Roles Played by DOCK11, a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor, in HBV Entry and Persistence in Hepatocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
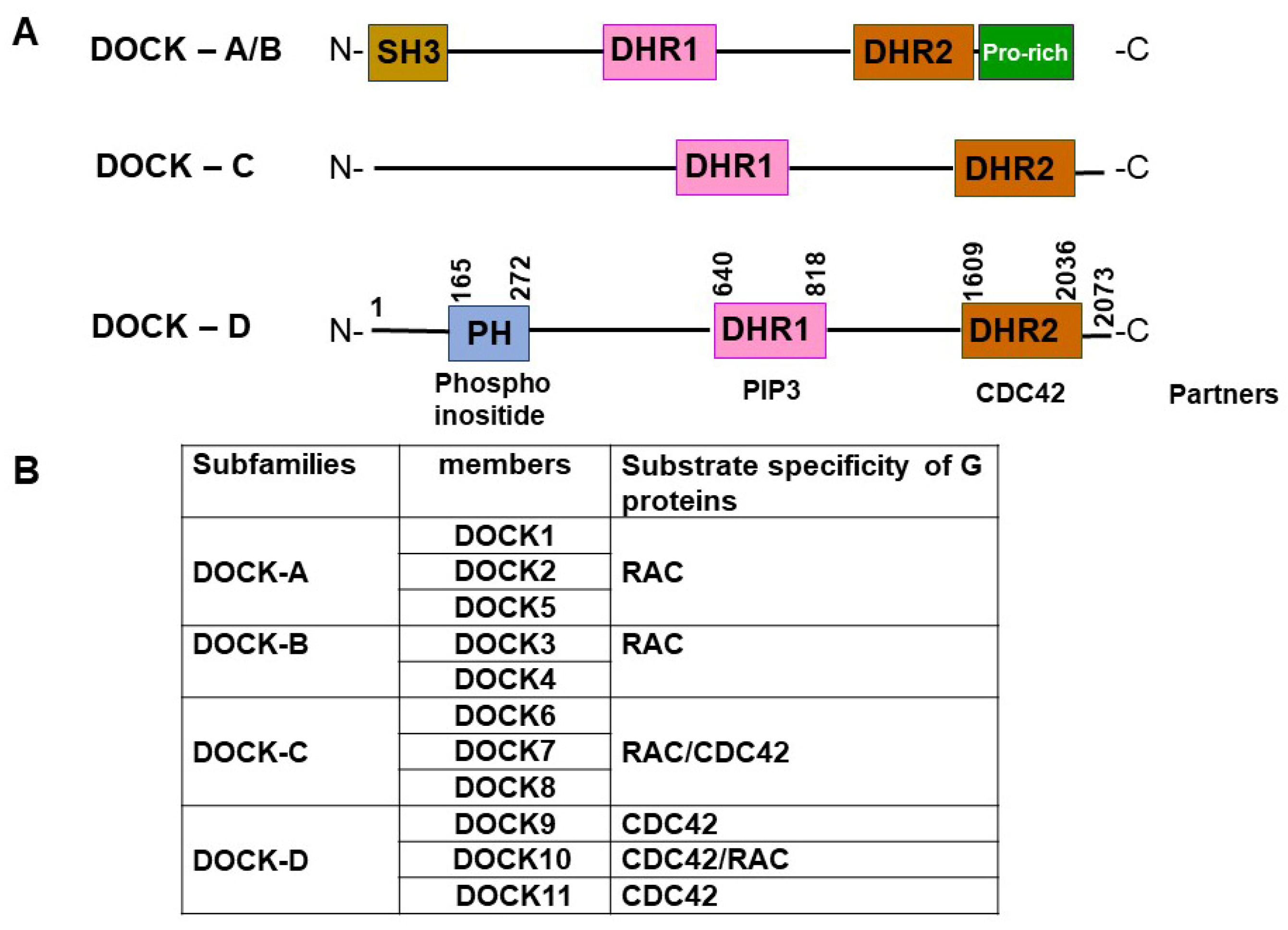
2. Structure of the DOCK11 Protein
3. Subcellular Localization and Expression Regulation of DOCK11
4. Roles of DOCK11 in HBV Cell Entry and Persistence in Hepatocytes
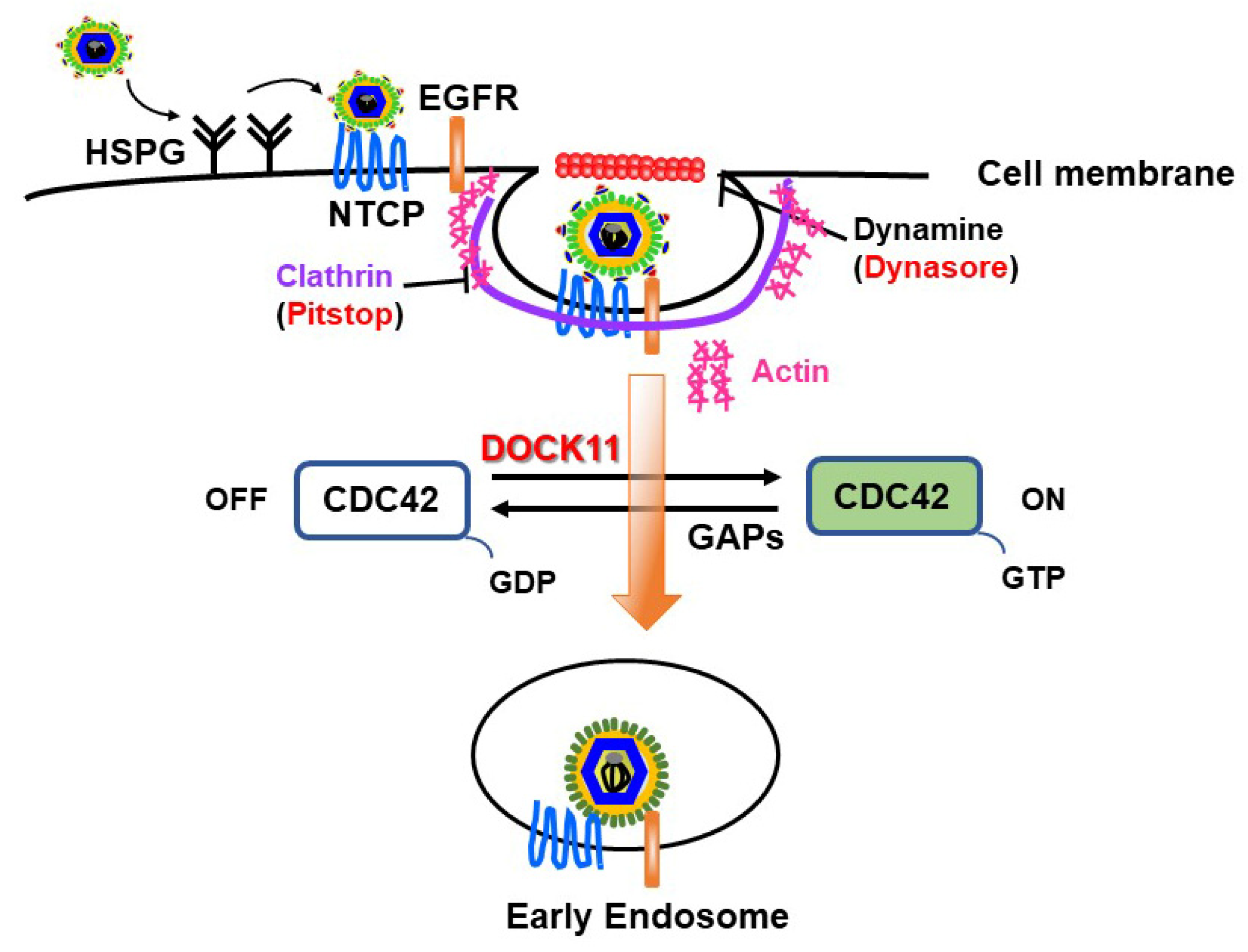
4.1. DOCK11 Enhances Early Stages of HBV Life Cycle
4.2. DOCK11 and AGAP2 Regulate ARF1 to Promote the Retrograde Trafficking of HBV in the Cytoplasm
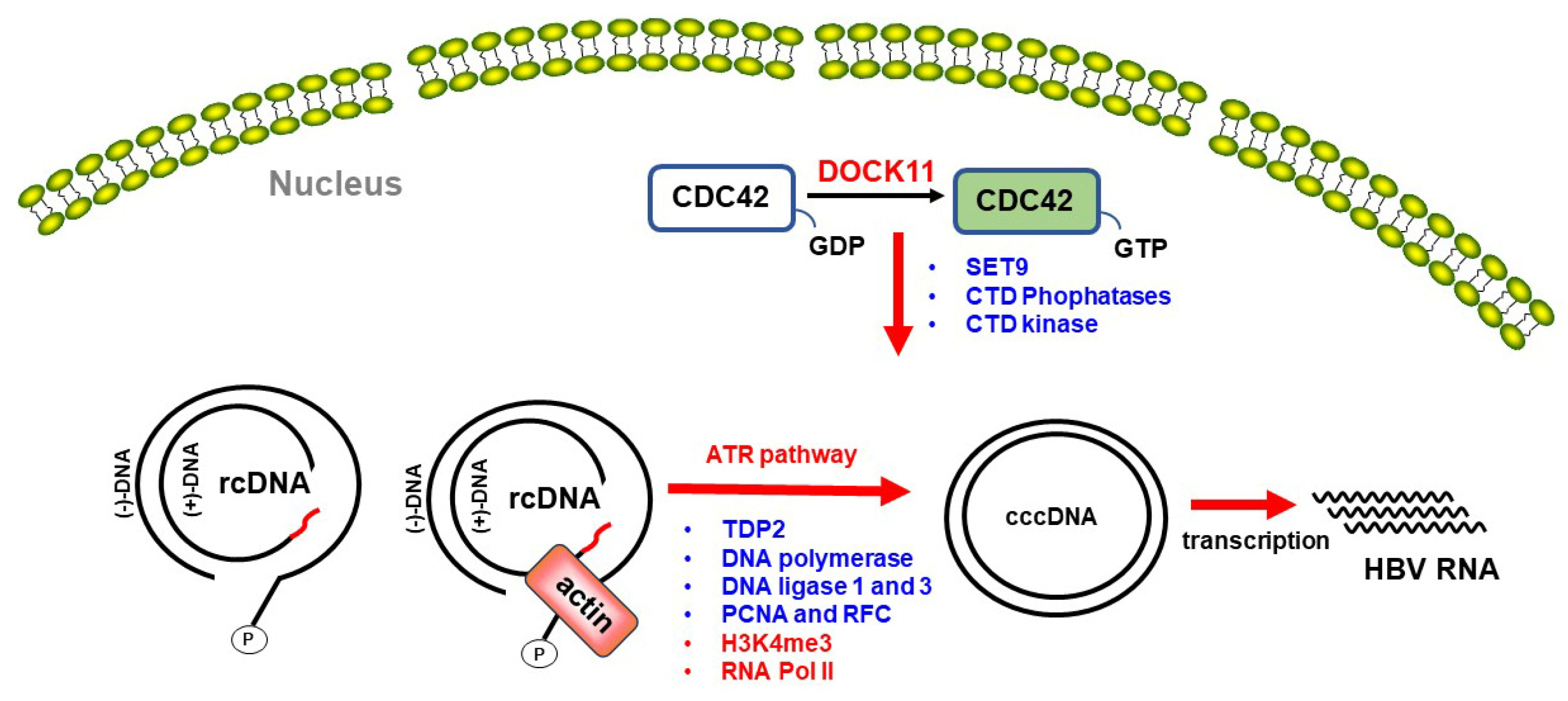
4.3. Predicted Roles of DOCK11 in DNA Repair and HBV cccDNA Formation in the Nucleus
5. Biological Functions of DOCK11 in Other Pathological Conditions
6. Pharmacologic Inhibition of DOCK11
7. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishikimi, A.; Meller, N.; Uekawa, N.; Isobe, K.I.; Schwartz, M.A.; Maruyama, M. Zizimin2: A Novel, DOCK180-Related Cdc42 Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor Expressed Predominantly in Lymphocytes. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, W.; Baird, D.; Feng, Q.; Cerione, R.A. Identification of a DOCK180-Related Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor That Is Capable of Mediating a Positive Feedback Activation of Cdc42. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35253–35262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, N.; Irani-Tehrani, M.; Kiosses, W.B.; Del Pozo, M.A.; Schwartz, M.A. Zizimin1, a Novel Cdc42 Activator, Reveals a New GEF Domain for Rho Proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelo, E.; Bernardo, M.V.; Gimeno, L.; Alcaraz-García, M.J.; Majado, M.J.; Parrado, A. Dock10, a Novel CZH Protein Selectively Induced by Interleukin-4 in Human B Lymphocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3411–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côté, J.F.; Vuori, K. GEF What? Dock180 and Related Proteins Help Rac to Polarize Cells in New Ways. Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukimoto-Niino, M.; Ihara, K.; Murayama, K.; Shirouzu, M. Structural Insights into the Small GTPase Specificity of the DOCK Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2021, 71, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côté, J.F.; Vuori, K. Identification of an Evolutionary Conserved Superfamily of DOCK180-Related Proteins with Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Activity. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4901–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadea, G.; Blangy, A. Dock-Family Exchange Factors in Cell Migration and Disease. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 93, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Yamauchi, J.; Sanbe, A.; Tanoue, A. Dock6, a Dock-C Subfamily Guanine Nucleotide Exchanger, Has the Dual Specificity for Rac1 and Cdc42 and Regulates Neurite Outgrowth. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.P.; Bitsina, C.; Gray, J.L.; Von Delft, F.; Brennan, P.E. RHO to the DOCK for GDP Disembarking: Structural Insights into the DOCK GTPase Nucleotide Exchange Factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, A.; Côté, J.F.; Barford, D. Structural Biology of DOCK-Family Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors. FEBS Lett. 2023, 597, 794–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meller, N.; Merlot, S.; Guda, C. CZH Proteins: A New Family of Rho-GEFs. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4937–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadea, G.; Sanz-Moreno, V.; Self, A.; Godi, A.; Marshall, C.J. DOCK10-Mediated Cdc42 Activation Is Necessary for Amoeboid Invasion of Melanoma Cells. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurin, M.; Côté, J.F. Insights into the Biological Functions of Dock Family Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namekata, K.; Kimura, A.; Kawamura, K.; Harada, C.; Harada, T. Dock GEFs and Their Therapeutic Potential: Neuroprotection and Axon Regeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2014, 43, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunimura, K.; Uruno, T.; Fukui, Y. DOCK Family Proteins: Key Players in Immune Surveillance Mechanisms. Int. Immunol. 2020, 32, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggs, C.M.; Keles, S.; Chatila, T.A. DOCK8 Deficiency: Insights into Pathophysiology, Clinical Features and Management. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 181, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, L.; Bobkov, A.A.; Patel, M.; Jaroszewski, L.; Bankston, L.A.; Stec, B.; Vuori, K.; Côté, J.F.; Liddington, R.C. Structural Basis of Membrane Targeting by the Dock180 Family of Rho Family Guanine Exchange Factors (Rho-GEFs). J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13211–13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meller, N.; Westbrook, M.J.; Shannon, J.D.; Guda, C.; Schwartz, M.A. Function of the N-Terminus of Zizimin1: Autoinhibition and Membrane Targeting. Biochem. J. 2008, 409, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Kuroki, K.; Shimakami, T.; Murai, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Shirasaki, T.; Nio, K.; Sugimoto, S.; Nishikawa, T.; Okada, H.