Developing Two Spectral Disease Indices for Detection of Wheat Leaf Rust (Pucciniatriticina)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.1.1. Cultivation Condition and Pathogen Inoculation
2.1.2. Data Collection
- Camera model: Canon DIGITAL IXUS 85 IS;
- F-109 number: f/3.2;
- Shutter speed: 1/60.
2.2. Extraction of Disease Reflectance Spectra
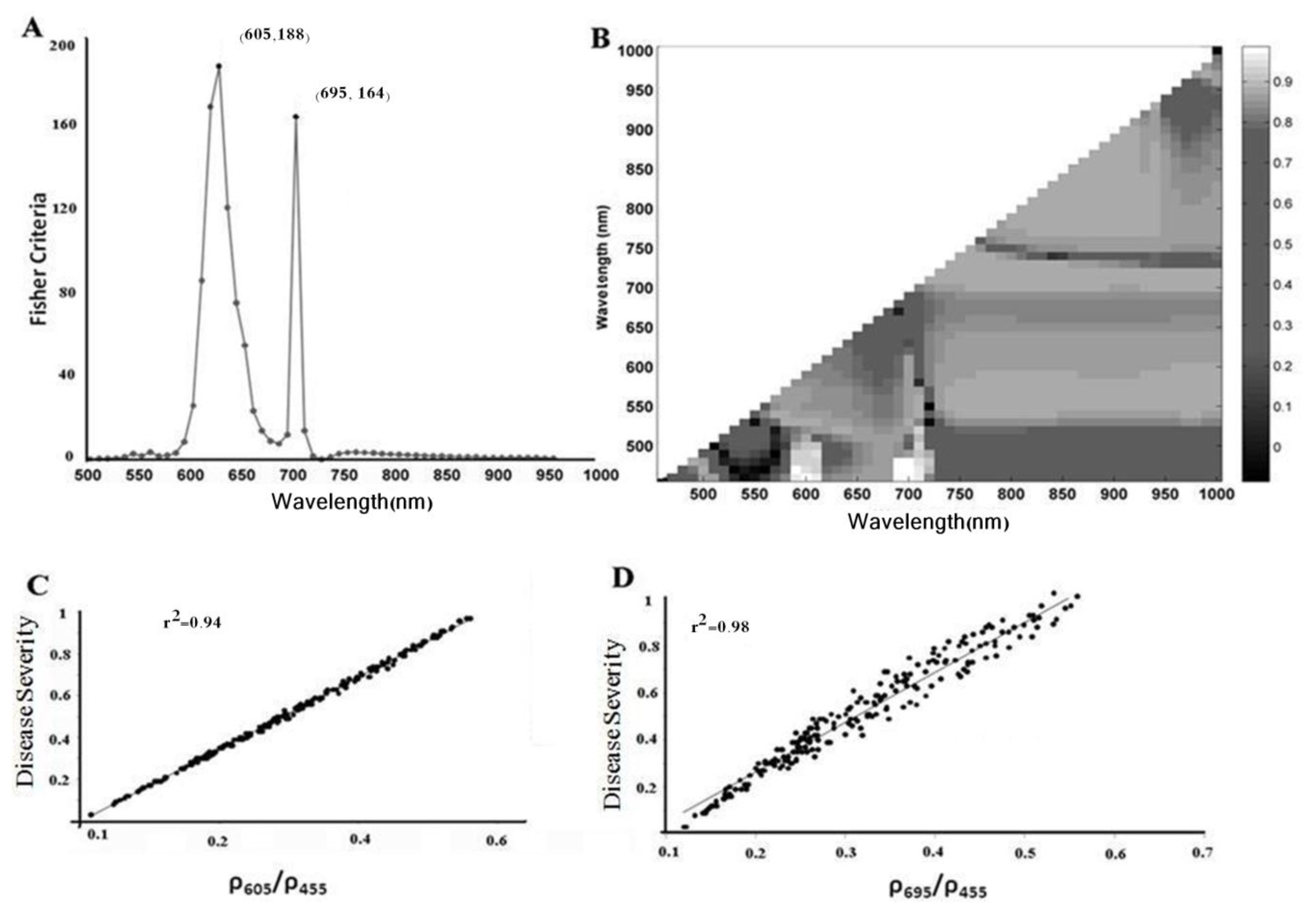
2.3. Selection of Suitable Wavelength for Disease Severity Index
2.4. Comparison of the Results with Other SVIs
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Disease Development in Leaves Inoculated with Rust
3.2. Evaluation of the Reflectance Spectra of Disease Symptoms
- (a)
- Selection of 60 random infected leaf spectra consisting of various disease symptoms
- (b)
- Using the estimated spectra of disease symptoms (Figure 3) and calculating the fraction of each disease symptom in each leaf by deploying Equation (1). These values are called estimated values.
