Accounting for Uncertainties of the TRMM Satellite Estimates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Resources
| Station Name | Latitude | Longitude | Elevation |
| Elizabethtown | 34.6 | -78.583 | 40 |
| Rockingham Airport | 34.883 | -79.75 | 109 |
| Charlestown Muni | 32.899 | -80.041 | 14.6 |
| Bush Field | 33.37 | -81.965 | 45.1 |
| Daniel Fld | 33.467 | -82.033 | 128 |
| Mackall Aaf | 35.033 | -79.5 | 115 |
| Fayetteville | 34.983 | -78.883 | 58 |
| Columbia Metro | 33.942 | -81.118 | 68.6 |
| Columbia Owens | 33.967 | -80.983 | 59 |
| Lumberton | 34.61 | -79.059 | 38.4 |
| Maxton | 34.783 | -79.367 | 67 |
| Orangeburg | 33.467 | -80.85 | 60 |
| Darlington | 34.45 | -79.883 | 59 |
| York Coun | 34.983 | -81.05 | 204 |
| Greenville | 34.899 | -82.219 | 296 |
| Greenwood Airport | 34.233 | -82.15 | 192 |
| Monroe Airport | 35.017 | -80.617 | 207 |
| Simmons | 35.133 | -78.933 | 74 |
| Myrtle Beach | 33.68 | -78.918 | 7.6 |
| North myrtle beach | 33.816 | -78.721 | 10.1 |
| McClellanville | 33.153 | -79.364 | 2.7 |
| Blackville | 33.355 | -81.328 | 96.6 |
| Beaufort | 32.483 | -80.717 | 11.6 |
| Florence | 34.188 | -79.731 | 46 |

3. Model Description
| skip | where : | = | simulated field (rain rate) | |
| = | satellite estimates | |||
| = | multiplicative error term | |||
| = | random error term |
| where : | = | observed rainfall (here, gauge measurements) | |
| = | satellite estimates before bias removal | ||
| n | = | number of time steps | |
| = | overall bias |
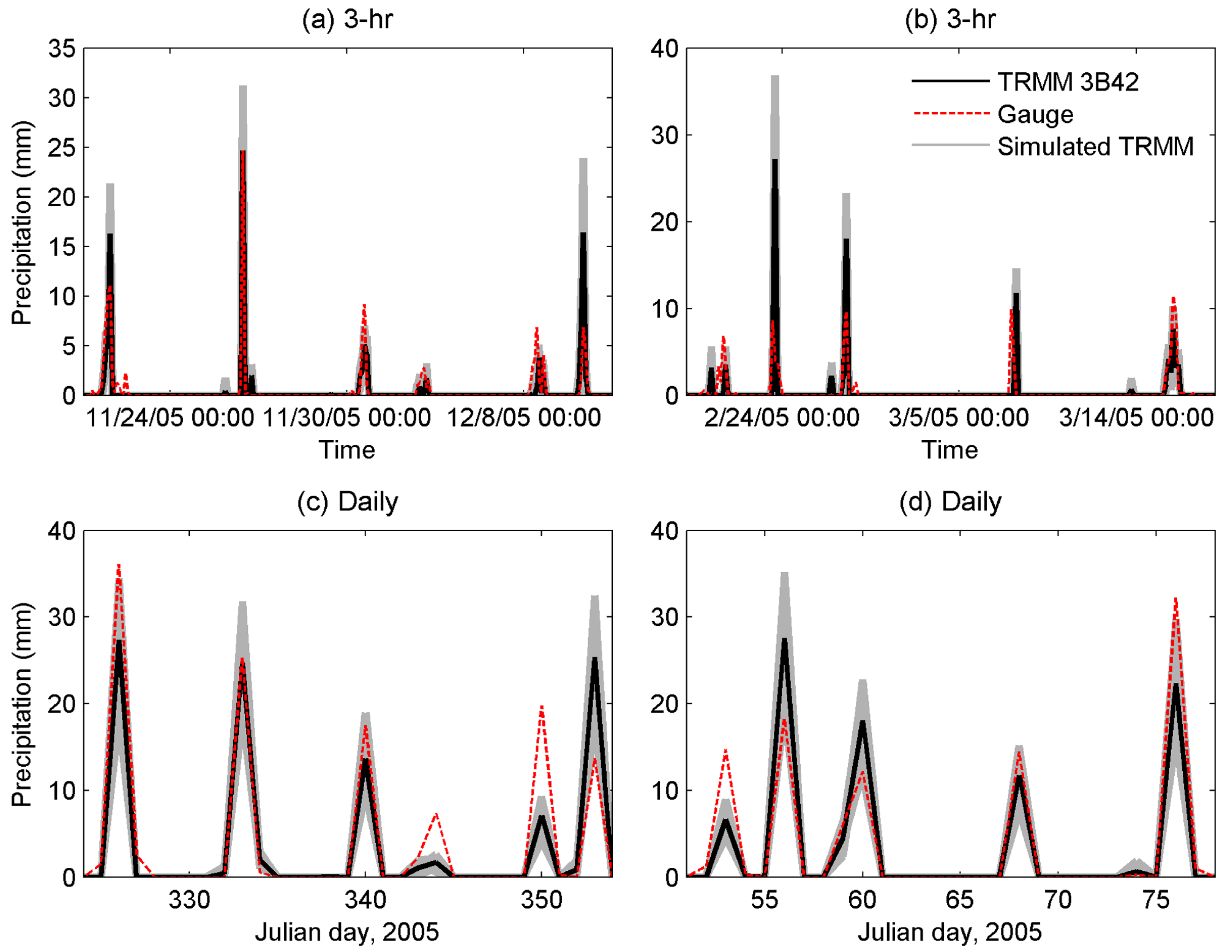
4. Results and Discussion
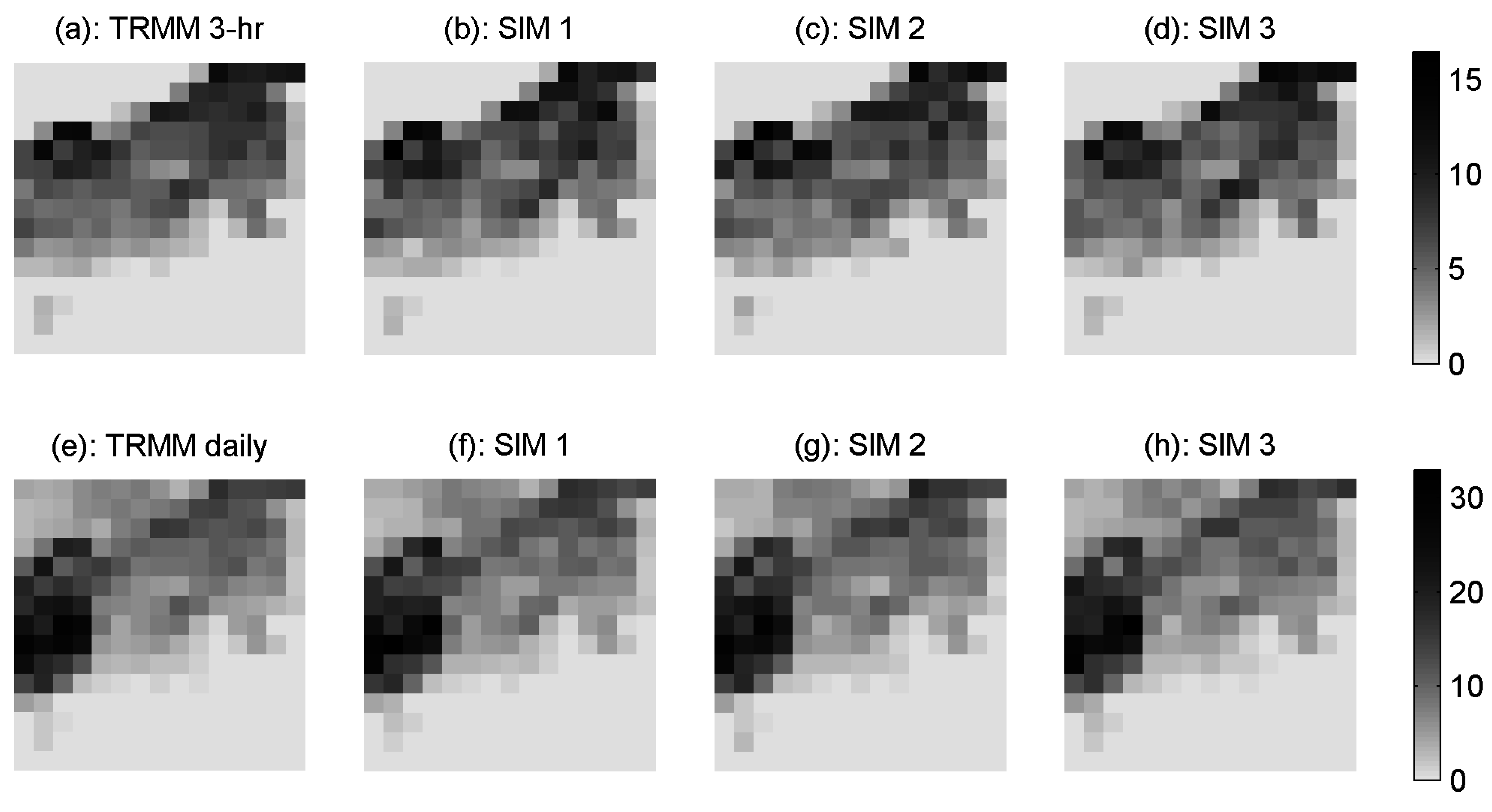

| 20 Gauges | 15 Gauges | 10 Gauges | 5 Gauges | ||||||||
| Data | 3-hr | daily | 3-hr | daily | 3-hr | daily | 3-hr | daily | |||
| TRMM (1/1/05-12/31/05) | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 4.2 | 3.1 | 6.4 | 5.2 | |||
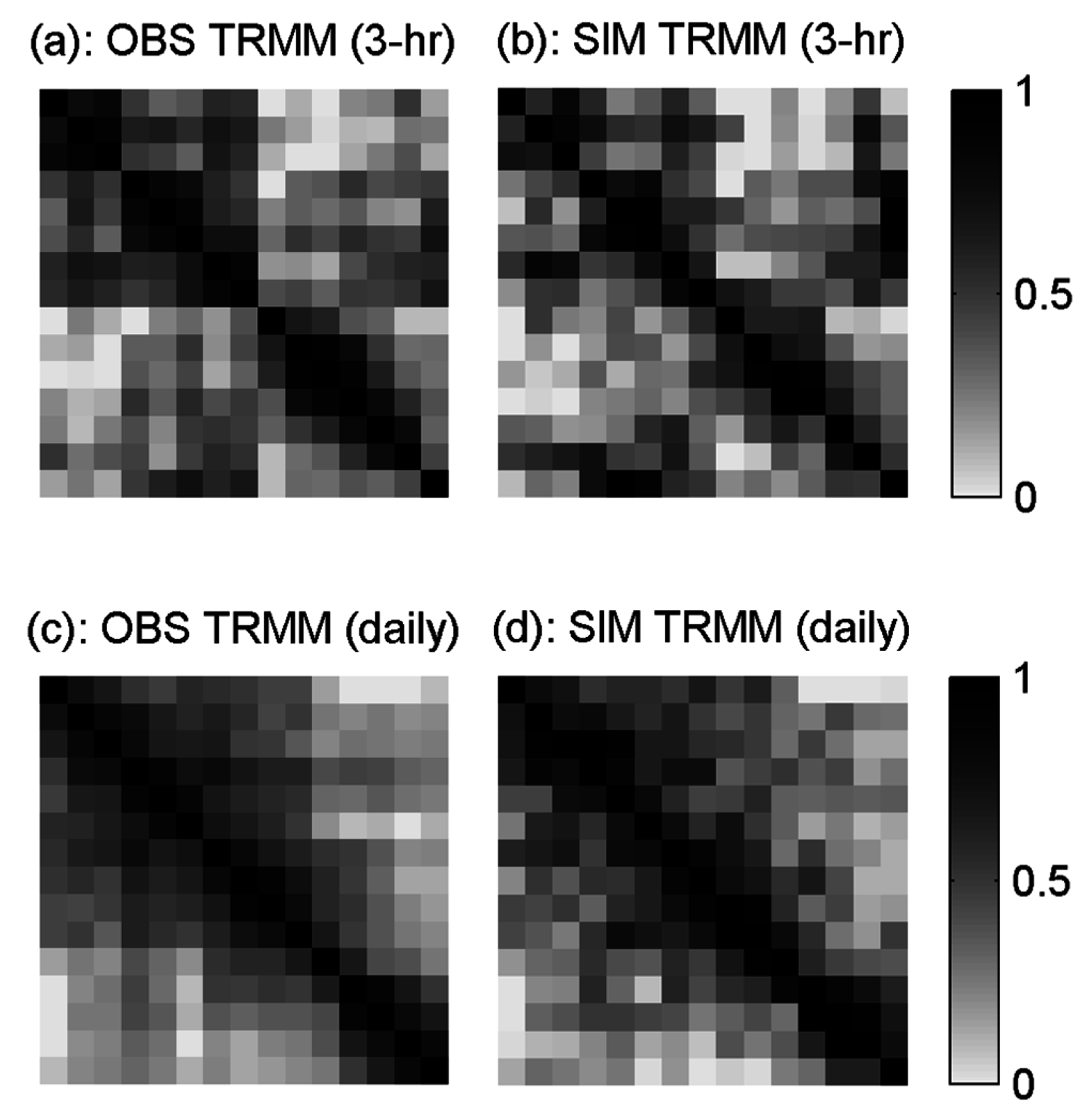


5. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability; Exit EPA Disclaimer Contribution of Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Parry, M.L., Canziani, O.F., Palutikof, J.P., van der Linden, J., Hanson, C.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ruddiman, W. Plows, Plagues and Petroleum: How Humans Took Control of Climate; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, C.; Edwards, P. Changing the Atmosphere: Expert Knowledge and Environmental Governance; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; O’Connell, P.; Hosking, J. Modeling the effects of spatial variability in rainfall on catchment response. 2. Experiments with distributed and lumped models. J. Hydrol. 