Using Satellite Remote Sensing to Study the Impact of Climate and Anthropogenic Changes in the Mesopotamian Marshlands, Iraq
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Methods
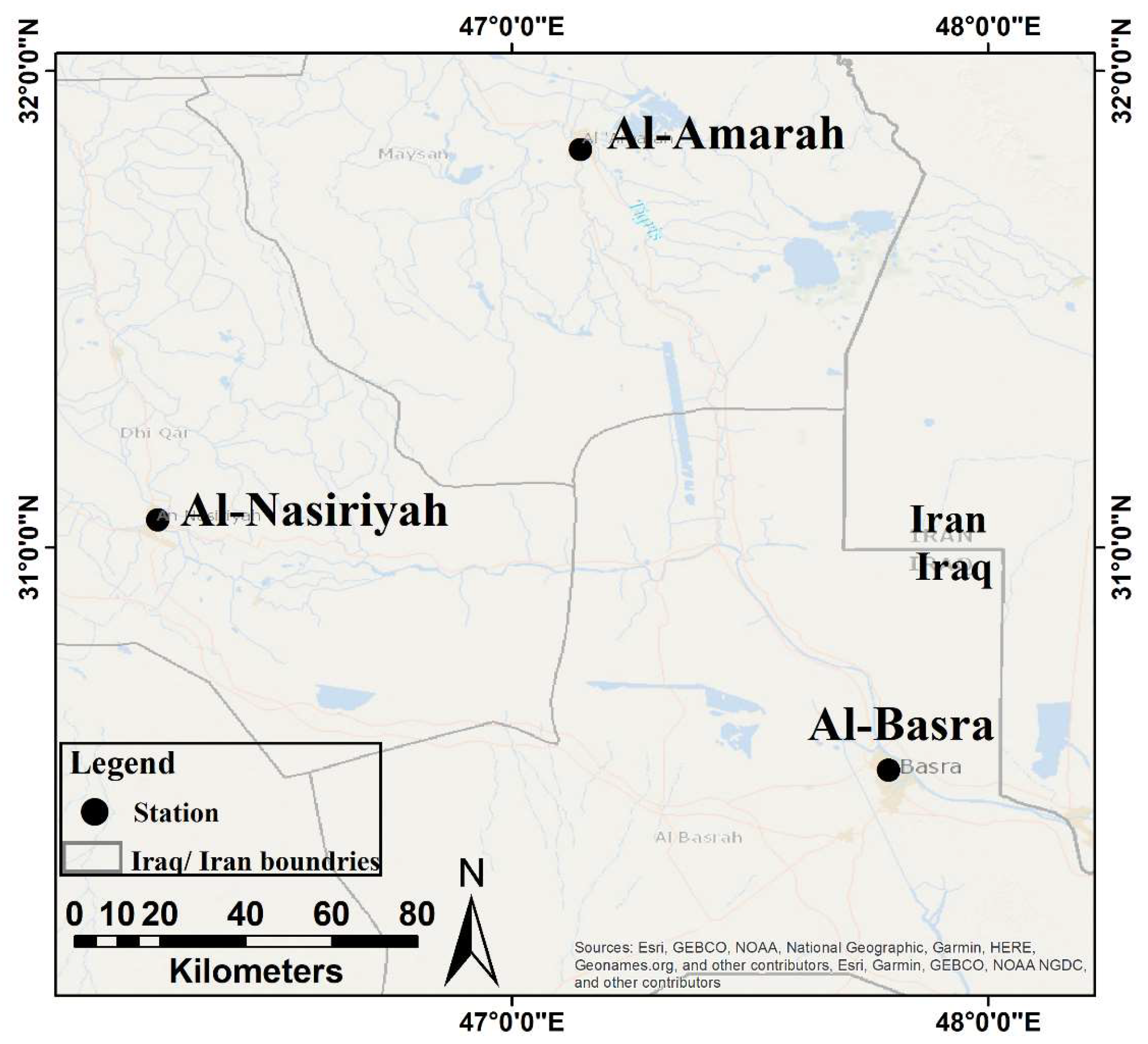
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Al-Hammar Marsh
2.1.2. The Central marshes
2.1.3. Al-Huwaiza Marsh
2.2. Satellite and Model Datasets
2.2.1. AVHRR LTDR V5 Daily NDVI Product
2.2.2. GLDAS
2.3. Landsat Images and Land Cover Classifications
2.4. In Situ Data
2.5. Long-Term Trends in Biomass Dynamics
2.6. Standardized NDVI Anomaly (SNA)
3. Results
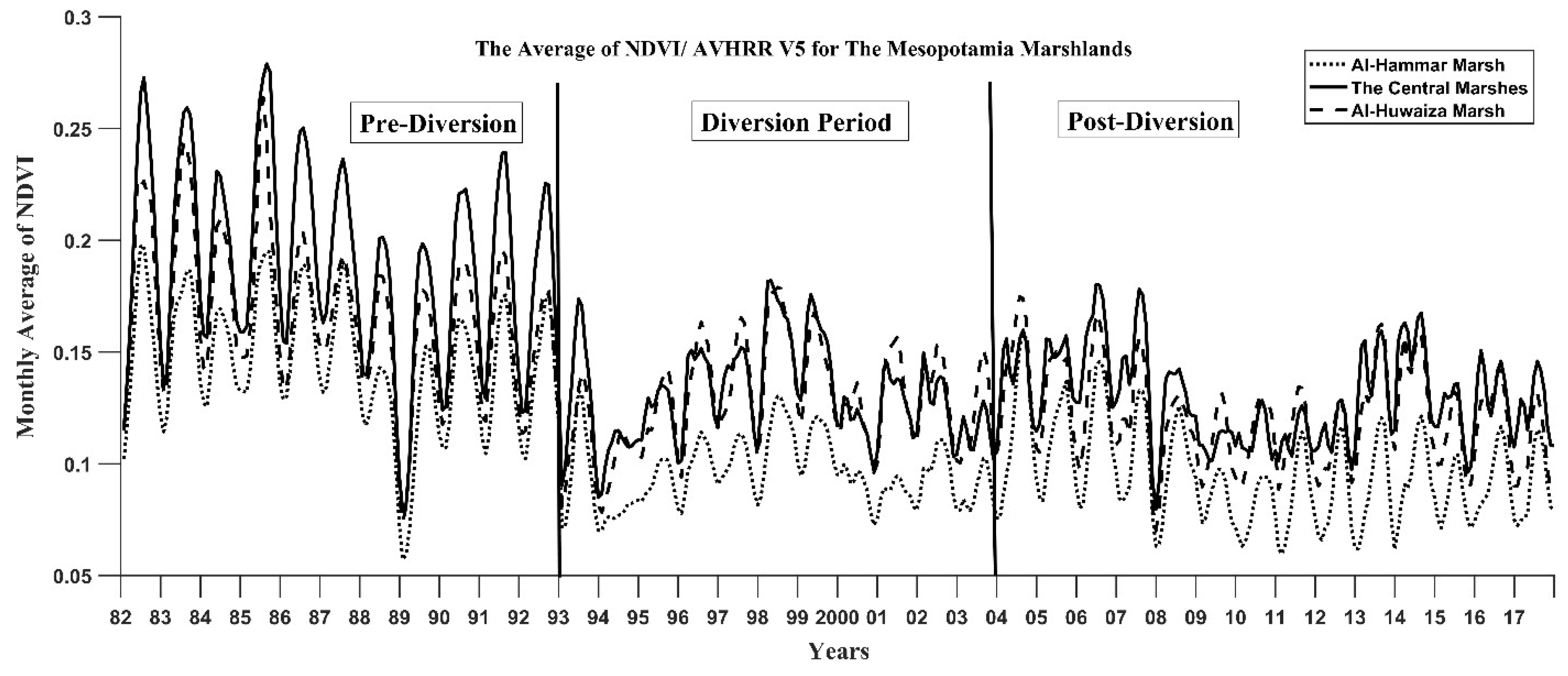
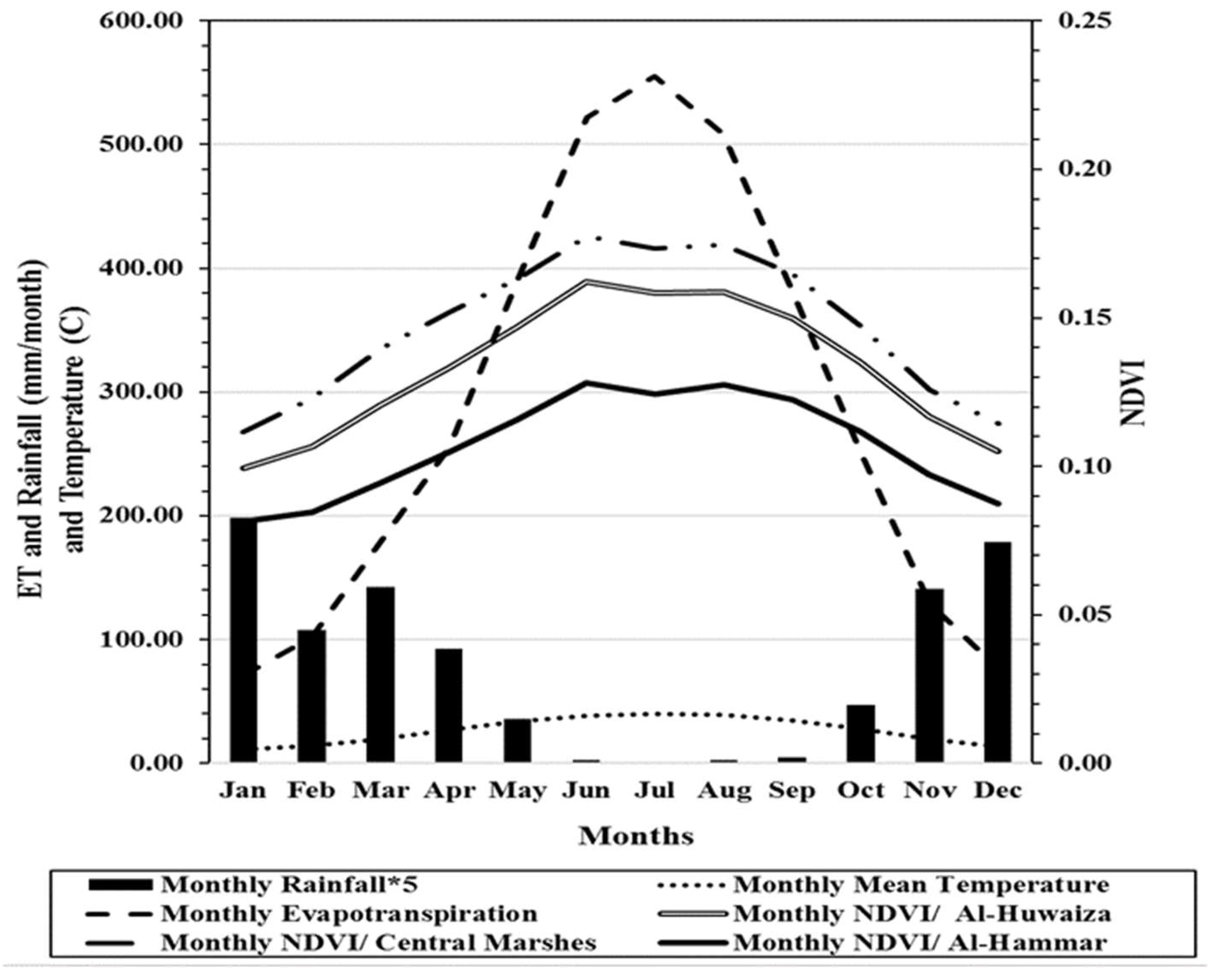
3.1. Monthly Time-Series Patterns in the Time Period from 1982 to 2017
3.2. Validation of Areas of Vegetation Productivity for Each Marsh
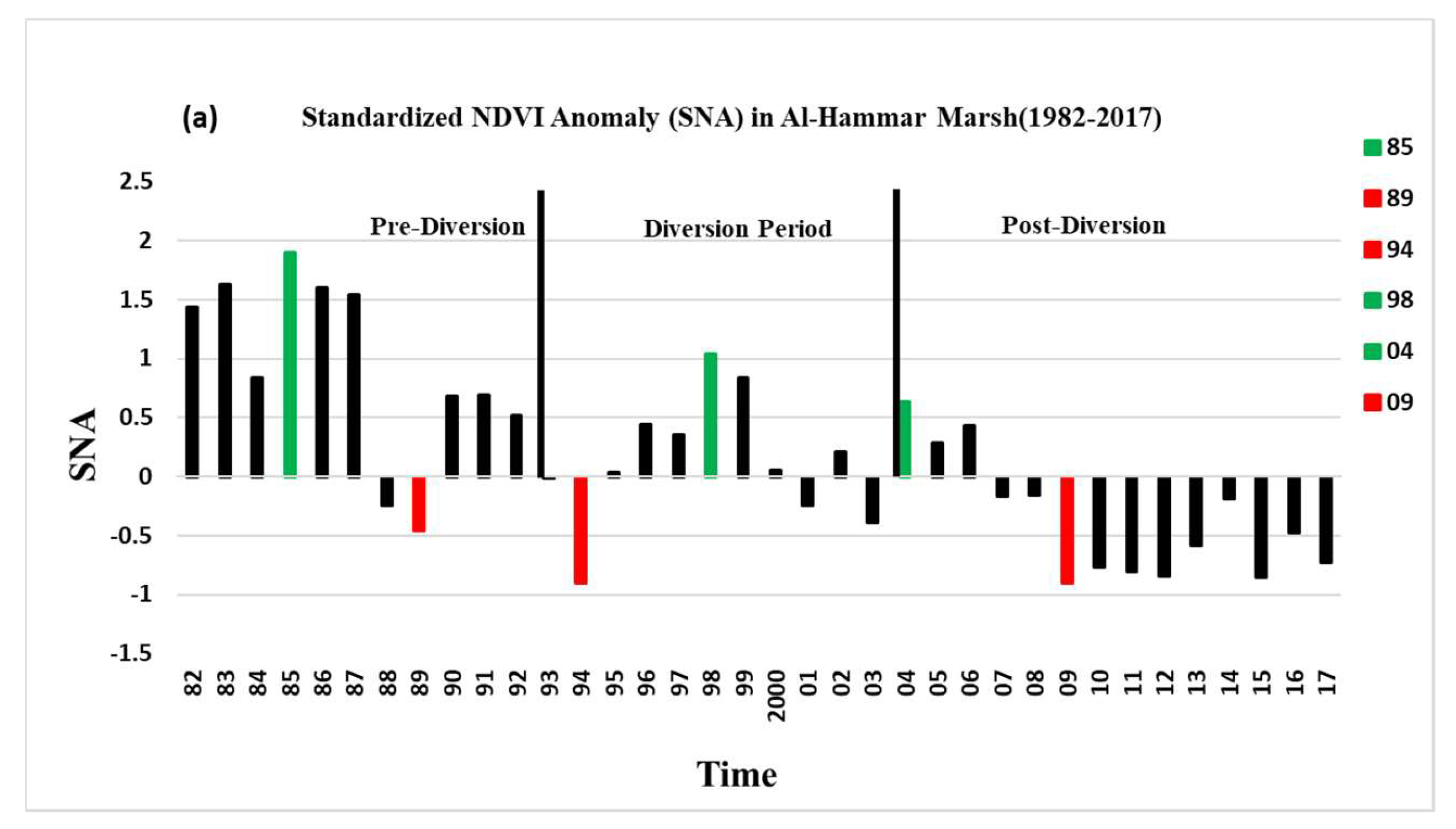
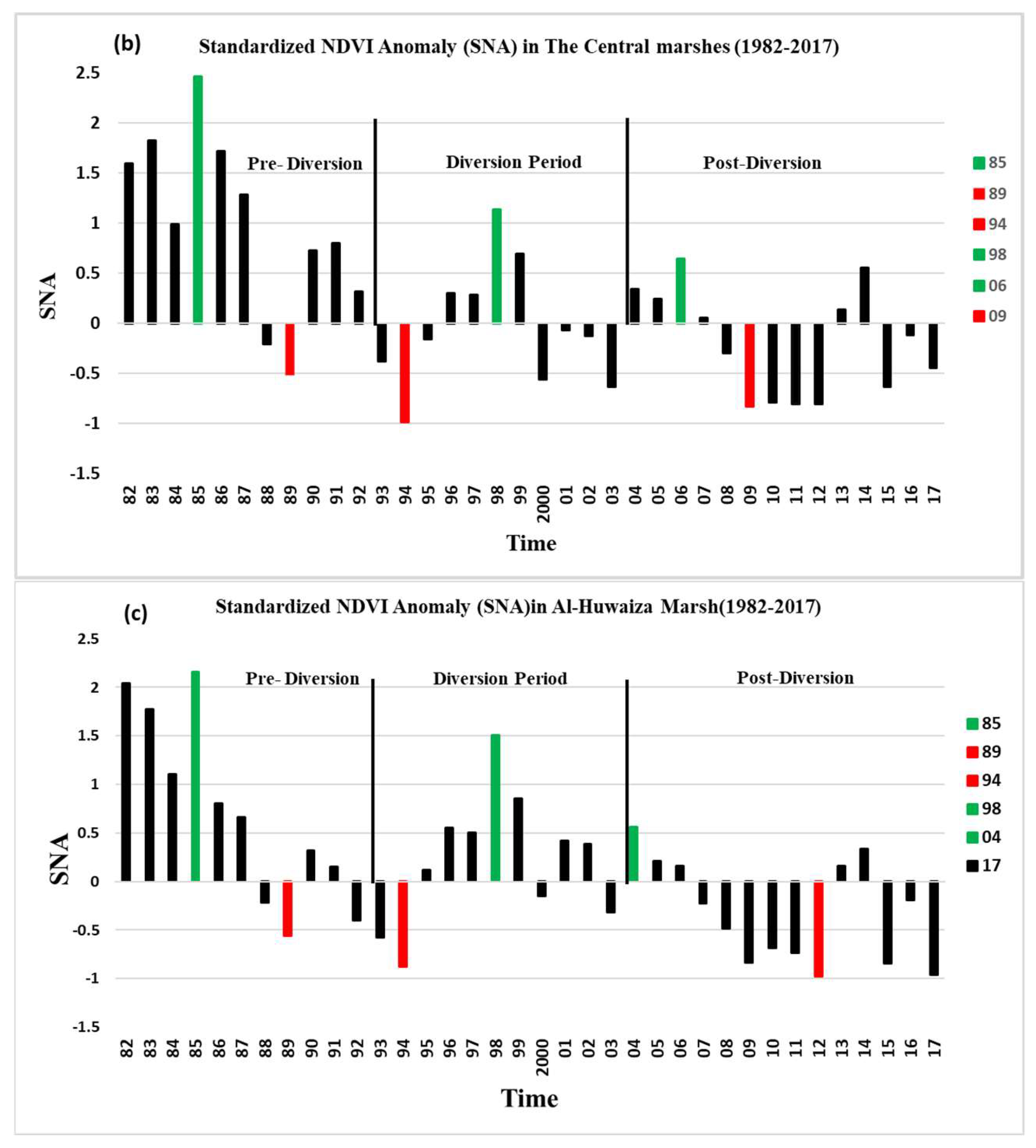
3.3. Standardized NDVI Anomaly (SNA) Analyses
3.4. Spatial Patterns
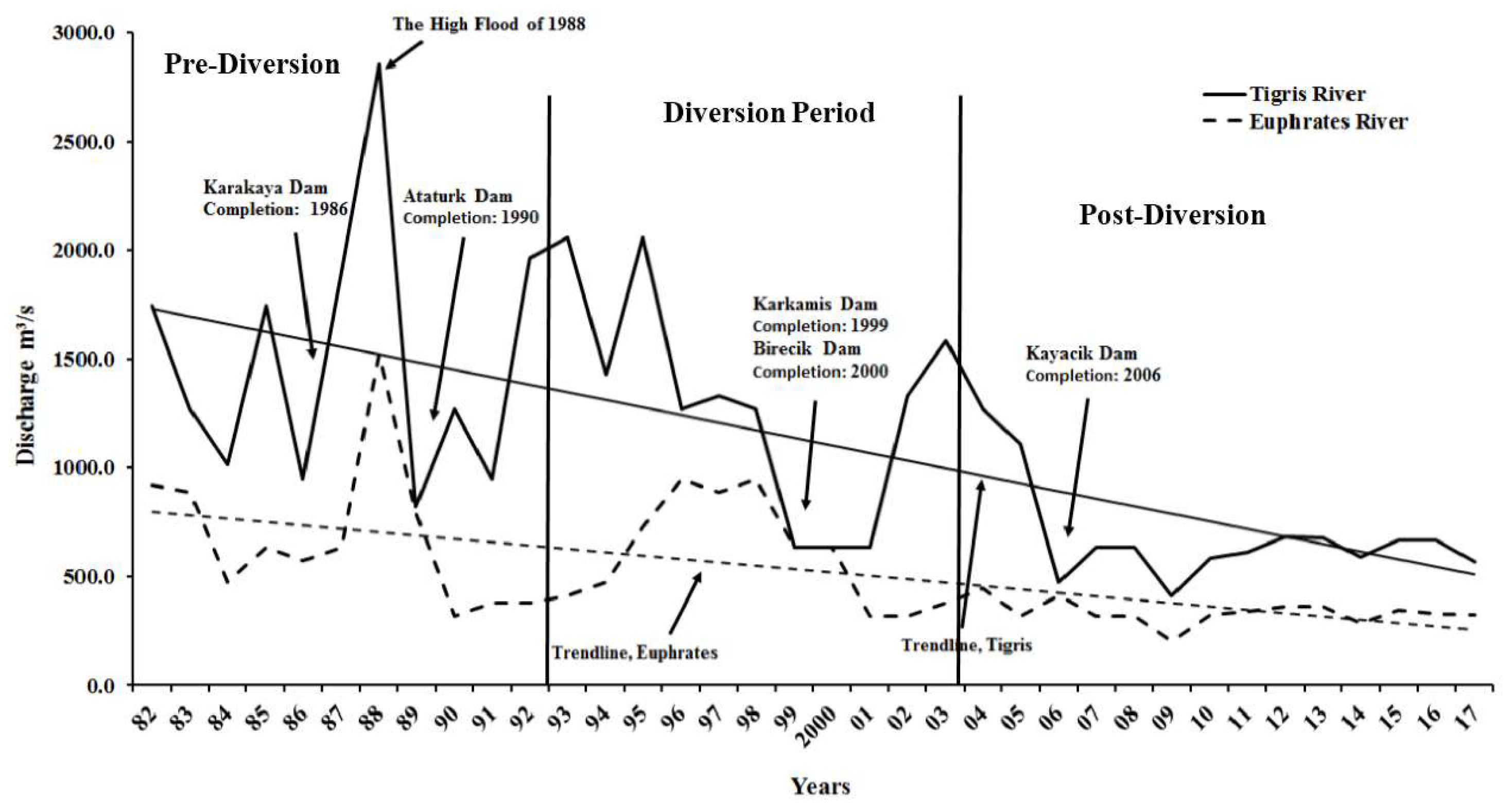
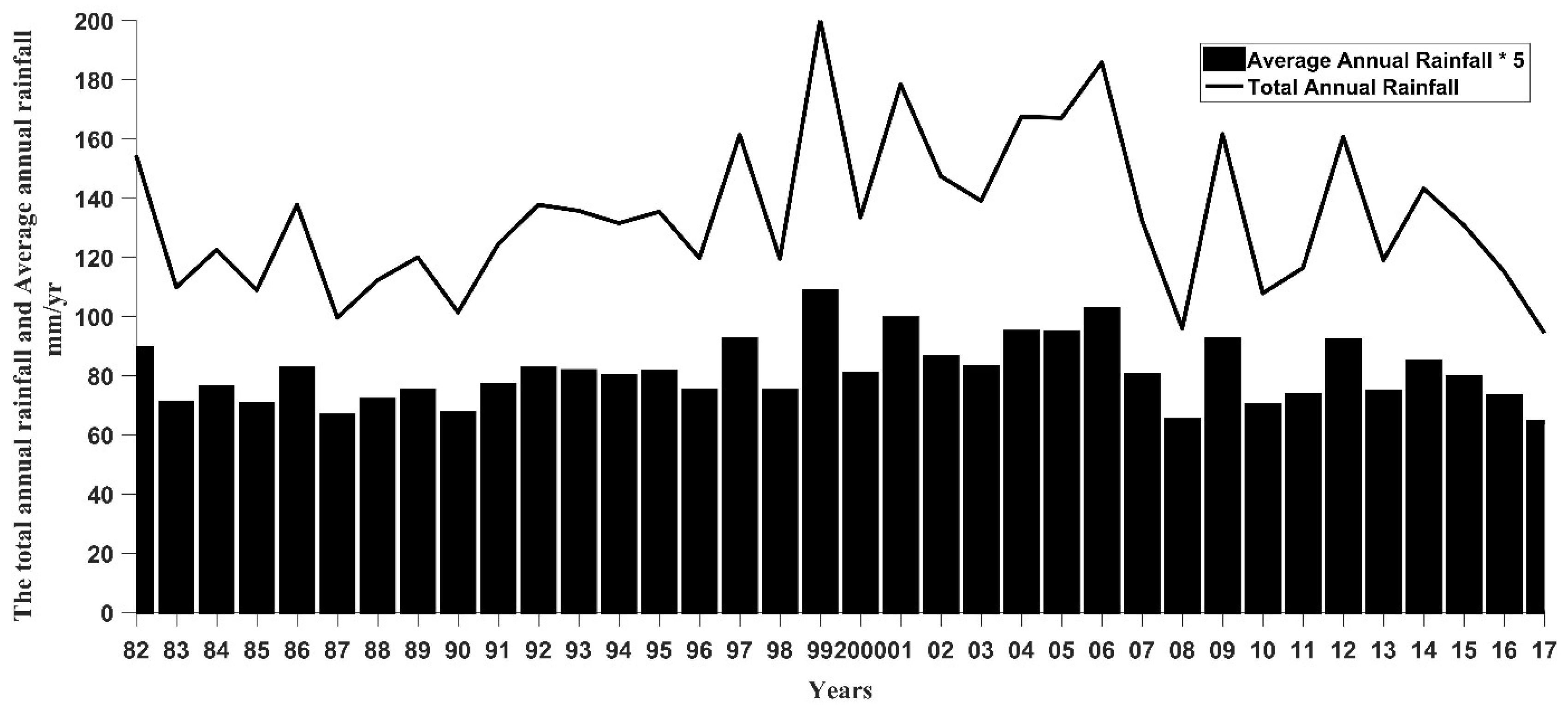
3.5. Ancillary Data Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maxwell, G. People of the Reeds; ASIN: B0007DMCTC; Harper: New York, NY, USA, 1957; 223p. [Google Scholar]
- Young, G. Return to the Marshes: Life with the Marsh Arabs of Iraq; Collins: London, UK, 1977; 224p, ISBN 9780571280971. [Google Scholar]
- Tiner, R.W.; Lang, M.W.; Klemas, V.V. Remote Sensing of Wetlands: Applications and Advances, 1st ed.; CRC Press and Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; 555p, ISBN 9781482237351. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Handal, A.; Hu, C. Modis observations of human-induced changes in the mesopotamian marshes in iraq. Wetlands 2015, 35, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.-R.M.; Hussain, N. Evaluation of fish assemblage environment in huwazah marsh, iraq using integrated biological index. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2014, 6, 6124–6129. [Google Scholar]
