Development of Intensity–Duration–Frequency (IDF) Curves over the United Arab Emirates (UAE) Using CHIRPS Satellite-Based Precipitation Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Dataset
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
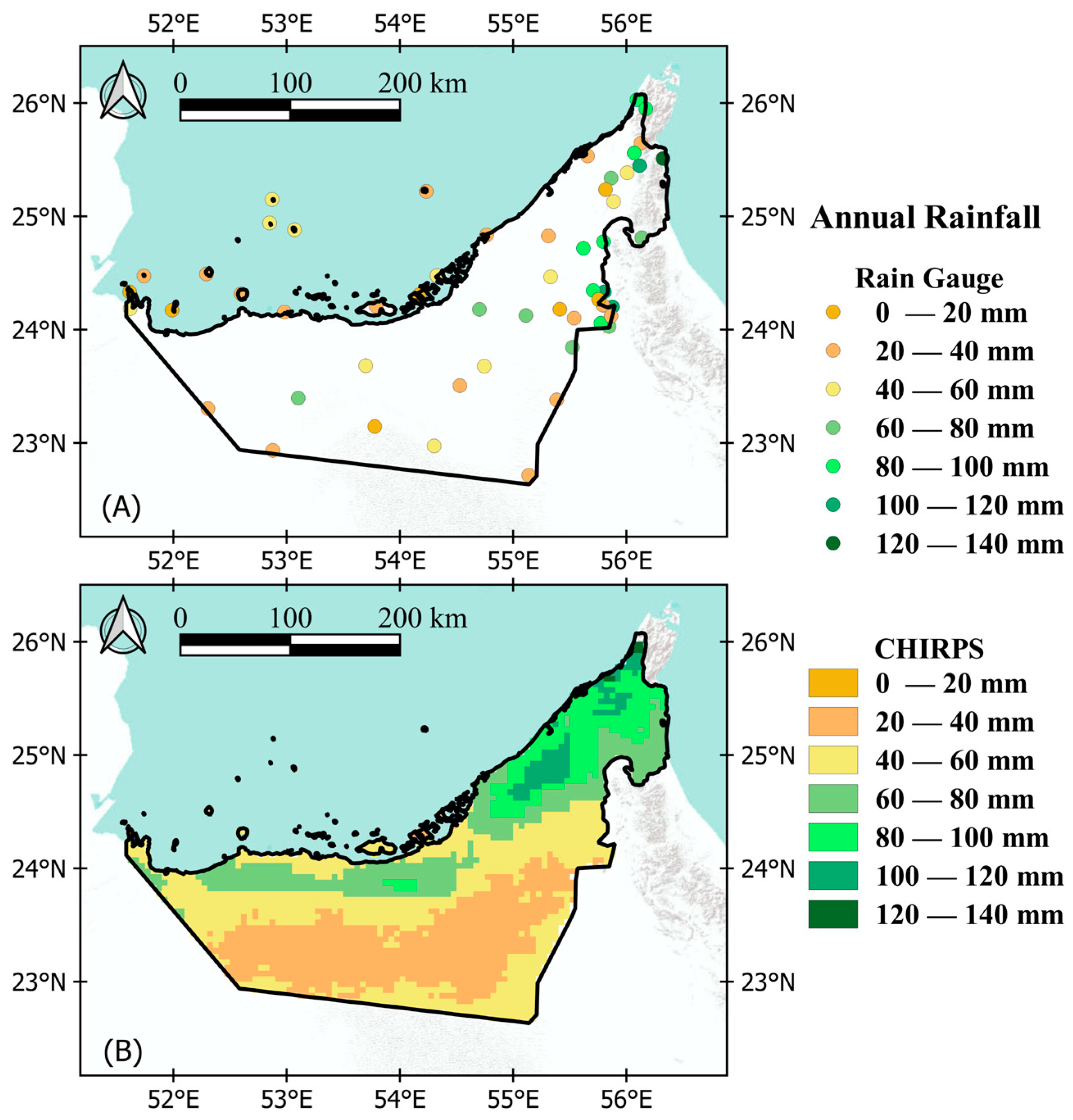
2.2.1. Rain Gauge Data
2.2.2. CHIRPS Precipitation Product
3. Methodology
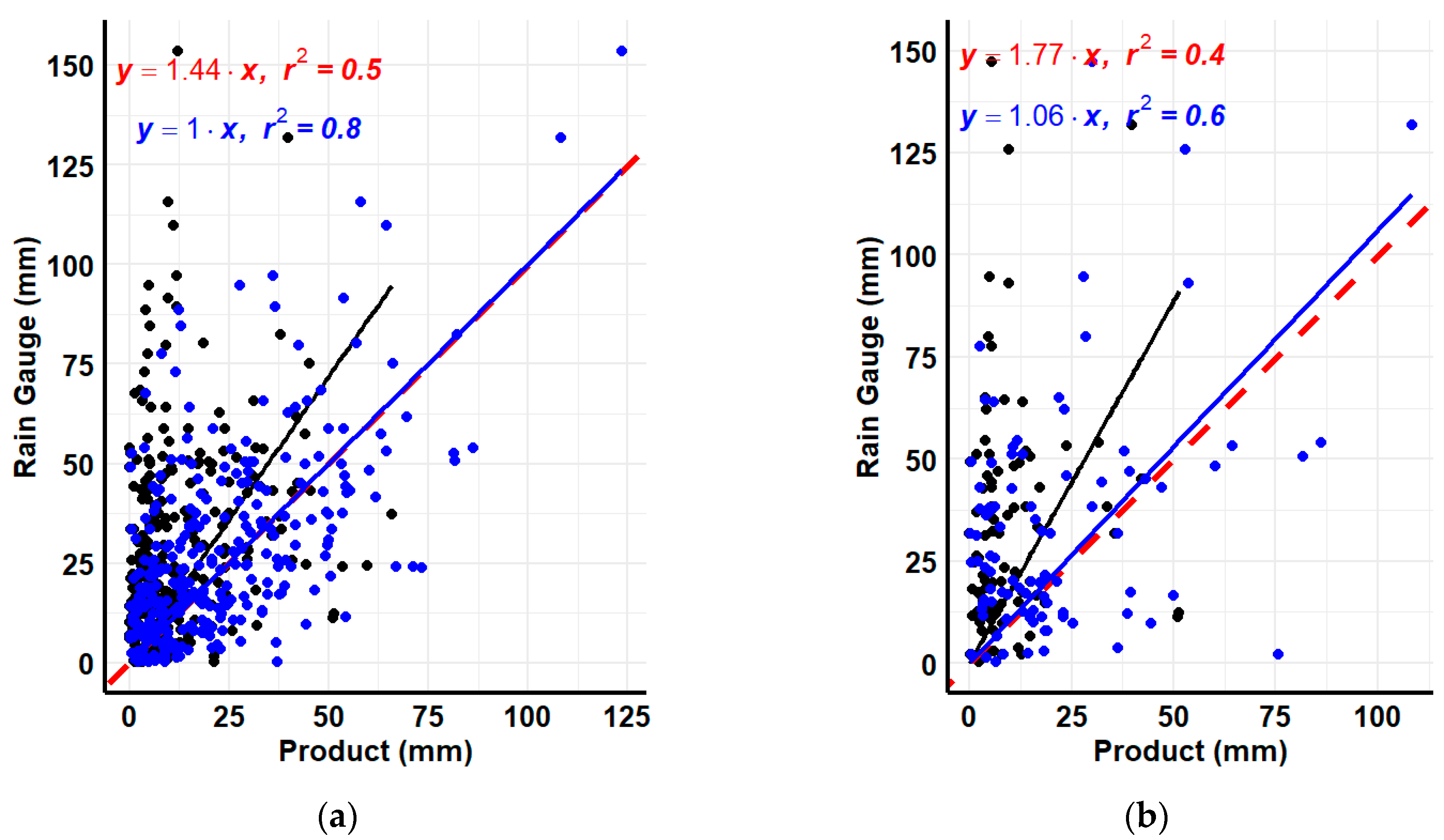
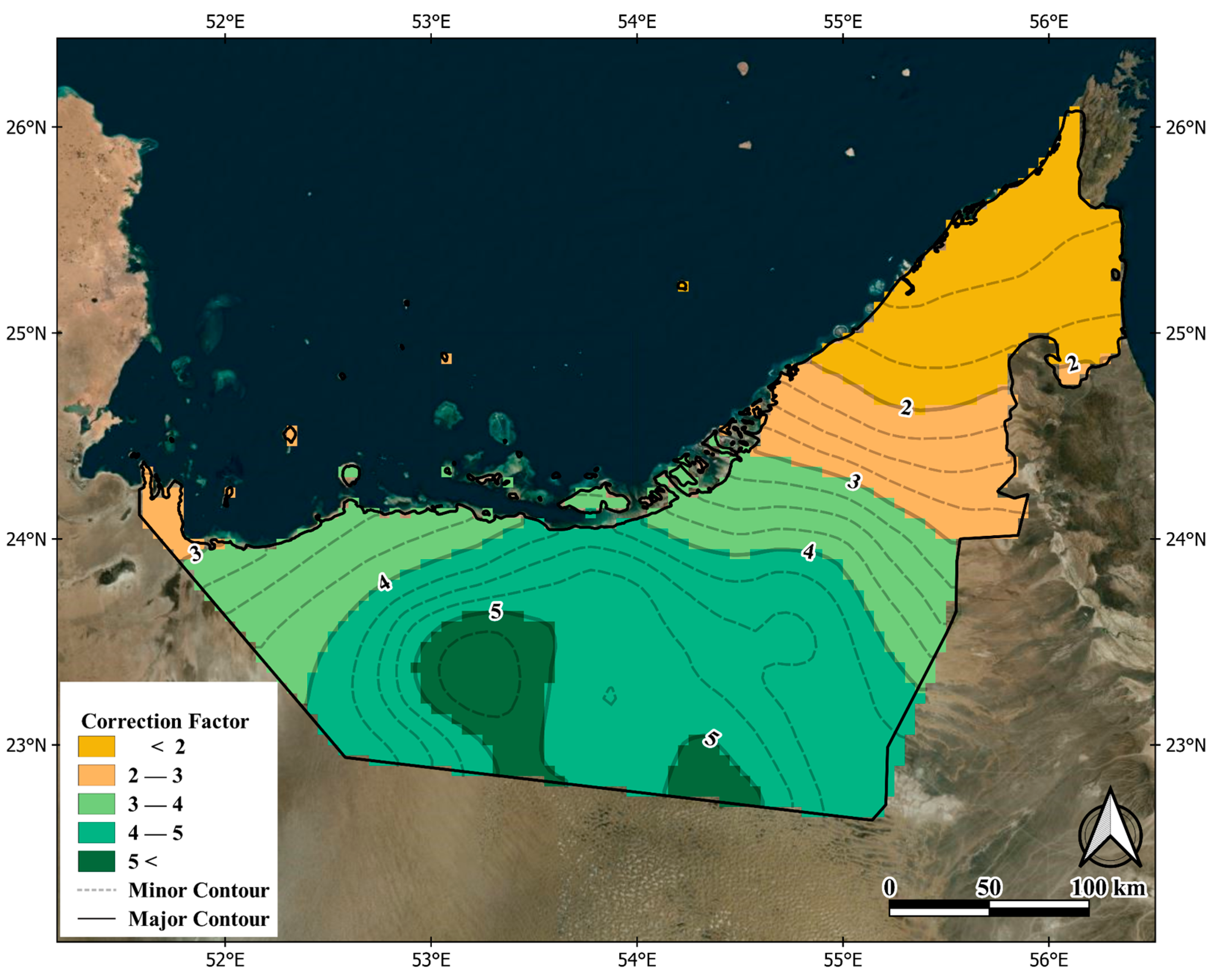
3.1. Bias Correction
3.2. Performance Criteria
3.3. IDF Development
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Bias Correction
4.2. Development of IDF Curves
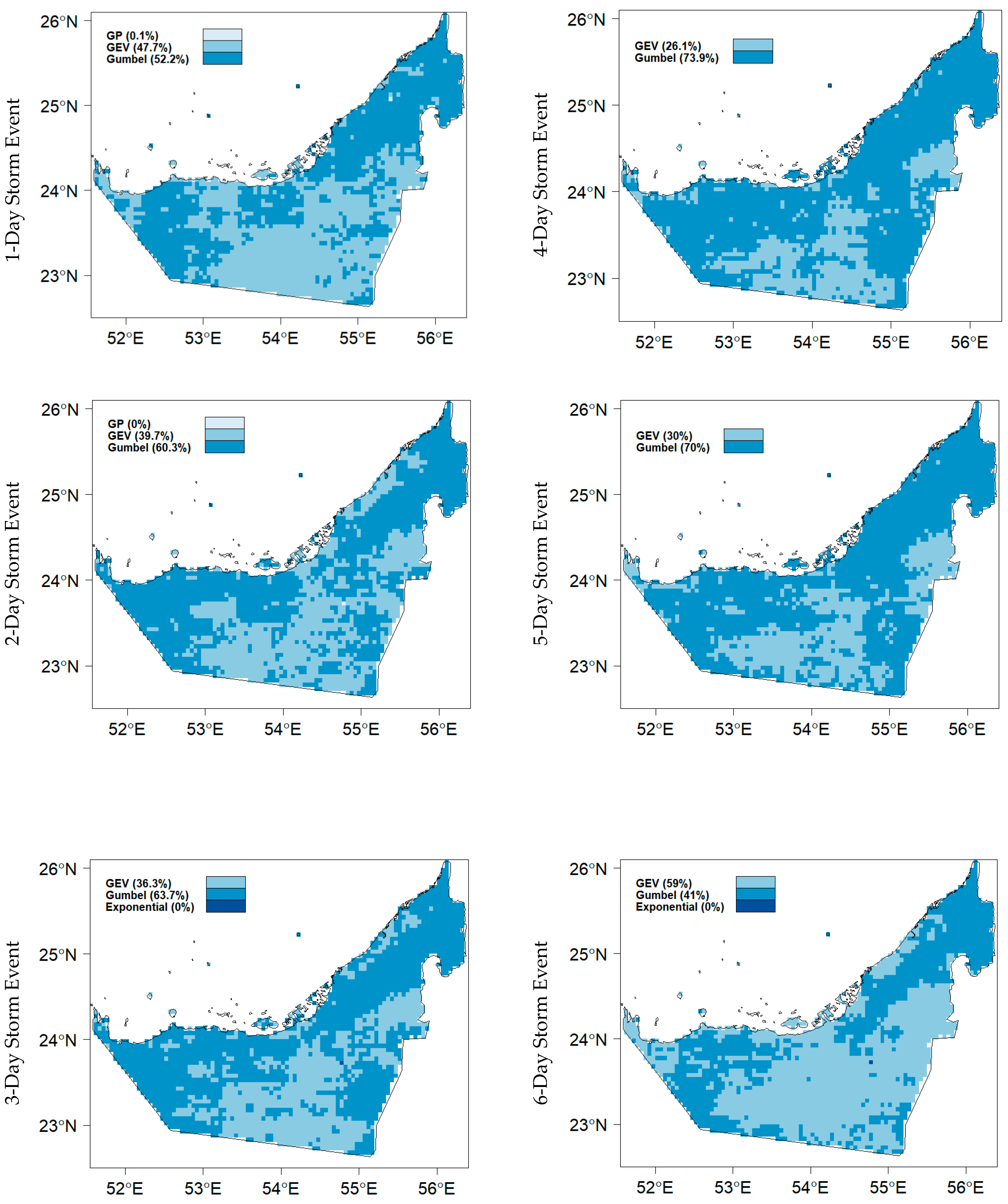
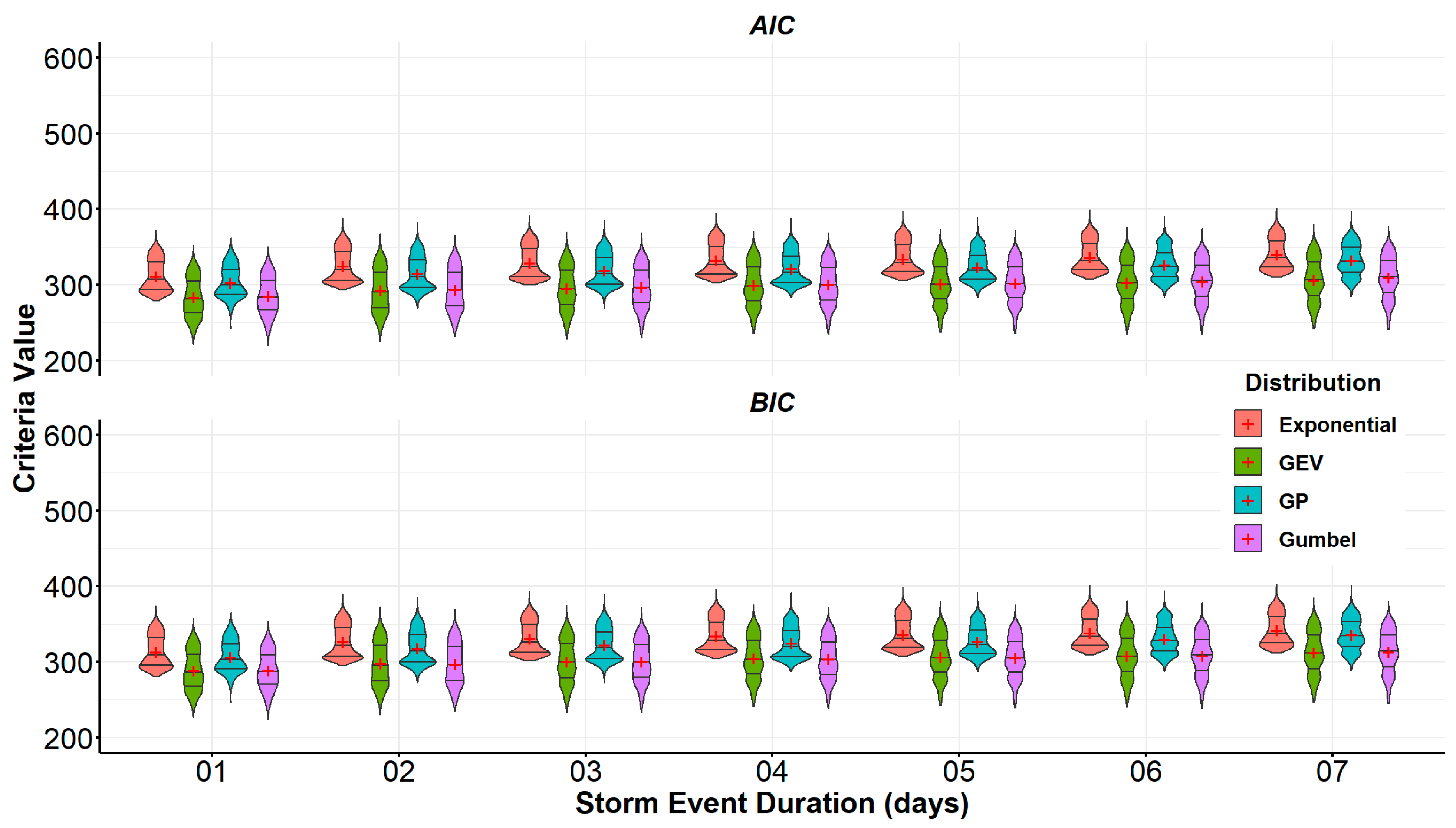
4.2.1. Fitting Statistical Distributions
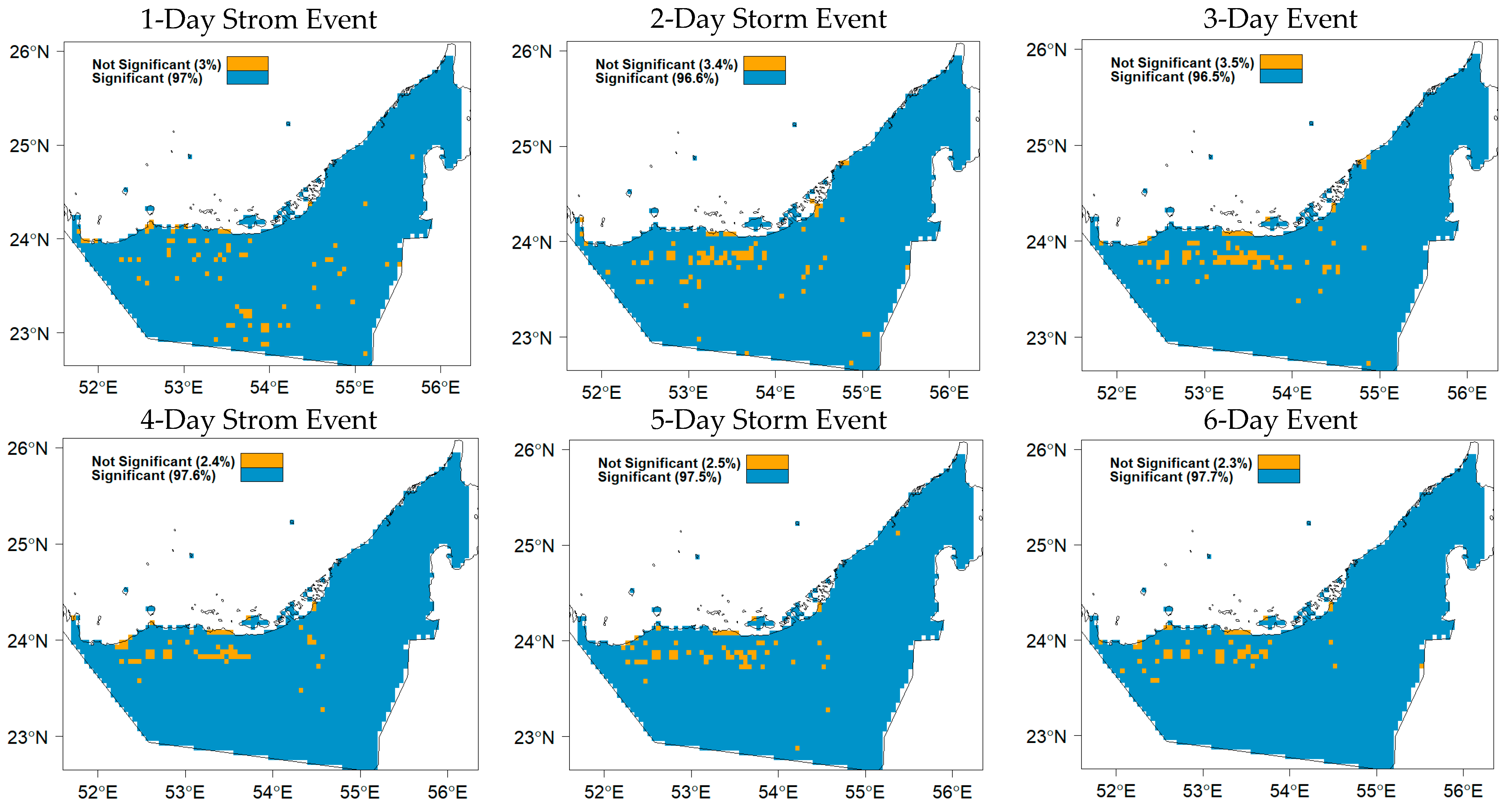
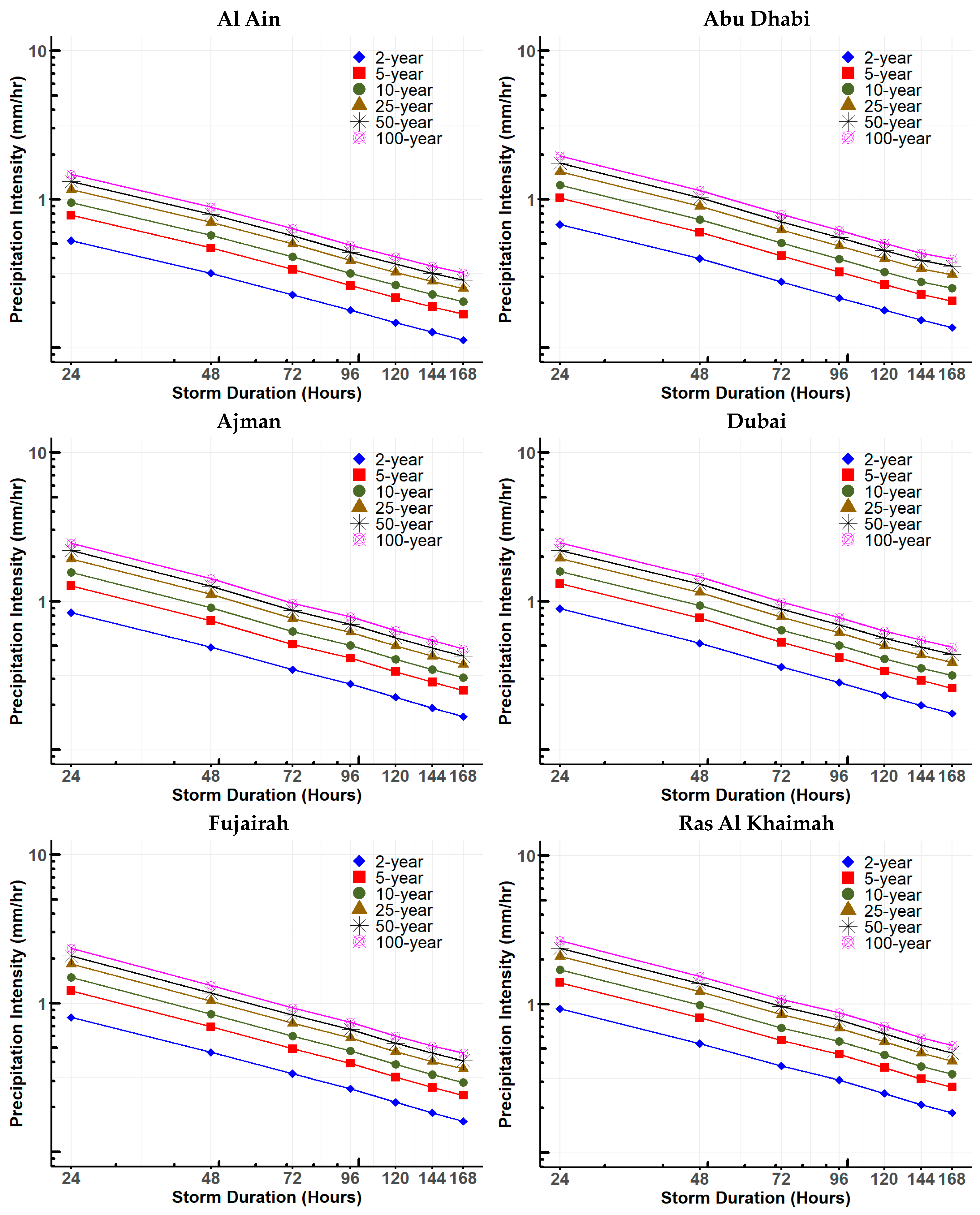
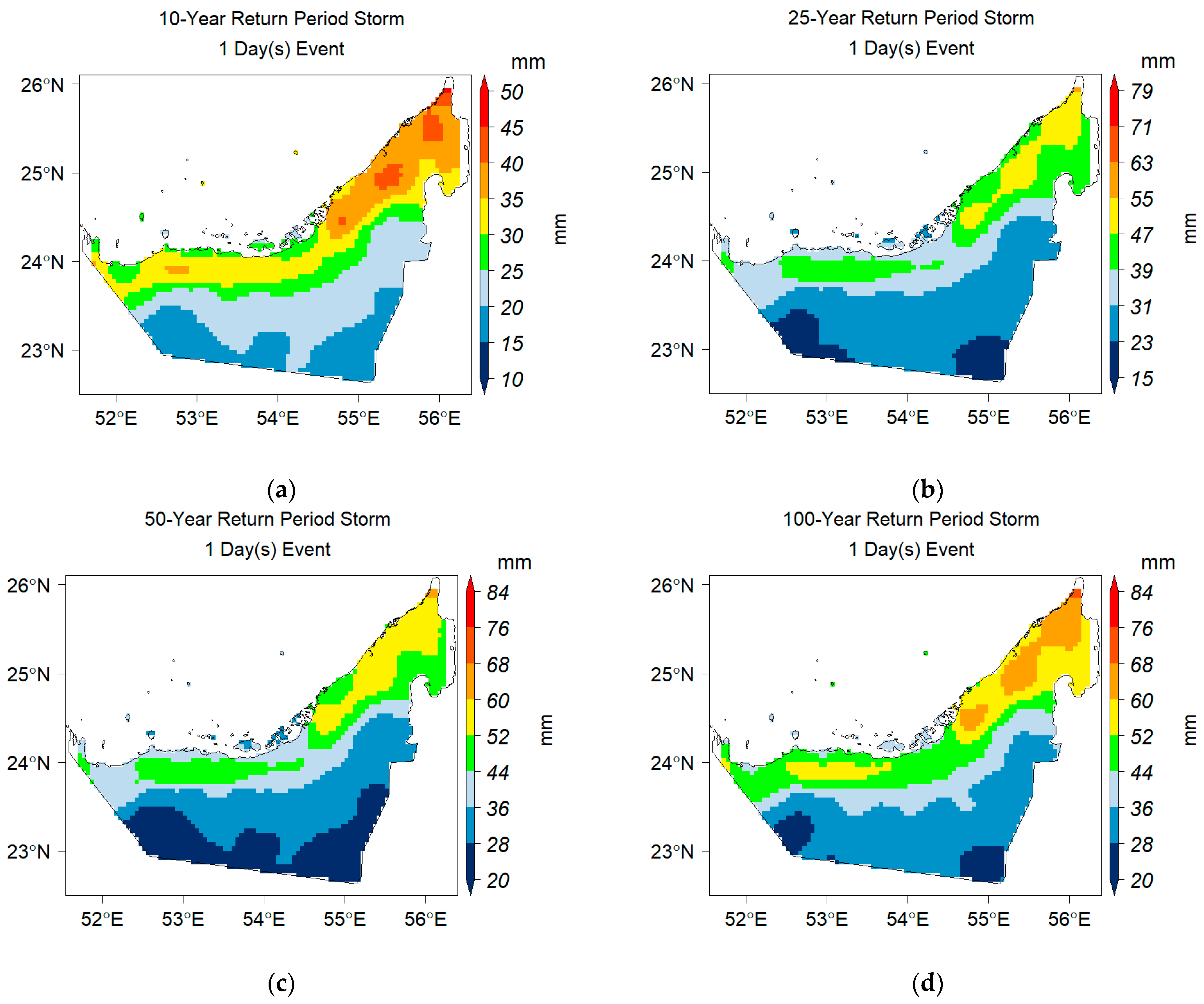
4.2.2. Developing the IDF Curves
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choubey, S.; Rina Kumari, R.; Chander, S.; Kumar, P. Analysis of Various Gauge Adjusted Merged Satellite Rainfall Products: A study for Major River Basins of Western India. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2023, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 April 2023; p. EGU23-13962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, P.; Padiyath, N.; Semioshkina, N.; Addad, Y.; Foulon, F.; Francis, D.; Voigt, G. Conceptualization of arid region radioecology strategies for agricultural ecosystems of the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 832, 154965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.; Mohamed, M.M.; Murad, A. Variability of Extreme Hydro-Climate Parameters in the North-Eastern Region of United Arab Emirates. Procedia Eng. 2016, 154, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Asanjan, A.A.; Faridzad, M.; Nguyen, P.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D. PERSIANN-CNN: Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information Using Artificial Neural Networks–Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 2273–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayugi, B.; Tan, G.; Ullah, W.; Boiyo, R.; Ongoma, V. Inter-comparison of remotely sensed precipitation datasets over Kenya during 1998–2016. Atmos. Res. 2019, 225, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.G.; Lo, M.H.; Famiglietti, J.S. Assessing surface water consumption using remotely-sensed groundwater, evapotranspiration, and precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wu, W.; He, D.; Li, Y.; Ji, X. Hydrological Simulation Using TRMM and CHIRPS Precipitation Estimates in the Lower Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tuo, Y.; Chiogna, G.; Disse, M. Evaluation of eight high spatial resolution gridded precipitation products in Adige Basin (Italy) at multiple temporal and spatial scales. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 573, 1536–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Clark, M.P.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Ma, Z.; Hong, Y. Have satellite precipitation products improved over last two decades? A comprehensive comparison of GPM IMERG with nine satellite and reanalysis datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; AghaKouchak, A.; Arkin, P.; Eylander, J.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; Harmon, R.; Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Imam, B.; Kuligowski, R.; Skahill, B.; et al. Advanced Concepts on Remote Sensing of Precipitation at Multiple Scales. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsumaiti, T.S.; Hussein, K.; Ghebreyesus, D.T.; Sharif, H.O. Performance of the CMORPH and GPM IMERG Products over the United Arab Emirates. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hong, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of high-resolution multi-sensor blended global precipitation products over the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebreyesus, D.; Sharif, H.O. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Precipitation Frequency in Texas Using High-Resolution Radar Products. Water 2020, 12, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siuki, S.K.; Saghafian, B.; Moazami, S. Comprehensive evaluation of 3-hourly TRMM and half-hourly GPM-IMERG satellite precipitation products. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Abitew, A.T.; Seonggyu, P.; Greewn, C.H.M.; Jeong, J. Spatiotemporal Evaluation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products in the Colorado River Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2023, 24, 1739–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furl, C.; Ghebreyesus, D.; Sharif, H.O. Assessment of the Performance of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products for Flood Events across Diverse Spatial Scales Using GSSHA Modeling System. Geosciences 2018, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, Y. Evaluating the performance of remote sensing precipitation products CMORPH, PERSIANN, and TMPA, in the arid region of northwest China. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2014, 118, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.A.; Marianetti, G.; Hinrichs, S. Validation of CHIRPS precipitation dataset along the Central Andes of Argentina. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, H.; Akgül, M.A. Performance evaluation of CHIRPS satellite precipitation estimates over Turkey. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2020, 142, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.; Huang, W.-R.; Liu, P.-Y.; Li, X. Validation of CHIRPS Precipitation Estimates over Taiwan at Multiple Timescales. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S. Performance assessment of CHIRPS, MSWEP, SM2RAIN-CCI, and TMPA precipitation products across India. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebreyesus, D.T.; Sharif, H.O. Development and Assessment of High-Resolution Radar-Based Precipitation Intensity-Duration-Curve (IDF) Curves for the State of Texas. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.; Ismail, T.; Shahid, S.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Dewan, A. Evaluating intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves of satellite-based precipitation datasets in Peninsular Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, E.; Gao, X. Climate change impacts on extreme events in the United States: An uncertainty analysis. Clim. Change 2015, 131, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.; Navarro, X.; Casas, M.C.; Ribalaygua, J.; Russo, B.; Pouget, L.; Redaño, A. Influence of climate change on IDF curves for the metropolitan area of Barcelona (Spain). Int. J. Clim. 2014, 34, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Babel, M.S.; Weesakul, S.; Vojinovic, Z. Developing Intensity–Duration–Frequency (IDF) Curves under Climate Change Uncertainty: The Case of Bangkok, Thailand. Water 2017, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Becker, A.; Huffman, G.J.; Muller, C.L.; Joe, P.; Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Kirschbaum, D.B. So, how much of the Earth’s surface is covered by rain gauges? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombadi, M.; Nguyen, P.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K. Developing intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves from satellite-based precipitation: Methodology and evaluation. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 7752–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perica, S.; Pavlovic, S.; Laurent, M.S.; Trypaluk, C.; Unruh, D.; Wilhite, O. Precipitation-Frequency Atlas of the United States, Texas. In NOAA Atlas 14; NOAA, National Weather Service: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marra, F.; Morin, E.; Peleg, N.; Mei, Y.; Anagnostou, E.N. Intensity–duration–frequency curves from remote sensing rainfall estimates: Comparing satellite and weather radar over the eastern Mediterranean. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 2389–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wendi, D.; Kim, D.E.; Liong, S.-Y. Deriving intensity–duration–frequency (IDF) curves using downscaled in situ rainfall assimilated with remote sensing data. Geosci. Lett. 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böer, B. An introduction to the climate of the United Arab Emirates. J. Arid Environ. 1997, 35, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M. The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER): Data products for the high spatial resolution imager on NASA’s Terra platform. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.C.; Peterson, P.J.; Landsfeld, M.F.; Pedreros, D.H.; Verdin, J.P.; Rowland, J.D.; Romero, B.E.; Husak, G.J.; Michaelsen, J.C.; Verdin, A.P. A quasi-global precipitation time series for drought monitoring. US Geol. Surv. Data Ser. 2014, 832, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, C.; Verdin, A.; Michaelsen, J.; Peterson, P.; Pedreros, D.; Husak, G. A global satellite-assisted precipitation climatology. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2015, 7, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiraie-Boroujerdy, P.-S.; Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S. Trends of precipitation extreme indices over a subtropical semi-arid area using PERSIANN-CDR. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2017, 130, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asong, Z.E.; Razavi, S.; Wheater, H.S.; Wong, J.S. Evaluation of Integrated Multisatellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) over Southern Canada against Ground Precipitation Observations: A Preliminary Assessment. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, K.A.; Alsumaiti, T.S.; Ghebreyesus, D.T.; Sharif, H.O.; Abdalati, W. High-Resolution Spatiotemporal Trend Analysis of Precipitation Using Satellite-Based Products over the United Arab Emirates. Water 2021, 13, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Andréasson, J.; Graham, L.P.; Olsson, J.; Rosberg, J.; Wetterhall, F. Distribution-based scaling to improve usability of regional climate model projections for hydrological climate change impacts studies. Hydrol. Res. 2010, 41, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omranian, E.; Sharif, H.O. Evaluation of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Satellite Rainfall Products over the Lower Colorado River Basin, Texas. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2018, 54, 882–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.S.; Stedinger, J.R. Generalized maximum-likelihood generalized extreme-value quantile estimators for hydrologic data. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.S.; Stedinger, J.R. Generalized Maximum Likelihood Pareto-Poisson estimators for partial duration series. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, F.J., Jr. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for goodness of fit. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1951, 46, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Shi, C.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J. Accuracy of CHIRPS Satellite-Rainfall Products over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakib, S.; Ghebreyesus, D.; Sharif, H.O. Performance Evaluation of IMERG GPM Products during Tropical Storm Imelda. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, M.; Chowdhury, R.; Shetty, A. Rainfall and Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves in the United Arab Emirates. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2014, Portland, OR, USA, 1–5 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Almheiri, K.B.; Rustum, R.; Wright, G.; Adeloye, A.J. Study of Impact of Cloud-Seeding on Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves of Sharjah City, the United Arab Emirates. Water 2021, 13, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.; Francis, D.; Nelli, N.; Cherif, C. Regional atmospheric circulation patterns driving consecutive fog events in the United Arab Emirates. Atmos. Res. 2023, 282, 106506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Statistical Index | Units | Equation | Perfect Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson’s correlation coefficient (CC) | Ratio | 1 | |
| Percentage Bias (RBIAS) | % | 0 | |
| Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) | mm | 0 | |
| Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) | Ratio | 1 | |
| Kling-Gupta Efficiency (KGE) | Ratio | 1 |
| Performance Metric | Calibration | Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Pearson Correlation Coefficient | 0.84 | 0.63 |
| Kling–Gupta Efficiency (KGE) | 0.81 | 0.53 |
| Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) | 0.82 | 0.43 |
| Percent Bias (%) | 5.10 | −13.20 |
| Root Mean Square Error (mm) | 1.68 | 10.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsumaiti, T.S.; Hussein, K.A.; Ghebreyesus, D.T.; Petchprayoon, P.; Sharif, H.O.; Abdalati, W. Development of Intensity–Duration–Frequency (IDF) Curves over the United Arab Emirates (UAE) Using CHIRPS Satellite-Based Precipitation Products. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010027
Alsumaiti TS, Hussein KA, Ghebreyesus DT, Petchprayoon P, Sharif HO, Abdalati W. Development of Intensity–Duration–Frequency (IDF) Curves over the United Arab Emirates (UAE) Using CHIRPS Satellite-Based Precipitation Products. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsumaiti, Tareefa S., Khalid A. Hussein, Dawit T. Ghebreyesus, Pakorn Petchprayoon, Hatim O. Sharif, and Waleed Abdalati. 2024. "Development of Intensity–Duration–Frequency (IDF) Curves over the United Arab Emirates (UAE) Using CHIRPS Satellite-Based Precipitation Products" Remote Sensing 16, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010027






