Ice-Nucleating Gut Microbes in Insects: A Scoping Review
Abstract
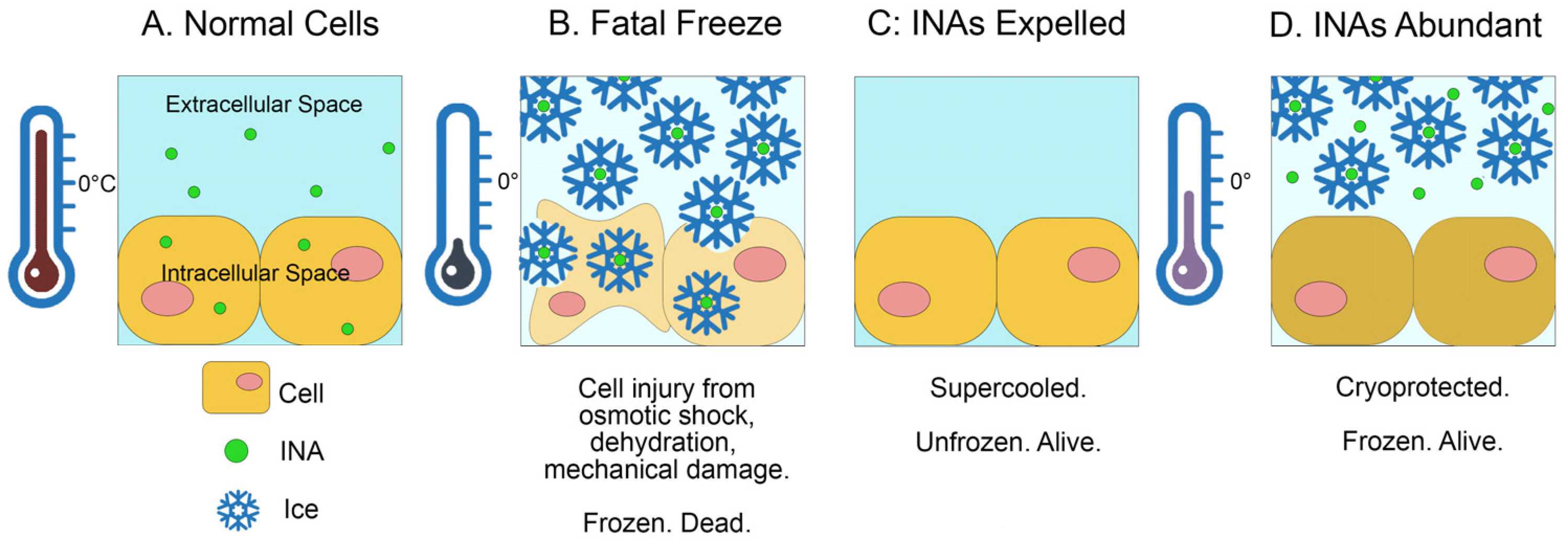
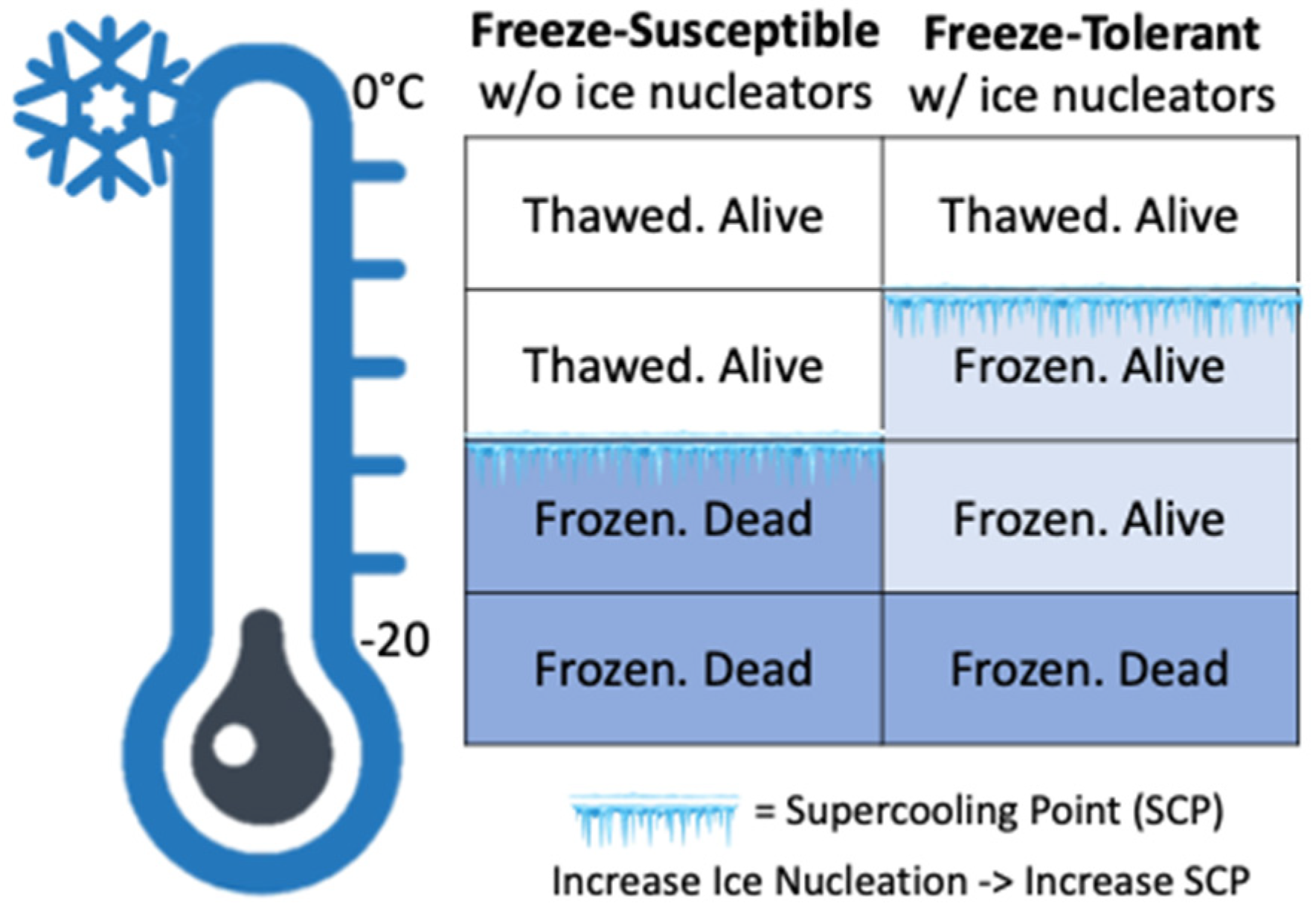
:1. Introduction
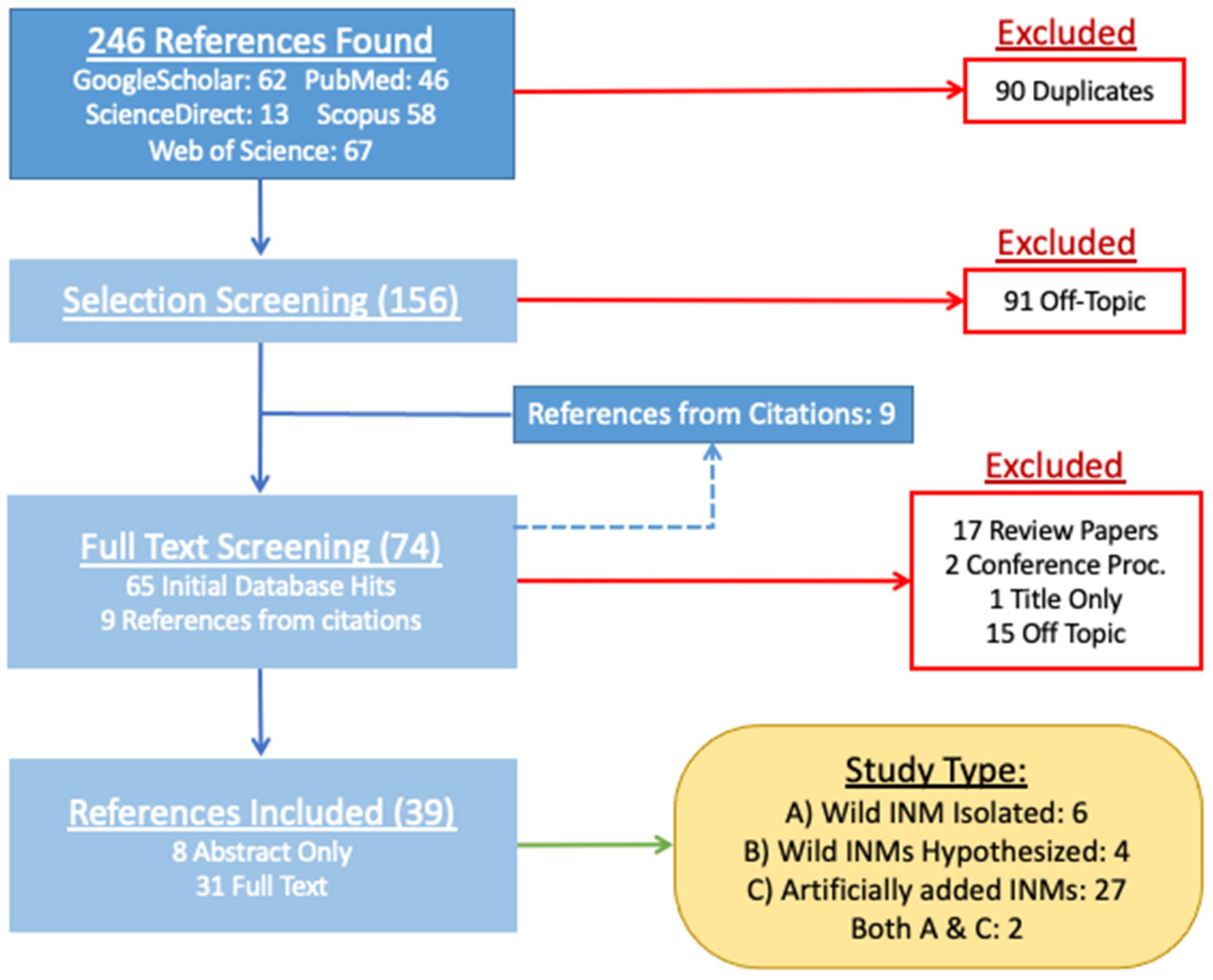
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forbes, J.; Bissoyi, A.; Eickhoff, L.; Reicher, N.; Hansen, T.; Bon, C.G.; Walker, V.K.; Koop, T.; Rudich, Y.; Braslavsky, I.; et al. Water-organizing motif continuity is critical for potent ice nucleation protein activity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosasih, V.; Prasetyo, N.; Sudianto, E.; Waturangi, D.E. Prevalence and characterization of Ice Nucleation Active (INA) bacteria from rainwater in Indonesia. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.C.; Moffett, B.F.; Demott, P.J.; Georgakopoulos, D.G.; Stump, W.L.; Franc, G.D. Measurement of ice nucleation-active bacteria on plants and in precipitation by quantitative PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochet, N.; Widehem, P. Ice crystallization by Pseudomonas syringae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki Leroy, R.; Galyan Elizabeth, L.; Chang-Chien, M.-M.; Caldwell Daniel, R. Ice Nucleation Induced by Pseudomonas syringae. Appl. Microbiol. 1974, 28, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindow, S. History of Discovery and Environmental Role of Ice Nucleating Bacteria. Phytopathology 2023, 113, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danks, H.V.; Kukal, O.; Ring, R.A. Insect Cold-Hardiness: Insights from the Arctic. Arctic 1994, 47, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan-Richards, M.; Marshall, C.J.; Biggs, P.J.; Trewick, S.A. Insect Freeze-Tolerance Downunder: The Microbial Connection. Insects 2023, 14, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z. Progress In The Research On Mechanism Of Insect Cold-hardiness. Insect Sci. 1997, 4, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klowden, M.J. (Ed.) Chapter 7—Circulatory Systems. In Physiological Systems in Insects, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 357–401. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, J.G. Insect antifreezes and ice-nucleating agents. Cryobiology 1982, 19, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.E., Jr.; Costanzo, J.P.; Mugano, J.A. Regulation of supercooling and ice nucleation in insects. Eur. J. Entomol. 1996, 93, 405–418. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, J.G.; Patterson, J.L. The role of ice nucleators in the frost tolerance of overwintering queens of the bald faced hornet. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1978, 59, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.E., Jr.; Lee, M.R.; Strong-Gunderson, J.M. Insect cold-hardiness and ice nucleating active microorganisms including their potential use for biological control. J. Insect Physiol. 1993, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadis, S.S.; Athanassiou, C.G. A review of insect cold hardiness and its potential in stored product insect control. Crop Prot. 2017, 91, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundheim, R. Physiological and ecological significance of biological ice nucleators. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 2002, 357, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, M.J.; Jewell, S.T. (Eds.) Assembling the Pieces of a Systematic Review: A Guide for Librarians; Rowman & Littlefield: Lanham, MD, USA, 2017; p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, R.; Sikora, L. Literature Reviews: Key Considerations and Tips from Knowledge Synthesis Librarians. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2022, 14, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, S.; Thomas, A. Steps for Conducting a Scoping Review. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2022, 14, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H.; McInerney, P.; Parker, D.; Soares, C.B. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. JBI Evid. Implement. 2015, 13, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, M.; Martin Misener, R.; Weeks, L.; Helwig, M. Covidence vs Excel for the title and abstract review stage of a systematic review. JBI Evid. Implement. 2016, 14, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango, R.A.; Bishell, A.B.; Ohno, K.M.; Shelton, T.G.; Schoville, S.D.; Carlos-Shanley, C. Seasonal shifts in gut microbiota and cold tolerance metrics in a northern population of Reticulitermes flavipes (Blattodea: Rhinotermitidae). Environ. Entomol. 2024, In Press, nvae027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worland, M.R. Factors that influence freezing in the sub-Antarctic springtail Tullbergia antarctica. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, B.J.; Kamble, S.T. Supercooling Differences in the Eastern Subterranean Termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 2004, 39, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, M.A.; Koch, R.L.; Burkness, E.C.; Bennett, K.; Ragsdale, D.W.; Hutchison, W.D. Supercooling Point of Bean Leaf Beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in Minnesota and a Revised Predictive Model for Survival at Low Temperatures. Environ. Entomol. 2005, 34, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Lee, R.E., Jr.; Lee, M.R.; Rutherford, S.T. Identification of Ice-Nucleating Active Pseudomonas fluorescens Strains for Biological Control of Overwintering Colorado Potato Beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.E., Jr.; Strong-Gunderson, J.M.; Lee, M.R.; Grove, K.S.; Riga, T.J. Isolation of ice nucleating active bacteria from insects. J. Exp. Zool. 1991, 257, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worland, R.; Block, W.; Rothery, P. Ice nucleation studies of two beetles from sub-antarctic South Georgia. Polar Biol. 1993, 13, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worland, M.R.; Block, W. Ice-Nucleating Bacteria from the Guts of Two Sub-Antarctic Beetles, Hydromedion sparsutum and Perimylops antarcticus (Perimylopidae). Cryobiology 1999, 38, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, J.G. Factors involved in overwintering survival of the freeze tolerant beetle, Dendroides canadensis. J. Comp. Physiol. 1980, 136, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.M.; Duman, J.G. Maintenance of the supercooled state in the gut fluid of overwintering pyrochroid beetle larvae, Dendroides canadensis: Role of ice nucleators and antifreeze proteins. