A Parametric Energy Model for Energy Management of Long Belt Conveyors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Conveyor Model

2.1. Conveyor Resistances
2.1.1. Primary and Slope Resistances
2.1.2. Special Resistance
2.1.3. Secondary Resistance
2.2. Modeling Energy Consumption
2.3. Modeling Bulk Material Flow
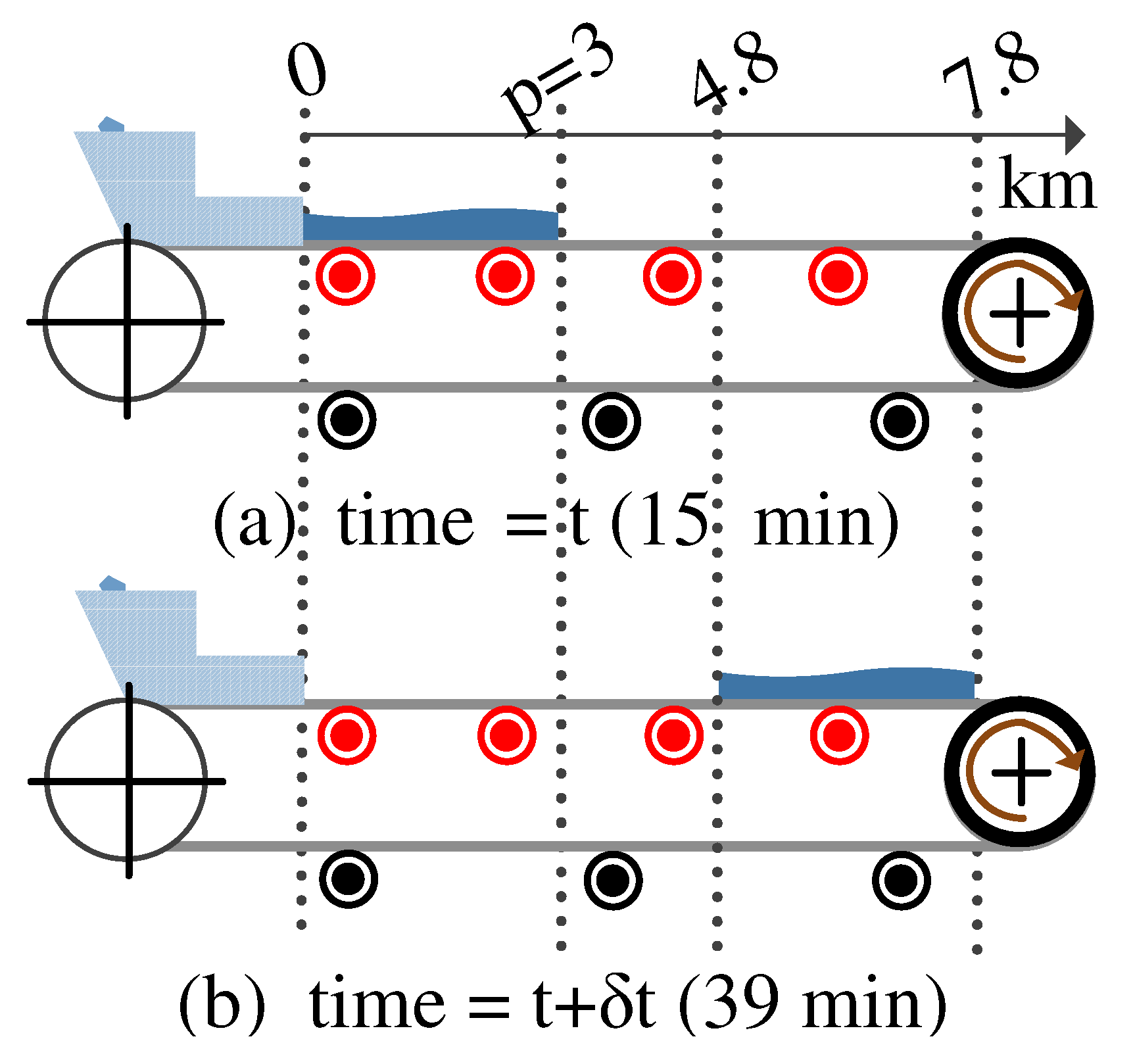
3. Model Verification
3.1. Steady-State Power Calculations

| Unit | Component | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | ||||
| L = 500 m | ||||
| kW | 191.3 | 41.7 | 145.7 | 3.9 |
| % | 100.0 | 21.8 | 76.1 | 2.1 |
| L = 2 km | ||||
| kW | 508.1 | 123.7 | 380.4 | 3.9 |
| % | 100.0 | 74.9 | 24.3 | 0.8 |

