Abstract
Multi-camera systems are widely used in the fields of airborne remote sensing and unmanned aerial vehicle imaging. The measurement precision of these systems depends on the accuracy of the extrinsic parameters. Therefore, it is important to accurately calibrate the extrinsic parameters between the onboard cameras. Unlike conventional multi-camera calibration methods with a common field of view (FOV), multi-camera calibration without overlapping FOVs has certain difficulties. In this paper, we propose a calibration method for a multi-camera system without common FOVs, which is used on aero photogrammetry. First, the extrinsic parameters of any two cameras in a multi-camera system is calibrated, and the extrinsic matrix is optimized by the re-projection error. Then, the extrinsic parameters of each camera are unified to the system reference coordinate system by using the global optimization method. A simulation experiment and a physical verification experiment are designed for the theoretical arithmetic. The experimental results show that this method is operable. The rotation error angle of the camera’s extrinsic parameters is less than 0.001rad and the translation error is less than 0.08 mm.
1. Introduction
Photogrammetry is widely used in aerial remote sensing [1,2,3]. More and more airborne remote sensing platforms are equipped with multi-camera systems to complete tasks such as image mosaic [4], terrain reconstruction [5,6] and monitoring [7,8,9]. In some multi-camera remote sensing photography systems, the angle between the optical axes of the cameras is large enough to obtain a large field of view (FOV), resulting in the non-overlapping of the FOV, and increasing the calibration difficulty of extrinsic parameters. However, the quality of terrain reconstruction and panoramic mosaic tasks depend on the accuracy of the camera extrinsic parameters. To solve this problem, we introduce a universal multi-camera extrinsic calibration method without common FOVs. The commonly used method for calibrating the extrinsic parameters is based on a two-dimensional target proposed by Zhang Z [10]. This method calculates the extrinsic matrix by placing the target in the public FOV of the cameras. In addition, there are also some calibration methods based on other targets such as: 1D target [11], plane-based targets [12,13], stereo targets [14,15], spheres target [16,17] and so on. When calibrating multiple cameras, the above method requires that the different cameras must have overlapping FOV, and the traditional calibration method is no longer applicable when the cameras have no common FOV, because the same target cannot be observed by different cameras.
To solve this problem, Gong et al. [18] and Dong et al. [19] used the three-dimensional reconstruction method to calculate the extrinsic matrix of cameras without a common FOV. These authors reconstruct the coding landmarks on the calibration plan by 3D scanner or visual method. Cameras without a common field of view capture different section of the plane, the non-overlapping FOVs are connected by the coding marks, and then the extrinsic parameter matrix can be solved. This method requires reconstruction of the large calibration plane in advance. The reconstruction process is complex and the calibration accuracy depends on the reconstruction accuracy. Moreover, it is difficult to ensure the reconstruction accuracy for the large-sized target planes. Xia et al. [20] used two fixed targets connected by metal rods to calibrate the non-overlapping-field camera. First, two targets are captured by a large FOV camera, and the pose relationship between the two fixed targets is computed by the pose recovery method. Then, the transformation matrix between targets is used to solve the extrinsic parameters between the cameras. This method requires a special target and is only suitable for binocular camera calibration. When the angle between the optical axes of the two cameras is large, it is difficult to create the target. Lu et al. [21] used a theodolite pair called a theodolite coordinate measurement system (TCMS) to calibrate the extrinsic parameters of the cameras. A calibration block was placed in the camera’s FOV by using the theodolite to measure the spatial coordinates of the marker points on the target. The transform matrix between the target coordinate system and the global coordinate system can be obtained, and then the transform matrix between the camera coordinate system and the global coordinate system can be obtained.
Lébraly et al. [22] introduced a calibration method by using plane mirrors. The key of this method is to build a virtual camera through the reflection of the flat mirror and to use the virtual camera to associate real cameras. There are some marks on the plane mirror, and the pose of the virtual camera relative to the real camera can be calculated by these marks. However, when the number of cameras is large, it is difficult to control the reflection scope of the flat mirror. Kumar et al. [23] also calibrated multiple cameras using flat mirrors. The method removes the need for cameras to observe the calibration object directly. The advantage of this method is that there is no need to place markers on the mirror and through a novel set of constraints the mirror pose is not needed for calibration.
Pagel et al. [24] introduced an extrinsic calibration method of multiple cameras with non-overlapping views in vehicles. In this paper, the calibration problem is divided into the problems of visual odometry and Hand-Eye Calibration. Visual odometry is calculated by the structure from the motion method, which is based on the corresponding image features of each camera, and then the visual odometry is optimized by sparse bundle adjustment (SBA). An Iterated Extended Kalman Filter (IEKF) algorithm is used to calculate the uncertainties of the transformation, and merge the redundant information to improve the calibration accuracy. By using the IEKF algorithm the extrinsic parameters can be continuously estimated and the system is able to perform a self-calibration. Liu et al. [25] proposed a calibration method for vision sensors with non-overlapping FOVs using a spot laser. By placing the laser in suitable positions, the laser line passes through the FOVs of multiple vision sensors. Utilizing the plane target to obtain the spatial coordinates of the intersection point of the laser line and the target in each camera coordinate system, the equation is established by using collinear conditions of the intersection points. By moving the laser line at least two positions, sufficient constraint equations can be established to solve the extrinsic parameter matrix.
