Plasmonic Coaxial Waveguides with Complex Shapes of Cross-Sections
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Coaxial Waveguide with Annular Central Rods
2.1. The Coaxial Waveguide with Two Nano-Sized Circular Tubes
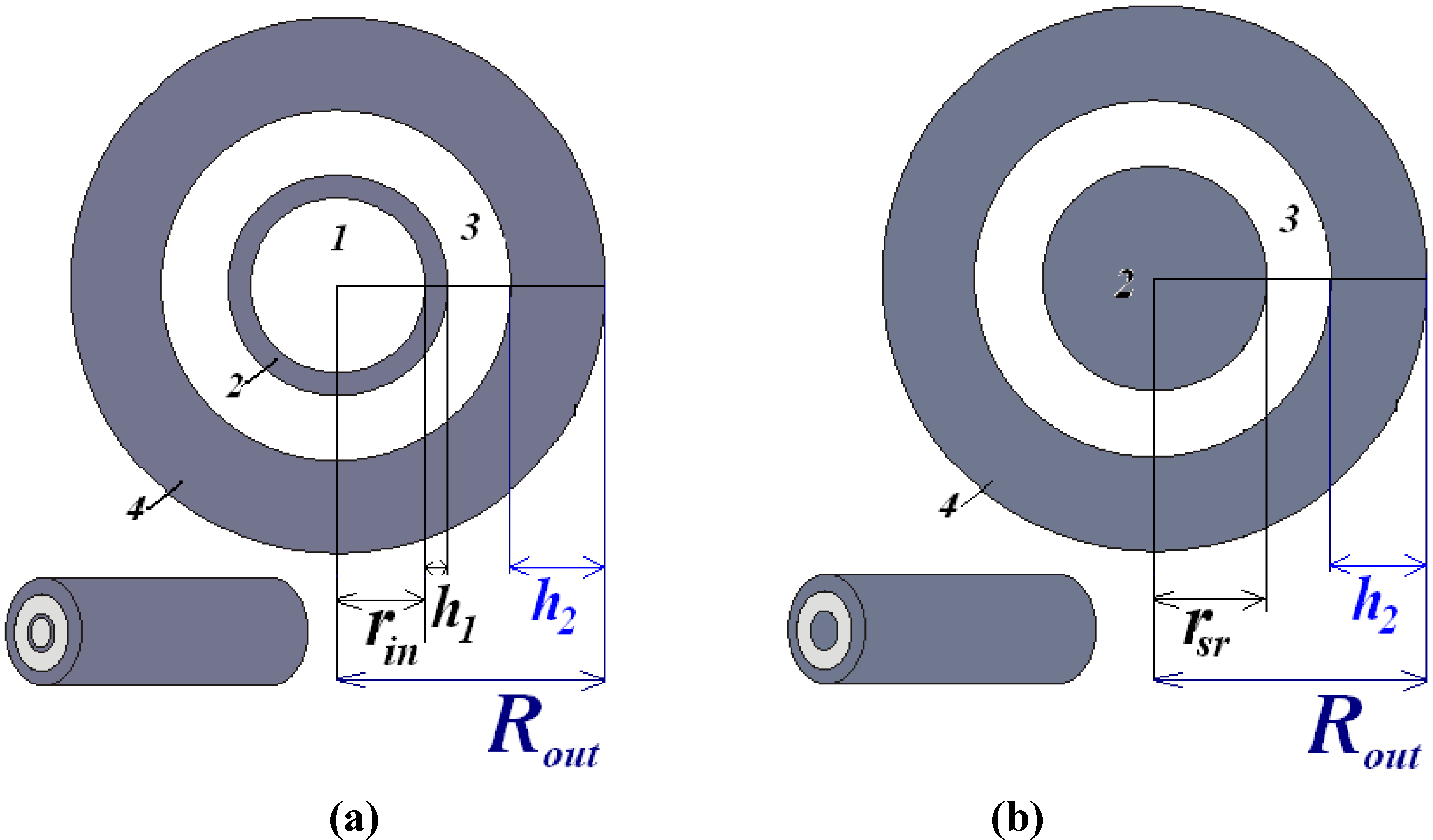
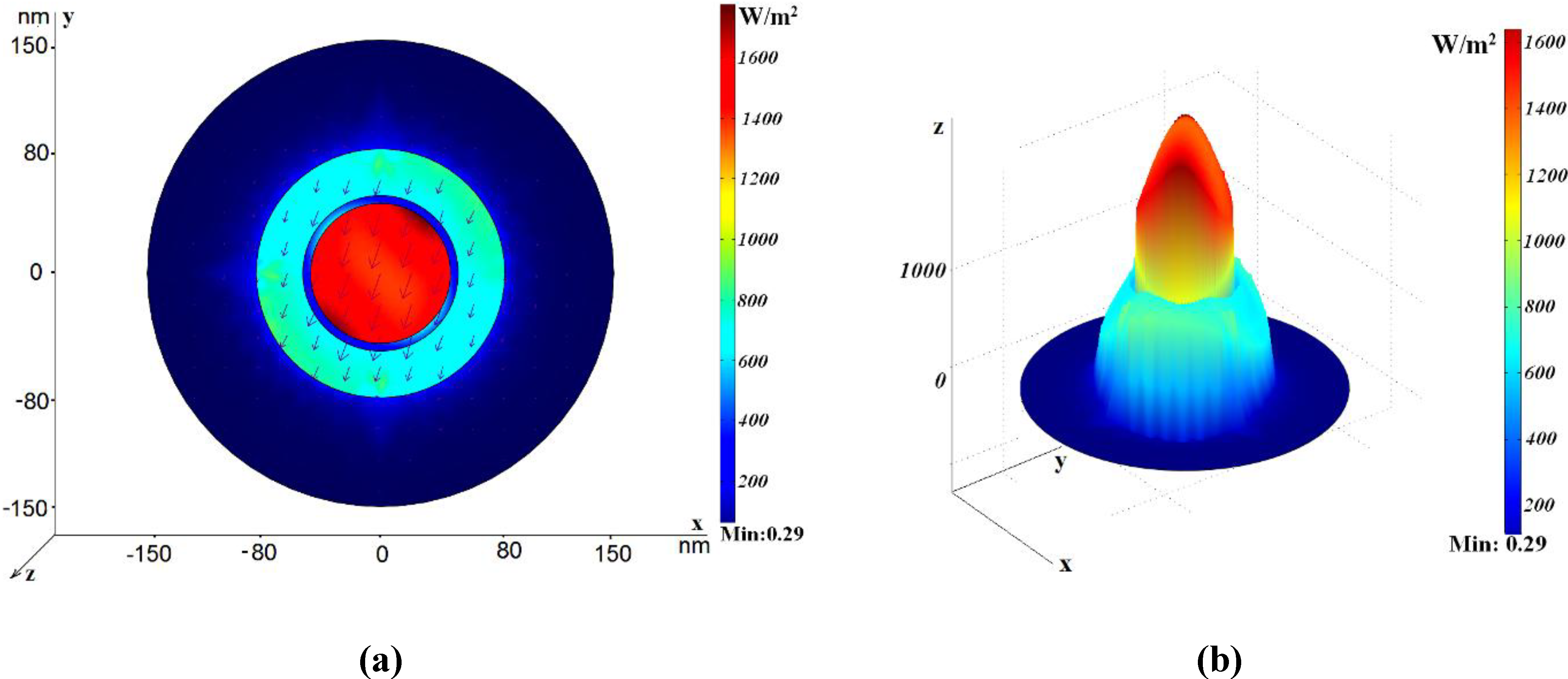
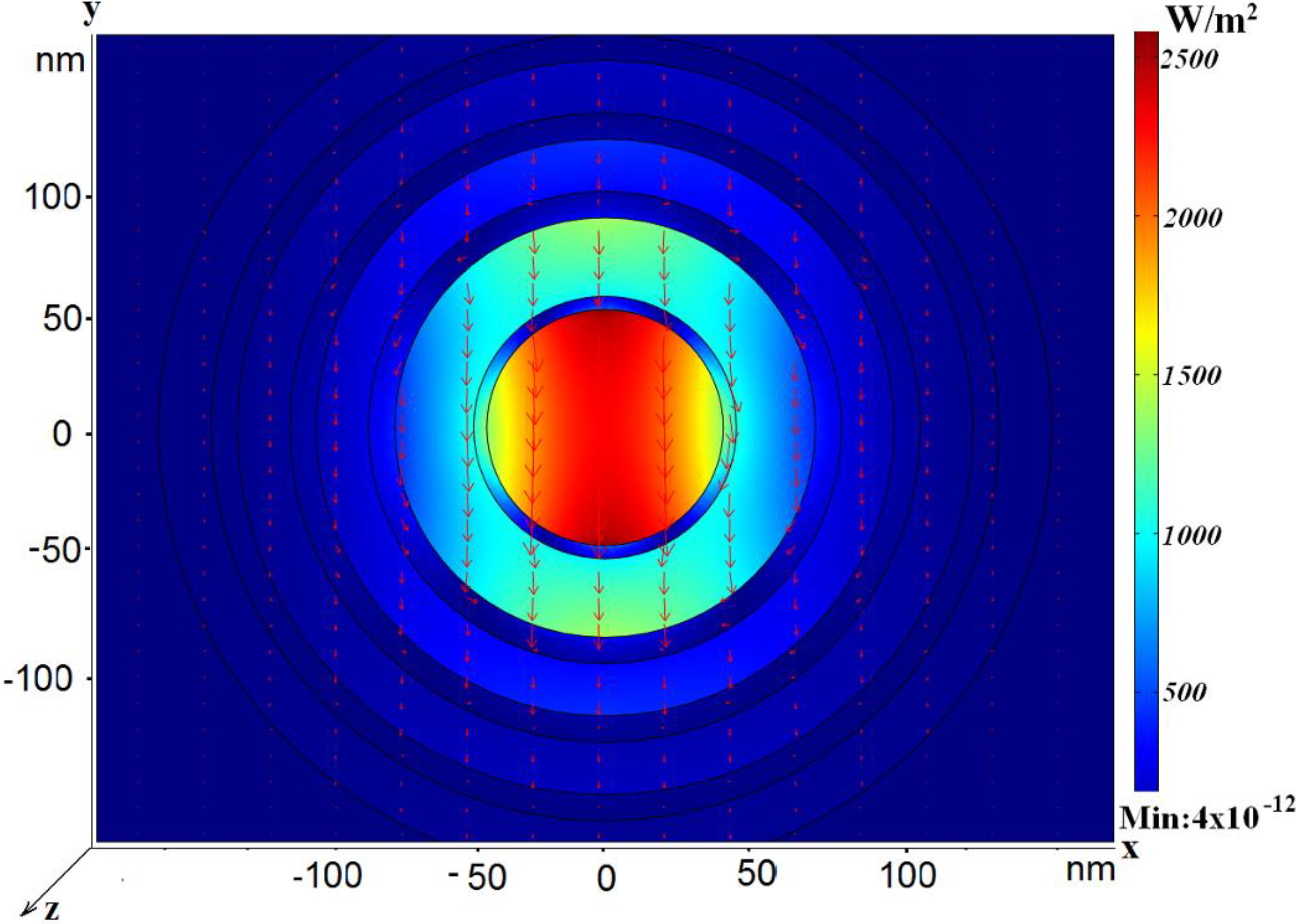
2.2. The Conventional Coaxial Waveguide with Nano-Sized Circular Rod

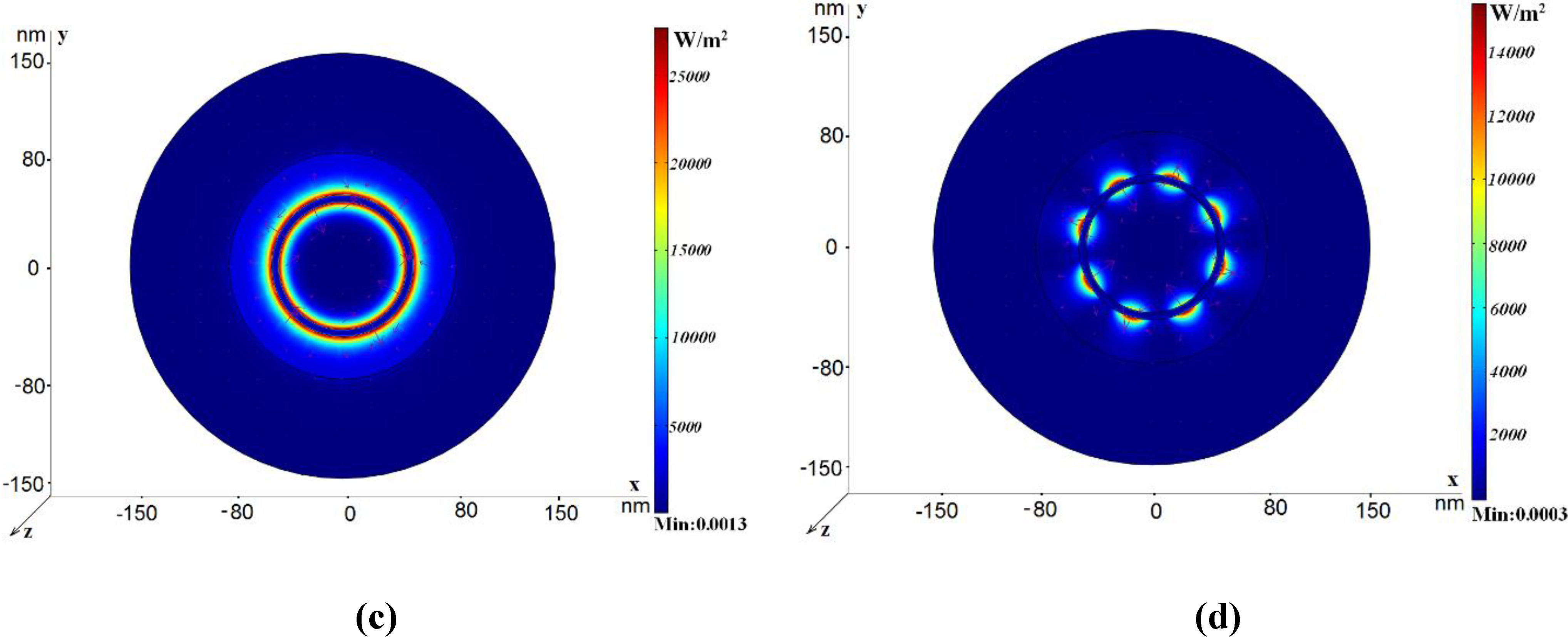
2.3. The Coaxial Waveguide with Multiple Nano-Sized Circular Annuli
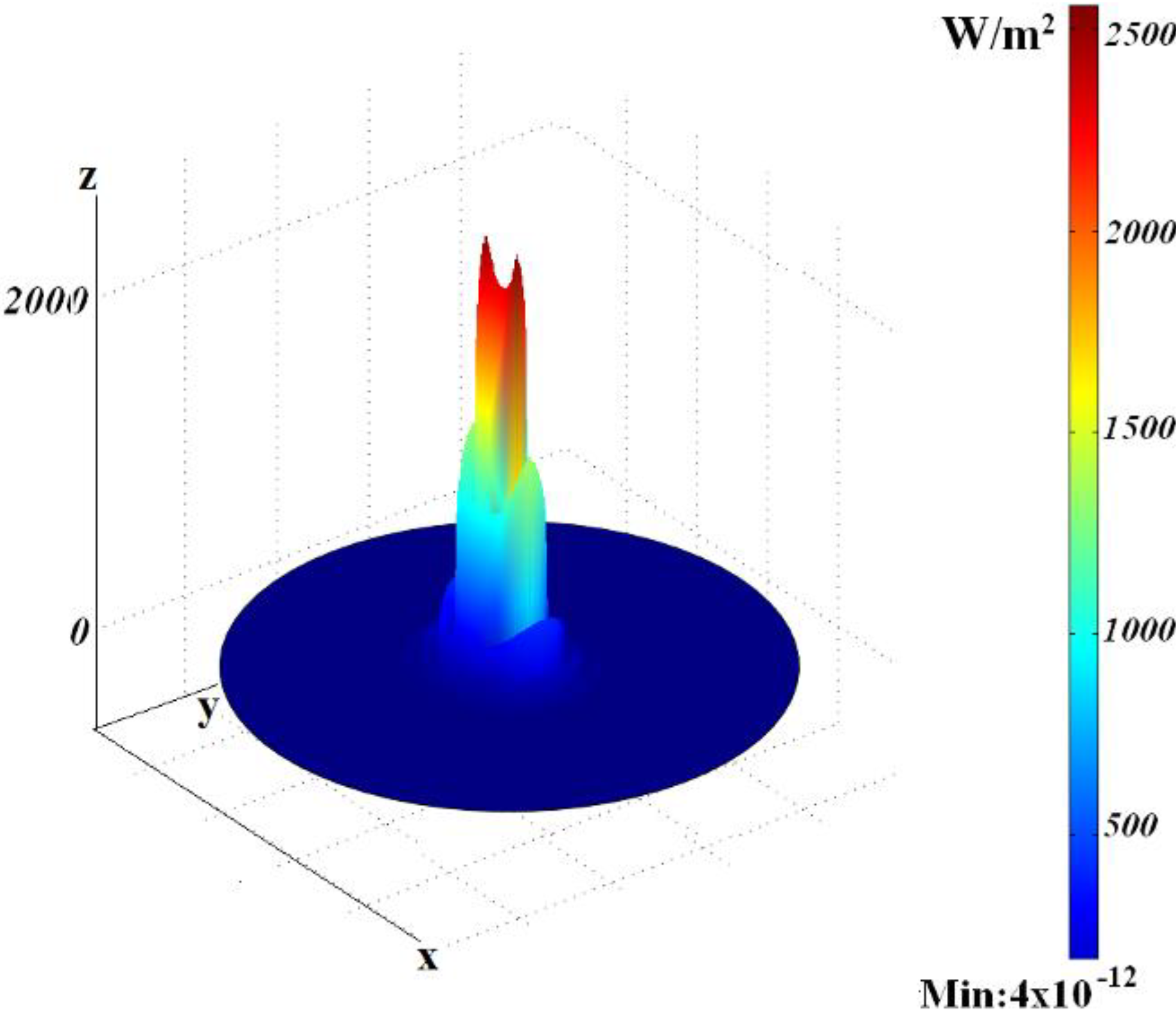
3. Coaxials with Elliptic-Type Central Rods
3.1. Field Distribution for Eigenmodes

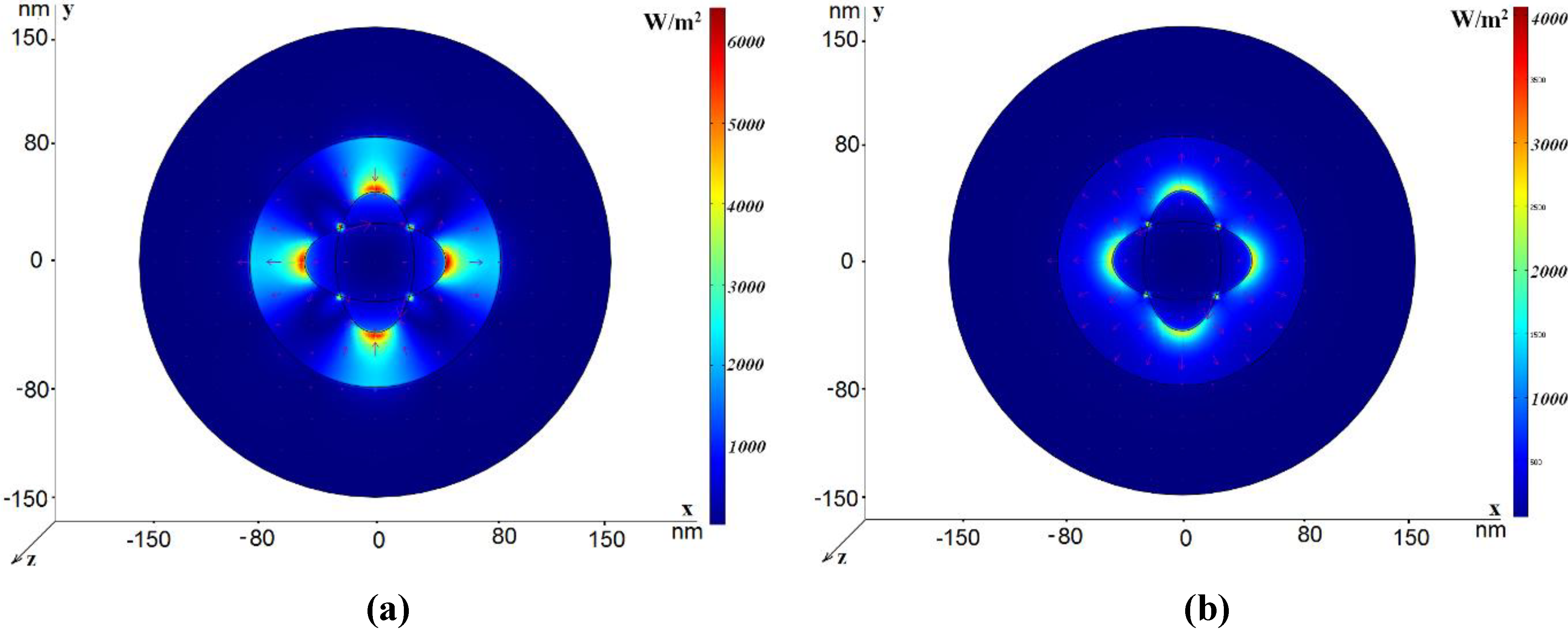

3.2. Excitation by a Dipole
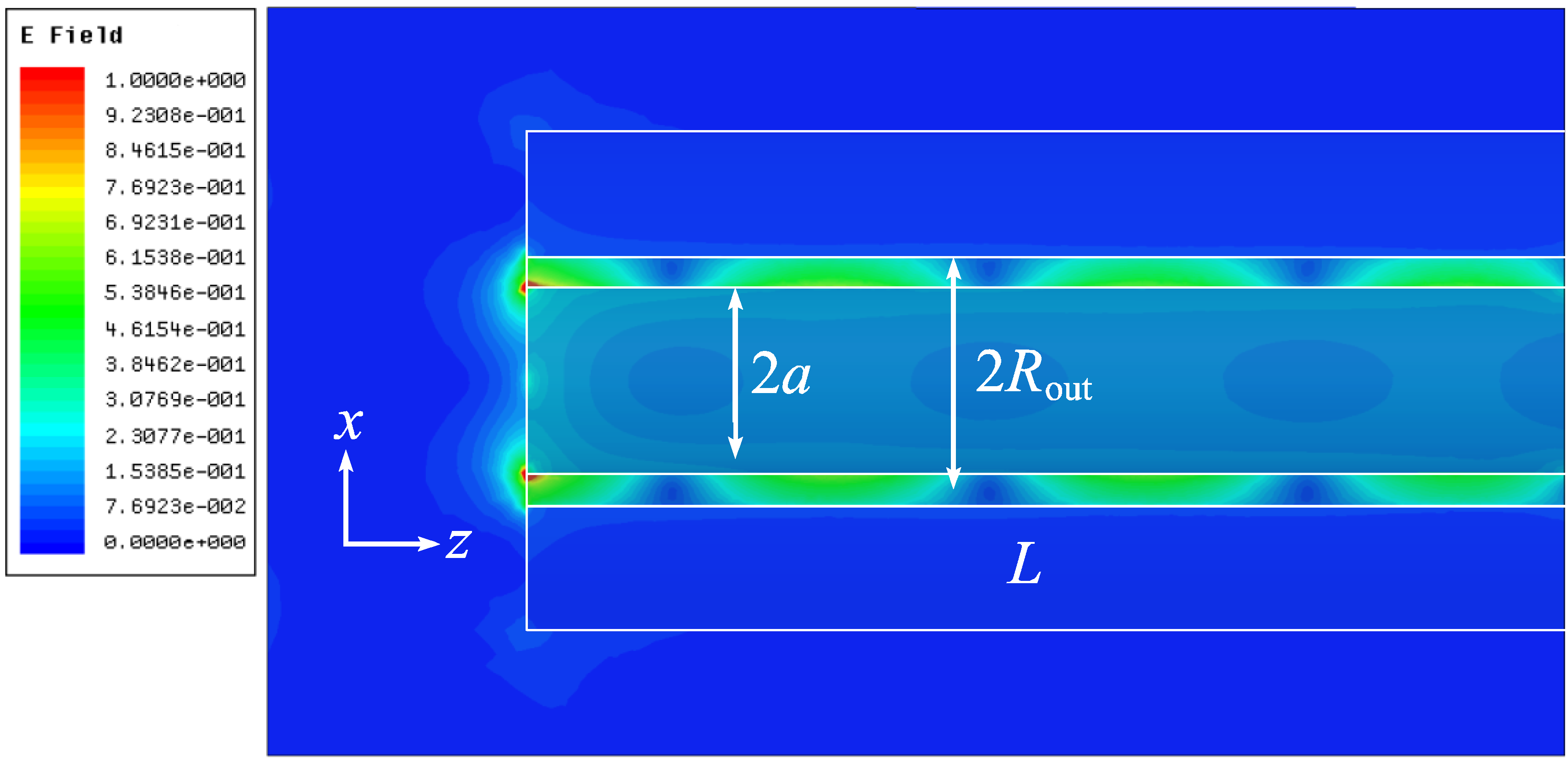
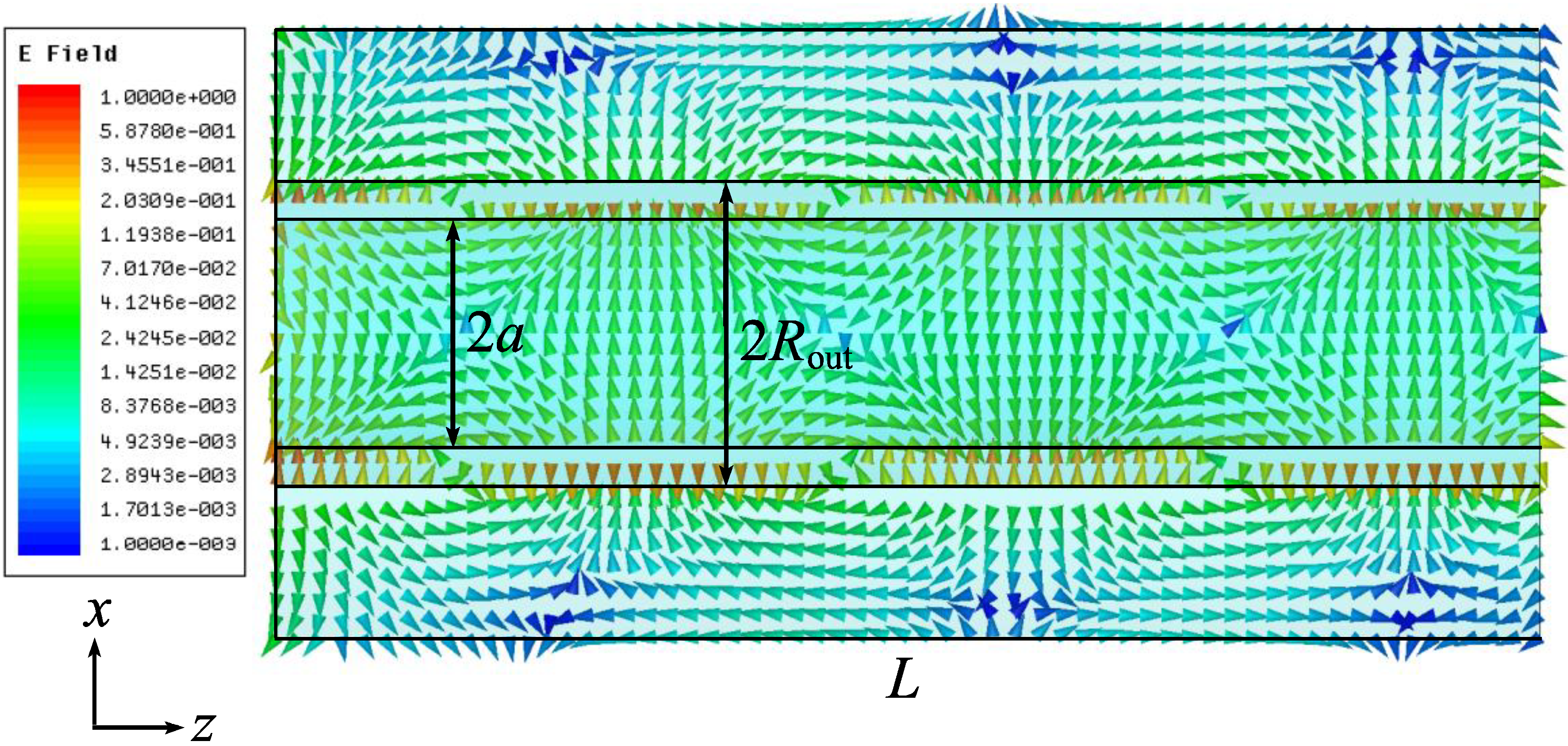
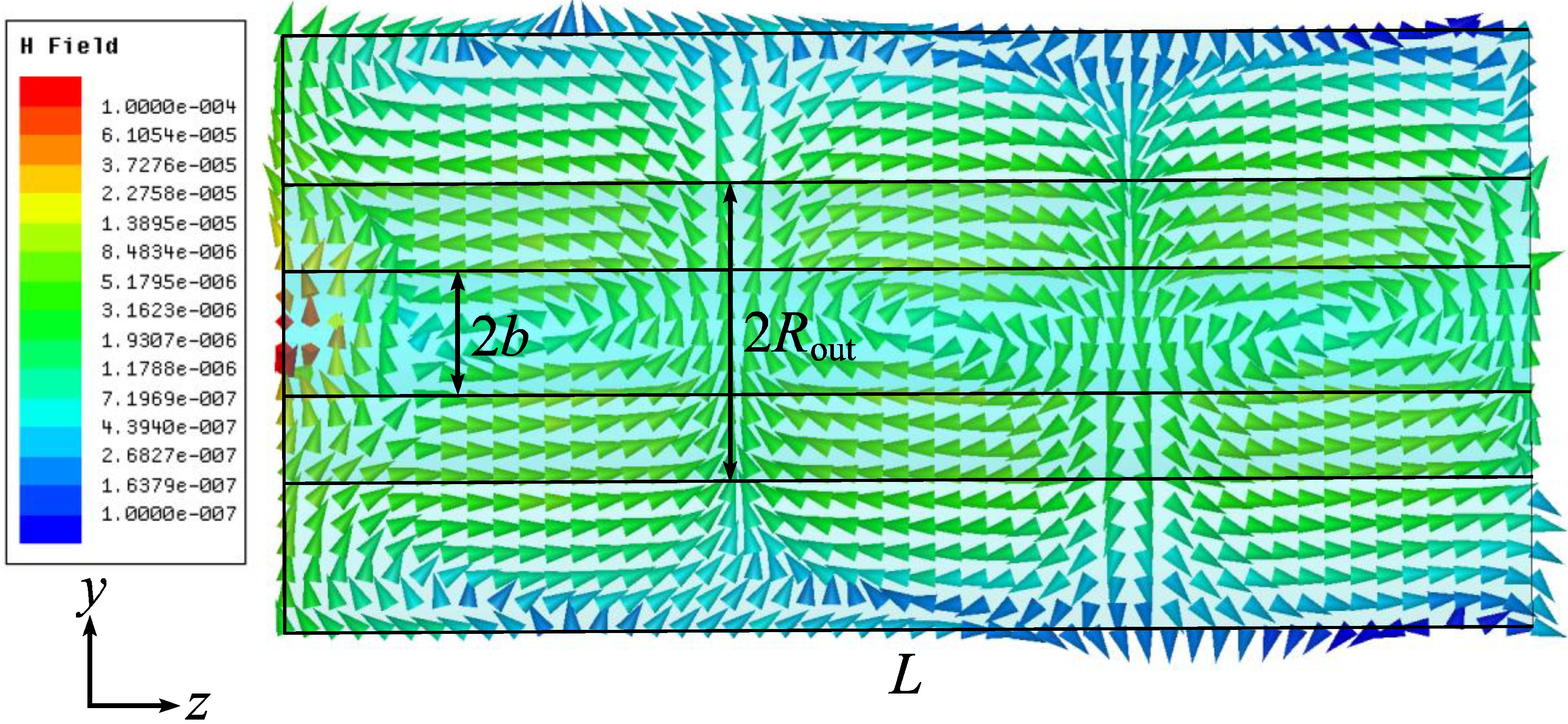
