Inertial and Damping Characteristics of DC Distributed Power Systems Based on Frequency Droop Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
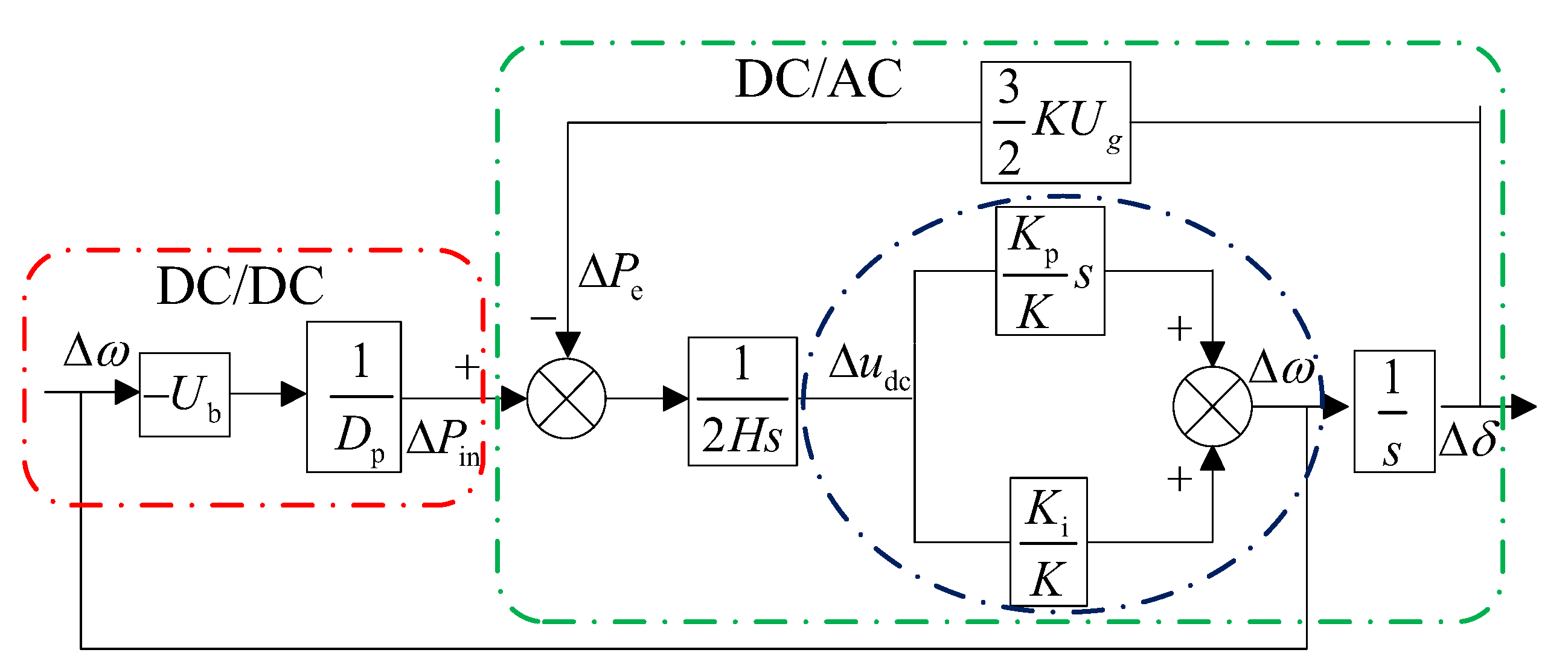
2. DC Distributed Power Systems Based on Frequency Droop Control
2.1. DC/DC Converter Control
2.2. Grid-Tied Inverter Control
3. Dynamic Analysis of the DC Distributed Power Systems
- (1)
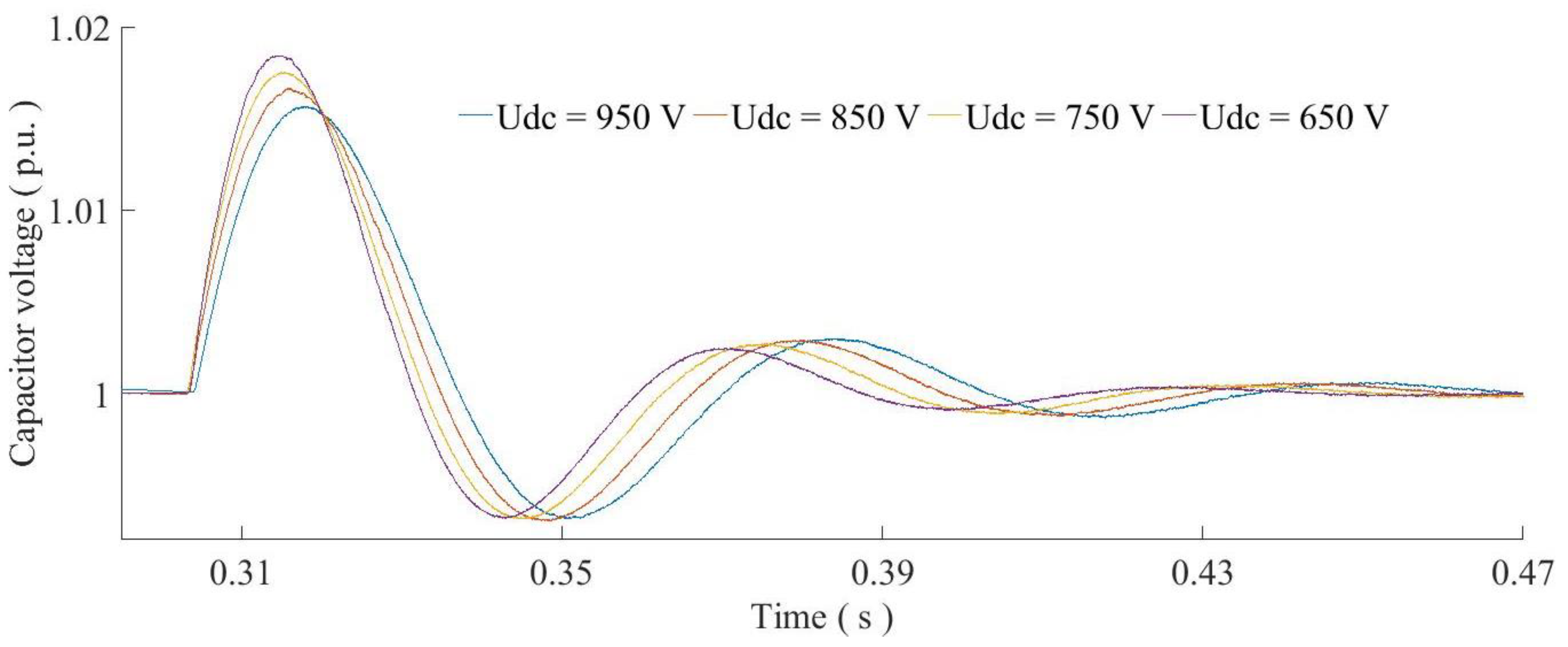
- The inertial level can be adjusted by the proportional controller gain Kp and the frequency droop coefficient Dp. Meanwhile, adjusting the capacitance of the DC-side capacitor C, the voltage of the DC distributed energy sources Ub, the inverter output voltage US and the capacitor rated voltage Udc can also equivalently adjust the inertial level of the system. When C increases, the system increases the buffering effect against external disturbances and improves the inertia level of the system, which are consistent with the actual situation.