In this paper, we propose a calibration method of multi-cameras without a common field of view based on multiple chessboard targets. The difference from this method and the traditional non-common-field calibration method is that the target does not need to be rigidly connected through a mechanical structure or with the aid of other auxiliary equipment, and the configuration is more flexible. This method has high accuracy and is suitable for the on-site calibration of the remote sensing imaging system. The number of chessboard targets is consistent with the number of cameras, so that each camera corresponds to a target. We keep the target stationary during the calibration process, and make the multi-camera system move multiple positions and shoot their corresponding targets. Sufficient equations can be obtained to solve the extrinsic parameters by moving at least two locations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Calibration Principle
When calibrating the multi-camera system used in airborne remote sensing, we select one camera as the reference coordinate system. The calibration purpose is to calculate the extrinsic matrix of the remaining cameras relative to the reference coordinate system. To reduce the accidental error introduced by single measurement and obtain robust measurement results, the method is divided into two steps: the relative extrinsic parameters between any two cameras are calculated first, and then the extrinsic parameters of each camera relative to the reference coordinate system are obtained using the redundant data based on the two camera calibration result.
2.1.1. Introduction of Two Cameras Calibration Method
The calibration principle of the extrinsic parameters is shown in Figure 1. First, we use the Zhang Z. [10] method to calibrate the intrinsic parameters of each camera. Without loss of generality, this article uses a 5-camera system as an example to introduce a multi-camera system calibration method without the common field of view used in airborne remote sensing.
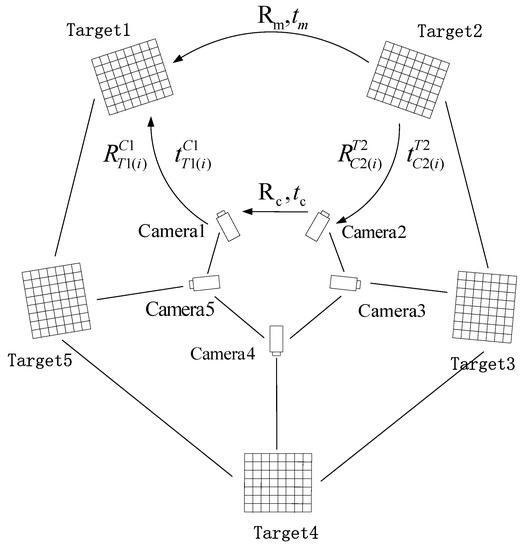
Figure 1.
Extrinsic parameters calibration schematic.
As shown in Figure 1, the FOVs of the five cameras do not overlap with each other, and the 5 cameras correspond to 5 checkerboard targets respectively. We first select any two cameras (such as camera1 and camera2) to introduce the calibration method between two cameras in the system. In the figure, and are the rotation matrix and translation matrix between the two cameras, and and are the rotation and translation matrix between the targets. are the rotation and translation matrix between the cameras and their corresponding target at the ith position of the multi-camera system. is the coordinates of the corner points of target 2 in the target 2 coordinate system; is the coordinates of the corner points of target 2 in the target 1 coordinate system. It can be seen from the figure that the relationship between and can be transformed by two different paths.
A set of equations for the unknown , , , can be obtained from Equations (1) and (2):
The rotation and translation matrix between cameras and the corresponding targets can be solved by the EPNP method [26]. The 4 pending matrices contain 24 unknown parameters, sorting Equation (3) can obtain 12 linear independent equations with unknown quantity. Enough constraint equations can be obtained by moving the multi-camera system at least twice, and we use the linear method to solve the , , , matrix. It should be noted that when moving the system, we should avoid pure translational motions, which will result in the independence of Equation (3), and makes the solution results unstable.
Matrix is the extrinsic matrix between the two cameras.
2.1.2. Optimization Method of Extrinsic Parameters Based on Reprojection Error
In the above linear solution process, the orthogonal constraint properties of the rotation matrix are not considered, and the solution results are susceptible to noise. Therefore, we use the linear solution result as the initial value, and an objective function is established by using the reprojection error. Then, we optimize the extrinsic parameter matrix between two cameras by using the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm [27]. In the optimization process, each rotation matrix is represented by Euler angles to ensure that the solution results meet the orthogonal constraints. The principle of the reprojection error between the two cameras is shown in Figure 2.
