Optimizing the Production of Biodiesel Using Lipase Entrapped in Biomimetic Silica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
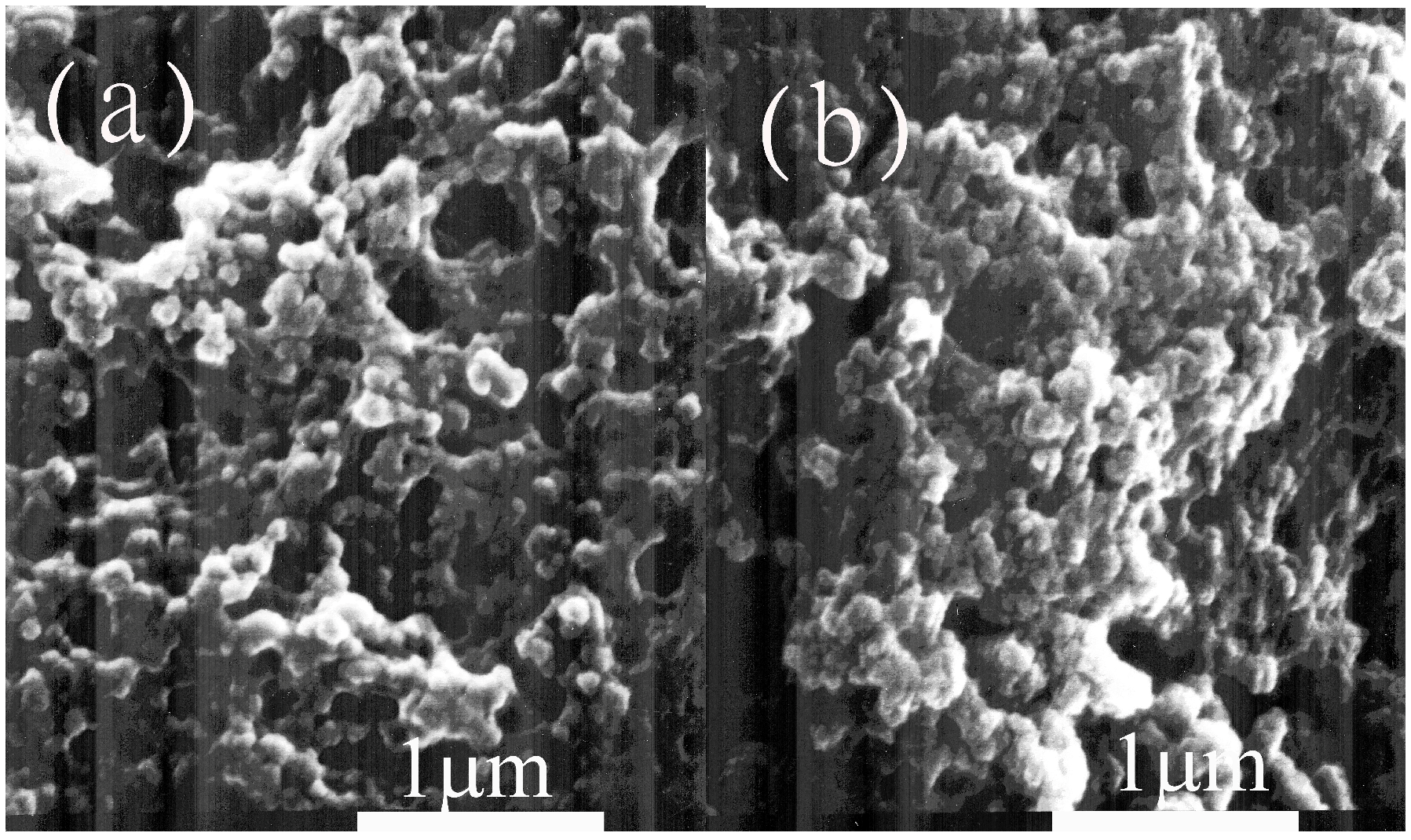
2.1. Characteristics of Entrapped Lipase
2.2. Model Fitting and Analysis of Variance
| Treatment No. a | Variable b | Conversion (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Molar ratio (methanol/oil) | n-Hexane (%, w/w of oil) | Waste cooking oil | Soybean oil | |
| 1 | 50 (1) | 5 (1) | 50 (0) | 69.2 | 59.1 |
| 2 | 50 (1) | 3 (−1) | 50 (0) | 60.7 | 52.6 |
| 3 | 35 (−1) | 5 (1) | 50 (0) | 61.7 | 54.6 |
| 4 | 35 (−1) | 3 (−1) | 50 (0) | 45.0 | 48.8 |
| 5 | 50 (1) | 4 (0) | 75 (1) | 72.5 | 56.3 |
| 6 | 50 (1) | 4 (0) | 25 (−1) | 70.9 | 56.3 |
| 7 | 35 (−1) | 4 (0) | 75 (1) | 66.1 | 50.0 |
| 8 | 35 (−1) | 4 (0) | 25 (−1) | 56.0 | 52.6 |
| 9 | 42.5 (0) | 5 (1) | 75 (1) | 74.0 | 66.8 |
| 10 | 42.5 (0) | 5 (1) | 25 (−1) | 73.7 | 68.1 |
| 11 | 42.5 (0) | 3 (−1) | 75 (1) | 70.9 | 60.6 |
| 12 | 42.5 (0) | 3 (−1) | 25 (−1) | 65.9 | 55.1 |
| 13 | 42.5 (0) | 4 (0) | 50 (0) | 72.2 | 62.1 |
| 14 | 42.5 (0) | 4 (0) | 50 (0) | 76.3 | 68.1 |
| 15 | 42.5 (0) | 4 (0) | 50 (0) | 72.5 | 68.0 |
| 16 | 42.5 (0) | 4 (0) | 50 (0) | 75.8 | 64.0 |
| 17 | 42.5 (0) | 4 (0) | 50 (0) | 74.1 | 65.9 |
| Source | Sum of squares | Degree of freedom | Mean square | F-value | Prob > F a,b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1039.99 | 9 | 115.55 | 18.13 | 0.0005 |
| Temperature (A) | 246.89 | 1 | 246.89 | 38.74 | 0.0004 |
| Substrate molar ratio (B) | 161.90 | 1 | 161.90 | 25.41 | 0.0015 |
| n-Hexane (C) | 36.04 | 1 | 36.04 | 5.66 | 0.0490 |
| A2 | 413.42 | 1 | 413.42 | 64.87 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 110.64 | 1 | 110.64 | 17.36 | 0.0042 |
| C2 | 18.46 | 1 | 18.46 | 2.90 | 0.1326 |
| AB | 16.71 | 1 | 16.71 | 2.62 | 0.1494 |
| AC | 18.16 | 1 | 18.16 | 2.85 | 0.1353 |
| BC | 5.49 | 1 | 5.49 | 0.86 | 0.3841 |
| Residual | 44.61 | 7 | 6.37 | – | – |
| Lack of fit | 30.96 | 3 | 10.32 | 3.02 | 0.1565 |
