The Peculiar Characteristics of Fish Type I Interferons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fish Type I Interferons: An Astonishing Diversity
2.1. Structural Diversity of IFN Sequences
2.2. Nomenclature Issues
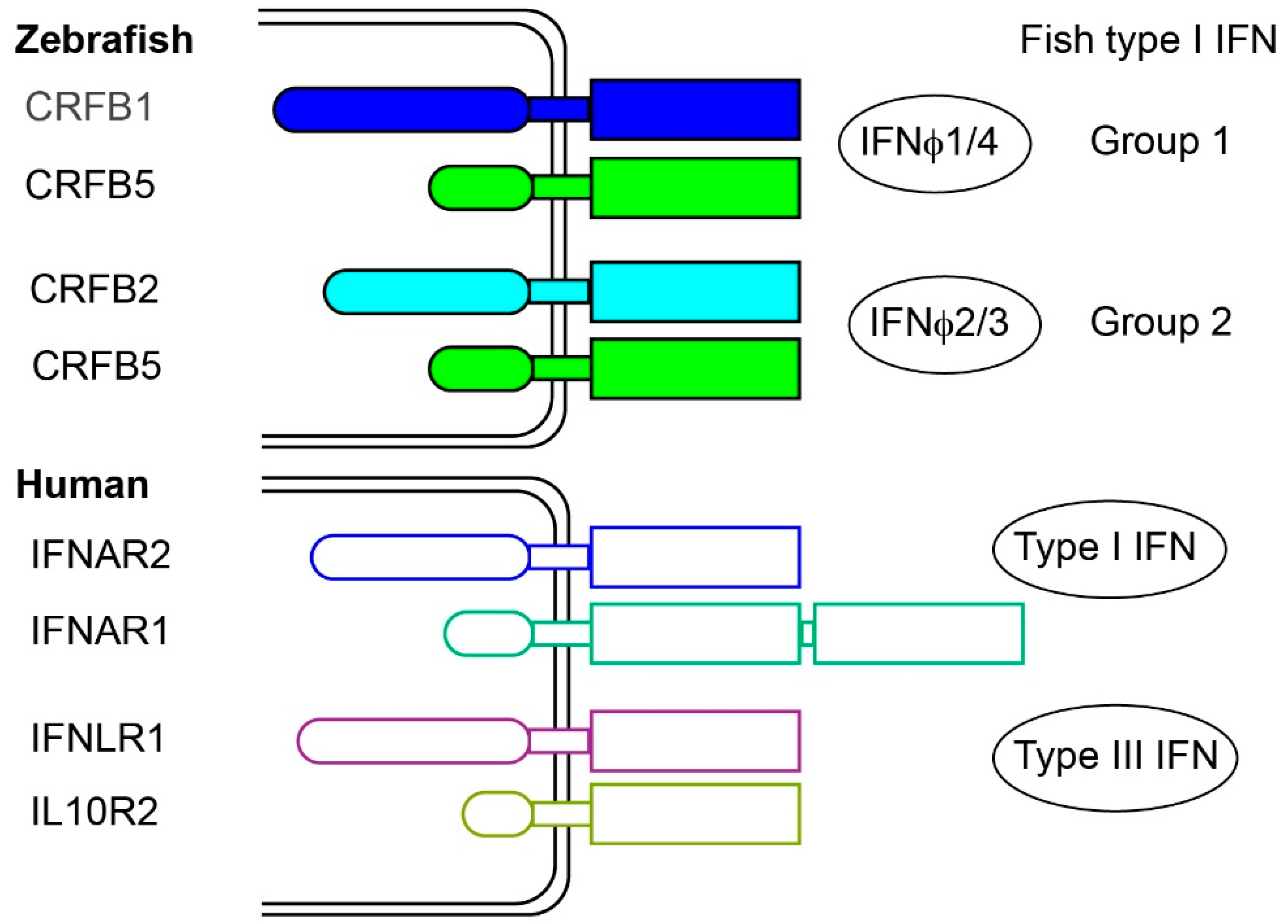
2.3. Fish Type I Receptors: Several CRFB Complexes
2.4. Multiple Transcripts and Intracellular IFNs
2.5. Evolutionary Pathway of Type I IFN
3. Differential Expression and Functional Properties of Fish Type I IFNs
3.1. Expression
3.1.1. Cyprinids
3.1.2. Salmonids
3.2. Control by IRFs
3.3. Functions
3.3.1. Cyprinids
3.3.2. Salmonids
3.3.3. Other Fish Groups
4. The Effectors of Fish Type I IFN: Parallel Evolution of Fish and Mammal ISG Genes and Families, Regional Expression and Regulation in Ontogeny
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The Function of Fish Cytokines. Biology (Basel) 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, A.; Lindenmann, J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. In Proceedings of the Royal Society of London; Series B, Containing Papers of a Biological Character; Royal Society: London, UK, 1957; Volume 147, pp. 258–267. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, T.; Mantei, N.; Schwarzstein, M.; Nagata, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Weissmann, C. Human leukocyte and fibroblast interferons are structurally related. Nature 1980, 285, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, T.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y.; Muramatsu, M. Molecular cloning of human interferon cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 4003–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, G.; Scagnolari, C.; Moschella, F.; Proietti, E. Twenty-five years of type I interferon-based treatment: A critical analysis of its therapeutic use. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoggins, J.W.; MacDuff, D.A.; Imanaka, N.; Gainey, M.D.; Shrestha, B.; Eitson, J.L.; Mar, K.B.; Richardson, R.B.; Ratushny, A.V.; Litvak, V.; et al. Pan-viral specificity of IFN-induced genes reveals new roles for cGAS in innate immunity. Nature 2014, 505, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoggins, J.W.; Wilson, S.J.; Panis, M.; Murphy, M.Y.; Jones, C.T.; Bieniasz, P.; Rice, C.M. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011, 472, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kinkelin, P.; Dorson, M. Interferon production in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) experimentally infected with Egtved virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1973, 19, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertsen, B.; Bergan, V.; Røkenes, T.; Larsen, R.; Albuquerque, A. Atlantic salmon interferon genes: Cloning, sequence analysis, expression, and biological activity. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2003, 23, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutfalla, G.; Crollius, H.R.; Stange-Thomann, N.; Jaillon, O.; Mogensen, K.; Monneron, D. Comparative genomic analysis reveals independent expansion of a lineage-specific gene family in vertebrates: The class II cytokine receptors and their ligands in mammals and fish. BMC Genom. 2003, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altmann, S.M.; Mellon, M.T.; Distel, D.L.; Kim, C.H. Molecular and functional analysis of an interferon gene from the zebrafish, Danio rerio. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 1992–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.; Nie, P.; Collet, B.; Secombes, C.J.; Zou, J. Identification of an additional two-cysteine containing type I interferon in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss provides evidence of a major gene duplication event within this gene family in teleosts. Immunogenetics 2009, 61, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Nie, P.; Secombes, C.J.; Zou, J. Intron-containing type I and type III IFN coexist in amphibians: Refuting the concept that a retroposition event gave rise to type I IFNs. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5038–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. Teleost fish interferons and their role in immunity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Tafalla, C.; Truckle, J.; Secombes, C.J. Identification of a second group of type I IFNs in fish sheds light on IFN evolution in vertebrates. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 3859–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamming, O.J.; Lutfalla, G.; Levraud, J.-P.; Hartmann, R. Crystal structure of Zebrafish interferons I and II reveals conservation of type I interferon structure in vertebrates. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8181–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereiro, P.; Costa, M.M.; Diaz-Rosales, P.; Dios, S.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. The first characterization of two type I interferons in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) reveals their differential role, expression pattern and gene induction. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 45, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Gorgoglione, B.; Taylor, N.G.; Summathed, T.; Lee, P.T.; Panigrahi, A.; Genet, C.; Chen, Y.M.; Chen, T.Y.; Hassan, M.U.; et al. Salmonids have an extraordinary complex type I IFN system: Characterization of the IFN locus in rainbow trout oncorhynchus mykiss reveals two novel IFN subgroups. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2273–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Robertsen, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B. Identification of an Atlantic salmon IFN multigene cluster encoding three IFN subtypes with very different expression properties. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfman, G.; Collette, B.; Facey, D.; Bowen, B. The Diversity of Fishes; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Aggad, D.; Mazel, M.; Boudinot, P.; Mogensen, K.E.; Hamming, O.J.; Hartmann, R.; Kotenko, S.; Herbomel, P.; Lutfalla, G.; Levraud, J.P. The two groups of zebrafish virus-induced interferons signal via distinct receptors with specific and shared chains. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3924–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casani, D.; Randelli, E.; Costantini, S.; Facchiano, A.M.; Zou, J.; Martin, S.; Secombes, C.J.; Scapigliati, G.; Buonocore, F. Molecular characterisation and structural analysis of an interferon homologue in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, S.; Chiang, Y.A.; Hikima, J.; Sakai, M.; Lo, C.F.; Wang, H.C.; Aoki, T. Expression and biological activity of two types of interferon genes in medaka (Oryzias latipes). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 48, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.; Milev-milovanovic, I.; Wilson, M.; Bengten, E.; Clem, L.W.; Miller, N.W.; Chinchar, V.G. Identification and expression analysis of cDNAs encoding channel catfish type I interferons. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 21, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.; Caccamo, M.; Laird, G.; Leptin, M. Conservation and divergence of gene families encoding components of innate immune response systems in zebrafish. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, W.E., 2nd. Interferon nomenclature recommendations. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 142, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levraud, J.P.; Boudinot, P.; Colin, I.; Benmansour, A.; Peyrieras, N.; Herbomel, P.; Lutfalla, G. Identification of the zebrafish IFN receptor: Implications for the origin of the vertebrate IFN system. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4385–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Greiner-Tollersrud, L.; Koop, B.F.; Robertsen, B. Atlantic salmon possesses two clusters of type I interferon receptor genes on different chromosomes, which allows for a larger repertoire of interferon receptors than in zebrafish and mammals. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 47, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergan, V.; Steinsvik, S.; Xu, H.; Kileng, Ø.; Robertsen, B. Promoters of type I interferon genes from Atlantic salmon contain two main regulatory regions. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 3893–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Purcell, M.K.; Laing, K.J.; Woodson, J.C.; Thorgaard, G.H.; Hansen, J.D. Characterization of the interferon genes in homozygous rainbow trout reveals two novel genes, alternate splicing and differential regulation of duplicated genes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-X.; Zou, J.; Nie, P.; Huang, B.; Yu, Z.; Collet, B.; Secombes, C.J. Intracellular interferons in fish: A unique means to combat viral infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lee, J.; Ma, W.; McVey, D.S.; Blecha, F. Expansion of amphibian intronless interferons revises the paradigm for interferon evolution and functional diversity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudinot, P.; Zou, J.; Ota, T.; Buonocore, F.; Scapigliati, G.; Canapa, A.; Cannon, J.; Litman, G.; Hansen, J.D. A tetrapod-like repertoire of innate immune receptors and effectors for coelacanths. J. Exp. Zool. Part B Mol. Dev. Evolut. 2014, 322, 415–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palha, N.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Briolat, V.; Lutfalla, G.; Sourisseau, M.; Ellett, F.; Wang, C.H.; Lieschke, G.J.; Herbomel, P.; Schwartz, O.; et al. Real-time whole-body visualization of Chikungunya Virus infection and host interferon response in zebrafish. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, Q.M.; Zhang, Y.B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Y.W.; Wu, M.; Gui, J.F. Zebrafish IRF1, IRF3, and IRF7 Differentially Regulate IFNPhi1 and IFNPhi3 Expression through Assembly of Homo- or Heteroprotein Complexes. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Wan, Q.; Su, J. Bioinformatics analysis of organizational and expressional characterizations of the IFNs, IRFs and CRFBs in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Munoz, A.; Roca, F.J.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. New insights into the evolution of IFNs: Activities genes and display powerful antiviral transient expression of IFN-dependent zebrafish group II IFNs induce a rapid and display powerful antiviral activities. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3440–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svingerud, T.; Solstad, T.; Sun, B.; Nyrud, M.L.J.; Kileng, Ø.; Greiner-Tollersrud, L.; Robertsen, B. Atlantic salmon type I IFN subtypes show differences in antiviral activity and cell-dependent expression: Evidence for high IFNb/IFNc-producing cells in fish lymphoid tissues. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5912–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, T.; Ogasawara, K.; Takaoka, A.; Tanaka, N. IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 623–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, Q.M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Gui, J.F. Zebrafish IRF1 regulates IFN antiviral response through binding to IFNvarphi1 and IFNvarphi3 promoters downstream of MyD88 signaling. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, Y.B.; Liu, T.K.; Gan, L.; Yu, F.F.; Liu, Y.; Gui, J.F. Characterization of fish IRF3 as an IFN-inducible protein reveals evolving regulation of IFN response in vertebrates. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7573–7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, Y.B.; Liu, T.K.; Shi, J.; Wang, B.; Gui, J.F. Fish MITA Serves as a Mediator for Distinct Fish IFN Gene Activation Dependent on IRF3 or IRF7. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Muñoz, A.; Roca, F.J.; Sepulcre, M.P.