Proportional-Resonant Control of Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Wind Turbines for Low-Voltage Ride-Through Enhancement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
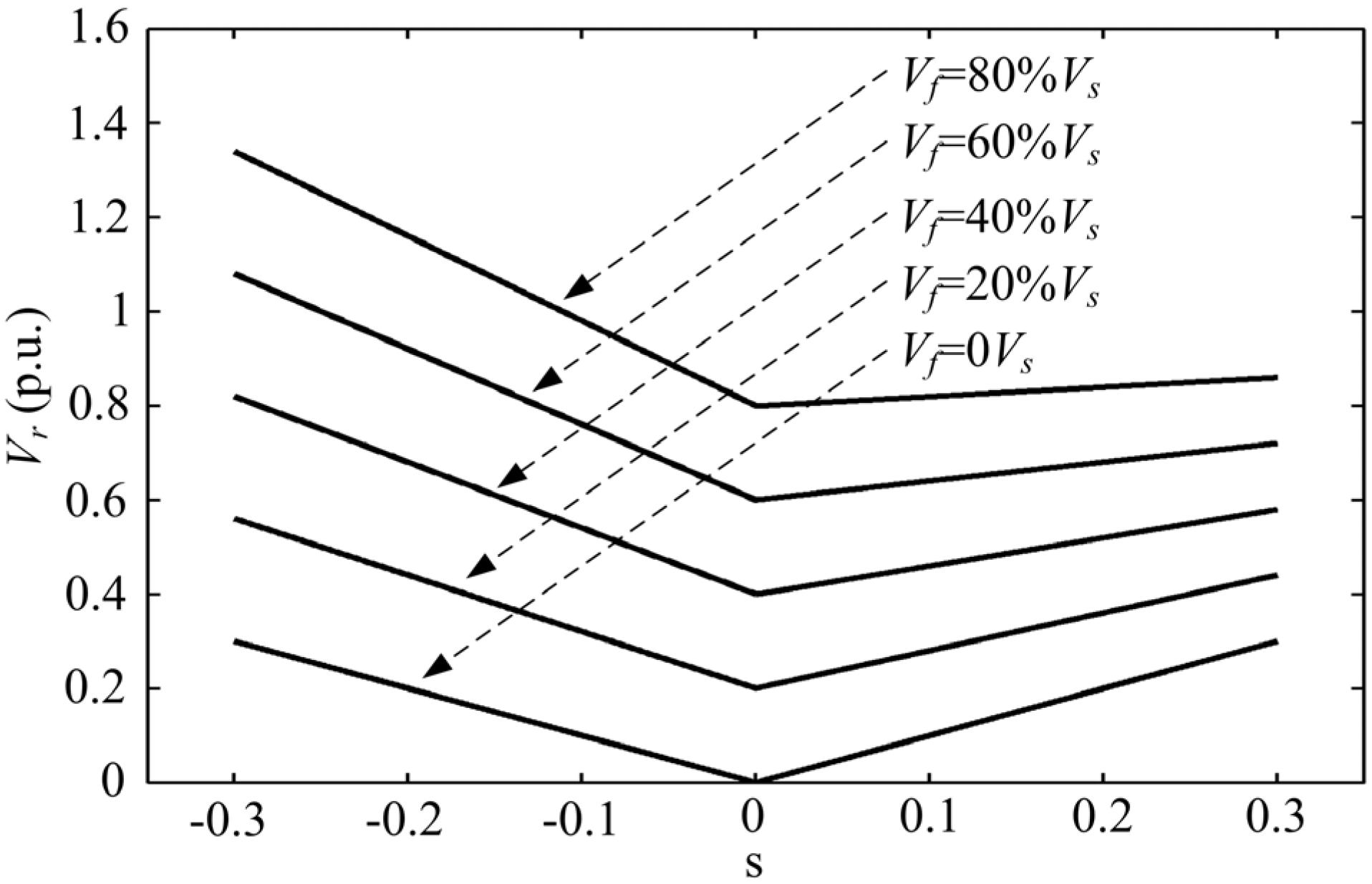
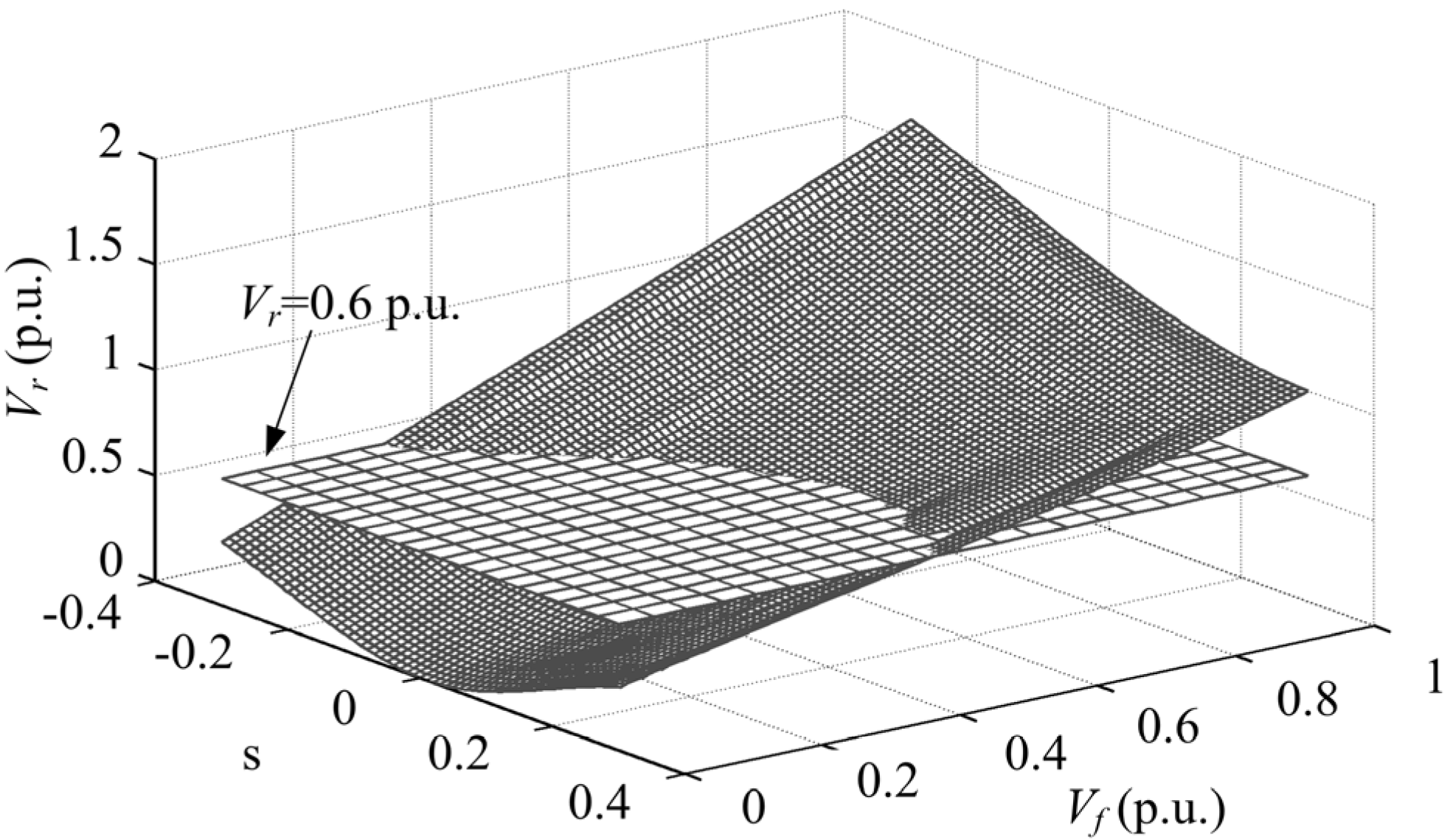
2. DFIG System Behavior during Grid Fault
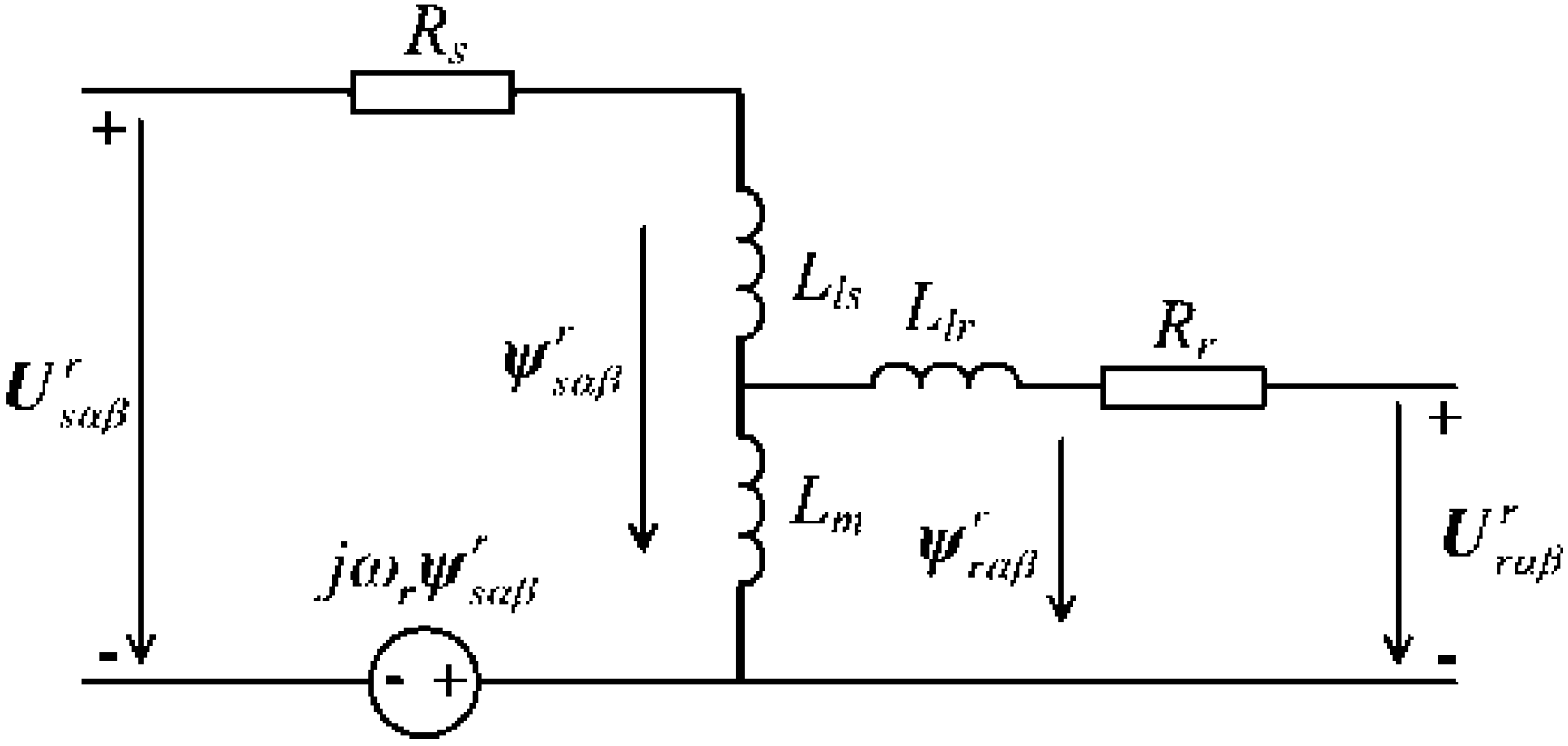


3. System Control
3.1. Proposed Control System Design


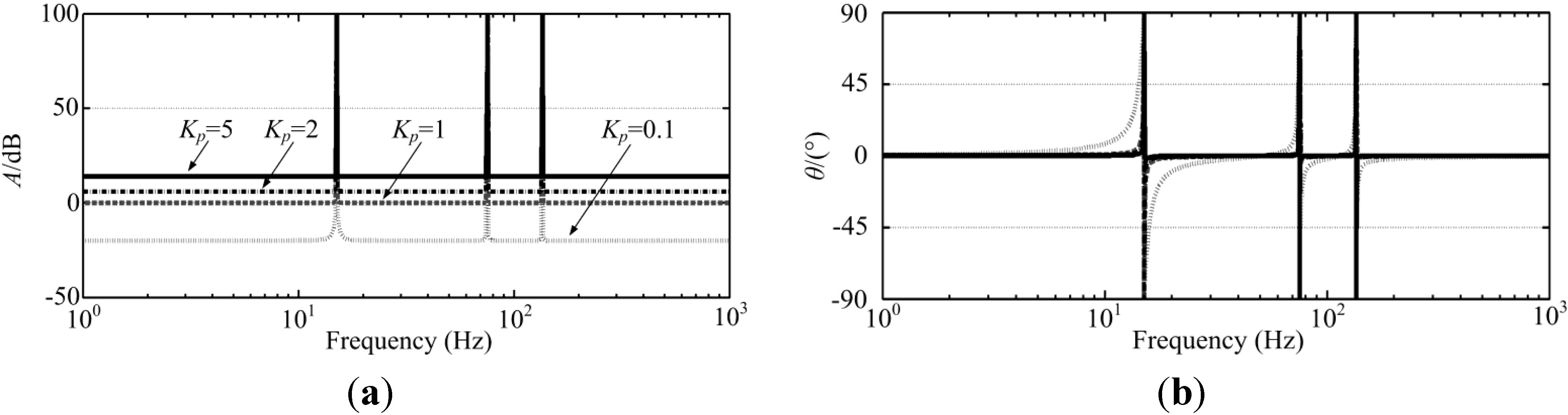
3.2. Simplification of the Auxiliary Controller
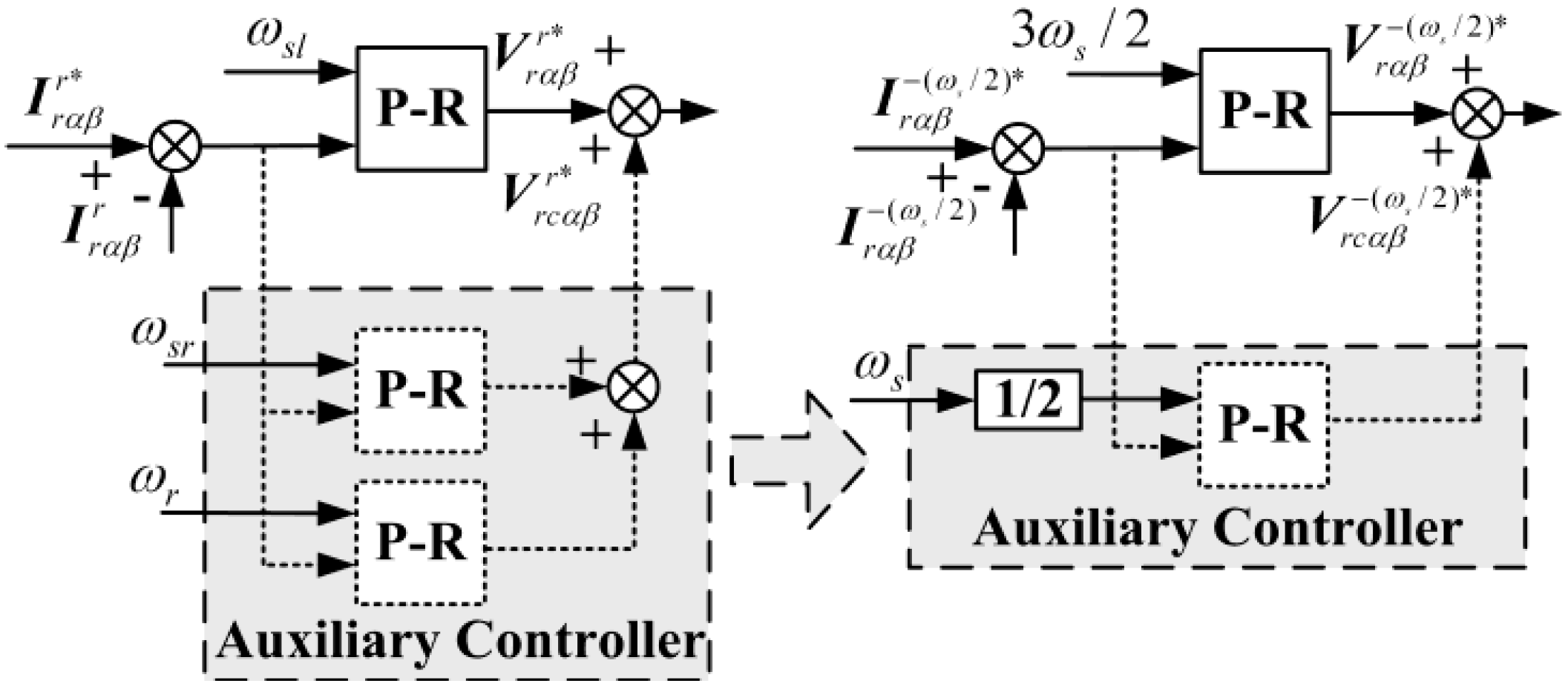
4. Simulation Results
| DFIG Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated generator power | 1.5 MW |
| Rated generator voltage | 0.575 kV |
| Frequency | 60 Hz |
| Stator resistance | 0.0014 Ω |
| Stator leakage inductance | 8.998 × 10−5 H |
| Rotor resistance | 9.9187 × 10−4 Ω |
| Rotor leakage inductance | 8.2088 × 10−5 H |
| Magnetizing inductance | 1.526 × 10−3 H |
| Pole pairs | 3 |
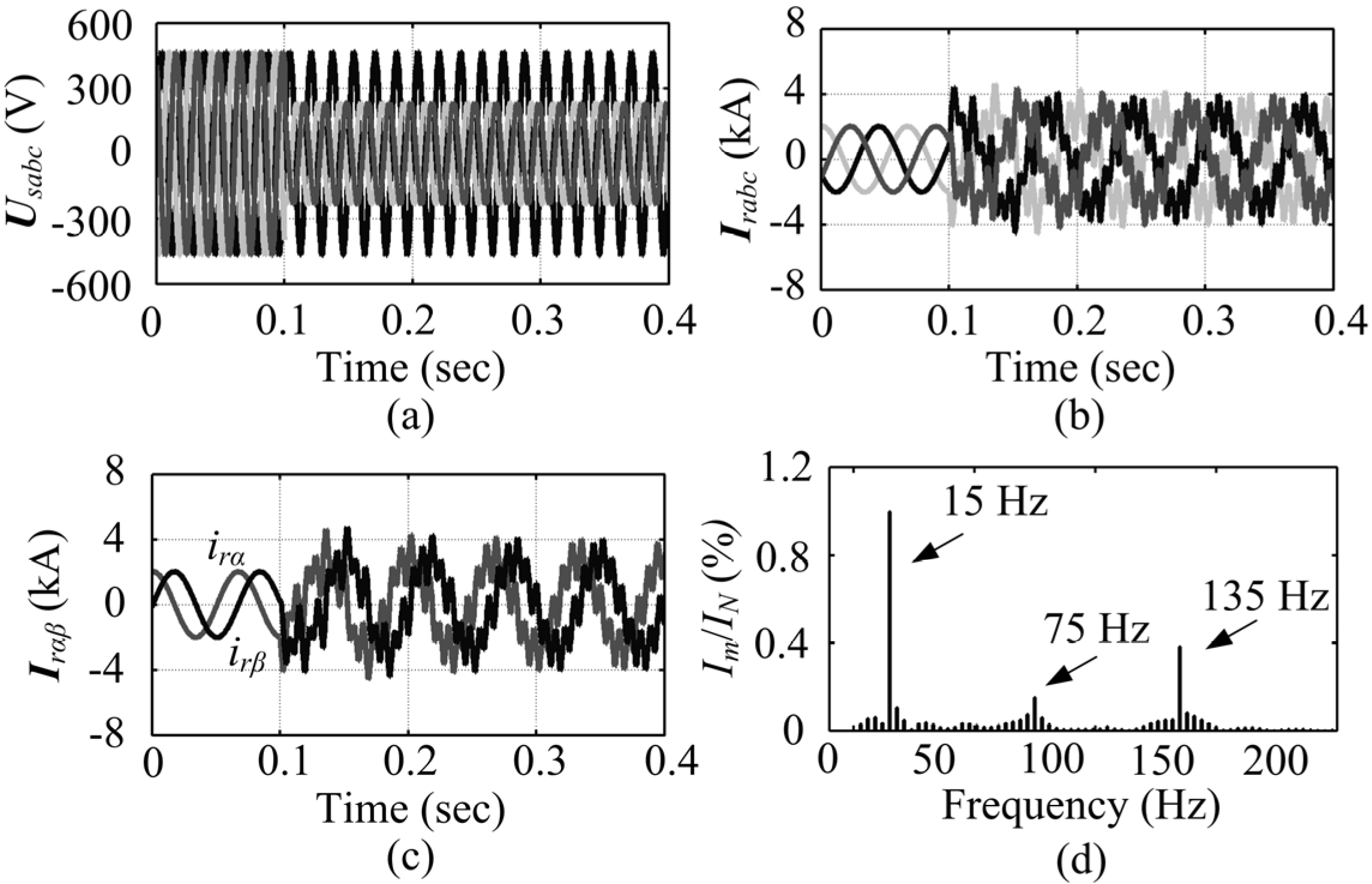
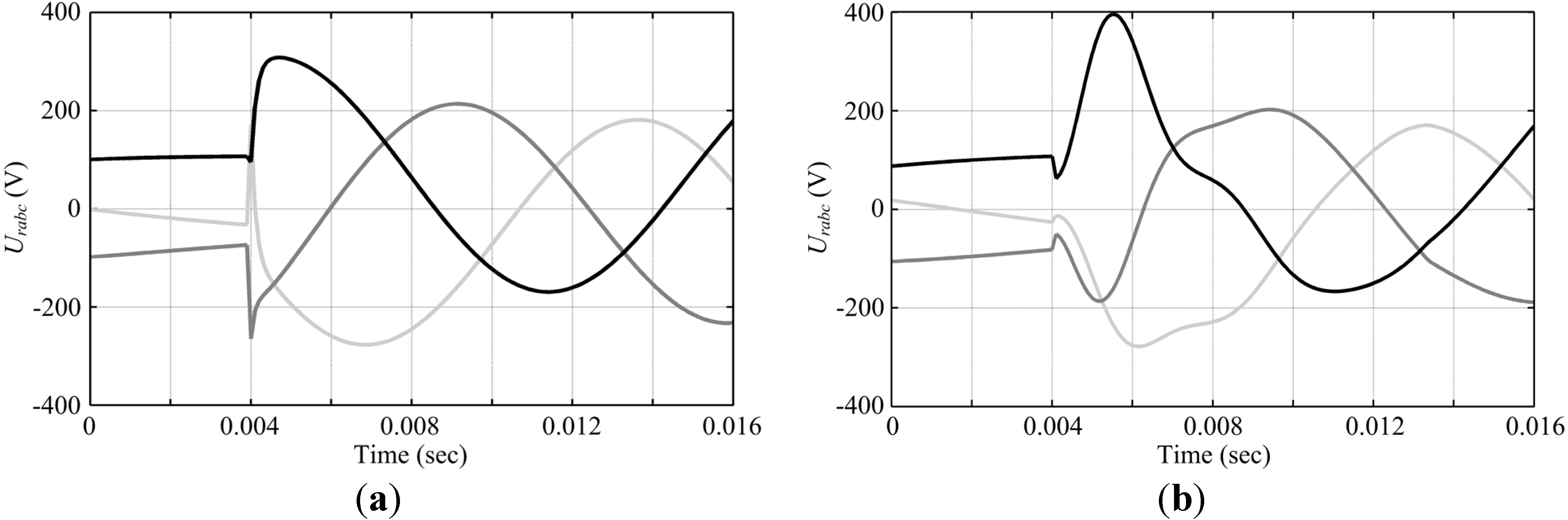
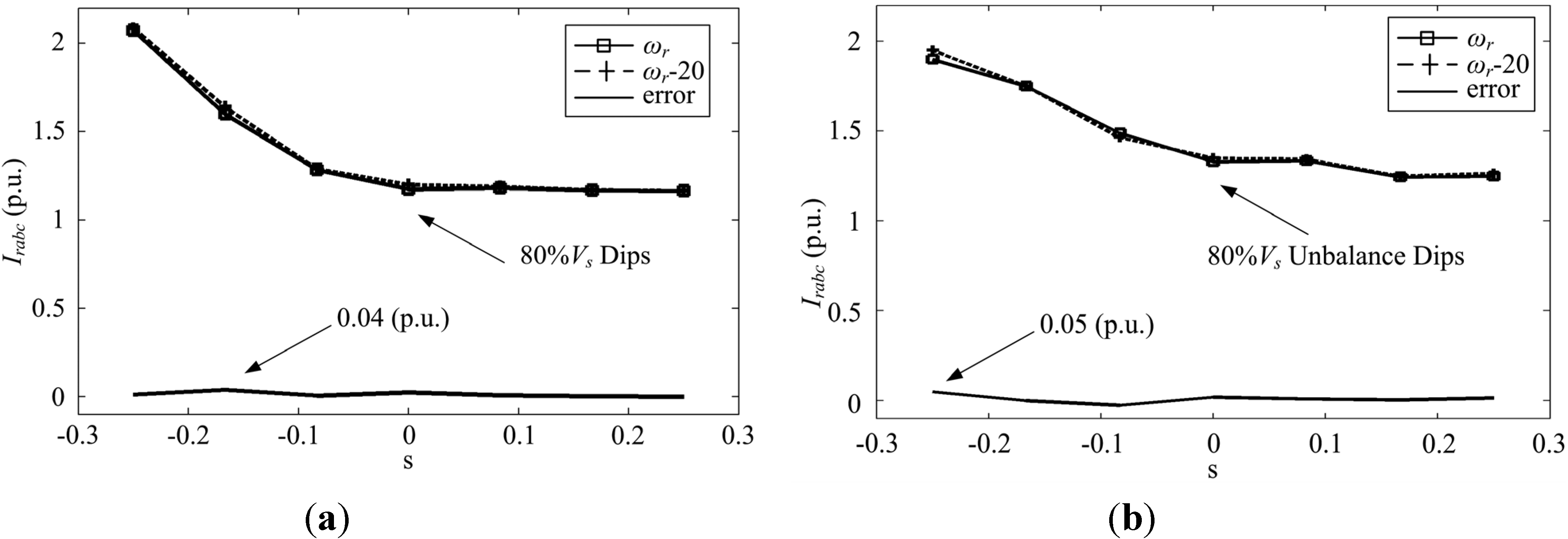
