Equine Immunoglobulin and Equine Neutralizing F(ab?)2 Protect Mice from West Nile Virus Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antigen Preparation
2.2. Inoculation of Horses
2.3. WNV-Specific Antibody Measurement
2.4. Immunoglobulin Purification
2.5. Preparation of F(ab′)2 Fragments
2.6. Mice, Virus, and Cells
2.7. WNV Plaque Reduction Neutralization Assay
2.8. Mouse Challenge and Antibody Treatment
3. Results
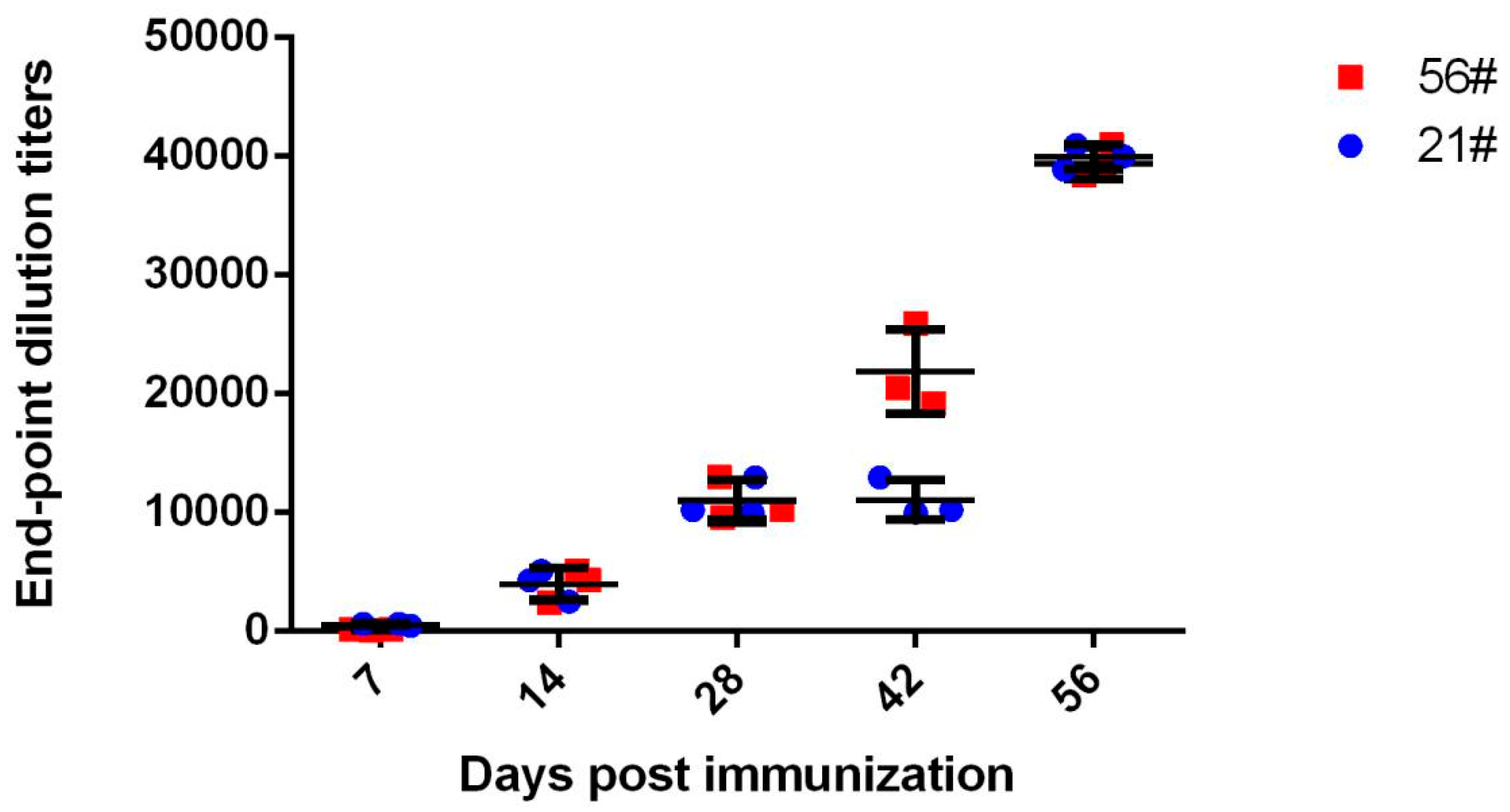
3.1. Immunization and Evaluation of Equine Antibodies
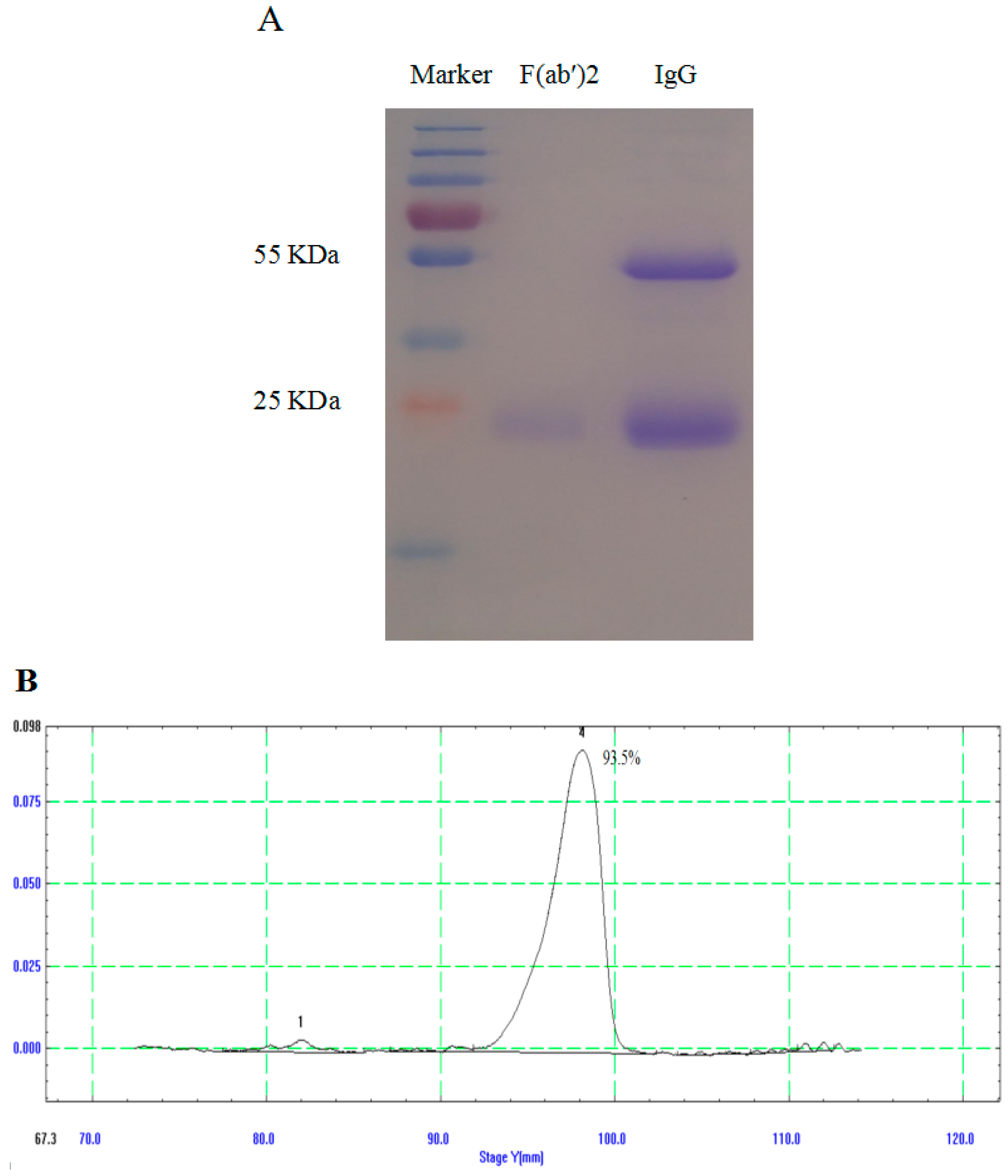
3.2. Generation and Purification of IgG and F(ab′)2
3.3. Equine Antibodies Neutralized WNV in Cell Culture
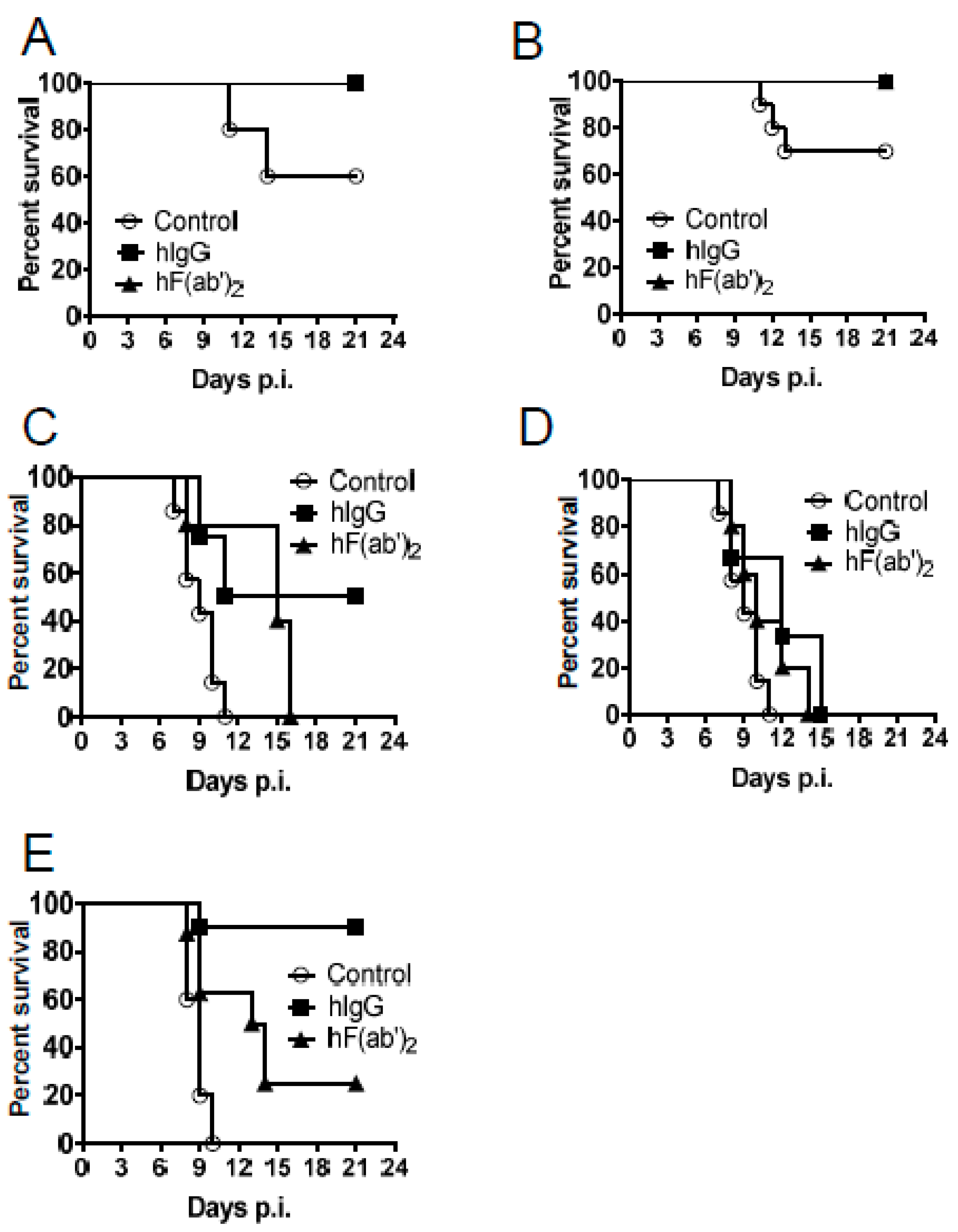
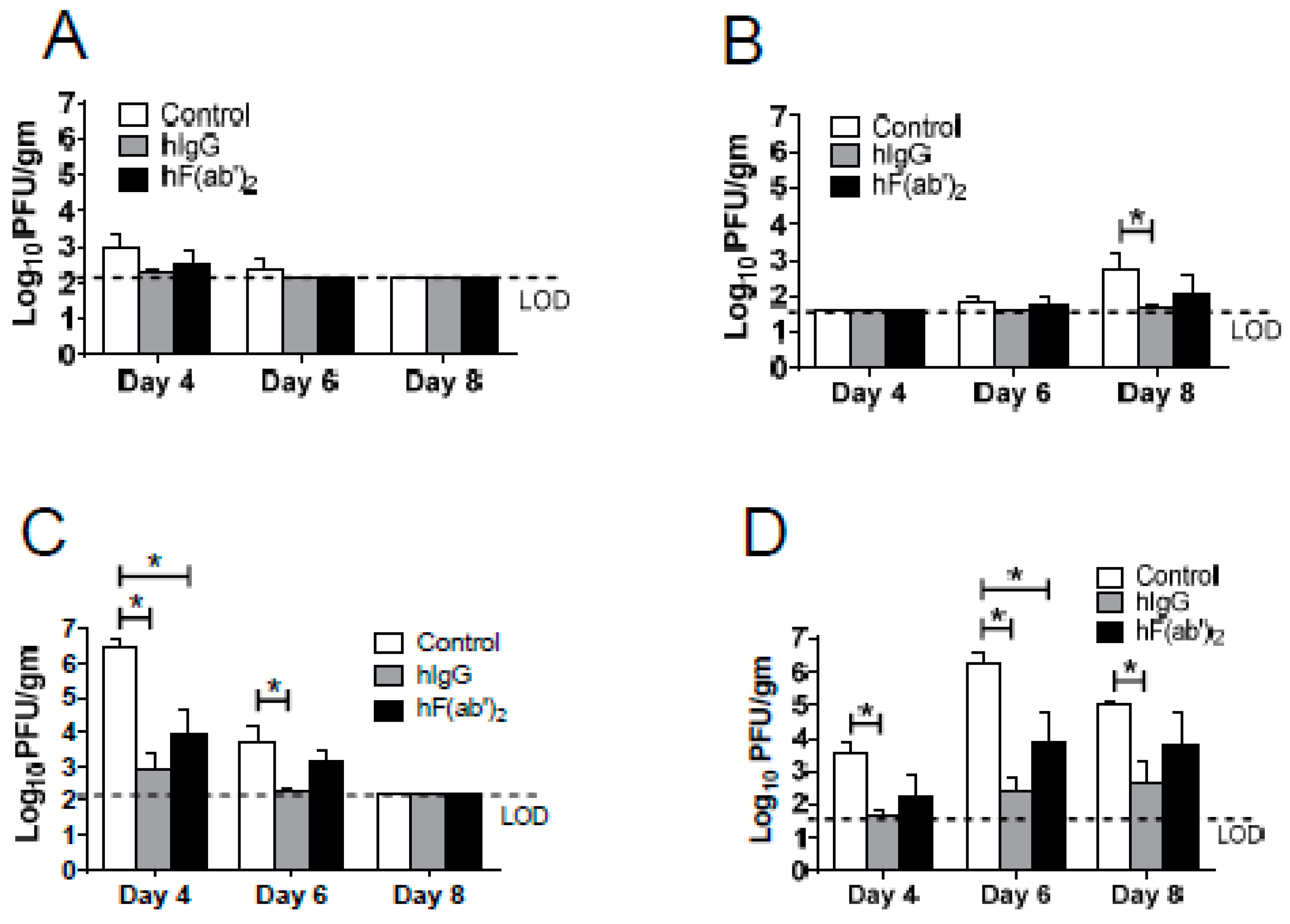
3.4. Passive Transfer of Equine Antibodies Protected WNV-Infected Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malone, R.W.; Homan, J.; Callahan, M.V.; Glasspool-Malone, J.; Damodaran, L.; Schneider, A.B.; Zimler, R.; Talton, J.; Cobb, R.R.; Ruzic, I.; et al. Zika virus: Medical countermeasure development challenges. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, M.S.; Diamond, M.S.; Gale, M., Jr. West Nile virus infection and immunity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, D.; Qu, X.; Guo, H.; Xu, X.; Mason, P.M.; Bourne, N.; Moriarty, R.; Gu, B.; et al. 2009 Novel imino sugar derivatives demonstrate potent antiviral activity against flaviviruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.C.; Liu, W.J.; Anraku, I.; Clark, D.C.; Pollitt, C.C.; Suhrbier, A.; Hall, R.A.; Khromykh, A.A. Single-round infectious partious enhance immunogenicity of a DNA vaccine against West Nile virus. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, M.R.; Moesker, B.; Goudsmit, J.; Jongeneelen, M.; Austin, S.K.; Oliphant, T.; Nelson, S.; Pierson, T.C.; Wilschut, J.; Throsby, M.; et al. Human monoclonal antibodies against West Nile virus induced by natural infection neutralize at a postattachment step. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6494–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Vogt, M.R.; Oliphant, T.; Engle, M.; Bovshik, E.I.; Diamond, M.S.; Beasley, D.W. The development of resistance to passive therapy by a potently neutralizing humanized West Nile virus monoclonal antibody. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.W.; Smee, D.F.; Julander, J.G.; Yamshchikov, V.F.; Sidwell, R.W.; Morrey, J.D. Error-prone replication of West Nile virus caused by ribavirin. Antivir. Res. 2005, 67, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrey, J.D.; Day, C.W.; JuLander, J.G.; Blatt, L.M.; Smee, D.F.; Sidwell, R.W. Effect of interferon-alpha and interferon-inducers on West Nile virus in mouse and hamster animal models. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2004, 15, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.Y.; Gu, F.; PHong, W.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Lim, S.P.; Davidson, A.; Vasudevan, S.G. Construction and characterization of a stable subgenomic dengue virus type 2 replicon system for antiviral compound and siRNA testing. Antivir. Res. 2007, 76, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, M.; Amsden, J.R. Successful treatment of West Nile virus infection after approximately 3 weeks into the disease course. Pharmacotherapy 2007, 27, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, M.S. Progresson the development of therapeutics against West. Nile Virus. Antivir. Res. 2009, 83, 215–216. [Google Scholar]