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. Zebrafish larvae are unable to mount a protective antiviral response against waterborne infection by spring viremia of carp virus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxx, G.M.; Cheng, G. The Roles of Type I Interferon in Bacterial Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Vaart, M.; van Soest, J.J.; Spaink, H.P.; Meijer, A.H. Functional analysis of a zebrafish myd88 mutant identifies key transcriptional components of the innate immune system. Dis. Models Mech. 2013, 6, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.J.; Sun, B.; Robertsen, B. Adjuvant activity of fish type I interferon shown in a virus DNA vaccination model. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.J.; Robertsen, C.; Sun, B.; Robertsen, B. Protection of Atlantic salmon against virus infection by intramuscular injection of IFNc expression plasmid. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4695–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Ao, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, X. Identification of Two Subgroups of Type I IFNs in Perciforme Fish Large Yellow Croaker Larimichthys crocea Provides Novel Insights into Function and Regulation of Fish Type I IFNs. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, J.-L.; Stange-Thomann, N.; Mauceli, E.; Bouneau, L.; Jaillon, O.; Aury, J.-M.; Ozouf-Costaz, C.; Bernot, A.; Nicaud, S.; Jaffe, D.; et al. Genome duplication in the teleost fish Tetraodon nigroviridis reveals the early vertebrate proto-karyotype. Nature 2004, 431, 946–957. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, A.; Schartl, M. Gene and genome duplications in vertebrates: The one-to-four (-to-eight in fish) rule and the evolution of novel gene functions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1999, 11, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magadan, S.; Sunyer, O.J.; Boudinot, P. Unique Features of Fish Immune Repertoires: Particularities of Adaptive Immunity Within the Largest Group of Vertebrates. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2015, 57, 235–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trobridge, G.D.; Leong, J.A. Characterization of a rainbow trout Mx gene. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995, 15, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.D.; la Patra, S. Induction of the rainbow trout MHC class I pathway during acute IHNV infection. Immunogenetics 2002, 54, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudinot, P.; Massin, P.; Blanco, M.; Riffault, S.; Benmansour, A. vig-1, a new fish gene induced by the rhabdovirus glycoprotein, has a virus-induced homologue in humans and shares conserved motifs with the MoaA family. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boudinot, P.; Salhi, S.; Blanco, M.; Benmansour, A.; Introduction, I.; America, N. Viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus induces vig-2, a new interferon-responsive gene in rainbow trout. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2001, 11, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Farrell, C.; Vaghefi, N.; Cantonnet, M.; Buteau, B.; Boudinot, P.; Benmansour, A. Survey of Transcript Expression in Rainbow Trout Leukocytes Reveals a Major Contribution of Interferon-Responsive Genes in the Early Response to a Rhabdovirus Infection. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 8040–8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briolat, V.; Jouneau, L.; Carvalho, R.; Palha, N.; Langevin, C.; Herbomel, P.; Schwartz, O.; Spaink, H.P.; Levraud, J.P.; Boudinot, P. Contrasted innate responses to two viruses in zebrafish: Insights into the ancestral repertoire of vertebrate IFN-stimulated genes. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4328–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozato, K.; Shin, D.M.; Chang, T.H.; Morse, H.C., 3rd. TRIM family proteins and their emerging roles in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, M.W.; Nisole, S.; Lynch, C.; Stoye, J.P. Trim5alpha protein restricts both HIV-1 and murine leukemia virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10786–10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, S.L.; Emerman, M.; Malik, H.S. Discordant Evolution of the Adjacent Antiretroviral Genes TRIM22 and TRIM5 in Mammals. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallery, D.L.; McEwan, W.A.; Bidgood, S.R.; Towers, G.J.; Johnson, C.M.; James, L.C. Antibodies mediate intracellular immunity through tripartite motif-containing 21 (TRIM21). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19985–19990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelbi-Alix, M.K.; Vidy, A.; el Bougrini, J.; Blondel, D. Rabies viral mechanisms to escape the IFN system: The viral protein P interferes with IRF-3, Stat1, and PML nuclear bodies. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006, 26, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudinot, P.; van der Aa, L.M.; Jouneau, L.; Pasquier, L.D.; Pontarotti, P.; Briolat, V.; Benmansour, A.; Levraud, J.P. Origin and evolution of TRIM proteins: New insights from the complete TRIM repertoire of zebrafish and pufferfish. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Aa, L.M.; Levraud, J.-P.; Yahmi, M.; Lauret, E.; Briolat, V.; Herbomel, P.; Benmansour, A.; Boudinot, P. A large new subset of TRIM genes highly diversified by duplication and positive selection in teleost fish. BMC Biol. 2009, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardiello, M.; Cairo, S.; Fontanella, B.; Ballabio, A.; Meroni, G. Genomic analysis of the TRIM family reveals two groups of genes with distinct evolutionary properties. BMC Evolut. Biol. 2008, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollmann, T.R.; Levy, O.; Montgomery, R.R.; Goriely, S. Innate immune function by Toll-like receptors: Distinct responses in newborns and the elderly. Immunity 2012, 37, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, R.; Jouneau, L.; Tacchi, L.; Macqueen, D.J.; Alzaid, A.; Secombes, C.J.; Martin, S.A.; Boudinot, P. Disparate developmental patterns of immune responses to bacterial and viral infections in fish. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Salmonid) | Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar (Salmonid) | Zebrafish Danio rerio (Cyprinid) | Channel Catfish Ictalurus punctatus (Ictalurid) | Medaka Oryzias latipes (Percomorph) | Turbot Scophthalmus maximus (Percomorph) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I (2C) | ||||||
| Sub Group a | ||||||
| IFNa1 (=IFN1) (NM 001124531) IFNa2 (=IFN2)( NM 001160505) IFNa3 (HF931021) IFNa4 (HF931022) | IFNa1 (NM 001123710) IFNa2 (NM 001123570) IFNa3 (EU768890) | IFNφ1 (=IFN, IFN1) (NM_207640.1) | IFN1 (AY267538) IFN2 (AY847295) IFN4 (AY847296) | IFNa (LC066594) | IFN2 (KJ150678) | |
| Sub Group d | ||||||
| IFNd1 (=IFN5) (NP_001152811) | IFNd1 (NM_001279092.1) | IFNφ4 (?) (NM_001161740.1) | IFNd (LC066595) | |||
| Sub Group e | ||||||
| IFNe1-7 (HF931030-6) | ||||||
| Group II (4C) | ||||||
| Sub Group b | ||||||
| IFNb1 (=IFN3) (NP_001153974) IFNb2 (=IFN4) (NP_001158515) IFNb3 (HF931023) IFNb4 (HF931024) IFNb5 (HF931025) | IFNb1 (EU735552) IFNb2 (EU768890) IFNb3 (EU768890) IFNb4 (EU768890) | |||||
| Sub Group c | ||||||
| IFNc1-4 (HF931026-9) | IFNc1-3 | IFNφ2 (NM_001111082.1) IFNφ3 (NM_001111083.1) | IFN1 (KJ150677) | |||
| Sub Group f | ||||||
| IFNf1-2 (HF931037-8) | ||||||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boudinot, P.; Langevin, C.; Secombes, C.J.; Levraud, J.-P. The Peculiar Characteristics of Fish Type I Interferons. Viruses 2016, 8, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8110298
Boudinot P, Langevin C, Secombes CJ, Levraud J-P. The Peculiar Characteristics of Fish Type I Interferons. Viruses. 2016; 8(11):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8110298
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoudinot, Pierre, Christelle Langevin, Christopher J. Secombes, and Jean-Pierre Levraud. 2016. "The Peculiar Characteristics of Fish Type I Interferons" Viruses 8, no. 11: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8110298
APA StyleBoudinot, P., Langevin, C., Secombes, C. J., & Levraud, J. -P. (2016). The Peculiar Characteristics of Fish Type I Interferons. Viruses, 8(11), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8110298