3.2. Variable Loading Calculations





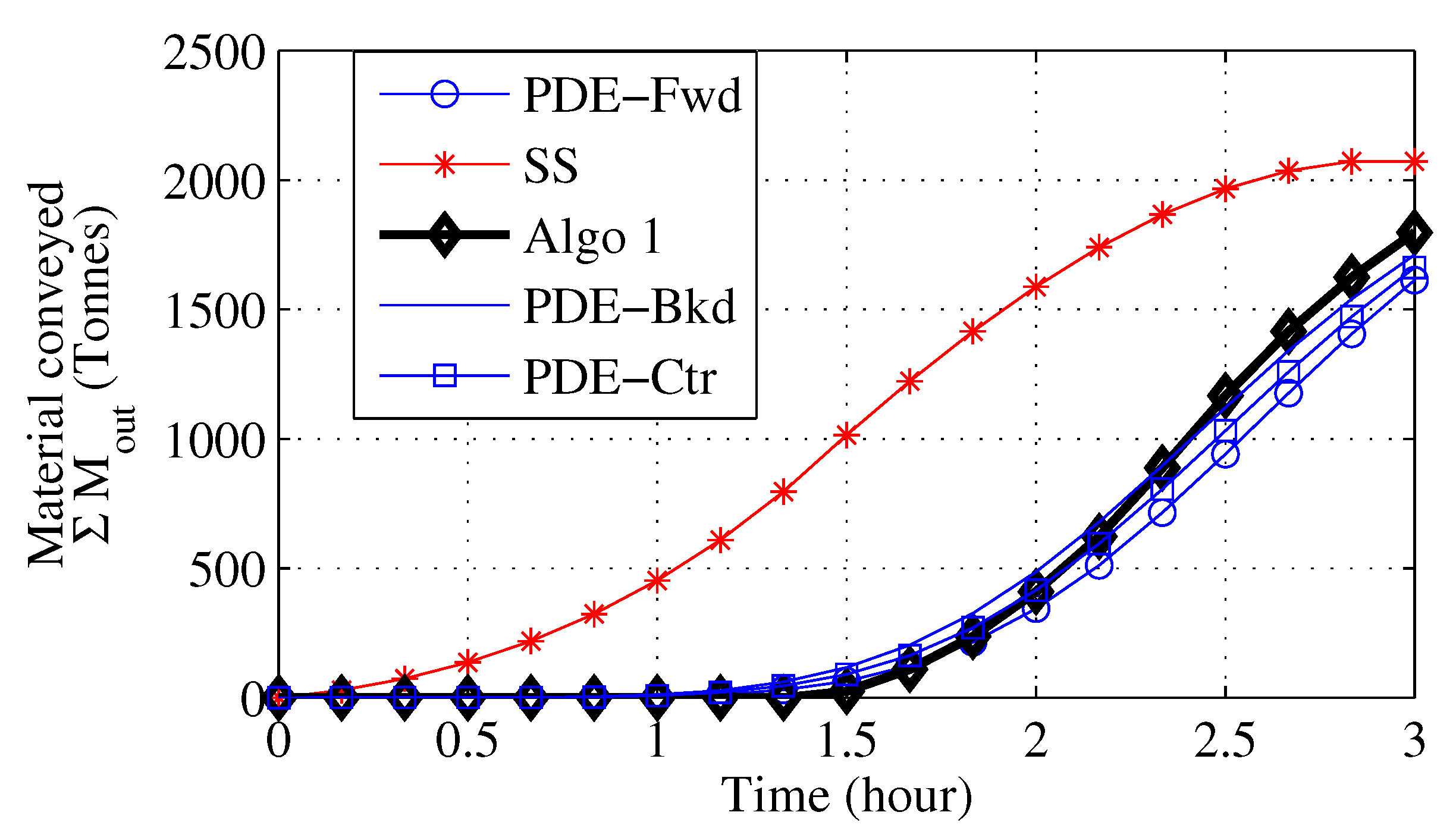
