Early Developmental Exposure to Triclosan Impacts Fecal Microbial Populations, IgA and Functional Activities of the Rat Microbiome
Abstract
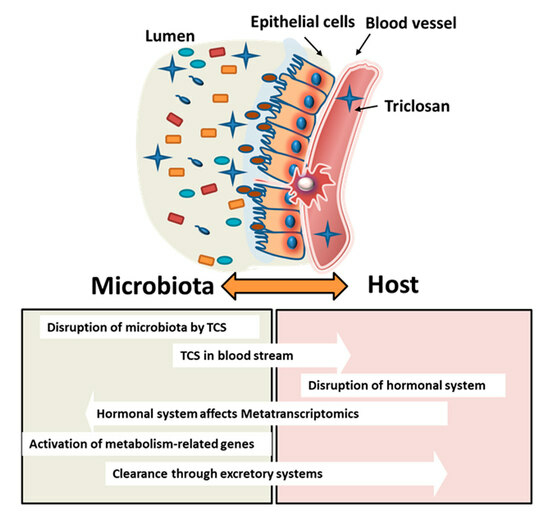
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animal Housing and Diet
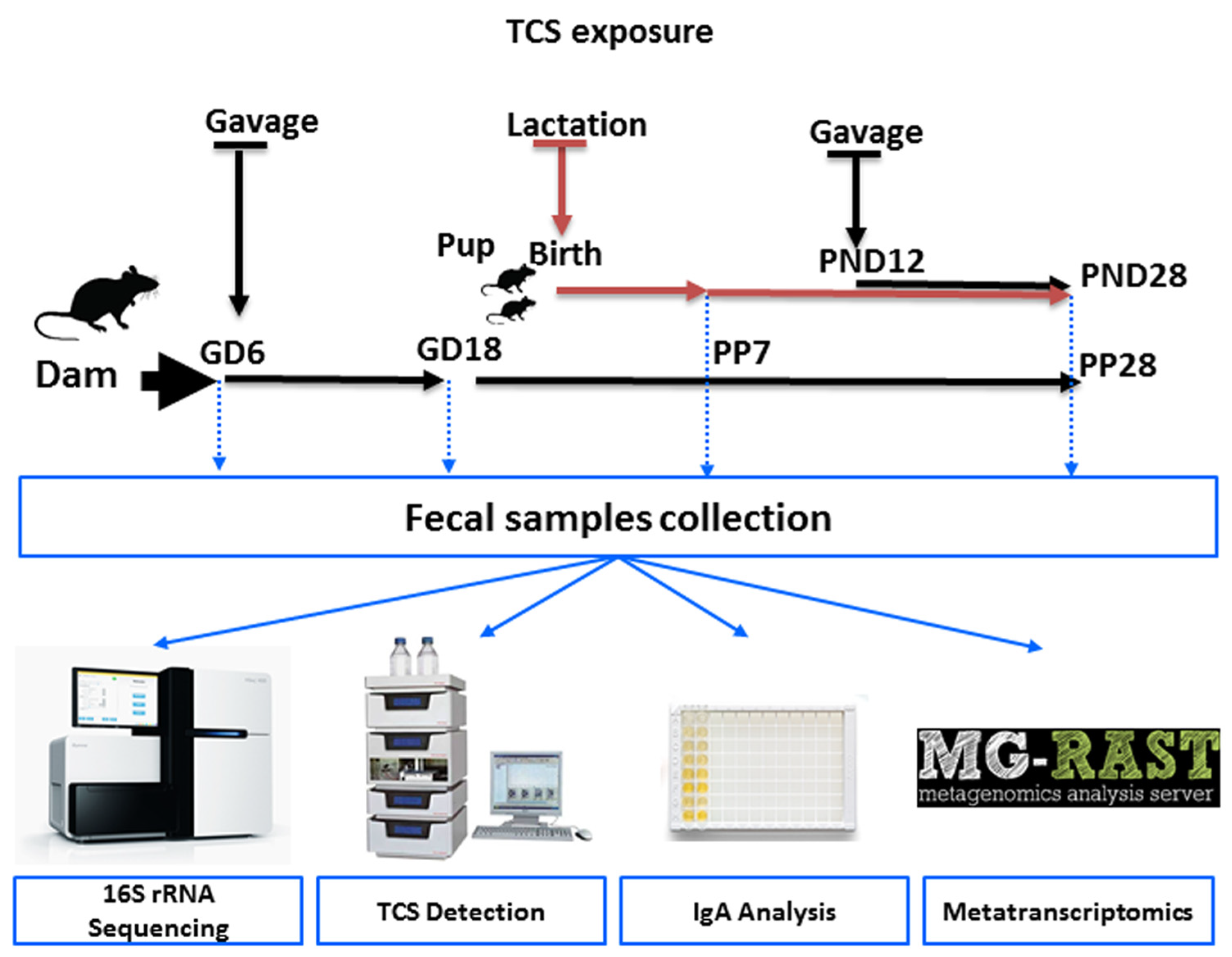
2.2. TCS Dose Selection and Exposure to Animals
2.3. Fecal Bacterial DNA and RNA Isolation
2.4. 16s rRNA Next-Generation Sequencing
2.5. Sequencing of the Metatranscriptome and Examination of Orthogroups (KO)
2.6. Quantification of TCS in Rat Feces Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.7. Quantification of Bound and Unbound IgA in Rat Feces Using ELISA
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
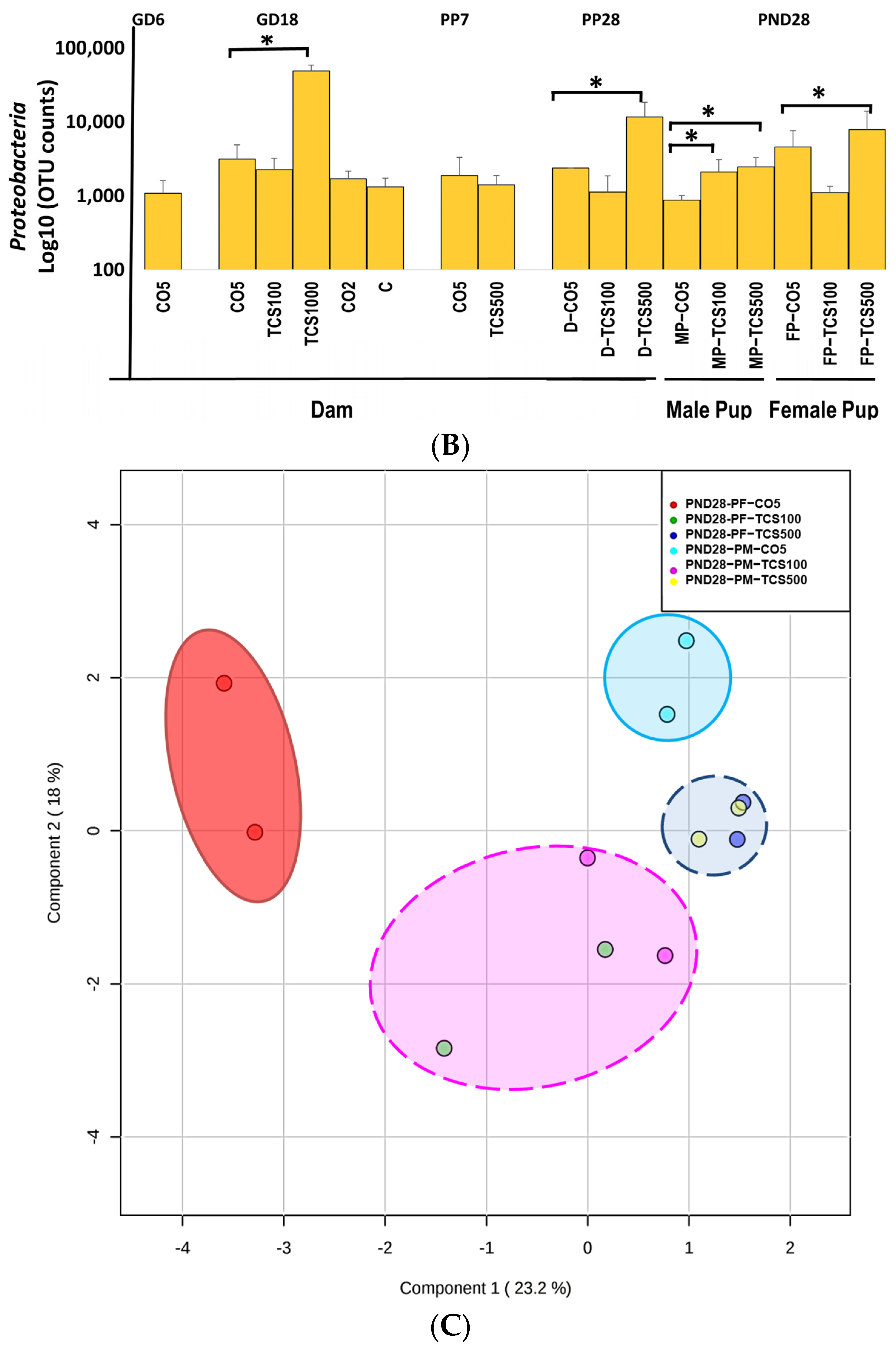
3.1. TCS Oral Exposure Is Associated with Alteration of Intestinal Commensal Bacterial Community Structure
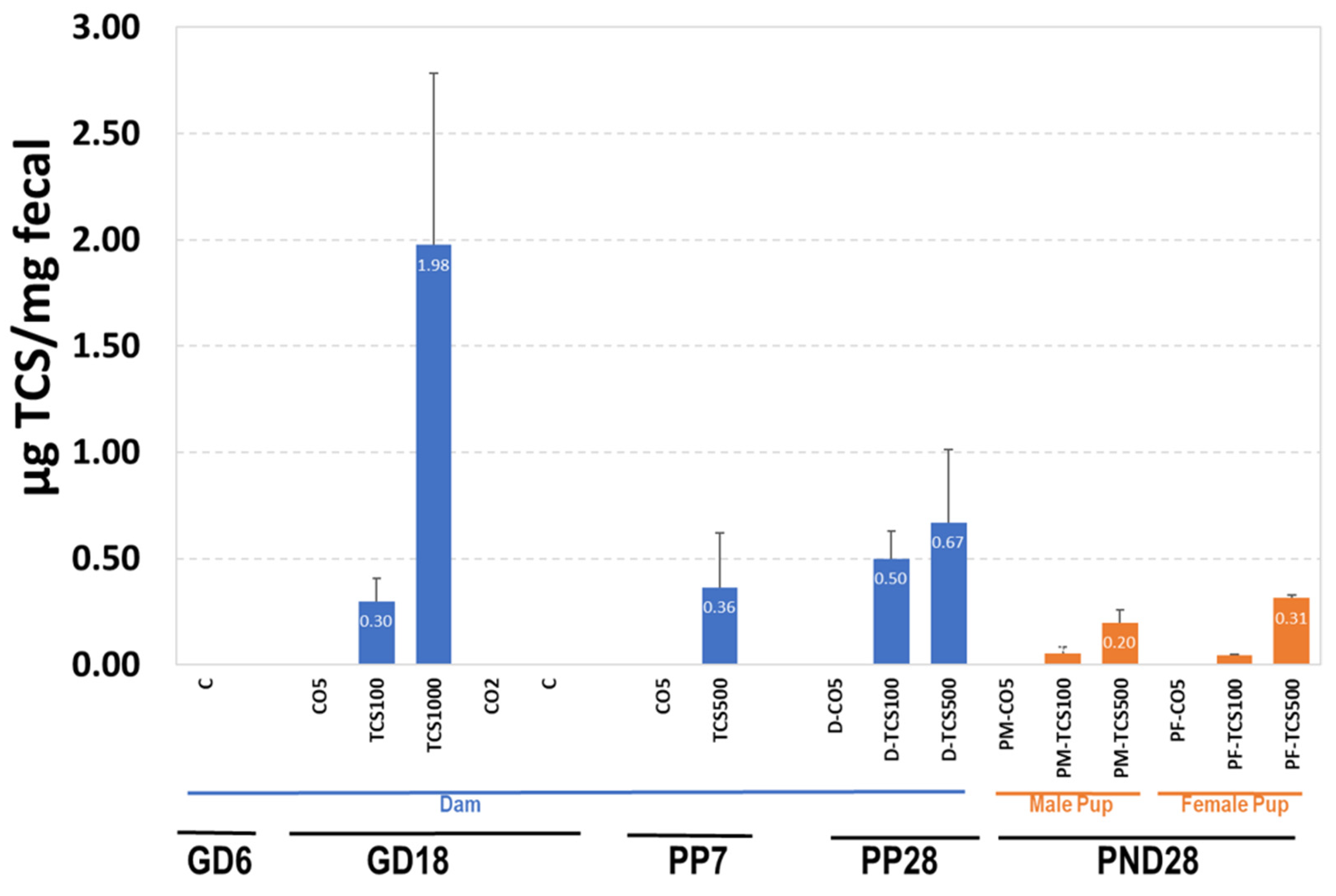
3.2. The Relationship between TCS Excreted in Feces and the Number of OTUs
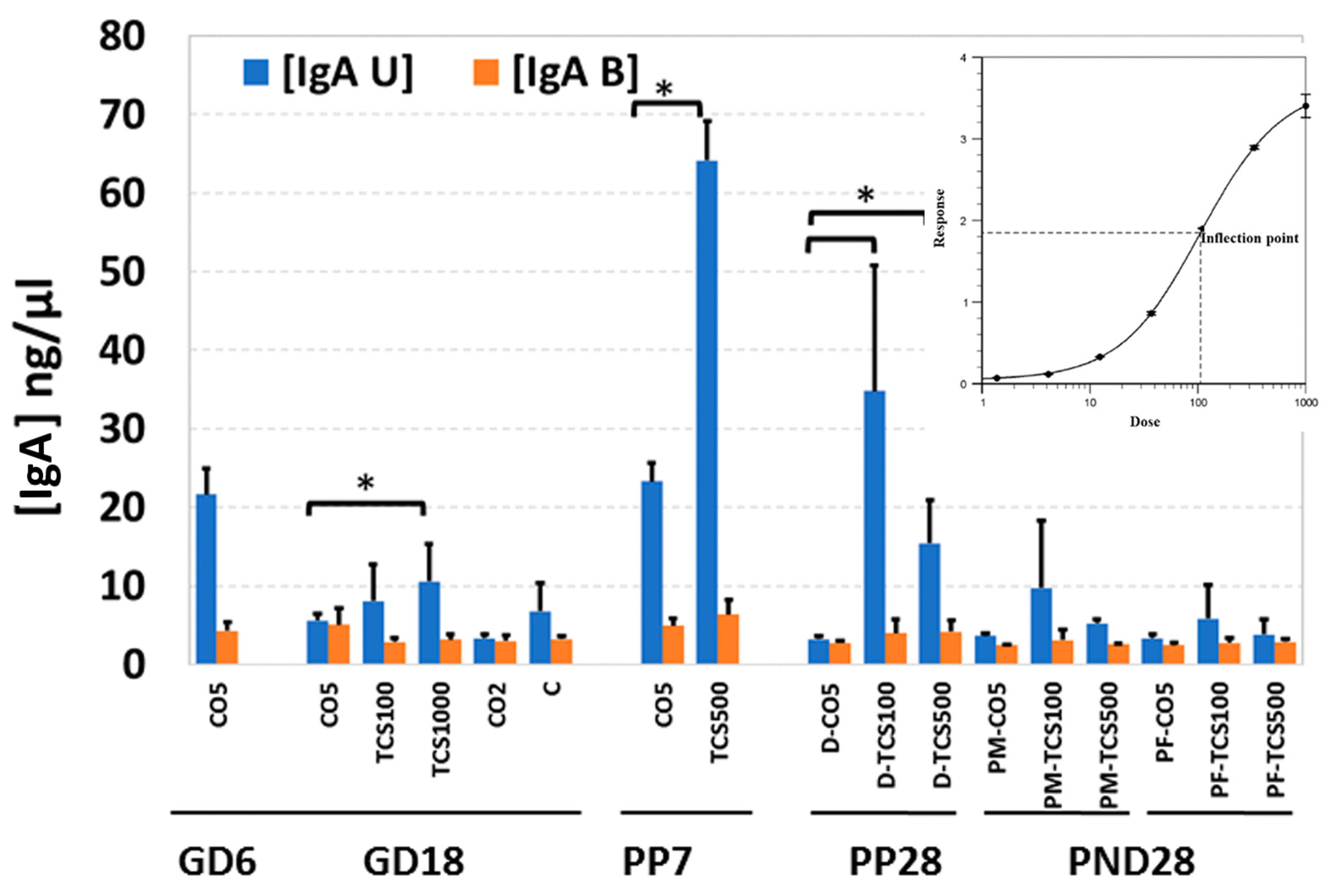
3.3. The Unbound IgA Influences the Microbiome after TCS Exposure
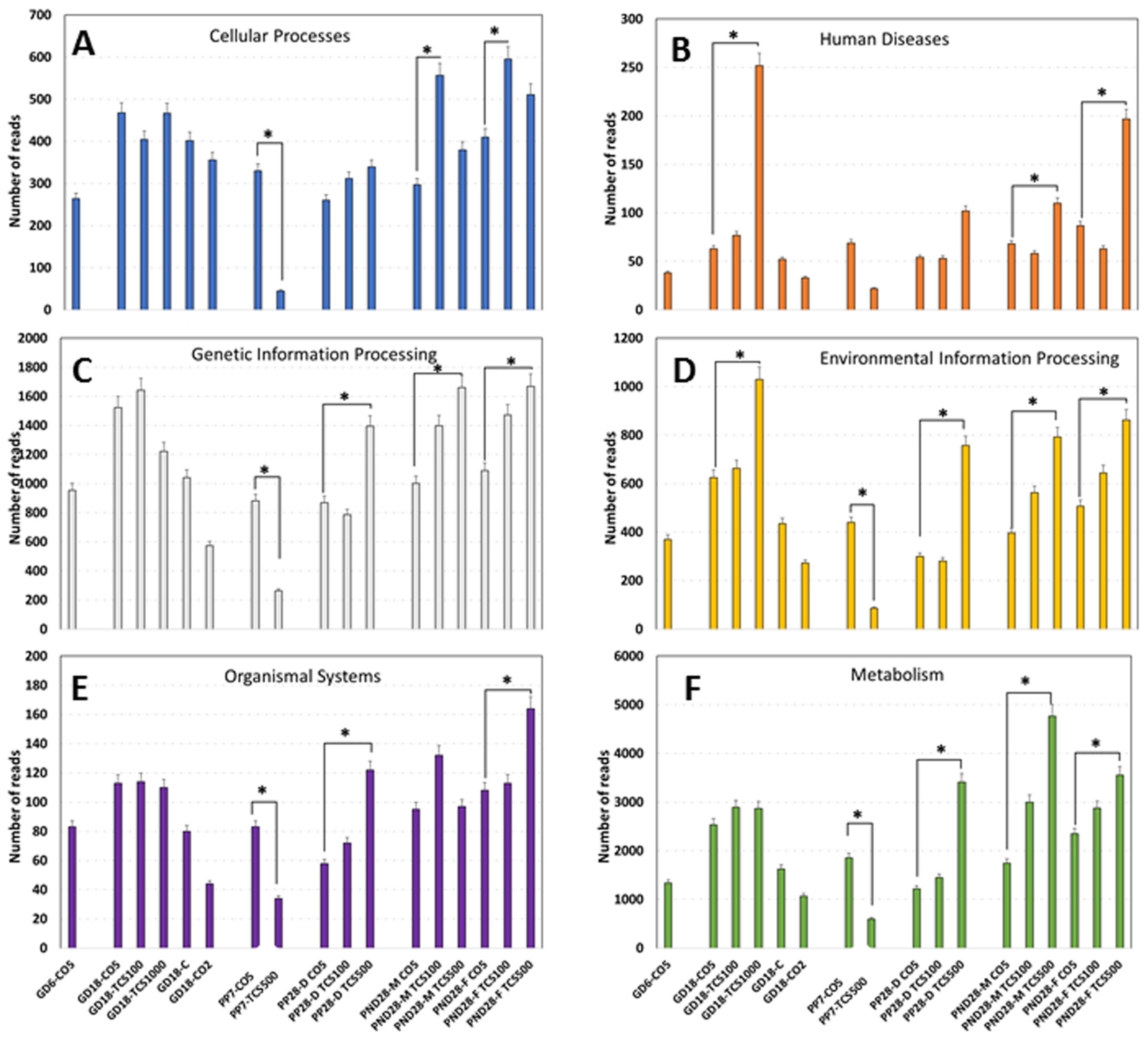
3.4. Examination of Intestinal Bacterial Functional Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GD | Gestation day |
| IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
| NOAEL | No-observed adverse effect level |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic unit |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PND | Postnatal day |
| PP | Postpartum |
| TCS | Triclosan |
References
- Food and Drug Adminnistration. Safety and effectiveness of consumer antiseptics: Topical antimicrobial drug products for over-the-counter human use. J. Fed. Regist. 2016, 81, 61106–61130. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherly, L.M.; Gosse, J.A. Triclosan exposure, transformation, and human health effects. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2017, 20, 447–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Adminnistration. Safety and Effectiveness of Consumer Antiseptics; Topical Antimicrobial Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use; Proposed Amendment of the Tentative Final Monograph; Reopening of Administrative Record. Fed. Regist. 2016, 21, 42911–42937. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, J.H.; Matsui, E.C.; Wood, R.A.; Keet, C.A. Urinary levels of triclosan and parabens are associated with aeroallergen and food sensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 453–460.