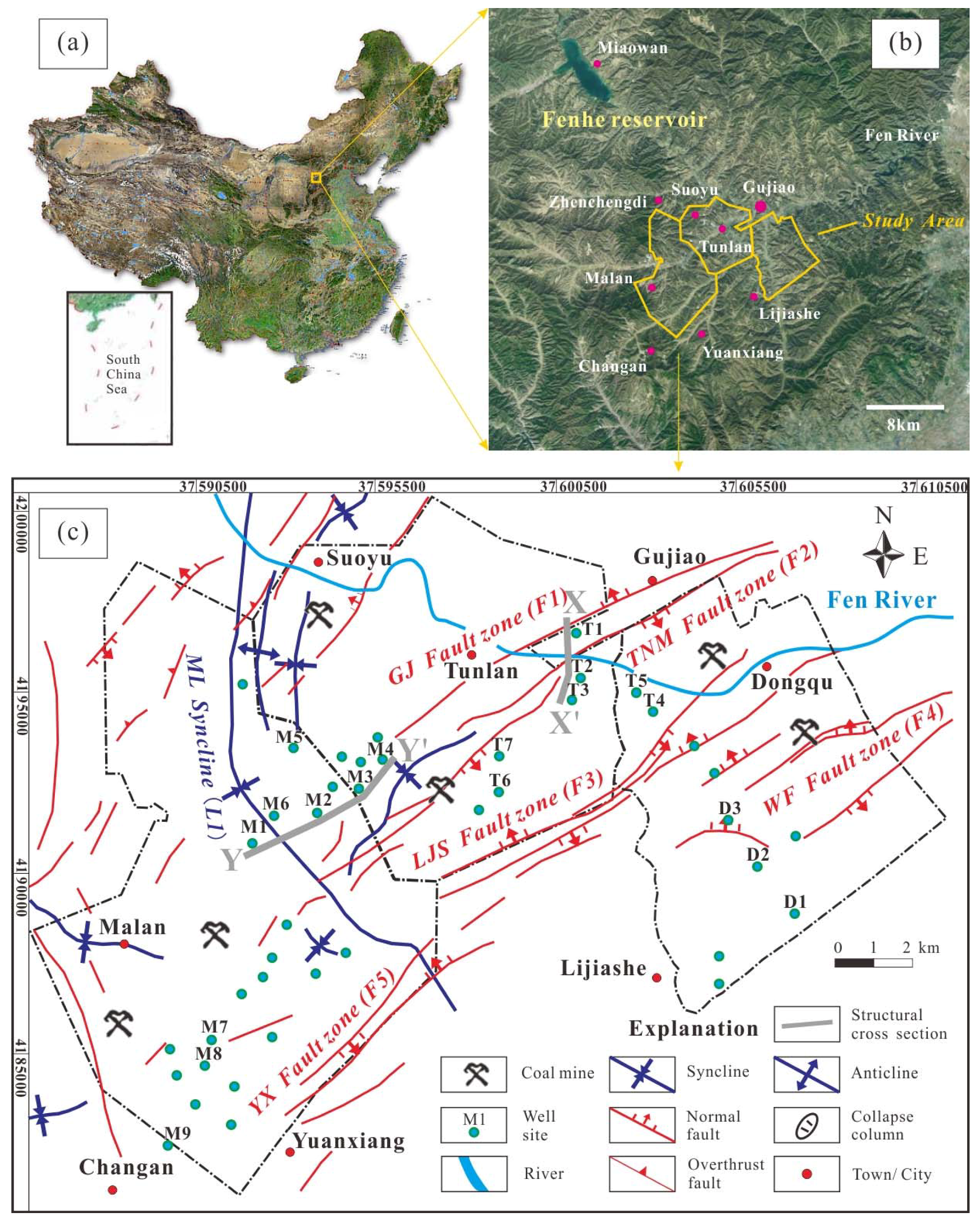
2. Geological Setting
3. Experiments and Methods
3.1. Samples and Experiments
3.2. Principle of Grey Correlation
- (1)
- Normalized treatment. This paper deals with the raw data by means of the homogenization method. The formula is as shown in Equation (4):where is transformed from , i = 1, 2, …, 8: k = 1, 2, …, 10. is the value of the i-th geological factor at the k-th sampling site.