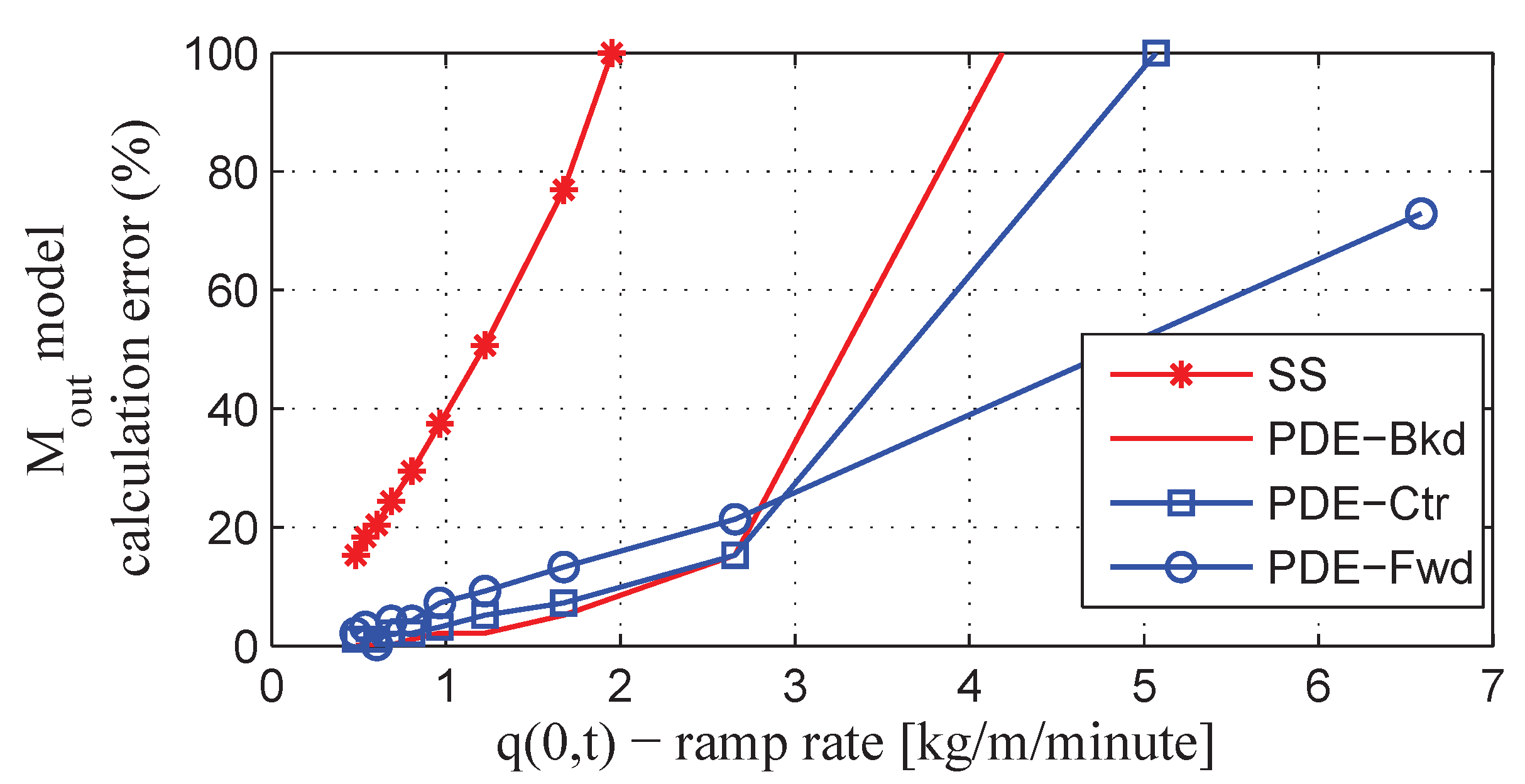
4. Parameter Identification

Parameter Estimation



5. Application Case-Study

6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations/Nomenclature
| Abbreviations: | |
| BC | Belt conveyor. |
| CBS | Conveyor belt system. |
| FDM | Finite difference method. |
| PDE | Partial differential equation. |
| SS | steady-state. |
| Symbols: | |
| η | Conveyor drive system efficiency. |
| π | Hourly electricity price R/kWh. |
| Energy model no-load parameter, N. | |
| Energy model density parameter, . | |
| A | Cross-sectional area of material on the belt. |
| C | A belt resistance factor. |
| E | Energy consumption of the conveyor, kWh. |
| F | Force on the conveyor belt, N. |
| H | Conveyor elevation height, m. |
| I | Input material feed rate, kg/s. |
| Mass of material entering the conveyor, kg. | |
| Mass of material discharged by the conveyor, kg. | |
| Matrix and vector values of the discrete model. | |
| Model parameter sensitivity to output power. | |
| Storage level at sample time n. | |
| Lower and upper storage bound. | |
| Number of space and time samples in discrete domain. | |
| L | Total length of the conveyor belt. |
| Length of CB covered by material with a uniform . | |
| P | Power consumed by the conveyor, kW. |
| Material mass per unit length at position x at time t, kg/m. | |
| Maximum mass per unit length. | |
| Average for the whole belt at a given time. | |
| Vector of ’s at a given time n. | |
| t | Time. |
| v | Conveyor belt speed, m/s. |
| x | Position; distance from conveyor’s tail, m. |
| Subscripts and superscripts: | |
| i | Position on the belt-in discrete domain. |
| n | Time-in discreet domain. |
| An estimate of a quantity/variable. |
References
- Mathaba, T.; Xia, X.; Zhang, J. Analysing the economic benefit of electricity price forecast in industrial load scheduling. Electr. Pow. Syst. Res. 2014, 116, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granell, R.; Axon, C.J.; Wallom, D.C.H. Predicting winning and losing businesses when changing electricity tariffs. Appl. Energy 2014, 133, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathaba, T.; Xia, X.; Zhang, J. Optimal scheduling of conveyor belt systems under critical peak pricing. In Proceedings of the International Power and Energy Conference (IPEC) 2012, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 12–14 December 2012; pp. 315–320.
- Fedorko, G.; Molnar, V.; Marasova, D.; Grincova, A.; Dovica, M.; Zivcak, J.; Toth, T.; Husakova, N. Failure analysis of belt conveyor damage caused by the falling material. Part I: Experimental measurements and regression models. Eng. Fail Anal. 2014, 36, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, C.A.; Roberts, A.W.; Jones, M.G. Calculating the Flexure Resistance of Bulk Solids Transported on Belt Conveyors. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2004, 21, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamorano, S. Main Article Belt Conveyor Technology Long Distance Conveying—Choosing the Right Option; Bulk Solids Handling: Houston, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ristić, L.B.; Jeftenić, B.I. Implementation of fuzzy control to improve energy efficiency of variable speed buk materail transportation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewijks, G. The design of high speed belt conveyors. In Proceedings of the Conference on Belt Conveying-BELTCON 10, Midrand, South Africa, 19–21 October 1999.
- Zhang, S.; Xia, X. Modeling and energy efficiency optimization of belt conveyors. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltermann, J.; Lodewijks, G.; Schott, D.L.; Rijsenbrij, J.C.; Dekkers, J.A.J.M.; Pang, Y. A methodology to predict power saving of troughed belt conveyors by speed control. Particul. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeftenić, B.; Ristić, L.; Bebić, M.; Štatkić, S.; Mihailović, I.; Jevtić, D. Optimal utilization of the bulk material transport system based on speed concontrol drives. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines—ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010.
- Hou, Y.; Meng, Q. Dynamic characteristics of conveyor belts. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2008, 18, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, X. Optimal control of operation efficiency of belt conveyor systems. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelberg, A.; Zhang, J.; Xia, X. An optimal control model for load shifting—With application in the energy management of a colliery. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. ISO 5048:1989 Continous Mechanical Handling Equipment-Belt Conveyor with Carrying Idlers—Calculation of Operating Power and Tensile Forces; Technical Report; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- CEMA. Belt Conveyor for Bulk Material, 6th ed.; Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association: Naples, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Phoenix Conveyor Belts Design Fundamentals-New DIN 22101. Hannoversche Strasse 88, D-21079 Hamburg, Germany. Available online: http://www.phoenix-ag.com (accessed on 16 April 2014).
- Mulani, I.G. Calculation of Artificial Friction Conveying Coefficient f, and a Comparision between ISO and CEMA; Bulk Material Handling by Conveyor Belt 5; Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration: Littleton, CO, USA, 2004; pp. 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, W.A. Partial Differential Equations-an Introduction, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Van Delft, T.J. Modeling and Model Predictive Control of a Conveyor-Belt Dryer-Applied to the Drying of Fish Feed. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tannehill, J.C.; Anderson, D.A.; Pletcher, R.H. Computational Fluid Mechnics and Heat Transfer, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Trefethen, L.N. Finite Difference and Spectral Methods for Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, X. A new energy calculation model of belt conveyor. In Proceedings of the IEEE AFRICON 2009, Nairobi, Kenya, 23–25 September 2009.
- Tessier, J.; Duchesne, C.; Bartolacci, G. A machine vision approach to on-line estimation of run-of-mine ore composition on conveyor belts. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthan, T.; Vaidyan, M.V. An FPGA-based parallel architecture for on-line parameter estimation using the RLS identification algorithm. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2014, 38, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, L.; Huang, B.; Craig, I. Dual particle filters of state and parameter estimation with application to a run-of-mine ore mill. J. Process Contr. 2012, 22, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariff and Charges Booklet 2013/14. Available online: www.eskom.co.za/tariffs (accessed on 24 January 2014).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mathaba, T.; Xia, X. A Parametric Energy Model for Energy Management of Long Belt Conveyors. Energies 2015, 8, 13590-13608. https://doi.org/10.3390/en81212375
Mathaba T, Xia X. A Parametric Energy Model for Energy Management of Long Belt Conveyors. Energies. 2015; 8(12):13590-13608. https://doi.org/10.3390/en81212375
Chicago/Turabian StyleMathaba, Tebello, and Xiaohua Xia. 2015. "A Parametric Energy Model for Energy Management of Long Belt Conveyors" Energies 8, no. 12: 13590-13608. https://doi.org/10.3390/en81212375
APA StyleMathaba, T., & Xia, X. (2015). A Parametric Energy Model for Energy Management of Long Belt Conveyors. Energies, 8(12), 13590-13608. https://doi.org/10.3390/en81212375