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribado, J.V.; Ley, C.; Haggerty, T.D.; Tkachenko, E.; Bhatt, A.S.; Parsonnet, J. Household triclosan and triclocarban effects on the infant and maternal microbiome. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalew, T.E.; Halden, R.U. Environmental exposure of aquatic and terrestrial biota to triclosan and triclocarban 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lépesová, K.; Krahulcová, M.; Mackuľak, T.; Bírošová, L. Sewage sludge as a source of triclosan-resistant bacteria. J. Acta Chim. Slovaca 2019, 12, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, B.; Scott, J.; Rosi-Marshall, E.J.; Kelly, J.J. Triclosan exposure increases triclosan resistance and influences taxonomic composition of benthic bacterial communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8923–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nietch, C.T.; Quinlan, E.L.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Impellitteri, C.A.; Raikow, D.; Walters, D. Effects of a chronic lower range of triclosan exposure on a stream mesocosm community. J. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2874–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braoudaki, M.; Hilton, A.C. Mechanisms of resistance in Salmonella enterica adapted to erythromycin, benzalkonium chloride and triclosan. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, R.; Mohajerani, H.; Bozorgmehr, F. Polyglactin 910 suture compared with polyglactin 910 coated with triclosan in dental implant surgery: Randomized clinical trial. J. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula, A.B.; Taparelli, J.R.; Alonso, R.C.B.; Innocentini-Mei, L.H.; Puppin-Rontani, R.M. Synthesis and application of triclosan methacrylate monomer in resin composites. J. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2019, 23, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Wong, L.-Y.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Urinary concentrations of triclosan in the US population: 2003–2004. J. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 116, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, T.J.; Zota, A.R.; Schwartz, J.M. Environmental chemicals in pregnant women in the United States: NHANES 2003–2004. J. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacy, S.L.; Eliot, M.; Etzel, T.; Papandonatos, G.; Calafat, A.M.; Chen, A.; Hauser, R.; Lanphear, B.P.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Ye, X.; et al. Patterns, variability, and predictors of urinary triclosan concentra-tions during pregnancy and childhood. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6404–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, S.; Sood, S.; Showkat, S.; Lite, C.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Vairamani, M.; Barathi, S.; Santosh, W. Detection of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) from maternal blood plasma and amniotic fluid in Indian population. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2017, 241, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voelker, R. Say goodbye to some antibacterials. JAMA 2016, 316, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Mou, L.; Qu, J.; Wu, L.; Liu, C. Adverse effects of triclosan exposure on health and potential molecular mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Triclosan Risk Assessment; Notice of Availability and Risk Reduction Options. EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0513FRL-8150-1: Federal Register. 2008. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2008/05/07/E8-9945/triclosan-risk-assessment-notice-of-availability-and-risk-reduction-options (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Heath, R.J.; Rubin, J.R.; Holland, D.R.; Zhang, E.; Snow, M.E.; Rock, C.O. Mechanism of triclosan inhibition of bacterial fatty acid synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11110–11114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, W.; Romano, K.A.; Gu, M.; Sanidad, K.Z.; Kim, D.; Yang, J.; Schmidt, B.; Panigrahy, D.; Pei, R. A common antimicrobial additive increases colonic inflammation and colitis-associated colon tumorigenesis in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Moon, H.; Lee, K.; Rhee, M.-S. Bactericidal effects of triclosan in soap both in vitro and in vivo. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 3345–3352. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, G.; Kaur, S.; Pulicharla, R.; Brar, S.; Cledón, M.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R. Triclosan: Current status, occurrence, environmental risks and bioaccumulation potential. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 5657–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesgate, R.; Grasha, P.; Maillard, J.-Y. Use of a predictive protocol to measure the antimicrobial resistance risks associated with biocidal product usage. Am. J. Infect. Control 2016, 44, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaulke, C.A.; Barton, C.L.; Proffitt, S.; Tanguay, R.L.; Sharpton, T.J. Triclosan exposure is associated with rapid restructuring of the microbiome in adult zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narrowe, A.B.; Albuthi-Lantz, M.; Smith, E.P.; Bower, K.J.; Roane, T.M.; Vajda, A.M.; Miller, C.S. Perturbation and restoration of the fathead minnow gut microbiome after low-level triclosan exposure. J. Microbiome 2015, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, A.C.; Pischel, L.; Ley, C.; Suh, G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Haggerty, T.D.; Ley, R.E.; Parsonnet, J. Crossover control study of the effect of personal care products containing triclosan on the microbiome. J. Msphere 2016, 1, e00056-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Raikhel, V.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Fernandez-Hernandez, H.; Lambertini, L.; Manservisi, F.; Falcioni, L.; Bua, L.; Belpoggi, F.; Teitelbaum, S.L. Effect of postnatal low-dose exposure to environmental chemicals on the gut microbiome in a rodent model. J. Microbiome 2016, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmyr, M.; Harden, F.; Toms, L.-M.L.; Mueller, J.F.; McLachlan, M.S.; Adolfsson-Erici, M.; Sandborgh-Englund, G. The influence of age and gender on triclosan concentrations in Australian human blood serum. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 393, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, M.H.; Tun, H.M.; Mahoney, J.J.; Konya, T.B.; Guttman, D.S.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; Sears, M.R. Postnatal exposure to household disinfectants, infant gut microbiota and subsequent risk of overweight in children. J. CMAJ 2018, 190, E1097–E1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankester, J.; Patel, C.; Cullen, M.R.; Ley, C.; Parsonnet, J. Urinary triclosan is associated with elevated body mass index in NHANES. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, A.; Baduel, C.; Toms, L.; Calafat, A.; Ye, X.; Hobson, P.; Broomhall, S.; Mueller, J. Use of pooled samples to assess human exposure to parabens, benzophenone-3 and triclosan in Queensland, Australia. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 85, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.M.; Yamanishi, S.; Sohn, J.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Leung, J.M.; Cho, I.; Kim, S.G.; Li, H.; Gao, Z.; Mahana, D. Altering the intestinal microbiota during a critical developmental window has lasting metabolic consequences. J. Cell 2014, 158, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. J. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, D.A.; McNulty, N.P.; Guruge, J.L.; Gordon, J.I. IgA response to symbiotic bacteria as a mediator of gut homeostasis. J. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, G.; Ladinsky, M.; Yu, K.; Sanders, J.; Yoo, B.; Chou, W.-C.; Conner, M.; Earl, A.; Knight, R.; Bjorkman, P. Gut microbiota utilize immunoglobulin A for mucosal colonization. J. Sci. 2018, 360, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodricks, J.V.; Swenberg, J.A.; Borzelleca, J.F.; Maronpot, R.R.; Shipp, A.M. Triclosan: A critical review of the experimental data and development of margins of safety for consumer products. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2010, 40, 422–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, A.; Maske, P.; Mote, C.; Dighe, V. Gestational and lactational exposure to triclosan causes impaired fertility of F1 male offspring and developmental defects in F2 generation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, J.S.; Chang, E.T.; Gentry, P.R.; Clewell, H.J.; Boffetta, P.; Cohen, S.M. Dose-response for assessing the cancer risk of inorganic arsenic in drinking water: The scientific basis for use of a threshold approach. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2019, 49, 36–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiani, M.H.; Khare, S.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Boy, R.; Ivanov, I.N.; Khodakovskaya, M. The impact of tomato fruits containing multi-walled carbon nanotube residues on human intestinal epithelial cell barrier function and intestinal microbiome composition. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3639–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.; Kolluru, P.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Gokulan, K. Aloin alters the intestinal bacterial community structure and short chain fatty acids metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 474. [Google Scholar]
- Gokulan, K.; Arnold, M.G.; Jensen, J.; Vanlandingham, M.; Twaddle, N.C.; Doerge, D.R.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Khare, S. Exposure to Arsenite in CD-1 Mice during Juvenile and Adult Stages: Effects on Intestinal Microbiota and Gut-Associated Immune Status. mBio 2018, 9, e01418-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A. The metagenomics RAST server—A public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wu, D. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of triclosan and triclocarban in cosmetic products. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2012, 34, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokulan, K.; Kumar, A.; Lahiani, M.H.; Sutherland, V.L.