Phylogenetic Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Infections in a Large Belgian Cohort Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Full-Length Genomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Sequences
2.3. Phylogenetic Construction
2.4. Transmission Cluster Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Sequencing Results
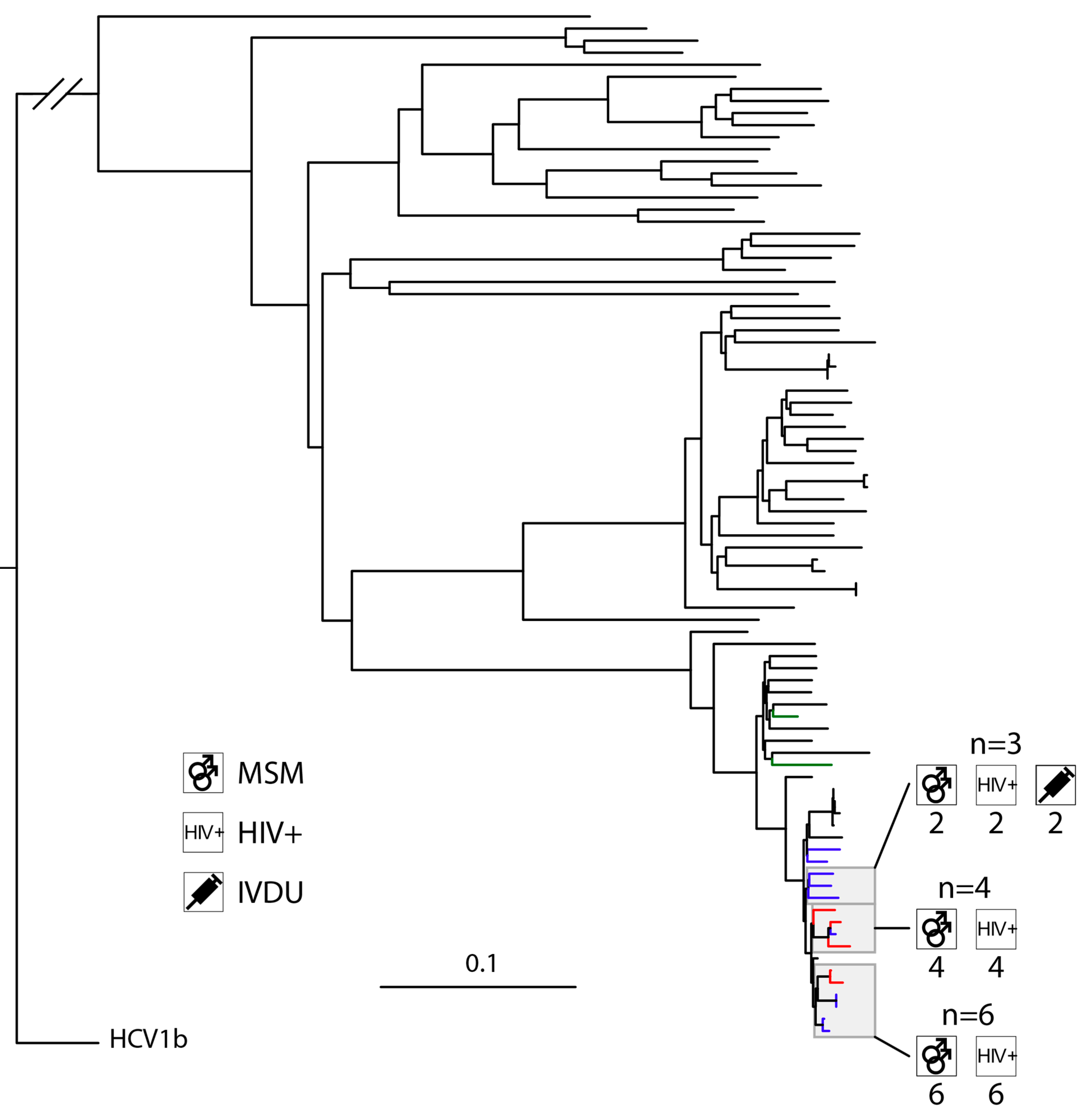
3.3. High Levels of Clustering in HIV-Positive MSM with HCV1a and 4d Infections
4. Discussion
4.1. The Spread of HCV1b Has Largely Been Suppressed
4.2. HCV3a Is Highly Prevalent in an Undersampled PWID Community
4.3. HCV Networks in Heterosexual PWID and MSM PWID Appear to Be Distinct
4.4. HCV4d Has Seen Substantial Transmission in HIV-Positive MSM
4.5. HIV-Positive MSM Transmit HCV across Municipal Borders
4.6. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization HCV Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 11 August 2022).