1996, 175, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, D.; Faures, J.; Woolhiser, D.; Lane, L.; Sorooshian, S. Measurement and analysis of small-scale convective storm rainfall variability. J. Hydrol. 1995, 173, 283–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faures, J.M.; Goodrich, D.; Woolhiser, D.; Sorooshian, S. Impact of small-scale spatial rainfall variability on runoff modeling. J. Hydrol. 1995, 173, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obled, C.; Wendling, J.; Beven, K. The sensitivity of hydrological models to spatial rainfall patterns: an evaluation using observed data. J. Hydrol. 1994, 159, 305–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliga, T.; Aron, G.; Aydin, K.; White, E. Simulation using radar rainfall rates and a unit hydrograph model (SYN-HYD) applied to GREVE watershed. In Am. Meteor. Soc., 25th Int. Conf. on Radar Hydrology, Paris, France, 1992; pp. 587–590.
- Corradini, C.; Singh, V. Effect of spatial variability of effective rainfall on direct runoff by geomorphoIogic approach. J. Hydrol. 1985, 81, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlin, M. The significance of rainfall in the study of hydrological processes at basin scale. J. Hydrol. 1983, 65, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troutman, B.M. Runoff prediction errors and bias in parameter estimation induced by spatial variability of precipitation. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 791–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawdy, D.; Bergman, J. Effect of rainfall variability on strearnflow simulation. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evolution of the PERSIANN system satellite-based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, M.; Gruber, A. GOES multispectral rainfall algorithm (GMSRA). J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 29, 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Adler, R.; Morrissey, M.; Bolvin, D.; Curtis, S.; R. Joyce, B.M.; Susskind, J. Global precipitation at one-degree daily resolution from multisatellite observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2001, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.; Huffman, G.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; Gruber, A.; Susskind, J.; Arkin, P. The version-2 Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979–present). J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1147–11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.; Janowiak, J.; Arkin, P.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed imagery using Artificial Neural Network-Cloud Classification System. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1834–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.; Moradkhani, H.; Sorooshian, S. Uncertainty quantification of satellite precipitation estimation and Monte Carlo assessment of the error propagation into hydrologic response. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W08421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellerby, T. Satellite rainfall uncertainty estimation using an artificial neural network. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Anagnostou, E. Using a multi-dimensional satellite rainfall error model to characterize uncertainty in soil moisture fields simulated by an offline land surface model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 776–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellerby, T.; Sun, J. Probabilistic and ensemble representations of the uncertainty in an IR/microwave satellite precipitation product. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, M.; Bell, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wood, E. Comparison of two methods for estimating the sampling-related uncertainty of satellite rainfall averages based on a large radar dataset. J. Climate 2003, 16, 3759–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.; Morrissey, M. Validation and uncertainty analysis of satellite rainfall algorithms. Prof. Geogr. 2000, 52, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Anagnostou, E.; Bagtzoglou, A. On Latin Hypercube sampling for efficient uncertainty estimation of satellite rainfall observations in flood prediction. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 776–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, M.; Greene, J. Uncertainty analysis of satellite rainfall algorithms over the tropical Pacific. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmosph. 1998, 103, 19569–19576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Chiu, L. Uncertainty in satellite rainfall estimates: Time series comparison. Adv. Space Res. 1997, 19, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Gebremichael, M. Estimating actual rainfall from satellite rainfall products. Atmosph. Res. 2009, 92, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.; Abdullah, A.; Martin, R.; North, G. Sampling errors for satellite-derived tropical rainfallMonte Carlo study using a spacetime stochastic model. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 95, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurmans, J.; Bierkens, M. Effect of spatial distribution of daily rainfall on interior catchment response of a distributed hydrological model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, D.; Uhlenbrook, S. Significance of spatial variability in precipitation for process-oriented modelling: results from two nested catchments using radar and ground station data. Hydrolo. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, K.; Goodrich, D.; Myers, D.; Sorooshian, S. Spatial characteristics of thunderstorm rainfall fields and their relation to runoff. J. Hydrol. 2003, 271, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, P.; Bouvier, C.; Cisner, L.; Dominguez, R. Influence of rainfall spatial variability on flood prediction. J. Hydrol. 2002, 260, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, V.; Moore, R. The sensitivity of catchment runoff models to rainfall data at different spatial scales. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2000, 4, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Choudhury, B.J.; Garcia, M. Multitemporal analysis of TRMM-based satellite precipitation products for land data assimilation applications. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 1165–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Anagnostou, E. Assessment of current passive-microwave- and infrared-based satellite rainfall remote sensing for flood prediction. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, G.; Krahewsj, W.F. Evaluation of the research-version TMPA threehourly 0.25°0.25° rainfall estimates over Oklahoma. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L05402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Habib, E.; Bárdossy, A. A. Modeling radar rainfall estimation uncertainties: A random error model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Villarini, G.; Krajewski, W.; Ciach, G.; Zimmerman, D. Product-Error-Driven generator of probable rainfall conditioned on WSR-88D precipitation estimates. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciach, G.; Krajewski, W.; Villarini, G. Product-error-driven uncertainty model for probabilistic quantitative precipitation estimation with NEXRAD data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 1325–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, U.; Berenguer, M.; Sempere-Torres, D.; Salvade, G. Ensemble radar precipitation estimation - a new topic on the radar horizon. In Proc. 4th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology ERAD 2006, Barcelon, Spain, September 18–22, 2006.