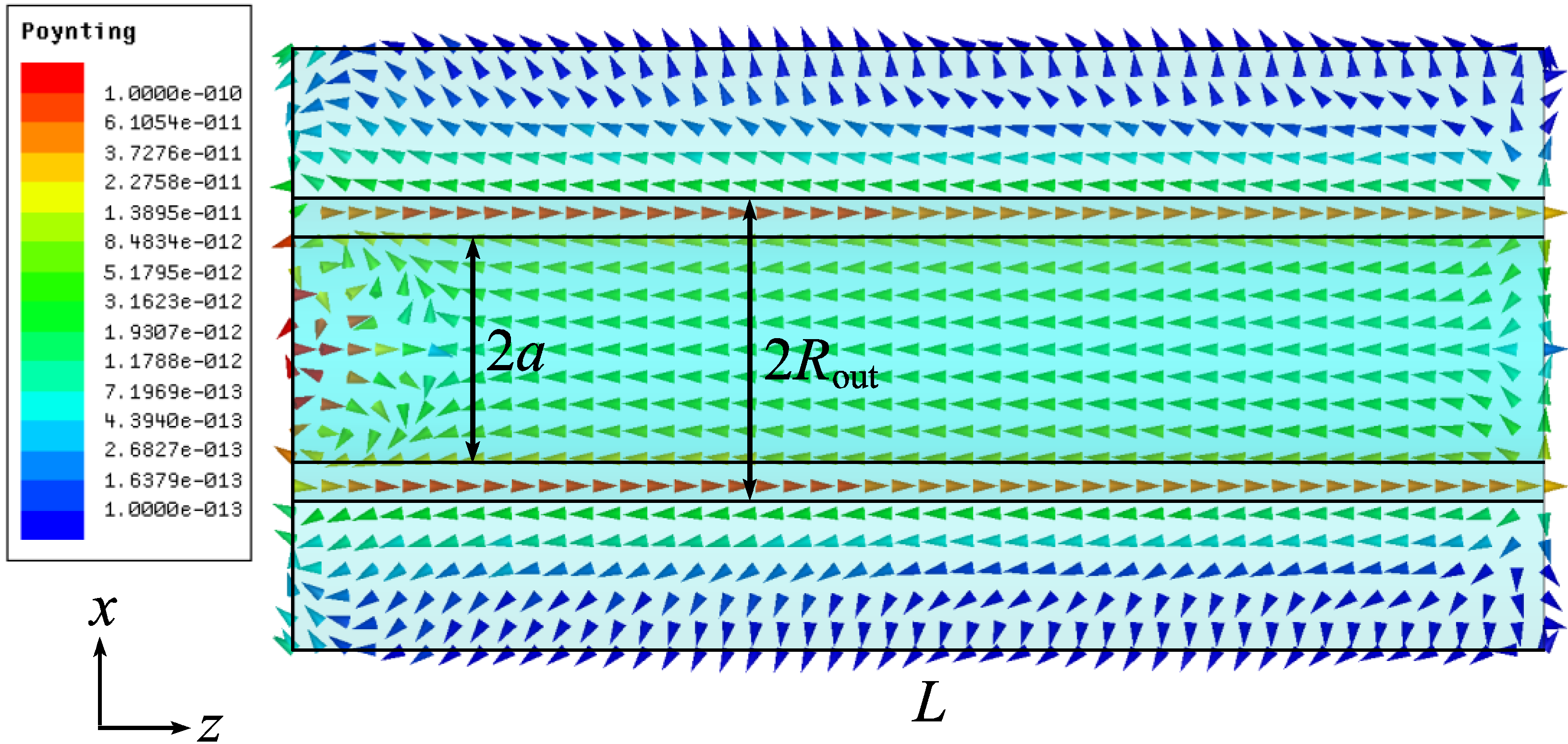

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Berini, P. Plasmon-polariton modes guided by a metal film of finite width. Opt. Lett. 1999, 24, 1011–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berini, P. Plasmon-polariton waves guided by thin lossy metal films of finite width: Bound modes of symmetric structures. Phys. Rev. 2000, B 61, 10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, W.L.; Dereux, W.L.; Ebbesen, T.W. Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 2003, 424, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenn, J.R.; Lamprecht, B.; Ditlbacher, H.; Schider, G.; Salerno, M.; Leitner, A.; Aussenegg, F.R. Non diffraction limited light transport by gold nanowires. Europhys. Lett. 2002, 60, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrter, U.; Dereux, A. Surface