Phaeoviral Infections Are Present in Macrocystis, Ecklonia and Undaria (Laminariales) and Are Influenced by Wave Exposure in Ectocarpales
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and DNA Extraction
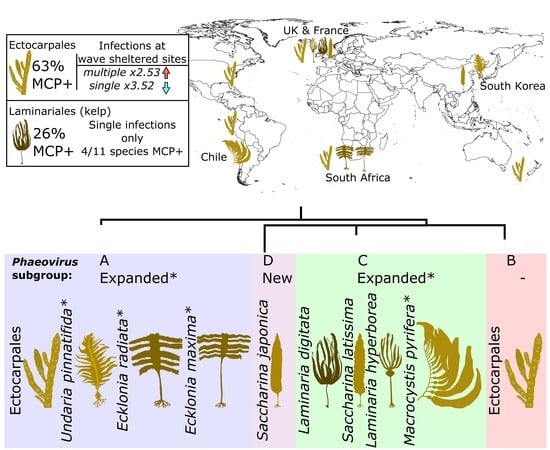
2.2. Map of Phaeoviral Prevalence
2.3. PCR, Sequencing, Real-Time PCR and High Resolution Melt (HRM) Analysis
2.4. Association Analyses
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis and Tree Construction
3. Results
3.1. Phaeoviral Prevalence in the Laminariales
3.2. Phylogeny of Phaeoviruses Including Novel Kelp MCPs
3.3. Phylogeny of Phaeoviruses Including MCP of Other Phycodnaviruses and Mimiviruses
3.4. Phaeoviral MCP from S. japonica
3.5. Phaeoviral Prevalence in Ectocarpales
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grattepanche, J.D.; Walker, L.M.; Ott, B.M.; Paim Pinto, D.L.; Delwiche, C.F.; Lane, C.E.; Katz, L.A. Microbial diversity in the eukaryotic SAR clade: Illuminating the darkness between morphology and molecular data. BioEssays 2018, 40, 1700198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cock, J.M.; Sterck, L.; Rouzé, P.; Scornet, D.; Allen, A.E.; Amoutzias, G.; Anthouard, V.; Artiguenave, F.; Aury, J.-M.; Badger, J.H.; et al. The Ectocarpus genome and the independent evolution of multicellularity in brown algae. Nature 2010, 465, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cock, J.M.; Coelho, S.M.; Brownlee, C.; Taylor, A.R. The Ectocarpus genome sequence: Insights into brown algal biology and the evolutionary diversity of the eukaryotes. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, H.; Hanyuda, T.; Draisma, S.G.A.; Wilce, R.T.; Andersen, R.A. Molecular phylogeny of two unusual brown algae, Phaeostrophion irregulare and Platysiphon Glacialis, proposal of the Stschapoviales ord. nov. and Platysiphonaceae fam. nov., and a re-examination of divergence times for brown algal orders. J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.F.; Marie, D.; Scornet, D.; Kloareg, B.; Cock, J.M. Proposal of Ectocarpus siliculosus (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae) as a model organism for brown algal genetics and genomics. J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steneck, R.; Graham, M.H.; Bourque, B.J.; Corbett, D.; Erlandson, J.M. Kelp forest ecosystems: Biodiversity, stability, resilience and future. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 436–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, P.K. Ecology of kelp communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1985, 16, 215–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumhansl, K.A.; Okamoto, D.K.; Rassweiler, A.; Novak, M.; Bolton, J.J.; Cavanaugh, K.C.; Connell, S.D.; Johnson, C.R.; Konar, B.; Ling, S.D.; et al. Global patterns of kelp forest change over the past half-century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13785–13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.H.; Kinlan, B.P.; Druehl, L.D.; Garske, L.E.; Banks, S. Deep-water kelp refugia as potential hotspots of tropical marine diversity and productivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16576–16580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mann, H.K. Seaweeds: Their productivity and strategy for growth. Science 1973, 182, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, D.C.; Rassweiler, A.R.; Arkema, K.K. Biomass rather than growth rate determines variation in net primary production by giant kelp. Ecology 2008, 89, 2493–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, R.H.; Branch, G.M.; Eekhout, S. Maintenance of an exceptional intertidal grazer biomass in South Africa: Subsidy by subtidal kelps. Ecology 1995, 76, 2314–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, H.; Norderhaug, K.M.; Fredriksen, S. Macrophytes as habitat for fauna. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 396, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclerc, J.C.; Riera, P.; Leroux, C.; Lévêque, L.; Davoult, D. Temporal variation in organic matter supply in kelp forests: Linking structure to trophic functioning. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 494, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, R.; Field, J.; Griffiths, C. Energy balance and significance of microorganisms in a kelp bed community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1982, 8, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norderhaug, K.M.; Christie, H.; Fossô, J.H.O.; Fredriksen, S.P.; Fosså, J.H.; Fredriksen, S.P.; Norderhaug, K.M.; Fredriksen, S.P. Fish-macrofauna interactions in a kelp (Laminaria hyperborea) forest. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, K.C.; Anderson, T.W. Consequences of habitat disturbance and recovery to recruitment and the abundance of kelp forest fishes. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2010, 386, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teagle, H.; Hawkins, S.J.; Moore, P.J.; Smale, D.A. The role of kelp species as biogenic habitat formers in coastal marine ecosystems. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2017, 492, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Løvås, S.M.; Tørum, A. Effect of the kelp Laminaria hyperborea upon sand dune erosion and water particle velocities. Coast. Eng. 2001, 44, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, G.A.; Winant, C.D. Effect of a kelp forest on coastal currents. Cont. Shelf Res. 1983, 2, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.M.B.; Bayliss-Smith, T.P. Kelp-plucking: Coastal erosion facilitated by bull-kelp Durvillaea antarctica at subantarctic Macquarie Island. Antarct. Sci. 1998, 10, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbee-Dexter, K.; Scheibling, R.E. Hurricane-mediated defoliation of kelp beds and pulsed delivery of kelp detritus to offshore sedimentary habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 455, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krumhansl, K.A.; Scheibling, R.E. Production and fate of kelp detritus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 467, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, M.I.; Fredriksen, S.; Christie, H. The impact of the kelp (Laminaria hyperborea ) forest on the organic matter content in sediment of the west coast of Norway. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D.; Williams, P.I.; Najera, J.; Whitehead, J.D.; Flynn, M.J.; Taylor, J.W.; Liu, D.; Darbyshire, E.; Carpenter, L.J.; Chance, R.; et al. Iodine observed in new particle formation events in the Arctic atmosphere during ACCACIA. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5599–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küpper, F.C.; Carpenter, L.J.; McFiggans, G.B.; Palmer, C.J.; Waite, T.J.; Boneberg, E.-M.; Woitsch, S.; Weiller, M.; Abela, R.; Grolimund, D.; et al. Iodide accumulation provides kelp with an inorganic antioxidant impacting atmospheric chemistry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6954–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nitschke, U.; Dixneuf, S.; Schmid, M.; Ruth, A.A.; Stengel, D.B. Contribution of living and degrading kelp to coastal iodine fluxes. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 1727–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamersley, M.R.; Sohm, J.A.; Burns, J.A.; Capone, D.G. Nitrogen fixation associated with the decomposition of the giant kelp Macrocystis pyrifera. Aquat. Bot. 2015, 125, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndes, G.A.; Lavery, P.S.; Doropoulos, C. Dual processes for cross-boundary subsidies: Incorporation of nutrients from reef-derived kelp into a seagrass ecosystem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 445, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Losada, I.J.; Hendriks, I.E.; Mazarrasa, I.; Marbà, N. The role of coastal plant communities for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinho, G.S.; Holdt, S.L.; Birkeland, M.J.; Angelidaki, I. Commercial cultivation and bioremediation potential of sugar kelp, Saccharina latissima, in Danish waters. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, N.J.; Austen, M.C.; Mangi, S.C.; Townsend, M. Economic valuation for the conservation of marine biodiversity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásquez, J.A.; Zuñiga, S.; Tala, F.; Piaget, N.; Rodríguez, D.C.; Vega, J.M.A. Economic valuation of kelp forests in northern Chile: Values of goods and services of the ecosystem. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.; Wernberg, T.; Connell, S.D.; Hobday, A.J.; Johnson, C.R.; Poloczanska, E.S. The “Great Southern Reef”: Social, ecological and economic value of Australia’ s neglected kelp forests. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2015, 67, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, A.H.; Camus, C.; Infante, J.; Neori, A.; Israel, Á.; Hernández-González, M.C.; Pereda, S.V.; Gomez-Pinchetti, J.L.; Golberg, A.; Tadmor-Shalev, N.; Critchley, A.T. Seaweed production: Overview of the global state of exploitation, farming and emerging research activity. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasahati, P.; Saffron, C.M.; Woo, H.C.; Liu, J.J. Potential of brown algae for sustainable electricity production through anaerobic digestion. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 135, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerregaard, R. Seaweed Aquaculture for Food Security, Income Generation and Environmental Health Seaweed Aquaculture for Food Security, Income Generation and Environmental Health in Tropical Developing Countries; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, A.J. Medicinal and pharmaceutical uses of seaweed natural products: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2004, 16, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Global Aquaculture Production. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fishery/statistics/global-aquaculture-production/query/en (accessed on 5 June 2018).
- Stévant, P.; Rebours, C.; Chapman, A. Seaweed aquaculture in Norway: Recent industrial developments and future perspectives. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1373–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.; Watson, L. Cultivating Laminaria digitata. Aquac. Explain. 2011, 26, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, C.; Infante, J.; Buschmann, A.H. Overview of 3 year precommercial seafarming of Macrocystis pyrifera along the Chilean coast. Rev. Aquac. 2016, 2014, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.K.; Sondak, C.F.A.; Beardall, J. The future of seaweed aquaculture in a rapidly changing world. Eur. J. Phycol. 2017, 52, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smale, D.A.; Burrows, M.T.; Moore, P.; O’Connor, N.; Hawkins, S.J. Threats and knowledge gaps for ecosystem services provided by kelp forests: A northeast Atlantic perspective. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 4016–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.H.; Harder, T.; Nielsen, S.; Kjelleberg, S.; Steinberg, P.D. Climate change and disease: Bleaching of a chemically defended seaweed. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 2958–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, S.; Fernandes, N.D.; Kumar, V.; Gardiner, M.; Thomas, T. Bacterial pathogens, virulence mechanism and host defence in marine macroalgae. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Zozaya-Valdes, E.; Kjelleberg, S.; Thomas, T.; Egan, S. Multiple opportunistic pathogens can cause a bleaching disease in the red seaweed Delisea pulchra. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 3962–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gachon, C.M.M.; Sime-Ngando, T.; Strittmatter, M.; Chambouvet, A.; Kim, G.H. Algal diseases: Spotlight on a black box. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottier-Cook, E.J.; Nagabhatla, N.; Badis, Y.; Campbell, M.L.; Chopin, T.; Dai, W.; Fang, J.; He, P.; Hewitt, C.L.; Kim, G.H.; et al. Safeguarding the Future of the Global Seaweed Aquaculture Industry; United Nations University (INWEH) and Scottish Association for Marine Science Policy Brief: Hamilton, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, D.C. More to Phaeovirus infections than first meets the eye. Perspect. Phycol. 2015, 2, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, D.C. Viruses of Seaweeds. In Studies in Viral Ecology: Microbial and Botanical Host Systems; Hurst, C.J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 204–215. ISBN 9780470623961. [Google Scholar]