- Erwin, K.L. Wetlands and global climate change: The role of wetland restoration in a changing world. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partow, H. The Mesopotamian Marshlands: Demise of an Ecosystem. Nairobi (Kenya): Division of Early Warning and Assessment, United Nations Environment Programme; UNEP Publication: Nairobi, Kenya, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lubinski, B.J.; Jackson, J.R.; Eggleton, M.A. Relationships between floodplain lake fish communities and environmental variables in a large river-floodplain ecosystem. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 2008, 137, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIMI (Canada-Iraq Marshlands Initiative). Managing for Change: The Present and Future State of the Marshes of Southern Iraq; University of Victoria: Victoria, British Columbia, UK; Canada and Canadian International Development Agency: Gatineau, QC, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Douabul, A.A.Z.; Al-Saad, H.T.; Abdullah, D.S.; Salman, N.A. Designated protected Marsh within Mesopotamia: Water quality. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Maltby, E. An Environmental and Ecological Study of the Marshlands of Mesopotamia Wetland Ecosystem; AMAR Appeal Trust; University of Exeter: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Vinez, M.; Leonard, S. The Iraq Marshlands: The Loss of the Garden of Eden and Its People; PLSI No. 3443; Illinois State University: Normal, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brasington, J. Monitoring marshland degradation using multispectral remote sensed imagery. In the Iraqi