- Kuo, G.; Choo, Q.L.; Alter, H.J.; Gitnick, G.L.; Redeker, A.G.; Purcell, R.H.; Miyamura, T.; Dienstag, J.L.; Alter, M.J.; Stevens, C.E.; et al. An Assay for Circulating Antibodies to a Major Etiologic Virus of Human Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis. Science 1989, 244, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busschots, D.; Kremer, C.; Koc, Ö.M.; Heyens, L.; Bielen, R.; Apers, L.; Florence, E.; Messiaen, P.; Van Laethem, K.; Van Wijngaerden, E.; et al. The Hepatitis C Cascade of Care in the Belgian HIV Population: One Step Closer to Elimination. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busschots, D.; Kremer, C.; Bielen, R.; Koc, Ö.M.; Heyens, L.; Dercon, E.; Verrando, R.; Windelinckx, T.; Maertens, G.; Bourgeois, S.; et al. Identification and Treatment of Viral Hepatitis C in Persons Who Use Drugs: A Prospective, Multicenter Outreach Study in Flanders, Belgium. Harm. Reduct. J. 2021, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanus, A.T.; Van De Laar, T.J.; Stolte, I.G.; Schinkel, J.; Heijman, T.; Coutinho, R.A.; Prins, M. Hepatitis C Virus Infections among HIV-Infected Men Who Have Sex with Men: An Expanding Epidemic. Aids 2009, 23, F1–F7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falade-Nwulia, O.; Suarez-Cuervo, C.; Nelson, D.R.; Fried, M.W.; Segal, J.B.; Sulkowski, M.S. Oral Direct-Acting Agent Therapy for Hepatitis C Virus Infection: A Systematic Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 166, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poordad, F.; Felizarta, F.; Yao, B.B.; Overcash, J.S.; Hassanein, T.; Agarwal, K.; Gane, E.; Shaw, D.; Waters, M.; Krishnan, P.; et al. Durability of Sustained Virological Response to Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir and Resistance Development: A Long-Term Follow-up Study. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lens, S.; Miralpeix, A.; Gálvez, M.; Martró, E.; González, N.; Rodríguez-Tajes, S.; Mariño, Z.; Saludes, V.; Reyes-Urueña, J.; Majó, X.; et al. HCV Microelimination in Harm Reduction Centres Has Benefits beyond HCV Cure but Is Hampered by High Reinfection Rates. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, C.; Kondili, L.A.; Staiano, L.; Cammarota, S.; Citarella, A.; Aloisio, M.P.; Annunziata, A.; Bernardi, F.F.; D’Avino, A.; D’Orazio, M.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Micro-Elimination Plan in Southern Italy: The “HCV ICEberg” Project. Pathogens 2023, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, M.J.; Kronfli, N.; Cabezas, J.; Sheehan, Y.; Thurairajah, P.H.; Lines, R.; Lloyd, A.R. Hepatitis C Elimination among People Incarcerated in Prisons: Challenges and Recommendations for Action within a Health Systems Framework. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachs, M.; Binter, T.; Chromy, D.; Schalk, H.; Pichler, K.; Bauer, D.; Simbrunner, B.; Hartl, L.; Schmidbauer, C.; Mayer, F.; et al. Outcomes of an HCV Elimination Program Targeting the Viennese MSM Population. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangia, A.; Cotugno, R.; Cocomazzi, G.; Squillante, M.M.; Piazzolla, V. Hepatitis C Virus Micro-Elimination: Where Do We Stand? World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade-Nwulia, O.; Hackman, J.; Mehta, S.H.; McCormick, S.D.; Kirk, G.D.; Sulkowski, M.; Thomas, D.; Latkin, C.; Laeyendecker, O.; Ray, S.C. Factors Associated with Phylogenetic Clustering of Hepatitis C among People Who Inject Drugs in Baltimore. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Liang, Z.; Cai, W.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Hu, F.; Lan, Y. Transmission Networks of Hepatitis C Virus among HIV/HCV-Coinfected Patients in Guangdong, China. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, R.; Lamers, S.L.; Massaccesi, G.; Osburn, W.; Ray, S.C.; Thomas, D.L.; Cox, A.L.; Laeyendecker, O. Complex Patterns of Hepatitis-C Virus Longitudinal Clustering in a High-Risk Population. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 58, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, S.R.; Wertheim, J.O.; Bull, R.A.; Matthews, G.V.; Lamoury, F.M.J.; Scheffler, K.; Hellard, M.; Maher, L.; Dore, G.J.; Lloyd, A.R.; et al. A Molecular Transmission Network of Recent Hepatitis C Infection in People with and without HIV: Implications for Targeted Treatment Strategies. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochstatter, K.R.; Tully, D.C.; Power, K.A.; Koepke, R.; Akhtar, W.Z.; Prieve, A.F.; Whyte, T.; Bean, D.J.; Seal, D.W.; Allen, T.M.