Design and Analysis of Surface-Mounted PM Vernier Machines Considering Harmonic Characteristics of Winding MMF
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Air-Gap Magnetic Field by Armature Windings
2.1. Structures of the SPMVM
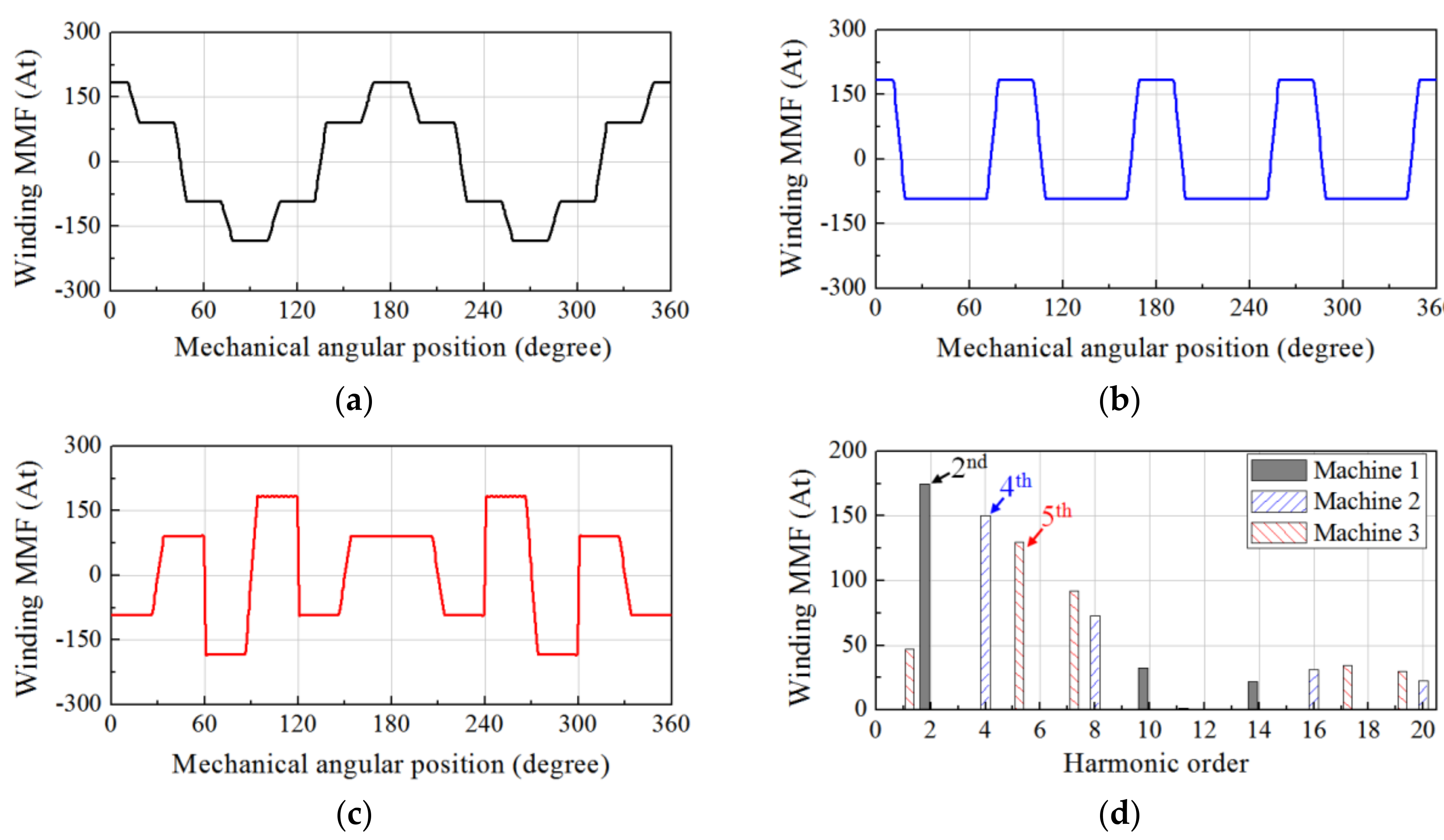
2.2. Winding MMF Distribution
- For Machine 1,
- For Machine 2,
- For Machine 3,where θso, Nc, and Imax are the slot opening, the number of turns per coil, and the peak value of the phase current, respectively.
