Xenobiotics Triggering Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Their Effect on Mouse Brain Respiratory Complexes †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals
2.3. Treatments
2.4. Preparation of Subcellular Fractions and Assays
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Alterations in the Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain
3.1.1. Effect of Porphyrinogenic Drugs
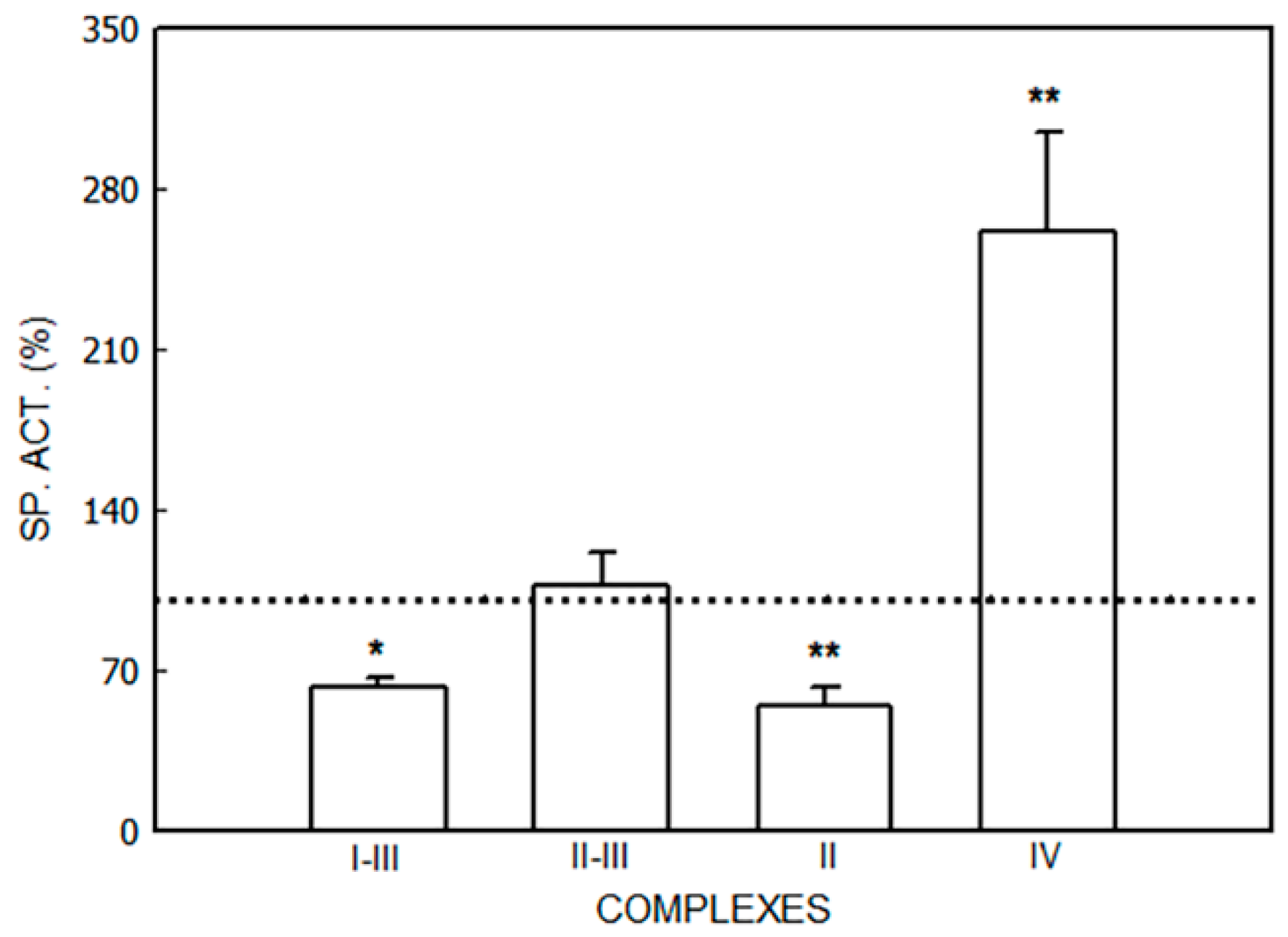
3.1.2. Effect of ALA
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramanujam, V.S.; Anderson, K.E. Porphyria Diagnostics-Part 1: A Brief Overview of the Porphyrias. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2015, 86, 17.20.1–17.20.26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.D. Heme biosynthesis and the porphyrias. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 128, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muschalek, W.; Hermasch, M.A.; Poblete-Gutiérrez, P.; Frank, J. The Porphyrias. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2022, 20, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerbino, G.; Gerez, E.; Varela, L.; Melito, V.; Parera, V.; Batlle, A.; Rossetti, M.V. Acute Intermittent Porphyria in Argentina. An update. J. Biomed. Biotech. 2015, 2015, 946387. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, A.; Sandri, G.; Marcacci, M.; Di Pierro, E.; Granata, F.; Cuoghi, C.; Marchini, S.; Pietrangelo, A.; Ventura, P. Endothelial dysfunction in Acute Hepatic Porphyrias. Diagnostics 2021, 12, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, P.E.; Edel, Y.; Mansour, R.; Mustafa, R.A.; Sandberg, S.; Members of the Acute Porphyria Expert Panel. Key terms and definitions in acute porphyrias: Results of an international Delphi consensus led by the European porphyria network. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2023, 46, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazamel, M.; Pischik, E.; Desnick, R.J. Pain in acute hepatic porphyrias: Updates on pathophysiology and management. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1004125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi Mehta, R.K.; Caress, J.B.; Rudnick, S.R.; Bonkovsky, H.L. Porphyric neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2021, 64, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demasi, M.; Penalti, C.; DeLucia, R.; Bechara, E. The prooxidant effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid in the brain tissue of rats: Implications in neuropsychiatric manifestations in porphyrias. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Penatti, C.; Resende, R.; Ulrich, H.; Britto, L.; Bechara, E. 5-Aminolevulinate and 4,5-dioxovalerate ions decrease GABA(A) receptor density in neuronal cells, synaptosomes and rat brain. Brain Res. 2006, 1093, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felitsyn, N.; McLeod, C.; Shroads, A.; Stacpoole, P.; Notterpek, L. The heme precursor delta-aminolevulinate blocks peripheral myelin formation. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, S.; Jaquet, V.; Trabace, L.; Krause, K.H. Severe Life Stress and Oxidative Stress in the Brain: From Animal Models to Human Pathology. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2013, 18, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, A.L.; McColl, K.E.L. Acute intermittent porphyria. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2005, 19, 135–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, K.; Yamamoto, J.; Tanaka, T.; Nakano, Y.; Kitagawa, T.; Nishizawa, S. 5-Aminolevulinic acid enhances mitochondrial stress upon ionizing irradiation exposure and increases delayed production of reactive oxygen species and cell death in glioma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunell, S.; Pomp, E.; Brun, A. Guide to drug porphyrogenicity prediction and drug prescription in the acute porphyrias. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 64, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stölzel, U.; Doss, M.O.; Schuppan, D. Clinical Guide and Update on Porphyrias. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 365–381.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Baig, N.; Badminton, M.; Schulenburg-Brand, D. Acute hepatic porphyria and anaesthesia: A practical approach to the prevention and management of acute neurovisceral attacks. BJA Educ. 2021, 21, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Chu, W.; Sheng, R.; Song, S.; Yang, J.; Ji, F.; Jin, X. Maternal anesthesia with sevoflurane during the mid-gestation induces social interaction deficits in offspring C57BL/6 mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 553, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, J.; Leng, Y. Mechanistic insight into sevoflurane-associated developmental neurotoxicity. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2022, 38, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Cui, J.; Junzhang, P. Effects of sevoflurane exposure during late pregnancy on brain development and beneficial effects of enriched environment on offspring cognition. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bains, R.; Moe, M.C.; Vinje, M.L.; Berg-Johnsen, J. Sevoflurane and propofol depolarize mitochondria in rat and human cerebrocortical synaptosomes by different mechanisms. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2009, 53, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neag, M.A.; Mitre, A.O.; Catinean, A.; Mitre, C.I. An Overview on the Mechanisms of Neuroprotection and Neurotoxicity of Isoflurane and Sevoflurane in Experimental Studies. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 165, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Lehto, A.; Klein, J. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by general anesthetic drugs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzaleh, A.M.; Enriquez de Salamanca, R.; Batlle, A. Administration of the anesthetic Isoflurane to mice: A model for Acute Intermittent Porphyria? J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 1992, 28, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Martinez, M.; Gerez, E.; Batlle, A.; Buzaleh, A.M. Heme oxygenase, aminolevulinate acid synthetase and the antioxidant system in the brain of mice treated with porphyrinogenic drugs. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2005, 51, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sampayo, R.; Lavandera, J.; Batlle, A.; Buzaleh, A.M. Sevoflurane: Its action on heme metabolism and Phase I drug metabolizing system. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2009, 55, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruspini, S.F.; Zuccoli, J.R.; Lavandera, J.V.; Martínez, M.d.C.; Oliveri, L.M.; Gerez, E.N.; Batlle, A.; Buzaleh, A.M. Effects of volatile anaesthetics on heme metabolism in a murine genetic model of Acute Intermittent Porphyria. A comparative study with other porphyrinogenic drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, J.; Buzaleh, A.M.; Fossati, M.; Azcurra, J.; Batlle, A. The effects of some porphyrinogenic drugs on the brain cholinergic system. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavandera, J.; Fossatti, M.; Azcurra, J.; Batlle, A.; Buzaleh, A.M. Glutamatergic System: Another target for the action of porphyrinogenic agents. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2009, 55, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lavandera, J.; Batlle, A.; Buzaleh, A.M. Metabolization of porphyrinogenic agents in brain: Involvement of the Phase I drug metabolizing system. A comparative study in liver and kidney. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 27, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavandera, J.; Rupini, S.; Batlle, A.; Buzaleh, A.M. Cytochrome P450 expression in mouse brain: Specific isoenzymes involved in phase I metabolizing system of porphyrinogenic agents in both microsomes and mitochondria. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavandera, J.; Batlle, A.; Buzaleh, A.M. Mice brain nitric oxide synthase response induced by anaesthetics and other porphyrinogenic drugs. Drug Metab. Lett. 2011, 5, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavandera, J.; Rodríguez, J.; Ruspini, S.; Meiss, R.; Zuccoli, J.R.; Martínez, M.d.C.; Gerez, E.; Batlle, A.; Buzaleh, A.M. Pleiotropic effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid in mouse brain. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkovsky, H.L.; Tschudy, D.P.; Weinbach, E.C.; Ebert, P.S.; Doherty, J.M. Porphyrin synthesis and mitochondrial respiration in acute intermittent porphyria: Studies using cultured human fibroblasts. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1975, 85, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, N.; Li, T.; Marion, B.; Faust, D.; Dozier, S.; Molina, A.; Rudnick, S.; Bonkovsky, H. Pilot study of mitochondrial bioenergetics in subjects with Acute Porphyrias. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 128, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, S.; Wang, F.; Cui, H. The role of mitochondria in reactive oxygen species generation and its Implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Cells 2018, 7, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercellino, I.; Sazanov, L.A. The assembly, regulation and function of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailey, H.A.; Medlock, A.E. A primer on heme biosynthesis. Biol. Chem. 2022, 403, 985–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Khalimonchuk, O.; Smith, P.M.; Winge, D.R. Structure, function, and assembly of heme centers in mitochondrial respiratory complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.A.; Moore, C.M.; Marcero, J.R.; Medlock, A.E.; Reddi, A.R.; Khalimonchuk, O. From synthesis to utilization: The ins and outs of mitochondrial heme. Cells 2020, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, S.; Schon, E. Mitochondrial Respiratory-Chain Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2656–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnari, J.; Suomalainen, A. Mitochondria: In sickness and in health. Cell 2012, 148, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightowlers, R.N.; Taylor, R.W.; Turnbull, D.M. Mutations causing mitochondrial disease: What is new and what challenges remain? Science 2015, 349, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Mercado-Ayon, E.; Mercado-Ayon, Y.; Dong, Y.N.; Halawani, S.; Ngaba, L.; Lynch, D.R. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 702, 108698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafourifar, P.; Asbury, M.L.; Joshi, S.S.; Kincaid, E.D. Determination of mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase activity. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 396, 424–444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navarro, A.; Gómez, C.; Sánchez-Pino, M.J.; González, H.; Bández, M.J.; Boveris, A.D.; Boveris, A. Vitamin E at high doses improves survival, neurological performance, and brain mitochondrial function in aging male mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 289, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E. Preparation of succinate dehydrogenase and reconstitution of succinate oxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1967, 10, 322–331. [Google Scholar]