plasmon polaritons on metal cylinders with dielectric core. Phys. Rev. 2001, B 64, 125420–125429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltasseva, A.; Volkov, V.S.; Nielsen, R.B.; Moreno, E.; Rodrigo, S.G.; Bozhevolnyi, S.I. Triangular metal wedges for subwavelength plasmon-polariton guiding at telecom wavelengths. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 5252–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigenbaum, E.; Orenstein, M. Plasmonic coaxial nano-cavities and waveguides. In Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of the IEEE, Montreal, Canada, 29 October–2 November 2006; Volume 260, pp. 260–261.
- Baida, F.I.; Belkhir, A.; Van Labeke, D.; Lamrous, O. Subwavelength metallic coaxial waveguides in the optical range: Role of the plasmonic modes. Phys. Rev. 2006, B 74, 205419. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, X.; Kempa, K. TEM-like optical mode of a coaxial nanowaveguide. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 1758–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alegret, J.; Johansson, P.; Käll, M. Green’s tensor calculations of plasmon resonances of single holes and hole pairs in thin gold films. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Liu, X. Mechanism of the superenhanced light transmission through 2D subwavelength coaxial hole arrays. Phys. Lett. A 2005, 344, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waele, R.; Burgos, S.P.; Polman, A.; Atwater, H.A. Plasmon dispersion in coaxial waveguides from single-cavity optical transmission measurements. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2832–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baida, F.I. Enhanced transmission through subwavelength metallic coaxial apertures by excitation of the TEM mode. Appl. Phys. B 2007, 89, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempa, K.; Wang, X.; Ren, Z.F.; Naughton, M.J. Discretely guided electromagnetic effective medium. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 043114–043116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baida, F.I.; Poujet, Y.; Salvi, J.; Van Labeke, D.; Guizal, B. Extraordinary transmission beyond the cut-off through sub-λ annular aperture arrays. Opt. Comm. 2009, 282, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Labeke, D.; Gerard, D.; Guizal, B.; Baida, F.I.; Li, L. An angle-independent Frequency Selective Surface in the optical range. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 11945–11951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baida, F.I.; Van Labeke, D. Three-dimensional structures for enhanced transmission through a metallic film: Annular aperture arrays. Phys. Rev. 2003, B 67, 155314–155320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordons, S.M.; Roberts, A. Resonance and extraordinary transmission in annular aperture arrays. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 12623–12628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topsakal, E.; Volakis, J.L. Frequency selective volumes for optical spatial filters. IEEE Antenn. Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2004, 3, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloviev, A.; Nefedov, I.; Tretyakov, S. Dual-polarized plasmonic nano-cables. In Proceedings of ICTON 2009, 11th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks, Azores, Portugal, 28 June–2 July 2009.
