New TA Index-Based Rollover Prevention System for Electric Vehicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Dynamic Model of Electric Vehicles
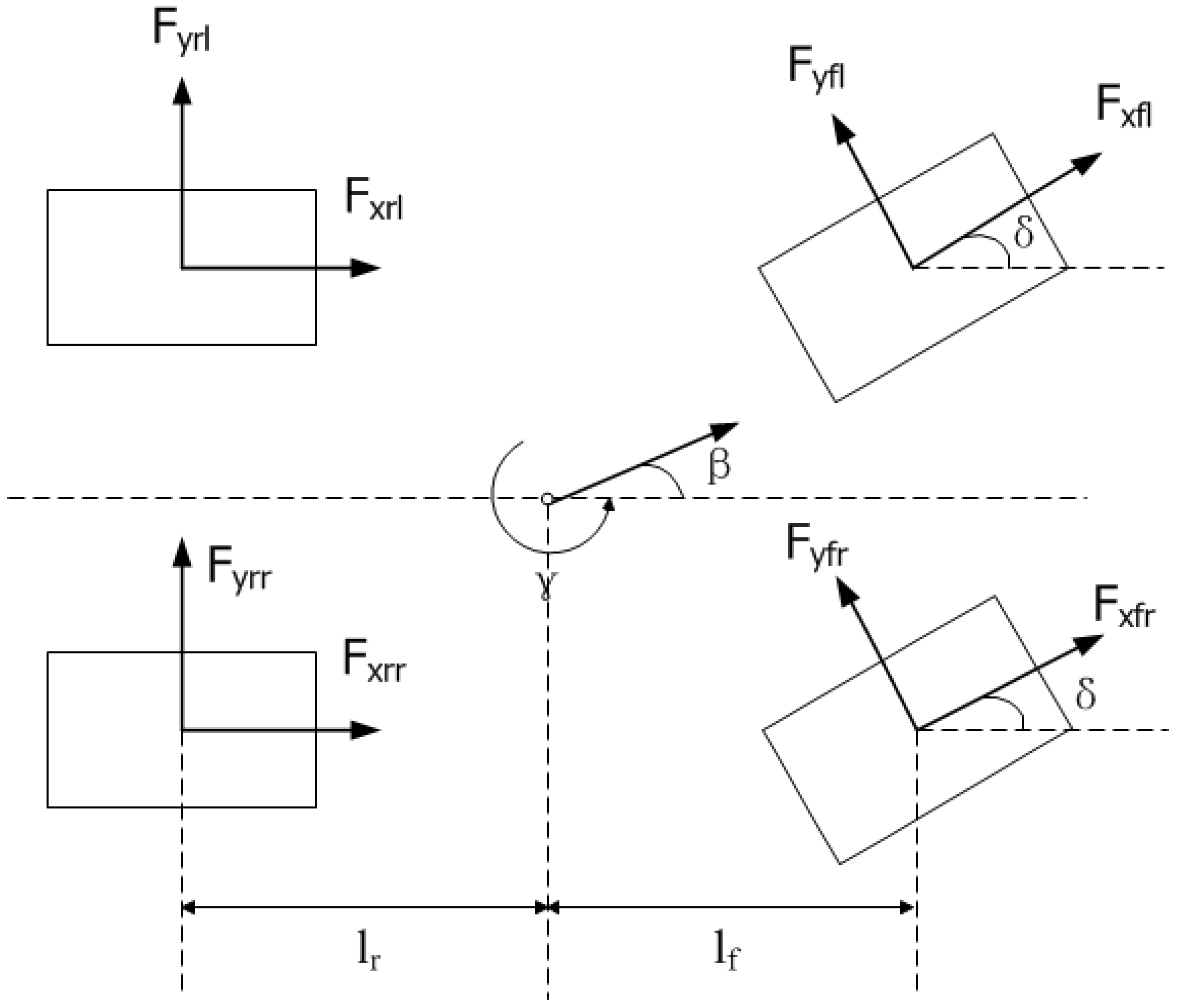
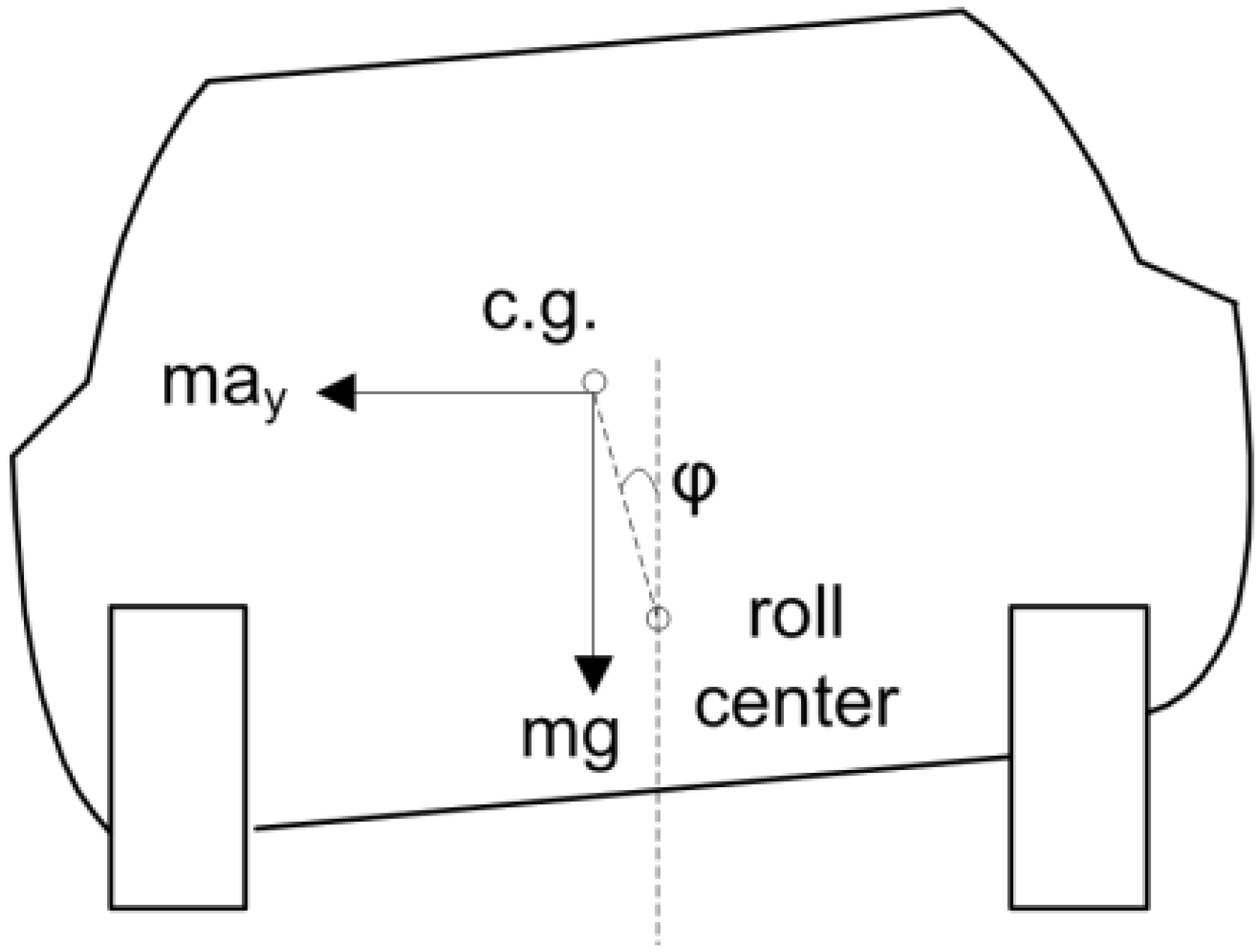

2.2. Wheel Status Indicator: TA


2.3. Three-Level Electric Vehicle Dynamic Control Structure

3. TAI Rollover Prevention Method
3.1. TAI Rollover Detection
3.2. Three-Level Electric Vehicle Anti-Rollover Controller
4. In-House EV Dynamic Model and Simulation Results
4.1. In-House EV Dynamic Model

4.2. Simulation Results
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Vehicle mass (M) | 400 kg |