- (2)
- Acquisition of the correlation coefficient. The correlations between controlling factors and gas content in the Nos. 2, 8, and 9 coal seams at different sampling sites are obtained by Equation (5).where is the correlation coefficient between the gas content and the i-th controlling factor at the k-th sampling site, is the absolute value acquired from the reference sequence and the comparison sequence; and are the maximum absolute difference and minimum absolute difference between the reference sequence and the comparison sequence, i = 1, 2, …, 8: k = 1, 2, …, 10; is the resolution coefficient, in the range of 0–1, and 0.5 is normal.
- (3)
- Evaluation of the correlation degree. For comparison, the average correlation coefficient of the reference sequence can be calculated by Equation (6), whereby the correlation between each influencing factor and gas content is obtained. Furthermore, the order of correlation can be provided in the order of large values to small values.where is the degree of correlation between the gas content and the i-th influencing factor, and n is the number of samples.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Gas Content
4.2. Geological Factors Affecting on Gas Content
4.2.1. Geological Structure
4.2.2. Burial Depth of Coal Seams
4.2.3. Roof Lithology and Thickness
4.2.4. Coal Metamorphism
4.2.5. Coal Thickness
4.2.6. Hydrodynamics
4.3. Factors of CBM Reservoirs Affecting on Gas Content
4.3.1. Moisture and Ash Yield
4.3.2. Porosity and Permeability
4.3.3. Adsorption Capacity of Coals
4.4. Gray Correlative Evaluation of Factors Affecting Gas Content
4.4.1. Evaluation Results
4.4.2. Classification of Gas Enrichment
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The highly variable gas content of different coal seams in the Gujiao area reflects the differences among tectonism, magmatism, hydrodynamism, and sedimentation. The geological structure divides the Gujiao area into two parts: synclines and normal faults. The three targeted coal seams have experienced two stage magmatic activities. The gas content of coal seams distributes along the groundwater flow from the north to the south, accumulating in the mid-south part of the Gujiao area.
- (2)
- The correlations between controlling factors and gas content are quantitatively evaluated by the gray correlation analysis. The main factors affecting gas content vary in different coal seams. Although many synthetic factors affecting gas content, the coal metamorphism, and geological structure should be the common main factors controlling gas content for these three targeted coal seams.
- (3)
- In the Gujiao area, the most favorable area for CBM enrichment is Block I, which is controlled by the different gas concentrations between No. 2 coal and Nos. 8 and 9 coals. A moderate burial depth (~500–800 m) and a relatively high coal rank (~1.25–1.55%) could effectively promote gas enrichment in the No. 2 coal seam. However, for Nos. 8 and 9 coals, the presence of a syncline and normal faults with good sealing capability together with low moisture content (~0.4–0.8%) can become a favorable area for CBM enrichment.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kayacan, E.; Ulutas, B.; Kaynak, O. Grey system theory-based models in time series prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ni, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Yu, T.; Feng, R. Experimental Study of CO2-Water-Mineral Interactions and Their Influence on the Permeability of Coking Coal and Implications for CO2-ECBM. Minerals 2018, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, K.; Elsworth, D.; Yao, Y.; Tang, D. Preliminary evaluation of gas content of the no. 2 coal seam in the Yanchuannan area, southeast ordos basin, China. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2014, 122, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Gayer, R.A. Mechanisms of coal metamorphism: Case studies from Paleozoic coalfields. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 215–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildenbrand, A.; Krooss, B.M.; Busch, A.; Gaschnitz, R. Evolution of methane sorption capacity of coal seams as a function of burial history—A case study from the Campine Basin, NE Belgium. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 66, 179–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashin, J.C.; Mcintyre-Redden, M.R.; Mann, S.D.; Kopaska-Merkel, D.C.; Varonka, M.; Orem, W. Relationships between water and gas chemistry in mature coalbed methane reservoirs of the Black Warrior Basin. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 126, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.T.; Yao, Y.B.; Liu, D.M. Critical tectonic events and their geological controls on gas generation, migration, and accumulation in the Weibei coalbed methane coalfield, southeast Ordos basin. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.H.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, X.J.; Yuan, Y.D.; Zhuang, X.G. Geological controls on gas saturation in the Yanchuannan coalbed methane field, southeastern Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 78, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.R. Hydrogeologic factors affecting gas content distribution in coal beds. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2002, 50, 363–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.; Anderson, B.; Crosdale, P.; Dingwall, J.; Leblang, G. Coal petrology and coal seam gas contents of the Walloon Subgroup—Surat Basin, Queensland, Australia. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2007, 70, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayana, C.; Crosdale, P.J. Role of coal type and rank on methane sorption characteristics of Bowen Basin, Australia coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1999, 40, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosdale, P.J.; Beamish, B.B.; Valix, M. Coalbed methane sorption related to coal composition. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 35, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Fu, X.; Ye, J.; Lin, D.; Tang, S.; Li, G. Geological controls and their mechanisms of coal-reservoir petrography and physics of coalbed methane occurrence in China. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 1999, 28, 14–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Qin, Y.; Wang, G.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Z. Numerical simulation of coalbed methane generation, dissipation and retention in SE edge of Ordos Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 82, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.; Day, S.J.; Killingley, J.S. Methane capacity of Bowen Basin coals related to coal properties. Fuel 1997, 76, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, J.J.; Boreham, C.J. Geological controls on exploitable coal seam gas distribution in Queensland. APPEA J. 2006, 46, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosdale, P.J.; Moore, T.A.; Mares, T.E. Influence of moisture content and temperature on methane adsorption isotherm analysis for coals from a low-rank, biogenically-sourced gas reservoir. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2008, 76, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.; Anderson, B.; Crosdale, P.; Dingwall, J.; Leblang, G. Revised geology and coal seam gas characteristics of the Walloon Subgroup—Surat Basin, Queensland. In Eastern Australasian Basins Symposium II: Petroleum Exploration Society of Australia; Boult, P.J., Johns, D.R., Lang, S.C., Eds.; PESA: Adelaide, Autralia, 2004; pp. 345–355. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Lin, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, M.; Song, Y. Geology of coalbedmethane reservoirs in the Southeast Qinshui Basin of China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2005, 62, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Luo, H. Production characteristics and the key factors in high-rank coalbed methane fields: A case study on the Fanzhuang Block, Southern Qinshui Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 96–97, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sang, S.; Wang, G.G.; Li, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Ren, B.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, Y. Block scale investigation on gas content of coalbed methane reservoirs in Southern Qinshui Basin with statistical model and visual map. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2014, 114, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zou, C.; Zhou, T.; Li, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W. Factors affecting coalbed methane (CBM) well productivity in the Shizhuangnan block of southern Qinshui basin, North China: Investigation by geophysical log, experiment and production data. Fuel 2017, 191, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, D.; Yao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Qiu, Y. Evaluation of the reservoir permeability of anthracite coals by geophysical logging data. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 87, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Gao, L.; Fang, Y. Factors controlling high-yield coalbed methane vertical wells in the Fanzhuang Block, Southern Qinshui Basin. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 134–135, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.D.; Liu, D.M.; Yao, Y.B.; Li, J.Q.; Qiu, Y.K. Geological controls on prediction of coalbed methane of No. 3 coal seam in Southern Qinshui Basin, North China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 88, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tang, D.; Tang, S.; Zhao, J.; Meng, Y.; Tao, S. A dynamic prediction model for gas-water effective permeability based on coalbed methane production data. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 121, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y. Evaluation of coal texture distributions in the southern Qinshui basin, North China: Investigation by a multiple geophysical logging method. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 140, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y. Current status and prospect of exploration and development of Gujiao CBM Project. China Coalbed Methane 2012, 5, 3–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Qin, Y.; Xie, Y.W.; Shen, J.; Han, B.B.; Huang, B.; Zhao, L. The division and geologic controlling factors of a vertical superimposed coalbed methane system in the northern Gujiao blocks, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 24, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Zeng, F.; Song, X.; Meng, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, J. Structural block division for further deep research in coalbed methane development in the Gujiao area, Xishan coalfield, North China. Arabian J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Zeng, F.; Song, X. Parameters controlling high-yield coalbed methane vertical wells in the B3 area, Xishan coal field, Shanxi, China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2016, 34, 711–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qin, Y.; Cai, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, G.; Huang, B. Control of coal facies to adsorption-desorption divergence of coals: A case from the Xiqu Drainage Area, Gujiao CBM Block, North China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 171, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, G. Identification of the coal structure and prediction of the fracturability in the No. 8 coal reservoir, Gujiao block, China. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2018, 36, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Evaluation of structured coal evolution and distribution by geophysical logging methods in the Gujiao Block, northwest Qinshui basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 51, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qin, Y.; Xie, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhao, L.; Huang, B.; Zhao, W. Coalbed methane system potential evaluation and favourable area prediction of Gujiao blocks, Xishan coalfield, based on multi-level fuzzy mathematical analysis. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Liu, D.M.; Ranjith, P.G.; Cai, Y.D.; Wang, Y.J. Geological controls on variable gas concentrations: A case study of the northern Gujiao Block, northwestern Qinshui Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Zeng, F.; Song, X.; Li, K.; Wang, J.; Feng, S.; Sun, B. Geologic structural controls on coalbed methane content of the no. 8 coal seam, gujiao area, Shanxi, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Jiang, B.