Abstract
This paper presents an analysis of the energy exchange resulting from a 2D steady magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) flow past a permeable surface with partial slip in the presence of the viscous dissipation effect under convective heating boundary conditions. A magnetic field can effectively control the motion of an electrically conducting fluid in micro scale systems, which can be applied for fluid transportation. Local similarity solutions for the transformed governing equations are obtained, and the reduced ordinary differential equations solved numerically via an explicit Runge-Kutta (4, 5) formula, the Dormand-Prince pair and shooting method, which is valid for fixed positions along the surface. The effects of various physical parameters, such as the magnetic parameter, the slip coefficient, the suction/injection parameter, the Biot number, the Prandtl number and the Eckert number, on the flow and heat transfer characteristics are presented graphically and discussed. The results indicate that the heat transfer rate increases with the increase in Biot number, slip coefficient, suction and magnetic parameter, whereas it decreases with the increase in Eckert number and injection.
1. Introduction
The problem of slip MHD flow with viscous dissipation past a permeable surface has many important technological and industrial applications, especially in Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS), such as micro MHD pumps [1], micromixing of physiological samples [2,3], biological transportation and drug delivery [4,5]. By producing Lorentz forces, the magnetic field is able to transport liquids in the mixing processes as an active micromixing technology method. Since most biological transportation applications based on magnetic fields are in the micro/nano systems [6,7,8], it is vital to consider the effect of velocity slip at the boundaries [9,10]. The permeability is another significant factor in micromixing of biological samples [2]. Therefore, transportation of conductive biological fluids in micro systems would greatly benefit from theoretical research in this area. Blood plasma, which is a Newtonian fluid, is very similar in physical properties to water. It is considered very important in blood flow modelling through arterial stenosis [11,12]. Most investigations assume that blood exists in the core region of the artery as a non-Newtonian fluid, whereas plasma is found in the peripheral layer as a Newtonian fluid [12].
Viscous dissipation effects are usually ignored in macro scale systems, in laminar flow in particular, except for very viscous liquids at comparatively high velocities. However, even for common liquids at laminar Reynolds numbers, frictional effects in micro scale systems may change the energy equation [13]. Koo and Kleinstreuer [14] have investigated the effects of viscous dissipation on the temperature field using dimensional analysis and experimentally validated computer simulations. Three common working fluids—water, methanol and iso-propanol—in different conduit geometries have been considered in this study. The authors concluded that the channel size was a key factor that determines the impact of viscous dissipation. Furthermore, viscous dissipation effects may be very significant for fluids with high viscosities and low specific heat capacities, even at relatively low Reynolds numbers. Accordingly, the viscous dissipation term should be considered in the micro scale systems.
Many researchers have studied, both analytically and numerically, slip boundary layer problems over different surface configurations. For example, the mass transfer effect on the moving wall boundary layer has been investigated by Fang [15], who later extended his work by considering the velocity slip at the wall [16]. Martin and Boyd [17] have analyzed the slip flow and heat transfer past a flat surface at constant wall temperature. Their results demonstrate that the boundary layer equations can be used to study flow at MEMS scale and provide useful information to study the effects of rarefaction on the shear stress and structure of the flow. According to their boundary layer theory, there is no temperature jump in liquid fluids. Yazdi et al. [18] have investigated the slip flow boundary layer past flat surface at constant heat flux boundary conditions. In a later work [19], they have considered the effect of permeability parameter on the slip flow regime. The findings of this study indicate that mass suction has a significant effect on the fluid velocity adjacent to the wall in the presence of partial slip. Furthermore, the same research team also studied liquid flow past open parallel microchannels embedded within a surface [20,21]. A no-slip condition was applied between microchannels, whereas a slip condition was applied to the open parallel microchannels.
MHD steady flow and heat transfer of a second grade fluid saturated in porous space was investigated by Hayat et al. [22], who found that the horizontal component of velocity increased as the slip parameter increased. The effect of thermal slip condition over a permeable stretching sheet was taken into account in the work by Hayat et al. [23], whilst, more recently, Qasim et al. [24] added the effects of thermal radiation and ohmic dissipation. Fang et al. [25] have demonstrated that the second order slip flow model is necessary to predict the flow characteristics accurately. Abbas et al. [26] have examined the heat transfer problem around an oscillatory infinite sheet with slip boundary condition, concluding that an increase in the slip parameter leads to a reduction in amplitude of the flow velocity, while with the increase in the thermal slip parameter the heat transfer from the sheet to the fluid becomes slower. In a similar work, Fang et al. [27] have evaluated slip MHD boundary layer over stretching sheet. Recently, Yazdi et al. [28,29] have investigated MHD liquid flow over nonlinear permeable stretching surface in the presence of the partial slip and high-order chemical reactions.
Unlike the common thermal boundary conditions, such as constant temperature or constant heat flux, Aziz [30] demonstrated that a similarity solution is possible if the convective heat transfer associated with the hot fluid on the lower surface of the plate is proportional to x−0.5. These results were later improved by Ishak [31] with the addition of the permeability effect along the surface. Yao et al. [32] have investigated the convective boundary condition along a stretching/shrinking sheet. Recently, Rahman [33] has evaluated the MHD flow over a flat plate with partial slip subjected to the convective surface heat flux at the boundary. The study findings indicate that the local similarity solution should be applied due to the dependency of slip coefficient on x-coordinate. However, even though problem plays a prominent role in the fluid flow and heat transfer control of micro scale systems, no attempt so far has been made to analyze MHD flow and heat transfer past a permeable surface with partial slip and viscous dissipation.
2. Mathematical Formulation
In the present work, we considered slip MHD flow and heat transfer past a permeable horizontal surface at a convective surface boundary condition in the presence of viscous dissipation effects. The flow configuration is illustrated in Figure 1.
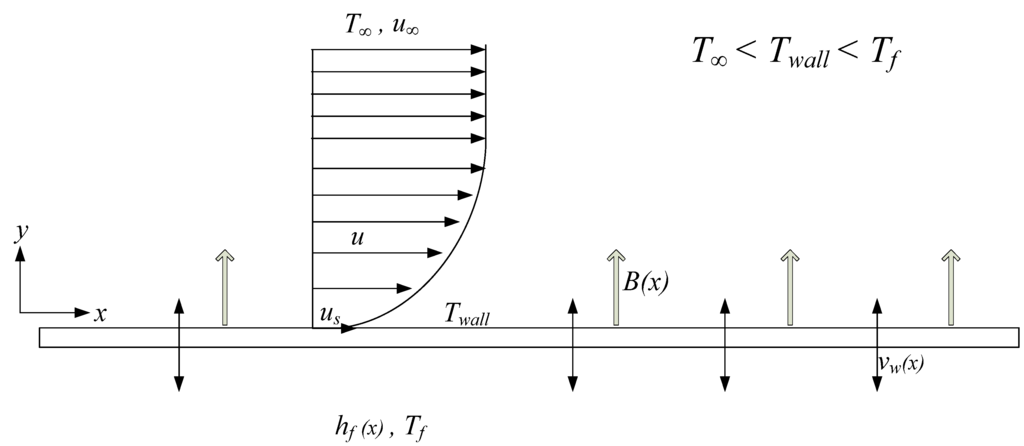
Figure 1.
Physical model of flow and heat transfer in the present work.
Let us assume that the fluid is incompressible, Newtonian and continuum with free stream velocity u∞ and temperature T∞ Moreover, it is subjected to a transverse magnetic field applied in the vertical direction with varying strength B, as a function of x, is given by:
where x is the coordinate along the plate measured from the leading edge. Because the magnetic Reynolds number is assumed small, the induced magnetic field is negligible and can be ignored. Under these conditions, the effect of the induced magnetic field is negligible in comparison to the applied magnetic field and can thus be ignored. The fluid that decelerates due to the viscous action of the surface is propagated by the magnetic forces that counteract the viscous effect [34]. A permeable surface is considered with mass transfer velocity as a function of x:
Thus, the viscous dissipation term should be investigated in the slip flow regimes along a permeable surface, whereby the positive y-coordinate is measured perpendicular to the x-coordinate in the outward direction towards the fluid. The corresponding velocity components in the x and y directions are denoted as u and v, respectively. The bottom of the surface is heated due to convective heat transfer from a hot fluid at a temperature Tf, yielding a heat transfer coefficient hf as a function of x, with its strength given as follows:
It is assumed that Tf > Twall > T∞ as well as that the velocity gradients in the x-direction are small compared to those in the y-direction. Within the framework of the above-noted assumptions, the boundary layer equations governing the MHD convective flow and heat transfer in the presence of viscous dissipation are written in the usual notation as:
where associated boundary conditions are given as:
The last term in the above momentum Equation (5) describes the pressure gradient, which is obtained from the momentum equation at the edge of the boundary layer [35]. Moreover, vw(x) is the mass transfer due to suction vw(x) < 0 or injection vw(x) > 0. The velocity slip, us is proportional to the local wall shear stress and is given by [17,18]:
where l is the slip length constant proportional to the velocity slip. For liquid fluids, l is described as the interaction length. Moreover, if the velocity profile is linearly extrapolated into the wall, the slip length would correspond to the depth at which the velocity would decline to zero [36]. However, if the fluid flow adjacent to the wall is in thermodynamic equilibrium, the no-slip boundary condition is applicable. Martin and Boyd [17] have indicated that the appropriate assumption for the flow of liquids at the micro scale systems is to neglect temperature jump, because of the lack of data on the thermal accommodation coefficient. The following similarity variables are used in the present work:
It is also useful to introduce a slip coefficient using similarity variables:
where K is the slip coefficient defined for liquids by:
The slip coefficient K is a dimensionless parameter of the amount of slip, ranging from zero (total adhesion) to infinity (full slip). Now the fundamental partial differential Equations (5) and (6) can be transformed to ordinary differential equations by substituting similarity variables (9) into Equations (5) and (6) as follows:
For these equations, the associated boundary conditions are given as:
where a, fw, Pr, Ec, and M represent the Biot number (the equivalent dimensionless convective heat transfer parameter), the suction/injection parameter, the Prandtl number, the Eckert number and the magnetic parameter, respectively:
It should be noted that fw is negative for mass injection (vw0> 0) cases and positive in the presence of suction (vw0< 0) at the surface. From the definitions (15), it is clear that fw, a and M are independent of x. Moreover, the Biot number a is a ratio of the internal thermal resistance of the plate to the boundary layer thermal resistance of the hot fluid at the bottom of the surface. Thus, as the only parameter that exhibits a dependence on the x-coordinate is slip coefficient K, the problem must be solved locally. Consequently, given the fixed values of the x-coordinate the local similarity solution would be achieved correctly for momentum and energy equations. The nonlinear differential Equations (12) and (13) are solved numerically as a one-way coupled problem by applying the explicit Runge-Kutta (4, 5) formula, the Dormand-Prince pair and the shooting method, subject to the associated boundary conditions (14). Finally, the skin friction coefficient and the local surface heat flux can be obtained as follows:
3. Results and Discussion
A comparison of the velocity gradient, temperature distribution, and temperature gradient adjacent to the wall between the present results, using the Dormand-Prince pair and the shooting method, and those obtained previously are shown in Table 1. It is evident that our results are well-matched with the previous convective surface boundary condition problem of Aziz [30] and Ishak [31]. An excellent agreement is also reached with the results of a slip-flow problem of Rahman [33], obtained by Nachtsheim-Swigert iteration procedure for Pr = 1, M = 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of the velocity gradient at the wall f''(0), temperature distribution θ(0), and temperature gradient |θ'(0)| at the wall between the present results and those obtained previously.
