Upregulation of miRNA-4776 in Influenza Virus Infected Bronchial Epithelial Cells Is Associated with Downregulation of NFKBIB and Increased Viral Survival
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Viruses and Their Infections
2.3. Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.4. miRNA Microarray
2.5. Transfection Studies
2.6. Imaging with Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Overexpression of NFKBIB
2.7.1. Validation of miRNA by Ago Immunoprecipitation
2.7.2. Luciferase Assay
2.8. Western Immunoblotting
2.9. Viral Plaque Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
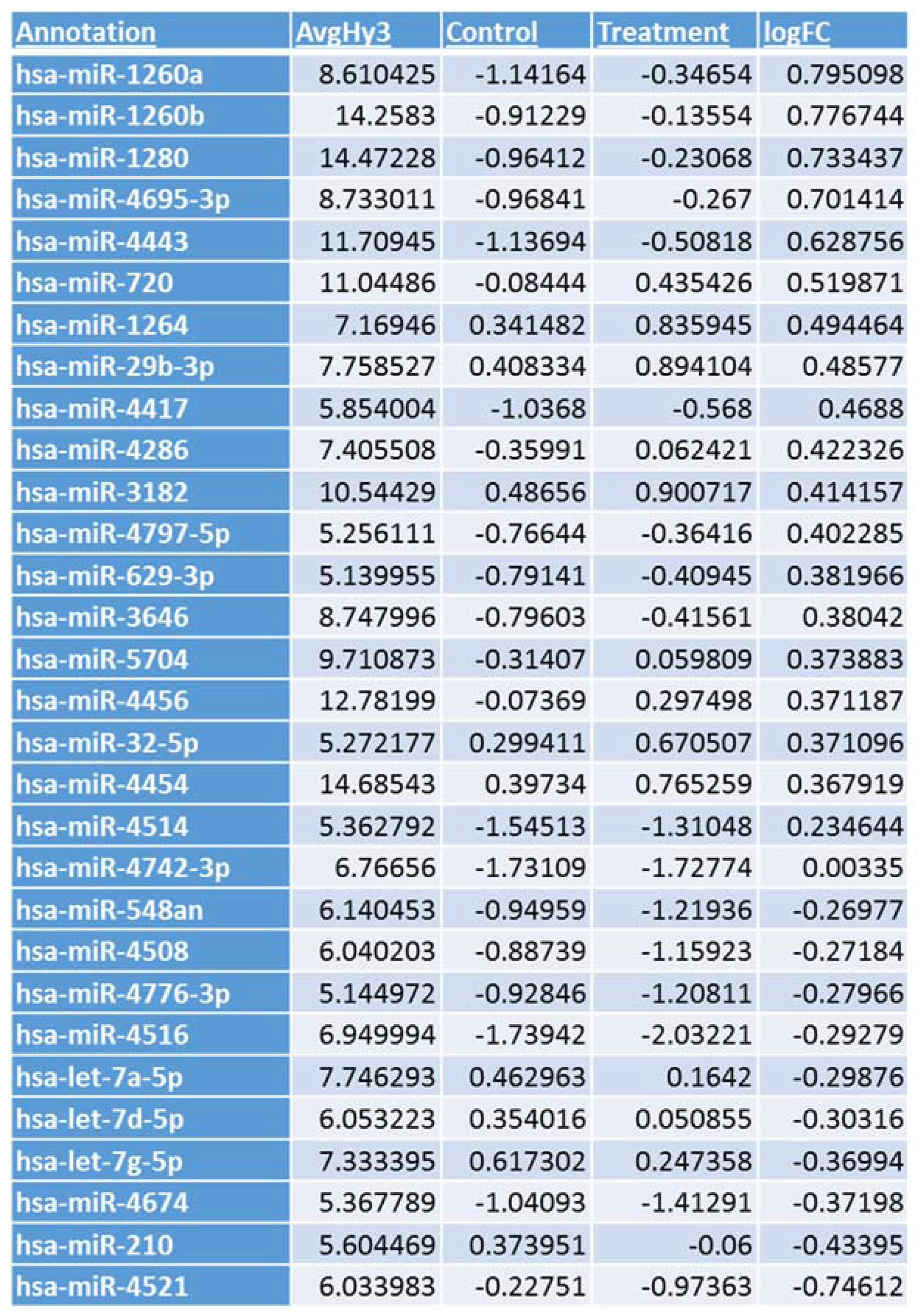
3.1. Microarray Analysis
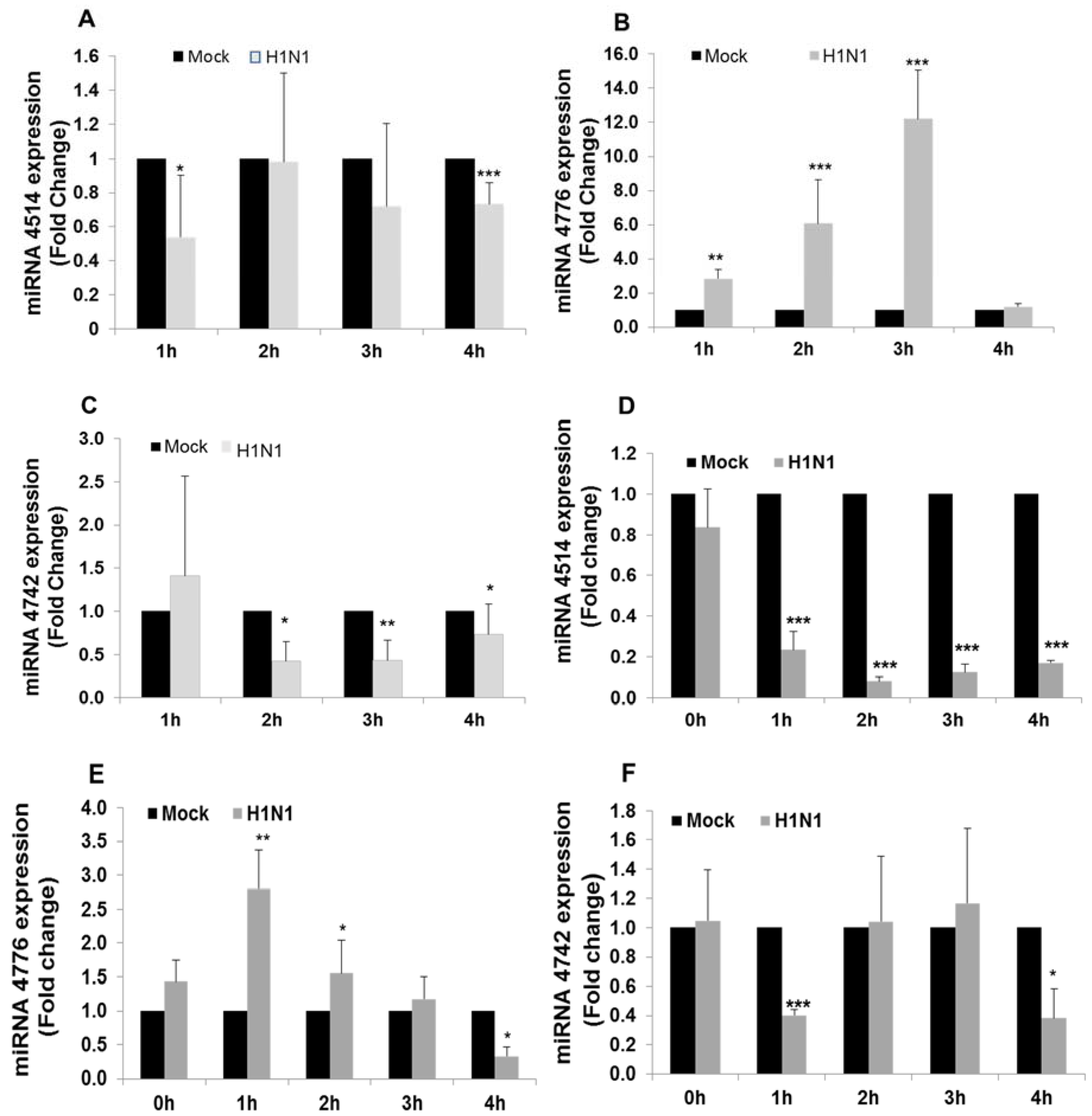
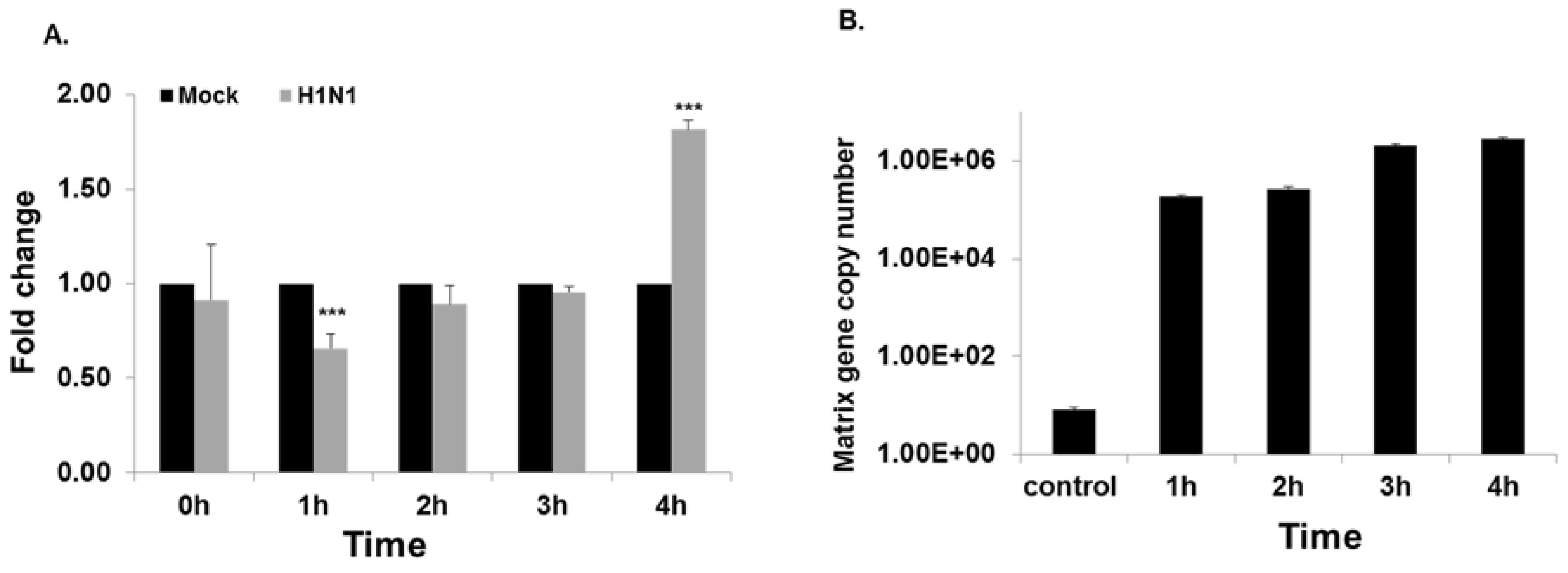
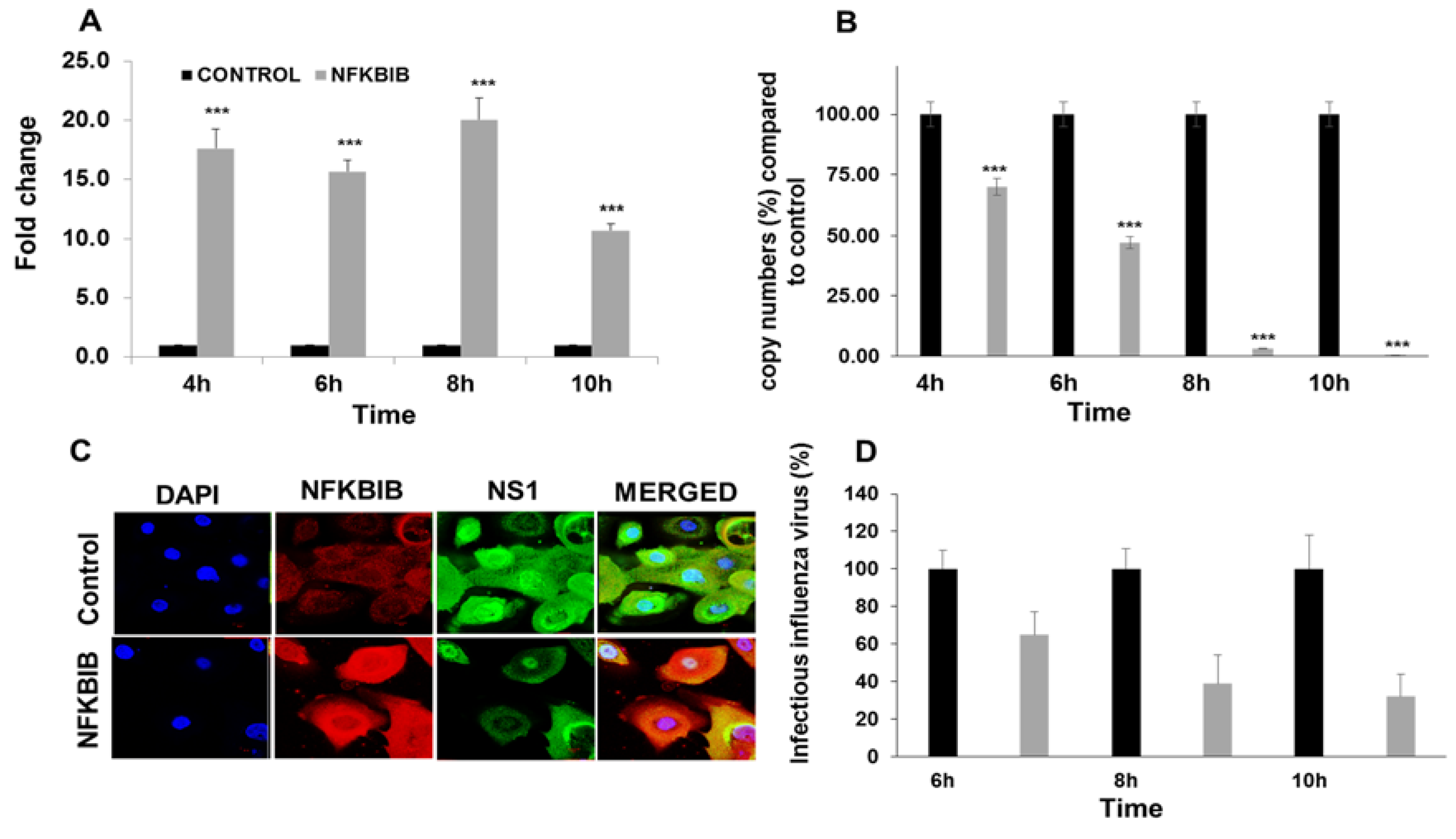
3.2. miRNA and NFKBIB Expression
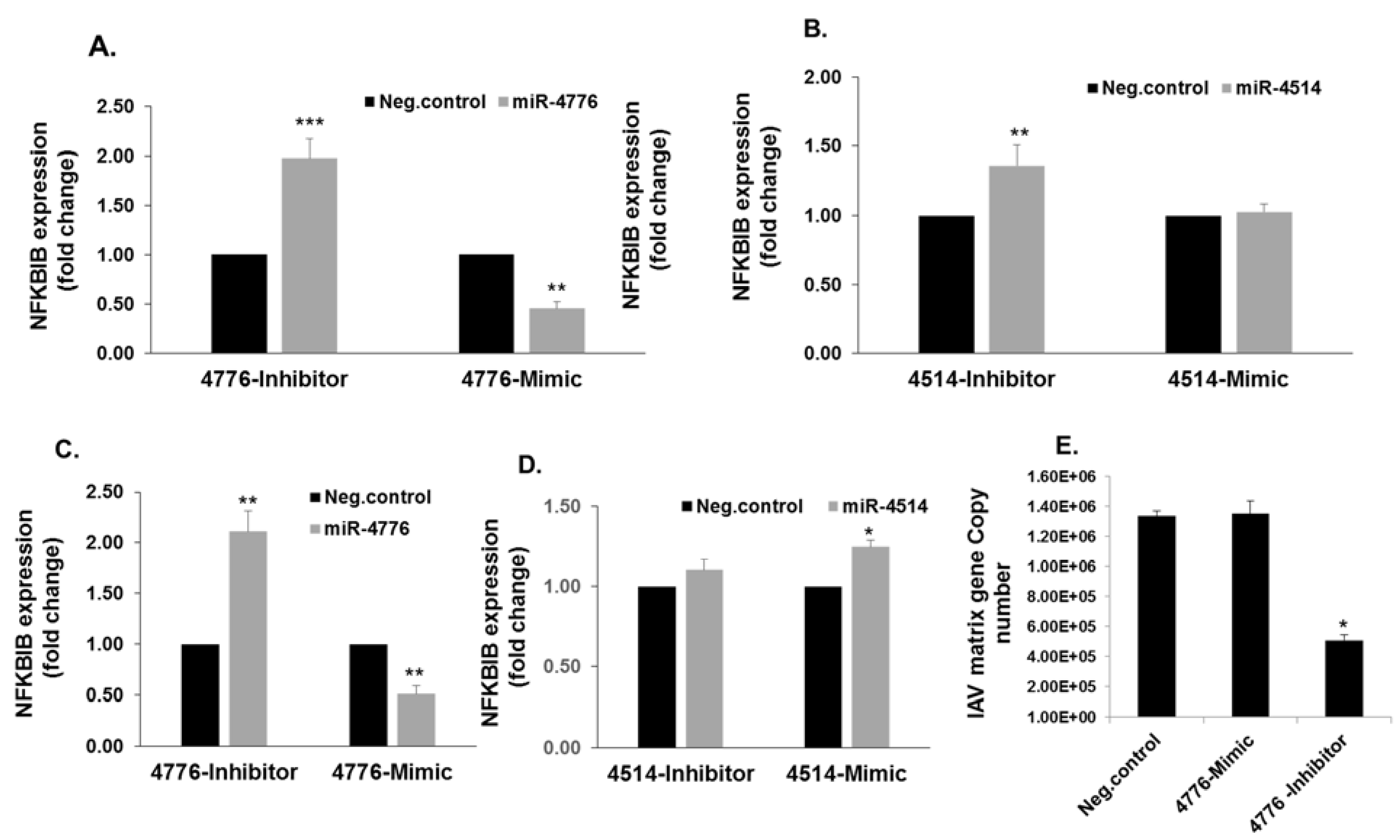
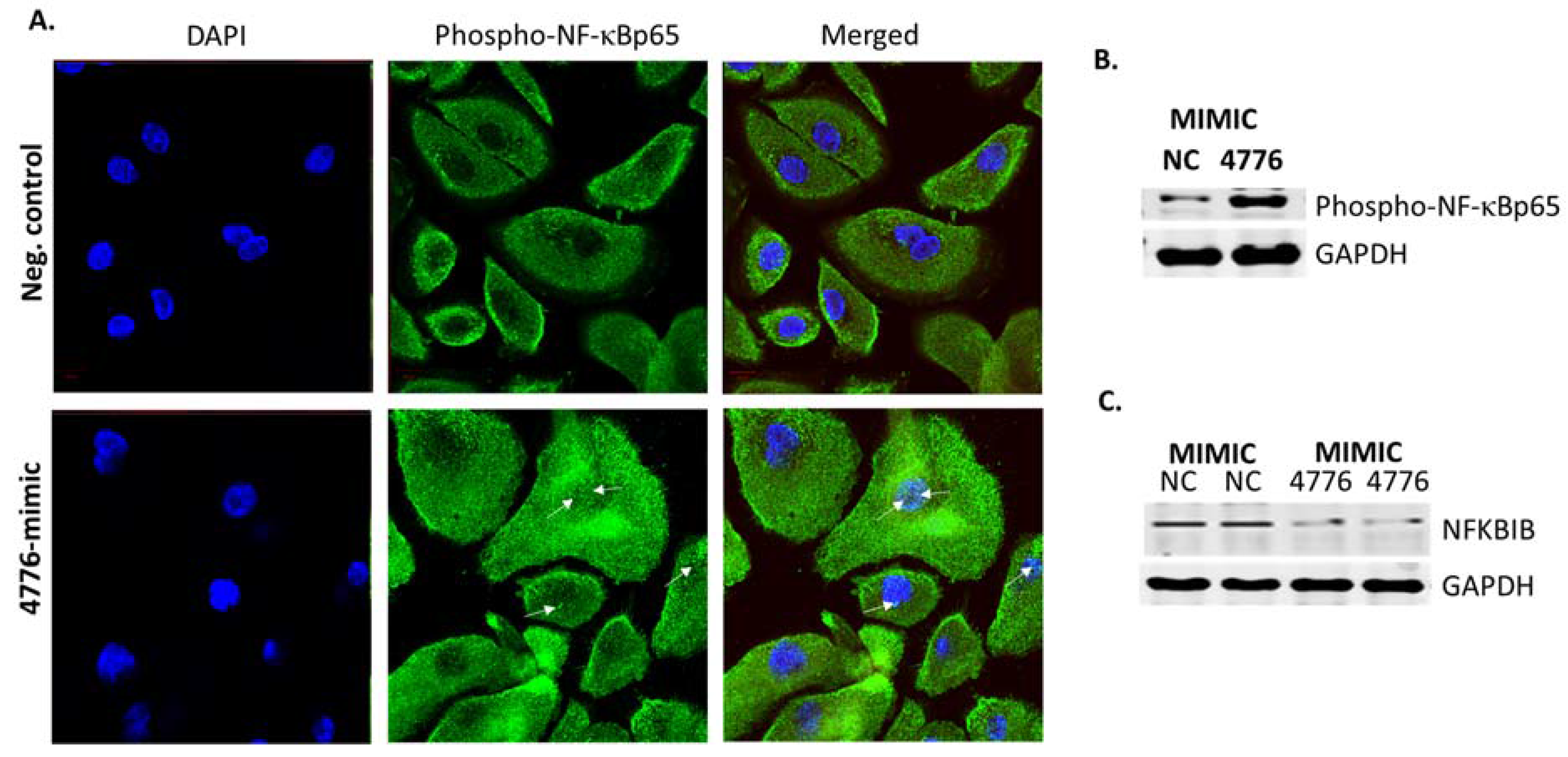
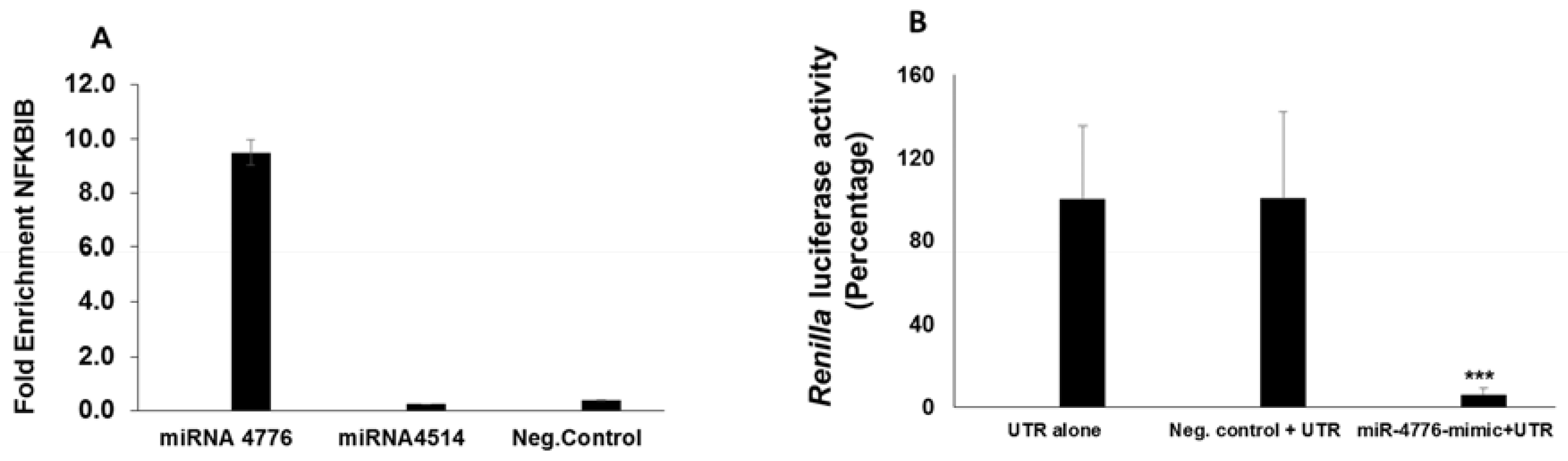
3.3. Functional Analysis of miR-4776 and miR-4514
3.4. miRNA Target Confirmation Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, W.W.; Shay, D.K.; Weintraub, E.; Brammer, L.; Bridges, C.B.; Cox, N.J.; Fukuda, K. Influenza-associated hospitalizations in the United States. JAMA 2004, 292, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Liu, H.; Gao, S.; Jiang, W.; Huang, W. Cellular microRNAs inhibit replication of the H1N1 influenza A virus in infected cells. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8849–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, N.D.; Gilmore, T.D. Good cop, bad cop: The different faces of NF-kappaB. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Neriah, Y.; Karin, M. Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-kappaB as the matchmaker. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurzer, W.J.; Planz, O.; Ehrhardt, C.; Giner, M.; Silberzahn, T.; Pleschka, S.; Ludwig, S. Caspase 3 activation is essential for efficient influenza virus propagation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2717–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Sandbulte, M.R.; Thomas, P.G.; Webby, R.J.; Homayouni, R.; Pfeffer, L.M. NFkappaB negatively regulates interferon-induced gene expression and anti-influenza activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11678–11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Dudziak, D.; Dirmeier, U.; Hobom, G.; Riedel, A.; Schlee, M.; Staudt, L.M.; Rosenwald, A.; Behrends, U.; Bornkamm, G.W.; et al. Active NF-kappaB signalling is a prerequisite for influenza virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurzer, W.J.; Ehrhardt, C.; Pleschka, S.; Berberich-Siebelt, F.; Wolff, T.; Walczak, H.; Planz, O.; Ludwig, S. NF-κB-dependent induction of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and Fas/FasL is crucial for efficient influenza virus propagation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30931–30937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flory, E.; Kunz, M.; Scheller, C.; Jassoy, C.; Stauber, R.; Rapp, U.R.; Ludwig, S. Influenza virus-induced NF-κB-dependent gene expression is mediated by overexpression of viral proteins and involves oxidative radicals and activation of IkappaB kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8307–8314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, M.; Zheng, H.; Muster, T.; Palese, P.; Beg, A.A.; Garcia-Sastre, A. Influenza A virus NS1 protein prevents activation of NF-kappaB and induction of alpha/beta interferon. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 11566–11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, S.; Pleschka, S.; Planz, O.; Wolff, T. Ringing the alarm bells: Signalling and apoptosis in influenza virus infected cells. Cell Microbiol. 