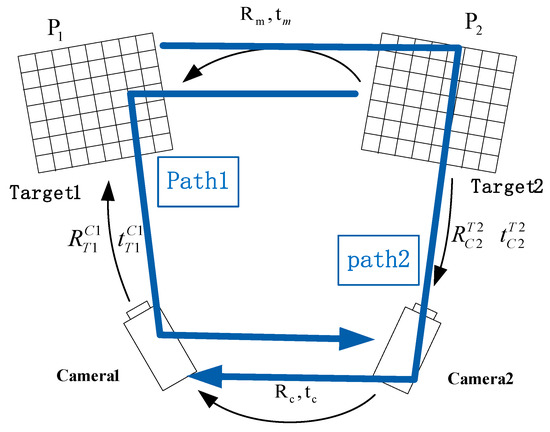
Figure 2.
Reprojection error optimization schematic.
The coordinate of the jth corner point on target 1 is transformed to the camera 1 coordinate system by path 2, and we can obtain the re-projected image coordinate of the corner point from the intrinsic parameter matrix of camera 1. The coordinate of the corner point on target 2 is transformed to the camera 2 coordinate system by path 1, and we can obtain the re-projected image coordinate of the corner point from the intrinsic parameter matrix of camera 2. According to the camera model, we have:
The reprojection error equation is:
where and denote the intrinsic parameters matrix of the two cameras, and denote the coordinates of the jth corner point on the two targets in the target coordinate system, I denotes a 3 × 3 unit matrix. and denote the image coordinates, which remove the lens distortion. By using Levenberg-Marquardt method [27] to solve Equation (6), the optimized extrinsic parameter matrix can be obtained.
2.2. The Global Optimal Method of Multi-Cameras Calibration
In this section, we introduce the global calibration method of multi-cameras. Without loss of generality, we select the camera coordinate system of camera 1 in Figure 1 as the reference coordinate system of the multi-view system. We can calculate the extrinsic parameter matrix of an arbitrary camera relative to camera 1 by using the methods mentioned in Section 2.1. In this way, the extrinsic matrix of the cameras relative to the reference coordinate system can be obtained. However, this way cannot make full use of redundant motion information, and any accidental calibration noise will affect the calibration result. To solve this problem, a robust calibration method is proposed in this paper. First, the extrinsic matrix between any two cameras is calculated using the method described in Section 2.1, and then the redundant extrinsic parameter data are used to optimize the extrinsic matrix of each camera relative to the reference coordinate system by the global optimization method. In this way, for a multi-camera system, the effect of single calibration error on the final calibration results can be effectively reduced, and the calibration accuracy can be improved.
2.2.1. Global Optimization Method of Rotation Matrices in Extrinsic Parameters.
To obtain accurate global calibration data, the rotation matrix and the translation matrix are optimized separately. The optimization of rotation matrix is inspired by refer [28], in which the relative pose relationship between sequential images is improved and this method is used for 3D reconstruction. We refer to the idea of this method and optimize the extrinsic parameters of the cameras relative to the reference coordinate system. denotes the rotation matrix of the camera i relative to the reference coordinate system. denotes the rotation matrix between camera i and camera j. By using the method in the Section 2.1, we can obtain the rotation matrix between any two cameras. And then, we have:
The above formula can be divided into 3 parts:
where , , denote columns of , where , Equation (8) can be arranged into a form of linear equations:
The rotation matrices between any two cameras can be organized into the equation as shown in Equation (9). Taking a 5-camera system as an example, = 10 equations as shown in Equation (9) can be obtained. The 10 sets of equations can be combined and written into an over-determined linear equation like . Where is a matrix of 30 × 15 dimensions that is made by stacking all relative rotation matrices and is made by stacking all columns of camera extrinsic parameters . By solving the linear equation, the rotation matrix of each camera relative to the reference coordinate system can be obtained. The orthonormality constraints are forced by projecting the approximate rotation to the closest rotation in the Frobenius norm using SVD. In this case, the global rotation parameters of each camera are obtained by 10 sets of relative rotation, which can effectively reduce the influence of single measurement noise on global calibration accuracy because of the use of the redundancy rotation matrix.
2.2.2. Global Optimization Method of Translation Vector in Extrinsic Parameters.
Based on the global rotation extrinsic parameters, in this section the optimization method of global translation extrinsic parameters is introduced. Using the method mentioned in Section 2.1, we can obtain the translation vector between any two cameras. Where denotes the translation vector between camera i and camera j. denotes the translation vector of camera i in the reference coordinate system. Then, we have [29]:
Equation (11) can be organized as
where , , . The translation vector between any two cameras can be organized into the equation as shown in Equation (12). Taking a 5-camera system as an example, = 10 equations as shown in Equation (12) can be obtained. The 10 sets of equations can be combined and written into an over-determined linear equation like . Where is a matrix of 30 × 15 dimensions that is made by stacking identity matrix, and is made by stacking all camera translation parameters . is a vector of 30 × 1 dimensions that is made by the elements in vector . By solving the linear equation, we can obtain the translation vectors , of each camera relative to the reference coordinate system. In this case the influence of single measurement noise can effectively be reduced by using the redundant translation vector.
After obtaining the matrix and vector through the above two subsections, we can obtain the extrinsic matrix of each camera relative to the reference coordinate system .