| M | Pr | K | a | Rahman | Aziz | Ishak | Present results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33] | [33] | [33] | [30] | [31] | |||||||
| f''(0) | θ(0) | |θ'(0)| | |θ'(0)| | |θ'(0)| | f''(0) | θ(0) | |θ'(0)| | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.01 | 1.0440 | 0.0236 | 0.0098 | 1.0440 | 0.0237 | 0.0098 | ||
| 0.5 | 1.0440 | 0.5478 | 0.2261 | 1.0440 | 0.5480 | 0.2261 | |||||
| 1 | 1.0440 | 0.7078 | 0.2921 | 1.0440 | 0.7078 | 0.2920 | |||||
| 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.6987 | 0.0208 | 0.0098 | 0.6987 | 0.0209 | 0.0098 | ||||
| 0.5 | 0.6987 | 0.5163 | 0.2418 | 0.6987 | 05164 | 0.2417 | |||||
| 1 | 0.6987 | 0.6811 | 0.3189 | 0.6987 | 0.6812 | 0.3188 | |||||
| 0 | 0.72 | 0 | 0.05 | 0.0428 | 0.0428 | 0.0428 | 0.0428 | ||||
| 0.1 | 0.0747 | 0.0747 | 0.0747 | 0.0747 | |||||||
| 0.2 | 0.1193 | 0.1193 | 0.1193 | 0.1193 | |||||||
| 0.4 | 0.1701 | 0.1700 | 0.1699 | 0.1700 | |||||||
| 0.6 | 0.1981 | 0.1981 | 0.1980 | 0.1980 | |||||||
| 0.8 | 0.2160 | 0.2159 | 0.2159 | 0.2159 | |||||||
| 1 | 0.2282 | 0.2282 | 0.2282 | 0.2282 | |||||||
| 5 | 0.2793 | 0.2791 | 0.2791 | 0.2791 | |||||||
| 10 | 0.2873 | 0.2871 | 0.2871 | 0.2871 | |||||||
| 20 | 0.2915 | 0.2913 | 0.2913 | 0.2913 | |||||||
3.1. Effects on Velocity Field and Friction
Figure 2(a),(b) shows the velocity profiles f'(η) and velocity gradient f''(η), respectively, for various values of the suction/injection parameter when K = 0.5 and M = 0.5. Since in this case the similarity solution is local, i.e. the results are obtained at a specific location on the wall (x-coordinate), η corresponds to distances perpendicular to that point (y). In the presence of suction, the velocity profiles tend to increase monotonically, and the boundary layer becomes thinner. On the other hand, increased injection tends to enhance the boundary layer thicknesses. Thus, it is evident that, in the slip flow regime, velocity adjacent to the wall can be manipulated through suction/injection parameter. Moreover, the interception point between velocity gradient profiles suggests faster decrements for high suction at the wall.
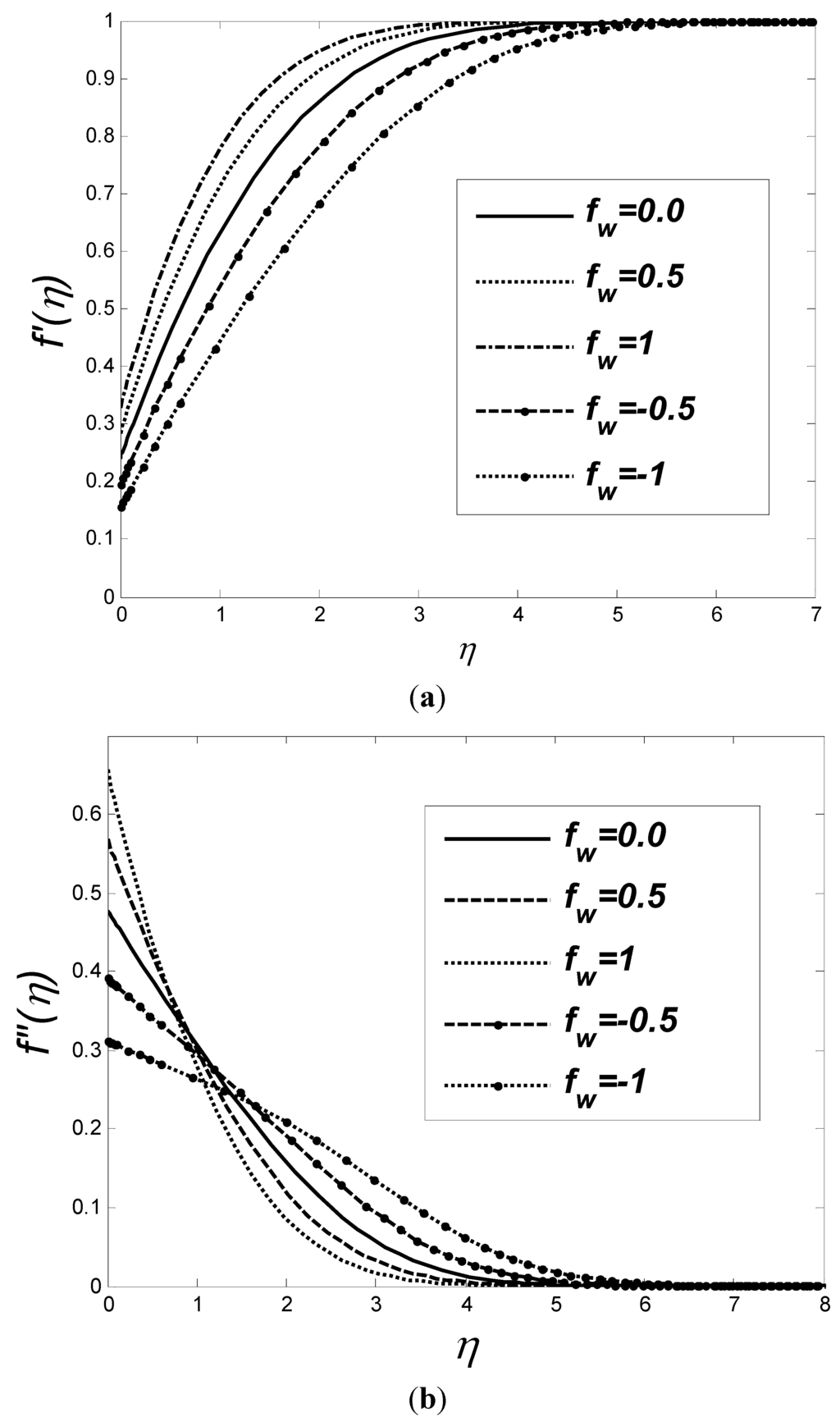
Figure 2.
Distribution of velocity (a) and velocity gradient (b) as a function of η for various values of fw when K = 0.5, M = 0.5.
Figure 3(a),(b) illustrate the variation of the velocity f'(η) and velocity gradient f''(η) profiles, respectively, for various values of slip coefficient K when fw = 0.2 and M = 0.5. It is noted that an increase in K corresponds to a rise in the fluid velocity adjacent to the wall. Consequently, the wall velocity gradient decreases. Moreover, the boundary layer thickness becomes thinner in the slip flow regime.