- (2)
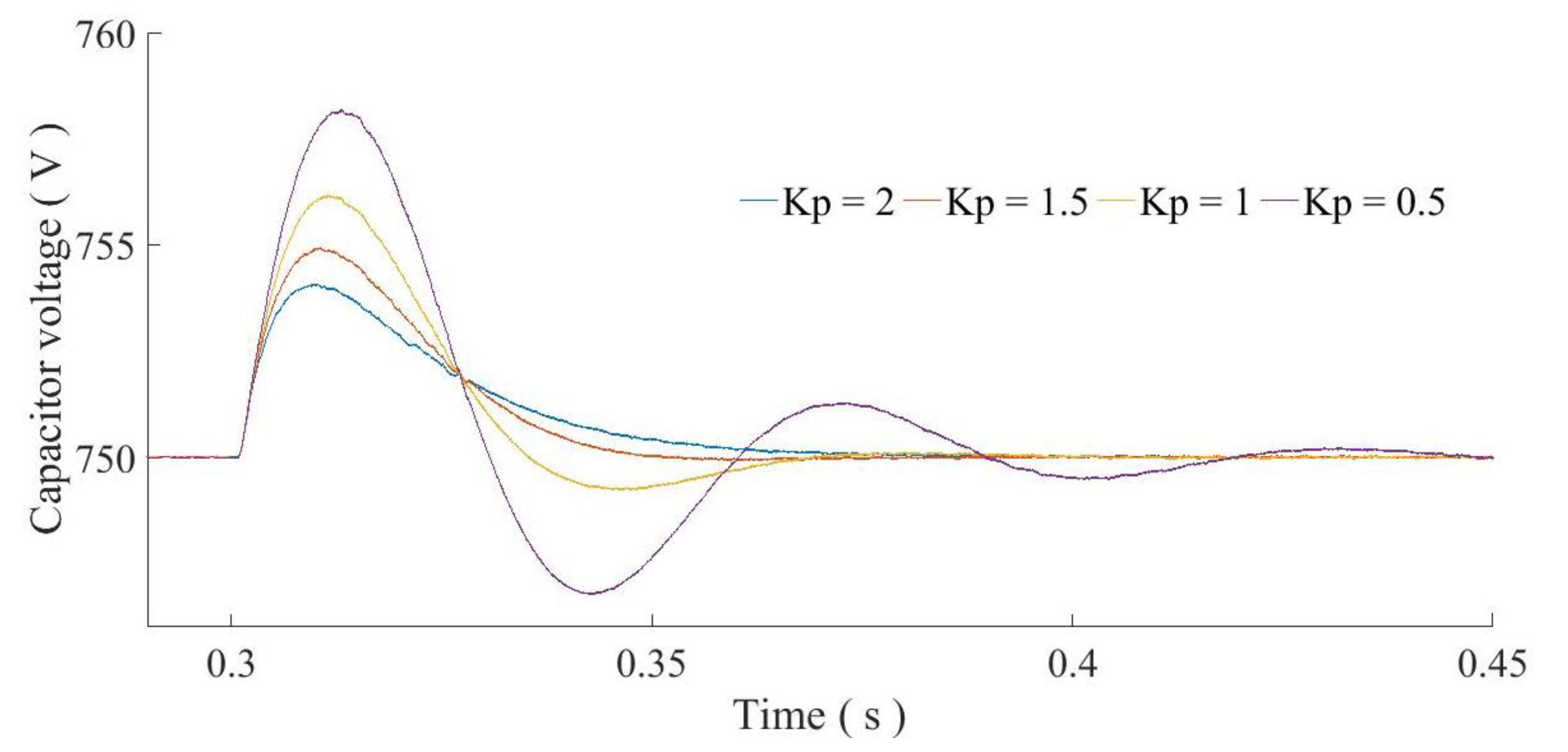
- Changing the frequency droop coefficient Dp and the PI controllers of the DC bus voltage control loop can be equivalent to adjusting the damping effect of the system.