3. Results
3.1. A Simulation Experiment of Two Cameras
In this paper, the above theory and calibration accuracy are analyzed by simulation experiment and physical experiments respectively. First, a two-camera calibration model is simulated and tested. For all experiments, we use an internally calibrated camera with a focal length of 16 mm and pixel size of 4.8 um×4.8 um. The image resolution is 1280 × 1024, the principal point is in the ideal optical center. The target contains 12 × 12 grid of feature points and the interval between points is 30 mm in both directions. We compare the accuracy of the linear solution and the optimization of re-projection error algorithm solution. In the calculation process, the different levels of noise are added to pixel coordinates of the corner points, which are extracted from images. The noise is divided into 10 levels from 0 pixels to 2 pixels, to verify the robustness of the proposed algorithm. The noise values are Gaussian distributed with a standard deviation of 0–2 pixels in 10 steps.
In the simulation experiment, the true value of the three relative rotation angles between the two cameras are R = [0.5233 rad, 0.6977 rad, 0.6977 rad], the true value of the translational vector is T = [106 mm, −5 mm, 2 mm]. During the simulation the cameras moved ten times. The pose relationship between the camera and target is calculated using the EPNP [26] algorithm. For each noise level, 100 tests are carried out. The RMS errors of the three rotation angles and the three translations at different noise levels is shown in Figure 3. The ordering of the Euler angles in experiment is Roll, Yaw, and Pitch.
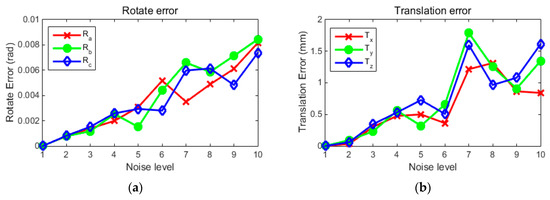
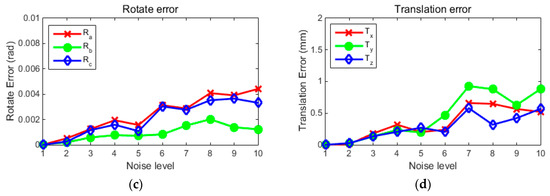
Figure 3.
The RMS error curve of the calibration result affected by noise. The graph (a) shows the three rotation angle error curves obtained with the linear solution method with ten noise levels. The graph (b) shows the translation error curve obtained with the linear solution method with ten noise levels. The graph (c) is the rotation angle error curve after optimization of the re-projection error. The graph (d) is the translation error curve after optimization of the re-projection error.
Experimental results show that the linear algorithm is easily affected by noise. With the increase in noise level, the error of rotation angle increases exponentially, and the error of translation oscillates greatly. When the re-projection error optimization method and the orthogonal constraint are taken into account, the rotation angle error is obviously suppressed, and the improvement of the yaw angle accuracy is most obvious. At the same time, the translation error has also been suppressed to a certain extent.
3.2. Simulation Experiment of Multi-Camera Extrinsic Parameters Calibration with the Global Optimization Method
After calculating the extrinsic parameter matrix between any two cameras, the global optimization method is used to calculate the extrinsic parameter matrices of all cameras relative to the reference coordinate system. We analyzed the error variation of the extrinsic parameters before and after global optimization.
The simulation experiment takes a five-camera system as an example. Using the method in Section 2.1 to calculate the extrinsic matrix between any two cameras, and we can obtain 10 sets of extrinsic parameters. Ten levels of noise are added to the 10 sets of extrinsic parameters. The noise added to the rotation angles range from 0.001 rad to 0.01 rad, and the translation noise ranges from 0.05 mm to 0.5 mm. For each noise level, 100 tests are carried out. The extrinsic parameters of the five cameras relative to the reference coordinate system are shown in Table 1. Without loss of generality, we take camera 3 as an example, before and after optimization, the changes in the RMS errors of the extrinsic parameters are shown in Figure 4.

Table 1.
The extrinsic of each camera relative to the reference coordinate system.
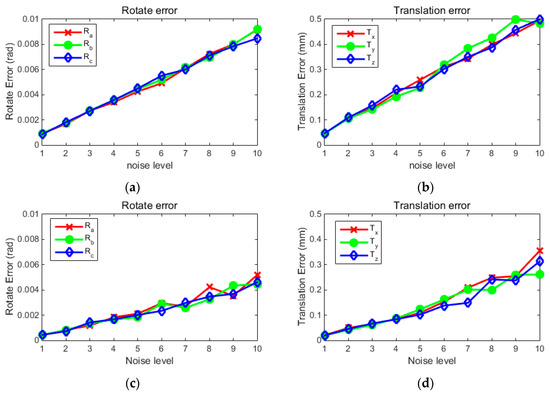
Figure 4.