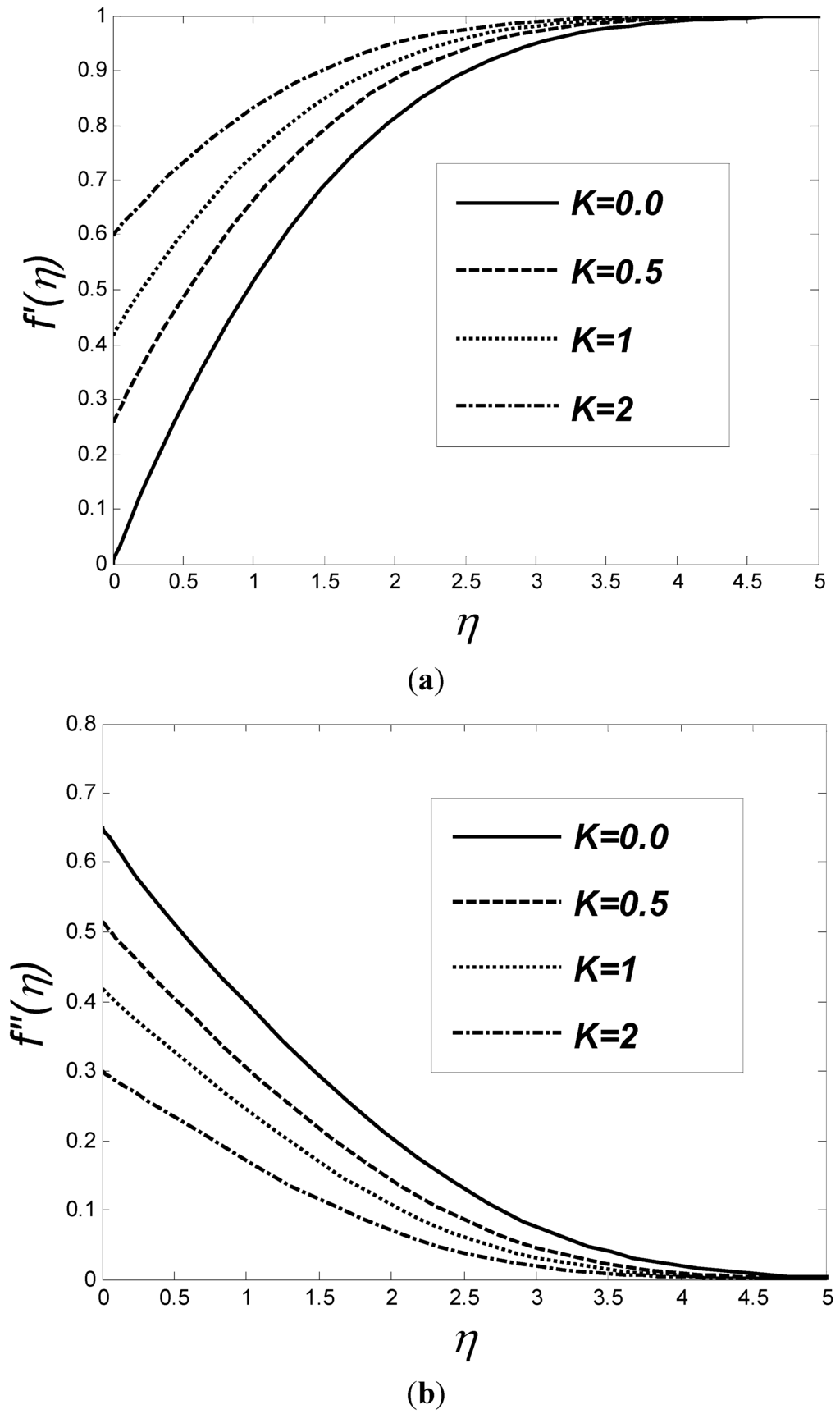
Figure 3.
Distribution velocity (a) and velocity gradient (b) as a function of η for various values of K when M = 0.5, fw = 0.2.
The combined effect of the slip coefficient K, the suction/injection parameter fw and magnetic parameter M on the velocity and velocity gradient adjacent to the wall has been illustrated in Figure 4(a),(b), respectively. It is evident that an increase in all magnetic parameter, suction and slip coefficient tends to increase fluid velocity adjacent to the wall. Moreover, in the presence of the slip, the magnetic parameter can increase fluid velocity both inside the boundary layer and adjacent to the wall effectively. As the sum of last two terms of the momentum equation is positive, fluid motion in the boundary layer region increases as a result of Lorenz force. Consequently, the electrically conducting fluid receives a push from the magnetic force—the mechanism by which the magnetic field has the potential to manipulate an electrically conducting fluid in the micro scale system. Finally, it can be observed that skin friction coefficient increases with the increase of magnetic parameter and suction, while slip coefficient shows an opposite effect.
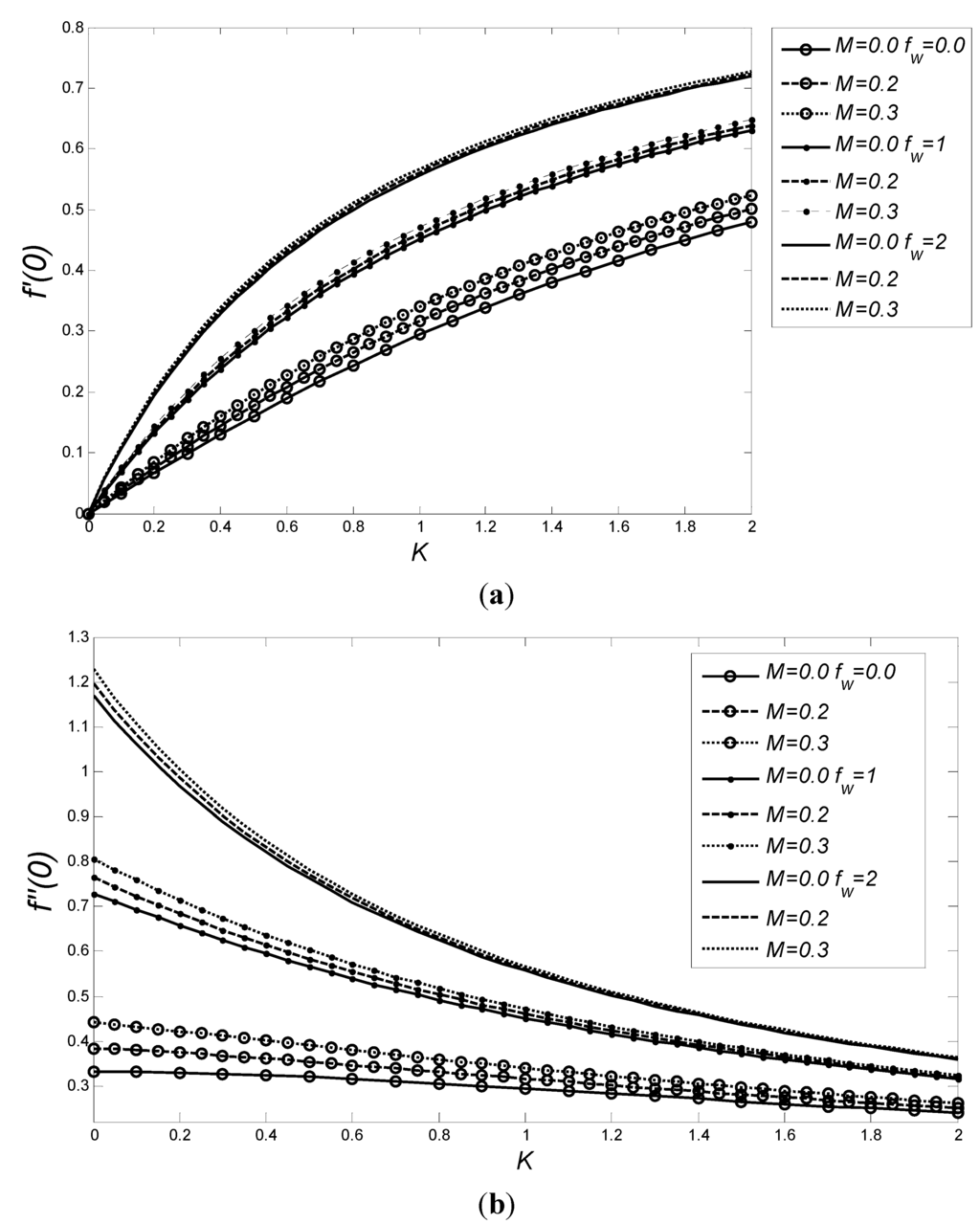
Figure 4.
(a) Variation of the f'(0) and (b) f''(0) as a function of K for various values of fw and M.
3.2. Effects on Temperature Field and Heat Transfer
The dimensionless temperature (𝜂) and temperature gradient |𝜃′(𝜂)| profiles for different values of the Biot number a (0.1, 1, 5 or 100, corresponding to an increase in convective heating) when Pr = 7, K = 0.5, fw = 0.2, Ec = 0 and M = 0.5 are shown in Figure 5(a),(b), respectively. Given that convective heating increases with Biot number, a → ∞ simulates the isothermal surface, shown in Figure 5(a), where θ(0) = 1 as a→∞. In fact, a high Biot number indicates that the internal thermal resistance of the plate is higher than the boundary layer thermal resistance. As a result, these figures illustrate that an increase in the Biot number leads to increase of both fluid temperature and temperature gradient, efficiently.