| Pure error | 13.65 | 4 | 3.41 | – | – |
| Cor total | 1084.60 | 16 | – | – | – |
| Source | Sum of squares | Degrees of freedom | Mean square | F-value | Prob > F a,b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 668.11 | 9 | 74.23 | 13.28 | 0.0013 |
| Temperature (A) | 42.24 | 1 | 42.24 | 7.56 | 0.0286 |
| Substrate molar ratio (B) | 123.32 | 1 | 123.32 | 22.06 | 0.0022 |
| n-Hexane (C) | 0.32 | 1 | 0.32 | 0.06 | 0.8184 |
| A2 | 451.64 | 1 | 451.64 | 80.79 | <0.0001 |
| B2 | 9.50 | 1 | 9.50 | 1.70 | 0.2335 |
| C2 | 9.25 | 1 | 9.25 | 1.65 | 0.2393 |
| AB | 0.11 | 1 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.8907 |
| AC | 1.72 | 1 | 1.72 | 0.31 | 0.5960 |
| BC | 11.66 | 1 | 11.66 | 2.09 | 0.1920 |
| Residual | 39.13 | 7 | 5.59 | – | – |
| Lack of fit | 11.80 | 3 | 3.93 | 0.58 | 0.6610 |
| Pure error | 27.33 | 4 | 6.83 | – | – |
| Cor total | 707.24 | 16 | – | – | – |
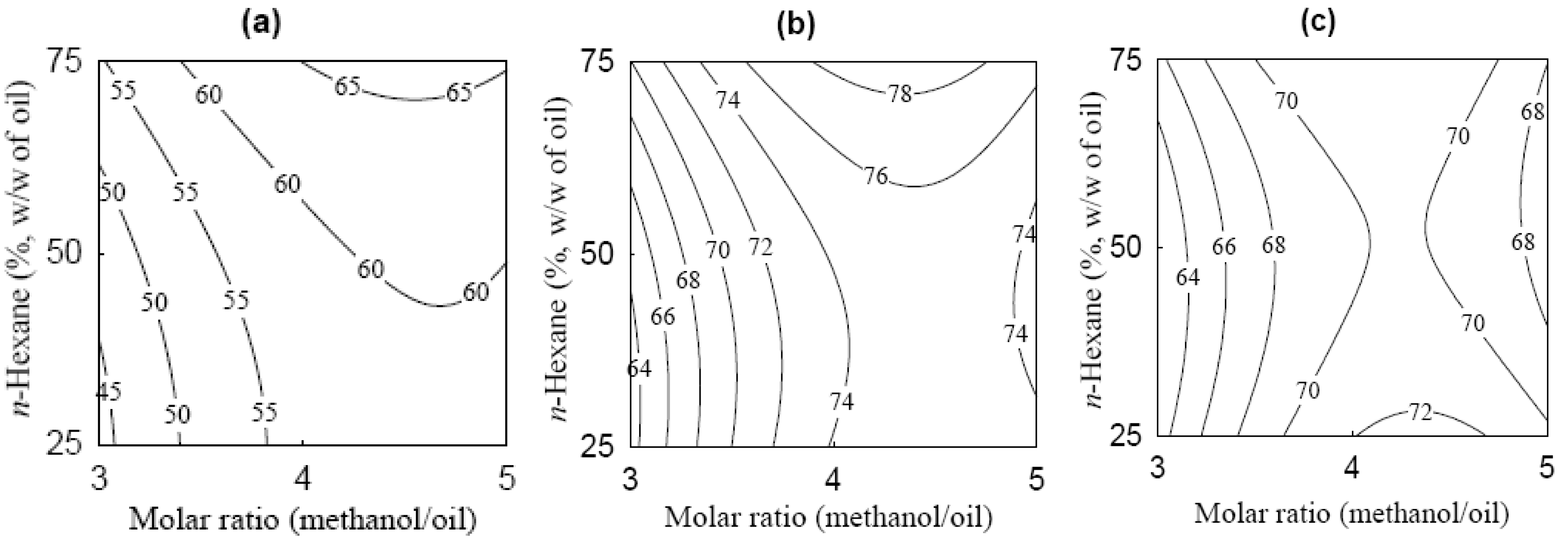
2.3. Effects of Variables and Their Optimization

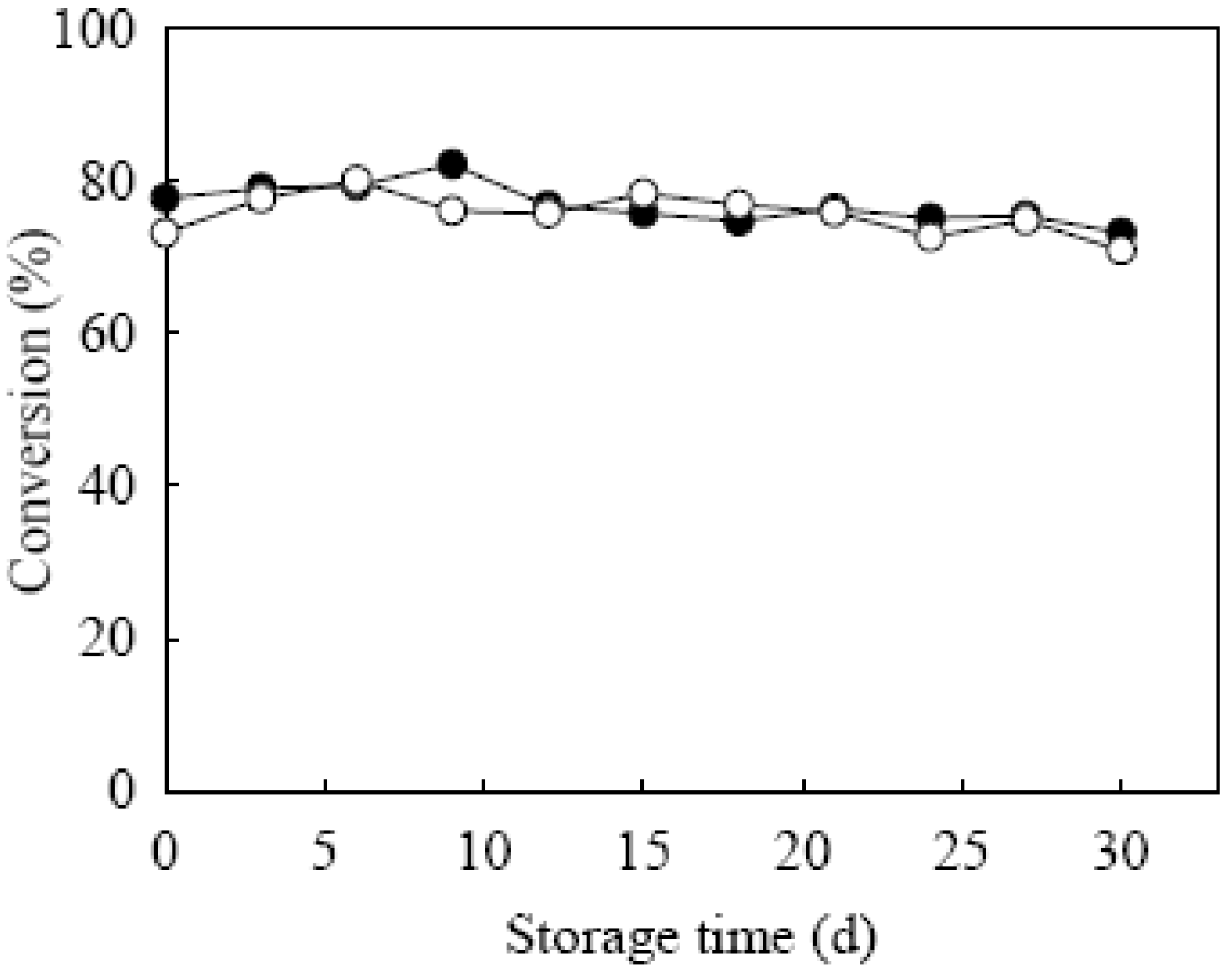
2.4. Storage Stability and Reusability of Entrapped Lipase
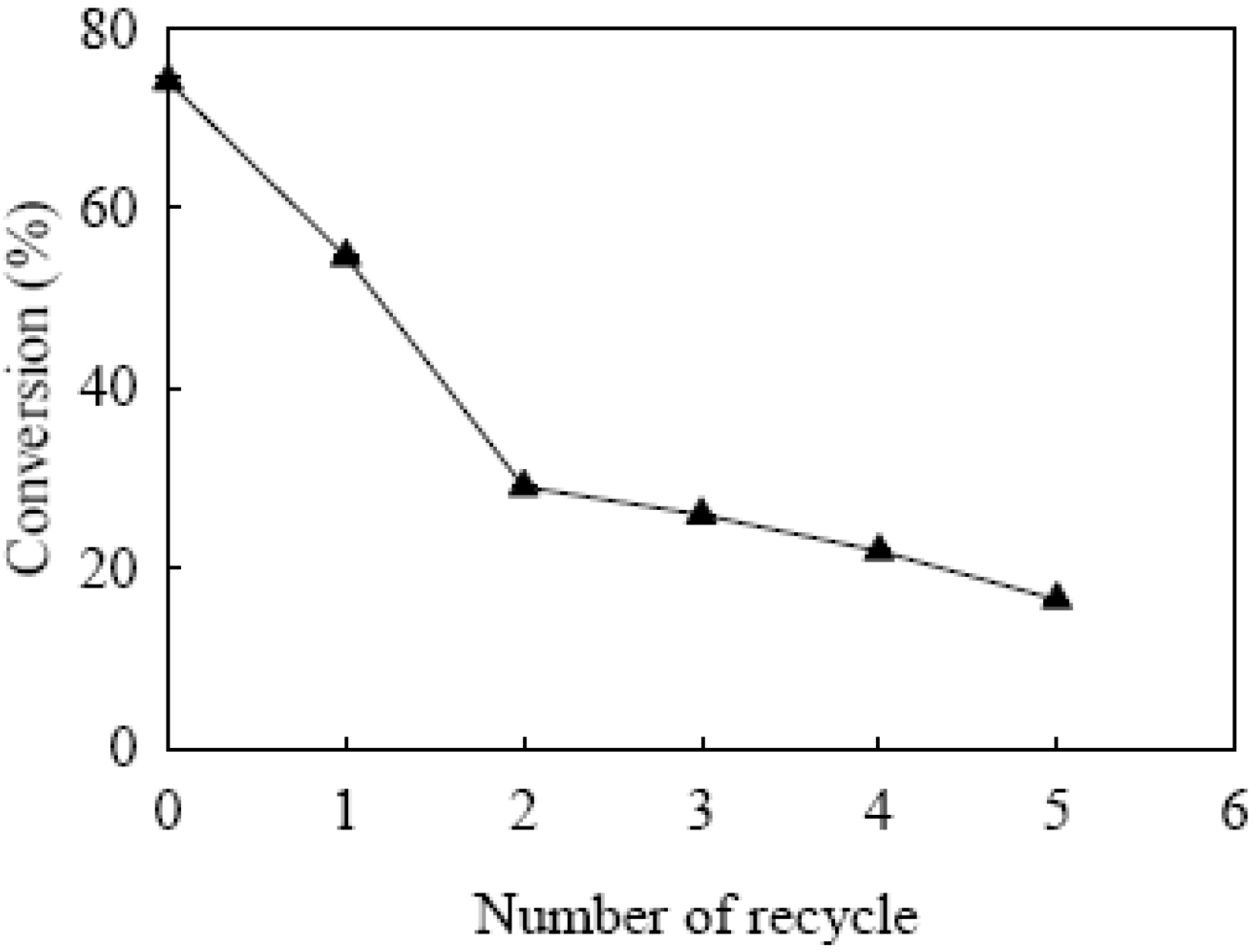
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Entrapment of Lipase
3.2. Assay for Lipase Activity
3.3. Experimental Design
3.4. Transesterification of Oil to Biodiesel
3.5. Analysis of FAME
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Canakci, M.; Sanli, H. Biodiesel production from various feedstocks and their effects on the fuel properties. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canakci, M.; Gerpen, J.V. Biodiesel production from oils and fats with high free fatty acids. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Importance of biodiesel as transportation fuel. Energ. Policy 2007, 35, 4661–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisen, P.; Sanodiya, B.; Thakur, G.; Baghel, R.; Prasad, G. Biodiesel production with special emphasis on lipase-catalyzed transesterification. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, F.; Shah, A.A.; Hameed, A. Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegannathan, K.R.; Abang, S.; Poncelet, D.; Chan, E.S.; Ravindra, P. Production of biodiesel using immobilized lipase—A critical review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2008, 28, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Fuentes, I.E.; Viseras, C.A.; Ubiali, D.; Terreni, M.; Alcántara, A.R. Different phyllosilicates as supports for lipase immobilisation. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2001, 11, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salis, A.; Sanjust, E.; Solinas, V.; Monduzzi, M. Characterisation of Accurel MP1004 polypropylene powder and its use as a support for lipase immobilisation. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2003, 24–25, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H.; Li, B.; Sasaki, T.; Miyazaki, C.; Kajino, T.; Inagaki, S. Immobilized enzymes in ordered mesoporous silica materials and improvement of their stability and catalytic activity in an organic solvent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 2001, 44–45, 755–762. [Google Scholar]
- Macario, A.; Giordano, G.; Frontera, P.; Crea, F.; Setti, L. Hydrolysis of alkyl ester on lipase/silicalite-1 catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2008, 122, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Fornes, V.; Jorda, J.L.; Rey, F.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Guisan, J.M.; Mateo, C. Electrostatic and covalent immobilisation of enzymes on ITQ-6 delaminated zeolitic materials. Chem. Commun. 2001, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, H.F.; de Lima, R.; Roberto, I.C. Rice Straw as a Support for Immobilization of Microbial Lipase. Biotechnol. Prog. 2001, 17, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lei, L.; Zhou, L.; Pan, F. Facile synthesis of amino-silane modified superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and application for lipase immobilization. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 150, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.I.; Ham, H.O.; Oh, S.-D.; Park, H.G.; Chang, H.N.; Choi, S.-H. Immobilization of Mucor javanicus lipase on effectively functionalized silica nanoparticles. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2006, 39, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.M.; Pereira, E.B.; de Castro, H.F. Immobilization of lipase on chitin and its use in nonconventional biocatalysis. Biomacromolecules 2003, 5, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.; Shah, S.; Gupta, M.N. Preparation of biodiesel by lipase-catalyzed transesterification of high free fatty acid containing oil from Madhuca indica. Energy Fuels 2006, 21, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.-F.; Jones, K.; Marmer, W.; Foglia, T. Production of alkyl esters from tallow and grease using lipase immobilized in a phyllosilicate sol-gel. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Kurokawa, Y. Hydrolysis of 1,2-diacetoxypropane by immobilized lipase on cellulose acetate-TiO2 gel fiber derived from the sol-gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2001, 21, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddini, H.; Gao, X.; Joshi, S.; Wagner, P.R. Immobilization of Pseudomonas cepacia lipase by sol-gel entrapment and its application in the hydrolysis of soybean oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddini, H.; Gao, X.; Joshi, S. Immobilization of Candida rugosa lipase by sol-gel entrapment and its application in the hydrolysis of soybean oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2003, 80, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddini, H.; Gao, X. Characterization of sol-gel immobilized lipases. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orçaire, O.; Buisson, P.; Pierre, A.C. Application of silica aerogel encapsulated lipases in the synthesis of biodiesel by transesterification reactions. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2006, 42, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macario, A.; Moliner, M.; Corma, A.; Giordano, G. Increasing stability and productivity of lipase enzyme by encapsulation in a porous organic–inorganic system. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 118, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macario, A.; Verri, F.; Diaz, U.; Corma, A.; Giordano, G. Pure silica nanoparticles for liposome/lipase system encapsulation: Application in biodiesel production. Catal. Today 2013, 204, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-C.; Kuan, I.-C.; Hong, J.-R.; Tsai, B.-H.; Lee, S.-L.; Yu, C.-Y. Activity enhancement and stabilization of lipase from Pseudomonas cepacia in polyallylamine-mediated biomimetic silica. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancor, L.; Luckarift, H.R. Bioinspired enzyme encapsulation for biocatalysis. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröger, N.; Deutzmann, R.; Sumper, M. Polycationic peptides from diatom biosilica that direct silica nanosphere formation. Science 1999, 286, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, S.V.; Clarson, S.J.; Perry, C.C. On the role(s) of additives in bioinspired silicification. Chem. Commun. 2005, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 405–463. [Google Scholar]
- Soumanou, M.M.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Improvement in lipase-catalyzed synthesis of fatty acid methyl esters from sunflower oil. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2003, 33, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, D.; Paine, G.; Patwardhan, S.V.; Perry, C.C. Towards an understanding of (bio)silicification: The role of amino acids and lysine oligomers in silicification. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2231–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pencreac’h, G.; Leullier, M.; Baratti, J.C. Properties of free and immobilized lipase from Pseudomonas cepacia. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 56, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Sugihara, A.; Tominaga, Y. Enzymatic conversion of waste edible oil to biodiesel fuel in a fixed-bed bioreactor. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureddini, H.; Gao, X.; Philkana, R.S. Immobilized Pseudomonas cepacia lipase for biodiesel fuel production from soybean oil. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CNS Online Service. Availanle online: http://www.cnsonline.com.tw/?locale=en_US (accessed on 20 March 2013).
- Encinar, J.M.; González, J.F.; Rodríguez-Reinares, A. Ethanolysis of used frying oil. Biodiesel preparation and characterization. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckarift, H.R.; Spain, J.C.; Naik, R.R.; Stone, M.O. Enzyme immobilization in a biomimetic silica support. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaieda, M.; Samukawa, T.; Kondo, A.; Fukuda, H. Effect of methanol and water contents on production of biodiesel fuel from plant oil catalyzed by various lipases in a solvent-free system. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 91, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuan, I.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, B.-H.; Lee, S.-L.; Lee, W.-T.; Yu, C.-Y. Optimizing the Production of Biodiesel Using Lipase Entrapped in Biomimetic Silica. Energies 2013, 6, 2052-2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042052
Kuan I-C, Lee C-C, Tsai B-H, Lee S-L, Lee W-T, Yu C-Y. Optimizing the Production of Biodiesel Using Lipase Entrapped in Biomimetic Silica. Energies. 2013; 6(4):2052-2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042052
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuan, I-Ching, Chia-Chi Lee, Bing-Hong Tsai, Shiow-Ling Lee, Wei-Ting Lee, and Chi-Yang Yu. 2013. "Optimizing the Production of Biodiesel Using Lipase Entrapped in Biomimetic Silica" Energies 6, no. 4: 2052-2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6042052