- Delaroque, N.; Müller, D.G.; Bothe, G.; Pohl, T.; Knippers, R.; Boland, W.; Muller, D.G.; Bothe, G.; Pohl, T.; Knippers, R.; Boland, W. The complete DNA sequence of the Ectocarpus siliculosus virus EsV-1 genome. Virology 2001, 287, 112–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, D.C.; Park, Y.; Yoon, H.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, S.W.; Meints, R.H.; Ivey, R.G.; Choi, T.J. Genomic analysis of the smallest giant virus—Feldmannia sp. virus 158. Virology 2009, 384, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkowitz, E.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Orton, R.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Smith, D.B. Virus taxonomy: The database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D708–D717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, D.A.; Stevens, K.; Peters, A.F.; Bond, P.; Harper, G.M.; Brownlee, C.; Brown, M.T.; Schroeder, D.C. Phaeoviruses discovered in kelp (Laminariales). ISME J. 2017, 11, 2869–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delaroque, N.; Maier, L.; Knippers, R.; Müller, D.G. Persistent virus integration into the genome of its algal host, Ectocarpus siliculosus (Phaeophyceae). J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bräutigam, M.; Klein, M.; Knippers, R.; Müller, D.G. Inheritance and meiotic elimination of a virus genome in the host Ectocarpus siliculosus (Phaeophyceae). J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, I.; Müller, D.G.; Katsaros, C. Entry of the DNA virus, Ectocarpus fasciculatus virus type 1 (Phycodnaviridae), into host cell cytosol and nucleus. Phycol. Res. 2002, 50, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, I.; Wolf, S.; Delaroque, N.; Müller, D.G.; Kawai, H. A DNA virus infecting the marine brown alga Pilayella littoralis (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae) in culture. Eur. J. Phycol. 1998, 33, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, D.G.; Kawai, H.; Stache, B.; Lanka, S. A virus infection in the marine brown alga Ectocarpus siliculosus (Phaeophyceae). Bot. Acta 1990, 103, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.G.; Brautigam, M.; Knippers, R. Virus infection and persistence of foreign DNA in the marine brown alga Feldmannia simplex (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae). Phycologia 1996, 35, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.G.; Parodi, E. Transfer of a marine DNA virus from Ectocarpus to Feldmannia (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae): Aberrant symptoms and restitution of the host. Protoplasma 1993, 175, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.G.; Sengco, M.; Wolf, S.; Bräutigam, M.; Schmid, C.E.; Kapp, M.; Knippers, R. Comparison of two DNA viruses infecting the marine brown algae Ectocarpus siliculosus and E. fasciculatus. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 2329–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cassar, S.C.; Zhang, D.; Gopalakrishnan, M. A novel potassium channel encoded by Ectocarpus siliculosus virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 326, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaroque, N.; Boland, W.; Müller, D.G.; Knippers, R. Comparisons of two large phaeoviral genomes and evolutionary implications. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 57, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, K.; Weynberg, K.; Bellas, C.; Brown, S.; Brownlee, C.; Brown, M.T.; Schroeder, D.C. A novel evolutionary strategy revealed in the phaeoviruses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sengco, M.R.; Bräutigam, M.; Kapp, M.; Müller, D.G. Detection of virus DNA in Ectocarpus siliculosus and E. fasciculatus (Phaeophyceae) from various geographic areas. Eur. J. Phycol. 1996, 31, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, D.G.; Westermeier, R.; Morales, J.; Reina, G.G.; del Campo, E.; Correa, J.A.; Rometscha, E. Massive prevalence of viral DNA in Ectocarpus (Phaeophyceae, Ectocarpales) from two habitats in the North Atlantic and South Pacific. Bot. Mar. 2000, 43, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, L.M.; Lewis, G.D.; Pearson, M.N. Virus-like particles associated with dieback symptoms in the brown alga Ecklonia radiata. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1997, 30, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallot-Lavallée, L.; Blanc, G. A glimpse of nucleo-cytoplasmic large DNA virus biodiversity through the eukaryotic genomics window. Viruses 2017, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, N.; Zhang, X.; Miao, M.; Fan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; et al. Saccharina genomes provide novel insight into kelp biology. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beattie, D.; Lachnit, T.; Dinsdale, E.; Thomas, T.; Steinberg, P.D. Novel ssDNA viruses detected in the virome of bleached, habitat-forming kelp Ecklonia radiata. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Kawai, T.; Nakaoka, M.; Yotsukura, N. Effective DNA extraction method for fragment analysis using capillary sequencer of the kelp, Saccharina. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, M.D.; Mattio, L.; Wernberg, T.; Anderson, R.J.; Uwai, S.; Mohring, M.B.; Bolton, J.J. A molecular investigation of the genus Ecklonia (Phaeophyceae, Laminariales) with special focus on the Southern Hemisphere. J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, M.D.; Mattio, L.; Anderson, R.J.; Bolton, J.J. A phylogeographic investigation of the kelp genus Laminaria (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae), with emphasis on the South Atlantic Ocean. J. Phycol. 2017, 53, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, S.M.; Scornet, D.; Dartevelle, L.; Peters, A.F.; Cock, J.M. How to cultivate Ectocarpus. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.F.; van Wijk, S.J.; Cho, G.Y.; Scornet, D.; Hanyuda, T.; Kawai, H.; Schroeder, D.C.; Cock, J.M.; Boo, S.M. Reinstatement of Ectocarpus crouaniorum Thuret in Le Jolis as a third common species of Ectocarpus (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae) in Western Europe, and its phenology at Roscoff, Brittany. Phycol. Res. 2010, 58, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrier, B.; Coelho, S.M.; Le Bail, A.; Tonon, T.; Michel, G.; Potin, P.; Kloareg, B.; Boyen, C.; Peters, A.F.; Cock, J.M. Development and physiology of the brown alga Ectocarpus siliculosus: Two centuries of research. New Phytol. 2008, 177, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QGIS. QGIS Geographic Information System; Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project. Available online: https://qgis.org/en/site/ (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- Albert, M.; Andler, J.; Bah, T.; Barbry-Blot, P.; Barraud, J.F.; Baxter, B. Inkscape 0.92. Available online: https://inkscape.org/en/ (accessed on 1 April 2018).
- Al-Kandari, M.A.; Highfield, A.C.; Hall, M.J.; Hayes, P.; Schroeder, D.C. Molecular tools separate harmful algal bloom species, Karenia mikimotoi, from different geographical regions into distinct sub-groups. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Mrbayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Scornavacca, C. Dendroscope 3: An interactive tool for rooted phylogenetic trees and networks. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, T.; Harris, S.R.; Berriman, M.; Parkhill, J.; McQuillan, J.A. Artemis: An integrated platform for visualization and analysis of high-throughput sequence-based experimental data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. Algaebase. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- Yutin, N.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; Koonin, E.V. Mimiviridae: Clusters of orthologous genes, reconstruction of gene repertoire evolution and proposed expansion of the giant virus family. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, J.B.; Larsen, A.; Bratbak, G.; Sandaa, R.A. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the Phycodnaviridae virus family, using amplified fragments of the major capsid protein gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3048–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starko, S.; Boo, G.H.; Martone, P.T.; Lindstrom, S.C. A molecular investigation of Saccharina sessilis from the Aleutian Islands reveals a species complex, necessitating the new combination Saccharina subsessilis. Algae 2018, 33, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, J.; Sieracki, M.E.; Molestina, R.; Keeling, P.; Massana, R.; Ruiz-Trillo, I. The others: Our biased perspective of eukaryotic genomes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiewsakun, P.; Katzourakis, A. Endogenous viruses: Connecting recent and ancient viral evolution. Virology 2015, 479–480, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, J.J.; Anderson, R.; Smit, A.; Rothman, M. South African kelp moving eastwards: The discovery of Ecklonia maxima (Osbeck) Papenfuss at De Hoop Nature Reserve on the south coast of South Africa. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 34, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filée, J. Route of NCLDV evolution: The genomic accordion. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raybaud, V.; Beaugrand, G.; Goberville, E.; Delebecq, G.; Destombe, C.; Valero, M.; Davoult, D.; Morin, P.; Gevaert, F. Decline in Kelp in West Europe and Climate. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernberg, T.; Thomsen, M.S.; Tuya, F.; Kendrick, G.A.; Staehr, P.A.; Toohey, B.D. Decreasing resilience of kelp beds along a latitudinal temperature gradient: Potential implications for a warmer future. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2010, 13, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loureiro, R.; Gachon, C.M.M.; Rebours, C. Seaweed cultivation: Potential and challenges of crop domestication at an unprecedented pace. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.A.; Kurath, G.; Brito, I.L.; Purcell, M.K.; Read, A.F.; Winton, J.R.; Wargo, A.R. Potential drivers of virulence evolution in aquaculture. Evol. Appl. 2016, 9, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Epstein, G.; Smale, D.A. Undaria pinnatifida: A case study to highlight challenges in marine invasion ecology and management. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 8624–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smale, D.A.; Wernberg, T.; Yunnie, A.L.E.; Vance, T. The rise of Laminaria ochroleuca in the Western English Channel (UK) and comparisons with its competitor and assemblage dominant Laminaria hyperborea. Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.E.; Power, A.O. Release of invasive plants from fungal and viral pathogens. Nature 2003, 421, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borer, E.T.; Hosseini, P.R.; Seabloom, E.W.; Dobson, A.P. Pathogen-induced reversal of native dominance in a grassland community. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5473–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robledo, D.R.; Sosa, P. a.; Garcia-Reina, G.; Müller, D.G. Photosynthetic performance of healthy and virus-infected Feldmannia irregularis and F. simplex (Phaeophyceae). Eur. J. Phycol. 1994, 29, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Infection Type | Sheltered | Exposed | Total Number of Isolates |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Ectocarpus siliculosus | |||
| None | 169 (162.0) | 5 (12) | 174 |
| Subgroup A only | 139 (147.1) | 19 (10.9) | 158 |
| Subgroup B only | 12 (11.2) | 0 (0.8) | 12 |
| Both | 72 (71.7) | 5 (5.3) | 77 |
| Total number of isolates | 392 | 29 | 421 |
| (b) Ectocarpus crouaniorum | |||
| None | 43 (27.3) | 7 (22.7) | 50 |
| Subgroup A only | 46 (63.9) | 71 (53.1) | 117 |
| Subgroup B only | 4 (3.8) | 3 (3.2) | 7 |
| Both | 25 (23.0) | 17 (19.0) | 42 |
| Total number of isolates | 118 | 98 | 216 |
| (c) Ectocarpus fasciculatus | |||
| None | 69 (58.8) | 46 (56.2) | 115 |
| Subgroup A only | 13 (14.3) | 15 (13.7) | 28 |
| Subgroup B only | 1 (9.7) | 18 (9.3) | 19 |
| Both | 9 (9.2) | 9 (8.8) | 18 |
| Total number of isolates | 92 | 88 | 180 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McKeown, D.A.; Schroeder, J.L.; Stevens, K.; Peters, A.F.; Sáez, C.A.; Park, J.; Rothman, M.D.; Bolton, J.J.; Brown, M.T.; Schroeder, D.C. Phaeoviral Infections Are Present in Macrocystis, Ecklonia and Undaria (Laminariales) and Are Influenced by Wave Exposure in Ectocarpales. Viruses 2018, 10, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080410
McKeown DA, Schroeder JL, Stevens K, Peters AF, Sáez CA, Park J, Rothman MD, Bolton JJ, Brown MT, Schroeder DC. Phaeoviral Infections Are Present in Macrocystis, Ecklonia and Undaria (Laminariales) and Are Influenced by Wave Exposure in Ectocarpales. Viruses. 2018; 10(8):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080410
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcKeown, Dean A., Joanna L. Schroeder, Kim Stevens, Akira F. Peters, Claudio A. Sáez, Jihae Park, Mark D. Rothman, John J. Bolton, Murray T. Brown, and Declan C. Schroeder. 2018. "Phaeoviral Infections Are Present in Macrocystis, Ecklonia and Undaria (Laminariales) and Are Influenced by Wave Exposure in Ectocarpales" Viruses 10, no. 8: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080410
APA StyleMcKeown, D. A., Schroeder, J. L., Stevens, K., Peters, A. F., Sáez, C. A., Park, J., Rothman, M. D., Bolton, J. J., Brown, M. T., & Schroeder, D. C. (2018). Phaeoviral Infections Are Present in Macrocystis, Ecklonia and Undaria (Laminariales) and Are Influenced by Wave Exposure in Ectocarpales. Viruses, 10(8), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10080410