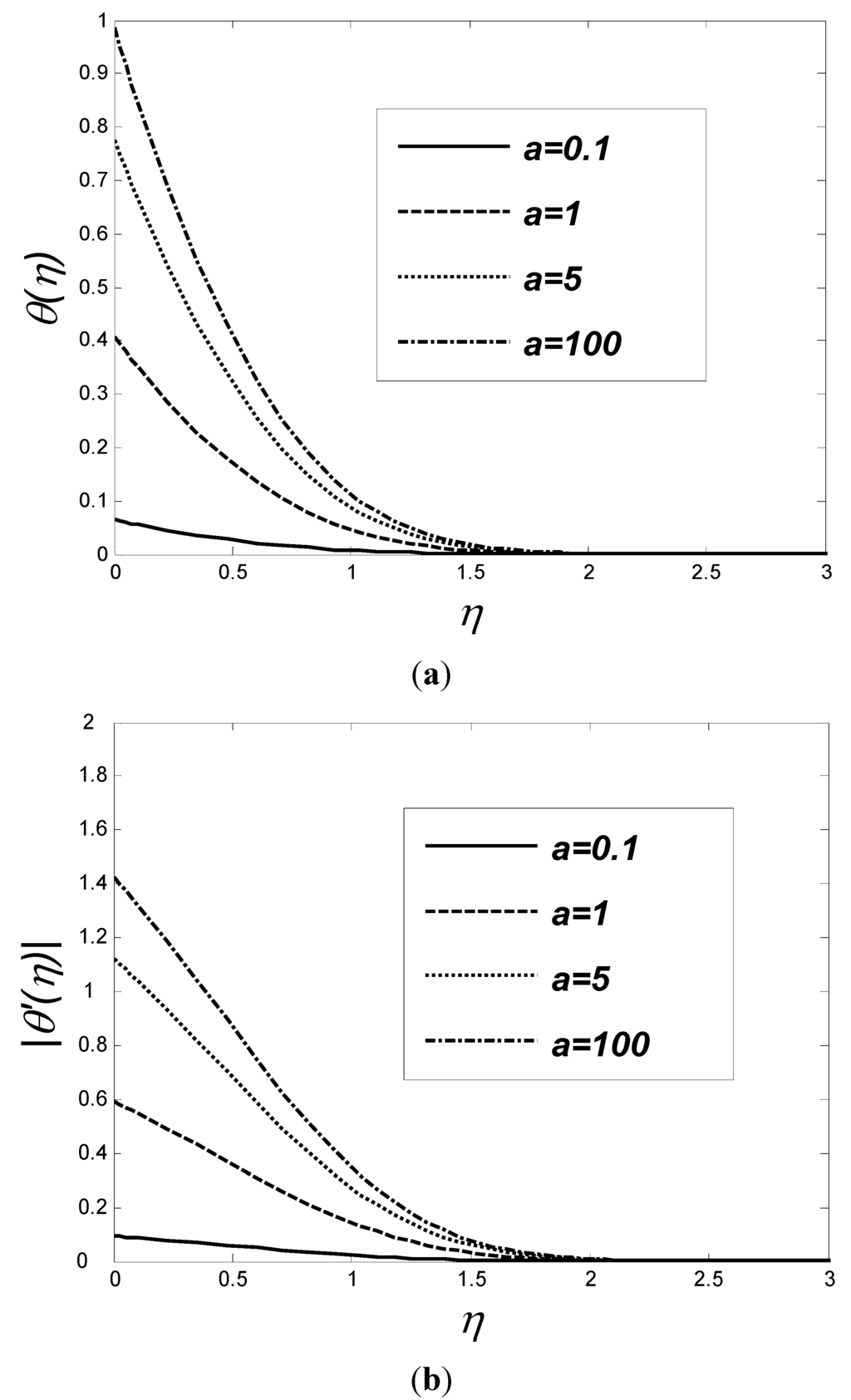
Figure 5.
Distribution of temperature (a) and temperature gradient (b) as function of η for various values of Biot number a when Pr = 7, K = 0.5, fw = 0.2, Ec = 0 and M = 0.5.
Figure 6(a),(b) depicts dimensionless temperature and temperature gradient for various values of Ec when a = 5, K = 0.5, fw = 0.2, Pr = 7 and M = 0.5. Although an increase in the temperature profiles, as well as the thickness of the boundary layer, is observed with an increase in the Eckert number, it yields a decrease in the rate of heat transfer. Thus, by varying the Eckert number, the wall temperature distribution can be manipulated. Figure 6(b) depicts the heat transfer rate decrease with the Eckert number, where the interception point between temperature gradient profiles, indicates faster decrement for lower Eckert numbers.
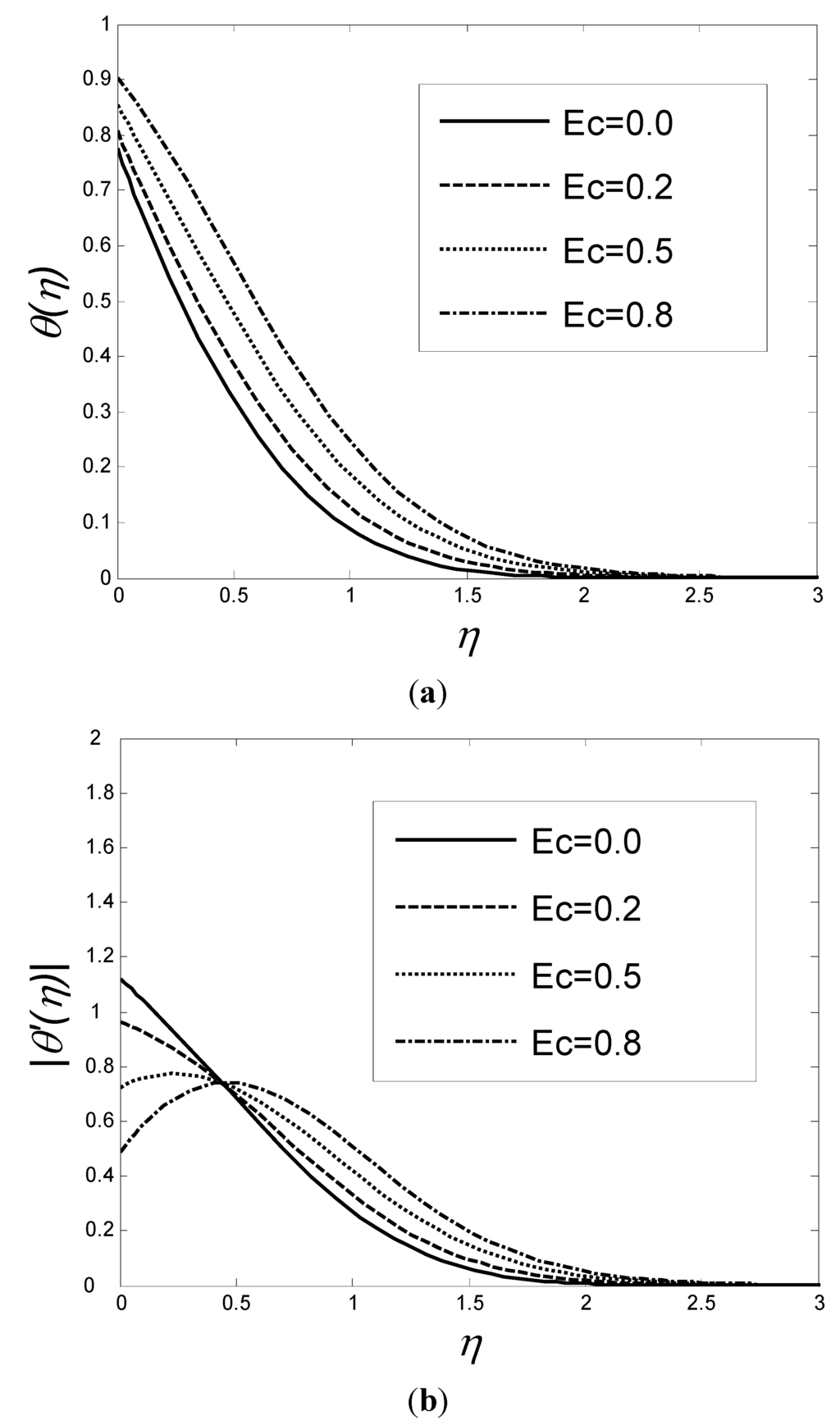
Figure 6.
Distribution of temperature (a) and temperature gradient (b) as a function of η for various values of Ec when a = 5, K = 0.5, fw = 0.2, Pr = 7 and M = 0.5.
Temperature profiles and the corresponding gradients for various values of K at Pr = 7, Ec = 0.5, fw = 0.2, a = 5 and M = 0.5 are shown in Figure 7(a),(b) respectively. It is evident that, at high slip coefficients, the temperature reduces faster and the boundary layer becomes thinner. This suggests that the heat transfer rate of liquids increases significantly with the increase of slip flow coefficient, as the change from 0 to 2 yields an increase in the heat transfer rate over surface structure by up to around 75%.