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Transmission Clusters in Public Health and Correctional Settings, Wisconsin, USA, 2016–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks-Davis, R.; Daraganova, G.; Aitken, C.; Higgs, P.; Tracy, L.; Bowden, S.; Jenkinson, R.; Rolls, D.; Pattison, P.; Robins, G.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Phylogenetic Clustering Is Associated with the Social-Injecting Network in a Cohort of People Who Inject Drugs. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Table 1—Confirmed HCV Genotypes/Subtypes|ICTV. Available online: https://ictv.global/sg_wiki/flaviviridae/hepacivirus/table1 (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Cuypers, L.; Li, G.; Libin, P.; Piampongsant, S.; Vandamme, A.-M.; Theys, K. Genetic Diversity and Selective Pressure in Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes 1–6: Significance for Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment and Drug Resistance. Viruses 2015, 7, 5018–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuypers, L.; Perez, A.B.; Chueca, N.; Aldamiz-Echevarria, T.; Alados, J.C.; Martinez-Sapina, A.M.; Merino, D.; Pineda, J.A.; Tellez, F.; Espinosa, N.; et al. Relapse or Reinfection after Failing Hepatitis C Direct Acting Antiviral Treatment: Unravelled by Phylogenetic Analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoury, F.M.J.; Jacka, B.; Bartlett, S.; Bull, R.A.; Wong, A.; Amin, J.; Schinkel, J.; Poon, A.F.; Matthews, G.V.; Grebely, J.; et al. The Influence of Hepatitis C Virus Genetic Region on Phylogenetic Clustering Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, E.; Ip, C.L.C.C.; Badhan, A.; Christiansen, M.T.; Adamson, W.; Ansari, M.A.; Bibby, D.; Breuer, J.; Brown, A.; Bowden, R.; et al. Comparison of Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies for Comprehensive Assessment of Full-Length Hepatitis C Viral Genomes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2470–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manso, C.F.; Bibby, D.F.; Lythgow, K.; Mohamed, H.; Myers, R.; Williams, D.; Piorkowska, R.; Chan, Y.T.; Bowden, R.; Ansari, M.A.; et al. Technical Validation of a Hepatitis C Virus Whole Genome Sequencing Assay for Detection of Genotype and Antiviral Resistance in the Clinical Pathway. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Dai, J.; Luo, H.; Jia, M.; Song, Z. Complete Genome Sequencing and Evolutionary Analysis of HCV Subtype 6xg from IDUs in Yunnan, China. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Q.; Shan, Z.; Zhong, H.; Rong, X.; Fu, Y. Complete Genome Sequencing and Evolutionary Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Subtype 6a, Including Strains from Guangdong Province, China. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gededzha, M.P.; Selabe, S.G.; Blackard, J.T.; Kyaw, T.; Mphahlele, M.J. Near Full-Length Genome Analysis of HCV Genotype 5 Strains from South Africa. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, Y.; Hayashida, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kikuchi, Y.; Mizokami, M.; Oka, S.; Gatanaga, H. Full-Genome Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus in Japanese and Non-Japanese Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 in Tokyo. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2019, 80, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, Y.; Hayashida, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Uemura, H.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kikuchi, Y.; Mizokami, M.; Oka, S.; Gatanaga, H. Full-Genome Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus in HIV-Coinfected Hemophiliac Japanese Patients. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopsen, J.; Matthews, G.; Rockstroh, J.; Applegate, T.L.; Bhagani, S.; Rauch, A.; Grebely, J.; Sacks-Davis, R.; Ingiliz, P.; Boesecke, C.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Transmission between Eight High-Income Countries among Men Who Have Sex with Men: A Whole-Genome Analysis. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e622–e631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsall, D.; Ansari, M.A.; Ip, C.; Trebes, A.; Brown, A.; Klenerman, P.; Buck, D.; STOP-HCV Consortium; Piazza, P.; Barnes, E.; et al. Ve-SEQ: Robust, Unbiased Enrichment for Streamlined Detection and Whole-Genome Sequencing of HCV and Other Highly Diverse Pathogens. F1000Research 2015, 4, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trim Galore. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/trim_galore/ (accessed on 13 March 2018).