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1997, 167, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, K.; Sato, M. Survival and Characteristics of Ice Nucleation-active Bacteria on Mulberry Trees (Morus spp.) and in Mulberry Pyralid (Glyphodes pyloalis). Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 1995, 61, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, Y.; Sonoda, S.; Yoshida, H.; Tsumuki, H. Identification of tissues showing the lowest tolerance to freezing in larvae of the rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis. Physiol. Entomol. 2005, 30, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuki, H.; Konno, H.; Maeda, T.; Okamoto, Y. An ice-nucleating active fungus isolated from the gut of the rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis Walker (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Insect Physiol. 1992, 38, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuki, H. Review of low temperature tolerance and ice nuclei in insects, with special emphasis on larvae of the rice stem borer, Chilo suppressalis Walker. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2000, 44, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, J.I.; Kita, K.; Tanno, K. Bacteria in the gut determines the supercooling point of diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella, pupae reared on germinating radish seeds (Raphanus sativus L. var. acanthiformis Makino). Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1989, 33, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, J.I.; Kita, K.; Tanno, K. INA bacteria isolated from diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella L. pupae (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae). Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1991, 35, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, J.I.; Yoshida, T.; Owada, T.; Kita, K.; Tanno, K. Erwinia herbicola: Ice nucleation active bacteria isolated from diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella L. pupae. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1991, 35, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K. Supercooling ability in the house spider, Achaearanea tepidariorum: Effect of field-collected and laboratory-reared prey. Naturwissenschaften 2001, 88, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Udagawa, T. Cold adaptation of the terrestrial isopod, Porcellio scaber, to subnivean environments. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1993, 163, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, J.P.; Humphreys, T.L.; Lee, R.E., Jr.; Moore, J.B.; Lee, M.R.; Wyman, J.A. Long-term reduction of cold hardiness following ingestion of ice-nucleating bacteria in the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata. J. Insect Physiol. 1998, 44, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.E., Jr.; Litzgus, J.D.; Mugnano, J.A.; Lee, M.R.; Horton, D.R.; Dunley, J. Evaluation of Ice-nucleating Microorganisms For Reducing The Supercooling Capacity And Cold-hardiness Of Cacopsylla pyricola (Hemiptera: Psyllidae). Can. Entomol. 