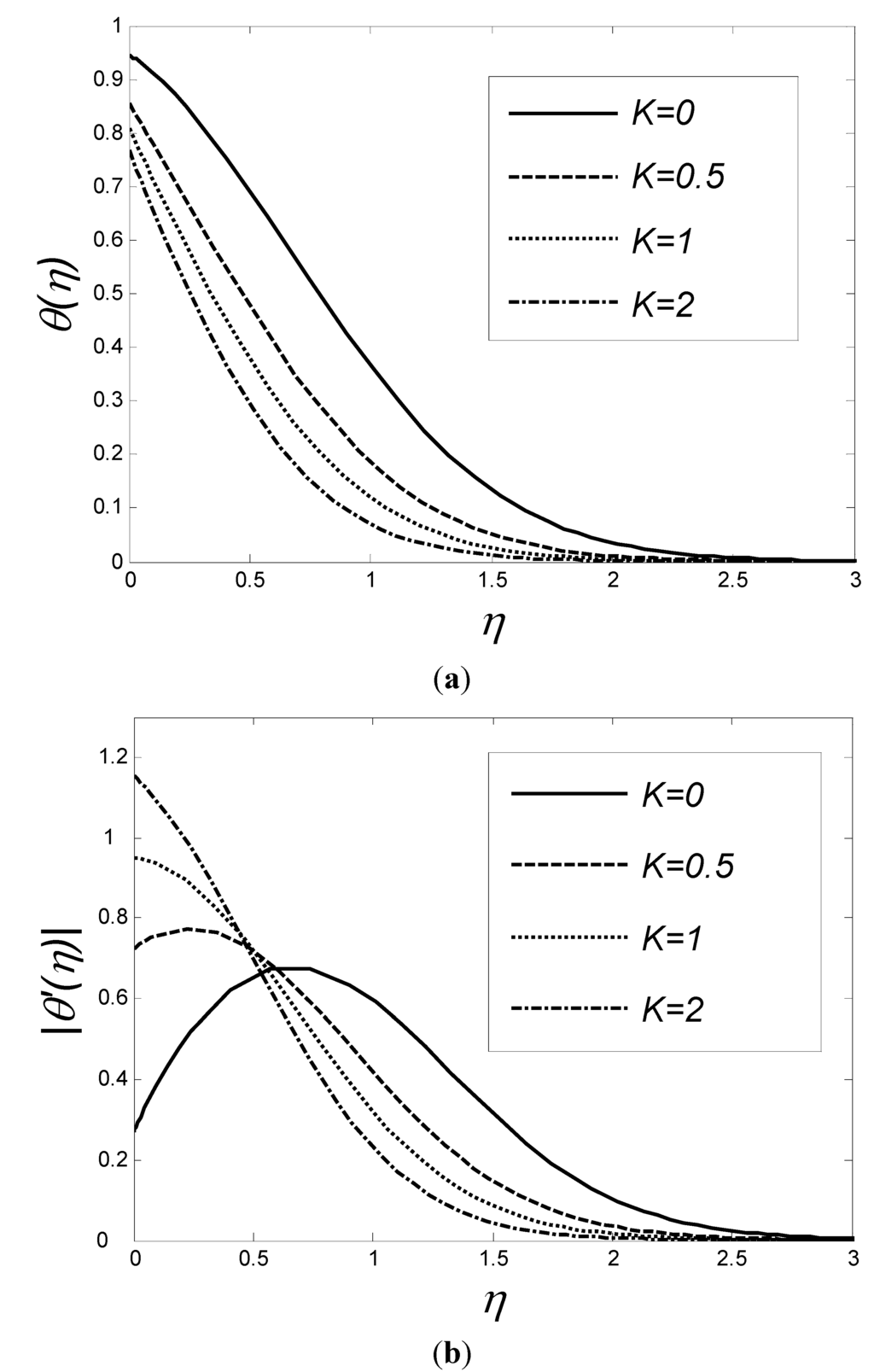
Figure 7.
Distribution of temperature (a) and temperature gradient (b) as a function of η for various values of K when Pr = 7, Ec = 0.5, fw = 0.2, a = 5 and M = 0.5.
Figure 8(a),(b) shows the effect of magnetic parameter on temperature and temperature gradient profiles, respectively, when Pr = 7, Ec = 0.5, fw = 0.2, K = 0.5 and a = 5. It is evident that the increase of the magnetic parameter results in the decrease of temperature profiles. Moreover, the interception point between temperature gradient profiles suggests faster decrements for high magnetic parameters.
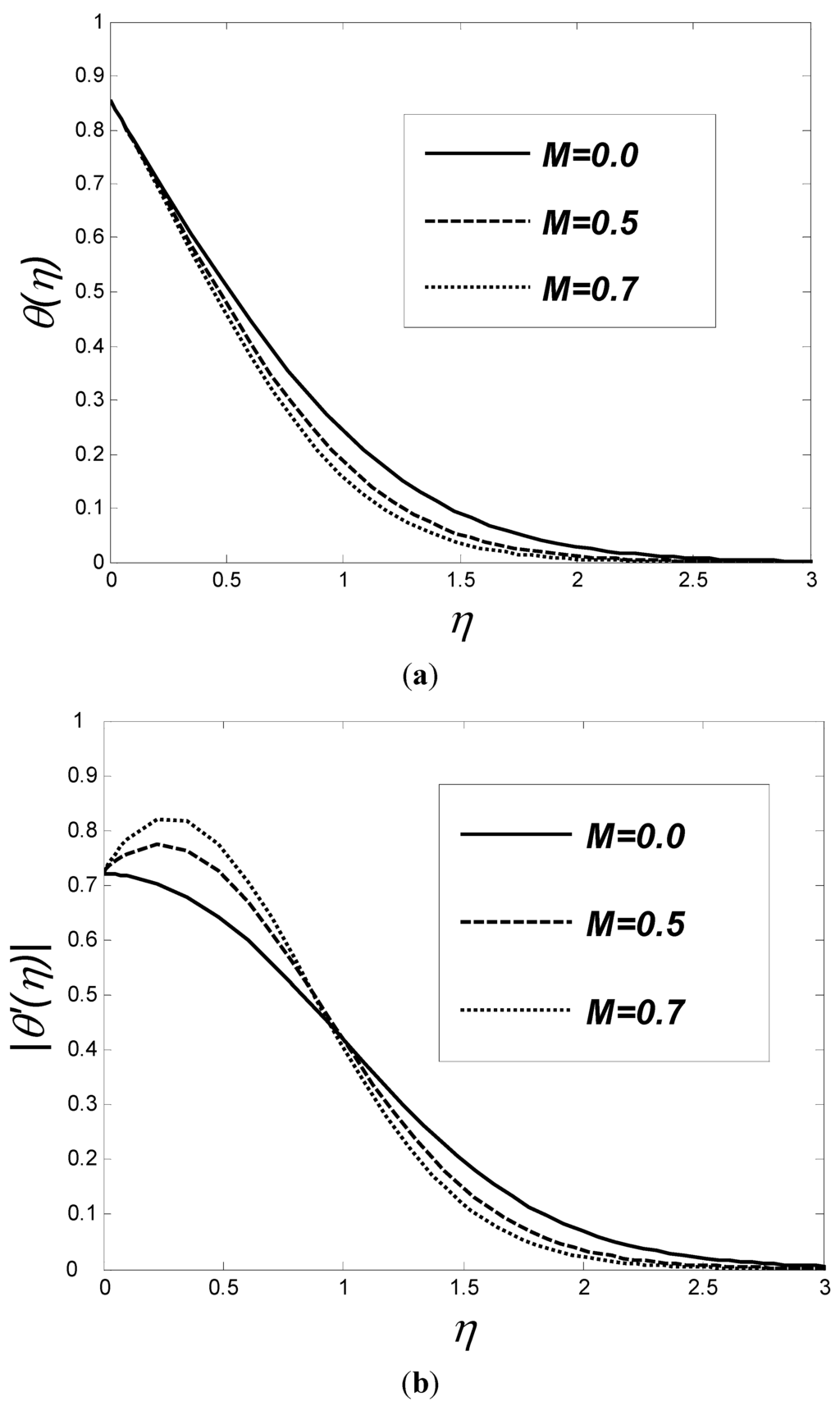
Figure 8.
Distribution of temperature (a) and temperature gradient (b) as a function of η for various values of M when Pr = 7, Ec = 0.5, fw = 0.2, K = 0.5 and a = 5.
Figure 9(a),(b) depicts the temperature and the corresponding gradient profiles for various values of Prandtl number when K = 0.5, a = 5, fw = 0.2, M = 0.5 and Ec = 0.5, indicating that an increase in the Prandtl number results in a faster decrease in the temperature profiles as well as the thickness of the boundary layer, causing the increase in the heat transfer rate.