Marshlands: A Human and Environmental Study; Nicholson, E., Clark, P., Eds.; Politico’s: London, UK, 2002; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, C.J. The Status of Mesopotamian Marsh Restoration in Iraq: A Case Study of Transboundary Water Issues and Internal Water Allocation Problems; Towards New Solutions in Managing Environmental Crisis; University of Helsinki: Helsinki, Finland.
- Fitzpatrick, R.W. Changes in Soil and Water Characteristics of Natural, Drained and Re-Flooded Soils in the Mesopotamian Marshlands: Implications for Land Management Planning; Client Report; CSIRO Land and Water: Canberra, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, C.J.; Reiss, P.; Hussain, N.A.; Alwash, A.J.; Pool, D.J. The restoration potential of the Mesopotamian marshes of Iraq. Science 2005, 307, 1307–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacoub, S.; Roffa, S.; Tawfiq, J. Geology Al-Amara—Al-Nasiriya—Al-Basrah Area; GEOSURV Int. Rep. No. 1386; GEOSURV: Baghdad, Iraq, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hilli, M.R.; Warner, B.G.; Asada, T.; Douabul, A. An assessment of vegetation and environmental controls in the 1970s of the Mesopotamian wetlands of southern Iraq. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 17, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, A.T.; Al-Ma’amar, A.F.; Jabbar, M.F.A. Change detections in marsh areas, south Iraq, using remote sensing and GIS applications. Iraqi Bull. Geol. Min. 2010, 6, 17–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdan, M.; Asada, T.; Hassan, F.; Warner, B.; Douabul, A.; Al-Hilli, M.; Alwan, A. Vegetation response to re-flooding in the Mesopotamian wetlands, southern Iraq. Wetlands 2010, 30, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.A. Studying of the environmental changes in marsh area using Landsat satellite images. J. Asian Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 427. [Google Scholar]