- (c)
- Extracting the real fraction of disease symptoms for the selected spectra using the digital images. These values are called observed values.
- (d)
- Calculating the correlation coefficient between the estimated and observed values.
3.3. Estimating the Disease Severity
3.4. Comparison Suggested Indices with Other SVIs
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
- Author ContributionsAshourloo D. and Mobasheri M.R. developed the concept and research plan. Mobasheri was primary supervisor and leaded the campaign and field working. Huete A. co-supervisor of this work. Ashourloo, Mobasheri and Huete provided expert knowledge about methods, interpretations, participated in the discussions, editing and revisions of the paper. All authors discussed the results and implications and commented on the manuscript at all stages.
References
- Sankaran, S.; Mishra, A.; Ehsani, R.; Davis, C. A review of advanced techniques for detecting plant diseases. Comput. Electron. Agric 2010, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Roelofsen, H.D.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Kooistra, L.; Witte, J.-P.M. Trait estimation in herbaceous plant assemblages from in situ canopy spectra. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 6323–6345. [Google Scholar]
- Delalieux, S.; Auwerkerken, A.; Verstraeten, V.W.; Somers, B.; Valcke, R.; Lhermitte, S.; Keulemanss, J.; Coppin, P. Hyperspectral reflectance and fluorescence imaging to detect scab induced stress in Apple leaves. Remote Sens 2009, 1, 858–874. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, U.; Bürling, K.; Oerke, E.-C. Sensor use in plant protection. Gesunde Pflanz 2008, 60, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Pu, R.; Huang, W.; Yuan, L.; Luo, J.; Wang, J. Using in-situ hyperspectral data for detecting and discriminating yellow rust disease from nutrient stresses. Field Crops Res 2012, 134, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hillnhütter, C.; Mahlein, A.-K.; Sikora, R.A.; Oerke, E.-C. Remote sensing to detect plant stress induced by Heterodera schachtii and Rhizoctonia solani in sugar beet fields. Field Crops Res 2011, 122, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Moshou, D.; Bravo, C.; West, J.; Wahlen, S.; McCartney, A.; Ramon, H. Automatic detection of “yellow rust” in wheat using reflectance measurements and neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric 2004, 44, 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Rumpf, T.; Welke, P.; Dehne, H.-W.; Plümer, L.; Steiner, U.; Oerke, E.-C. Development of spectral indices for detecting and identifying plant diseases. Remote Sens. Environ 2013, 128, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.-C.; Pu, R.-L.; Wang, J.-H.; Huang, W.-J.; Yuan, L.; Luo, J.-H. Detecting powdery mildew of winter wheat using leaf level hyperspectral measurements. Comput. Electron. Agric 2012, 85, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Stark, R.; Rundquist, D. Novel algorithms for remote estimation of vegetation fraction. Remote Sens. Environ 2002, 80, 76–87. [Google Scholar]
- Peñuelas, J.; Baret, F.; Filella, I. Semiempirical indices to assess carotenoids/chlorophyll a ratio from leaf spectral reflectance. Photosynthetica 1995, 31, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, R.A.; Perry, E.M.; Pierce, F.J.; Mekuria, T. The potential of spectral reflectance technique for the detection of Grapevine leaf roll-associated virus-3 in two red-berried wine grape cultivars. Comput. Electron. Agric 2009, 66, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Wang, K.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Bai, J.; Xiao, C.; Lai, J. Spectrum Characteristics of Cotton Canopy Infected with Verticillium Wilt and Inversion of Severity Level. In IFIP International Federation for Information Processing; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 1169–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, H.H. Using Hyperspectral Reflectance Data for Discrimination between Healthy and Diseased Plants, and Determination of Damage-level in Diseased Plants. Proceedings of the 31st Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 16–18 October 2002; pp. 49–54.