- Hunt, M.; Gall, A.; Ong, S.H.; Brener, J.; Ferns, B.; Goulder, P.; Nastouli, E.; Keane, J.A.; Kellam, P.; Otto, T.D. IVA: Accurate de Novo Assembly of RNA Virus Genomes. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2374–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wymant, C.; Blanquart, F.; Golubchik, T.; Gall, A.; Bakker, M.; Bezemer, D.; Croucher, N.J.; Hall, M.; Hillebregt, M.; Hoe Ong, S.; et al. Easy and Accurate Reconstruction of Whole HIV Genomes from Short-Read Sequence Data with Shiver. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.I.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A Novel Method for Rapid Multiple Sequence Alignment Based on Fast Fourier Transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.A.; Strimmer, K.; Vingron, M.; Von Haeseler, A. TREE-PUZZLE: Maximum Likelihood Phylogenetic Analysis Using Quartets and Parallel Computing. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackman, J.; Falade-Nwulia, O.; Patel, E.U.; Mehta, S.H.; Kirk, G.D.; Astemborski, J.; Ray, S.C.; Thomas, D.L.; Laeyendecker, O. Correlates of Hepatitis C Viral Clustering among People Who Inject Drugs in Baltimore HHS Public Access. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 77, 104078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.T.; Pierard, F.; Beuselinck, K.; Bonsall, D.; Bowden, R.; Lagrou, K.; Nevens, F.; Schrooten, Y.; Simmonds, P.; Vandamme, A.M.; et al. Full-Genome next-Generation Sequencing of Hepatitis C Virus to Assess the Accuracy of Genotyping by the Commercial Assay LiPA and the Prevalence of Resistance-Associated Substitutions in a Belgian Cohort. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 155, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maeght, S.; Henrion, J.; Bourgeois, N.; de Galocsy, C.; Langlet, P.; Michielsen, P.; Reynaert, H.; Robaeys, G.; Sprengers, D.; Orlent, H.; et al. A Pilot Observational Survey of Hepatitis C in Belgium. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2008, 71, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wiessing, L.; Ferri, M.; Grady, B.; Kantzanou, M.; Sperle, I.; Cullen, K.J.; EMCDDA DRID Group; Hatzakis, A.; Prins, M.; Vickerman, P.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus Infection Epidemiology among People Who Inject Drugs in Europe: A Systematic Review of Data for Scaling up Treatment and Prevention. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheï, C.; Wollants, E.; Verbeeck, J.; Van Ranst, M.; Robaeys, G.; Van Damme, P.; Buntinx, F. Molecular Epidemiology of Hepatitis C among Drug Users in Flanders, Belgium: Association of Genotype with Clinical Parameters and with Sex- and Drug-Related Risk Behaviours. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2005, 24, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micalessi, M.I.; Gérard, C.; Ameye, L.; Plasschaert, S.; Brochier, B.; Vranckx, R. Distribution of Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes among Injecting Drug Users in Contact with Treatment Centers in Belgium, 2004–2005. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilbaz, N.; Kuloğlu, M.; Evren, E.C.; Paltun, S.C.; Bilici, R.; Noyan, C.O.; Kulaksizoglu, B.; Karabulut, V.; Umut, G.; Unubol, B.; et al. HCV Genotype Distribution among People Who Inject Drug in Turkey: Findings from Multicenter and Cross-Sectional Study. Subst. Abus. 2023, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinsbroek, E.; Glass, R.; Edmundson, C.; Hope, V.; Desai, M. Patterns of Injecting and Non-Injecting Drug Use by Sexual Behaviour in People Who Inject Drugs Attending Services in England, Wales and Northern Ireland, 2013–2016. Int. J. Drug Policy 2018, 55, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, S.E.; Wilkinson, A.L.; O’Keefe, D.; Bourne, A.; Doyle, J.S.; Hellard, M.; Dietze, P.; Pedrana, A. Does Sexuality Matter? A Cross-Sectional Study of Drug Use, Social Injecting, and Access to Injection-Specific Care among Men Who Inject Drugs in Melbourne, Australia. Harm. Reduct. J. 2023, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, E.A.; Fish, J.N.; Upchurch, D.M. Sexual Orientation Disparities in Substance Use: Investigating Social Stress Mechanisms in a National Sample. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visseaux, B.; Hué, S.; Le Hingrat, Q.; Salmona, M.; Lebourgeois, S.; Delaugerre, C.; Descamps, D.; Chaix, M.L.; Ghosn, J. Phylogenetic Investigation of HCV-4d Epidemic in Paris MSM HIV Population Reveals a Still Active Outbreak and a Strong Link to the Netherlands. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 785.e1–785.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, M.; van de Laar, T.; Kupfer, B.; Stellbrink, H.J.; Kümmerle, T.; Mauss, S.; Knecht, G.; Berger, A.; Bruisten, S.; Rockstroh, J.K. Phylogenetic Analysis of Acute Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 4 Infections among Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Men Who Have Sex with Men in Germany. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.; Dion, R.; Simard, M.; Vachon, M.; Martel-Laferrière, V.; Serhir, B.; Longtin, J. Outbreaks: Molecular Surveillance of Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes Identifies the Emergence of a Genotype 4d Lineage among Men in Quebec, 2001–2017. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2019, 45, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.P.; Lin, A.W.; Wong, K.H.; Wong, N.S.; Lee, S.S. Diverse Origins of Hepatitis C Virus in HIV Co-Infected Men Who Have Sex with Men in Hong Kong. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhommerig, J.W.; Bezemer, D.; Molenkamp, R.; Van Sighem, A.I.; Smit, C.; Arends, J.E.; Lauw, F.N.; Brinkman, K.; Rijnders, B.J.; Newsum, A.M.; et al. Limited Overlap between Phylogenetic HIV and Hepatitis C Virus Clusters Illustrates the Dynamic Sexual Network Structure of Dutch HIV-Infected MSM. Aids 2017, 31, 2147–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouyos, R.D.; Rauch, A.; Böni, J.; Yerly, S.; Shah, C.; Aubert, V.; Klimkait, T.; Kovari, H.; Calmy, A.; Cavassini, M.; et al. Clustering of HCV Coinfections on HIV Phylogeny Indicates Domestic and Sexual Transmission of HCV. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraschiv, S.; Banica, L.; Nicolae, I.; Niculescu, I.; Abagiu, A.; Jipa, R.; Pineda-Peña, A.C.; Pingarilho, M.; Neaga, E.; Theys, K.; et al. Epidemic Dispersion of HIV and HCV in a Population of Co-Infected Romanian Injecting Drug Users. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popping, S.; Cuypers, L.; Claassen, M.A.A.; van den Berk, G.E.; De Weggheleire, A.; Arends, J.E.; Boerekamps, A.; Molenkamp, R.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Verbon, A.; et al. Persistent Transmission of HCV among Men Who Have Sex with Men despite Widespread Screening and Treatment with Direct-Acting Antivirals. Viruses 2022, 14, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Baelen, L.; Plettinckx, E.; Antoine, J.; Gremeaux, L. Prevalence of HCV among People Who Inject Drugs in Brussels—A Respondent-Driven Sampling Survey. Harm. Reduct. J. 2020, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerekamps, A.; van den Berk, G.E.; Lauw, F.N.; Leyten, E.M.; van Kasteren, M.E.; van Eeden, A.; Posthouwer, D.; Claassen, M.A.; Dofferhoff, A.S.; Verhagen, D.W.M.; et al. Declining Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Incidence in Dutch Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Men Who Have Sex with Men after Unrestricted Access to HCV Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1360–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castry, M.; Cousien, A.; Bellet, J.; Champenois, K.; Pialoux, G.; Yazdanpanah, Y.; Costagliola, D.; Grabar, S.; Deuffic-Burban, S. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Incidence among Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM) Living with HIV: Results from the French Hospital Database on HIV (ANRS CO4-FHDH) Cohort Study, 2014 to 2017. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2001321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Combating Hepatitis B and C to Reach Elimination by 2030: Advocacy Brief; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Busschots, D.; Ho, E.; Blach, S.; Nevens, F.; Razavi, H.; Van Damme, B.; Vanwolleghem, T.; Robaeys, G. Ten Years Countdown to Hepatitis C Elimination in Belgium: A Mathematical Modeling Approach. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cohort (# of ORFs) | Subtype | Gender | Gender of Attraction | HIV Status | IVDU History | Country of Origin | Iatrogenic Infections | Year of Birth (IQR) | Year of Diagnosis (IQR) | Year of Sampling (IQR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 224) |  |  |  | 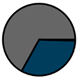 | 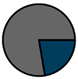 |  | 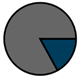 | 1959 (1966–1973) | 2000 (2008–2012) | 2013 (2015–2016) |
| Leuven (n = 111) | 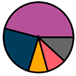 | 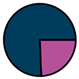 | 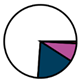 |  |  | 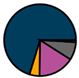 | 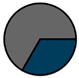 | 1955 (1964–1972) | 1999 (2005–2012) | 2014 (2015–2016) |
| Antwerp (n = 42) | 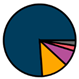 |  | 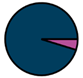 |  | 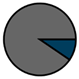 | 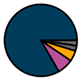 |  | 1964 (1967–1972) | 2009 (2011–2013) | 2009 (2011–2013) |
| Genk (n = 71) |  | 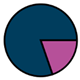 | 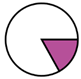 | 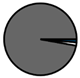 | 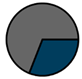 | 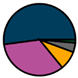 | 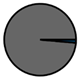 | 1960 (1966–1975) | 2002 (2008–2012) | 2013 (2015–2016) |
| Legend |  1a 1a 1b 1b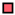 3a 3a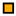 4d 4d Other Other |  Male Male Female Female No data No data | 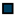 Same Same  Opposite Opposite  Either Either  No data No data | 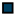 HIV+ HIV+ HIV- HIV- No data No data | 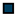 IVDU IVDU No recorded IVDU No recorded IVDU | 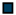 Belgium Belgium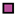 Europe Europe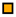 Russia and Asia Russia and Asia Other Other No data No data |  Iatrogenic Iatrogenic Not iatrogenic Not iatrogenic |
| 1a (n = 78) | 1b (n = 83) | 3a (n = 29) | 4d (n = 17) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 70 (89.74%) | 57 (68.67%) | 28 (96.55%) | 15 (88.24%) |
| Year of birth (IQR) | 1965 (1961–1971) | 1961 (1950–1970) | 1967 (1965–1979) | 1968 (1966–1973) |
| Year of diagnosis (IQR) | 2009 (2006–2012) | 2004 (1998–2011) | 2009 (2002–2013) | 2011 (2010–2013) |
| Year of sampling (IQR) | 2014 (2011–2015) | 2015 (2014–2016) | 2015 (2014–2017) | 2013 (2011–2017) |
| IVDU | 24 (30.77%) | 6 (7.23%) | 15 (51.72%) | 4 (23.53%) |
| HIV + MSM | 39 (50.00%) | 3 (3.61%) | 2 (6.90%) | 13 (76.47%) |
| Iatrogenic infection | 5 (6.41%) | 24 (28.92%) | 3 (10.34%) | 1 (5.88%) |