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Khare, S. Differential Toxicological Outcome of Corn Oil Exposure in Rats and Mice as Assessed by Microbial Composition, Epithelial Permeability, and Ileal Mucosa-Associated Immune Status. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 180, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, S.; Maruya, M.; Kato, L.M.; Suda, W.; Atarashi, K.; Doi, Y.; Tsutsui, Y.; Qin, H.; Honda, K.; Okada, T.J.I. Foxp3+ T cells regulate immunoglobulin A selection and facilitate diversification of bacterial species responsible for immune homeostasis. Immunity 2014, 41, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabb, M.M.; Kholodovych, V.; Grün, F.; Zhou, C.; Welsh, W.J.; Blumberg, B. Highly chlorinated PCBs inhibit the human xenobiotic response mediated by the steroid and xenobiotic receptor (SXR). J. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, A.; Olea, N.; Olea-Serrano, F. Human exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals: Assessing the total estrogenic xenobiotic burden. J. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1997, 16, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitelbaum, S.L.; Mervish, N.; Moshier, E.L.; Vangeepuram, N.; Galvez, M.P.; Calafat, A.M.; Silva, M.J.; Brenner, B.L.; Wolff, M.S. Associations between phthalate metabolite urinary concentrations and body size measures in New York City children. J. Environ. Res. 2012, 112, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, K.G.; Schall, R.A.; Chevrier, J.; Tyler, K.; Aguirre, H.; Bradman, A.; Holland, N.T.; Lustig, R.H.; Calafat, A.M.; Eskenazi, B. Prenatal and postnatal bisphenol A exposure and body mass index in childhood in the CHAMACOS cohort. J. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geens, T.; Dirtu, A.C.; Dirinck, E.; Malarvannan, G.; Van Gaal, L.; Jorens, P.G.; Covaci, A. Daily intake of bisphenol A and triclosan and their association with anthropometric data, thyroid hormones and weight loss in overweight and obese individuals. J. Environ. Int. 2015, 76, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Cao, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Sun, P.; Chen, L. Exposure of pregnant mice to triclosan causes insulin resistance via thyroxine reduction. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 160, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajao, C.; Andersson, M.A.; Teplova, V.V.; Nagy, S.; Gahmberg, C.G.; Andersson, L.C.; Hautaniemi, M.; Kakasi, B.; Roivainen, M.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M. Mitochondrial toxicity of triclosan on mammalian cells. J. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Rawls, J.F. Microbial influences on gut development and gut-brain communication. Development 2021, 148, dev194936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, A.L.; Gilbert, J.A. Is triclosan harming your microbiome? J. Sci. 2016, 353, 348–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bever, C.S.; Rand, A.A.; Nording, M.; Taft, D.; Kalanetra, K.M.; Mills, D.A.; Breck, M.A.; Smilowitz, J.T.; German, J.B.; Hammock, B.D. Effects of triclosan in breast milk on the infant fecal microbiome. J. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrow, D.I.; Felker, J.M.; Baker, K.H. Impacts of triclosan in greywater on soil microorganisms. J. Appl. Environ. Soil. Sci. 2011, 2011, 646750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdankhah, S.P.; Scheie, A.A.; Høiby, E.A.; Lunestad, B.-T.; Heir, E.; Fotland, T.Ø.; Naterstad, K.; Kruse, H. Triclosan and antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: An overview. J. Microb. Drug Resist. 2006, 12, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suller, M.; Russell, A. Triclosan and antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Mao, L.; Nguyen, S.H.; Duarte, T.; Coin, L.; Bond, P.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J. Triclosan at environmentally relevant concentrations promotes horizontal transfer of multidrug resistance genes within and across bacterial genera. J. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xiao, J.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Fu, J.; Shen, J.; et al. Infant exposure to parabens, triclosan, and triclocarban via breastfeeding and formula supplementing in southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y. Buccal absorption of triclosan following topical mouthrinse application. Am. J. Dent. 2000, 13, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirota, R.; Ohya, Y.; Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Fukutomi, Y.; Muto, G.; Ngatu, N.R.; Nakamura, T.; Nakamura, H. Triclosan-induced alteration of gut microbiome and aggravation of asthmatic airway response in aeroallergen-sensitized mice. Allergy 2019, 74, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. J. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eeckhaut, V.; Machiels, K.; Perrier, C.; Romero, C.; Maes, S.; Flahou, B.; Steppe, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Sas, B.; Ducatelle, R. Butyricicoccus pullicaecorum in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2013, 62, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Ma, Y.; Huang, W.; Ling, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Zeng, A.