The extrinsic parameters’ RMS error curve of camera 3 before and after global optimization. The graph (a) shows the three rotation angle error curves obtained before optimization with ten noise levels. The graph (b) shows the translation error curve obtained before optimization with ten noise levels. The graph (c) is the rotation angle error curve after optimization with ten noise levels. The graph (d) is the translation error curve after optimization with ten noise levels.
The experimental results show that the global optimization method can effectively suppress the random noise of single calibration. Because the noise of this simulation experiment is directly added to three Euler angles and three translations of the extrinsic parameters, so the error has a linear relationship with the noise level before optimization. It can be seen from the graph that the rotation angle error is obviously suppressed after optimization. From the figure we see within a certain noise level, the relationship between the rotation angle RMS error and noise level is linear. From Section 2.2.2 we can see that since the global optimization of the translation vector depends on the rotation angle, the noise of the rotation angle has a great influence on the translation vector. The experimental results show that when the noise level is higher and the rotation angle error increases, the error of the translation vector increases more intense.
To illustrate the applicability of the algorithm to all cameras, we give the extrinsic parameters errors of the remaining cameras relative to the reference coordinate system (camera coordinate system of the camera 1) at different noise levels (level 2 and level 5 which are consistent with Figure 4). The errors before and after optimization are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The errors before and after optimization of the remaining cameras.
3.3. Two Camera Experiment with Real Image
The above simulation experiment tests the robustness of the algorithm. In order to verify the validity of the algorithm, the following physical experiments are designed to verify the algorithm described in the article. First, we verify the calibration method of the binocular system. The method described herein can also be applicable to calibration cameras with a common field of view. In order to obtain the true value of the extrinsic parameters, a binocular camera system with partially overlapping FOVs is used to verify the method. The intrinsic parameters of the two cameras are shown in Table 3. Because the FOVs of the cameras are partially overlap, the Calibration Toolbox for Matlab [30] method is used to calibrate the extrinsic parameters of the two cameras as true values. The true value of the rotation angles is [−0.2024 rad, 0.1583 rad, 0.0191 rad], and the true value of the translation is [−215.709 mm, −1.769 mm, 13.586 mm]. To obtain accurate results in the experiment, we have evaluated the accuracy of the Calibration Toolbox, the reprojection error of the checkerboard corners is less than 0.3 pixels. At the same time, the Calibration Toolbox can calculate the confidence interval for the calibration results. The confidence interval of the rotation angles is ±[0.00067 rad, 0.00086 rad, 0.00010 rad], the confidence interval of the translation vector is ±[0.008215 mm, 0.01422 mm, 0.04773 mm]. The above results show that the calibration results of the toolbox have high precision and the results can be used as a standard to test the proposed algorithm. Then, 15 experiments are performed using the method proposed in this article, as shown in Figure 5. The error between 15 experimental values and true values is shown in Figure 6.

Table 3.
Intrinsic parameters of the two cameras.
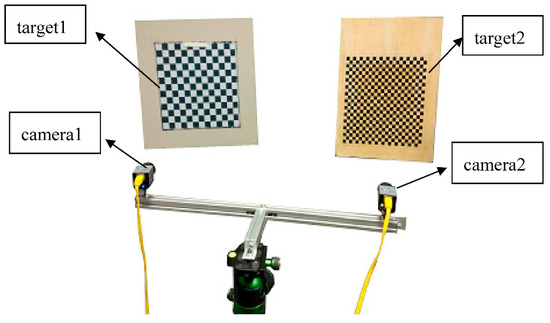
Figure 5.
The two cameras experimental setup.
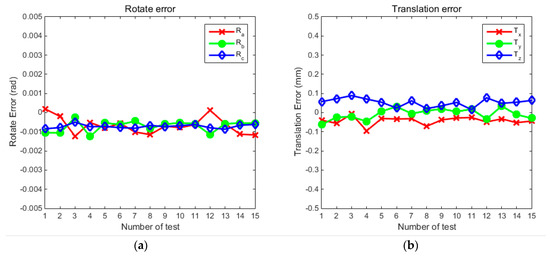
Figure 6.
The error curves of the calibration results for the two-camera experiment. (a) the three rotation angle error curves; (b) the translation error curves.
The experimental setup is shown in Figure 5, we keep the target position stationary and the camera is moved 10 positions, and then the extrinsic matrix between the two cameras can be solved.
The experimental results show that the error of the three rotation angles is within 0.002 rad, where the RMS error of the roll angle is 0.0041, the RMS error of the yaw
angle is 0.0039, and the RMS error of the pitch angle is 0.0056. The difference between the mean value and true value of the roll angle is 9.023 × 10−4
, the difference between the mean value and the true value of the yaw angle is 9.417 × 10−4, and the difference between the mean value and the
true value of the pitch angle is 0.0014. The error of the three translational is within 0.08 mm, where the RMS error in the x-direction displacement is 0.1816, the RMS
error in the y-direction displacement is 0.1102, and the RMS error in the z-direction is 0.2206. The difference between the mean value and the true value
in the x direction is 0.0424, the difference between the mean value and the true value in the y direction is 0.0073, and the difference between the mean
value and the true value in the z direction is 0.0531.