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Utilizes a Retrograde Trafficking Route via the Trans-Golgi Network to Avoid Lysosomal Degradation. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 533–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.L.; von Delft, F.; Brennan, P.E. Targeting the Small GTPase Superfamily through Their Regulatory Proteins. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 6342–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mark Roe, S.; Marshall, C.J.; Barford, D. Activation of Rho GTPases by DOCK Exchange Factors Is Mediated by a Nucleotide Sensor. Science 2009, 325, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-corcuera, A.; Ansorena, E.; Montiel-duarte, C.; Iraburu, M.J. AGAP2: Modulating TGFβ1-Signaling in the Regulation of Liver Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-lafuente, N.; Minguela, A.; Moraleda, J.M.; Muro, M.; Parrado, A. Variable Distribution of Dock-d Proteins between Cytosol and Nucleoplasm in Cell Lines, Effect of Interleukin-4 on Dock10 in B-cell Lymphoid Neoplasms, and Validation of a New Dock10 Antiserum for Immunofluorescence Studies. Antibodies 2021, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, M.; Tabata, N.; Yonemura, Y.; Shirasaki, T.; Murai, K.; Wang, Y.; Ishida, A.; Okada, H.; Honda, M.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor DOCK11-Binding Peptide Fused with a Single Chain Antibody Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, P.T.B.; Nio, K.; Shimakami, T.; Kuroki, K.; Li, Y.Y.; Sugimoto, S.; Takayama, H.; Okada, H.; Kaneko, S.; Honda, M.; et al. Super-Resolution Microscopy Analysis of Hepatitis B Viral CccDNA and Host Factors. Viruses 2023, 15, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakabe, I.; Asai, A.; Iijima, J.; Maruyama, M. Age-Related Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor, Mouse Zizimin2, Induces Filopodia in Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells. Immun. Ageing 2012, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, Y.; Fujiwara, M.; Sakamoto, A.; Tsushima, H.; Nishikimi, A.; Maruyama, M. The Immunosenescence-Related Factor DOCK11 Is Involved in Secondary Immune Responses of B Cells. Immun. Ageing 2022, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrado, A. Expression of DOCK9 and DOCK11 Analyzed with Commercial Antibodies: Focus on Regulation of Mutually Exclusive First Exon Isoforms. Antibodies 