Turning Waste into Value: Nanosized Natural Plant Materials of Solanum incanum L. and Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir with Promising Antimicrobial Activities
Abstract
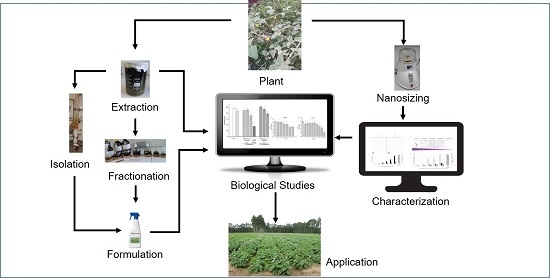
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Nanosizing of Dried Fruit of S. incanum and Bark of P. erinaceus
2.3. Extraction Methods
2.4. Biological Activity Assays Involving Steinernema feltiae, Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae
3. Results
3.1. Homogenized Particles of S. incanum
3.2. Homogenized Particles of P. erinaceus
3.3. Biological Activity of Processed Samples and Respective Extracts against S. feltiae
3.4. Biological Activity of Processed Samples and Extracts of P. erinaceus against E. coli
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| h | hours |
| HSS | High Speed Stirring |
| HPH | High Pressure Homogenization |
| LD | Laser Diffraction |
| PCS | Photon Correlation Spectroscopy |
References
- Jacob, C.K.G.; Slusarenko, A.J.; Winyard, P.G.; Burkholz, T. Recent Advances in Redox Active Plant and Microbial Products; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.L.; Wang, W.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chen, C.F. Nonsteroidal constituents from Solanum incanum L. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2000, 47, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, K.; Kubo, I. Isolation of steroidal glycoalkaloids from solanum-incanum by 2 countercurrent chromatographic methods. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaman-Mbaya, V.; Muhammed, S.I. Antibiotic action of Solanum incanum Linnaeus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1976, 6, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittikpina, N.K.; Ejike, C.; Estevam, E.C.; Nasim, M.J.; Griffin, S.; Chaimbault, P.; Kirsch, G.; Atakpama, W.; Batawila, K.; Jacob, C. Togo to go: Products and compounds deriveed from local plants for the treatment of diseases endemic in sub-saharan Africa. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 13, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbonnier, M. Arbres, Arbustes et Lianes des Zones Sèches d'Afrique de l'Ouest %w Copyright Cirad; Editions Quae: Versailles, France, 2009; p. 574. [Google Scholar]
- Tittikpina, N.K. Contribution à L’évaluation des Propriétés Anti-Microbiennes de: Pterocarpus Erinaceus Poir (Faboïdeae), Daniellia Oliveri (Rolfe) Hutch. et Dalz (Caesalpinoïdeae) et Anchomanes Difformis (Blume) Engler (Araceae), Utilisées en Médecine Traditionnelle dans la Préfecture de Tchamba (TOGO). Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lomé (University of Lomé), Lomé, Togo, 2012; p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- Tittikpina, N.K.; Agban, A.; Gbogbo, K.A.; Hoekou, Y.P.; Pereki, H.; Batawila, K.; Akpagana, K. Évaluation des Propriétés Antimicrobiennes de Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir (Faboïdeae) et Daniellia oliveri (Rolfe) Hutch. et Dalz (Caesalpinoïdeae), utilisées en médecine traditionnelle au Togo. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2013, 7, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchacondo, T.; Karou, S.D.; Agban, A.; Bako, M.; Batawila, K.; Bawa, M.L.; Gbeassor, M.; de Souza, C. Medicinal plants use in central Togo (Africa) with an emphasis on the timing. Pharmacogn. Res. 2012, 4, 92–103. [Google Scholar]
- Fahr, A. Voigt Pharmazeutische Technologie; Deutscher Apotheker Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jahnke, S. The Theory of High-Pressure Homogenization. In Dispersion Techniques for Laboratory and Industrial Scale Processing; Wiss. Verlag-Ges.: Luebeck, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Keck, C.M.; Muller, R.H. Drug nanocrystals of poorly soluble drugs produced by high pressure homogenisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 62, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevam, E.C.; Griffin, S.; Nasim, M.J.; Zielinski, D.; Aszyk, J.; Osowicka, M.; Dawidowska, N.; Idroes, R.; Bartoszek, A.; Jacob, C. Inspired by nature: The use of plant-derived substrate/enzyme combinations to generate antimicrobial activity in situ. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.; Baldauf, A.; Ba, L.A.; Jamier, V.; Khairan, K.; Sarakbi, M.B.; Reum, N.; Schneider, M.; Roseler, A.; Becker, K.; et al. Selective antimicrobial activity associated with sulfur nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czepukojc, B.; Viswanathan, U.M.; Raza, A.; Ali, S.; Burkholz, T.; Jacob, C. Tetrasulfanes as selective modulators of the cellular thiolstat. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2013, 188, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (mic) of antimicrobial substances. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zgoda, J.R.; Porter, J.R. A convenient microdilution method for screening natural products against bacteria and fungi. Pharm. Biol. 2001, 39, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamizadeh, K.; Gerst, M.; Scholz, P.; Arntjen, A.; Keck, C.M. Nano-Curry for Improved Health . In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the German Pharmaceutical Society (DPHG), Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 24–26 September 2014; p. 19.
- Scholz, P.; Arntjen, A.; Muller, R.H.; Keck, C.M. Artcrystal® process for industrial nanocrystal production optimization of the art miccra pre-milling step. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 465, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Griffin, S.; Tittikpina, N.K.; Al-marby, A.; Alkhayer, R.; Denezhkin, P.; Witek, K.; Gbogbo, K.A.; Batawila, K.; Duval, R.E.; Nasim, M.J.; et al. Turning Waste into Value: Nanosized Natural Plant Materials of Solanum incanum L. and Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir with Promising Antimicrobial Activities. Pharmaceutics 2016, 8, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics8020011
Griffin S, Tittikpina NK, Al-marby A, Alkhayer R, Denezhkin P, Witek K, Gbogbo KA, Batawila K, Duval RE, Nasim MJ, et al. Turning Waste into Value: Nanosized Natural Plant Materials of Solanum incanum L. and Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir with Promising Antimicrobial Activities. Pharmaceutics. 2016; 8(2):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics8020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleGriffin, Sharoon, Nassifatou Koko Tittikpina, Adel Al-marby, Reem Alkhayer, Polina Denezhkin, Karolina Witek, Koffi Apeti Gbogbo, Komlan Batawila, Raphaël Emmanuel Duval, Muhammad Jawad Nasim, and et al. 2016. "Turning Waste into Value: Nanosized Natural Plant Materials of Solanum incanum L. and Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir with Promising Antimicrobial Activities" Pharmaceutics 8, no. 2: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics8020011
APA StyleGriffin, S., Tittikpina, N. K., Al-marby, A., Alkhayer, R., Denezhkin, P., Witek, K., Gbogbo, K. A., Batawila, K., Duval, R. E., Nasim, M. J., Awadh-Ali, N. A., Kirsch, G., Chaimbault, P., Schäfer, K.-H., Keck, C. M., Handzlik, J., & Jacob, C. (2016). Turning Waste into Value: Nanosized Natural Plant Materials of Solanum incanum L. and Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir with Promising Antimicrobial Activities. Pharmaceutics, 8(2), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics8020011