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, C.F.; Fu, X.H.; Wei, C.T. Coupling Control of Tectonic Dynamical Conditions to Coalbed Methane Reservoir Formation in the Qinshui Basin, Shanxi, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2008, 82, 1355–1362. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ping, J.; Yan, S.; Gu, P.; Wu, Z.; Hu, C. Application of MIKE SHE to study the impact of coal mining on river runoff in Gujiao mining area, Shanxi, China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, D.; Tang, D.; Tang, S.; Yao, C.; Huang, W. Preliminary evaluation of the coalbed methane production potential and its geological controls in the Weibei Coalfield, Southeastern Ordos Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 78, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, W.P.; Levine, J.R. Direct Method Determination of the Gas Content of Coal: Procedures and Results; US Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1994.
- Diamond, W.P.; Schatzel, S.J. Measuring the gas content of coal: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 35, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.L. Introduction to Grey system theory. J. Grey Syst. 1989, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Lv, Y.; Tao, S. High production indexes and the key factors in coalbed methane production: A case in the Hancheng block, southeastern Ordos Basin, China. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2015, 130, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, X. Gray correlation degree analysis of controlling factors on coal deformation. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2011, 29, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Chen, P.; Shen, J.; Liang, Z.; Yang, H. Study on the Prediction of Gas Content Based on Grey Relational Analysis and BP Neural Network. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications (BIC-TA), Huangshan, China, 12–14 July 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 677–685. [Google Scholar]
- Pashin, J.C. Variable gas saturation in coalbed methane reservoirs of the Black Warrior Basin: Implications for exploration and production. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 82, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, W.B.J. Coalbed gas systems, resources, and production and a review of contrasting cases from the San Juan and Powder River basins. AAPG Bull. 2002, 86, 1853–1890. [Google Scholar]
- Sperrevik, S.; Færseth, R.B.; Gabrielsen, R.H. Experiments on clay smear formation along faults. Pet. Geosci. 2000, 6, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Tang, D.; Xu, H.; Xu, T.; Chen, B.; Hu, P.; Yin, Z.; Wu, P.; He, G. Geological characteristics and CBM exploration potential evaluation: A case study in the middle of the southern Junggar Basin, NW China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 30, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardon, S.M.; Eble, C.F.; Hower, J.C.; Takacs, K.; Mastalerz, M.; Bustin, R.M. Organic petrology, geochemistry, gas content and gas composition of Middle Pennsylvanian age coal beds in the Eastern Interior (Illinois) Basin: Implications for CBM development and carbon sequestration. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 127, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, G.; Li, G.; Yang, F.; Liu, H. Influence of the tectonic thermal events in Yanshan epoch on coalbed methane enrichment and high-productivity in Xishan coal field in Taiyuan. Nat. Gas Ind. 2005, 25, 29–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yee, D.; Seidle, J.P.; Hanson, W.B. Gas sorption on coal and measurement of gas content. Hydrocarb. Coal AAPG Stud. Geol. 1993, 38, 203–218. [Google Scholar]
- Bustin, R.M.; Clarkson, C.R. Geological controls on coalbed methane reservoir capacity and gas content. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1998, 38, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.B. Porosity, Permeability and favorable Production Region of Coal Reservoirs in Gujiao Block, Xishan. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]














| Coal Seam | Sample Number | Gas Content (m3/t) | Cas Composition (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Average | CH4 | CO2 | N2 | ||
| 2 | 26 | 13.05 | 4.13 | 7.37 | 92.11 | 0.87 | 6.61 |
| 8 | 45 | 16.46 | 3.97 | 8.74 | 93.01 | 1.04 | 5.51 |