| Quarter vehicle mass (m) | 100 kg |
| Wheel equivalent radius (r) | 276 mm |
| Distance between the vehicle center of gravity and the front axle (lf) | 1.0 m |
| Distance between the vehicle center of gravity and the front axle (lr) | 1.3 m |
| Track width (lw) | 1.5 m |
| Vehicle yaw inertial (Jz) | 251 kgm2 |
| Height of the vehicle center of gravity (h) | 0.4 m |

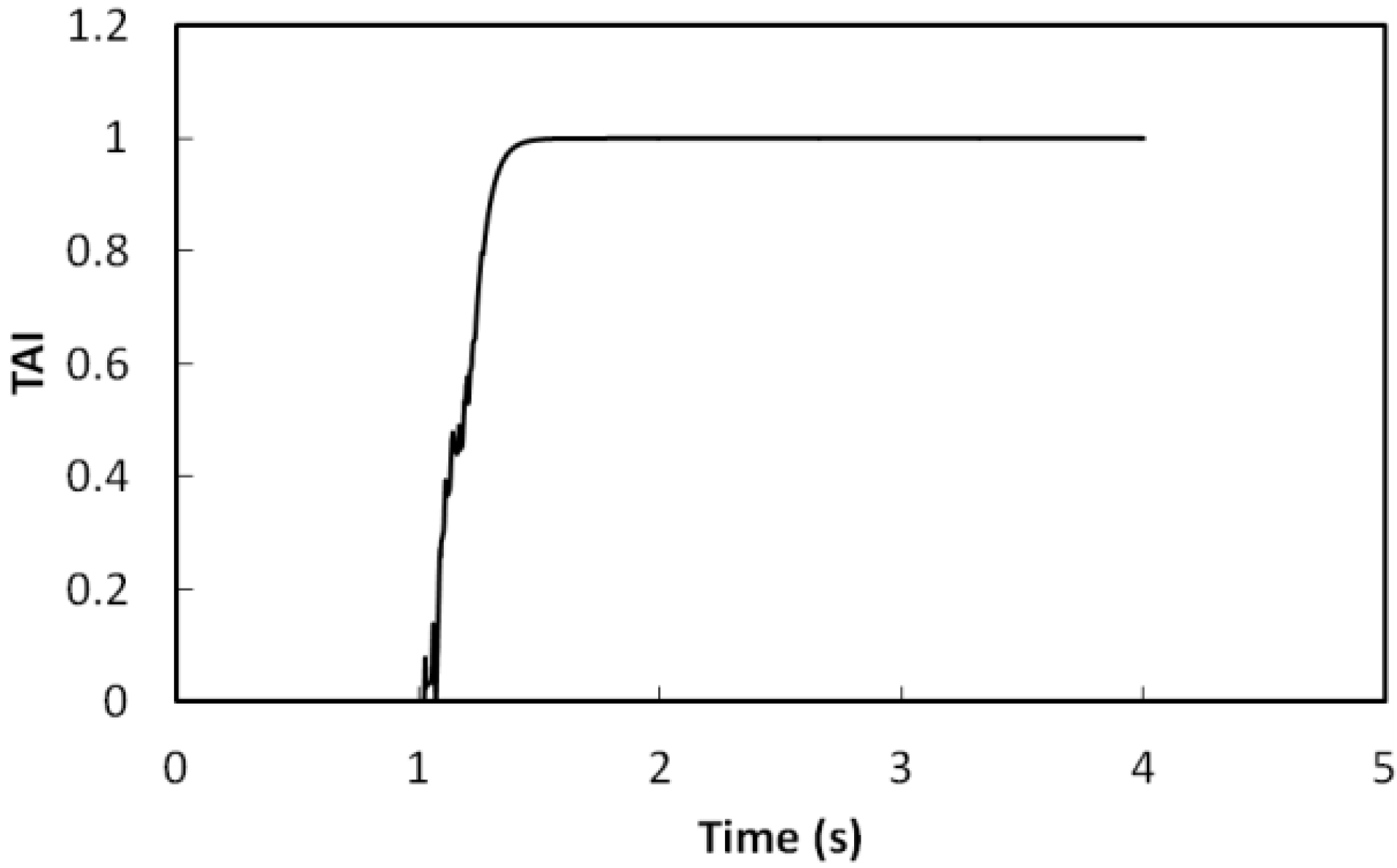


5. Experimental Results

| Parameters | Value/Type |
|---|---|
| Length of the body | 2500 mm |
| Width of the body | 1600 mm |
| Height of the body | 1400 mm |