3.4. Real Data Experiment of Global Optimization Calibration for Multi-Cameras
The previous section has verified the two camera calibration method, in order to verify the global optimization process of multi-camera systems, a 4-camera system without common field of view is built to verify the accuracy of the calibration algorithm based on the reprojection error and global optimization. To verify the accuracy of the calibration algorithm under real conditions, cameras in this experiment have no overlapping FOVs. Since the extrinsic parameters’ true value of cameras without a common field of view cannot be directly calculated, we verify the accuracy of extrinsic parameters by indirect methods with a coordinate measuring machine. The experimental device is shown in Figure 7.
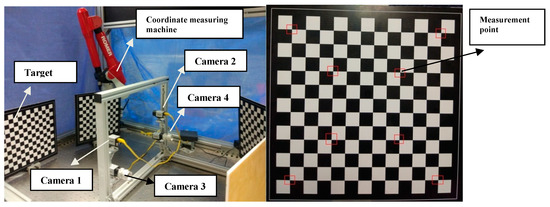
Figure 7.
The left figure shows the experimental setup, and the right figure shows the measurement points marked by the red box on the target.
In this experiment, 4 checkerboard targets are used to calibrate 4 cameras. First, using the method described in Section 2.1 to calculate the extrinsic parameter matrix between any two cameras, a total of 6 combinations can be obtained. Then, using the global optimization method to calculate the extrinsic parameters of each camera relative to the reference coordinate system through 6 sets of extrinsic parameter data. Since the position of the camera relative to the corresponding checkerboard can be calculated by EPNP algorithm [26], we can use the extrinsic parameters between the checkerboards to obtain the extrinsic parameters between the corresponding cameras, and we used it as ground truth.
Without loss of generality, we use the extrinsic parameters of camera 1 and camera 2 as an example to verify the algorithm. The extrinsic parameters between the corresponding checkerboard targets are obtained using a coordinate measuring machine. The measurement method of the extrinsic parameters between the checkerboard targets is as follows:
(1) Select 8 corner points on target 1, and measure the coordinates of the 8 points using the coordinate measuring machine. The position of the eight points on target 1 is shown in Figure 7.
(2) Measure the 8 points on target 2 at the same position as target 1.
(3) Establish constraint equations with Absolute Directional Algorithm [31], then we can obtain the extrinsic parameters between the two targets using the coordinates of the 8 points. The equation is shown in Equation (13):
where denotes the coordinates of corner point on target 1 and denotes the coordinates of corner point on target 2.
The spatial coordinates of the measured points on target 1 and target 2 in the coordinate system of the three coordinates are shown in Figure 8 and the coordinate values of the 8 points are shown in Table 4.
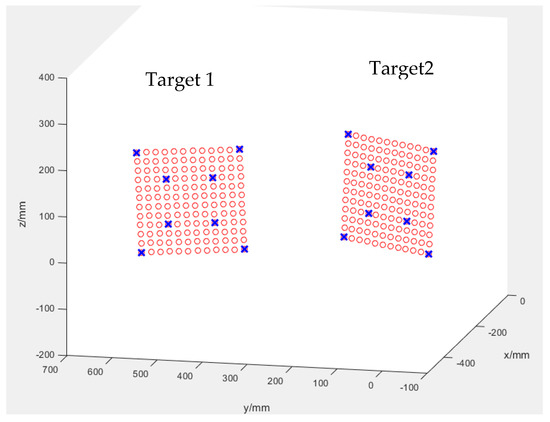
Figure 8.
The spatial coordinates of the measured points on target 3 and target 4. The red circle represents the corner point of the targets, and the blue crosses represent the measured points.

Table 4.
Coordinate values of measuring points.
The coordinate measuring machine we used is the Romer model of the Hexagon company. The measurement accuracy of the coordinate measuring machine is 5μm. The accuracy of the coordinate measuring machine is much higher than the vision measurement system we used. Therefore, we can use the coordinate measuring machine to evaluate the accuracy of the visual system in the experiment. We have evaluated the measurement results of the coordinate measuring machine, and calculated the residuals of Equation (13) using the measured data. Using the data in Table 4, the residual of Equation (13) is 0.2365 mm (the sum of the residuals of the 8 corner points). The smaller residual value indicates that the coordinate measuring machine has higher measurement accuracy and can be used to verify the accuracy of the proposed algorithm.
A total of 15 experiments were carried out, the experiment results are shown in Table 5, and the errors between calculated results and the ground truth data measured using a coordinate measuring machine are shown in Figure 9.

Table 5.
The experiment results and the truth value measured by a coordinate measuring machine.
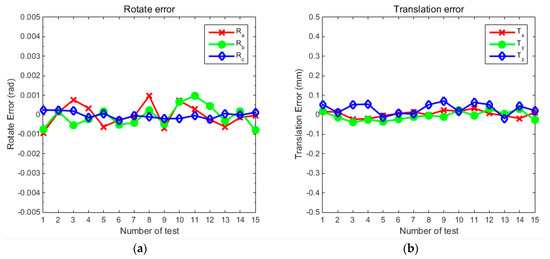
Figure 9.