1999, 131, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Sun, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, T.; Qi, J. Transgenic ice nucleation-active Enterobacter cloacae reduces cold hardiness of corn borer and cotton bollworm larvae. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 51, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Abe, K.; Sato, M. Biological control of an insect pest by gut-colonizing Enterobacter cloacae transformed with ice nucleation gene. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Sato, M. Gut Colonization by an Ice Nucleation Active Bacterium, Erwinia (Pantoea) ananas Reduces the Cold Hardiness of Mulberry Pyralid Larvae. Cryobiology 1999, 38, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong-Gunderson, J.M.; Lee, R.E.; Lee, M.R.; Tammy, J.R. Ingestion of ice-nucleating active bacteria increases the supercooling point of the lady beetle Hippodamia convergens. J. Insect Physiol. 1990, 36, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lai, Y. The Effect of Ice-Nucleation-Active Bacteria on Metabolic Regulation in Evergestis extimalis (Scopoli) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Overwintering Larvae on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Insects 2022, 13, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Lee, R.E.; Wyman, J.A.; Lee, M.R.; Rutherford, S.T. Field Persistence of Ice-Nucleating Bacteria in Overwintering Colorado Potato Beetles. Biol. Control 2001, 21, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Rutherford, S.T.; Lee, R.E.; Lee, M.R. Enhancement of Ice-Nucleating Activity in Pseudomonas fluorescens and Its Effect on Efficacy against Overwintering Colorado Potato Beetles. Biol. Control 2001, 21, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, C.E.; Phillips, S.A., Jr. Potential of Ice-Nucleating Active Bacteria for Management of the Red Imported Fire Ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Environ. Entomol. 1996, 25, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigerwald, K.A.; Lee, M.R.; Lee, R.E.; Marshall, J.C. Effect of biological ice nucleators on insect supercooling capacity varies with anatomic site of application. J. Insect Physiol. 1995, 41, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong-Gunderson, J.M.; Lee, R.E.; Lee, M.R. Topical Application of Ice-Nucleating-Active Bacteria Decreases Insect Cold Tolerance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Watanabe, M. Transmission of ice-nucleating active bacteria from a prey reduces cold hardiness of a predator (Araneae: Theridiidae). Naturwissenschaften 2003, 90, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.E., Jr.; Costanzo, J.P.; Kaufman, P.E.; Lee, M.R.; Wyman, J.A. Ice-Nucleating Active Bacteria Reduce the Cold-Hardiness of the Freeze-Intolerant Colorado Potato Beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1994, 87, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.E., Jr.; Steigerwald, K.A.; Wyman, J.A.; Costanzo, J.P.; Lee, M.R. Anatomic Site of Application of Ice-Nucleating Active Bacteria Affects Supercooling in the Colorado Potato Beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Environ. Entomol. 