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Shearer, D.; Gamkrelidze, I.; Nguyen, M.H.; Chen, D.S.; Van Damme, P.; Abbas, Z.; Abdulla, M.; Rached, A.A.; Adda, D.; Aho, I.; et al. Global Prevalence, Treatment, and Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in 2016: A Modelling Study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukuda, S.; Watashi, K. Hepatitis B Virus Biology and Life Cycle. Antivir. Res. 2020, 182, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.G.; Boyd, A.; Combe, E.; Testoni, B.; Zoulim, F. Covalently Closed Circular DNA: The Ultimate Therapeutic Target for Curing HBV Infections. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Seeger, C. Hepadnavirus Genome Replication and Persistence. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, S.; Shirasaki, T.; Yamashita, T.; Iwabuchi, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Takamura, Y.; Ukita, Y.; Deshimaru, S.; Okayama, T.; Ikeo, K.; et al. DOCK11 and DENND2A Play Pivotal Roles in the Maintenance of Hepatitis B Virus in Host Cells. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishitsuji, H.; Ujino, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Harada, K.; Zhang, J.; Sugiyama, M.; Mizokami, M.; Shimotohno, K. Novel Reporter System to Monitor Early Stages of the Hepatitis B Virus Life Cycle. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrscher, C.; Roingeard, P.; Blanchard, E. Hepatitis B Virus Entry into Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium Taurocholate Cotransporting Polypeptide Is a Functional Receptor for Human Hepatitis B and D Virus. eLife 2012, 2012, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Saso, W.; Sugiyama, R.; Ishii, K.; Ohki, M.; Nagamori, S.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Ryo, A.; Yun, J.H.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Is a Host-Entry Cofactor Triggering Hepatitis B Virus Internalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8487–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.S.; Smythe, E.; Ayscough, K.R. Functions of Actin in Endocytosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2049–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qualmann, B.; Kessels, M.M.; Kelly, R.B. Molecular Links between Endocytosis and the Actin Cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, A.C.; Way, M. The Non-Canonical Roles of Clathrin and Actin in Pathogen Internalization, Egress and Spread. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macovei, A.; Petrareanu, C.; Lazar, C.; Florian, P.; Branza-Nichita, N. Regulation of Hepatitis B Virus Infection by Rab5, Rab7, and the Endolysosomal Compartment. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6415–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Kazakov, T.; Popa, A.; DiMaio, D. Vesicular Trafficking of Incoming Human Papillomavirus 16 to the Golgi Apparatus and Endoplasmic Reticulum Requires γ-Secretase Activity. mBio 2014, 5, e01777-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, L.; Popoff, V. Tracing the Retrograde Route in Protein Trafficking. Cell 2008, 135, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Personnic, N.; Bärlocher, K.; Finsel, I.; Hilbi, H. Subversion of Retrograde Trafficking by Translocated Pathogen Effectors. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, J.G.; Jackson, C.L. ARF Family G Proteins and Their Regulators: Roles in Membrane Transport, Development and Disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Vargas, J.; Teppa, E.; Amirache, F.; Boson, B.; de Oliveira, R.P.; Combet, C.; Böckmann, A.; Fusil, F.; Freitas, N.; Carbone, A.; et al. A Fusion Peptide in Pres1 and the Human Protein-Disulfide Isomerase Erp57 Are Involved in Hepatitis b Virus Membrane Fusion Process. eLife 2021, 10, e64507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Hildt, E. Intracellular Trafficking of HBV Particles. Cells 2020, 2, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, B.; Stockl, L.; Gutzeit, C.; Roos, M.; Lupberger, J.; Schwartlander, R.; Gelderblom, H.; Sauer, I.M.; Hofschneider, P.H.; Hildt, E. A Novel System for Efficient Gene Transfer into Primary Human Hepatocytes via Cell-Permeable Hepatitis B Virus-like Particle. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sołtysik, K.; Ohsaki, Y.; Tatematsu, T.; Cheng, J.; Fujimoto, T. Nuclear Lipid Droplets Derive from a Lipoprotein Precursor and Regulate Phosphatidylcholine Synthesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, B.; Glebe, D.; Kann, M. Lipid-Mediated Introduction of Hepatitis B Virus Capsids into Nonsusceptible Cells Allows Highly Efficient Replication and Facilitates the Study of Early Infection Events. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5465–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilfling, F.; Thiam, A.R.; Olarte, M.J.; Wang, J.; Beck, R.; Gould, T.J.; Allgeyer, E.S.; Pincet, F.; Bewersdorf, J.; Farese, R.V.; et al. Arf1/COPI Machinery Acts Directly on Lipid Droplets and Enables Their Connection to the ER for Protein Targeting. eLife 2014, 3, e01607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, S.; Nassal, M. A Role for the Host DNA Damage Response in Hepatitis B Virus CccDNA Formation—And Beyond? Viruses 2017, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Yan, R.; Xu, J.Z.; Zhang, H.; Shen, S.; Mitra, B.; Marchetti, A.; Kim, E.S.; Guo, H. Characterization of the Termini of Cytoplasmic Hepatitis B Virus Deproteinated Relaxed Circular DNA. J. Virol. 