Errors between the calculated results and the ground truth data. (a) The figure on the left shows three rotation angle errors; (b) the figure on the right shows three translation errors.
It can be seen from the above experimental results that the three rotation angle errors are within 0.001rad, the RMS error of the roll angle is 0.0021, the RMS error of the yaw angle is 0.0020, and the RMS error of the pitch angle is 0.00065. The difference between the mean value and the true value is −2.323 × 10−5, the difference between the mean value and the true value of the yaw angle is −7.779 × 10−5, and the difference between the mean value and the true value of the pitch angle is −2.632 × 10−5. The errors of the three translational values are within 0.08 mm, the RMS value in the x direction is 0.0655, the RMS value in the y direction is 0.0877, and the RMS value in the z direction is 0.1611. The difference between the average value and the true value of the x-direction displacement is 4.734 × 10−3. The difference between the mean value and the true value of the y-direction displacement is −6.176 × 10−3, and the difference between average value and the true value the z-direction displacement is 3.111 × 10−2.
To illustrate the applicability of the algorithm to all cameras, we present the extrinsic parameters errors of the remaining cameras relative to the reference coordinate system (camera coordinate system of the camera 1). The maximum values of the errors in 15 experiments are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
The maximum values of the errors in 15 experiments.
From the Table 6, we can see that the optimization results of the remaining cameras are consistent with the results of camera 2 as shown in Figure 9. The three rotation angle errors of these cameras are within 0.001rad, and the three translational errors of these cameras are within 0.08 mm. The accuracy of the extrinsic parameters is improved after optimization. Compared with the two-camera experiment in Section 3.3, after global optimization, the calibration accuracy has been obviously improved. The main performance is: the three angles of the extrinsic parameters and the average of the three translations are all close to the true value, and the RMS error has also been suppressed to a certain extent.
4. Discussion
In this paper, two steps of the optimization method are used to improve the calibration accuracy. In the first step, the re-projection error optimization method is used to optimize the extrinsic parameters of any two cameras in the system. In the second step, the global optimization method is used to calculate the extrinsic parameters of each camera. The extrinsic parameters are relative to the reference coordinate system and are optimized by redundant information. From the experimental results in Section 3, it can be found that after the two optimization processes, the noise has been effectively suppressed. It should be noted that when the multi-camera system is moved, if the camera pose changes with a large range, the time of iterative calculation in the re-projection error optimization process will be reduced. As the number of movements increase, the initial value of the linear solution is closer to the true value. When the number of the movement is greater than 8, the initial value is more stable. We use the Euler angle to calculate the extrinsic parameters, which will result in gimbal lock when the angle changes greatly. The multi-camera system described in this paper is used for ground observation or visual measurement. The yaw angle of the cameras varies greatly, while the pitch angle and roll angle of the cameras varies little. Therefore, due to the small change of roll angle and pitch angle, the gimbal lock phenomenon will not occur in practical applications.
To demonstrate the advantages of this method more clearly, a comparative analysis is conducted with the existing method. These are typical calibration methods for cameras without common FOVs in recent years. Since these papers are all a description of the accuracy of the translation, we use the translation accuracy as a standard to compare. The results are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Comparison with previous work.
It can be seen from Table 7, the accuracy of our method is close to the reconfigurable target method [20], and better than the other two methods. The reconfigurable target method requires artificial marks to calculate the pose relationship between sub-targets before each measurement, the operation process is complicated. The 3D reconstruction method [19] needs large and high-precision targets, which is difficult to create especially when the angle between the optical axis of the camera is large. These three methods are only applicable to the laboratory environment. The method in this paper does not require the aid of lasers or other special targets. It is easy to operate and has high precision. Our method is not limited by the angle between the cameras’ optical axis. Therefore it is suitable for on-site calibration in airborne remote sensing.