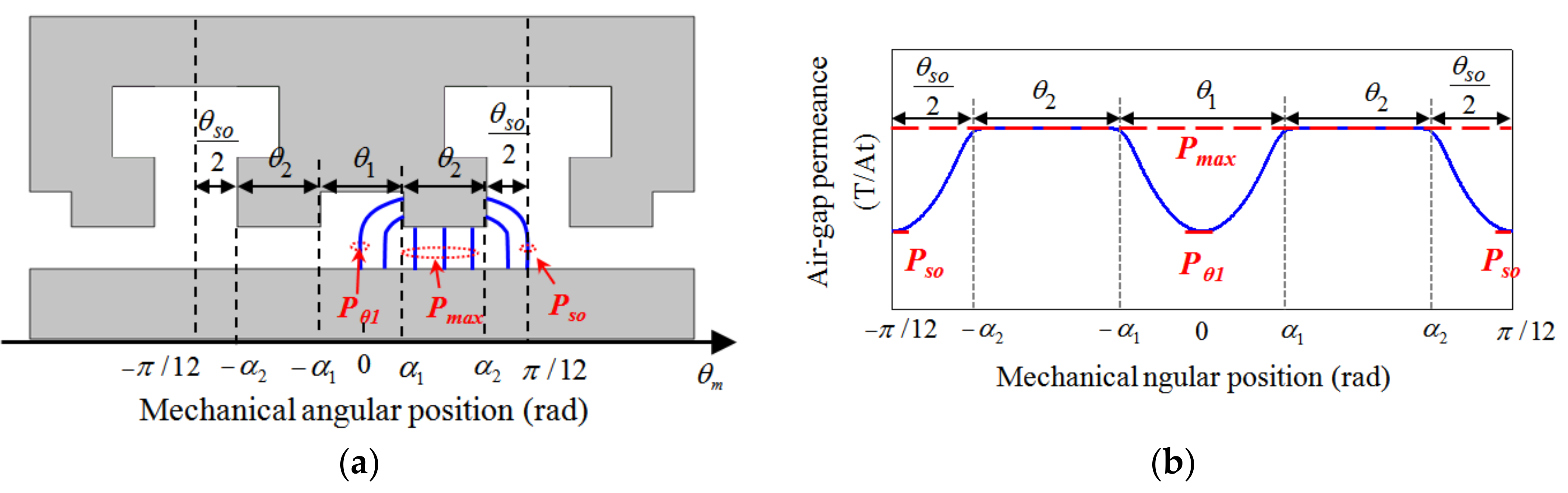
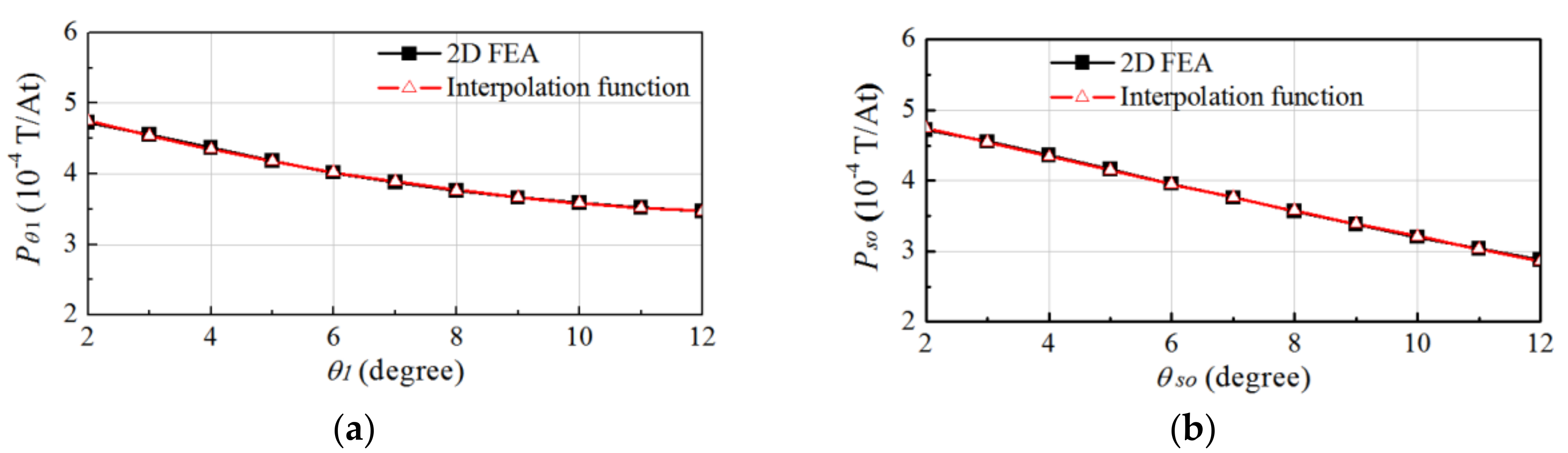
2.3. Permeance Distribution
2.4. Flux Density Distribution by the Windings
- For Machine 1,
- For Machine 2,
- For Machine 3,
3. Simulation Study
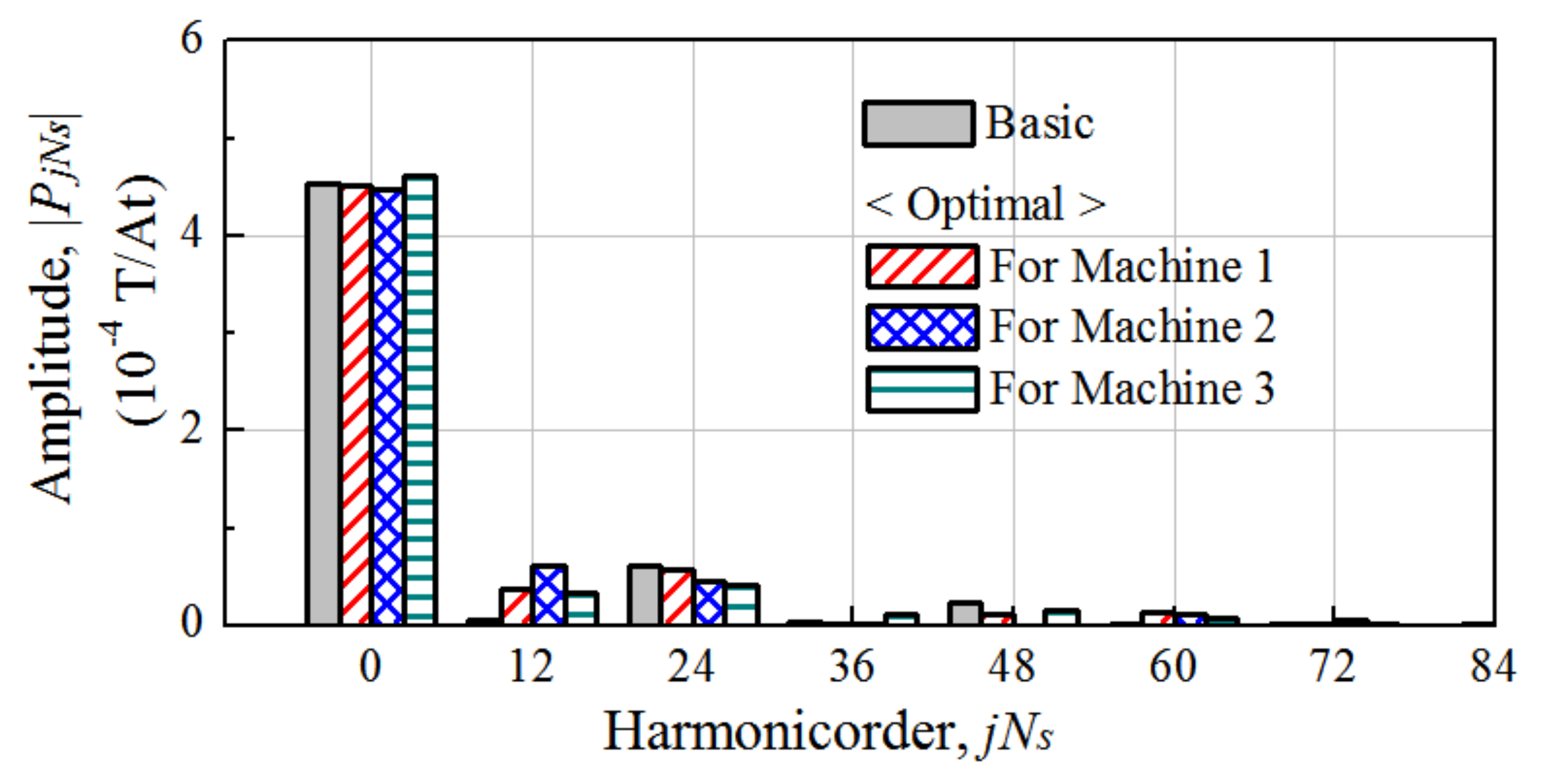
3.1. Optimization of the FMP Shape
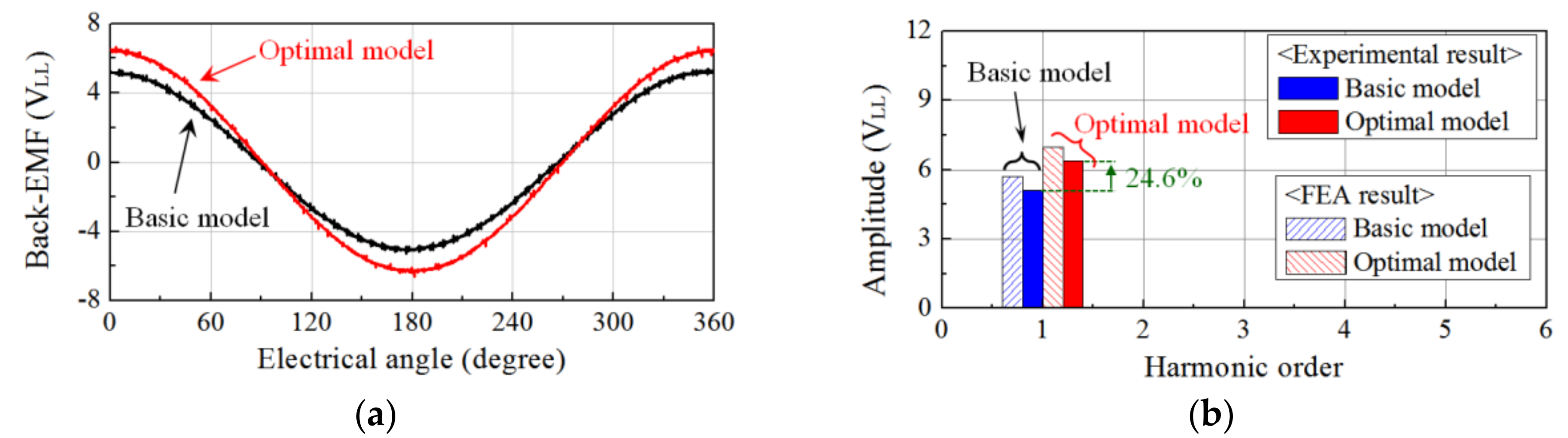
3.2. Back EMF and Torque Characteristics
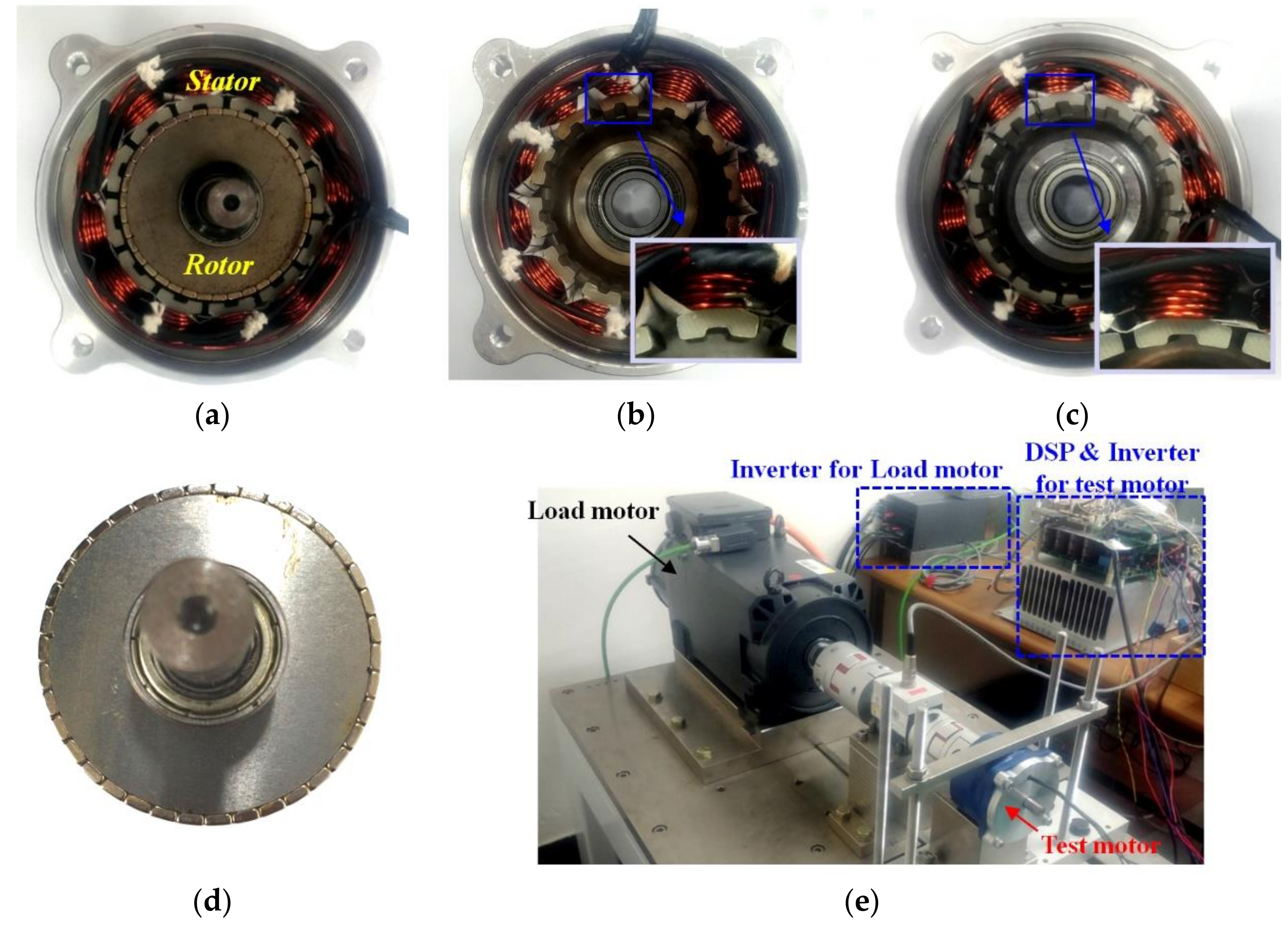
4. Experiment and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, F.; Kim, M.; Kwon, B.; Baek, J. A small axial-flux vernier machine with ring-type magnets for the auto-focusing lens drive system. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Cheng, R. Hybrid stator design of fault-tolerant permanent-magnet vernier machines for direct-drive applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ho, S.L.; Fu, W.N.; Zhang, X. Design optimization of a novel doubly fed dual-rotor flux-modulated machine for hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Yang, J.; Zhao, W.; Ji, J.; Chen, Q.; Gong, W. Design and analysis of a new fault-tolerant permanent-magnet vernier machine for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 4176–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Qu, R.; Li, D.; Li, J. A high torque density vernier PM machines for hybrid electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Hangzhou, China, 17–20 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- B. Design of a Direct Drive Permanent Magnet Vernier Generator for a Wind Turbine System. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Portland, OR, USA, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 4275–4282.
- Li, X.; Chau, K.T.; Cheng, M. Analysis, design and experimental verification of a field-modulated permanent-magnet machine for direct-drive wind turbines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qu, R.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Zhou, G. Design of a dual-stator LTS vernier machine for direct-drive wind power generation. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wn, F.; El-Refaie, A.M. Permanent magnet vernier machine: A review. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Ho, S.L.; Fu, W.N.; Wang, L.L. Quantitative comparison of novel vernier permanent magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2032–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, A.; Lipo, T.A. Generic torque-maximizing design methodology of surface permanent-magnet vernier machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Vukoti´c, M.; Miljavec, D. Design of a permanent-magnet flux-modulated machine with a high torque density and high power factor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lipo, T.A. Operation and design principles of a PM vernier motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3656–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Chang, J. Influences of winding MMF harmonics on torque characteristics in surface-mounted permanent magnet vernier machines. Energies 2017, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, A.E. A mathematical development of the theory of the magnetomotive force of windings. J. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1923, 61, 749–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Instantaneous magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent magnet dc motors, Part III. Effect of stator slotting. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1933, 29, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, D.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Comparison of PM brushless motors, having either all teeth or alternate teeth wound. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Machine | FMP Shape | Design Variables [degree] | Working Harmonic [mT] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ1 | θ2 | θso | Analytical | FEA | ||
| 1 | Basic | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 10.31 | 10.33 |
| Optimal | 10.64 | 7 | 5.36 | 11.27 | 11.22 | |
| 2 | Basic | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 14.45 | 14.38 |
| Optimal | 12.38 | 7.05 | 3.52 | 17.96 | 17.77 | |
| 3 | Basic | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 15.47 | 15.26 |
| Optimal | 8.82 | 8.59 | 4 | 18.95 | 18.62 | |
| Machine | FMP Shape | Fundamental of Back-EMF [VLL] | Average Torque [Nm] | Torque Ripple [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basic | 4.4 (100%) | 1.03 (100%) | 7.5 |
| Optimal | 4.77 (108.4%) | 1.12 (108.4%) | 4.2 | |
| 2 | Basic | 5.62 (100%) | 1.32 (100%) | 3.7 |
| Optimal | 6.93 (123.2%) | 1.62 (123.2%) | 3.8 | |
| 3 | Basic | 5.71 (100%) | 1.34 (100%) | 1.9 |
| Optimal | 6.97 (122.1%) | 1.63 (122.1%) | 1.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, D.; Chang, J. Design and Analysis of Surface-Mounted PM Vernier Machines Considering Harmonic Characteristics of Winding MMF. Energies 2019, 12, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12050897
Jang D, Chang J. Design and Analysis of Surface-Mounted PM Vernier Machines Considering Harmonic Characteristics of Winding MMF. Energies. 2019; 12(5):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12050897
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Daekyu, and Junghwan Chang. 2019. "Design and Analysis of Surface-Mounted PM Vernier Machines Considering Harmonic Characteristics of Winding MMF" Energies 12, no. 5: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12050897
APA StyleJang, D., & Chang, J. (2019). Design and Analysis of Surface-Mounted PM Vernier Machines Considering Harmonic Characteristics of Winding MMF. Energies, 12(5), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12050897