- Konorov, S.O.; Beloglazov, V.I.; Melnikov, L.A.; Zheltikov, A.M. Waveguide modes of electromagnetic radiation in hollow-core microstructure and photonic-crystal fibers. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2003, 96, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, R. Photonic crystal fibers. Science 2003, 299, 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Z.-X.; Wang, A.C.-L.; Flattery, J.; Kornreich, P. Metal cylinder nano scale photonic crystal fiber. In Proceedings of SPIE, Ottawa, Canada, 4 June 2007; Volume 6796, pp. 679610:1–679610:8.
- Sempere, L.N.P.; Schmidt, M.A.; Tyagi, H.K.; Poulton, C.G.; Russell, P.S.J. Metal nanowire arrays in photonic crystal fibers. In Proceedings of IEEE/LEOS Winter Topical Meeting Series, Sorrento, Italy, 14–16 January 2008; pp. 206–207.
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozina, O.; Nefedov, I.; Melnikov, L.; Karilainen, A. Plasmonic Coaxial Waveguides with Complex Shapes of Cross-Sections. Materials 2011, 4, 104-116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4010104
Kozina O, Nefedov I, Melnikov L, Karilainen A. Plasmonic Coaxial Waveguides with Complex Shapes of Cross-Sections. Materials. 2011; 4(1):104-116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4010104
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozina, Olga, Igor Nefedov, Leonid Melnikov, and Antti Karilainen. 2011. "Plasmonic Coaxial Waveguides with Complex Shapes of Cross-Sections" Materials 4, no. 1: 104-116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4010104