2006, 8, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahl, H.L.; Baeuerle, P.A. Expression of influenza virus hemagglutinin activates transcription factor NF-κB. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, C.; Ruckle, A.; Hrincius, E.R.; Haasbach, E.; Anhlan, D.; Ahmann, K.; Banning, C.; Reiling, S.J.; Kuhn, J.; Strobl, S.; et al. The NF-κB inhibitor SC75741 efficiently blocks influenza virus propagation and confers a high barrier for development of viral resistance. Cell Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.; Natoli, G.; Ghosh, G. Transcriptional regulation via the NF-κB signaling module. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6706–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, R.; Kearns, J.D.; Lynch, C.; Vu, D.; Ngo, K.A.; Basak, S.; Ghosh, G.; Hoffmann, A. IkappaBbeta enhances the generation of the low-affinity NF-κB/RelA homodimer. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; May, M.J.; Kopp, E.B. NF-κB and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 225–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palombella, V.J.; Rando, O.J.; Goldberg, A.L.; Maniatis, T. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-κB1 precursor protein and the activation of NF-kappa B. Cell 1994, 78, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Cheng, G.; Shu, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W.; et al. miR-20a enhances cisplatin resistance of human gastric cancer cell line by targeting NFKBIB. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, K.; Steptoe, A.L.; Martin, H.C.; Wani, S.; Nones, K.; Waddell, N.; Mariasegaram, M.; Simpson, P.T.; Lakhani, S.R.; Gabrielli, B.; et al. MicroRNA-182-5p targets a network of genes involved in DNA repair. RNA 2013, 19, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othumpangat, S.; Noti, J.D.; Beezhold, D.H. Lung epithelial cells resist influenza A infection by inducing the expression of cytochrome C oxidase VIc which is modulated by miRNA 4276. Virology 2014, 468–470, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othumpangat, S.; Noti, J.D.; Blachere, F.M.; Beezhold, D.H. Expression of non-structural-1A binding protein in lung epithelial cells is modulated by miRNA-548an on exposure to influenza A virus. Virology 2013, 447, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spackman, E.; Senne, D.A.; Myers, T.J.; Bulaga, L.L.; Garber, L.P.; Perdue, M.L.; Lohman, K.; Daum, L.T.; Suarez, D.L. Development of a Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase PCR Assay for Type A Influenza Virus and the Avian H5 and H7 Hemagglutinin Subtypes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3256–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, M.R.; Sonenberg, N.; Filipowicz, W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottwein, E.; Cullen, B.R. Viral and cellular microRNAs as determinants of viral pathogenesis and immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundhoff, A.; Sullivan, C.S. Virus-encoded microRNAs. Virology 2011, 411, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doench, J.G.; Petersen, C.P.; Sharp, P.A. siRNAs can function as miRNAs. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othumpangat, S.; Walton, C.; Piedimonte, G. MicroRNA-221 modulates RSV replication in human bronchial epithelium by targeting NGF expression. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 2003, 113, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Xin, Z.T.; Liang, Y.; Ly, H. NF-κB signaling differentially regulates influenza virus RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9880–9889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiss, G.K.; Salvatore, M.; Tumpey, T.M.; Carter, V.S.; Wang, X.; Basler, C.F.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Palese, P.; Katze, M.G.; et al. Cellular transcriptional profiling in influenza A virus-infected lung epithelial cells: The role of the nonstructural NS1 protein in the evasion of the host innate defense and its potential contribution to pandemic influenza. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10736–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.K.; Liu, Q.; Tikoo, S.K.; Babiuk, L.A.; Zhou, Y. Effect of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway on influenza A virus propagation. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matranga, C.; Tomari, Y.; Shin, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Zamore, P.D. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell 2005, 123, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.I.; Chendrimada, T.P.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. Human RISC couples microRNA biogenesis and posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell 2005, 123, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X. Evaluating the microRNA targeting sites by luciferase reporter gene assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 936, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krek, A.; Grun, D.; Poy, M.N.; Wolf, R.; Rosenberg, L.; Epstein, E.J.; MacMenamin, P.; da