- (3)
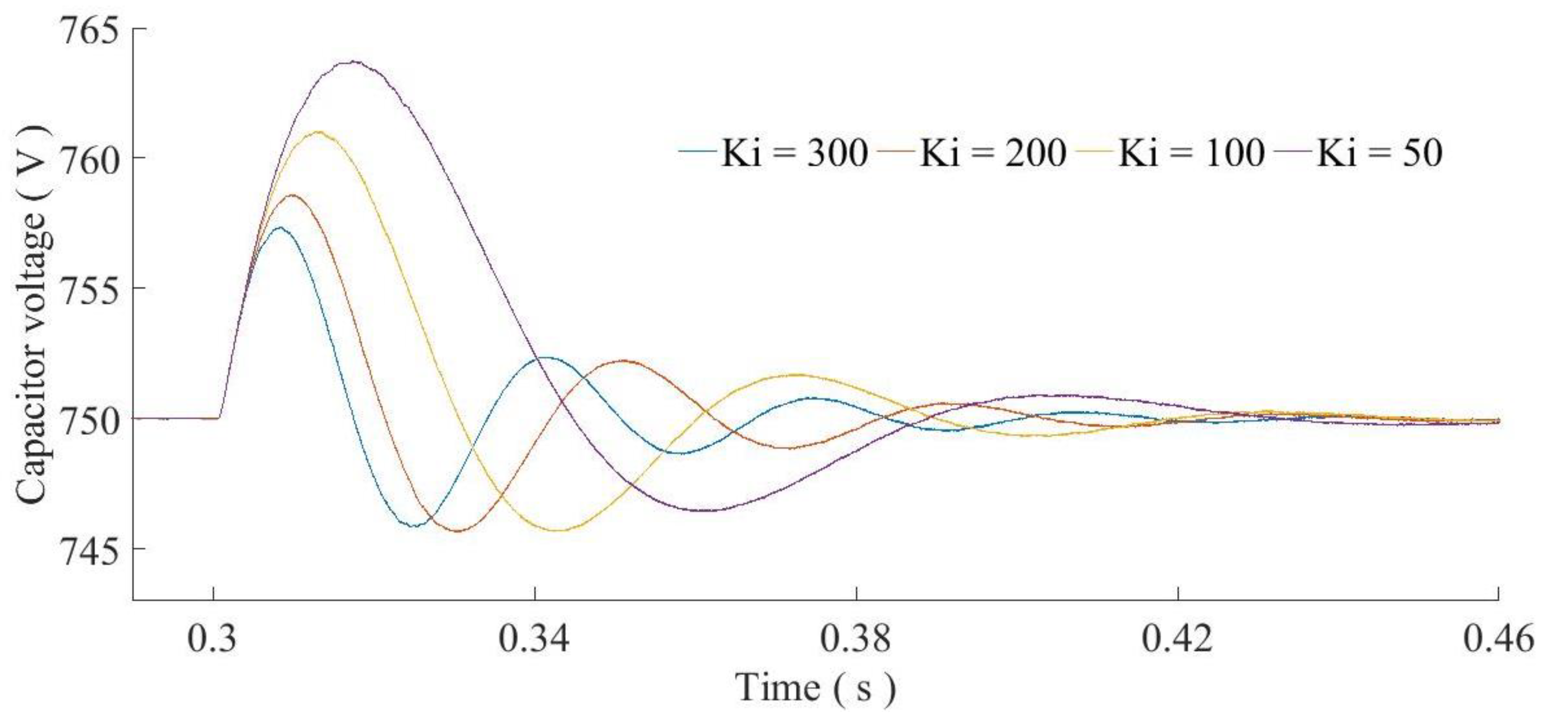
- The synchronization capability can be changed by adjusting the integral controller gain Ki.