- Peltier, L.C. The geographic cycle in periglacial regions as it is related to climatic geomorphology. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1950, 40, 214–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fookes, P.G.; Dearman, W.R.; Franklin, J.A. Some engineering aspects of rock weathering with field examples from dartmoor and elsewhere. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 1971, 4, 139–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwash, A.; Alwash, S.; Cattarossi, A. Iraq’s marshlands-demise and the impending rebirth of an ecosystem. In Critical Transitions in Water and Environmental Resources Management; World Water and Environmental Resources Congress: Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, 2004; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.C.; Woodcock, C.; Song, C.; Huang, X.; Lu, J.; Kaufmann, R. Monitoring land-use change in the pearl river delta using landsat tm. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1985–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, J.; Franklin, J.; Roberts, D.A. A comparison of methods for monitoring multitemporal vegetation change using thematic mapper imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, C.; Davidson, N.; Spiers, A.; Stevenson, N. Global wetland inventory—Current status and future priorities. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1999, 50, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozesmi, S.L.; Bauer, M.E. Satellite remote sensing of wetlands. Wetlands Ecol. Manag. 2002, 10, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higginbottom, T.P.; Symeonakis, E. Assessing land degradation and desertification using vegetation index data: Current frameworks and future directions. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9552–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. Comparison and evaluation of annual NDVI time series in china derived from the NOAA AVHRR LTDR and terra MODIS mod13c1 products. Sensors 2017, 17, 1298. [Google Scholar]
- El Saleous, N.; Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Townshend, J.; Tucker, C.; Goward, S. Improvements in the global biospheric record from the advanced very high resolution radiometer (AVHRR). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1251–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedelty, J.; Devadiga, S.; Masuoka, E.; Brown, M.; Pinzon, J.; Tucker, C.; Vermote, E.; Prince, S.; Nagol, J.; Justice, C. Generating a long-term land data record from the avhrr and modis instruments. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 1021–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Vermote, E. Climate Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (C-ATBD): AVHRR Land Bundle-Surface Reflectance and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index. 2013.f3. Available online: https://www.ncdc.noaa. gov (accessed on 20 September 2018).
- Moreno Ruiz, J.A.; Riaño, D.; Arbelo, M.; French, N.H.F.; Ustin, S.L.; Whiting, M.L. Burned area mapping time series in Canada (1984–1999) from NOAA-AVHRR LTDR: A comparison with other remote sensing products and fire perimeters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.A.M.; Lázaro, J.R.G.; Cano, I.D.Á.; Leal, P.H. Burned area mapping in the north American boreal forest using Terra-MODIS LTDR (2001–2011): A comparison with the mcd45a1, mcd64a1 and ba geoland-2 products. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 815–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghulam, A.; Kasimu, A.; Kusky, T. In Normalization of modified perpendicular drought index using ltdr and gimms dataset for drought assessment in the united states. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2008–2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; pp. III-856–III-859. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Reconstruction of a complete global time series of daily vegetation index trajectory from long-term avhrr data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal avhrr data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.J. Canopy reflectance, photosynthesis and transpiration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1985, 6, 1335–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.-J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunetta, R.; Lyons, J. Geospatial Data Accuracy Assessment; No. EPA/600/R-03/064; US Environmental Protection Agency: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2003.
- Townshend, J.R.; Justice, C.O. Towards operational monitoring of terrestrial systems by moderate-resolution remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V. The role of satellite remote sensing in the prediction of ungauged basins. Hydrol. Processes 2004, 18, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V. Soil moisture at watershed scale: Remote sensing techniques. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V. Beyond grace: Using satellite data for groundwater investigations. Ground Water 2016, 54, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narumalani, S.; Mishra, D.R.; Rothwell, R.G. Analyzing landscape structural change using image interpretation and spatial pattern metrics. GISci. Remote Sens. 2004, 41, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 337–342. ISBN 0131453610. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.B. Introduction to Remote Sensing, 4th ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; 625p, ISBN 9781593853198. [Google Scholar]
- Vlek, P.L.; Le, Q.B.; Tamene, L. Assessment of land degradation, its possible causes and threat to food security in Sub-Saharan Africa. In Food Security and Soil Quality; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 57–86. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.B.; Tamene, L.; Vlek, P.L. Multi-pronged assessment of land degradation in west africa to assess the importance of atmospheric fertilization in masking the processes involved. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2012, 92, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinbilek, D. Development and management of the Euphrates–Tigris basin. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2004, 20, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, I.E.; Al-Ansari, N.; Sherwany, G.; Knutsson, S. Expected future of water resources within the Tigris–Euphrates rivers basin, Iraq. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2014, 6, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, A.K.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Water Footprints of Nations; Value of Water Research Report Series No.30; IHE No.16; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ASIA, I.W. Euphrates River Basin. In Inventory of Shared Water Resources in Western Asia. Beirut; UN, ESCWA: Beirut, Lebanon, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, K. Annual precipitation in the river basin for (Iraq, Turkey, Iran, and Syria), Scale 1:5,300,000. Tigris and Euphrates River Basin Map. 2010. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1828/2397 (accessed on 22 September 2018).