1996, 25, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.E., Jr.; Strong-Gunderson, J.M.; Lee, M.R.; Davidson, E.C. Ice-Nucleating Active Bacteria Decrease the Cold-Hardiness of Stored Grain Insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 1992, 85, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignon, J.; Haubruge, E.; Gaspar, C. Effect of ice-nucleating bacteria (Pseudomonas syringae Van Hall) on insect susceptibility to sub-zero temperatures. J. Stored Prod. Res. 1998, 34, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Lee, R.E.; Lee, M.R.; Wyman, J.A. Long-term retention of ice-nucleating active Pseudomonas fluorescens by overwintering colorado potato beetles. Cryo Lett. 2000, 21, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Strong-Gunderson, J.M.; Lee, R.E., Jr.; Lee, M.R. Ice nucleating active bacteria increase insect mortality at high subzero temperatures. Cryo Lett. 1994, 15, 385–392. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M. Effects of ingestion and excretion of ice-nucleating-active bacteria on the supercooling ability and cold hardiness in larvae of the clover leaf weevil, Hypera punctata. Cryo Lett. 1999, 20, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.R.; Lee, R.E., Jr.; Strong, J.M.; Minges, S.R.; Mugnano, J.A. Reduction of insect cold-hardiness using ice-nucleating active fungi and surfactants. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1998, 89, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-L.; Chiou, T.-K.; Jiang, S.-T. Isolation of ice-nucleating active bacterium from mackerel and its properties. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwath, K.L.; Duman, J.G. Yearly Variations in the Overwintering Mechanisms of the Cold-Hardy Beetle Dendroides canadensis. Physiol. Zool. 1984, 57, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, J. The inhibition of ice nucleators by insect antifreeze proteins is enhanced by glycerol and citrate. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2002, 172, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, P.; Pouleur, S.; Richard, C. The Effect Of High Temperature Storage On The Capacity Of An Ice-nucleating-active Bacterium And Fungus To Reduce Insect Cold-tolerance. Can. Entomol. 1995, 127, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, P.G. Reduction of Cold Tolerance of Stored-Product Insects by Ice-Nucleating-Active Bacteria. Environ. Entomol. 1993, 22, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R.; Lee, R.E., Jr.; Strong-Gunderson, J.M.; Minges, S.R. Isolation of Ice-Nucleating Active Bacteria from the Freeze-Tolerant Frog, Rana sylvatica. Cryobiology 1995, 32, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, L.; Xu, K.; Zhang, S.; Gao, F.; Fan, Y. Research Progresses on the Function and Detection Methods of Insect Gut Microbes. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanie, D.E.W. Distribution of Ice Nucleation-Active (INA) Bacteria from Rain-water and Air. HAYATI J. Biosci. 