- West, J.S.; Bravo, C.; Oberti, R.; Lemaire, D.; Moshou, D.; McCartney, H.A. The potential of optical canopy measurement for targeted control of field crop disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol 2003, 41, 593–614. [Google Scholar]
- Belasque, L.; Gasparoto, M.C.G.; Marcassa, L.G. Detection of mechanical and disease stresses in citrus plants by fluorescence spectroscopy. Appl. Opt 2008, 47, 1922–1926. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.M.; Cheng, C.H. Spectral characteristics of rice plants infested by brown planthoppers. Proc. Natl. Sci. Counc. Repub. China Part B Life Sci 2001, 25, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.M.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, R.K. Changes in spectral characteristics of rice canopy infested with brown planthopper and leaffolder. Crop. Sci 2007, 47, 329–335. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.R.; Ying, Y.B.; Fu, X.P.; Zhu, S.P. Near-infrared spectroscopy in detecting leaf miner damage on tomato leaf. Biosyst. Eng 2007, 96, 447–454. [Google Scholar]
- Bolton, M.; Kolmer, J.; Garvin, D. Wheat leaf rust caused by Puccinia triticina. Mol. Plant. Patol 2008, 9, 563–575. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C.; Bancal, M.-O.; Ney, B.; Lannou, C. Wheat leaf photosynthesis loss due to leaf rust, with respect to lesion development and leaf nitrogen status. New Phytol 2005, 165, 227–241. [Google Scholar]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Steiner, U.; Dehne, H.-W.; Oerke, E.-C. Spectral signatures of sugar beet leaves for the detection and differentiation of diseases. Precis. Agric 2010, 11, 413–431. [Google Scholar]
- Rumpf, T.; Mahlein, A.-K.; Steiner, U.; Oerke, E.-C.; Dehne, H.-W.; Plümer, L. Early detection and classification of plant diseases with support vector machines based on hyperspectral reflectance. Comput. Electron. Agric 2010, 74, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Steiner, U.; Hillnhütter, C.; Dehne, H.-W.; Oerke, E.-C. Hyperspectral imaging for small-scale analysis of symptoms caused by different sugar beet diseases. Plant. Methods 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.G. Use of multispectral radiometry in wheat yellow rust experiments. OEPP/EPPO Bull 1991, 21, 651–658. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Lamb, D.W.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J. Identification of yellow rust in wheat using in-situ spectral reflectance measurements and airborne hyperspectral imaging. Precis. Agric 2007, 8, 187–119. [Google Scholar]
- Devadas, R.; Lamb, D.W.; Simpfendorfer, S.; Backhouse, D. Evaluating ten spectral vegetation indices for identifying rust infection in individual wheat leaves. Precis. Agric 2009, 10, 459–470. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, J.; Menz, G. Multi-temporal wheat disease detection by multi-spectral remote sensing. Precis. Agric 2007, 8, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ashourloo, D.; Mobasheri, M.R.; Huete, A. Evaluating the effect of different wheat rust disease symptoms on vegetation indices using hyperspectral measurements. Remote Sens 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hiary, H.; Bani-Ahmad, S.; Reyalat, M.; Braik, M.; ALRahamneh, Z. Fast and accurate detection and classification of plant diseases. Int. J. Comput. Appl 2011, 17, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zurita-Milla, R.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Schaepman, M.E. Unmixing-based LANDSAT TM and MERIS FR data fusion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett 2008, 5, 453–457. [Google Scholar]
- Dennison, P.E.; Roberts, D.A. Endmember selection for multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis using endmember average RMSE. Remote Sens. Environ 2003, 87, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Smith, R.B.; de Pauw, E. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and their relationships with agricultural crop characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ 2000, 71, 158–182. [Google Scholar]
- Filella, I.; Serrano, L.; Serra, J.; Penuelas, J. Evaluating wheat nitrogen status with canopy reflectance indices and discriminant analysis. Crop. Sci 1995, 35, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Gamon, J.A.; Penuelas, J.; Field, C.B. A narrow-waveband spectral index that tracks diurnal changes in photosynthetic efficiency. Remote Sens. Environ 1992, 41, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Haboudane, D.; John, R.; Millera, J.R.; Tremblay, N.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Dextraze, L. Integrated narrow-band vegetation indices for prediction of crop chlorophyll content for application to precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ 2002, 81, 416–426. [Google Scholar]
- Penuelas, J.; Gamon, J.A.; Fredeen, A.L.; Merino, J.; Field, C.B. Reflectance indices associated with physiological changes in nitrogen- and water-limited sunflower leaves. Remote Sens. Environ 1995, 48, 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Merzlyak, M.N.; Chivkunova, O.B. Optical properties and nondestructive estimation of anthocyanin content in plant leaves. Photochem. Photobiol 2001, 74, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.S.; Daughtry, C.S.T.; Chappelle, E.W.; McMurtrey, J.E. The Use of High Spectral Resolution Bands for Estimating Absorbed Photosynthetically Active Radiation (APAR). Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Physical Measurements and Signatures in Remote Sensing, Val d’Isère, France, 17–21 January 1994; pp. 299–306.