- Engle, M.J.; Diamond, M.S. Antibody prophylaxis and therapy against West Nile virus infection in wild-type and immunodeficient mice. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12941–12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahmen, U.; Dirsch, O.; Li, J.; Fiedle, M.; Lu, M.; Rispeter, K.; Picucci, M.; Broelsch, C.E.; Roggendorf, M. Adoptive transfer of immunity: A new strategy to interfere with severe hepatitis virus reinfection after woodchuck liver transplantation. Transplant 2004, 77, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, G.; Kantipong, P.; Jongsakul, K.; de Souza, M.; Burnouf, T. Passive transfer of scrub typhus plasma to patients with AIDS: A descriptive clinical study. QJM 2001, 94, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.; Attanath, P.; Quiambao, B.; Singhasivanon, V.; Chanthavanich, P.; Montalban, C.; Lutsch, C.; Pepin-Covatta, S.; le Mener, V.; Miranda, M.; et al. Evaluation of the safety, immunogenicity, and pharmacokinetic profile of a new, highly purified, heat-treated equine rabies immunoglobulin, administered either alone or in association with a purified, Vero-cell rabies vaccine. Acta Trop. 1998, 70, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, L.; Banyard, A.C.; van Dolleweerd, C.; Horton, D.L.; Ma, J.K.; Fooks, A.R. Passive immunity in the prevention of rabies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J.; Pla, D. Preclinical analysis of the efficacy of a polyspecific antivenom through antivenomics and neutralization assays. J. Proteomics 