Blend Segregation in Tablets Manufacturing and Its Effect on Drug Content Uniformity—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Powder Segregation Basics
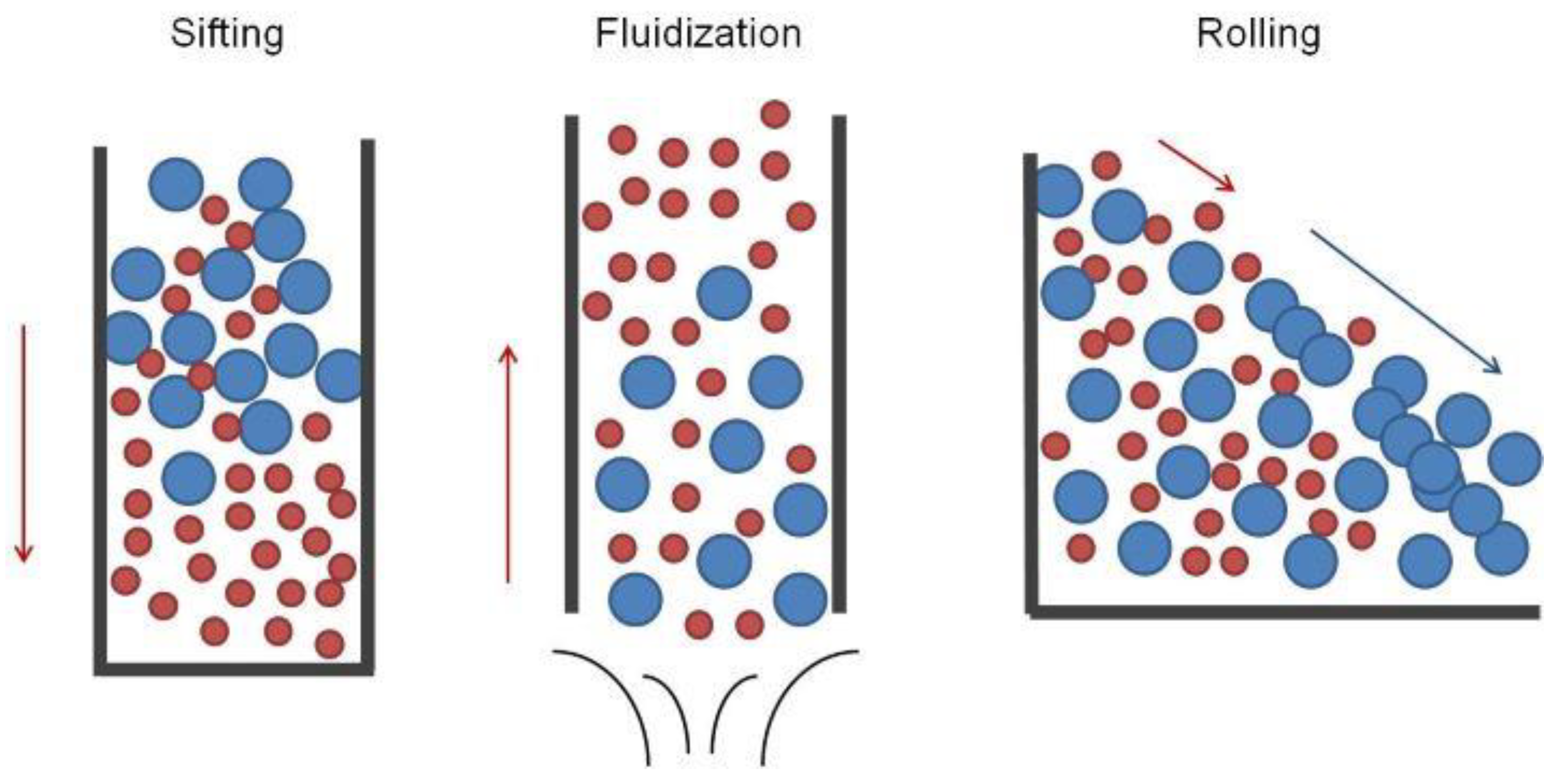
2.1. Segregation Mechanisms and Causes
- the particle size ratio of segregating components in a binary mixture must be at least 1.3:1
- sufficiently large mean particle size; the exact universal value, however, has not been determined
- free-flowing material
2.2. Segregation Testing
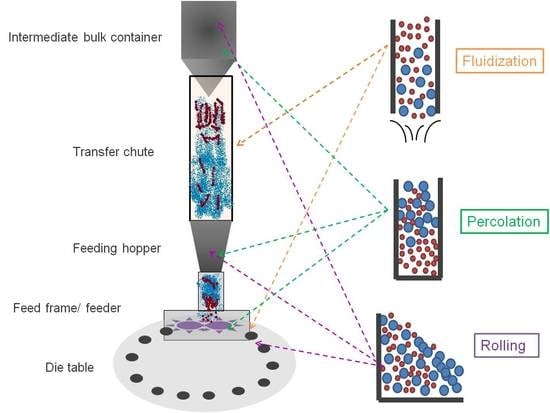
3. Blend Segregation Phenomena at Different Stages of the Tableting Process
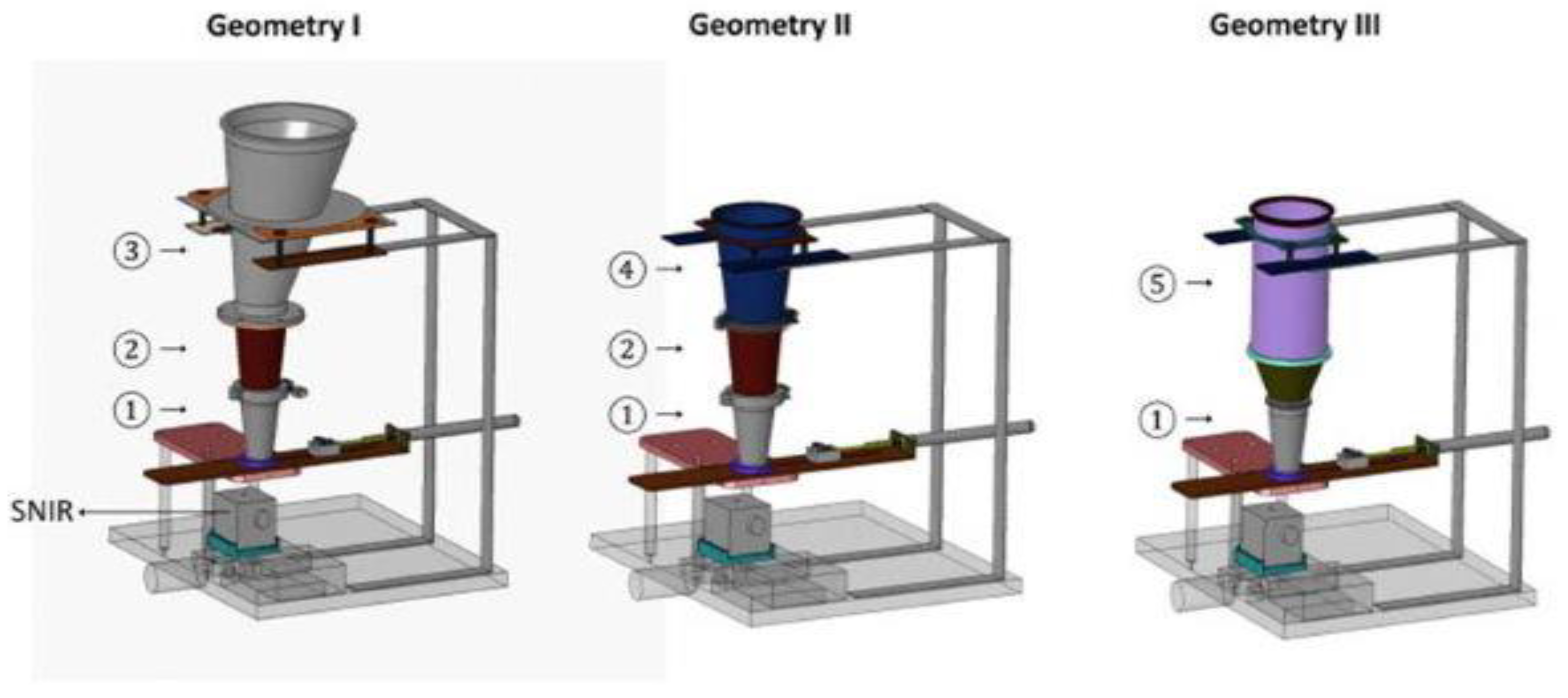
3.1. Blend Transfer from Bulk Container to Tablet Press Feeder
3.2. Blend Segregation in Hoppers
3.3. Blend Segregation during Die Filling
3.3.1. Studies on Segregation in Stationary Die and Moving Shoe
3.3.2. Studies on Segregation in Rotary Tablet Presses
Gravity Feeding
Force Feeding
4. Content Uniformity Improvement and Segregation Prevention by (Pre)Formulation and Processing Choices
4.1. Examples of Blends for Direct Compression
4.2. Examples of Granulated Blends
4.3. New Perspective: Continous Manufacturing for the Improvement of Content Uniformity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Bergum, J.S.; Prescott, J.K.; Tejwani, R.W.; Garcia, T.P.; Clark, J.; Brown, W. Current Events in Blend and Content Uniformity. Pharm. Eng. 2014, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, T.; Bergum, J.; Prescott, J.; Tejwani, R.; Parks, T.; Clark, J.; Brown, W.; Muzzio, F.; Patel, S.; Hoiberg, C. Recommendations for the Assessment of Blend and Content Uniformity: Modifications to Withdrawn FDA Draft Stratified Sampling Guidance. J. Pharm. Innov. 2014, 10, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayeed-Desta, N.; Pazhayattil, A.B.; Collins, J.; Doshi, C. A Science and Risk-Based Pragmatic Methodology for Blend and Content Uniformity Assessment. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, D.J.; van den Ban, S.; Denham, M.; Barylski, I. Real Time Release Testing of Tablet Content and Content Uniformity. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 537, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, J.D.; Rauk, A.P. Use of Bayesian Methods to Analyze and Visualize Content Uniformity Capability Versus United States Pharmacopeia and ASTM Standards. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, B.C.; Garcia-Munoz, S. How Do Formulation and Process Parameters Impact Blend and Unit Dose Uniformity? Further Analysis of the Product Quality Research Institute Blend Uniformity Working Group Industry Survey. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.K.; Garcia, T.P. A Solid Dosage and Blend Content Uniformity Troubleshooting Diagram. Pharm. Technol. 2001, 25, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, J.W. Overcoming Particle Segregation in the Pharmaceutical and Cosmetics Industries. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1988, 14, 2749–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Puri, V.M. Methods for Minimizing Segregation: A Review. Part. Sci. Technol. 2004, 22, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalode, P.; Ierapetritou, M. A Review of Existing Mixing Indices in Solid-Based Continuous Blending Operations. Powder Technol. 2020, 373, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, S.R.; Dyroy, A.; Enstad, G.G. Segregation Mechanisms and Their Quantification Using Segregation Testers. In IUTAM Symposium on Segregation in Granular Flows; Rosato, A.D., Blackmore, D.L., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott, J.K.; Hossfeld, R.J. Maintaining Product Uniformity and Uninterrupted Flow to Direct-Compression Tableting Presses. Pharm. Technol. 1994, 18, 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, J.W.; Royal, T.A.; Goodwill, D.J. Understanding and Eliminating Particle Segregation Problems. Bulk Solids Handl. 1986, 6, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, T.; Garg, V.; Salehi, H.; Bradley, M.S.A. Correlations between Segregation Intensity and Material Properties Such as Particle Sizes and Adhesions and Novel Methods for Assessment. Powder Technol. 2021, 387, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Metzger, M.J.; Glasser, B.J. Effect of Particle Size Distribution on Segregation in Vibrated Systems. Powder Technol. 2013, 237, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriendt, L.; Gatumel, C.; Berthiaux, H. Experimental Evidence of Mixture Segregation by Particle Size Distribution. Part. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaklič, M.; Kočevar, K.; Srčič, S.; Dreu, R. Particle Size-Based Segregation of Pharmaceutical Powders in a Vertical Chute with a Closed Bottom: An Experimental Evaluation. Powder Technol. 2015, 278, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrs, B.R.; Amidon, G.E.; Meury, R.H.; Secreast, P.J.; King, H.M.; Skoug, C.J. Particle Size Limits to Meet USP Content Uniformity Criteria for Tablets and Capsules. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilden, J.; Schrad, M.; Kuehne-Willmore, J.; Sloan, J. A First-Principles Model for Prediction of Product Dose Uniformity Based on Drug Substance Particle Size Distribution. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 2364–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunuguntla, D.R.; Weinhart, T.; Thornton, A.R. Comparing and Contrasting Size-Based Particle Segregation Models. Comput. Part. Mech. 2017, 4, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karttunen, A.-P.; Wikström, H.; Tajarobi, P.; Fransson, M.; Sparén, A.; Marucci, M.; Ketolainen, J.; Folestad, S.; Korhonen, O.; Abrahmsén-Alami, S. Comparison between Integrated Continuous Direct Compression Line and Batch Processing—The Effect of Raw Material Properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 133, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberg, C.; Boetker, J.P.; Rantanen, J.; Pein-Hackelbusch, M. Using 3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping of Characterization Tools for Investigating Powder Blend Behavior. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Han, X.; Ladyzhynsky, N.; Deanne, R. Assessing Powder Segregation Potential by near Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy and Correlating Segregation Tendency to Tabletting Performance. Powder Technol. 2013, 236, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marucci, M.; Al-Saaigh, B.; Boissier, C.; Wahlgren, M.; Wikström, H. Sifting Segregation of Ideal Blends in a Two-Hopper Tester: Segregation Profiles and Segregation Magnitudes. Powder Technol. 2018, 331, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.R.; Badawy, S.I.F.; Szemraj, M.M.; Gray, D.B.; Hussain, M.A. Assessment of Segregation Potential of Powder Blends. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2007, 12, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abatzoglou, N.; Simard, J.-S. Prediction of Segregation Tendency Occurrence in Dry Particulate Pharmaceutical Mixtures: Development of a Mathematical Tool Adapted for Granular Systems Application. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2005, 10, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, N.; Simard, J.-S. Prediction of Segregation Tendency in Dry Particulate Pharmaceutical Mixtures: Application of an Adapted Mathematical Tool to Cohesive and Non-Cohesive Mixtures. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2010, 15, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römerová, S.; Dammer, O.; Zámostný, P. Streamlining of the Powder Mixing Process Based on a Segregation Test. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wilkinson, S.K.; Stitt, E.H.; Marigo, M. Investigating Mixing and Segregation Using Discrete Element Modelling (DEM) in the Freeman FT4 Rheometer. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.L.; Desai, P.M.; Zaidi, S.A.M.; Elkes, R.; Acharya, S.; Truong, T.; Armstrong, C. High-Throughput Blend Segregation Evaluation Using Automated Powder Dispensing Technology. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 159, 105702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Garg, V.; Salehi, H.; Bradley, M.S.A. An Experimental Study on Free-Surface Rolling Segregation and Correlations with Angle of Repose and Particle Sphericity. Powder Technol. 2021, 379, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, C.; Gopireddy, S.R.; Scherließ, R.; Urbanetz, N.A. A DEM Approach to Assess the Influence of the Paddle Wheel Shape on Force Feeding during Pharmaceutical Tableting. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, H.W.; Blackwood, D.O.; Polizzi, M.; Clarke, H. Monitoring Blend Potency in a Tablet Press Feed Frame Using near Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 80, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo-Ortiz, D.; Colon, Y.; Romañach, R.J.; Méndez, R. Analysis of Powder Phenomena inside a Fette 3090 Feed Frame Using In-Line NIR Spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselin, R.; Durão, P.; Abatzoglou, N.; Guay, J.-M. Monitoring the Concentration of Flowing Pharmaceutical Powders in a Tableting Feed Frame. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, C.; Gopireddy, S.R.; Scherließ, R.; Urbanetz, N.A. Investigation of Powder Flow within a Pharmaceutical Tablet Press Force Feeder—A DEM Approach. Powder Technol. 2019, 345, 616–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, E.D.; Conway, S.L.; Zega, J.A.; Glasser, B.J. Segregation of Powders during Gravity Flow through Vertical Pipes. Pharm. Technol. 2004, 28, 78–96. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, T.; Paul, K.A.; Bradley, M.S.A.; Immins, L.; Preston, C.; Scott, J.F.; Welfare, E.H. Investigations on Air Induced Segregation of Pharmaceutical Powders and Effect of Material Flow Functions. Powder Technol. 2010, 203, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.M.; Acharya, S.; Armstrong, C.; Wu, E.L.; Zaidi, S.A.M. Underpinning Mechanistic Understanding of the Segregation Phenomena of Pharmaceutical Blends Using a Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectrometer Embedded Segregation Tester. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 154, 105516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentzler, M.; Michaels, J.N.; Tardos, G.I. Quantification of Segregation Potential for Polydisperse, Cohesive, Multi-Component Powders and Prediction of Tablet Die-Filling Performance—A Methodology for Practical Testing, Re-Formulation and Process Design. Powder Technol. 2015, 285, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teżyk, M.; Jakubowska, E.; Milczewska, K.; Milanowski, B.; Voelkel, A.; Lulek, J. The Influence of Direct Compression Powder Blend Transfer Method from the Container to the Tablet Press on Product Critical Quality Attributes: A Case Study. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.F.; Gan, J.Q.; Pinson, D.; Zhou, Z.Y. Size-Induced Segregation of Granular Materials during Filling a Conical Hopper. Powder Technol. 2018, 340, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, J.F.; Hoffmann, M.; Hughes, H.; Hutchins, P.; Tobyn, M. Monitoring Process Induced Attrition of Drug Substance Particles within Formulated Blends. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 470, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, J.F.; Dennis, A.B.; Hutchins, P.; Jones, J.W.; Musembi, P.; Tobyn, M. Determination of Process Variables Affecting Drug Particle Attrition within Multi-Component Blends during Powder Feed Transmission. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leersnyder, F.; Vanhoorne, V.; Bekaert, H.; Vercruysse, J.; Ghijs, M.; Bostijn, N.; Verstraeten, M.; Cappuyns, P.; Van Assche, I.; Vander Heyden, Y.; et al. Breakage and Drying Behaviour of Granules in a Continuous Fluid Bed Dryer: Influence of Process Parameters and Wet Granule Transfer. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 115, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryckaert, A.; Ghijs, M.; Portier, C.; Djuric, D.; Funke, A.; Vervaet, C.; De Beer, T. The Influence of Equipment Design and Process Parameters on Granule Breakage in a Semi-Continuous Fluid Bed Dryer after Continuous Twin-Screw Wet Granulation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketterhagen, W.R.; Curtis, J.S.; Wassgren, C.R.; Kong, A.; Narayan, P.J.; Hancock, B.C. Granular Segregation in Discharging Cylindrical Hoppers: A Discrete Element and Experimental Study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 6423–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketterhagen, W.R.; Curtis, J.S.; Wassgren, C.R.; Hancock, B.C. Modeling Granular Segregation in Flow from Quasi-Three-Dimensional, Wedge-Shaped Hoppers. Powder Technol. 2008, 179, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketterhagen, W.R.; Hancock, B.C. Optimizing the Design of Eccentric Feed Hoppers for Tablet Presses Using DEM. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2010, 34, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.F.; Gan, J.Q.; Yu, A.B.; Pinson, D.; Zhou, Z.Y. Segregation of Granular Binary Mixtures with Large Particle Size Ratios during Hopper Discharging Process. Powder Technol. 2020, 361, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos Gil, E.; Gosselin, R.; Abatzoglou, N. NIRS Methodology for Measuring Radial and Axial Concentration Profiles in Flowing Granular Mixtures. Powder Technol. 2012, 224, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, N.; Castellanos Gil, E.; Gosselin, R. Influence of Hopper Geometry on Radial and Axial Concentration Profiles of Segregated and Homogenized Granular Mixture Flows. Powder Technol. 2014, 262, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karande, A.D.; Heng, P.W.S.; Liew, C.V. In-Line Quantification of Micronized Drug and Excipients in Tablets by near Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy: Real Time Monitoring of Tabletting Process. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 396, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, P.R.; Fruhmann, G.; Sacher, S.; Straka, G.; Sowinski, S.; Khinast, J.G. PAT for Tableting: Inline Monitoring of API and Excipients via NIR Spectroscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinka, I.C.; Schneider, L.C.R.; Cocks, A.C.F. Measurement of the Flow Properties of Powders with Special Reference to Die Fill. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 280, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.C.R.; Sinka, I.C.; Cocks, A.C.F. Characterisation of the Flow Behaviour of Pharmaceutical Powders Using a Model Die–Shoe Filling System. Powder Technol. 2007, 173, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinka, I.C.; Motazedian, F.; Cocks, A.C.F.; Pitt, K.G. The Effect of Processing Parameters on Pharmaceutical Tablet Properties. Powder Technol. 2009, 189, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, L.A.; Sinka, I.C. Effect of Particle Size and Density on the Die Fill of Powders. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 84, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, C.-Y.; Kafui, K.D.; Thornton, C. Numerical Analysis of Density-Induced Segregation during Die Filling. Powder Technol. 2010, 197, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, C.-Y.; Thornton, C. The Effects of Air and Particle Density Difference on Segregation of Powder Mixtures during Die Filling. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, C.-Y.; Kafui, K.D.; Thornton, C. 3D DEM/CFD Analysis of Size-Induced Segregation during Die Filling. Powder Technol. 2011, 206, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhvatayeva, A.; Hare, C.; Wu, C.Y. Size-Induced Segregation during Die Filling. Int. J. Pharm. X 2019, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Aragón, C.; Alba-Elías, F.; González-Marcos, A.; Ordieres-Meré, J. Improving the Feeder Shoe Design of an Eccentric Tablet Press Machine. Powder Technol. 2020, 372, 542–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yoshinaga, S.; Tsunazawa, Y.; Tokoro, C. Numerical Investigation of Segregation Behavior of Multi-Sized Particles during Pharmaceutical Mini-Tablet Die Filling. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Aragón, C.; Alba-Elías, F.; González-Marcos, A.; Ordieres-Meré, J. Segregation in the Tank of a Rotary Tablet Press Machine Using Experimental and Discrete Element Methods. Powder Technol. 2018, 328, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, C.; Gopireddy, S.R.; Scherließ, R.; Urbanetz, N.A. Simulation of Particle Size Segregation in a Pharmaceutical Tablet Press Lab-Scale Gravity Feeder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, R.; Shiosaka, Y.; Kadota, K.; Takagaki, K.; Noguchi, T.; Shimosaka, A.; Shirakawa, Y. Size-Induced Segregation during Pharmaceutical Particle Die Filling Assessed by Response Surface Methodology Using Discrete Element Method. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Vega, N.O.; Romañach, R.J.; Méndez, R. Feed Frame: The Last Processing Step before the Tablet Compaction in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Ortiz, D.; Muzzio, F.J.; Méndez, R. Particle Size Segregation Promoted by Powder Flow in Confined Space: The Die Filling Process Case. Powder Technol. 2014, 262, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Ortiz, D.; Méndez, R. Relationship between Residence Time Distribution and Forces Applied by Paddles on Powder Attrition during the Die Filling Process. Powder Technol. 2015, 278, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, C.; Gopireddy, S.R.; Scherließ, R.; Urbanetz, N. Numerical Analysis of the Die Filling Process Within a Pharmaceutical Tableting Machine. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2018, 90, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, R.; Velazquez, C.; Muzzio, F.J. Effect of Feed Frame Design and Operating Parameters on Powder Attrition, Particle Breakage, and Powder Properties. Powder Technol. 2012, 229, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Thommes, M. Residence Time and Mixing Capacity of a Rotary Tablet Press Feed Frame. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dülle, M.; Özcoban, H.; Leopold, C.S. Analysis of the Powder Behavior and the Residence Time Distribution within a Production Scale Rotary Tablet Press. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 125, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazi, N.; Liu, Z.; Bhatt, C.; Kiang, S.; Cuitino, A. Investigating the Effect of APAP Crystals on Tablet Behavior Manufactured by Direct Compression. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muselík, J.; Franc, A.; Doležel, P.; Goněc, R.; Krondlová, A.; Lukášová, I. Influence of Process Parameters on Content Uniformity of a Low Dose Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient in a Tablet Formulation According to GMP. Acta Pharm. Zagreb Croat. 2014, 64, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yousaf, A.M.; Jee, J.-P.; Hwang, S.R.; Maeng, H.-J.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.-G.; Cho, K.H. Development of Direct Compression Entecavir 0.5 Mg-Loaded Tablet Exhibiting Enhanced Content Uniformity. Powder Technol. 2014, 267, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Wu, H.; Shen, M.; Augsburger, L.L.; Lyon, R.C.; Khan, M.A.; Hussain, A.S.; Hoag, S.W. Quality-by-Design (QbD): Effects of Testing Parameters and Formulation Variables on the Segregation Tendency of Pharmaceutical Powder Measured by the ASTM D 6940-04 Segregation Tester. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4485–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Tanaka, C.; Yuasa, H.; Sakamoto, T. Utility of Microcrystalline Cellulose for Improving Drug Content Uniformity in Tablet Manufacturing Using Direct Powder Compression. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.G.; Truitt, B.F.; Kong, A.; Leyva, N.; Luner, P.E. Influence of Formulation Composition and Processing on the Content Uniformity of Low-Dose Tablets Manufactured at Kilogram Scale. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2009, 14, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, J.; Langdon, B.A.; Hicks, I.; Song, D.; Li, F.; Kathiria, L.; Kane, A.; Ranade, G.; Agarwal, K. A Quality-by-Design Study for an Immediate-Release Tablet Platform: Examining the Relative Impact of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Properties, Processing Methods, and Excipient Variability on Drug Product Quality Attributes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- am Ende, M.T.; Moses, S.K.; Carella, A.J.; Gadkari, R.A.; Graul, T.W.; Otano, A.L.; Timpano, R.J. Improving the Content Uniformity of a Low-Dose Tablet Formulation through Roller Compaction Optimization. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2007, 12, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherholz, M.L.; Wan, B.; McGeorge, G. A Rational Analysis of Uniformity Risk for Agglomerated Drug Substance Using NIR Chemical Imaging. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, T.; Nagato, T.; Kanou, Y.; Matsui, K.; Natsuyama, S.; Kawanishi, T.; Hiyama, Y. Detection of Component Segregation in Granules Manufactured by High Shear Granulation with Over-Granulation Conditions Using near-Infrared Chemical Imaging. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Emady, H.; Kašpar, O.; Tokárová, V.; Muzzio, F.; Štěpánek, F.; Ramachandran, R. The Effects of Improper Mixing and Preferential Wetting of Active and Excipient Ingredients on Content Uniformity in High Shear Wet Granulation. Powder Technol. 2015, 278, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, S.; Smrčka, D.; Kataria, A.; Emady, H.; Muzzio, F.; Štěpánek, F.; Ramachandran, R. Analysis of the Origins of Content Non-Uniformity in High-Shear Wet Granulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 528, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkhade, D.M. Comparative Impact of Different Binder Addition Methods, Binders and Diluents on Resulting Granule and Tablet Attributes via High Shear Wet Granulation. Powder Technol. 2017, 320, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundozah, A.L.; Yang, J.; Tridon, C.C.; Cartwright, J.J.; Omar, C.S.; Salman, A.D. Assessing Particle Segregation Using Near-Infrared Chemical Imaging in Twin Screw Granulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 568, 118541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teżyk, M.; Milanowski, B.; Ernst, A.; Lulek, J. Recent Progress in Continuous and Semi-Continuous Processing of Solid Oral Dosage Forms: A Review. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1195–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Vega, N.O.; Román-Ospino, A.; Scicolone, J.; Muzzio, F.J.; Romañach, R.J.; Méndez, R. Assessment of Blend Uniformity in a Continuous Tablet Manufacturing Process. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 560, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, S.; Sahay, A.; Meng, W.; Muzzio, F. Diminished Segregation in Continuous Powder Mixing. Powder Technol. 2017, 309, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.J.; Almaya, A.; Kramer, T.T.; Hofer, J.D. A Demonstration of Mixing Robustness in a Direct Compression Continuous Manufacturing Process. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakio, S.; Ervasti, T.; Tajarobi, P.; Wikström, H.; Fransson, M.; Karttunen, A.-P.; Ketolainen, J.; Folestad, S.; Abrahmsén-Alami, S.; Korhonen, O. Provoking an End-to-End Continuous Direct Compression Line with Raw Materials Prone to Segregation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 109, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karttunen, A.-P.; Poms, J.; Sacher, S.; Sparén, A.; Ruiz Samblás, C.; Fransson, M.; Martin De Juan, L.; Remmelgas, J.; Wikström, H.; Hsiao, W.-K.; et al. Robustness of a Continuous Direct Compression Line against Disturbances in Feeding. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 574, 118882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jakubowska, E.; Ciepluch, N. Blend Segregation in Tablets Manufacturing and Its Effect on Drug Content Uniformity—A Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111909
Jakubowska E, Ciepluch N. Blend Segregation in Tablets Manufacturing and Its Effect on Drug Content Uniformity—A Review. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(11):1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111909
Chicago/Turabian StyleJakubowska, Emilia, and Natalia Ciepluch. 2021. "Blend Segregation in Tablets Manufacturing and Its Effect on Drug Content Uniformity—A Review" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 11: 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13111909