- Schapira, H.V.; Cooper, J.M.; Dexter, D.; Jenner, P.; Clark, J.B.; Marsden, C.D. Mitochondrial Complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonetani, T.; Ray, G.S. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1965, 240, 3392–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, A.; Randall, R. Protein measurement with the Follin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadov, S.; Jang, S.; Chapa-Dubocq, X.R.; Khuchua, Z.; Camara, A.K. Mitochondrial respiratory supercomplexes in mammalian cells: Structural versus functional role. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikramdeo, K.S.; Sudan, S.K.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, S.; Dasgupta, S. Mitochondrial respiratory complexes: Significance in human mitochondrial disorders and cancers. J. Cell Physiol. 2022, 237, 4049–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Sun, P.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H. Mitochondrial quality control in the brain: The physiological and pathological roles. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1075141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, R.J.; Nijtmans, L.G.; Van den Heuvel, L.P.; Smeitink, J.A. Mitochondrial complex I: Structure, function and pathology. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2006, 29, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramov, A.Y.; Angelova, P.R. Cellular mechanisms of complex I-associated pathology. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 1963–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, G.; Abla, H.; Gasparre, G.; Porcelli, A.M.; Iommarini, L. The Oncojanus Paradigm of Respiratory Complex I. Genes 2018, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandini, F.; Nappi, G.; Greenamyre, J.T. Quantitative study of mitochondrial complex I in platelets of parkinsonian patients. Mov. Disord. 1998, 13, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bains, R.; Moe, M.C.; Larsen, G.A.; Berg-Johnsen, J.; Vinje, M.L. Volatile anaesthetics depolarize neural mitochondria by inhibition of the electron transport chain. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2006, 50, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimin, P.I.; Woods, C.B.; Kayser, E.B.; Ramirez, J.M.; Morgan, P.G.; Sedensky, M.M. Isoflurane disrupts excitatory neurotransmitter dynamics via inhibition of mitochondrial complex I. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wei, H. Anesthetic neurotoxicity: Apoptosis and autophagic cell death mediated by calcium dysregulation. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 60, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homedan, C.; Laafia, J.; Schmitt, C.; Gueguen, N.; Lefebvre, T.; Karim, Z.; Desquiret-Dumas, V.; Wetterwald, C.; Deybach, J.C.; Gouyac, L.; et al. Acute intermittent porphyria causes hepatic mitochondrial energetic failure in a mouse model. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 51, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, F.; Garcia, S.; Padgett, K.R.; Moraes, C.T. A defect in the mitochondrial complex III, but not complex IV, triggers early ROS-dependent damage in defined brain regions. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 5066–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, M.; Marles-Wright, J.; Smith, A. Structure-function relationships in heme-proteins. DNA Cell Biol. 2002, 21, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timón-Gómez, A.; Nývltová, E.; Abriata, L.A.; Vila, A.J.; Hosler, J.; Barrientos, A. Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis: Recent developments. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 76, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, C.R. The di-heme family of respiratory complex II enzymes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1827, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persichini, T.; Mazzone, V.; Polticelli, F.; Moreno, S.; Venturini, G.; Clementi, E. Mitochondrial type I nitric oxide synthase physically interacts with cytochrome c oxidase. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 384, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Ashino, T.; Kobayashi, Y. Chemical-induced coordinated and reciprocal changes in heme metabolism, cytochrome P450 synthesis and others in the liver of humans and rodents. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 41, SP89–SP103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massart, J.; Begriche, K.; Hartman, J.H.; Fromenty, B. Role of Mitochondrial Cytochrome P450 2E1 in Healthy and Diseased Liver. Cells 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P. Cytochrome P450 2E1 and Its Roles in Disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 322, 109056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homedan, C.; Schmitt, C.; Laafi, J.; Gueguen, N.; Desquiret-Dumas, V.; Lenglet, H.; Karim, Z.; Gouya, L.; Deybach, J.C.; Simard, G.; et al. Mitochondrial energetic defects in muscle and brain of a Hmbs−/− mouse model of acute intermittent porphyria. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 5015–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, M.S.; Parihar, A.; Villamena, F.A.; Vaccaro, P.S.; Ghafourifar, P. Inactivation of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I leads mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase to become pro-oxidative. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez, L.; Bombicino, S.; Iglesia, D.; Rukavina Mikusic, I.; D’Annunzio, V. Mitochondrial complex I inactivation after ischemia-reperfusion in the stunned heart. In Advances in Biochemistry in Health and Disease. Biochemistry of Oxidative Stress: Physiopathology and Clinical Aspects; Gelpi, R., Boveris, A., Poderoso, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 245–257. [Google Scholar]
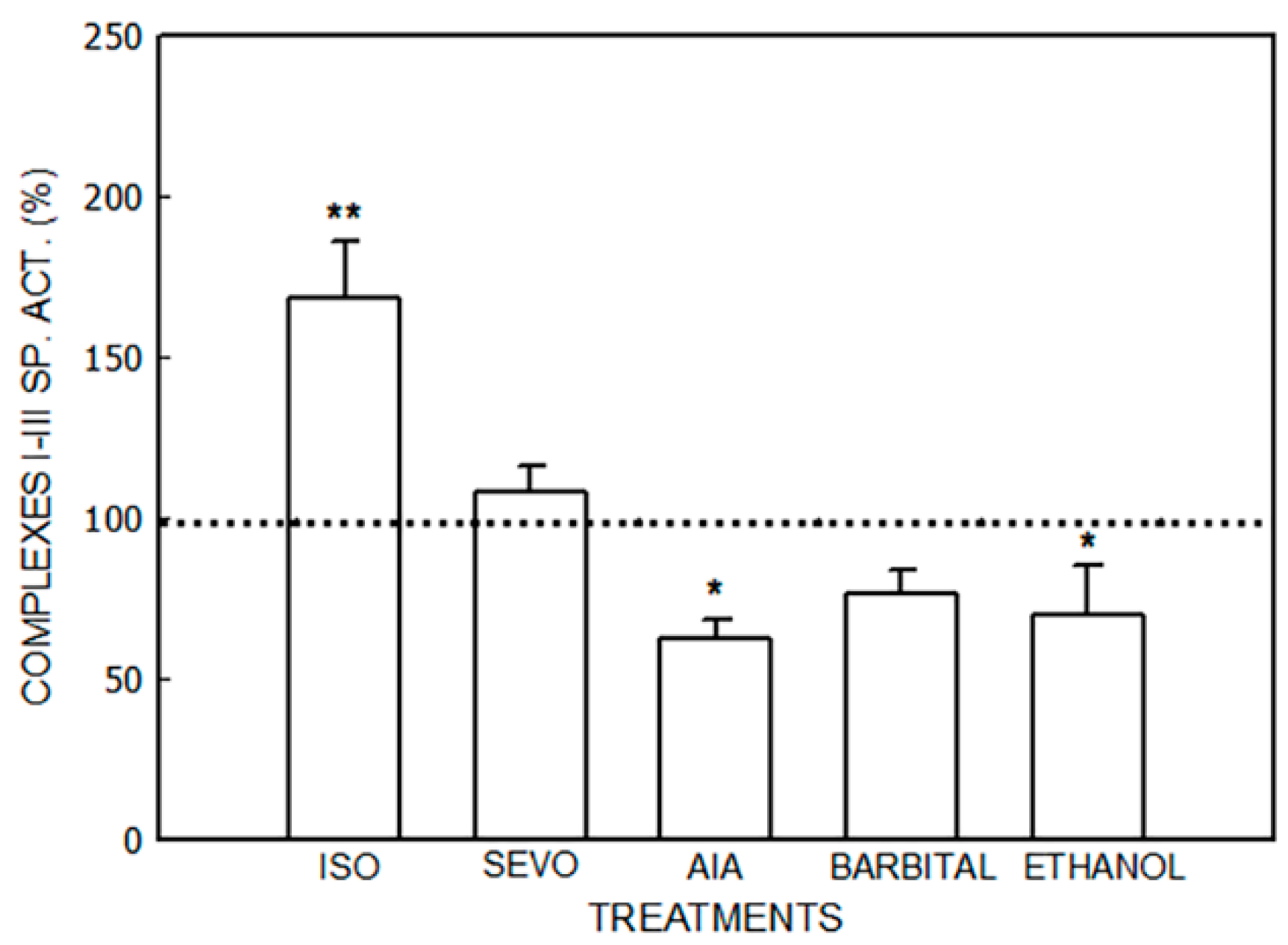




| Treatment | Group | SP. ACT I–III/SP. ACT. II–III |
| Isoflurane | Control | 4.03 ± 0.99 |
| Treated | 2.14 ± 0.17 | |
| Sevoflurane | Control | 9.06 ± 1.95 |
| Treated | 5.23 ± 0.87 | |
| Allylisopropilacetamide | Control | 5.38 ± 0.78 |
| Treated | 3.90 ± 0.26 | |
| Barbital | Control | 2.41 ± 0.21 |
| Treated | 1.82 ± 0.31 | |
| Ethanol | Control | 10.05 ± 0.26 |
| Treated | 13.40 ± 1.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuccoli, J.R.; Martínez, M.d.C.; Vallecorsa, P.; Buzaleh, A.M. Xenobiotics Triggering Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Their Effect on Mouse Brain Respiratory Complexes. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 308-319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010019
Zuccoli JR, Martínez MdC, Vallecorsa P, Buzaleh AM. Xenobiotics Triggering Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Their Effect on Mouse Brain Respiratory Complexes. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2024; 14(1):308-319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuccoli, Johanna Romina, María del Carmen Martínez, Pablo Vallecorsa, and Ana María Buzaleh. 2024. "Xenobiotics Triggering Acute Intermittent Porphyria and Their Effect on Mouse Brain Respiratory Complexes" Journal of Xenobiotics 14, no. 1: 308-319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010019







