Oral Liquid Formulation of Levothyroxine Is Stable in Breakfast Beverages and May Improve Thyroid Patient Compliance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Levothyroxine Oral Solution
2.3. Matrices (Beverages)
2.4. Instrumentation and Analytical Conditions
| Time (min) | Eluent A (%) | Eluent B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 98.0 | 2.0 |
| 2.00 | 2.0 | 98.0 |
| 2.40 | 2.0 | 98.0 |
| 2.50 | 98.0 | 2.0 |
| 3.00 | 98.0 | 2.0 |
| Parent | Product | CollisionEnergy | Start | Stop | s-lens | Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 651.900 | 197.112 | 52 | 0.29 | 2.25 | 107 | Triiodothyronine |
| 651.900 | 224.150 | 37 | 0.29 | 2.25 | 107 | Triiodothyronine |
| 651.900 | 606.016 | 9 | 0.29 | 2.25 | 107 | Triiodothyronine |
| 777.865 | 324.066 | 39 | 1.37 | 2.07 | 139 | Levothyroxine (T4) |
| 777.865 | 351.091 | 32 | 1.37 | 2.07 | 139 | Levothyroxine |
| 777.865 | 732.002 | 9 | 1.37 | 2.07 | 139 | Levothyroxine |
| 783.810 | 357.102 | 49 | 1.37 | 2.07 | 180 | [13C6]L-thyroxine |
| 783.810 | 640.045 | 25 | 1.37 | 2.07 | 180 | [13C6]L-thyroxine |
| 783.810 | 737.960 | 25 | 1.37 | 2.07 | 180 | [13C6]L-thyroxine |
2.5. Preparation of Calibration Standards, Internal Standards, and Quality Controls
2.6. Stability Samples Preparation
2.7. Sample Extraction
2.8. Method Validation
2.9. Abbreviations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Validation
3.1.1. Specificity

3.1.2. Linearity and Quantification Limit
| Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| Biasmean at the LLOQ (0.4 µg/mL, N = 3 per matrix) | Milk: 2.2% |
| Tea: 5.3% | |
| Coffee: 2.3% | |
| Coffee with milk: −1.0% | |
| Orange juice: 1.4% | |
| Biasmean above the LLOQ (0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.4 µg/mL, N = 3 per matrix) | Milk: from −3.3% to 1.3% |
| Tea: from −2.5% to 1.1% | |
| Coffee: from −6.1% to 4.2% | |
| Coffee with milk: from −2.4% to 2.7% | |
| Orange juice: from −0.22% to 4.3% | |
| Precision (CV%) at the LLOQ (0.4 µg/mL, N = 3 per matrix) | Milk: 3.3% |
| Tea: 10% | |
| Coffee: 9.2% | |
| Coffee with Milk: 12% | |
| Orange juice: 1.9% | |
| Precision (CV%) above the LLOQ (0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 and 1.4 µg/mL, N = 3 per matrix) | Milk: from 0.0% to 4.7% |
| Tea: from 2.6% to 11.2% | |
| Coffee: from 1.6% to 7.9% | |
| Coffee with milk: from 0.69% to 6.8% | |
| Orange juice: from 0.66% to 8.4% |

3.1.3. Accuracy and Precision
3.1.4. Recovery and Matrix Effects
| Matrix | Parameter | QC Low (0.4 µg/mL) | QC Medium (1.0 µg/mL) | QC High (1.4 µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ||||
| Milk | Ccal (µg/mL) | 0.434 | 0.983 | 1.396 |
| 0.401 | 0.996 | 1.403 | ||
| 0.422 | 1.063 | 1.351 | ||
| 0.392 | 1.012 | 1.465 | ||
| 0.418 | 0.992 | 1.392 | ||
| 0.414 | 1.062 | 1.458 | ||
| Cexp (µg/mL) | 0.40 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| Cmean (µg/mL) | 0.41 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| RE (%) | 103 | 102 | 101 | |
| CV (%) | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.0 | |
| Tea | Ccal (µg/mL) | 0.456 | 0.893 | 1.333 |
| 0.453 | 0.971 | 1.406 | ||
| 0.397 | 1.049 | 1.494 | ||
| 0.422 | 0.944 | 1.382 | ||
| 0.373 | 0.942 | 1.444 | ||
| 0.405 | 1.017 | 1.526 | ||
| Cexp (µg/mL) | 0.40 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| Cmean (µg/mL) | 0.42 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| RE (%) | 104 | 96.9 | 102 | |
| CV (%) | 7.8 | 5.8 | 5.0 | |
| Coffee | Ccal (µg/mL) | 0.395 | 0.995 | 1.353 |
| 0.458 | 0.936 | 1.452 | ||
| 0.390 | 1.142 | 1.502 | ||
| 0.392 | 1.034 | 1.515 | ||
| 0.392 | 1.060 | 1.321 | ||
| 0.458 | 0.972 | 1.389 | ||
| Cexp (µg/mL) | 0.40 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| Cmean (µg/mL) | 0.41 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| RE (%) | 104 | 102 | 102 | |
| CV (%) | 8.2 | 7.2 | 5.6 | |
| B | ||||
| Coffee with Milk | Ccal (µg/mL) | 0.370 | 1.084 | 1.329 |
| 0.399 | 0.997 | 1.364 | ||
| 0.398 | 0.909 | 1.437 | ||
| 0.374 | 0.916 | 1.486 | ||
| 0.392 | 1.027 | 1.358 | ||
| 0.410 | 0.956 | 1.236 | ||
| Cexp (µg/mL) | 0.40 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| Cmean (µg/mL) | 0.39 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| RE (%) | 97.6 | 98.2 | 97.8 | |
| CV (%) | 4.0 | 6.9 | 6.3 | |
| Orange juice | Ccal (µg/mL) | 0.389 | 0.962 | 1.315 |
| 0.385 | 0.982 | 1.468 | ||
| 0.451 | 0.973 | 1.366 | ||
| 0.349 | 1.071 | 1.217 | ||
| 0.369 | 0.986 | 1.346 | ||
| 0.358 | 0.943 | 1.327 | ||
| Cexp (µg/mL) | 0.40 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| Cmean (µg/mL) | 0.38 | 1.0 | 1.3 | |
| RE (%) | 95.9 | 98.6 | 95.7 | |
| CV (%) | 9.5 | 4.5 | 6.1 | |
| Matrix | QC Low 0.4 µg/mL (%) | QC Medium 1.0 µg/mL (%) | QC High 1.4 µg/mL (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | 70 | 73 | 84 |
| Tea | 90 | 80 | 83 |
| Coffee | 79 | 81 | 102 |
| Coffee + Milk | 71 | 92 | 91 |
| Orange juice | 82 | 82 | 82 |
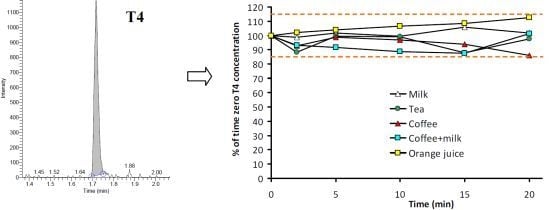
3.2. Stability of T4 in Beverages
| Time (min) | Milk | Tea | Coffee | Coffee + Milk | Orange juice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100.0 (0.6) | 100.0 (9.9) | 100 (5.8) | 100 (13.0) | 100 (10.1) |
| 2 | 98.8 (2.9) | 88.5 (5.6) | 92.6 (3.4) | 93.1 (2.4) | 102.0 (2.5) |
| 5 | 101.7 (2.3) | 99.4 (15.6) | 98.7 (9.1) | 91.6 (3.9) | 104.0 (5.6) |
| 10 | 99.5 (4.4) | 99.1 (7.2) | 96.9 (2.0) | 88.7 (4.1) | 106.5 (1.2) |
| 15 | 106.0 (5.1) | 87.9 (2.9) | 93.8 (7.4) | 87.6 (1.5) | 108.5 (6.1) |
| 20 | 101.7 (5.1) | 97.8 (6.1) | 85.9 (4.4) | 101.2 (10.4) | 112.7 (10.5) |

4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandel, S.J.; Brent, G.A.; Larsen, P.R. Levothyroxine therapy in patients with thyroid disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 1993, 119, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, K.W.; Kirschsieper, H.E. Aspects of the absorption of oral L-thyroxine in normal man. Metabolism 1977, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamson, M.J.; Pamplin, C.L.; Rolleri, R.L.; Klein, I. Quantitation of a substantial reduction in levothyroxine (T4) absorption by food. Thyroid 2004, 14, 876. [Google Scholar]
- Bach-Huynh, T.G.; Nayak, B.; Loh, J.; Soldin, S.; Jonklaas, J. Timing of levothyroxine administration affects serum thyrotropin concentration. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3905–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.L.S.; Araki, F.S.; Graf, H.; de Carvalho, G.A. Serum thyrotropin levels following levothyroxine administration at breakfast. Thyroid 2013, 23, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seechurn, S.; Sharma, S.; Oyibo, S. Administration of levothyroxine 45–60 min before breakfast improves biochemical availability as evidenced by reduced thyrotropin Levels. Open J. Endocr. Metab. Dis. 2012, 2, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.S.H.; Ovalle, F. Use of soy protein supplement and resultant need for increased dose of levothyroxine. Endocr. Pract. 2001, 7, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenga, S.; Bartolone, L.; Squadrito, S.; Lo Giudice, F.; Trimarchi, F. Delayed intestinal absorption of levothyroxine. Thyroid 1995, 5, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenga, S.; Bartolone, L.; Pappalardo, M.A.; Russo, A.; Lapa, D.; Giorgianni, G.; Saraceno, G.; Trimarchi, F. Altered intestinal absorption of L-Thyroxine caused by coffee. Thyroid 2008, 18, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja, J.J.; Laitinen, K.; Neuvonen, P.J. Effects of grapefruit juice on the absorption of levothyroxine. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 60, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenga, S.; Ducharme, M.P. Comparison of the intestinal absorption of levothyroxine (LT4): Tablet vs. soft gel capsule formulation. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 3–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, R.; Saraceno, G.; Trimarchi, F.; Benvenga, S. A novel formulation of l-thyroxine (l-T4) reduces the problem of l-T4 malabsorption by coffee observed with traditional tablet formulations. Endocrine 2013, 43, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraceno, G.; Vita, R.; Trimarchi, F.; Benvenga, F. Two novel formulations of l-T4 (oral solution and soft gel capsule) are refractory to the coffee-induced intestinal malabsorption of tablet l-T4. Eur. Thyroid J. 2013, 2, P132–P145. [Google Scholar]
- Vita, T.; Benvenga, S. Tablet levothyroxine (l-T4) malabsorption induced by proton pump inhibitor: A problem that was solved by switching to l-T4 in soft gel capsule. Endocr. Pract. 2013, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, I.; Formenti, A.M.; Gandossi, E.; Mittempergher, F.; Casella, C.; Agosti, B.; Cappelli, C. Oral liquid L-thyroxine (l-T4) may be better absorbed compared to l-T4 tablets following bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2013, 23, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, C.; Pirola, I.; Gandossi, E.; Formenti, A.M.; Castellano, M. Oral liquid levothyroxine treatment at breakfast: A mistake? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 170, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation; Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2001.
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernareggi, A.; Grata, E.; Pinorini, M.T.; Conti, A. Oral Liquid Formulation of Levothyroxine Is Stable in Breakfast Beverages and May Improve Thyroid Patient Compliance. Pharmaceutics 2013, 5, 621-633. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5040621
Bernareggi A, Grata E, Pinorini MT, Conti A. Oral Liquid Formulation of Levothyroxine Is Stable in Breakfast Beverages and May Improve Thyroid Patient Compliance. Pharmaceutics. 2013; 5(4):621-633. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5040621
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernareggi, Alberto, Elia Grata, Maria Teresa Pinorini, and Ario Conti. 2013. "Oral Liquid Formulation of Levothyroxine Is Stable in Breakfast Beverages and May Improve Thyroid Patient Compliance" Pharmaceutics 5, no. 4: 621-633. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5040621
APA StyleBernareggi, A., Grata, E., Pinorini, M. T., & Conti, A. (2013). Oral Liquid Formulation of Levothyroxine Is Stable in Breakfast Beverages and May Improve Thyroid Patient Compliance. Pharmaceutics, 5(4), 621-633. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics5040621