4. Simulation Verification
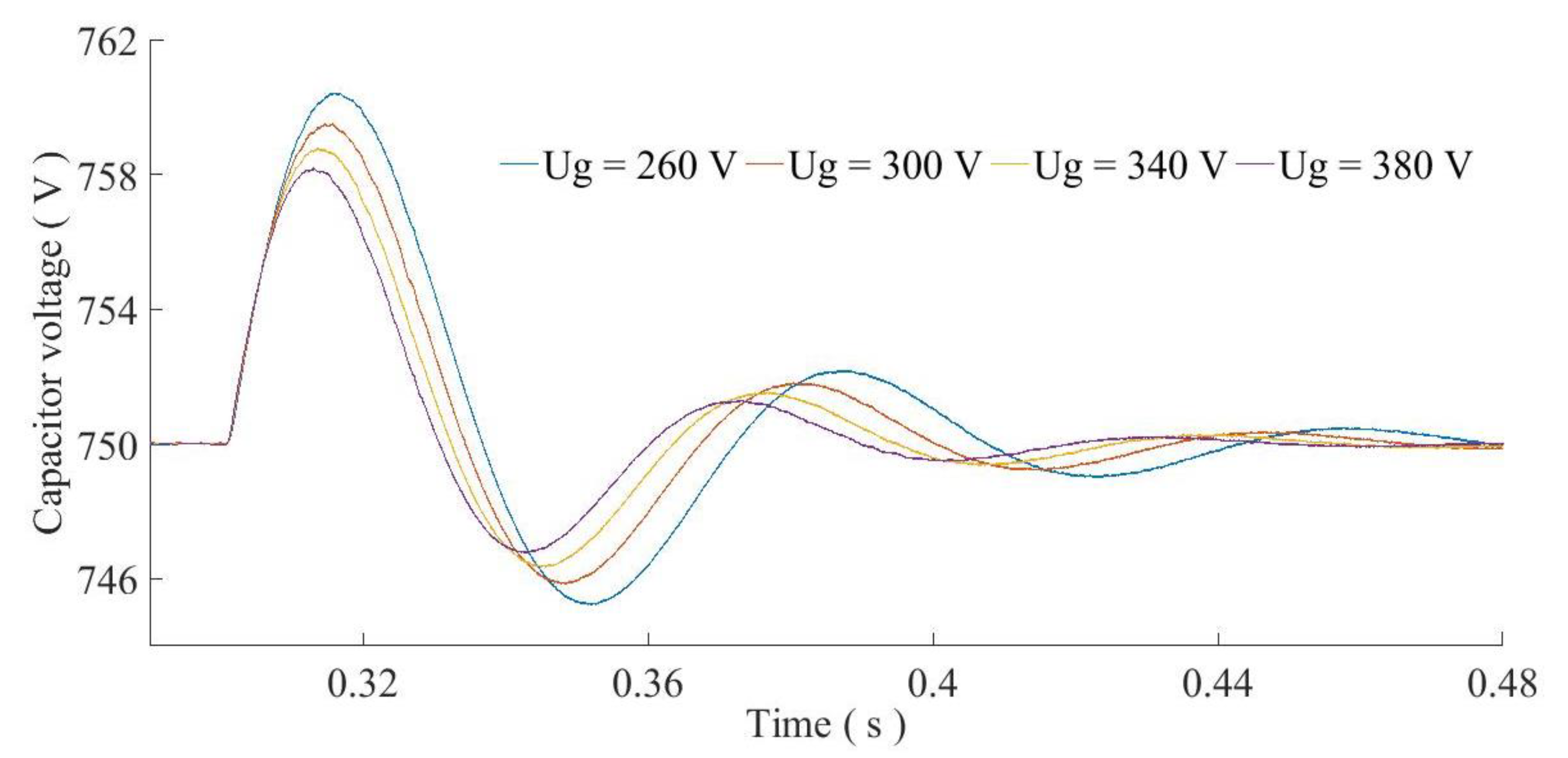
4.1. Damping Characteristics Verification
4.2. Inertial Characteristics’ Verification
4.3. Synchronization Characteristics’ Verification
4.4. Stability Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soder, L.; Hofmann, L.; Orths, A.; Holttinen, H.; Wan, Y.H.; Tuohy, A. Experience from wind integration in some high penetration areas. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemlou, S.; Mehraeen, S. Stability of multi-generator power system with penetration of renewable energy sources. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Doherty, R.; Mullane, A.; Nolan, G.; Burke, D.J.; Bryson, A.; O’Malley, M. An assessment of the impact of wind generation on system frequency control. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wong, K.P. Advanced control strategies of pmsg-based wind turbines for system inertia support. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 3027–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, P.; Xu, Z. Coordinated control schemes of super-capacitor and kinetic energy of dfig for system frequency support. Energies 2018, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, R. Some aspects of stability in microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Wang, L. Small-signal stability analysis of an autonomous hybrid renewable energy power generation/energy storage system part i: Time-domain simulations. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Guerrero, J.M. Dynamic phasors-based modeling and stability analysis of droop-controlled inverters for microgrid applications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 2980–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, D.; Xu, L. Direct power control of dfig with constant switching frequency and improved transient performance. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogaku, N.; Prodanovic, M.; Green, T.C. Modeling, analysis and testing of autonomous operation of an inverter-based microgrid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.C.; Konstantopoulos, G.C. Current-limiting droop control of grid-connected inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 5963–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Chen, M.; Matas, J.; Guerrero, J.M.; Qian, Z.M. Design and analysis of the droop control method for parallel inverters considering the impact of the complex impedance on the power sharing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintai, T.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. Oscillation damping of a distributed generator using a virtual synchronous generator. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2014, 29, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, J.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. Power system stabilization using virtual synchronous generator with alternating moment of inertia. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevrani, H.; Ise, T.; Miura, Y. Virtual synchronous generators: A survey and new perspectives. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 54, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ruan, X.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Lv, Z.; Zhong, Q.C. Small-signal modeling and parameters design for virtual synchronous generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4292–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Yuan, X.; Hu, J. Modeling of grid-connected vscs for power system small-signal stability analysis in dc-link voltage control timescale. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 3981–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hu, J.; Yuan, X. Modeling and large-signal stability of DFIG wind turbine in dc-voltage control time scale. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Boston, MA, USA, 17–21 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arco, S.; Suul, J.A. Equivalence of virtual synchronous machines and frequency-droops for converter-based microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhuo, F.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yi, H. Static synchronous generator model: A new perspective to investigate dynamic characteristics and stability issues of grid-tied pwm inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 6264–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Lv, Q.; Geng, H.; Yang, G. An equivalent synchronous generator model for current-controlled voltage source converters considering the dynamic of phase-locked-loop. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016—42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 23–26 Octorber 2016; pp. 2235–2240. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.; Geng, H.; Yang, G. Phillips-Heffron model for current-controlled power electronic generation unit. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2018, 6, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L.; Lin, J. An inertia simulation method based on improved double-loop control for grid-connected inverters. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 3rd International Future Energy Electronics Conference and ECCE Asia (IFEEC 2017—ECCE Asia), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 3–7 June 2017. [Google Scholar]









| Symbol | Meaning | Value | Symbol | Meaning | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ug | Grid line-to-line voltage (V) | 380 | Udc | Voltage of the DC-side capacitor (V) | 750 |
| C | Capacitance of the DC-side capacitor (mF) | 5 | Ub | Voltage of the DC distributed energy sources (V) | 350 |
| L | Filter inductance (mH) | 4 | f0 | Grid frequency (Hz) | 60 |
| Ki | I gain of current loop | 100 | fs | Switching frequency (kHz) | 10 |
| Kp | P gain of current loop | 0.1 |
| Symbol | Meaning | Value | Symbol | Meaning | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ug | Grid line-to-line voltage (V) | 380 | Ub | Voltage of the DC distributed energy sources (V) | 350 |
| C | Capacitance of the DC-side capacitor (mF) | 5 | Udc | Voltage of the DC-side capacitor (V) | 750 |
| Kp | The proportional controller gain of the DC bus voltage control | 1 | Ki | The integral controller gain of the DC bus voltage control | 100 |
| f0 | Grid frequency (Hz) | 60 | L | Filter inductance (mH) | 4 |
| fs | Switching frequency (kHz) | 12 | Dp | The frequency droop coefficient | 1.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiu, L.; Xiong, L.; Yang, P.; Kang, Z. Inertial and Damping Characteristics of DC Distributed Power Systems Based on Frequency Droop Control. Energies 2018, 11, 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092418
Xiu L, Xiong L, Yang P, Kang Z. Inertial and Damping Characteristics of DC Distributed Power Systems Based on Frequency Droop Control. Energies. 2018; 11(9):2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092418
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiu, Liancheng, Liansong Xiong, Ping Yang, and Zhiliang Kang. 2018. "Inertial and Damping Characteristics of DC Distributed Power Systems Based on Frequency Droop Control" Energies 11, no. 9: 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092418
APA StyleXiu, L., Xiong, L., Yang, P., & Kang, Z. (2018). Inertial and Damping Characteristics of DC Distributed Power Systems Based on Frequency Droop Control. Energies, 11(9), 2418. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11092418