5. Conclusions
In this article, we propose a flexible multi-camera calibration method without common field of view to be used in an airborne remote sensing field. The characteristics of this method include: (1) the target is flexible and does not need a specific mechanical device. It is very suitable for rapid and on-site calibration in airborne remote sensing. (2) A multi-camera system calibration and optimization method is proposed. Experiments show that the optimization method based on the projection error effectively improves the accuracy of the linear solution in binocular calibration. For multi camera calibration, the global optimization method can effectively improve the effect of a single calibration error or system error on the final calibration result. (3) The experimental results show that when the baseline distance between the cameras is approximately 0.5 m, the calibration accuracy of the rotation angle of the binocular system is within 0.002 rad, and the calibration accuracy of the translation is within 0.15 mm. For the multi camera system, the accuracy of the three rotation angles is within 0.001 rad, and the accuracy of the three translations is within 0.08 mm by using the global optimization. Experiments show that the optimization algorithm proposed in this paper has better robustness and higher accuracy, this method can guarantee the quality of the tasks such as multi-camera image mosaic and terrain reconstruction in remote sensing field. The next work is conducted to reduce the computational complexity of the projection error optimization. In this way, the calculation speed of this method will be further accelerated.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Y. and X.W.; Data curation, L.Y. and J.Z.; Funding acquisition, X.W.; Investigation, L.Y., Y.N., K.Z. and J.Z.; Methodology, L.Y., X.W., Y.N. and K.Z.; Software, L.Y.; Validation, L.Y.; Writing—original draft, Lei Yin; Writing—review & editing, X.W.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 60872097 and No. 61179043), the National High Technology Research and Development Program 863(Grant No.2010AA122200).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their critical, helpful, and constructive comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned aerial systems for photogrammetry and remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaerts, J. The use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for remote sensing and mapping. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Rupnik, E.; Nex, F.; Toschi, I.; Remondino, F. Aerial multi-camera systems: Accuracy and block triangulation issues. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.; Lucieer, A.; Watson, C. An automated technique for generating georectified mosaics from ultra-high resolution unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imagery, based on structure from motion (SfM) point clouds. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1392–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Dubbini, M.; Gattelli, M.; Stecchi, F.; Fabbri, S.; Gabbianelli, G. Using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) for high-resolution reconstruction of topography: The structure from motion approach on coastal environments. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6880–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwin, S.; Lucieer, A. Assessing the accuracy of georeferenced point clouds produced via multi-view stereopsis from unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imagery. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1573–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Oleire-Oltmanns, S.; Marzolff, I.; Peter, K.D.; Ries, J.B. Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for monitoring soil erosion in Morocco. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3390–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandois, J.P.; Ellis, E.C. Remote sensing of vegetation structure using computer vision. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1157–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Shinozuka, M. A vision-based system for remote sensing of bridge displacement. NDT E Int. 2006, 39, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Camera calibration with one-dimensional objects. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurdjos, P.; Crouzil, A.; Payrissat, R. Another way of looking at plane-based calibration: The centre circle constraint. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Copenhagen, Denmark, 28–31 May 2002; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 252–266. [Google Scholar]
- Gurdjos, P.; Sturm, P. Methods and geometry for plane-based self-calibration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Madison, WI, USA, 18–20 June 2003; pp. 491–496. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, R.Y. An efficient and accurate camera calibration technique for 3D machine vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 22–26 June1986; pp. 364–374. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, R. A versatile camera calibration technique for high-accuracy 3D machine vision metrology using off-the-shelf TV cameras and lenses. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. 1987, 3, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Davis, L. Complete camera calibration using spheres: A dual space approach. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 2003, 206, 782–789. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wong, K.Y. Camera calibration with spheres: Linear approaches. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing 2005 (ICIP 2005), Genova, Italy, 14 September 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; p. II-1150. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G. Flexible global calibration of multiple cameras with nonoverlapping fields of view using circular targets. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 3122–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Shao, X.; Kang, X.; Yang, F.; He, X. Extrinsic calibration of a non-overlapping camera network based on close-range photogrammetry. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 6363–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, R.; Hu, M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y. Global calibration of multi-cameras with non-overlapping fields of view based on photogrammetry and reconfigurable target. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2018, 29, 065005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.S.; Li, Y.F. A global calibration method for large-scale multi-sensor visual measurement systems. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2004, 116, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lébraly, P.; Deymier, C.; Ait-Aider, O.; Royer, E.; Dhome, M. Flexible extrinsic calibration of non-overlapping cameras using a planar mirror: Application to vision-based robotics. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on IEEE Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 5640–5647. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.K.; Ilie, A.; Frahm, J.M.; Pollefeys, M. Simple calibration of non-overlapping cameras with a mirror. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2008. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pagel, F. Extrinsic self-calibration of multiple cameras with non-overlapping views in vehicles. In Proceedings of the International Society for Optics and Photonics, Video Surveillance and Transportation Imaging Applications, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–5 February 2014; Volume 9026, p. 902606. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhang, G. External parameter calibration of widely distributed vision sensors with non-overlapping fields of view. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepetit, V.; Moreno-Noguer, F.; Fua, P. Epnp: An accurate o (n) solution to the PNP problem. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2009, 81, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, K.; Nielsen, H.B.; Tingleff, O. Methods for Non-Linear Least Squares Problems; Informatics and Mathematical Modelling, Technical University of Denmark, DTU: Lyngby, Denmark, 1999; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Martinec, D.; Pajdla, T. Robust rotation and translation estimation in multiview reconstruction. In Proceedings of the CVPR’07. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Cui, Z.; Tan, P. A global linear method for camera pose registration. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 481–488. [Google Scholar]
- Camera Calibration Toolbox for Matlab. Available online: http://robots.stanford.edu/cs223b04/JeanYvesCalib/index.html#links (accessed on 5 June 2018).
- Horn, B.K. Closed-form solution of absolute orientation using unit quaternions. JOSA A 1987, 4, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).