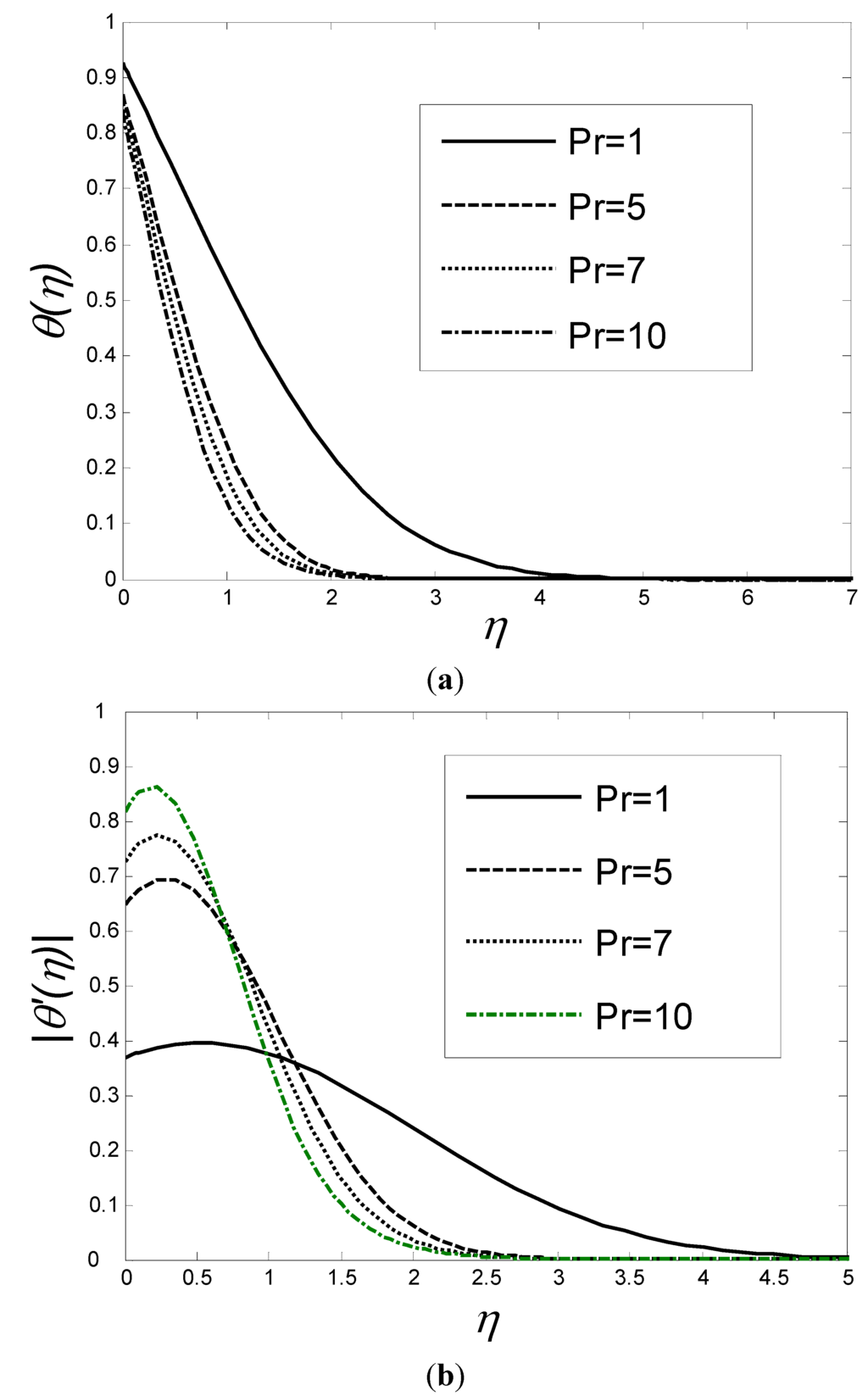
Figure 9.
Distribution of temperature (a) and temperature gradient (b) as a function of η for various values of Pr when K = 0.5, a = 5, fw = 0.2, M = 0.5 and Ec = 0.5.
Figure 10(a),(b) illustrates the effect of slip coefficient and Biot number on θ(0) and |θ'(0)|, respectively, for M = 0.3, Pr = 7, fw = 0.2 and Ec = 0.2. It is evident that both the fluid temperature adjacent to the wall and the heat transfer rate increase effectively with an increase in Biot number. In contrast, although the increase in the slip coefficient also increases the heat transfer rate, it reduces the wall temperature. It is interesting to note that the slip boundary condition can become a useful alternative technique of drag reduction, while increasing heat-transfer effectiveness.
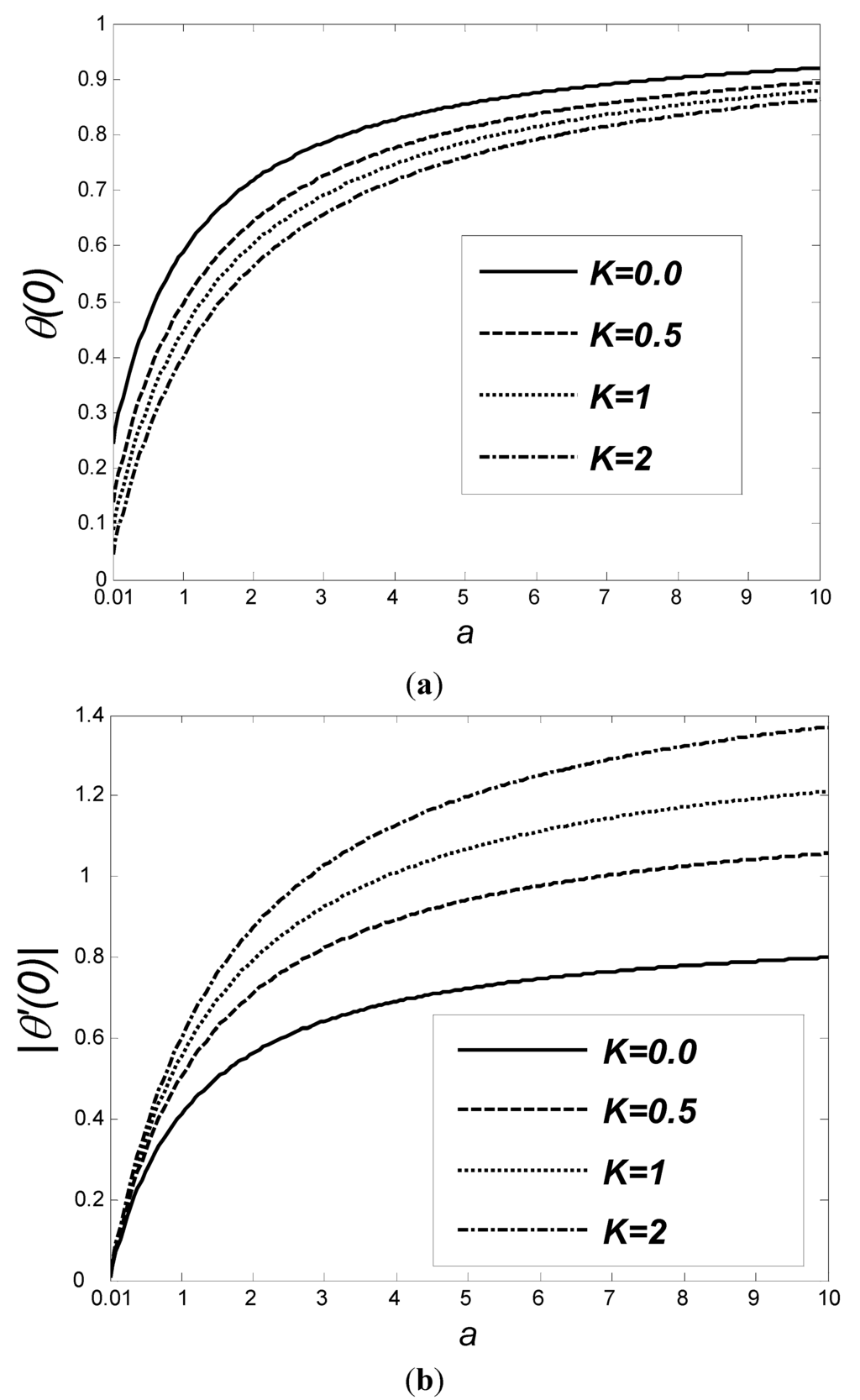
Figure 10.
(a) Variation of the θ(0) and (b) |θ'(0)| as a function of a for various values of K when M = 0.3, Pr = 7, fw = 0.2 and Ec = 0.2.
Figure 11(a),(b) shows the effect of K and Ec on θ(0) and |θ'(0)| respectively when a = 0.1, fw = 0.2, Pr = 7 and M = 0.5. In high wall shear stress conditions, viscous dissipation effect is important. Thus, the effects of viscous dissipation should be much more important for low slip coefficients, illustrated in Figure 11(a),(b). Furthermore, the Eckert number can decrease the heat transfer rate, whereas it tends to increase wall temperature.
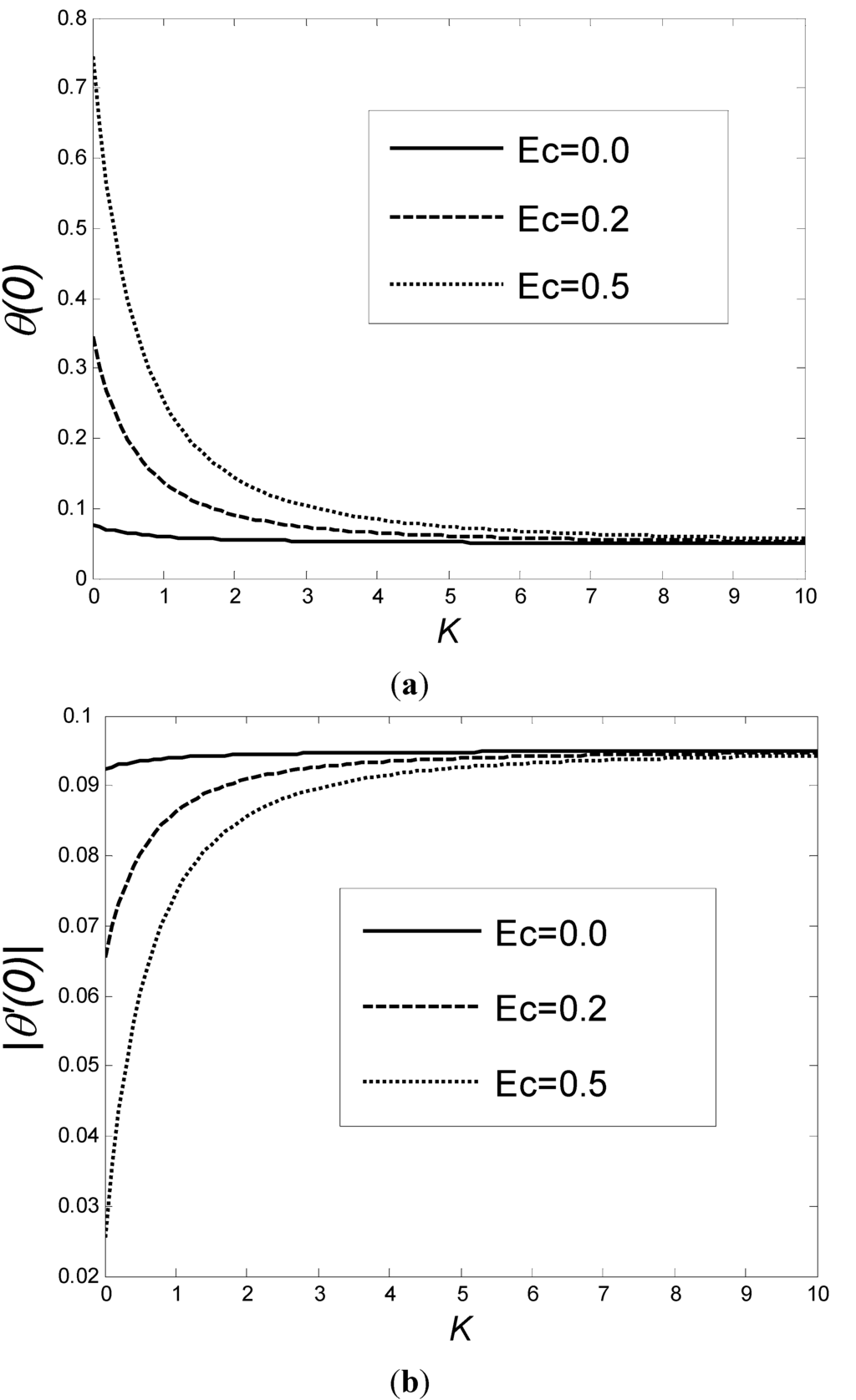
Figure 11.