4.1. Three-Phase Fault
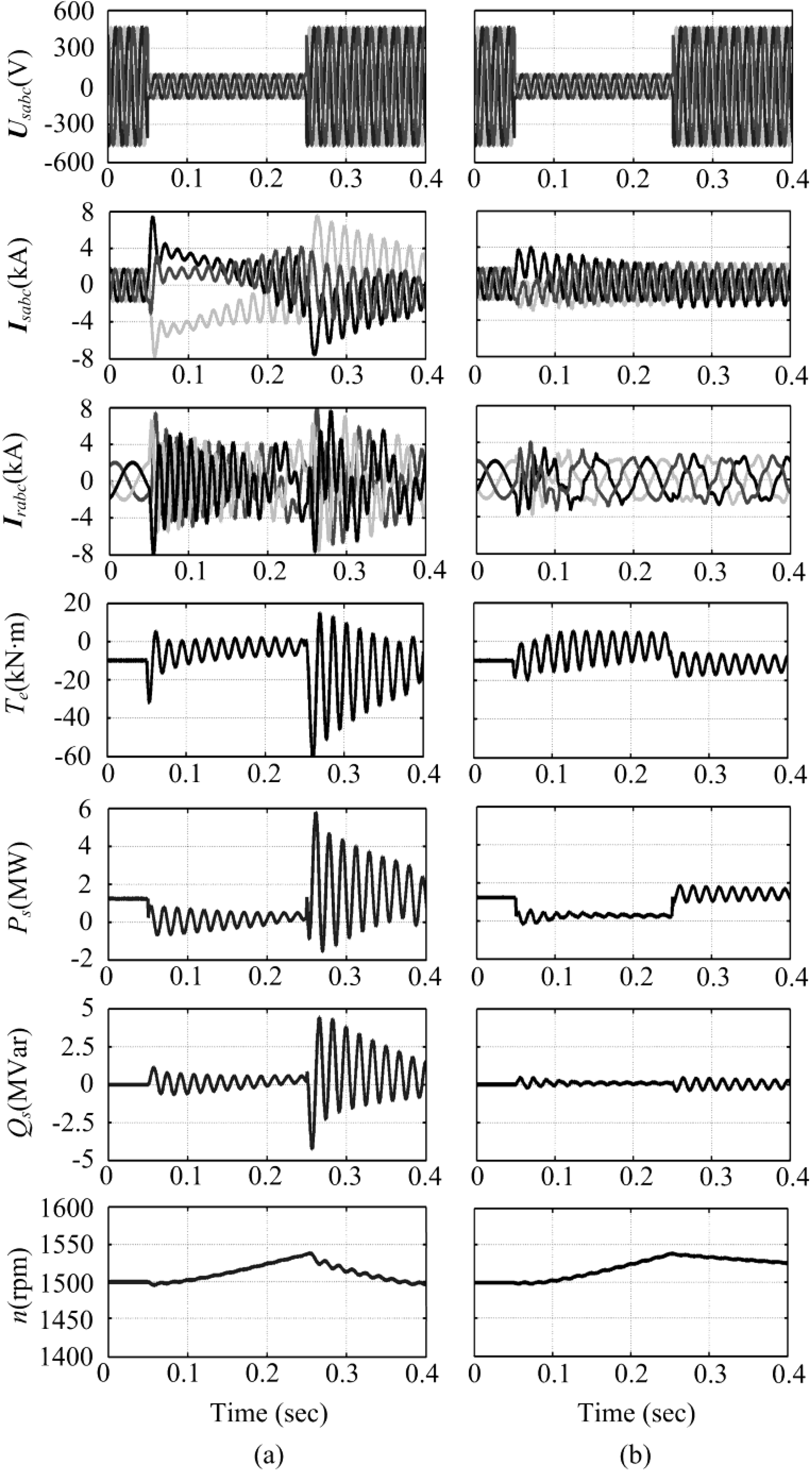
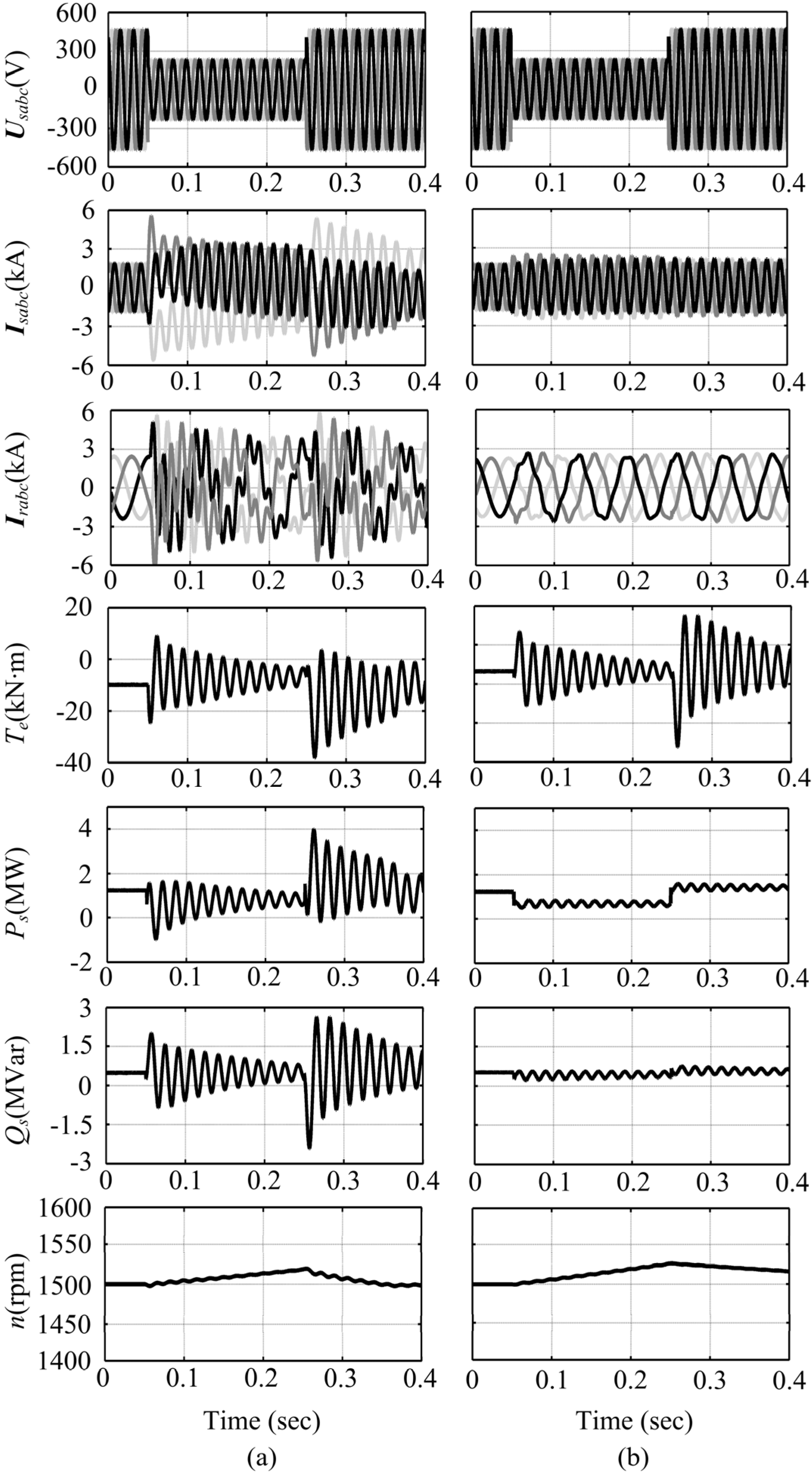
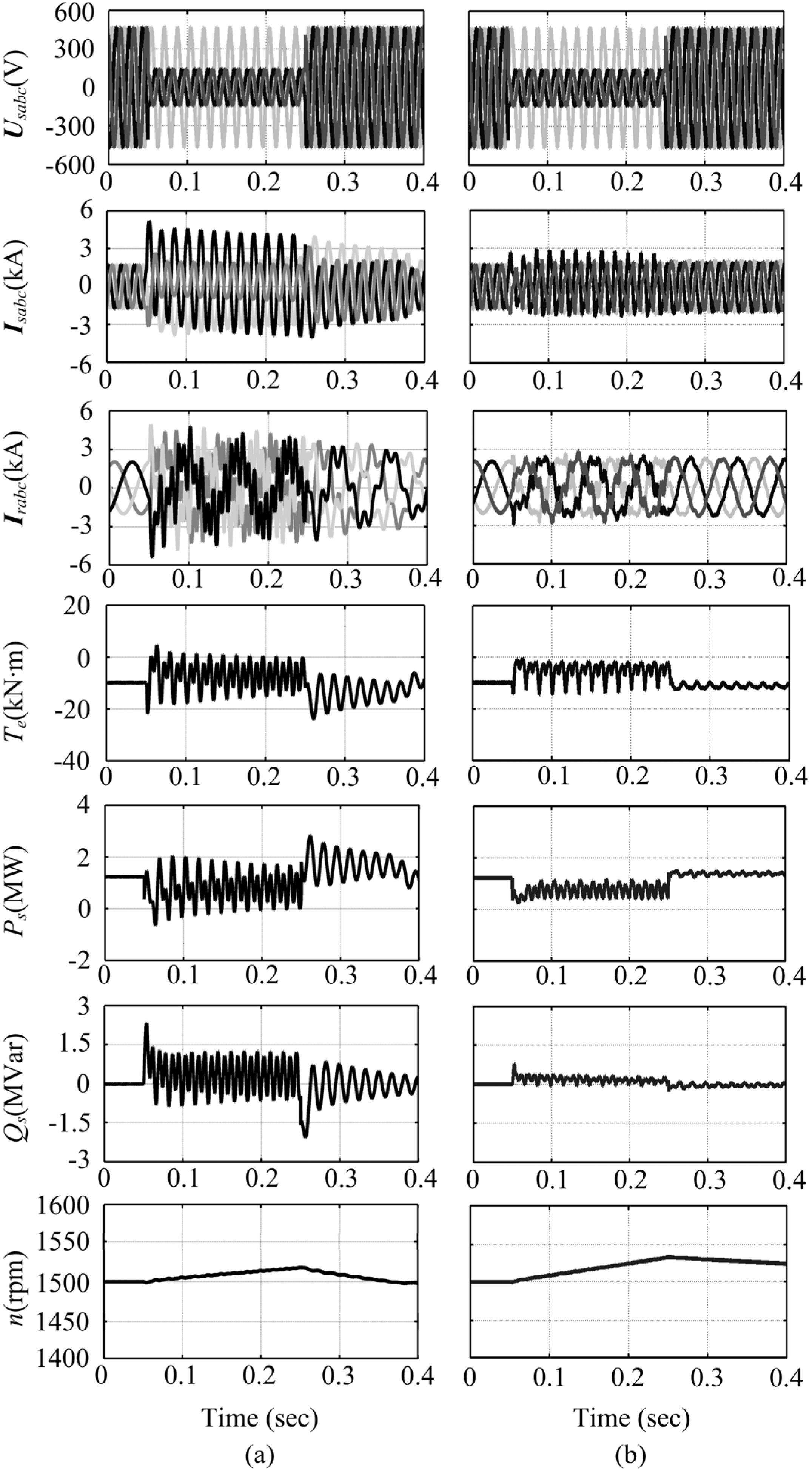
4.2. Phase-Phase-Ground Fault
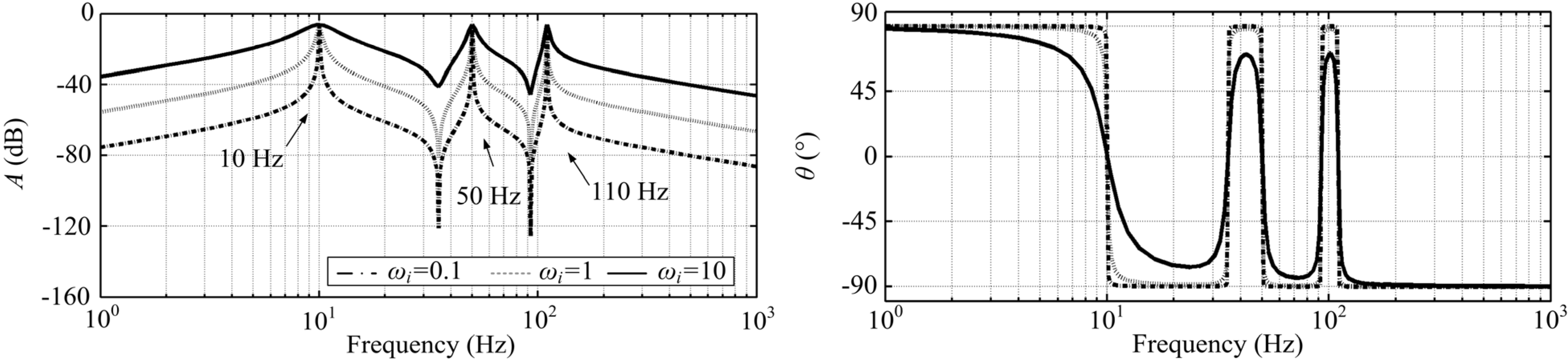
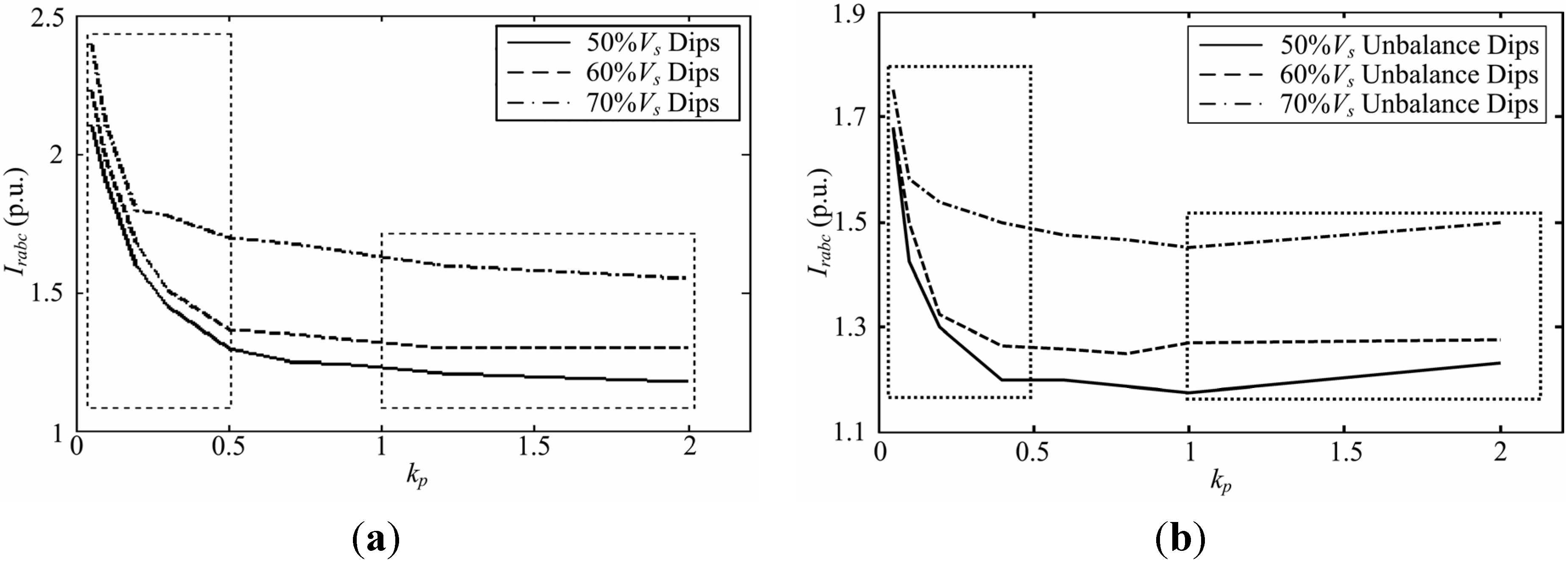
4.3. Control System Analysis
5. Conclusions
Nomenclature
| Us, Ur | Stator and rotor voltage vectors. |
| Is, Ir | Stator and rotor current vectors. |
| ψs, ψr | Stator and rotor flux linkage vectors. |
| ωs, ωr | Stator and rotor angular frequencies. |
| Ls, Lr | Stator and rotor self inductances. |
| Lls, Llr | Stator and rotor leakage inductances. |
| Lm | Mutual inductance. |
| Rs, Rr | Stator and rotor resistances |
Subscripts
| α, β | Stationary α–β axis. |
| s, r | Stator, rotor. |
| +, DC,− | Positive, DC and negative components. |
| 0, 1, 2 | Positive, DC and negative components in rotor αr βr reference frame. |
Superscripts
| r | Rotor αr βr reference frames. |
| * | Reference value for controller. |
Acknowledgments
References