2020, 95, e00922-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis B Virus CccDNA Is Formed through Distinct Repair Processes of Each Strand. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Hariharan, A.; Bastianello, G.; Toyama, Y.; Shivashankar, G.V.; Foiani, M.; Sheetz, M.P. DNA Damage Causes Rapid Accumulation of Phosphoinositides for ATR Signaling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropberger, P.; Mercier, A.; Robinson, M.; Zhong, W.; Ganem, D.E.; Holdorf, M. Mapping of Histone Modifications in Episomal HBV CccDNA Uncovers an Unusual Chromatin Organization Amenable to Epigenetic Manipulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5715–E5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Kim, E.S.; Guo, H. Epigenetic Regulation of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA: Implications for Epigenetic Therapy against Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2017, 66, 2066–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Bai, L.; Chen, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Z. In Situ Analysis of Intrahepatic Virological Events in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, P.; Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.L.; Kornblihtt, A.R. C-Terminal Domain (CTD) Phosphatase Links Rho GTPase Signaling to Pol II CTD Phosphorylation in Arabidopsis and Yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8197–E8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.A.; Ham, A.J.L.; Clark, C.N.; Meller, N.; Law, B.K.; Chytil, A.; Cheng, N.; Pietenpol, J.A.; Moses, H.L. Identification of Novel Smad2 and Smad3 Associated Proteins in Response to TGF-Β1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 105, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedl, P.; Wolf, K. Tumour-Cell Invasion and Migration: Diversity and Escape Mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almstrup, K.; Leffers, H.; Lothe, R.A.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Sonne, S.B.; Nielsen, J.E.; De Meyts, E.R.; Skotheim, R.I. Improved Gene Expression Signature of Testicular Carcinoma in Situ. Int. J. Androl. 