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Berjón, A.; López-Lozano, R.; Miller, J.R.; Martín, P.; Cachorro, V.; González, M.R.; Frutos, A. Assessing vineyard condition with hyperspectral indices: Leaf and canopy reflectance simulation in a row-structured discontinuous canopy. Remote Sens. Environ 2005, 99, 271–287. [Google Scholar]
- Broge, N.H.; Leblanc, E. Comparing prediction power and stability of broadband and hyperspectral vegetation indices for estimation of green leaf area index and canopy chlorophyll density. Remote Sens. Environ 2000, 76, 156–172. [Google Scholar]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.R.; Pattery, E.; Zarco-Tejad, P.J.; Strachan, I.B. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: Modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ 2004, 90, 337–352. [Google Scholar]





| Variable | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NBNDVI | Narrow-band normalised difference vegetation index | (R850 − R680)/(R850 + R680) [33] |
| NRI | Nitrogen reflectance index | (R570 − R670)/(R570 + R670) [34] |
| PRI | Photochemical reflectance index | (R570 − R531)/(R570 + R531) [35] |
| TCARI | The transformed chlorophyll absorption and reflectance Index | 3 × [(R700 − R670) − 0.2 × (R700 − R550) × (R700/R670)] [36] |
| SIPI | Structural independent pigment index | (R800 − R445)/(R800 − R680) [37] |
| PhRI | Physiological reflectance index | (R550 − R531)/(R550 + R531) [38] |
| NPCI | Normalized pigment chlorophyll ratio index | (R680 − R430)/(R680 + R430) [39] |
| ARI | Anthocyanin reflectance index | ARI = (R550) −1 − (R700) −1[40] |
| CARI | Chlorophyll absorption ratio index | (|(a670 + R670 + b)|/(a2 + 1)1/2) × (R700/R670) a = (R700 − R550)/150, b = R550 − (a × 550) [40] |
| GI | Green index | R554/R677[41] |
| TVI | Triangular vegetation index | 0.5[120(R750 − R550) − 200(R670 − R550)] [42] |
| Class Precision | Prediction | Ground Truth | Class Precision |
|---|---|---|---|
| LRASI_1ρ605 | Rust | Healthy | |
| Rust | 140 | 20 | 87% |
| Healthy | 11 | 127 | 91% |
| Class recall | 93% | 86% | 89.5 |
| LRASI_2ρ605 | Rust | Healthy | |
| Rust | 148 | 22 | 87% |
| Healthy | 21 | 135 | 86% |
| Class recall | 87% | 86% | 86.5% |
| Disease Severity | Classification Error % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LRASI_1ρ605 | LRASI_2ρ605 | |||
| Rust | Healthy | Healthy | Rust | |
| 1%–5% | 35 | 44 | 47.7 | 32 |
| 5%–10% | 10.2 | 14.3 | 16 | 17.2 |
| 10%–20% | 7.2 | 11.6 | 12.4 | 9.8 |
| 20%–30% | 5.1 | 7.6 | 8.3 | 7.4 |
| 30%–40% | 3.6 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 4.5 |
| 40%–50% | 3.9 | 2.4 | 2.7 | 5 |
| 50%–60% | 1.2 | 2.2 | 0.9 | 1.7 |
| 60%–70% | 3 | 4.7 | 2.4 | 3.7 |
| 70%–80% | 5.1 | 4.5 | 3.7 | 3.5 |
| >80% | 4.8 | 5 | 4.1 | 4.4 |
| Disease Severity | Classification Error % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBNDVI | NDVI | PRI | ||||
| