Recent Advances in 18F-Labeled Amino Acids Synthesis and Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Metal-Free 18F-AA Synthesis
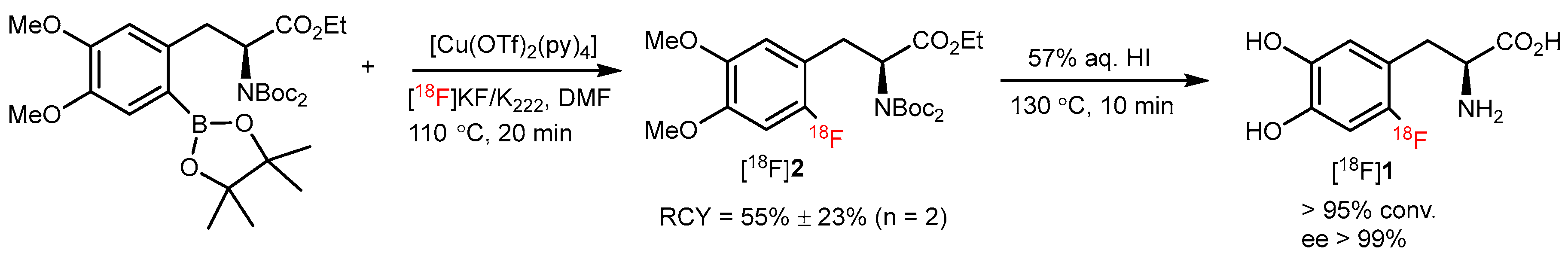
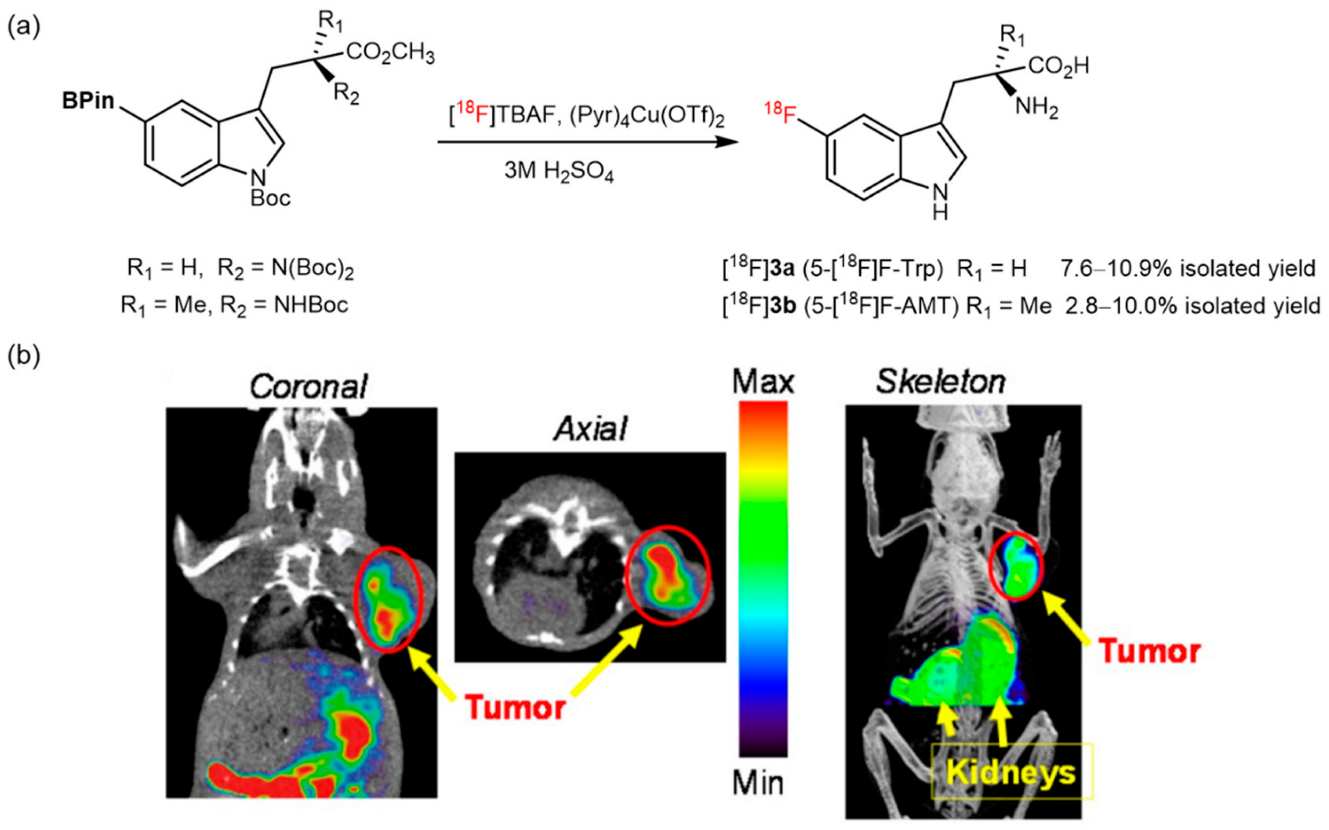
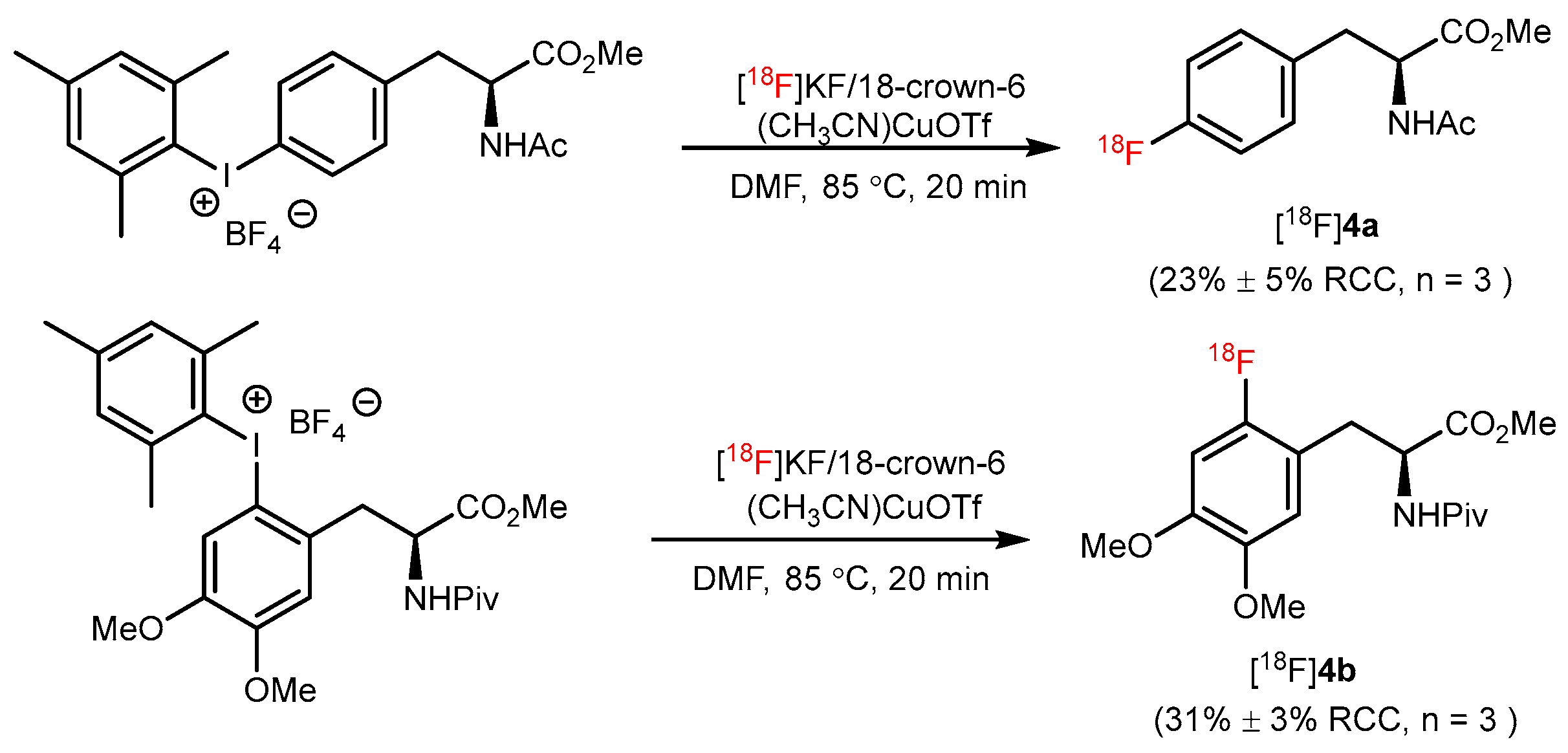
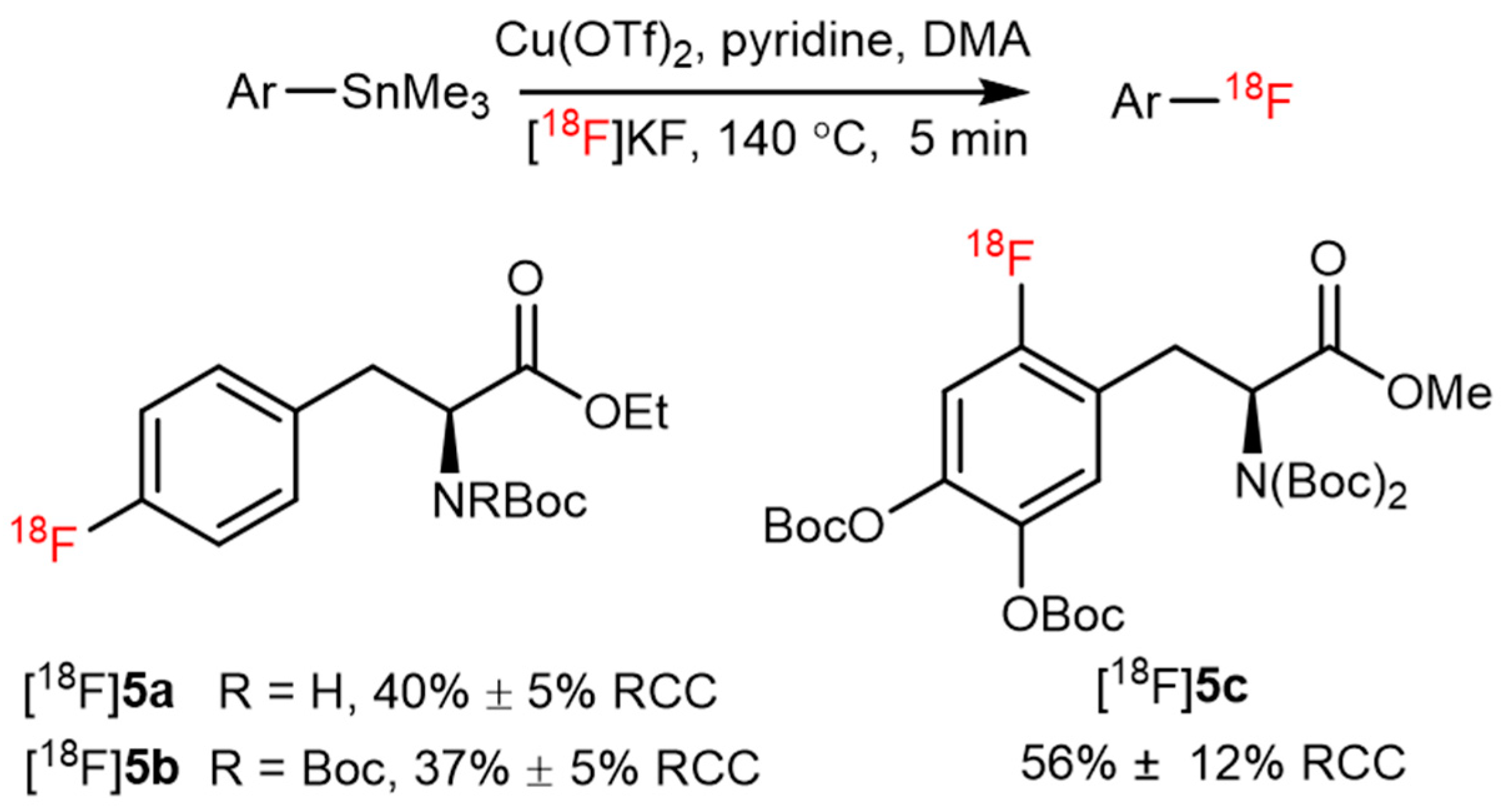
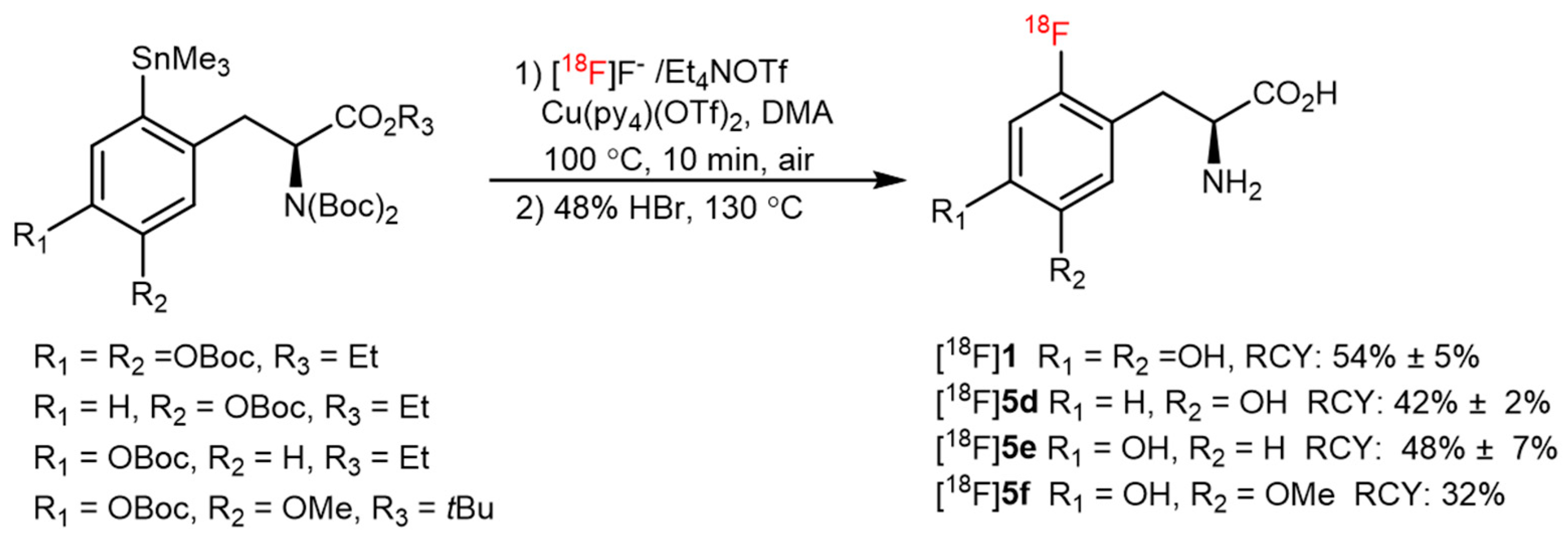
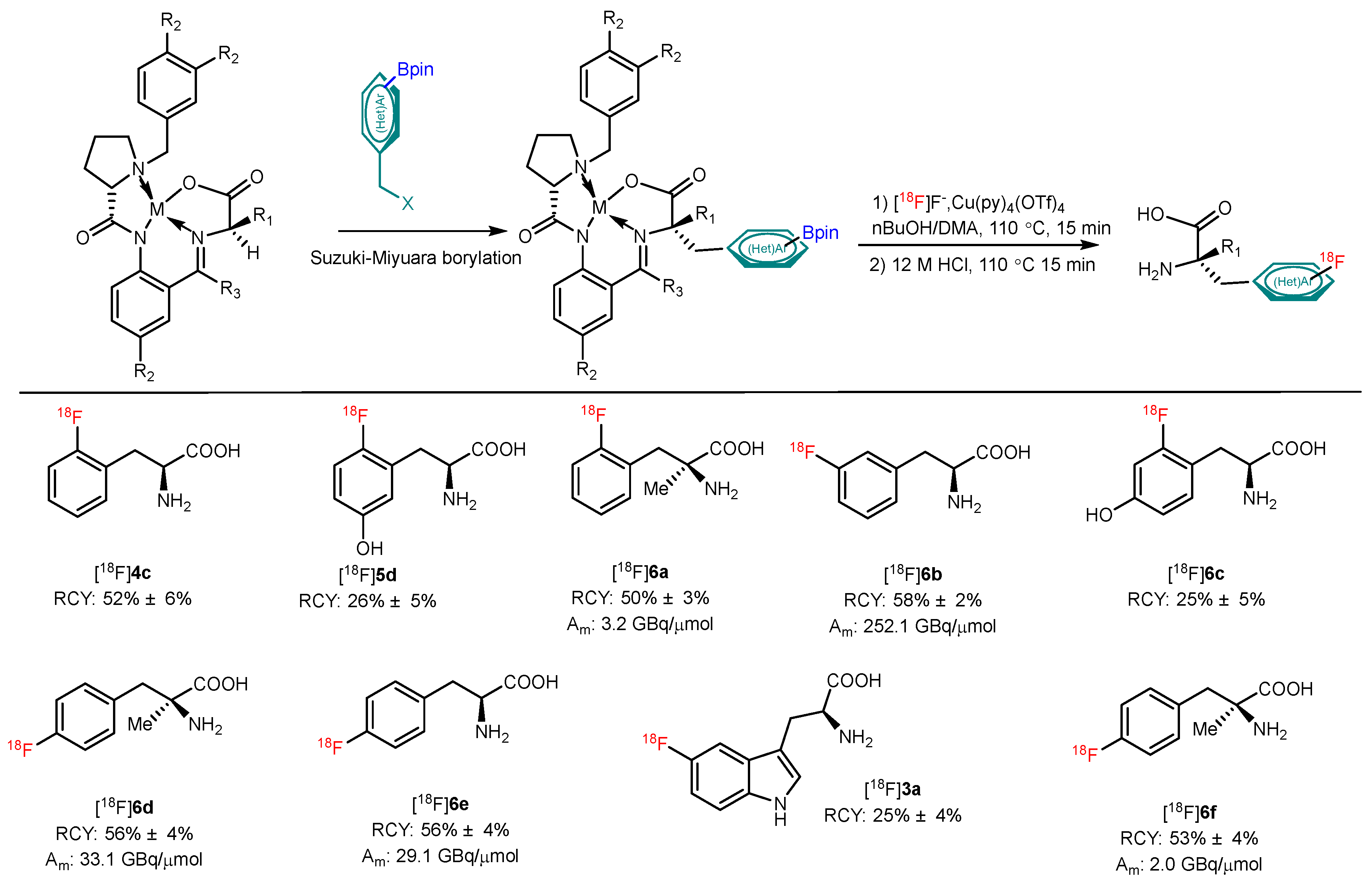
3. Copper-Catalyzed 18F-AA Synthesis
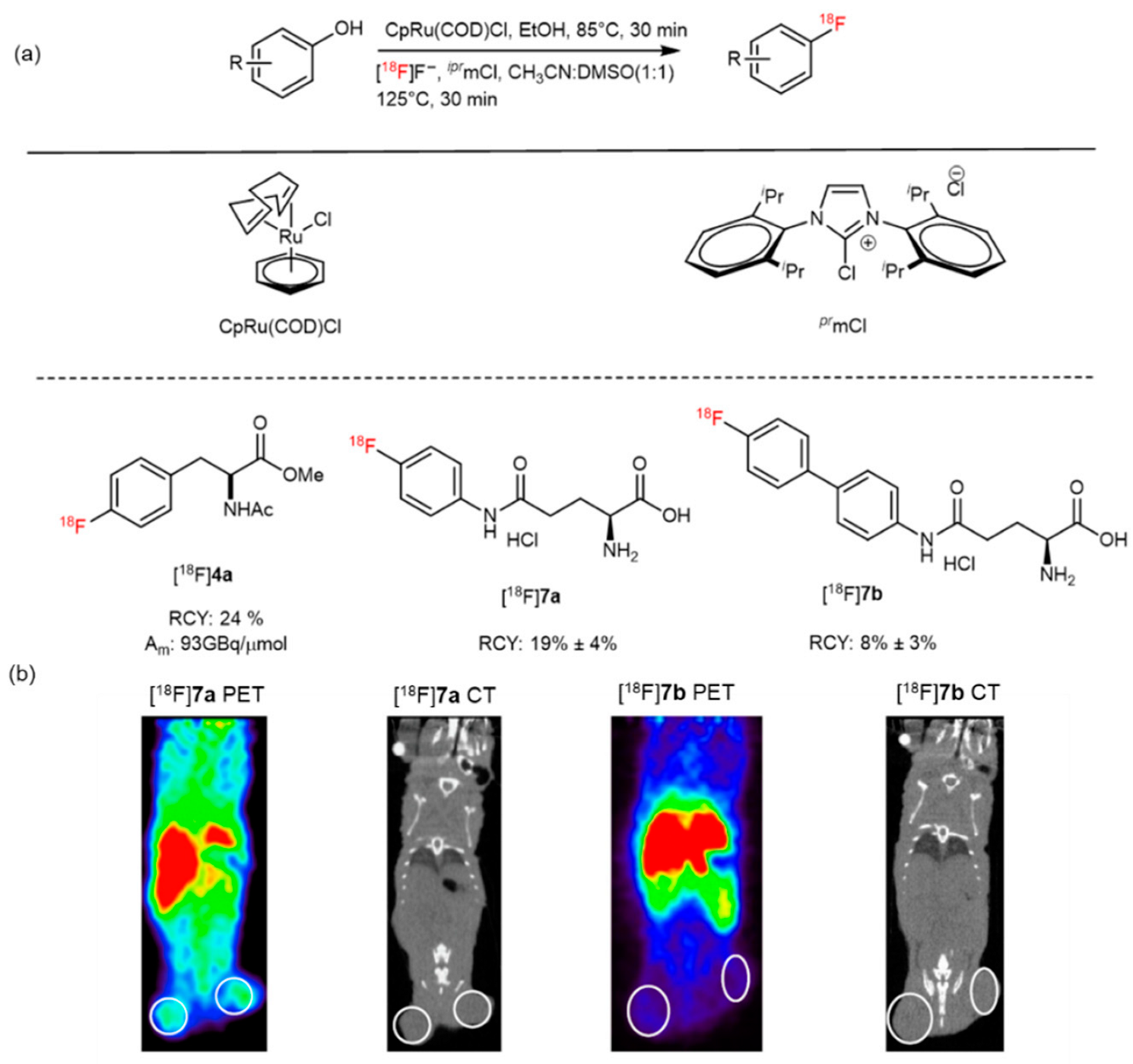
4. Ruthenium-Catalyzed 18F-AA Synthesis
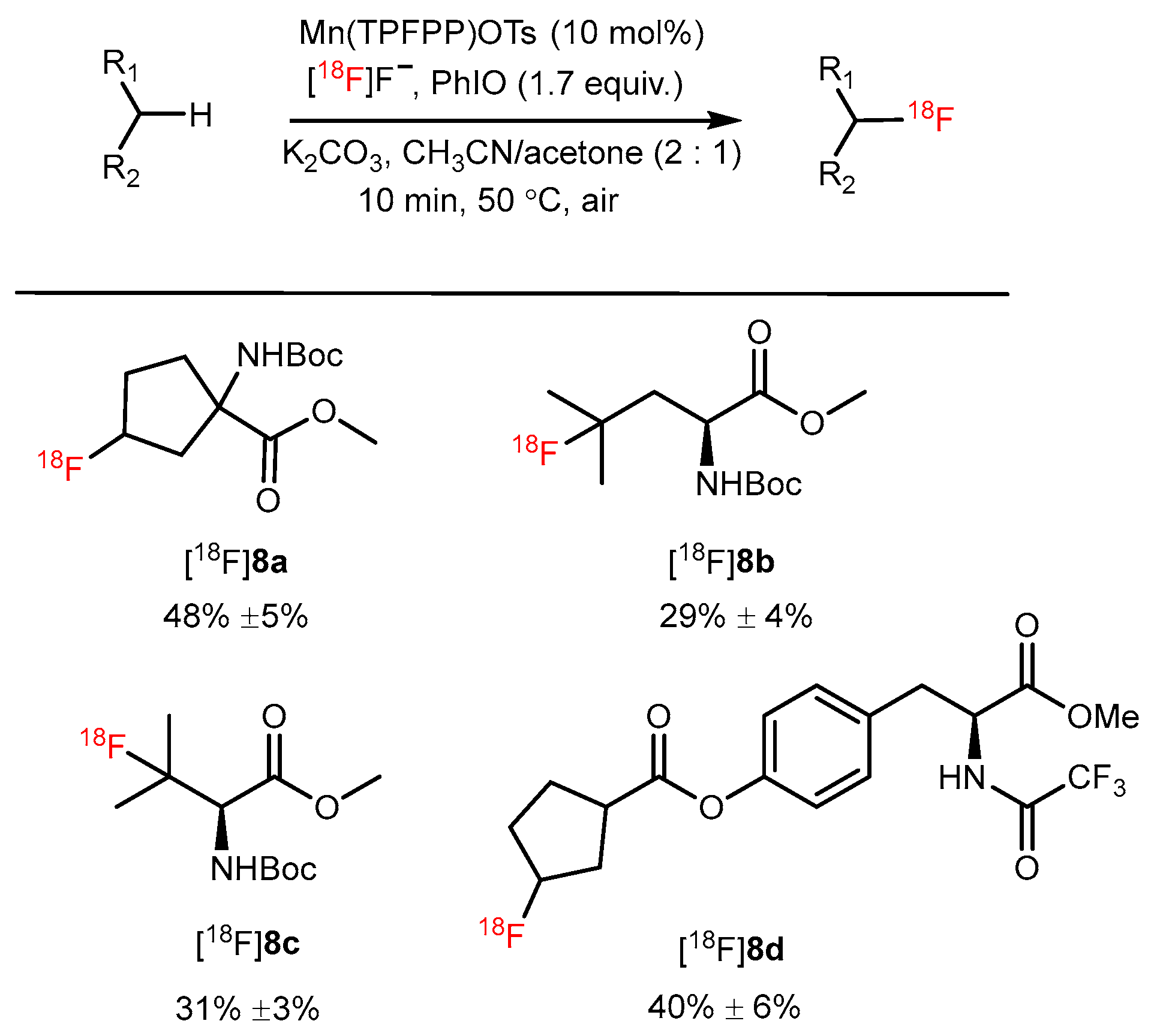
5. Manganese-Catalyzed 18F-AA Synthesis
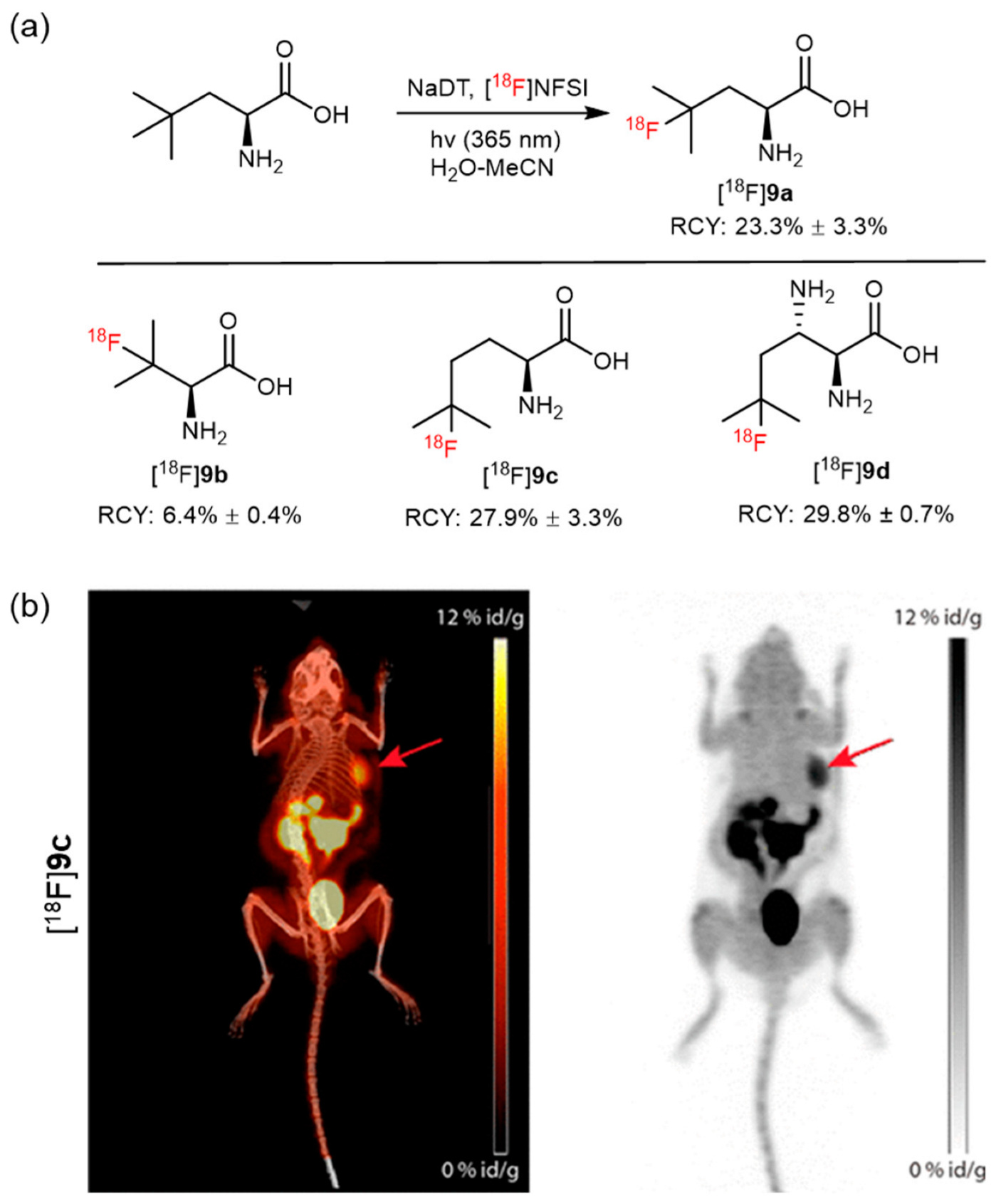
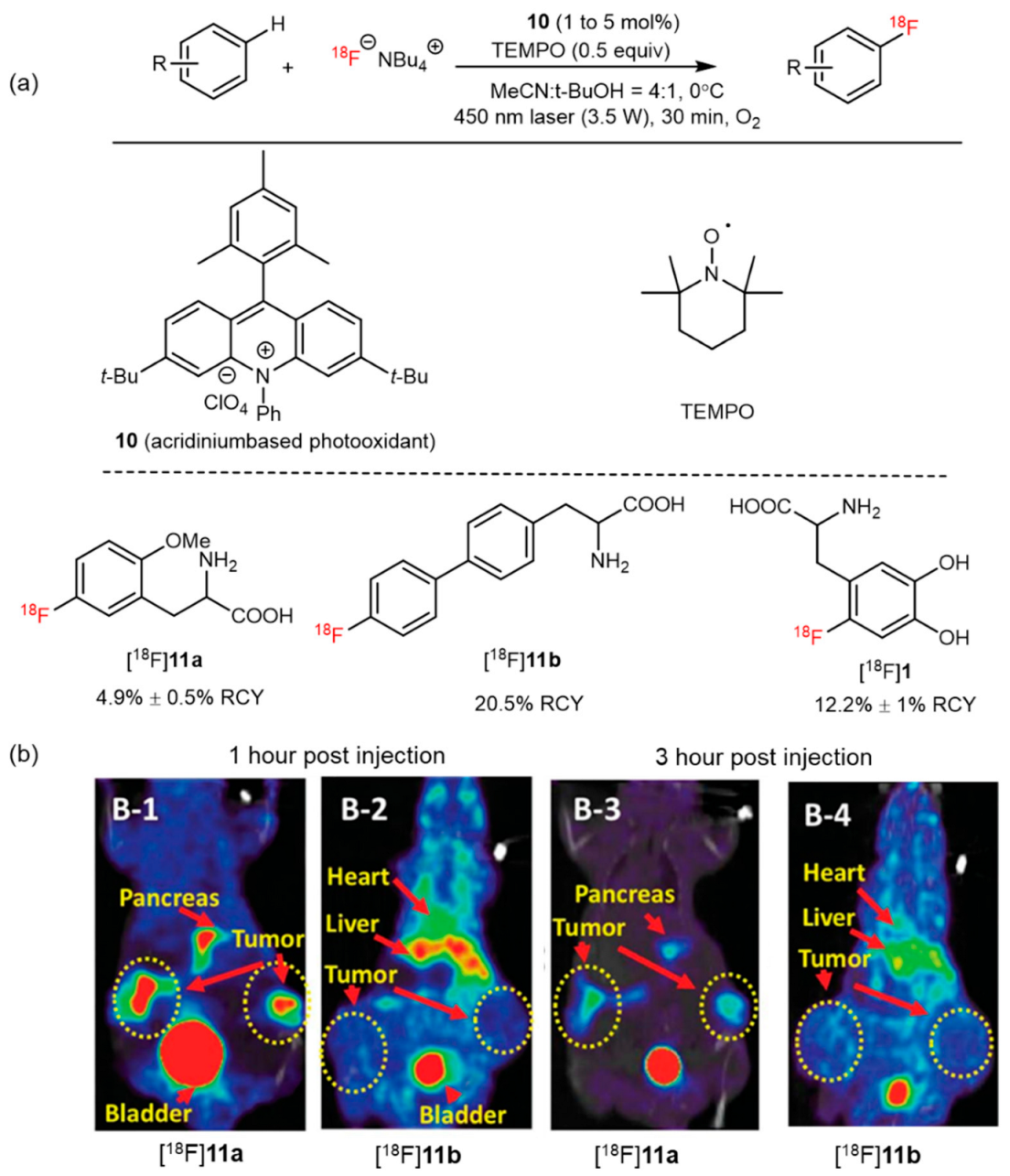
6. Photocatalyzed 18F-AA Synthesis
7. Synthesis of 18F-Labeled AAs via [18F]Trifluoromethylation Reaction
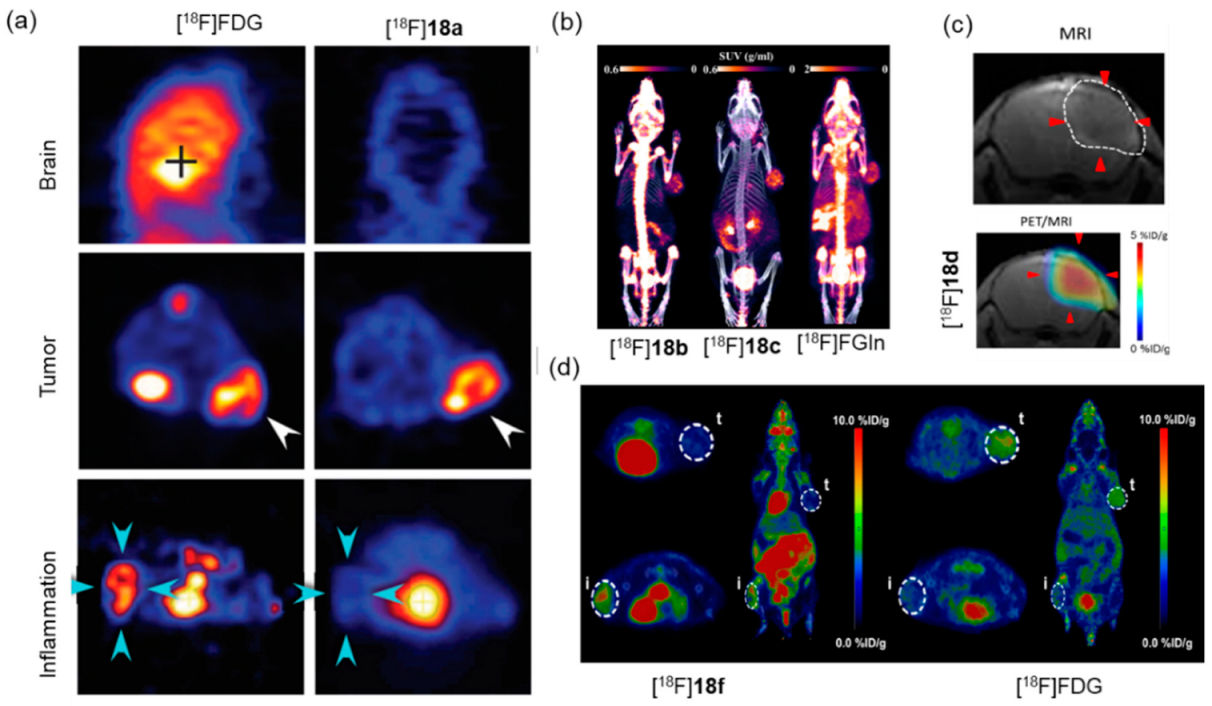
8. Synthesis of 18F-Labeled AAs via B-18F Bond Formation
9. Synthesis of 18F-Labeled AAs via P–18F Bond Formation
10. Synthesis of 18F-Labeled AAs via S–18F Bond Formation
11. Synthesis of 18F-Labeled AAs via Si–18F Bond Formation
12. Conclusions and Perspectives
- Easy synthesis and high stability of the precursor;
- High regioselectivity and functional group tolerance (to avoid manipulation of the protecting group);
- Scale-up synthesis with automation module.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shukla, A.K.; Kumar, U. Positron emission tomography: An overview. J. Med. Phys./Assoc. Med. Phys. India 2006, 31, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyra, V.; Parissis, J.; Kallergi, M.; Rizos, E.; Filippatos, G.; Kremastinos, D.; Chatziioannou, S. 18F-FDG PET/CT brain glucose metabolism as a marker of different types of depression comorbidity in chronic heart failure patients with impaired systolic function. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotan, E.; Friedman, K.P.; Davidson, T.; Shepherd, T.M. Brain 18F-FDG-PET: Utility in the Diagnosis of Dementia and Epilepsy. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. IMAJ 2020, 22, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shinde, S.S.; Maschauer, S.; Prante, O. Sweetening. Pharmaceutical Radiochemistry by 18F-Fluoroglycosylation: Recent Progress and Future Prospects. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunet, V.; Pomoni, A.; Hottinger, A.; Nicod-Lalonde, M.; Prior, J.O. Performance of 18F-FET versus 18F-FDG-PET for the diagnosis and grading of brain tumors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulipan, A.J.; Salberg, U.B.; Hole, K.H.; Vlatkovic, L.; Aarnes, E.-K.; Revheim, M.-E.; Lyng, H.; Seierstad, T. Amino acid transporter expression and 18F-FACBC uptake at PET in primary prostate cancer. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vettermann, F.J.; Diekmann, C.; Weidner, L.; Unterrainer, M.; Suchorska, B.; Ruf, V.; Dorostkar, M.; Wenter, V.; Herms, J.; Tonn, J.-C. L-type amino acid transporter (LAT)1 expression in 18F-FET-negative gliomas. EJNMMI Res. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vettore, L.; Westbrook, R.L.; Tennant, D.A. New aspects of amino acid metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, H.; Huang, L.; Prendergast, G.C.; Mellor, A.L. Immune control by amino acid catabolism during tumorigenesis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpera, R.; Isenegger, P.G.; Ghosez, M.; Straathof, N.J.; Cookson, R.; Blakemore, D.C.; Richardson, P.; Gouverneur, V. Synthesis of fluorinated alkyl aryl ethers by palladium-catalyzed C–O cross-coupling. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 6573–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagida, O.; Kanai, Y.; Chairoungdua, A.; Kim, D.K.; Segawa, H.; Nii, T.; Cha, S.H.; Matsuo, H.; Fukushima, J.-i.; Fukasawa, Y. Human L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): Characterization of function and expression in tumor cell lines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2001, 1514, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröer, S. Amino acid transporters as targets for cancer therapy: Why, where, when, and how. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConathy, J.; Yu, W.; Jarkas, N.; Seo, W.; Schuster, D.M.; Goodman, M.M. Radiohalogenated nonnatural amino acids as PET and SPECT tumor imaging agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 868–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Nie, D.; Tang, G.; Gao, S.; Liu, S.; Wen, F.; Tang, X. Radiosynthesis and biological evaluation of N-(2-[18F]fluoropropionyl)-3, 4-dihydroxy-l-phenylalanine as a PET tracer for oncologic imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2017, 50, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, H.J.; Herz, M.; Weber, W.; Heiss, P.; Senekowitsch-Schmidtke, R.; Schwaiger, M.; Stöcklin, G. Synthesis and radiopharmacology of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine for tumor imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 40, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiwata, K.; Shinoda, M.; Ishii, S.-I.; Nozaki, T.; Senda, M. Synthesis and evaluation of an 18F-labeled dopa prodrug as a PET tracer for studying brain dopamine metabolism. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1996, 23, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, W.; Lieberman, B.; Ploessl, K.; Kung, H.F. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of 18F labeled tyrosine derivatives as potential positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3482–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preshlock, S.; Tredwell, M.; Gouverneur, V. 18F-Labeling of arenes and heteroarenes for applications in positron emission tomography. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 719–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Rong, J.; Wang, L.; Vasdev, N.; Zhang, L.; Josephson, L.; Liang, S.H. Chemistry for positron emission tomography: Recent advances in 11C-, 18F-, 13N-, and 15O-labeling reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2580–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, R.; Ritter, T. 18F-Fluorination: Challenge and Opportunity for Organic Chemists. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 13873–13884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.; Clark, J.; Goulding, R. The preparation of fluorine-18 labelled radiopharmaceuticals. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1977, 28, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firnau, G.; Chirakal, R.; Garnett, E.S. Aromatic radiofluorination with [18F]fluorine gas: 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 1984, 25, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Diksic, M.; Farrokhzad, S. New synthesis of fluorine-18-labeled 6-fluoro-L-dopa by cleaving the carbon-silicon bond with fluorine. J. Nucl. Med. 1985, 26, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.; Wirth, T. [18F]6-fluoro-3, 4-dihydroxy-l-phenylalanine–recent modern syntheses for an elusive radiotracer. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuik, W.-J.; Kema, I.P.; Brouwers, A.H.; Zijlma, R.; Neumann, K.D.; Dierckx, R.A.; DiMagno, S.G.; Elsinga, P.H. In vivo biodistribution of no-carrier-added 6-18F-fluoro-3, 4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (18F-DOPA), produced by a new nucleophilic substitution approach, compared with carrier-added 18F-DOPA, prepared by conventional electrophilic substitution. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillouet, S.; Lemaire, C.; Bonmarchand, G.; Zimmer, L.; Le Bars, D. Large scale production of 6-[18F]fluoro-L-DOPA in a semi-automated system. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2001, 44, S868–S870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Ehrlichmann, W.; Uebele, M.; Machulla, H.-J.; Reischl, G. Automated synthesis of nca [18F] FDOPA via nucleophilic aromatic substitution with [18F]fluoride. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, 1650–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajenjo, J.; Destro, G.; Cornelissen, B.; Gouverneur, V. Closing the gap between 19F and 18F chemistry. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2021, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, F.; Gröner, B.; Hoffmann, C.; Craig, A.; Brugger, M.; Drzezga, A.; Timmer, M.; Neumaier, F.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Endepols, H.; et al. Evaluation of 3-l- and 3-d-[18F]Fluorophenylalanines as PET Tracers for Tumor Imaging. Cancers 2021, 13, 6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanam, M.K.; Ma, G.; Champagne, P.A.; Houk, K.N.; Murphy, J.M. Synthesis of [18F]fluoroarenes by nucleophilic radiofluorination of N-arylsydnones. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 13186–13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sap, J.B.; Meyer, C.F.; Ford, J.; Straathof, N.J.; Dürr, A.B.; Lelos, M.J.; Paisey, S.J.; Mollner, T.A.; Hell, S.M.; Trabanco, A.A. [18F]Difluorocarbene for Positron Emission Tomography. Nature 2022, 606, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiishi, N.; Brooks, A.F.; Topczewski, J.J.; Rodnick, M.E.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J. Copper-catalyzed [18F]fluorination of (mesityl)(aryl) iodonium salts. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3224–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, A.F.; Topczewski, J.J.; Ichiishi, N.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J. Late-stage [18F]fluorination: New solutions to old problems. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4545–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.S.; Kaur, T.; Preshlock, S.; Tanzey, S.S.; Winton, W.P.; Sharninghausen, L.S.; Wiesner, N.; Brooks, A.F.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J. Copper-mediated late-stage radiofluorination: Five years of impact on preclinical and clinical PET imaging. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2020, 8, 167–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tredwell, M.; Preshlock, S.M.; Taylor, N.J.; Gruber, S.; Huiban, M.; Passchier, J.; Mercier, J.; Génicot, C.; Gouverneur, V. A general copper-mediated nucleophilic 18F fluorination of arenes. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 7885–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platten, M.; von Knebel Doeberitz, N.; Oezen, I.; Wick, W.; Ochs, K. Cancer immunotherapy by targeting IDO1/TDO and their downstream effectors. Front. Immunol. 2015, 5, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platten, M.; Nollen, E.A.; Röhrig, U.F.; Fallarino, F.; Opitz, C.A. Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglio, B.C.; Fei, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; He, L.; Feng, H.; Wu, Z.; Lu, H.; Li, Z. Synthesis of 5-[18F]Fluoro-α-methyl tryptophan: New Trp based PET agents. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossine, A.V.; Brooks, A.F.; Makaravage, K.J.; Miller, J.M.; Ichiishi, N.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J. Synthesis of [18F]arenes via the copper-mediated [18F]fluorination of boronic acids. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5780–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, V.W. Hypervalent aryliodine compounds as precursors for radiofluorination. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 196–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modemann, D.J.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Urusova, E.A.; Zischler, J.; Craig, A.; Ermert, J.; Guliyev, M.; Endepols, H.; Neumaier, B. 2-[18F]Fluorophenylalanine: Synthesis by nucleophilic 18F-fluorination and preliminary biological evaluation. Synthesis 2019, 51, 664–676. [Google Scholar]
- Makaravage, K.J.; Brooks, A.F.; Mossine, A.V.; Sanford, M.S.; Scott, P.J. Copper-mediated radiofluorination of arylstannanes with [18F]KF. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 5440–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrad, F.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D.; Krapf, P.; Zischler, J.; Neumaier, B. A practical method for the preparation of 18F-labeled aromatic amino acids from nucleophilic [18F]fluoride and stannyl precursors for electrophilic radiohalogenation. Molecules 2017, 22, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.; Kolks, N.; Urusova, E.A.; Zischler, J.; Brugger, M.; Endepols, H.; Neumaier, B.; Zlatopolskiy, B.D. Preparation of labeled aromatic amino acids via late-stage 18F-fluorination of chiral nickel and copper complexes. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 9505–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyzavi, H.; Mandal, D.; Strebl, M.G.; Neumann, C.N.; D’Amato, E.M.; Chen, J.; Hooker, J.M.; Ritter, T. 18F-deoxyfluorination of phenols via Ru π-complexes. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguet, T.; Verhoeven, J.; Pauwelyn, G.; Hu, J.; Lambe, P.; De Lombaerde, S.; Piron, S.; Donche, S.; Descamps, B.; Goethals, I. Radiosynthesis, in vitro and preliminary in vivo evaluation of the novel glutamine derived PET tracers [18F]fluorophenylglutamine and [18F]fluorobiphenylglutamine. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2020, 86, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Placzek, M.S.; Krska, S.W.; McQuade, P.; Hooker, J.M.; Groves, J.T. Site-selective 18F fluorination of unactivated C–H bonds mediated by a manganese porphyrin. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Nodwell, M.B.; Yang, H.; Malik, N.; Merkens, H.; Bénard, F.; Martin, R.E.; Schaffer, P.; Britton, R. Site-Selective, Late-Stage C−H 18F-Fluorination on Unprotected Peptides for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12733–12736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, S.D.; Fan, H.; Chang, S.; Martin, R.E.; Britton, R. A Convenient Photocatalytic Fluorination of Unactivated C-H Bonds. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 4778–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodwell, M.B.; Yang, H.; Čolović, M.; Yuan, Z.; Merkens, H.; Martin, R.E.; Bénard, F.; Schaffer, P.; Britton, R. 18F-fluorination of unactivated C–H bonds in branched aliphatic amino acids: Direct synthesis of oncological positron emission tomography imaging agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3595–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Huang, Z.; Tay, N.E.; Giglio, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Nicewicz, D.A.; Li, Z. Direct arene C–H fluorination with 18F− via organic photoredox catalysis. Science 2019, 364, 1170–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; White, A.R.; Chen, W.; Wu, Z.; Nicewicz, D.A.; Li, Z. Direct Radiofluorination of Arene C–H Bonds via Photoredox Catalysis Using a Peroxide as the Terminal Oxidant. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 7971–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, N.E.; Chen, W.; Levens, A.; Pistritto, V.A.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Nicewicz, D.A. 19F-and 18F-arene deoxyfluorination via organic photoredox-catalysed polarity-reversed nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pees, A.; Vosjan, M.J.; Vasdev, N.; Windhorst, A.D.; Vugts, D.J. Fluorine-18 labelled Ruppert–Prakash reagent ([18F]Me3SiCF3) for the synthesis of 18F-trifluoromethylated compounds. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 5286–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, A.B.; Brambilla, M.; Exner, R.M.; Tredwell, M. Synthesis and Derivatization of 1, 1-[18F] Difluorinated Alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Born, D.; Sewing, C.; Herscheid, J.D.; Windhorst, A.D.; Orru, R.V.; Vugts, D.J. A universal procedure for the [18F]trifluoromethylation of aryl iodides and aryl boronic acids with highly improved specific activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11046–11050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Jeong, J.M. Design and synthesis of enantiopure 18F-labelled [18F]trifluoromethyltryptophan from 2-halotryptophan derivatives via copper (I)-mediated [18F] trifluoromethylation and evaluation of its in vitro characterization for the serotonergic system imaging. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2019, 62, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, L.; Yuan, G.; Tang, X.; Nie, D.; Jiang, S.; Yang, G.; Tang, G. Synthesis of enantiopure 18F-trifluoromethyl cysteine as a structure-mimetic amino acid tracer for glioma imaging. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Xie, D.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, D.; Wen, F.; Yang, Z.; Tang, G. 18F-Trifluoromethylated D-Cysteine as a Promising New PET Tracer for Glioma Imaging: Comparative Analysis with MRI and Histopathology in Orthotopic C6 Models. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 645162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, R.; Adam, M.J.; Ruth, T.J.; Perrin, D.M. Arylfluoroborates and alkylfluorosilicates as potential PET imaging agents: High-yielding aqueous biomolecular 18F-labeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 13094–13095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard-Gauthier, V.; Bailey, J.J.; Liu, Z.; Wängler, B.; Wängler, C.; Jurkschat, K.; Perrin, D.M.; Schirrmacher, R. From unorthodox to established: The current status of 18F-trifluoroborate-and 18F-SiFA-based radiopharmaceuticals in PET nuclear imaging. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lozada, J.; Wong, M.Q.; Greene, J.; Lin, K.