2007, 30, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, J.; Rashkova, C.; Castanon, I.; Zoghi, S.; Platon, J.; Ardy, R.C.; Fujiwara, M.; Chaves, B.; Schoppmeyer, R.; van der Made, C.I.; et al. Systemic Inflammation and Normocytic Anemia in DOCK11 Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussard, C.; Delage, L.; Gajardo, T.; Kauskot, A.; Batignes, M.; Goudin, N.; Stolzenberg, M.C.; Brunaud, C.; Panikulam, P.; Riller, Q.; et al. DOCK11 Deficiency in Patients with X-Linked Actinopathy and Autoimmunity. Blood 2023, 141, 2713–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vives, V.; Cres, G.; Richard, C.; Busson, M.; Ferrandez, Y.; Planson, A.G.; Zeghouf, M.; Cherfils, J.; Malaval, L.; Blangy, A. Pharmacological Inhibition of Dock5 Prevents Osteolysis by Affecting Osteoclast Podosome Organization While Preserving Bone Formation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vives, V.; Laurin, M.; Cres, G.; Larrousse, P.; Morichaud, Z.; Noel, D.; Côté, J.F.; Blangy, A. The Rac1 Exchange Factor Dock5 Is Essential for Bone Resorption by Osteoclasts. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikimi, A.; Uruno, T.; Duan, X.; Cao, Q.; Okamura, Y.; Saitoh, T.; Saito, N.; Sakaoka, S.; Du, Y.; Suenaga, A.; et al. Blockade of Inflammatory Responses by a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the Rac Activator DOCK2. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajiri, H.; Uruno, T.; Shirai, T.; Takaya, D.; Matsunaga, S.; Setoyama, D.; Watanabe, M.; Kukimoto-Niino, M.; Oisaki, K.; Ushijima, M.; et al. Targeting Ras-Driven Cancer Cell Survival and Invasion through Selective Inhibition of DOCK1. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.-Y.; Murai, K.; Lyu, J.; Honda, M. Roles Played by DOCK11, a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor, in HBV Entry and Persistence in Hepatocytes. Viruses 2024, 16, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050745
Li Y-Y, Murai K, Lyu J, Honda M. Roles Played by DOCK11, a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor, in HBV Entry and Persistence in Hepatocytes. Viruses. 2024; 16(5):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050745
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ying-Yi, Kazuhisa Murai, Junyan Lyu, and Masao Honda. 2024. "Roles Played by DOCK11, a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor, in HBV Entry and Persistence in Hepatocytes" Viruses 16, no. 5: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050745
APA StyleLi, Y.-Y., Murai, K., Lyu, J., & Honda, M. (2024). Roles Played by DOCK11, a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor, in HBV Entry and Persistence in Hepatocytes. Viruses, 16(5), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16050745