| 9 | 36 | 14.59 | 3.74 | 7.84 | 90.84 | 1.17 | 7.55 |
| Well ID | Coal No. | Geologic Structure | Depth m | Roof Thickness m | Ro,m % | TDS mg/L | Coal Thickness m | Mad % | Aad % | Gas Content m3/t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 2 | 2 | 679.91 | 1.80 | 1.08 | 1430 | 2.60 | 0.65 | 9.24 | 5.36 |
| M2 | 4 | 692.41 | 1.35 | 1.19 | 1510 | 2.66 | 0.85 | 17.52 | 6.84 | |
| M4 | 3 | 674.16 | 1.17 | 1.20 | 1370 | 2.64 | 0.56 | 25.94 | 6.23 | |
| M7 | 2 | 547.45 | 1.70 | 1.38 | 1350 | 1.70 | 0.93 | 21.48 | 5.11 | |
| M8 | 2.5 | 593.19 | 1.35 | 1.07 | 1310 | 1.43 | 0.90 | 39.19 | 6.53 | |
| T4 | 3 | 367.84 | 2.57 | 1.47 | 1020 | 2.35 | 0.59 | 13.10 | 5.41 | |
| T6 | 4 | 513.62 | 2.27 | 1.48 | 1490 | 2.40 | 0.73 | 7.47 | 13.05 | |
| T7 | 3 | 525.52 | 4.76 | 1.31 | 1300 | 2.31 | 0.69 | 24.54 | 9.04 | |
| T1 | 1 | 389.45 | 2.49 | 1.34 | 930 | 3.90 | 0.78 | 24.50 | 4.13 | |
| D2 | 3 | 419.73 | 3.49 | 1.54 | 1350 | 1.45 | 0.44 | 12.88 | 8.81 | |
| M1 | 8 | 2 | 771.98 | 0.19 | 1.08 | 1430 | 4.03 | 0.81 | 31.03 | 4.74 |
| M2 | 4 | 783.47 | 0.74 | 1.33 | 1510 | 4.40 | 0.90 | 13.07 | 12.09 | |
| M4 | 3 | 759.83 | 0.79 | 1.39 | 1370 | 4.56 | 0.47 | 15.28 | 12.59 | |
| M7 | 2 | 620.61 | 0.31 | 1.29 | 1350 | 3.22 | 0.70 | 13.97 | 6.22 | |
| M8 | 2.5 | 672.65 | 0.48 | 1.33 | 1310 | 3.15 | 0.86 | 28.87 | 6.31 | |
| T4 | 3 | 446.56 | 1.09 | 1.68 | 1020 | 3.26 | 0.52 | 12.67 | 12.03 | |
| T6 | 4 | 593.25 | 0.40 | 1.55 | 1490 | 1.36 | 0.75 | 10.19 | 13.94 | |
| T7 | 3 | 609.12 | 0.50 | 1.51 | 1300 | 2.10 | 0.65 | 16.87 | 16.46 | |
| T1 | 1 | 472.25 | 0.61 | 1.23 | 930 | 3.45 | 0.69 | 28.88 | 7.45 | |
| D2 | 3 | 502.63 | 1.24 | 1.75 | 1350 | 3.40 | 0.48 | 12.52 | 12.10 | |
| M1 | 9 | 2 | 786.33 | 1.33 | 1.25 | 1430 | 1.76 | 0.68 | 14.25 | 3.74 |
| M2 | 4 | 793.68 | 0.85 | 1.36 | 1510 | 1.8 | 0.86 | 34.31 | 8.38 | |
| M4 | 3 | 769.16 | 0.54 | 1.37 | 1370 | 1.44 | 0.49 | 21.35 | 10.94 | |
| M7 | 2 | 626.61 | 1.00 | 1.31 | 1350 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 15 | 5.48 | |
| M8 | 2.5 | 681.3 | 0.58 | 1.47 | 1310 | 1.8 | 0.82 | 15.22 | 5.74 | |
| T4 | 3 | 458.93 | 1.65 | 1.78 | 1020 | 2.07 | 0.5 | 7.76 | 12.31 | |
| T6 | 4 | 622.01 | 2.44 | 1.64 | 1490 | 1.48 | 0.77 | 10.58 | 14.59 | |
| T7 | 3 | 633.95 | 1 | 1.59 | 1300 | 1.94 | 0.74 | 37.28 | 7.62 | |
| T1 | 1 | 485.25 | 1.02 | 1.22 | 930 | 1.83 | 0.83 | 39.28 | 4.41 | |
| D2 | 3 | 514.93 | 0.68 | 1.80 | 1350 | 4.16 | 0.53 | 12.57 | 12.53 |
| Coal Seam | Degree/Order | Geologic Structure | Depth | Roof Thickness | Ro | Hydrologic Condition | Coal Thickness | Mad | Aad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Degree | 0.62 | 0.71 | 0.61 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.66 | 0.68 |
| Order | 6 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 3 | |
| 8 | Degree | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.67 | 0.66 |
| Order | 1 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 2 | 3 | |
| 9 | Degree | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.63 |
| Order | 1 | 6 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 4 | 5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Z.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Geological Factors and Reservoir Properties Affecting the Gas Content of Coal Seams in the Gujiao Area, Northwest Qinshui Basin, China. Energies 2018, 11, 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051044
Zou Z, Liu D, Cai Y, Wang Y, Li J. Geological Factors and Reservoir Properties Affecting the Gas Content of Coal Seams in the Gujiao Area, Northwest Qinshui Basin, China. Energies. 2018; 11(5):1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051044
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Zhuo, Dameng Liu, Yidong Cai, Yingjin Wang, and Jiapeng Li. 2018. "Geological Factors and Reservoir Properties Affecting the Gas Content of Coal Seams in the Gujiao Area, Northwest Qinshui Basin, China" Energies 11, no. 5: 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051044
APA StyleZou, Z., Liu, D., Cai, Y., Wang, Y., & Li, J. (2018). Geological Factors and Reservoir Properties Affecting the Gas Content of Coal Seams in the Gujiao Area, Northwest Qinshui Basin, China. Energies, 11(5), 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11051044