-S.; Yapp, D.; Perrin, D.M. Kit-like 18F-labeling of RGD-19F-arytrifluroborate in high yield and at extraordinarily high specific activity with preliminary in vivo tumor imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2013, 40, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, K.; Shao, Y.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Niu, G.; Chen, X. Boramino acid as a marker for amino acid transporters. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, Z.; Yulai, L.; Neng’an, Y.; Jian, L.; Xiaojuan, C.; Shuo, H. Modified Synthesis and Clinical Trial of [18F]-Phe-BF3. J. Isot. 2020, 33, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, D.R.; Thompson, C.B. Glutamine addiction: A new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Ying, H.; Wang, X.; Hua, S.; Ligorio, M.; Perera, R.M.; Ferrone, C.R.; Mullarky, E.; Shyh-Chang, N. Glutamine supports pancreatic cancer growth through a KRAS-regulated metabolic pathway. Nature 2013, 496, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, H.; Duan, D.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z. Preclinical study of an 18F-labeled glutamine derivative for cancer imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2018, 64, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Hong, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, M.; Han, Y.; Liu, Z. Side Chain Optimization Remarkably Enhances the in Vivo Stability of 18F-Labeled Glutamine for Tumor Imaging. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 5035–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Munasinghe, J.P.; Niu, G.; Teng, G.; Chen, X. Preclinical evaluation of an 18F-trifluoroborate methionine derivative for glioma imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Lang, L.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z. A metabolically stable boron-derived tyrosine serves as a theranostic agent for positron emission tomography guided boron neutron capture therapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2019, 30, 2870–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Kong, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Li, N.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. 18F-Boramino acid PET/CT in healthy volunteers and glioma patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3113–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Li, N.; Ma, W.; Feng, F.; Wang, Y. Metabolic characteristics of [18F]fluoroboronotyrosine (FBY) PET in malignant brain tumors. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2022, 106, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Han, Y.; Li, J.; Qin, M.; Fu, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z. 18F-alanine derivative serves as an ASCT2 marker for cancer imaging. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Mou, Z.; Feng, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Lv, S.; Li, Z. Direct 18F-Labeling of Biomolecules via Spontaneous Site-Specific Nucleophilic Substitution by F– on Phosphonate Prostheses. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 4261–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettig, W.J.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Beresford, H.R.; Oettgen, H.F.; Melamed, M.R.; Old, L.J. Cell-surface glycoproteins of human sarcomas: Differential expression in normal and malignant tissues and cultured cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 3110–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mayer, P.; Mayr, H. Ethenesulfonyl fluoride: The most perfect Michael acceptor ever found? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12664–12667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pascali, G.; Wyatt, N.; Matesic, L.; Klenner, M.A.; Sia, T.R.; Guastella, A.J.; Massi, M.; Robinson, A.J.; Fraser, B.H. Synthesis, bioconjugation and stability studies of [18F]ethenesulfonyl fluoride. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascali, G.; Matesic, L.; Zhang, B.; King, A.T.; Robinson, A.J.; Ung, A.T.; Fraser, B.H. Sulfur-fluorine bond in PET radiochemistry. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2017, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Du, W.-G.H.; Wang, N.; Xiong, H.; Gu, Y.; Noodleman, L.; Sharpless, K.B.; Yang, G. Sulfur [18F]Fluoride Exchange Click Chemistry Enabled Ultrafast Late-Stage Radiosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 3753–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, N.; Bertram, J.; Drewes, B.; Bahutski, V.; Timmer, M.; Schütz, M.B.; Krämer, F.; Neumaier, F.; Endepols, H.; Neumaier, B. Convenient PET-tracer production via SuFEx 18F-fluorination of nanomolar precursor amounts. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 237, 114383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovkova, L.; Könning, D.; Wängler, B.; Schirrmacher, R.; Schoof, S.; Arndt, H.D.; Jurkschat, K. SiFA-Modified Phenylalanine: A Key Compound for the Efficient Synthesis of 18F-Labelled Peptides. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2011, 2238–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scroggie, K.R.; Alcock, L.J.; Matos, M.J.; Bernardes, G.J.; Perkins, M.V.; Chalker, J.M. A silicon-labelled amino acid suitable for late-stage fluorination and unexpected oxidative cleavage reactions in the preparation of a key intermediate in the Strecker synthesis. Pept. Sci. 2018, 110, e24069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

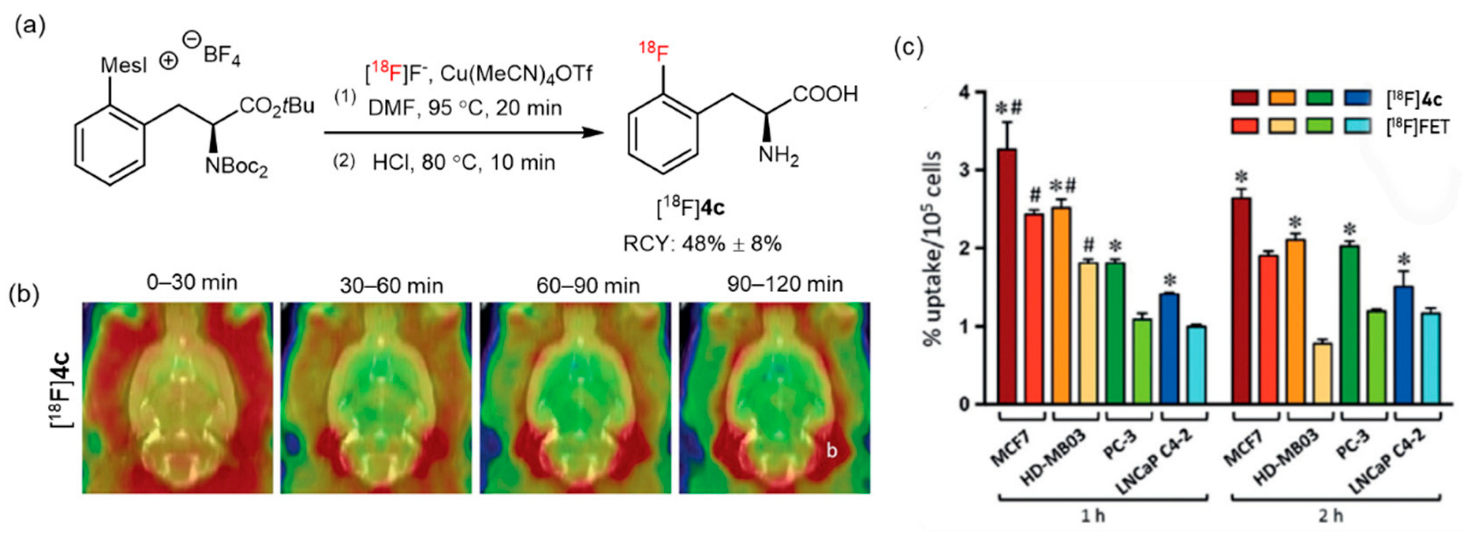




| Strategy | 18F Labeling Reaction Site | Example Radiotracer | Catalyst | Reaction Conditions | RCY | Advantages | Limitations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMRF | 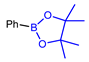 | [18F]2 | Cu(OTf)2(py)4 | [18F]KF/K222, DMF, 110 °C, 20 min | 55% ± 23% | High RCY; deprotection reaction was also carried out | Hard to perform on automation module | [35] |
| CMRF | 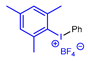 | [18F]4a | (CH3CN)4CuOTf | [18F]KF/18-crown-6, DMF, 85 °C, 20 min | (23% ± 5% RCC, n = 3) | Moderate temperature (85 °C); high selectivity | The corresponding precursors are difficult to synthesize | [32] |
| CMRF | 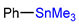 | [18F]5c | Cu(OTf)2, | [18F]KF, pyridine, DMA, 140 °C, 5 min | 56% ± 12% RCC | High functional group tolerance; high yield | Potential metal contamination | [42] |
| Ruthenium-mediated 18F-deoxyfluorination | 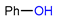 | [18F]7a | CpRu(COD)Cl, iprlmCl | [18F]F−, DMSO:MeCN = 1:1, 125 °C, 30 min | 19% ± 4% | Scale-up synthesis with automation | Potential metal contamination | [44] |
| Manganese porphyrin mediated 18Flabeling strategy | 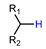 | [18F]8a | Mn(TPFPP)OTs | [18F]F−, PhIO, K2CO3, CH3CN/acetone, 10 min, 50 °C | 48% ± 5% | Without pre-activation in reaction site | Lack of automation synthesis study | [47] |
| Photo-aliphatic radiofluorination | 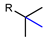 | [18F]9a | NaDT | [18F]NFSI, hv (365 nm) H2O/CH3CN, 40 min | 23% ± 3% | High regioselectivity | Relative low molar activity (<10 MBq/µmoL) | [50] |
| Photo-aromatic radiofluorination | 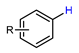 | [18F]11a | 10 | [18F]NBu4, TEMPO, MeCN:t-BuOH = 4:1, 0 °C, 450 nm laser (3.5 W), 30 min, O2 | 5% ± 1% | Large substrate scope | Hard to perform on the automation module | [51] |
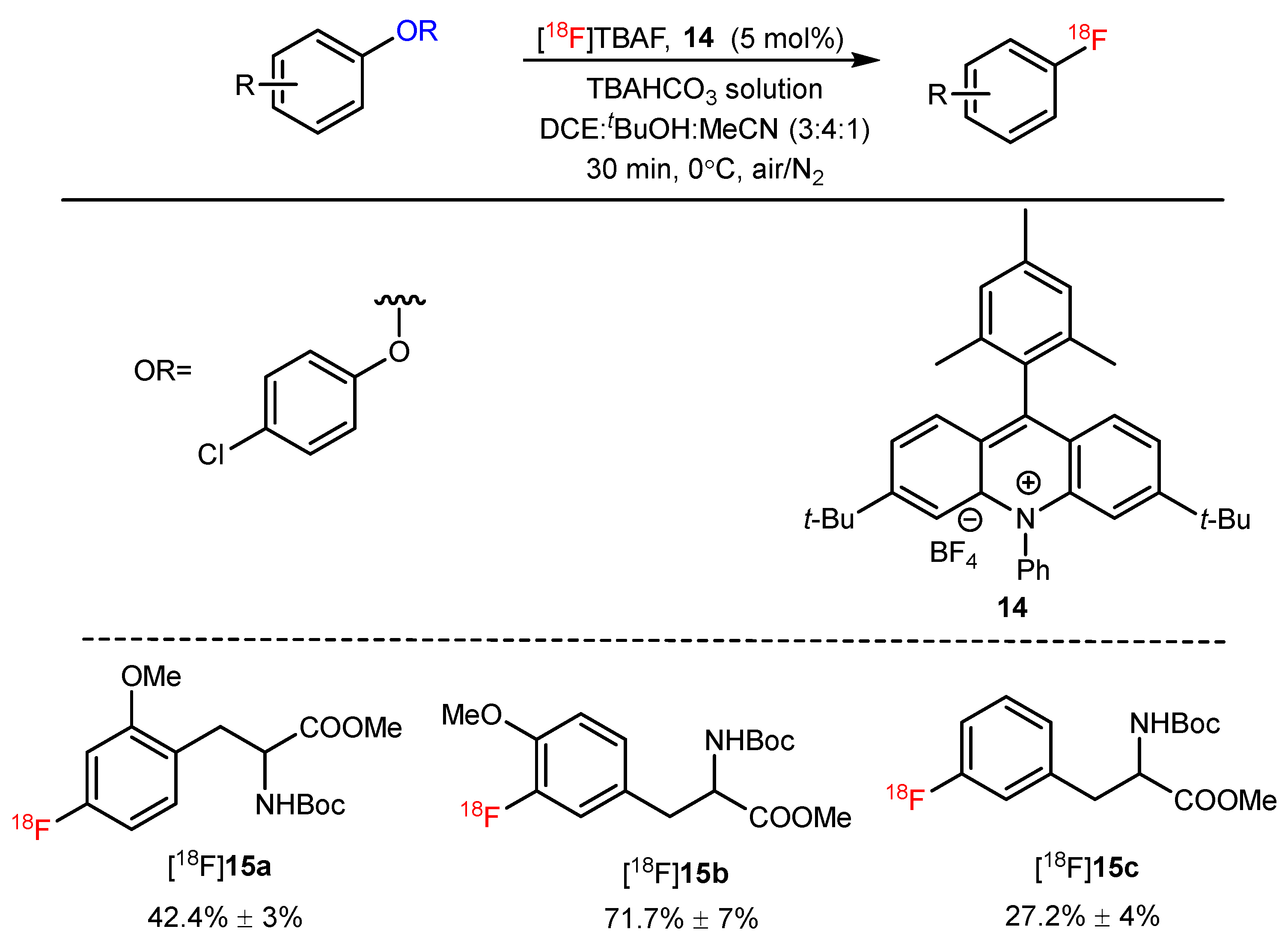
| Photoredox-catalyzed deoxyfluorination of phenol derivatives | 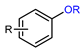 | [18F]15a | 14 | [18F]TBAF, TBAHCO3 solution, DCE:tBuOH:MeCN = 3:4:1, 30 min, 0 °C, air/N2 | 42% ± 3% | High yield | Substrates with unprotected amines are unsuitable | [53] |
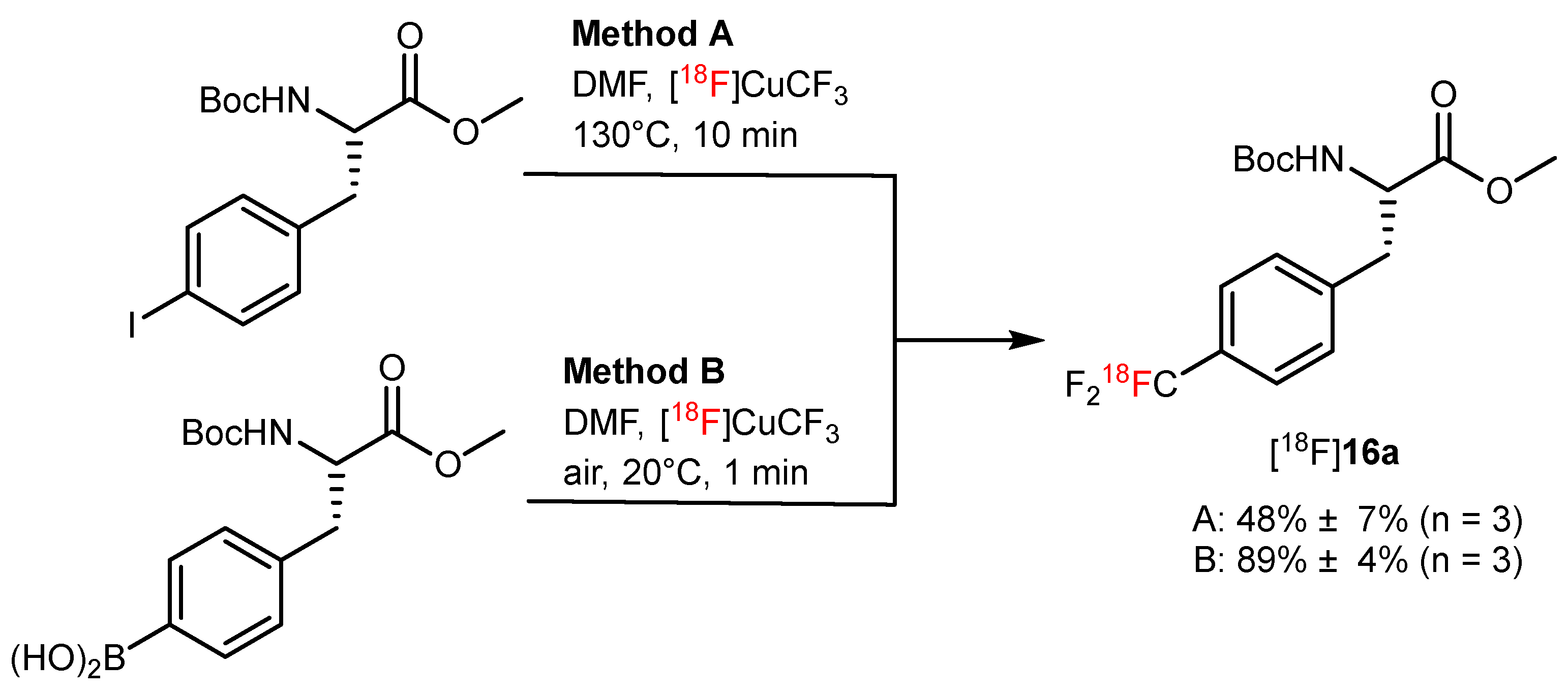
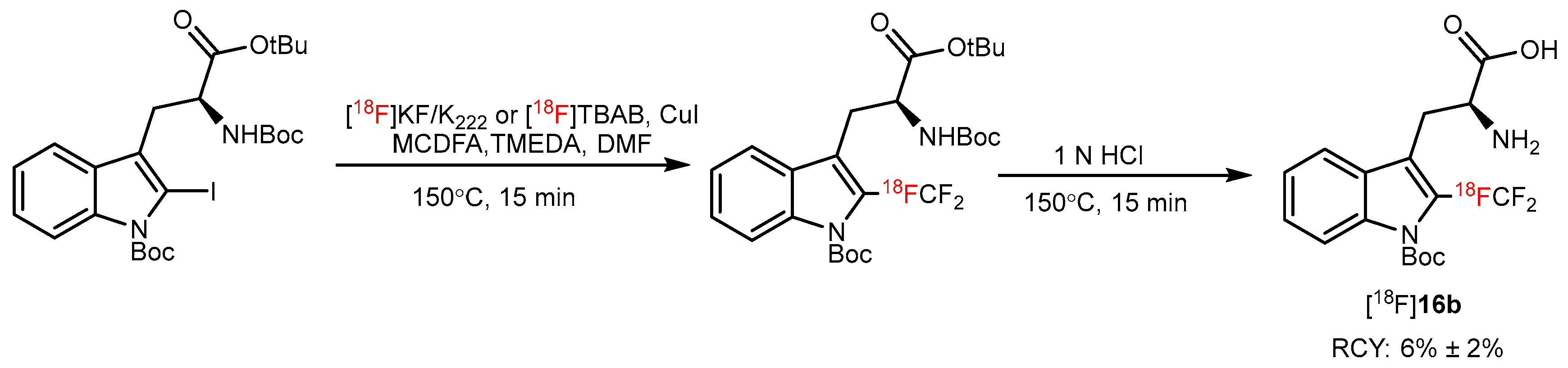
| Copper-mediated radio trifluoromethylation | 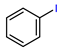 or or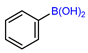 | [18F]16a | CuBr or CuI | DMF, [18F]HCF3, 130 °C, 10 min; or DMF, [18F]CuCF3 air, 20 °C, 1 min | 48% ± 7% | High molar activity (22 to 32 GBq/µmmol) | No PET imaging | [56] |
| Difluorocarbene-derived radio trifluoromethylthiolation | 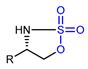 | [18F]17 | PDFA | [18F]KF/K222, S8 CH3CN, 70 °C, 5 min | 14% | Adopt a structure-based bioisosterism strategy | Relatively low RCY (14% ± 3%) | [58] |
| Isotope exchange reaction based on B-18/19F bond | 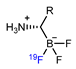 | [18F]18a | - | [18F]F−, pH = 2.5 pyridazine buffer, 80 °C, 5 min | >60% | Efficient synthesis; high yield and molar activity | It is hard to separate precursor from product | [63] |
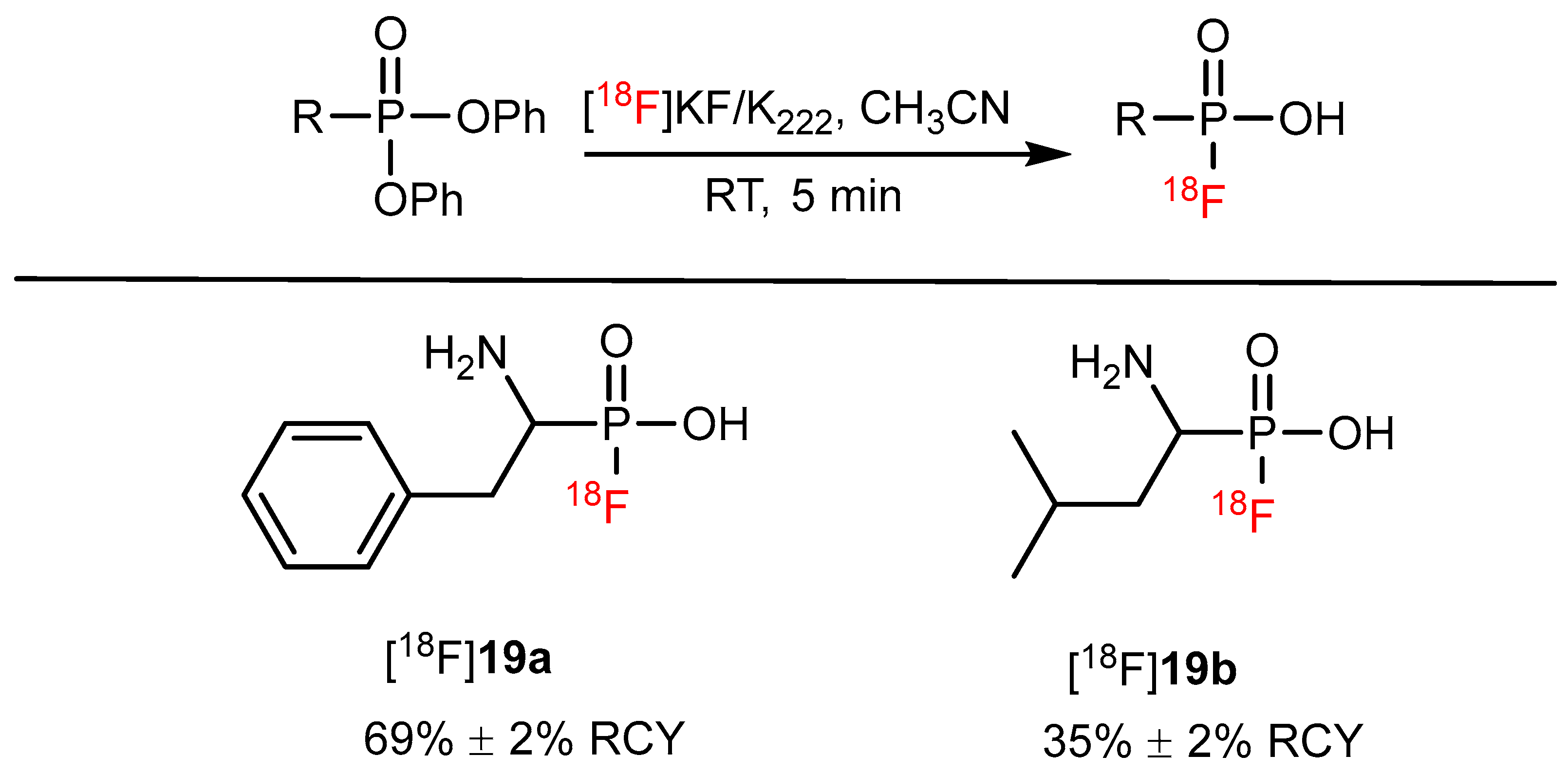
| Nucleophilic substitution reaction on phosphonates | 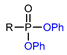 | [18F]19a | - | [18F]KF/K222, CH3CN, RT, 5 min | 69% ± 2% | High functional tolerance | No PET imaging | [74] |
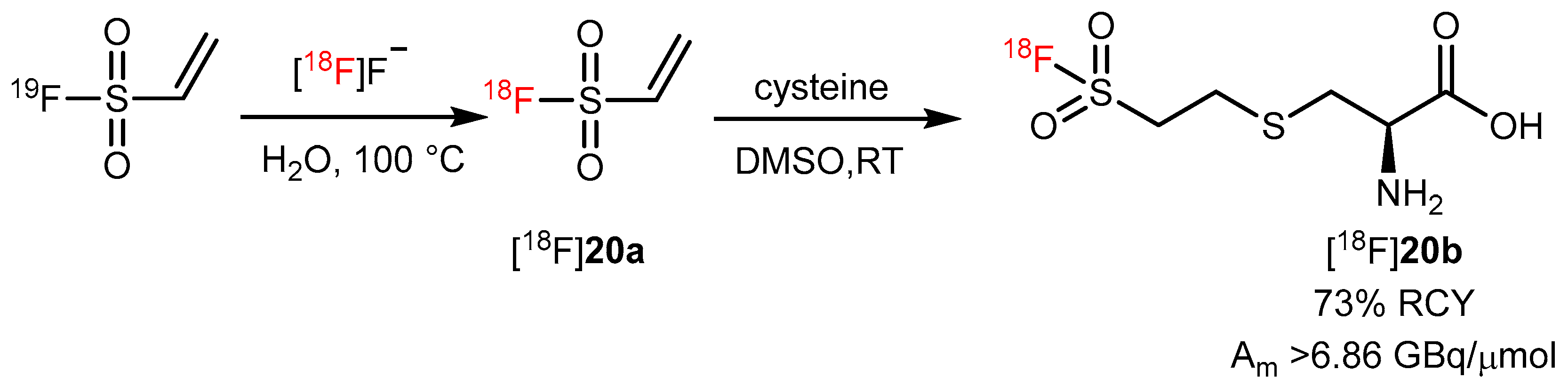
| Ethenesulfonyl fluoride as prosthetic group | 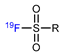 | [18F]20b | - | [18F]F−, H2O, 100 °C | 73% | An efficient way to label amino acids and proteins | Low stability in serum | [77] |
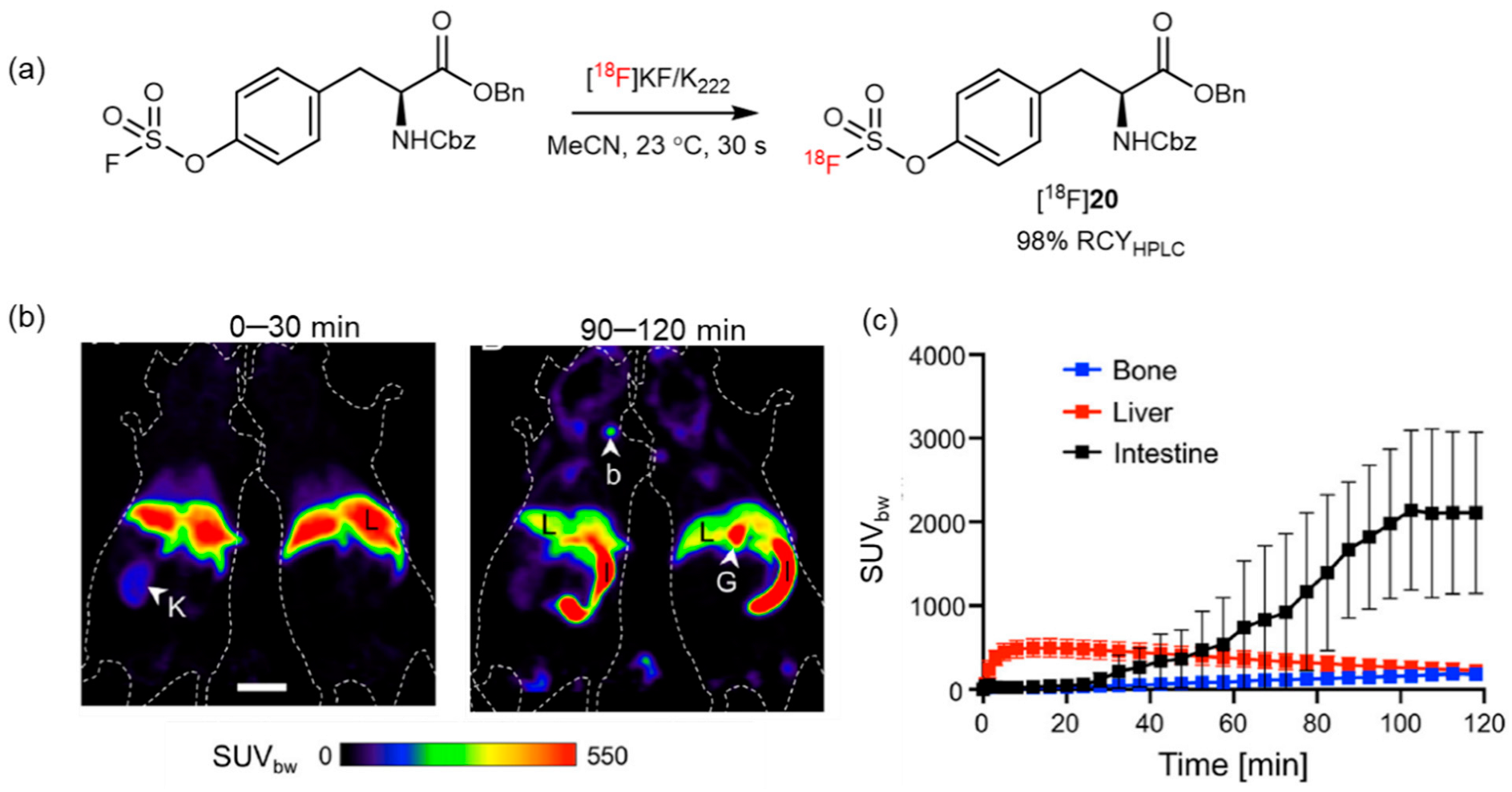
| Sulfur fluoride exchange reaction | 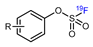 | [18F]21 | - | [18F]KF/K222, CH3CN, 23 °C, 30 s | 99% | Ultrafast, late-stage labeling | The corresponding precursors are difficult to synthesize | [79] |
| Isotope exchange reaction based on Si-18/19F bond | 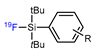 | [18F]22 | - | [18F]F−. DMSO, RT | 40–60% | Stable in aqueous media; suitable for late-stage fluorination | Huge prosthetic group may interfere with functional groups of AA | [82] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Lin, R.; Yao, S. Recent Advances in 18F-Labeled Amino Acids Synthesis and Application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102207
Wang C, Lin R, Yao S. Recent Advances in 18F-Labeled Amino Acids Synthesis and Application. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(10):2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102207
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chao, Rong Lin, and Shaobo Yao. 2022. "Recent Advances in 18F-Labeled Amino Acids Synthesis and Application" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 10: 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102207
APA StyleWang, C., Lin, R., & Yao, S. (2022). Recent Advances in 18F-Labeled Amino Acids Synthesis and Application. Pharmaceutics, 14(10), 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102207