(a) Variation of the θ(0) and (b) |θ'(0)| as a function of K for various values of Ec when a = 0.1, fw = 0.2, Pr = 7 and M = 0.5.
Figure 12(a),(b) depicts the effect of K, Pr and M on θ(0) and |θ'(0)|, respectively. It is evident that the increase in the magnetic parameter decreases the heat transfer rate, whereas it increases wall temperature. Figure 13(a),(b) show the combined effect of Ec, fw and a on θ(0) and |θ'(0)|, respectively, when K = 0.5, Pr = 7 and M = 0.3. In this context, it is important to mention that suction/injection refers to transpiration of the surface through which wall temperature can be reduced/increased, respectively, i.e., Eckert number increases fluid temperatures at the wall. Moreover, as suction increases the heat transfer rate, while injection has an opposite effect, suction/injection effect can be neglected at low Biot numbers where the boundary layer thermal resistance is high compared to the internal thermal resistance.
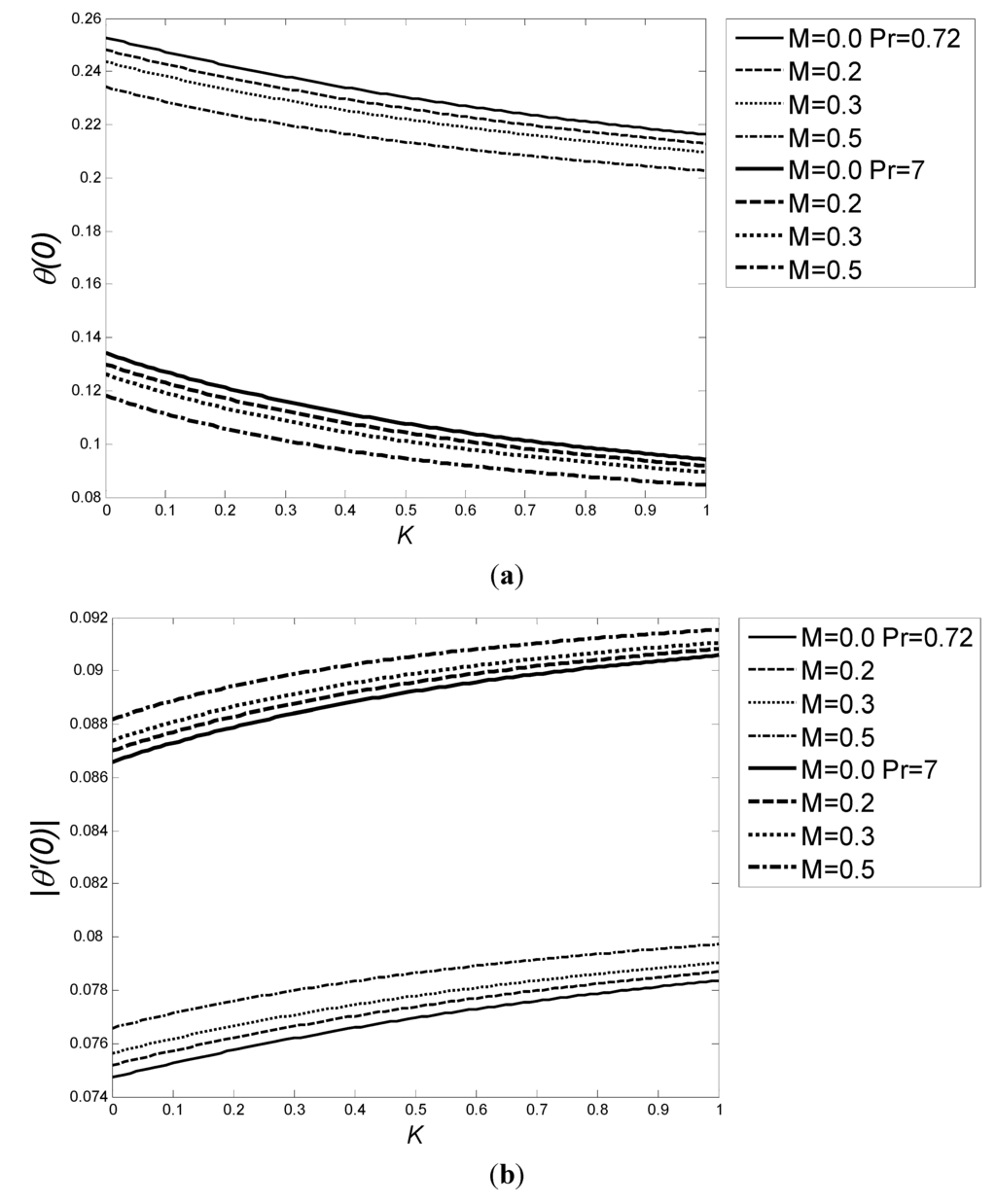
Figure 12.
(a) Variation of the θ(0) and (b) |θ'(0)| as a function of K for various values of M and Pr when a = 0.1, Ec = 0, and fw = 0.
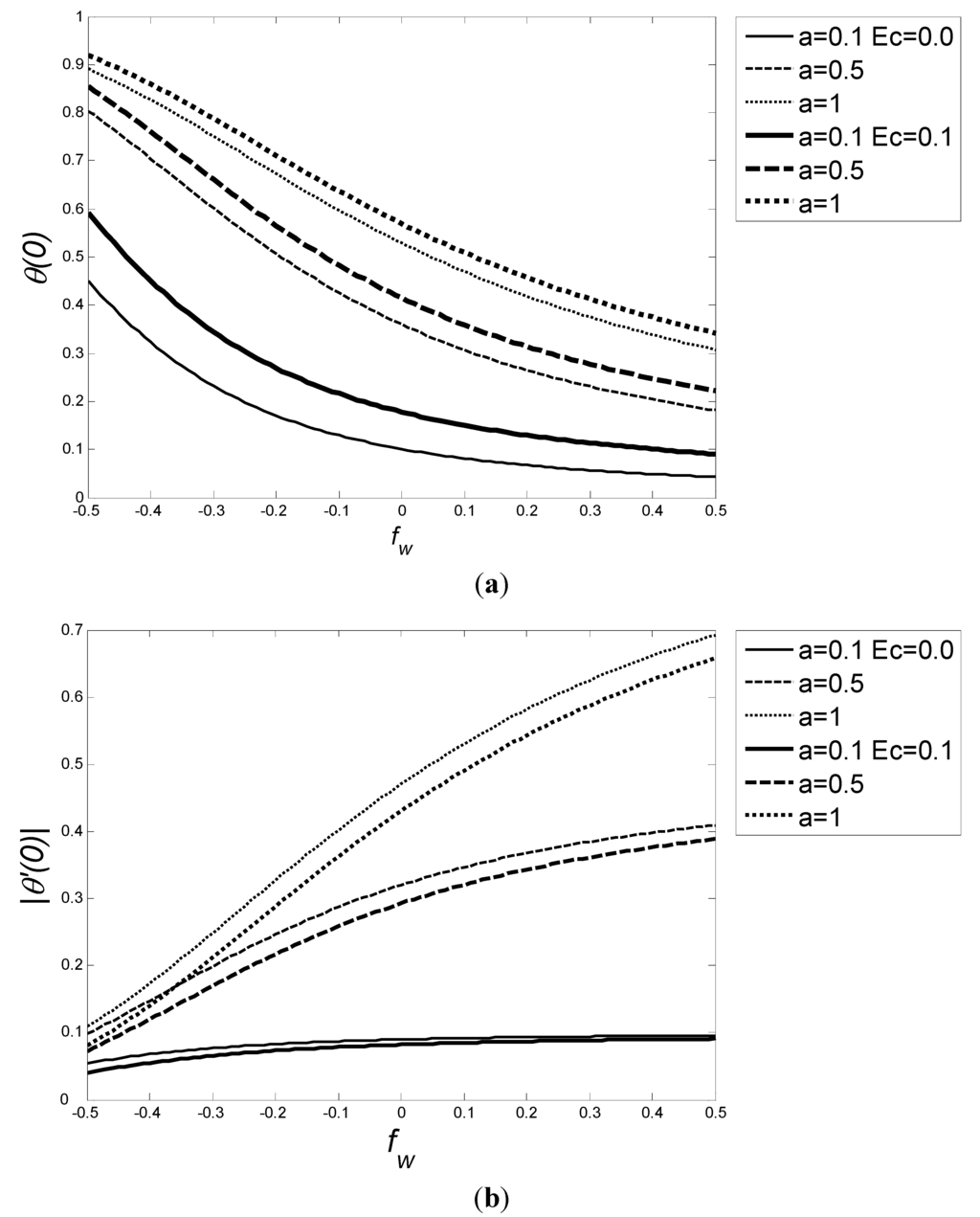
Figure 13.