2014, 105, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, M.S.; Ma, D.Y.; Thomas, S.; Lund, J.M.; Zhang, N.; Daffis, S.; Rudensky, A.Y.; Bevan, M.J.; Clark, E.A.; Kaja, M.K.; et al. IPS-1 is essential for the control of West Nile virus infection and immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Sato, S.; Yoneyama, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Uematsu, S.; Matsui, K.; Tsujimura, T.; Takeda, K.; Fujita, T.; Takeuchi, O.; et al. Cell type-specific involvement of RIG-I in antiviral response. Immunity 2005, 23, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Kawai, T.; Kato, H.; Sato, S.; Takahashi, K.; Coban, C.; Yamamoto, M.; Uematsu, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Takeuchi, O.; et al. Essential role of IPS-1 in innate immune responses against RNA viruses. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brien, J.D.; Lazear, H.M.; Diamond, M.S. Propagation, quantification, detection, and storage of West Nile virus. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2013, 31, 15D.3.1–15D.3.18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, X.; Gai, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Feng, N.; Chi, H.; Qiu, B.; Li, N.; et al. MERS-Cov virus-like particles produced in insect cells induce specific humoural and cellular imminity in rhesus macaques. Oncotarget 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Vijay, R.; Zhao, J.; Gale, M.; Diamond, M.S.; Perlman, S. MAVS expressed by hematopoietic cells is critical for control of West Nile virus infection and pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7098–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgue, B.; Zeller, H.; Deubel, V. The ecology and epidemiology of West Nile virus in Africa, Europe and Asia. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 267, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Yan, F.; Chen, Z.; Luo, D.; Duan, Y.; Yang, P.; Li, Z.; Peng, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Cross clade prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of polyvalent equine immunoglobulin F(ab′)2 against highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Ni, B.; Luo, D.; Zhao, G.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Xing, L.; et al. Inhibition of infection caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus by equine neutralizing antibody in aged mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.H.; Guo, Z.M.; Han, W.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, D.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Sun, S.Y.; Yang, Q.H.; Zheng, H.Y.; Wong, B.L.; et al. Preparation and development of equine hyperimmune globulin F(ab′)2. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Ni, B.; Zhao, G.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, L.; Pacal, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Xing, L.; Lin, Z.; et al. Protection frominfection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in a Chinese hamster model by equine neutralizing F(ab′)2. Viral Immunol. 2007, 20, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ni, B.; Du, X.; Zhao, G.; Gao, W.; Shi, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Luo, D.; et al. Protection of mammalian cells from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection by equine neutralizing antibody. Antivir. Ther. 2005, 10, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Ni, B.; Jiang, H.; Luo, D.; Pacal, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Xing, L.; Zhang, L.; Jia, Z.; et al. Inhibition of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus infection by equine neutralizing antibody in golden Syrian hamsters. Viral Immunol. 2007, 20, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Qiu, B.; Cao, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, F.; Jin, H.; Wang, T.; et al. Equine Immunoglobulin and Equine Neutralizing F(ab?)2 Protect Mice from West Nile Virus Infection. Viruses 2016, 8, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8120332
Cui J, Zhao Y, Wang H, Qiu B, Cao Z, Li Q, Zhang Y, Yan F, Jin H, Wang T, et al. Equine Immunoglobulin and Equine Neutralizing F(ab?)2 Protect Mice from West Nile Virus Infection. Viruses. 2016; 8(12):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8120332
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Jiannan, Yongkun Zhao, Hualei Wang, Boning Qiu, Zengguo Cao, Qian Li, Yanbo Zhang, Feihu Yan, Hongli Jin, Tiecheng Wang, and et al. 2016. "Equine Immunoglobulin and Equine Neutralizing F(ab?)2 Protect Mice from West Nile Virus Infection" Viruses 8, no. 12: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8120332
APA StyleCui, J., Zhao, Y., Wang, H., Qiu, B., Cao, Z., Li, Q., Zhang, Y., Yan, F., Jin, H., Wang, T., Sun, W., Feng, N., Gao, Y., Sun, J., Wang, Y., Perlman, S., Zhao, J., Yang, S., & Xia, X. (2016). Equine Immunoglobulin and Equine Neutralizing F(ab?)2 Protect Mice from West Nile Virus Infection. Viruses, 8(12), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8120332