Piedade, I.; Gunsalus, K.C.; Stoffel, M.; et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Othumpangat, S.; Bryan, N.B.; Beezhold, D.H.; Noti, J.D. Upregulation of miRNA-4776 in Influenza Virus Infected Bronchial Epithelial Cells Is Associated with Downregulation of NFKBIB and Increased Viral Survival. Viruses 2017, 9, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050094
Othumpangat S, Bryan NB, Beezhold DH, Noti JD. Upregulation of miRNA-4776 in Influenza Virus Infected Bronchial Epithelial Cells Is Associated with Downregulation of NFKBIB and Increased Viral Survival. Viruses. 2017; 9(5):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050094
Chicago/Turabian StyleOthumpangat, Sreekumar, Nicole B. Bryan, Donald H. Beezhold, and John D. Noti. 2017. "Upregulation of miRNA-4776 in Influenza Virus Infected Bronchial Epithelial Cells Is Associated with Downregulation of NFKBIB and Increased Viral Survival" Viruses 9, no. 5: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050094
APA StyleOthumpangat, S., Bryan, N. B., Beezhold, D. H., & Noti, J. D. (2017). Upregulation of miRNA-4776 in Influenza Virus Infected Bronchial Epithelial Cells Is Associated with Downregulation of NFKBIB and Increased Viral Survival. Viruses, 9(5), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9050094