- Clark, M.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Brandon, D.; Werner, K.; Hay, L.; Rajagopalan, B.; Yates, D. A resampling procedure for generating conditioned daily weather sequences. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Hay, L.; Rajagopalan, B.; Wilby, R. Schaake shuffle: A method for econstructing space-time variability in forecasted precipitation and temperature fields. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegram, G.; Clothier, A. Downscaling rainfields in space and time using the String of Beads model in time series mode. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2001, 5, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, A.; Srikanthan, R. A space and time model for design storm rainfall. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 104, 31623–31630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G. Estimates of root-mean-square random error for finite samples of estimated precipitation. J. Hydrometeorol. 1997, 36, 1191–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, W.; Georgakakos, K. Synthesis of radar rainfall data. Water Resour. Res. 1985, 21, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Adler, R.; Bolvin, D.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.; Bowman, K.; Stocker, E.; Wolff, D. The TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis: Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scale. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Henschke, A.; Adler, R. Evaluation of TMPA satellite-based research and real-time rainfall estimates during six tropical-related heavy rainfall events over Louisiana, USA. Atmosph. Res. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C.E. The Proof and Measurement of Association between Two Things. 1904. Available on line at: http://www.archive.org/stream/proofmeasurement00speauoft#page/n33/mode/2up (accessed September 9, 2009).
- Hollander, M.; Wolfe, D. Nonparametric Statistical Methods; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/.
Share and Cite
AghaKouchak, A.; Nasrollahi, N.; Habib, E. Accounting for Uncertainties of the TRMM Satellite Estimates. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 606-619. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs1030606
AghaKouchak A, Nasrollahi N, Habib E. Accounting for Uncertainties of the TRMM Satellite Estimates. Remote Sensing. 2009; 1(3):606-619. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs1030606
Chicago/Turabian StyleAghaKouchak, Amir, Nasrin Nasrollahi, and Emad Habib. 2009. "Accounting for Uncertainties of the TRMM Satellite Estimates" Remote Sensing 1, no. 3: 606-619. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs1030606
APA StyleAghaKouchak, A., Nasrollahi, N., & Habib, E. (2009). Accounting for Uncertainties of the TRMM Satellite Estimates. Remote Sensing, 1(3), 606-619. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs1030606