| Migrant | 13 (16.67%) | 31 (37.35%) | 13 (44.83%) | 6 (35.29%) |
| Viral Load (IQR) | 1.9 M (0.53 M–2.57 M) | 1.2 M (0.44 M–1.90 M) | 1.4 (0.43 M–1.90 M) | 0.9 M (0.29 M–4.60 M) |
| Genetic Distance | No. of Clusters | In Cluster | IVDU Odds Ratio (p-Value) | HIV + MSM Odds Ratio (p-Value) | Iatrogenic Odds Ratio (p-Value) | Migrant Odds Ratio (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | ||||||
| 2 | 9 | 28/78 (35.9%) | 0.25 (p = 0.022) | 37.00 (p = 0.000) | 0.43 (p = 0.649) | 0.27 (p = 0.119) |
| 4 | 10 | 42/78 (53.85%) | 0.63 (p = 0.461) | 18.33 (p = 0.000) | 0.20 (p = 0.175) | 0.20 (p = 0.030) |
| 6 | 13 | 49/78 (62.82%) | 0.59 (p = 0.319) | 10.88 (p = 0.000) | 0.13 (p = 0.061) | 0.12 (p = 0.003) |
| 8 | 14 | 57/78 (73.08%) | 1.15 (p = 1.000) | 6.76 (p = 0.002) | 0.08 (p = 0.017) | 0.10 (p = 0.001) |
| 1b | ||||||
| 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | 1 | 2/83 (2.41%) | 0.00 (p = 1.000) | 0.00 (p = 1.000) | 0.00 (p = 1.000) | 0.00 (p = 0.526) |
| 6 | 3 | 6/83 (7.23%) | 2.88 (p = 0.372) | 0.00 (p = 1.000) | 0.47 (p = 0.667) | 0.83 (p = 1.000) |
| 8 | 8 | 18/83 (21.69%) | 1.91 (p = 0.606) | 0.00 (p = 1.000) | 1.80 (p = 0.379) | 0.26 (p = 0.054) |
| 3a | ||||||
| 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | 1 | 3/29 (10.34%) | 2.00 (p = 1.000) | 0.00 (p = 1.000) | 0.00 (p = 1.000) | 2.73 (p = 0.573) |
| 8 | 1 | 4/29 (13.79%) | 0.92 (p = 1.000) | 0.00 (p = 1.000) | 0.00 (p = 1.000) | 1.27 (p = 1.000) |
| 4d | ||||||
| 2 | 4 | 9/17 (52.94%) | 0.00 (p = 0.029) | 4.80 (p = 0.294) | 0.00 (p = 0.471) | 0.08 (p = 0.050) |
| 4 | 3 | 13/17 (76.47%) | 0.18 (p = 0.219) | 5.50 (p = 0.219) | 0.00 (p = 0.235) | 0.44 (p = 0.584) |
| 6 | 4 | 15/17 (88.24%) | 0.25 (p = 0.426) | inf (p = 0.044) | inf (p = 1.000) | inf (p = 0.515) |
| 8 | 4 | 15/17 (88.24%) | 0.25 (p = 0.426) | inf (p = 0.044) | inf (p = 1.000) | inf (p = 0.515) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christensen, K.T.; Pierard, F.; Bonsall, D.; Bowden, R.; Barnes, E.; Florence, E.; Ansari, M.A.; Nguyen, D.; de Cesare, M.; Nevens, F.; et al. Phylogenetic Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Infections in a Large Belgian Cohort Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Full-Length Genomes. Viruses 2023, 15, 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122391
Christensen KT, Pierard F, Bonsall D, Bowden R, Barnes E, Florence E, Ansari MA, Nguyen D, de Cesare M, Nevens F, et al. Phylogenetic Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Infections in a Large Belgian Cohort Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Full-Length Genomes. Viruses. 2023; 15(12):2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122391
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristensen, Kasper T., Florian Pierard, David Bonsall, Rory Bowden, Eleanor Barnes, Eric Florence, M. Azim Ansari, Dung Nguyen, Mariateresa de Cesare, Frederik Nevens, and et al. 2023. "Phylogenetic Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Infections in a Large Belgian Cohort Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Full-Length Genomes" Viruses 15, no. 12: 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122391
APA StyleChristensen, K. T., Pierard, F., Bonsall, D., Bowden, R., Barnes, E., Florence, E., Ansari, M. A., Nguyen, D., de Cesare, M., Nevens, F., Robaeys, G., Schrooten, Y., Busschots, D., Simmonds, P., Vandamme, A.-M., Van Wijngaerden, E., Dierckx, T., Cuypers, L., & Van Laethem, K. (2023). Phylogenetic Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Infections in a Large Belgian Cohort Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Full-Length Genomes. Viruses, 15(12), 2391. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122391