- Yamamoto, M.; Motoyoshi, O. Active and reactive power control for doubly-fed wound rotor induction generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1991, 6, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.L.; Song, Z.F. Wind energy in China: current scenario and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, L.F.; Dinavahi, V. Real-time simulation of a wind energy system based on the doubly-fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 24, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slootweg, J.G.; de Haan, S.W.H.; Polinder, H.; Kling, W.L. General model for representing variable speed wind turbines in power system dynamics simulations. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, H.; Sato, H. Control and performance of a doubly-fed induction machine intended for a flywheel energy storage system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2002, 17, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yao, L.; Sasse, C. Grid integration of large DFIG-based wind farms using VSC transmission. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, F.M.; Anaya-Lara, O.; Jenkins, N.; Strbac, G. Control of DFIG-based wind generation for power network support. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.L.; Gu, X.; Shi, T.N.; Yan, Y. Neutral-Point potential balancing of three-level inverters in direct-driven wind energy conversion system. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2011, 26, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullane, A.; Lightbody, G.; Yacamini, R. Wind-turbine fault ridethrough enhancement. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Ran, L.; Bumby, J. Unbalanced-grid-fault ride-through control for a wind turbine inverter. IEEE Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Bauer, P.; Ferreira, J.A.; Pierik, J. Operation of grid-connected DFIG under unbalanced grid voltage condition. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 24, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.F.; Xia, C.L.; Shi, T.N. Assessing transient response of DFIG based wind turbines during voltage dips regarding main flux saturation and rotor deep-bar effect. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 3283–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causebrook, A.; Atkinson, D.J.; Jack, A.G. Fault ride-through of large wind farms using series dynamic braking resistors. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morren, J.; de Haan, S.W.H. Ride-through of wind turbines with doubly-fed induction generator during a voltage dip. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, A.; Harnefors, L.; Thiringer, T. Evaluation of current control methods for wind turbines using doubly-fed induction machines. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morren, J.; de Haan, S.W.H. Short-circuit current of wind turbines with doubly fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekken, T.A.; Mohan, N. Control of a doubly fed induction wind generator under unbalanced grid voltage conditions. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y. Dynamic modeling and control of DFIG based wind turbines under unbalanced network conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Enhanced control and operation of DFIG-based wind farms during network unbalance. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.B.; Xu, L. Improved control of DFIG systems during network unbalance using PI–R current regulators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Ran, L.; Tavner, P.J.; Yang, S. Control of a doubly fed induction generator in a wind turbine during grid fault ride-through. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.B.; He, Y.K.; Xu, L. Improved rotor current control of wind turbine driven doubly-fed induction generators during network voltage unbalance. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2010, 80, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Qiao, W.; Harley, R.G. Feed-forward transient current control for low-voltage ride-through enhancement of DFIG wind turbines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorescu, R.; Blaabjerg, F.; Liserre, M.; Loh, P.C. Proportional–resonant controllers and filters for grid-connected voltage-source converters. IEEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2006, 153, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmood, D.N.; Holmes, D.G. Stationary frame current regulation of PWM inverters with zero steady-state error. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2003, 18, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, C.; Song, Z.F. Proportional-resonant control for dual PWM converter in doubly fed wind generation system. Proc. CSEE 2009, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Timbus, A.; Liserre, M.; Teodorescu, R.; Rodriguez, P.; Blaabjerg, F. Evaluation of current controllers for distributed power generation systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Blaabjerg, F.; Chen, W.J.; Xu, D.H. Stator current harmonic control with resonant controller for doubly fed induction generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3207–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaeinedjad, R.; Moallem, M.; Moschopoulos, G. Simulation of a wind turbine with doubly fed induction generator by FAST and Simulink. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Wang, M.; Song, Z.-F.; Xia, C.-L. Proportional-Resonant Control of Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Wind Turbines for Low-Voltage Ride-Through Enhancement. Energies 2012, 5, 4758-4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5114758
Yan Y, Wang M, Song Z-F, Xia C-L. Proportional-Resonant Control of Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Wind Turbines for Low-Voltage Ride-Through Enhancement. Energies. 2012; 5(11):4758-4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5114758
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yan, Meng Wang, Zhan-Feng Song, and Chang-Liang Xia. 2012. "Proportional-Resonant Control of Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Wind Turbines for Low-Voltage Ride-Through Enhancement" Energies 5, no. 11: 4758-4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5114758
APA StyleYan, Y., Wang, M., Song, Z.-F., & Xia, C.-L. (2012). Proportional-Resonant Control of Doubly-Fed Induction Generator Wind Turbines for Low-Voltage Ride-Through Enhancement. Energies, 5(11), 4758-4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/en5114758