| Weight | 400 kg |
| Wheel radius | 276 mm |
| Power of the motor | 4 kw |
| Voltage of the battery | 96 V |
| Controller | MicroAutoBox |
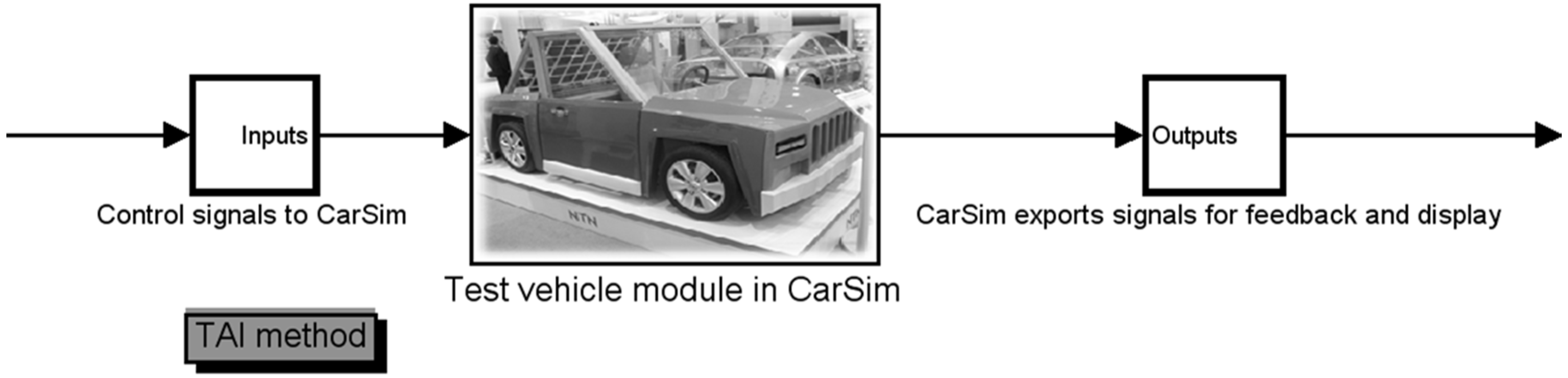

5.1. Without Control



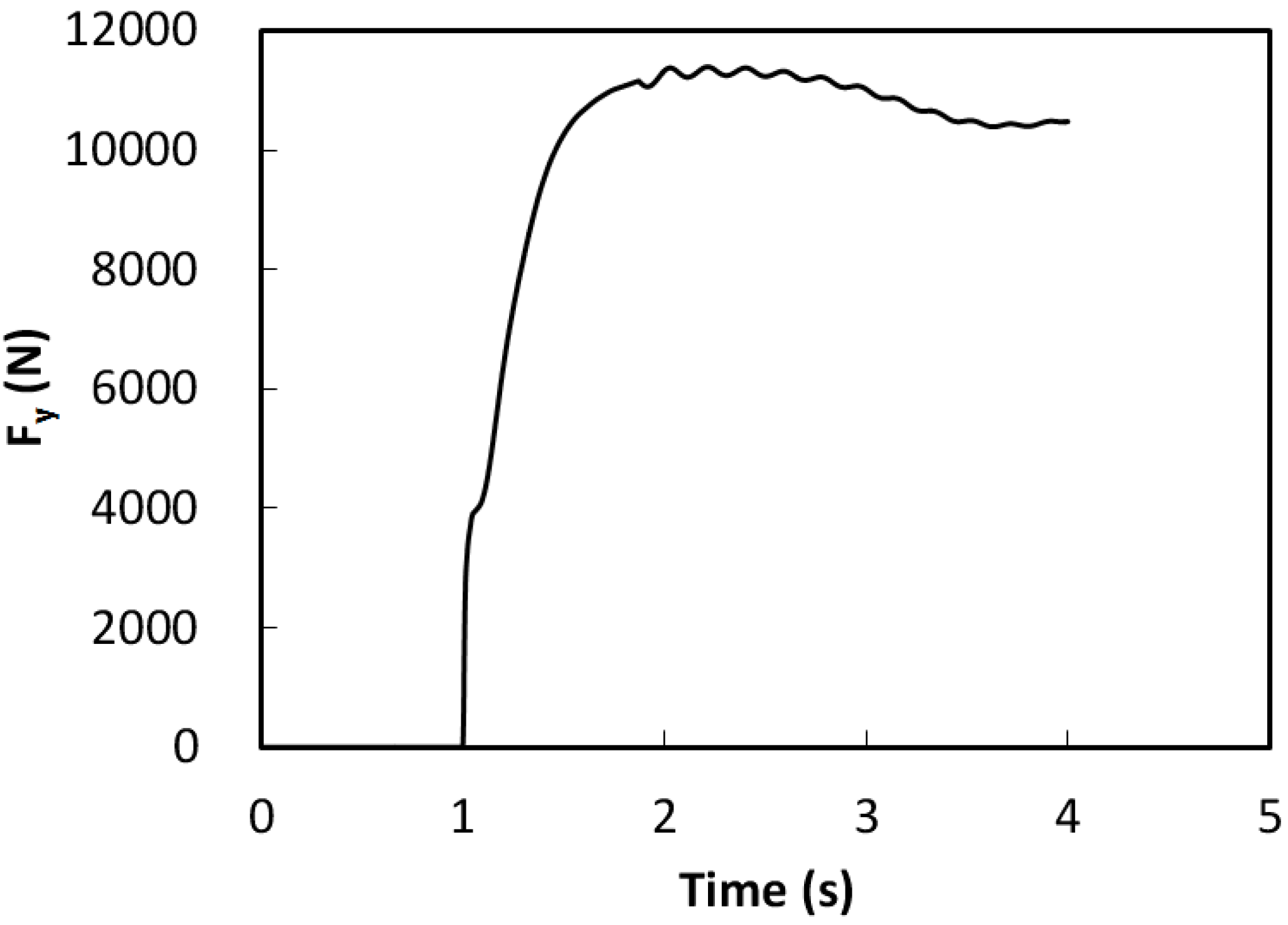
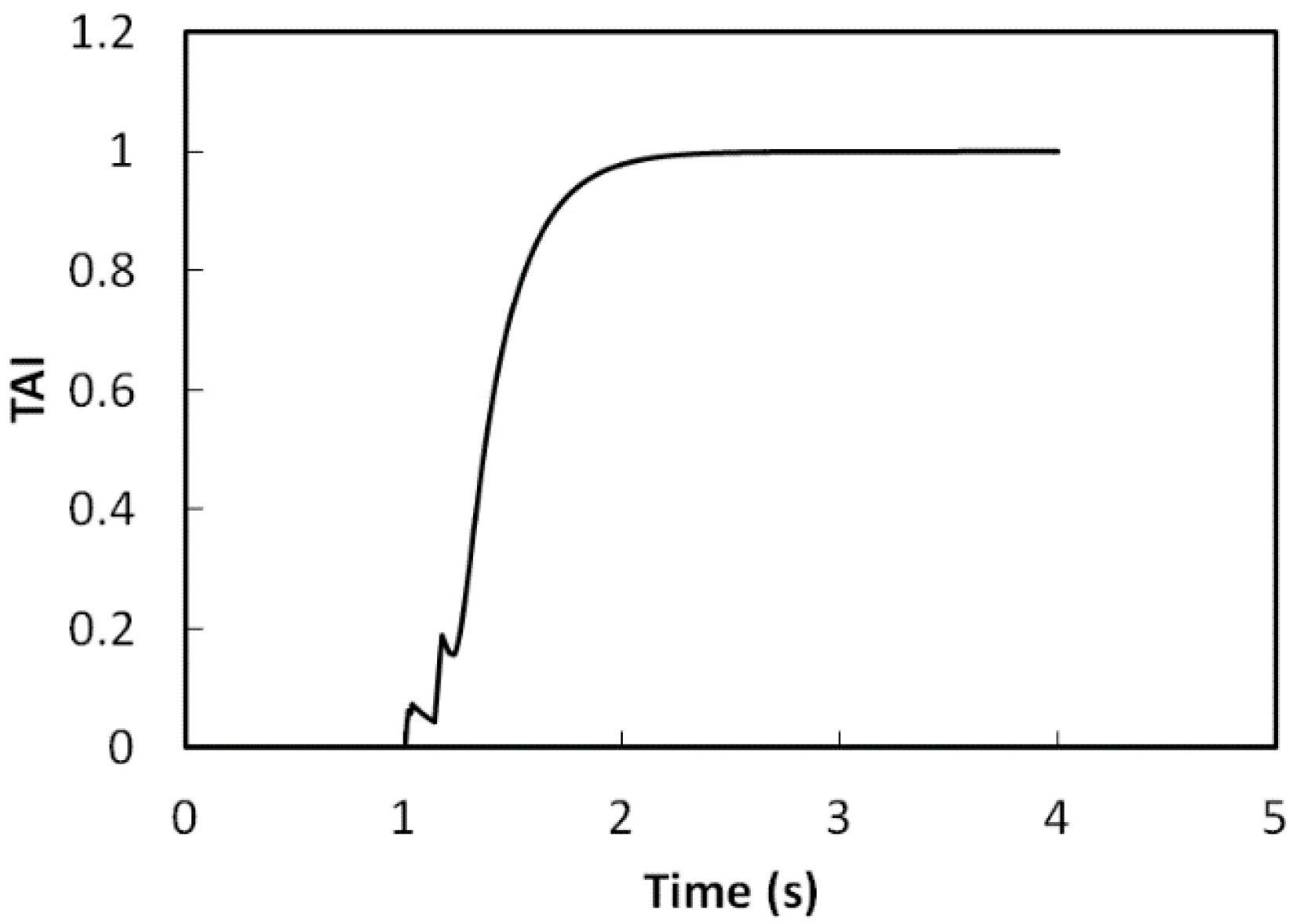
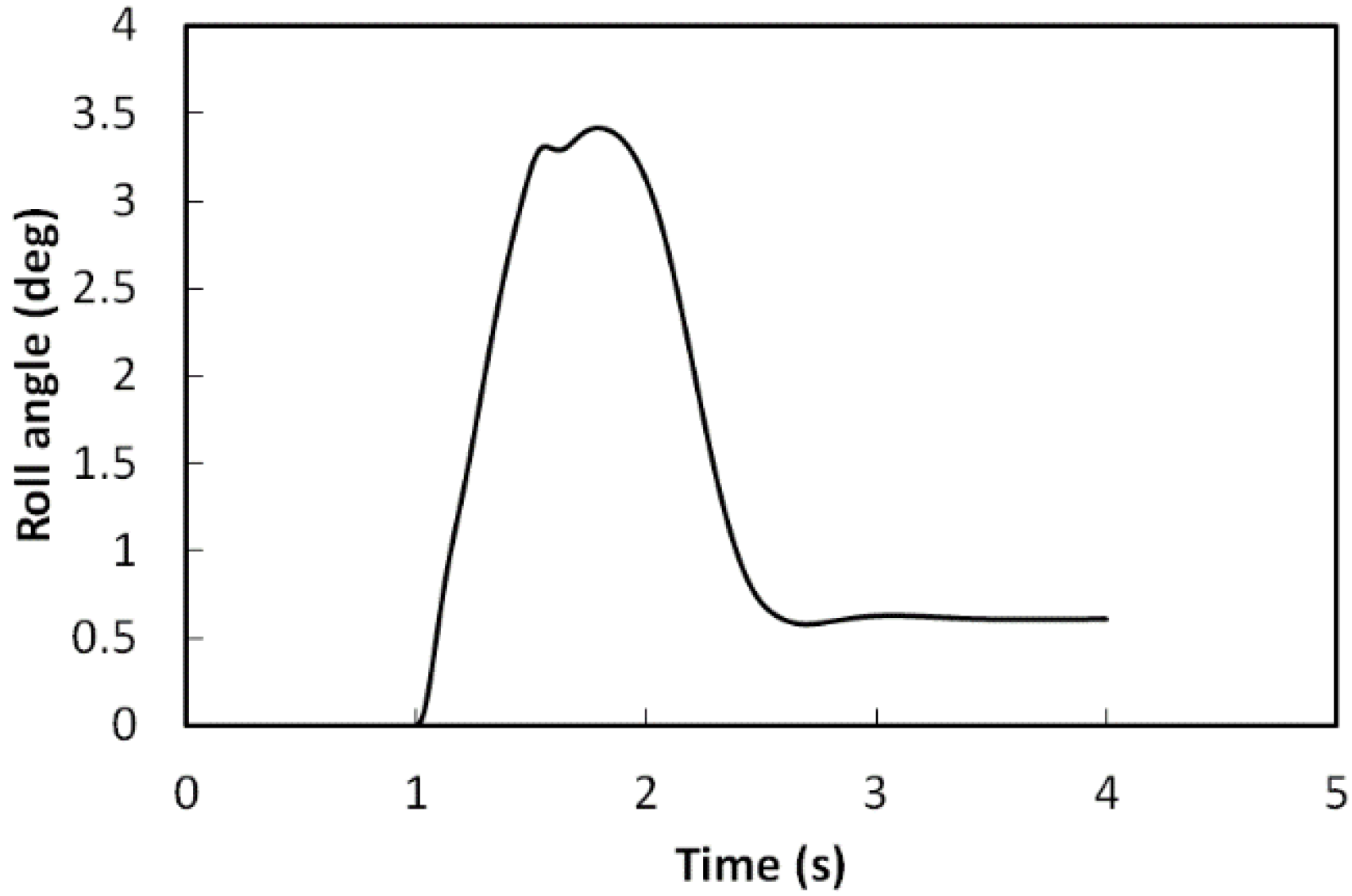
5.2. With Middle Level Control



5.3. With Upper Level Control



6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Nomenclature
| V | Vehicle longitudinal velocity |
Wheel angular velocity | |
Wheel equivalent radius | |
Wheel slip ratio | |