(a) Variation of the θ(0) and (b) |θ'(0)| as a function of fw for various values of a and Ec when K = 0.5, Pr = 7 and M = 0.3.
4. Conclusions
Due to the unique mechanisms of fluid flow and heat transfer control in micro scale devices, this paper evaluates the slip MHD flow and heat transfer of an electrically conducting liquid over a permeable surface in the presence of the viscous dissipation effects under convective boundary conditions. A local similarity solution is applied at a fixed point along the surface. Based on the results presented above, the following specific conclusions have been reached:
- The skin friction coefficient increases with the rise of both suction and M, while it decreases with K and injection. Moreover, the effects of both M and fw on the wall shear stress are much more significant at low K.
- Changes in M and fw in the presence of slip boundary condition can efficiently manipulate the wall fluid velocity, which increases with the increase of M, K and suction.
- The wall temperature decreases with the increase in K, M, Pr and suction, whereas it increases with the increase of Ec, a, and injection.
- The heat transfer rate increases with the increase of Pr, a, K, M and suction, while it decreases with the increase of Ec and injection.
- In the slip flow regime, under low Biot number conditions, the permeability effects on heat transfer rate tend to be negligible.
Nomenclature:
| a | Biot number |
| B | magnetic induction [Wb m−2] |
| Cf | local skin-friction coefficient |
| cp | specific heat at constant pressure [J kg−1 K−1] |
| Ec | Eckert number |
| f | dimensionless function |
| hf | convective heat transfer coefficient [W m−2 K−1] |
| K | slip coefficient |
| kT | thermal conductivity [W m−1 K−1] |
| l | slip length [m] |
| M | magnetic parameter |
| P | Pressure [Pa] |
| Pr | Prandtl number |
| Rex | local Reynolds number |
| Tf | temperature of the hot fluid at the bottom of the plate [K] |
| Tw | temperature at the surface of the plate [K] |
| T | temperature of the fluid within the boundary layer [K] |
| T∞ | temperature of the ambient fluid [K] |
| u∞ | free stream velocity [m s−1] |
| u, v | the x-, y-components of velocity [m s−1] |
| x, y | distance along and normal to the plate [m] |
Greek
| α | thermal diffusivity [m2 s–1] |
| η | similarity variable |
| θ | dimensionless temperature |
| μ | dynamic viscosity [Pa s] |
| ν∞ | kinematic viscosity [m2 s−1] |
| ρ | fluid density [kg m–3] |
| σ | electrical conductivity of the fluid [S m–1] |
Subscripts
| s | slip condition |
| w | surface condition |
| ∞ | ambient condition |
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia for sponsoring this work. They wish also to express their very sincere gratitude to the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
References
- Nisar, A.; Afzulpurkar, N.; Mahaisavariya, B.; Tuantranont, A. MEMS-based micropumps in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 130, 917–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Jang, L.S. Recent patents on micromixing technology and micromixers. Recent Patents Mech. Eng. 2009, 2, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capretto, L.; Cheng, W.; Hill, M.; Zhang, X. Micromixing within microfluidic devices. Top. Curr. Chem. 2011, 304, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kleinstreuer, C.; Li, J.; Koo, J. Microfluidics of nano-drug delivery. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 5590–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avsec, J. Nanofluid and Ferrofluid Slip Flow in Rectangular and Circular Microchannels. In Proceedings of 7th EUROMECH Solid Mechanics Conference, Lisbon, Portugal, 7–11 September 2009.
- Eijkel, J.C.T.; Berg, A. Nanofluidics: What is it and what can we expect from it? Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2005, 1, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad-el-Hak, M. The MEMS Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gad-el-Hak, M. Mems Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gad-el-Hak, M. The fluid mechanics of microdevices-The Freeman scholar lecture. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 1999, 121, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, L.; Barrat, J.L. Flow boundary conditions from nano-to micro-scales. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, K. Effects of the shape of stenosis on the resistance to blood flow through an artery. Bull. Math. Biol. 1985, 47, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponalagusamy, R.; Tamil Selvi, R. A study on two-layered model (casson-newtonian) for blood flow through an arterial stenosis: Axially variable slip velocity at the wall. J. Frankl. Inst. 2011, 348, 2308–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rij, J.; Ameel, T.; Harman, T. The effect of viscous dissipation and rarefaction on rectangular microchannel convective heat transfer. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2009, 48, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, J.; Kleinstreuer, C. Viscous dissipation effects in microtubes and microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2004, 47, 3159–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T. Further study on a moving-wall boundary-layer problem with mass transfer. Acta Mech. 2003, 163, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Lee, C.F. A moving-wall boundary layer flow of a slightly rarefied gas free stream over a moving flat plate. Appl. Math. Lett. 2005, 18, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.J.; Boyd, I.D. Momentum and heat transfer in a laminar boundary layer with slip flow. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2006, 20, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.H.; Abdullah, S.; Hashim, I.; Zaharim, A.; Sopian, K. Friction and Heat Transfer in Slip Flow Boundary Layer at Constant Heat Flux Boundary Conditions. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Mathematical Methods, Computational Techniques and Intelligent Systems, Corfu, Greece, 26–28 October 2008; pp. 207–212.
- Yazdi, M.H.; Abdullah, S.; Hashim, I.; Nopiah, Z. M.; Zaharim, A.; Sopian, K. Convective Heat Transfer of Slip Liquid Flow Past Horizontal Surface within the Porous Media at Constant Heat Flux Boundary Conditions. In Proceedings of the American Conference on Applied Mathematics: Recent Advances in Applied Mathematics, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, 27–29 January 2009; pp. 527–533.
- Yazdi, M.H.; Abdullah, S.; Hashim, I.; Sopian, K. Reducing Exergy Losses of Liquid Fluid Using Embedded Open Parallel Microchannels within the Surface. In Proceedings of the 13th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Mathematics, Puerto De La Cruz, Spain, 15–17 December 2008; pp. 345–350.
- Yazdi, M.H.; Abdullah, S.; Hashim, I.; Sopian, K.; Zaharim, A. Entropy generation analysis of liquid fluid past embedded open parallel microchannels within the surface. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 28, 462–470. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, T.; Javed, T.; Abbas, Z. Slip flow and heat transfer of a second grade fluid past a stretching sheet through a porous space. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 4528–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Qasim, M.; Mesloub, S. MHD flow and heat transfer over permeable stretching sheet with slip conditions. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2011, 66, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Hayat, T.; Hendi, A. Effects of slip conditions on stretching flow with ohmic dissipation and thermal radiation. Heat Transf.—Asian Res. 2011, 40, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Yao, S.; Zhang, J.; Aziz, A. Viscous flow over a shrinking sheet with a second order slip flow model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hayat, T.; Oberlack, M. Slip effects and heat transfer analysis in a viscous fluid over an oscillatory stretching surface. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2009, 59, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Zhang, J.; Yao, S. Slip MHD viscous flow over a stretching sheet—An exact solution. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 14, 3731–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.H.; Abdullah, S.; Hashim, I.; Sopian, K. Slip MHD liquid flow and heat transfer over non-linear permeable stretching surface with chemical reaction. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 3214–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.H.; Abdullah, S.; Hashim, I.; Sopian, K. Slip MHD Flow over Permeable Stretching Surface with Chemical Reaction. In Proceedings of 17th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 5–9 December 2010.
- Aziz, A. A similarity solution for laminar thermal boundary layer over a flat plate with a convective surface boundary condition. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 14, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A. Similarity solutions for flow and heat transfer over a permeable surface with convective boundary condition. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 217, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Fang, T.; Zhong, Y. Heat transfer of a generalized stretching/shrinking wall problem with convective boundary conditions. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2011, 16, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. Locally similar solutions for hydromagnetic and thermal slip flow boundary layers over a flat plate with variable fluid properties and convective surface boundary condition. Meccanica 2011, 46, 1127–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, V.J.; Center, N.A.R. On Flow of Electrically Conducting Fluids over a Flat Plate in the Presence of a Transverse Magnetic Field; National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1957; NACA TN 3971, Report no. 1358. [Google Scholar]
- Hang, X. Erratum to “An explicit analytic solution for convective heat transfer in an electrically conducting fluid at a stretching surface with uniform free stream”. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2005, 43, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, N.J.; Hendy, S.C. Effective slip length of nanoscale mixed-slip surfaces. ANZIAM J. 2009, 50, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).