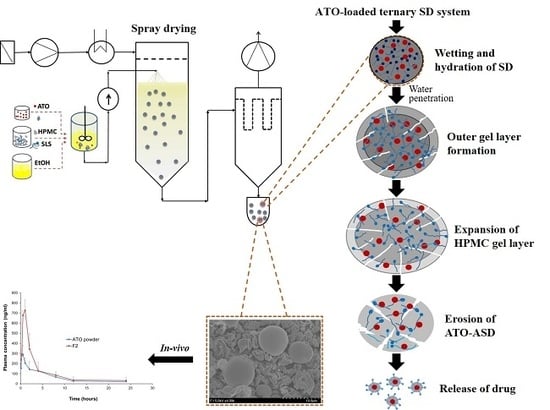
Spray-Dried Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Atorvastatin Calcium for Improved Supersaturation and Oral Bioavailability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Screening of Excipients
2.3. Preparation and Optimization of ATO-Loaded Solid Dispersions
2.4. Solubility of ATO in Solid Dispersions
2.5. In Vitro Dissolution Study
2.6. Physicochemical Characterization
2.6.1. Loading Efficacy
2.6.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.6.4. X-ray Powder Diffraction
2.7. Pharmacokinetic Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Excipients
3.2. Optimization of ATO-Loaded SD
3.3. Evaluation of ATO-Loaded SD
3.4. Physicochemical Characterization
3.5. Pharmacokinetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauss, D.J. Oral lipid-based formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenberg, M.; Kopp, S.; Dressman, J.B. Classification of orally administered drugs on the World Health Organization Model list of Essential Medicines according to the biopharmaceutics classification system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serajuddin, A.T.M. Salt formation to improve drug solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, V.J.; Nti-Addae, K.W. Prodrug strategies to overcome poor water solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, H.G. Effects of mechanical processing on phase composition. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T. Drug solubilization by complexation. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadlamudi, H.C.; Yalavarthi, P.R.; Nagaswaram, T.; Rasheed, A.; Peesa, J.P. In-vitro and pharmacodynamic characterization of solidified self microemulsified system of quetiapine fumarate. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Feng, X.; Williams, R.O.; Zhang, F. Characterization of amorphous solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFall, H.; Sarabu, S.; Shankar, V.; Bandari, S.; Murthy, S.N.; Kolter, K.; Lanley, N.; Kim, D.W.; Repka, M.A. Formulation of aripiprazole-loaded pH-modulated solid dispersions via hot-melt extrusion technology: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.S.; Din, F.U.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Youn, Y.S.; Oh, K.T.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Revaprazan-loaded surface-modified solid dispersion: Physicochemical characterization and in vivo evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 4, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Obi, N. Studies on Absorption of Eutectic Mixture. I. A comparison of the behavior of eutectic mixture of sulfathiazole and that of ordinary sulfathiazole in man. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1961, 9, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Obi, N.; Ueda, Y. Studies on absorption of eutectic mixture. II. Absorption of fused conglomerates of chloramphenicol and urea in rabbits. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1964, 12, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Hattori, Y.; Horie, Y.; Kamada, H.; Nagato, T.; Otsuka, M. Characterization of Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Pharmaceutical Compound with pH-Dependent Solubility Prepared by Continuous-Spray Granulator. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, D.N. Solid dispersions, part I: Recent evolutions and future opportunities in manufacturing methods for dissolution rate enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1501–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willart, J.F.; Descamps, M. Solid state amorphization of pharmaceuticals. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.B.; Patel, J.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Shukla, D. Revealing facts behind spray dried solid dispersion technology used for solubility enhancement. Saudi Pharm. J. 2015, 23, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, P.; Soundararajan, R.; Shanmugam, U.; Ramu, V. Development, characterization and solubility enhancement of comparative dissolution study of second generation of solid dispersions and microspheres for poorly water soluble drug. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, A.K.; Söderlind, E.; Viridén, A.; Schug, B.; Abrahamsson, B.; Knopke, C.; Tajarobi, F.; Blume, H.; Anschütz, M.; Welinder, A.; et al. The influence of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) molecular weight, concentration and effect of food on in vivo erosion behavior of HPMC matrix tablets. J. Control. Release 2014, 187, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghimire, M.; Hodges, L.A.; Band, J.; O’Mahony, B.; McInnes, F.J.; Mullen, A.B.; Stevens, H.N.E. In-vitro and in-vivo erosion profiles of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) matrix tablets. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, C.; Fureby, A.; Schuleit, M.; Dvinskikh, S.V.; Furó, I. Polymer mobilization and drug release during tablet swelling. A 1H NMR and NMR microimaging study. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, A.; Worku, Z.A.; Meeus, J.; Guns, S.; Van den Mooter, G. Manufacturing of solid dispersions of poorly water soluble drugs by spray drying: Formulation and process considerations. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 253–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, S.P.; Dugar, R.P. Application of surfactants in solid dispersion technology for improving solubility of poorly water soluble drugs. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Peng, T.; Huang, Z.; Singh, V.; Shi, Y.; Wen, T.; Lu, M.; Quan, G.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Polymer–surfactant system based amorphous solid dispersion: Precipitation inhibition and bioavailability enhancement of itraconazole. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangiri, A.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Garjani, A.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Hamishehkar, H.; Asadpour-Zeynali, K.; Adibkia, K. Evaluation of physicochemical properties and in vivo efficiency of atorvastatin calcium/ezetimibe solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 82, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desager, J.P.; Horsmans, Y. Clinical pharmacokinetics of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors. Clin. Pharmacokinet 1996, 31, 348–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, H.S.; Goa, K.L. Atorvastatin: An Updated Review of Its Pharmacological Properties and Use in Dyslipidaemia. Drugs 2001, 61, 1835–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, A.P.; McTavish, D. Atorvastatin: A Review of Its Pharmacology and Therapeutic Potential in the Management of Hyperlipidemias. Drugs 1997, 53, 828–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilla, D.D.J.; Whitfield, L.R.; Gibson, D.M.; Sedman, A.J.; Posvar, E.L. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of atorvastatin, an inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 60, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, A.; Bellosta, S.; Baetta, R.; Fumagalli, R.; Paoletti, R.; Bernini, F. New insights into the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of statins. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 84, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Su, X.; Xu, M.; Hu, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro/vivo evaluation of polymer-assisting formulation of atorvastatin calcium based on solid dispersion technique. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, E.S.; Baek, I.H.; Cho, W.; Hwang, S.J.; Kim, M.S. Preparation and Evaluation of Solid Dispersion of Atorvastatin Calcium with Soluplus® by Spray Drying Technique. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, M.S.; Barman, R.K.; Ali, M.A.; Noguchi, S.; Iwao, Y.; Itai, S.; Wahed, M.I.I. Formulation Development and In-Vivo Evaluation of Atorvastatin Calcium Solid Dispersion in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Mice. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2018, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, N.; Deecaraman, M.; Rani, C.; Mohanraj, K.P.; Venkateskumar, K. Formulation development and in vitro evaluation of nanosuspensions loaded with Atorvastatin calcium. Asian J. Pharm. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, K.A.; Higuchi, T. Phase Solubility Techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–212. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, D.A.; Bhatt, K.K.; Shankar, M.B.; Mehta, R.S.; Gandhi, T.R.; Baldania, S.L. RP-HPLC determination of atorvastatin calcium and amlodipine besylate combination in tablets. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 68, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medarević, D.; Djuriš, J.; Barmpalexis, P.; Kachrimanis, K.; Ibrić, S. Analytical and computational methods for the estimation of drug-polymer solubility and miscibility in solid dispersions development. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.M.; Mejia-Ariza, R.; Ilevbare, G.A.; McGettigan, H.E.; Sriranganathan, N.; Taylor, L.S.; Davis, R.M.; Edgar, K.J. Interplay of degradation, dissolution and stabilization of clarithromycin and its amorphous solid dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4640–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdock, G.A. Safety assessment of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as a food ingredient. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaipal, A.; Pandey, M.M.; Charde, S.Y.; Raut, P.P.; Prasanth, K.V.; Prasad, R.G. Effect of HPMC and mannitol on drug release and bioadhesion behavior of buccal discs of buspirone hydrochloride: In-vitro and in-vivo pharmacokinetic studies. Saudi Pharm. J. 2015, 23, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeser, K.A.; Patterson, J.E.; Zeitler, J.A.; Rades, T. The role of configurational entropy in amorphous systems. Pharmaceutics 2010, 2, 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Poudel, B.K.; Marasini, N.; Woo, J.S.; Choi, H.G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Development of raloxifene-solid dispersion with improved oral bioavailability via spray-drying technique. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2013, 36, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.D.; Sung, J.H.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, J.O.; Lee, B.J.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.G. Novel valsartan-loaded solid dispersion with enhanced bioavailability and no crystalline changes. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsi, S.G.; Ayres, J.W. Processing factors in development of solid solution formulation of itraconazole for enhancement of drug dissolution and bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 229, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyanes, A.; Fina, F.; Martorana, A.; Sedough, D.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Development of modified release 3D printed tablets (printlets) with pharmaceutical excipients using additive manufacturing. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 527, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.; Elyafi, E.; Khaliq, A.; Mohammed, A.R.; Al-Khattawi, A. Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs via Mesoporous Silica: Impact of Drug Overloading on Release and Thermal Profiles. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panghal, D.; Nagpal, M.; Thakur, G.S.; Arora, S. Dissolution improvement of atorvastatin calcium using modified locust bean gum by the solid dispersion technique. Sci. Pharm. 2013, 82, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.L. Thermal analysis of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and methylcellulose: Powders, gels and matrix tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 179, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craye, G.; Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Laitinen, R. Characterization of amorphous and co-amorphous simvastatin formulations prepared by spray drying. Molecules 2015, 20, 21532–21548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, F.D.; Aragão, C.F.S.; Moura, T.; Raffin, F.N. Compatibility study between chlorpropamide and excipients in their physical mixtures. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 97, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Formulation | Drug (g) | HPMC (g) | SLS (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
| F2 | 1 | 1 | 0.1 |
| F3 | 1 | 2 | 0.1 |
| F4 | 1 | 4 | 0.1 |
| F5 | 1 | 8 | 0.1 |
| Formulations | ATO | F2 |
|---|---|---|
| AUC (h·ng/mL) | 1557.34 ± 221.46 | 2,621.60 ± 318.99 * |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 328.83 ± 46.56 | 786.23 ± 84.72 * |
| Tmax (h) | 0.40 ± 0.14 | 0.70 ± 0.27 |
| t1/2 (h) | 4.15 ± 0.54 | 4.64 ± 1.45 |
| Kel (h−1) | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.09 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, J.; Giri, B.R.; Song, E.S.; Bae, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.W. Spray-Dried Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Atorvastatin Calcium for Improved Supersaturation and Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090461
Kwon J, Giri BR, Song ES, Bae J, Lee J, Kim DW. Spray-Dried Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Atorvastatin Calcium for Improved Supersaturation and Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(9):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090461
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Jaewook, Bhupendra Raj Giri, Eon Soo Song, Jinju Bae, Junseong Lee, and Dong Wuk Kim. 2019. "Spray-Dried Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Atorvastatin Calcium for Improved Supersaturation and Oral Bioavailability" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 9: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090461
APA StyleKwon, J., Giri, B. R., Song, E. S., Bae, J., Lee, J., & Kim, D. W. (2019). Spray-Dried Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Atorvastatin Calcium for Improved Supersaturation and Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics, 11(9), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090461