- Munro, D.; Touron, H. The estimation of marshland degradation in southern Iraq using multitemporal landsat tm images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jema, W.S. Social-Ecological Assessment Framework for the Restoration of the Iraqi Mesopotamian Marshlands; Royal Roads University: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, C.J.; Hussain, N.A. Restoring the garden of Eden: An ecological assessment of the marshes of iraq. AIBS Bull. 2006, 56, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lami, H. Hyrdochemical and Sedimentological Study of the Northwestern Part of Hor al-Huwizah, Misan Governorate, South of Iraq. Unpub. Master’s Thesis, University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq, 2008. (In Arabic). [Google Scholar]
- Muhsin, I.J. Al-hawizeh marsh monitoring method using remotely sensed images. Iraqi J. Sci. 2011, 52, 381–387. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ansari, N.; Knutsson, S.; Ali, A. Restoring the Garden of Eden, Iraq. J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2012, 2, 53–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, M.; Ahmadalipour, A.; Moradkhani, H. Apprehensive drought characteristics over Iraq: Results of a multidecadal spatiotemporal assessment. Geosciences 2018, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, S. Ancient Mesopotamia; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999; 272p, ISBN 0521573343. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56; FAO-Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome (http://www. fao. org/docrep). ARPAV (2000), La caratterizzazione climatica della Regione Veneto, Quaderni per. Geophysics 1998, 156, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Buringh, P. Soils and Soil Conditions in Iraq; ASIN: B0006BTMJS; Ministry of Agriculture: Baghdad, Iraq, 1960; 322p.





| Marsh | Area in (km2) | Water Supply |
|---|---|---|
| The Al-Hammar | 3000–4000 | The Euphrates River |
| The Central marshes | 3000–4000 | The Tigris and Euphrates rivers |
| The Al-Huwaiza | 3000–3500 | The Tigris and Karkheh rivers |
| Sensor/Model | Variable | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVHRR 1 | NDVI 2 | 0.05° | Monthly | 1981–present |
| GLDAS 3 | Surface Temperature | 1.0° | Monthly | 1979–present |
| Field Data www.meteoseism.gov.iq | Evapotranspiration and Precipitation | 3 Sites | Monthly | 1982–2015 and 1982–2017 |
| Field Observations The Ministry of Water Resources, Iraq. www.mowr.gov.iq | Annual Discharge of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers | Yearly | 1982–2017 |
| Reference Points | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Water | Vegetation | Barren | Row Total | |
| Water | 39 | 0 | 0 | 39 | |
| Classified Data | Vegetation | 1 | 39 | 0 | 40 |
| Barren | 0 | 1 | 40 | 41 | |
| Column Total | 40 | 40 | 40 | 120 | |
| Overall Accuracy = 118/120 = 98% Producer’s Accuracy (omission error) Water = 39/40 = 98% 2% omission error Vegetation = 39/40 = 98% 2% omission error Barren = 40/40 = 100% 0% omission error User’s Accuracy (commission error) Water = 39/40 = 98% 2% commission error Vegetation = 40/40 = 100% 0% commission error Barren = 40/41 = 98% 2% commission error | |||||
| Percentage of Water Area | |||
| Time | Al-Hammar | The Central marshes | Al-Huwaiza |
| 1985 | 13 | 3 | 13 |
| 1989 | 17 | 4 | 11 |
| 1994 | 5 | 2 | 10 |
| 1998 | 8 | 3 | 8 |
| 2004 | 10 | 5 | 15 |
| 2009 | 7 | 2 | 4 |
| Percentage change % | −6 | −1 | −9 |
| Percentage of vegetation area from classified Landsat images | |||
| Time | Al-Hammar | The Central marshes | Al-Huwaiza |
| 1985 | 46 | 58 | 39 |
| 1989 | 18 | 30 | 32 |
| 1994 | 6 | 11 | 21 |
| 1998 | 22 | 22 | 38 |
| 2004 | 40 | 25 | 30 |
| 2009 | 16 | 10 | 23 |
| Percentage change % | −30 | −48 | −16 |
| Percentage of vegetation area from AVHRR/NDVI | |||
| Time | Al-Hammar | The Central marshes | Al-Huwaiza |
| 1985 | 33.3 | 51 | 50 |
| 1989 | 20.2 | 33 | 34 |
| 1994 | 2 | 2 | 18 |
| 1998 | 7 | 9.8 | 35 |
| 2004 | 20 | 28.5 | 41 |
| 2009 | 11.8 | 9 | 29 |
| Percentage change % | −21.5 | −48 | −16 |
| Percentage of barren area | |||
| Time | Al-Hammar | The Central marshes | Al-Huwaiza |
| 1985 | 41 | 39 | 48 |
| 1989 | 65 | 66 | 68 |
| 1994 | 89 | 87 | 57 |
| 1998 | 70 | 76 | 55 |
| 2004 | 51 | 73 | 55 |
| 2009 | 77 | 88 | 73 |
| Percentage change % | 36 | 49 | 25 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albarakat, R.; Lakshmi, V.; Tucker, C.J. Using Satellite Remote Sensing to Study the Impact of Climate and Anthropogenic Changes in the Mesopotamian Marshlands, Iraq. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101524
Albarakat R, Lakshmi V, Tucker CJ. Using Satellite Remote Sensing to Study the Impact of Climate and Anthropogenic Changes in the Mesopotamian Marshlands, Iraq. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(10):1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101524
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbarakat, Reyadh, Venkat Lakshmi, and Compton J. Tucker. 2018. "Using Satellite Remote Sensing to Study the Impact of Climate and Anthropogenic Changes in the Mesopotamian Marshlands, Iraq" Remote Sensing 10, no. 10: 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101524
APA StyleAlbarakat, R., Lakshmi, V., & Tucker, C. J. (2018). Using Satellite Remote Sensing to Study the Impact of Climate and Anthropogenic Changes in the Mesopotamian Marshlands, Iraq. Remote Sensing, 10(10), 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10101524