2011, 18, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.R.; Van den Bussche, R.A.; Wichman, H.A.; Orser, C.S. Unusual pattern of bacterial ice nucleation gene evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1994, 11, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavini, F.; Mergaert, J.; Beji, A.; Mielcarek, C.; Izard, D.; Kersters, K.; De Ley, J. Transfer of Enterobacter agglomerans (Beijerinck 1888) Ewing and Fife 1972 to Pantoea gen. nov. as Pantoea agglomerans comb, nov. and Description of Pantoea dispersa sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1989, 39, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, H.; Ishikawa, H. Phylogenetical relationship based on groE genes among phenotypically related Enterobacter, Pantoea, Klebsiella, Serratia and Erwinia species. J. General. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 43, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergaert, J.; Verdonck, L.; Kersters, K. Transfer of Erwinia ananas (synonym, Erwinia uredovora) and Erwinia stewartii to the Genus Pantoea emend. as Pantoea ananas (Serrano 1928) comb. nov. and Pantoea stewartii (Smith 1898) comb. nov., Respectively, and Description of Pantoea stewartii subsp. indologenes subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1993, 43, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.L.; Preston, G.M. Pseudomonas syringae: Enterprising epiphyte and stealthy parasite. Microbiology 2019, 165, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrken, U. Correlative influence of gut appearance, water content and thermal hysteresis on whole body supercooling point of adult bark beetles, Ips acuminatus Gy11. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1995, 112, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, D.A.; Pow, B.; Kristensen, M.; Ramløv, H.; Marshall, C.J. Ice-active proteins and cryoprotectants from the New Zealand alpine cockroach, Celatoblatta quinquemaculata. J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodkova, M.; Hodek, I.V.O. Temperature Regulation of Supercooling and Gut Nucleation in Relation to Diapause of Pyrrhocoris apterus (L.) (Heteroptera). Cryobiology 1997, 34, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurian-Sherman, D.; Lindow, S.E. Ice nucleation and its application. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1992, 3, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colinet, H.; Boivin, G. Insect parasitoids cold storage: A comprehensive review of factors of variability and consequences. Biol. Control 2011, 58, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Order/Family | Insect Species | FT/FS | Microbe Species | Location | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collembola; Tullbergiidae | Tullbergia antarctica | FS | Unidentified | Kerguelen archipelago | [26] |
| Blattodea; Rhinotermitidae | Reticulitermes flavipes | FS | Unidentified | NE, USA | [27] |
| Coleoptera; Chrysomelidae | Cerotoma trifurcata | FS [28] | Pseudomonas fluorescens | - | [29] ^ |
| Pseudomonas putida | - | ||||
| Pseudomonas syringae | - | ||||
| Enterobacter taylorae | OH, USA | [30] | |||
| Enterobacter agglomerans | |||||
| Coleoptera; Perimylopidae | Hydromedion sparsutum | FT | Pseudomonas sp. | South Georgia | [31,32] * |
| Perimylops antarcticus | FT | Unidentified | |||
| Coleoptera; Pyrochroidae | Dendroides canadensis | FT [33] | Pseudomonas fluorescens | IN, USA | [34] |