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Dietary Lactobacillus plantarum ST-III alleviates the toxic effects of triclosan on zebrafish (Danio rerio) via gut microbiota modulation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborgh-Englund, G.; Adolfsson-Erici, M.; Odham, G.; Ekstrand, J. Pharmacokinetics of triclosan following oral ingestion in humans. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2006, 69, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees Clayton, E.M.; Todd, M.; Dowd, J.B.; Aiello, A.E. The impact of bisphenol A and triclosan on immune parameters in the US population, NHANES 2003–2006. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Han, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, A.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Jin, J.; Li, H.; Chen, G. Chronic triclosan exposure induce impaired glucose tolerance by altering the gut microbiota. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 183, 114305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A. Whither triclosan? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 693–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O. New concepts in the generation and functions of IgA. J. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, E.; Balmer, M.L.; Fritz, J.H.; Hapfelmeier, S. Functional flexibility of intestinal IgA–broadening the fine line. J. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lahiani, M.; Gokulan, K.; Sutherland, V.; Cunny, H.C.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Khare, S. Early Developmental Exposure to Triclosan Impacts Fecal Microbial Populations, IgA and Functional Activities of the Rat Microbiome. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 193-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010012
Lahiani M, Gokulan K, Sutherland V, Cunny HC, Cerniglia CE, Khare S. Early Developmental Exposure to Triclosan Impacts Fecal Microbial Populations, IgA and Functional Activities of the Rat Microbiome. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2024; 14(1):193-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleLahiani, Mohamed, Kuppan Gokulan, Vicki Sutherland, Helen C. Cunny, Carl E. Cerniglia, and Sangeeta Khare. 2024. "Early Developmental Exposure to Triclosan Impacts Fecal Microbial Populations, IgA and Functional Activities of the Rat Microbiome" Journal of Xenobiotics 14, no. 1: 193-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010012