Drive motor torque | |
| J | Wheel inertia |
| g | Gravity acceleration |
Vehicle side slip angle | |
Yaw | |
| lf | Distance between the vehicle center of gravity and the front axle |
| lr | Distance between the vehicle center of gravity and the rear axle |
| Cu | Cornering stiffness of the front tire |
| Cr | Cornering stiffness of the rear tire |
Slip angle of the front wheel | |
Slip angle of the rear wheel | |
| Mz | Direct yaw moment from the wheel torque difference |
| Jz | Vehicle yaw inertial |
Steering angle | |
| hs | Distance between the vehicle center of gravity and the roll center of the sprung mass |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, G.; Ou, X.; Zhang, X. Development of electric vehicles use in China: A study from the perspective of life-cycle energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Energy Policy 2013, 59, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, M.; Yang, L. Study on the economic and environmental benefits of different EV powertrain topologies. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 86, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Overview and prospects on distributed drive electric vehicles and its energy saving strategy. Prz. Elektrotech. 2012, 88, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Ouyang, M.; Lu, D.; Li, J.; Lu, L. Energy efficiency optimization of electric vehicle driven by in-wheel motors. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2013, 14, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Z. The Regenerative Braking Control Strategy of Four-Wheel-Drive Electric Vehicle Based on Power Generation Efficiency of Motors; SAE Technical Paper; Society of Automotive Engineers: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hori, Y. Future vehicle driven by electricity and control-research on four-wheel-motored “UOT electric march II”. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, C.; Li, M.; Xu, M. A kriging assisted direct torque control of brushless DC motor for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Conference Natural Computation (ICNC), Shanghai, China, 2011.
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Ma, C.; Xu, M. Kriging assisted on-line torque calculation for brushless DC motors used in electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium Conference on Industrial Electron (ISIE), Hangzhou, China, 2012.
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Xu, M. Kriging assisted on-line torque calculation for brushless DC motors used in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Long, B.; Lim, S.T.; Ryu, J.H.; Chong, K.T. Energy-regenerative braking control of electric vehicles using three-phase brushless direct-current motors. Energies 2014, 7, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Xu, M. A new anti-skid control method for electric vehicles using motor torque and wheel acceleration. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. D 2014. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, C.; Mostefai, L.; Denai, M.; Hori, Y. Direct yaw-moment control of an in-wheel-motored electric vehicle based on body slip angle fuzzy observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, G.; Zhao, W.; Miao, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, H. A neural network combined inverse controller for a two-rear-wheel independently driven electric vehicle. Energies 2014, 7, 4614–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.; Wang, Y.; Fujimoto, H.; Hori, Y. Lateral stability control of electric vehicle based on disturbance accommodating kalman filter using the integration of single antenna GPS receiver and yaw rate sensor. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2013, 8, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Novellis, L.; Sorniotti, A.; Gruber, P.; Pennycott, A. Comparison of feedback control techniques for torque-vectoring control of fully electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 3612–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, W.; Xu, K.; Song, Z. An intelligent regenerative braking strategy for electric vehicles. Energies 2011, 4, 1461–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennycott, A.; de Novellis, L.; Gruber, P.; Sorniotti, A. Optimal braking force allocation for a four-wheel drive fully electric vehicle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I 2014, 228, 621–628. [Google Scholar]
- Pennycott, A.; de Novellis, L.; Sabbatini, A.; Gruber, P.; Sorniotti, A. Reducing the motor power losses of a four-wheel drive, fully electric vehicle via wheel torque allocation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D 2014, 228, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xu, M.; Wang, H. Dynamic emulation of road/tyre longitudinal interaction for developing electric vehicle control systems. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2011, 49, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhao, Q. Acceleration-to-torque ratio based anti-skid control for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Mechatronic and Embedded Systems and Application, Qingdao, China, 15–17 July 2010.
- Phanomchoeng, G.; Rajamani, R. Real-time estimation of rollover index for tripped rollovers with a novel unknown input nonlinear observer. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamani, R.; Piyabongkarn, D. New paradigms for the integration of yaw stability and rollover prevention functions in vehicle stability control. IEEE Trans. Intell. Trans. Syst. 2013, 14, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Kim, D.; Yi, K. Design of a rollover index-based vehicle stability control scheme. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2007, 45, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyabongkarn, D.; Lew, J.Y.; Rajamani, R.; Grogg, J.A. Active driveline torque-management systems. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2010, 30, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, S.; Corless, M.; Shorten, R. A methodology for the design of robust rollover prevention controllers for automotive vehicles with active steering. Int. J. Control. 2007, 80, 1763–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamani, R. Vehicle Dynamics and Control, 2nd ed.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bevly, D.M.; Ryu, J.; Gerdes, J.C. Integrating INS sensors with GPS measurements for continuous estimation of vehicle sideslip, roll, and tire cornering stiffness. IEEE Trans. Intell. Trans. Syst. 2006, 7, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.Y.; Ko, J.W.; Lee, S.M.; Cheon, J.S.; Kim, H.S. Vehicle velocity estimation using effective inertia for an in-wheel electric vehicle. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2014, 15, 815–821. [Google Scholar]
- Bayar, K.; Wang, J.; Rizzoni, G. Development of a vehicle stability control strategy for a hybrid electric vehicle equipped with axle motors. Proc. Inst. of Mech. Eng. Part D 2012, 226, 795–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Yoo, J.; Yi, K. Driving control algorithm for maneuverability, lateral stability, and rollover prevention of 4WD electric vehicles with independently driven front and rear wheels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 2987–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baffet, G.; Charara, A.; Lechner, D.; Thomas, D. Experimental evaluation of observers for tire–road forces, sideslip angle and wheel cornering stiffness. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2008, 46, 501–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M. Vehicle Handling Dynamics: Theory and Application; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mitschke, M.; Wallentowitz, H. Dynamik der Kraftfahrzeuge; Chinese Version; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pacejka, H.B.; Bakker, E. The magic formula tyre model. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1992, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacejka, H.B. Tyre and Vehicle Dynamics; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Li, M. New TA Index-Based Rollover Prevention System for Electric Vehicles. Energies 2015, 8, 2008-2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8032008
Liu X, Xu M, Li M. New TA Index-Based Rollover Prevention System for Electric Vehicles. Energies. 2015; 8(3):2008-2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8032008
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiang, Min Xu, and Mian Li. 2015. "New TA Index-Based Rollover Prevention System for Electric Vehicles" Energies 8, no. 3: 2008-2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8032008
APA StyleLiu, X., Xu, M., & Li, M. (2015). New TA Index-Based Rollover Prevention System for Electric Vehicles. Energies, 8(3), 2008-2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8032008