| Lepidoptera; Crambidae | Glyphodes pyloalis | - | Pseudomonas syringae pv. Mori | Ibarakai, Japan | [35] |
| Erwinia herbicola | |||||
| Erwinia ananas | |||||
| Chilo suppressalis | FT [36] | Fusarium moniliforme var. subglutinans | Okayama, Japan | [37,38] * | |
| Lepidoptera; Plutellidae | Plutella xylostella | - | Erwinia herbicola | Japan | [39,40,41] * |
| Orthoptera; Gryllidae | Dianemobius mikado | - | Unidentified | Hokkaido, Japan | [42] |
| † Malacostraca; Isopoda; Porcellionidae | Porcellio scaber | FS [43] | Unidentified |
| Microbe Species | Strain | Source | Effect | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria: | ||||
| Enterobacter agglomerans | BBI | Cerotoma trifurcata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) | ↑ SCP | [44,45] |
| [same study] | ↑ SCP | [30] | ||
| Enterobacter cloacae † | Enc181-I | Transgenic | ↑ SCP | [46] |
| Enc2022-I | ↑ SCP | |||
| WBMH-3-CMr (pICE6S13) | ↑ SCP | [47] | ||
| Enterobacter taylorae | [same study] | Cerotoma trifurcata | ↑ SCP | [30] |
| Erwinia ananas | Mei7-CM | Glyphodes pyloalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) | ↑ SCP | [48] |
| TM2 | ↑ SCP | [47,48] | ||
| Erwinia ananas †† | 110 | Zea mays leaves | ↑ SCP | [46] |
| IN10-CM | Thea sinensis buds | ↑ SCP | [47,48] | |
| Erwinia herbicola | 265G-2 | - | ↑ SCP | [30,49] |
| Erwinia pyrifoliae | 1.3333 | - | ↑ SCP | [50] |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | F-12 | Rana sylvatica (wood frog) | ↑ SCP | [44,45] |
| F26-4C | ↑ SCP | [29,51,52] | ||
| 88–335 | Cerotoma trifurcata | ↑ SCP | [29] | |
| Pseudomonas putida | F-31 | Rana sylvatica | ↑ SCP | [44,45] |
| Hr6-1 | Cerotoma trifurcata | ↑ SCP | [29,52] | |
| Pseudomonas syringae | 1.32 | - | ↑ SCP | [50] |
| 1.7277 | - | ↑ SCP | ||
| C-9 [ATCC 39254] | - | ↑ SCP | [53] | |
| cit 7 | Plant rot/Epiphyte | ↑ SCP | [29,30,44,45,49,54,55] | |
| Hr6-3B | Cerotoma trifurcata | ↑ SCP | [29] | |
| Mei40-CM | Glyphodes pyloalis | ↑ SCP | [47,48] | |
| Ni23 | - | ↑ SCP | [56] | |
| Snomax® | Genencor International, Rochester, NY, USA | ↑ SCP | [45,57,58,59,60] | |
| unknown | - | ↑ SCP | [61,62,63] | |
| Xanthomonas campestris | unknown | - | None | [63] |
| Fungi: | ||||
| Fusarium acuminatum | 303 | - | ↑ SCP | [64] |
| Fusarium avenaceum | 411 | - | ↑ SCP | [45,64] |
| - | - | ↑ SCP | [54] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shelomi, M. Ice-Nucleating Gut Microbes in Insects: A Scoping Review. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 708-720. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020046
Shelomi M. Ice-Nucleating Gut Microbes in Insects: A Scoping Review. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(2):708-720. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020046
Chicago/Turabian StyleShelomi, Matan. 2024. "Ice-Nucleating Gut Microbes in Insects: A Scoping Review" Microbiology Research 15, no. 2: 708-720. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020046
APA StyleShelomi, M. (2024). Ice-Nucleating Gut Microbes in Insects: A Scoping Review. Microbiology Research, 15(2), 708-720. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020046






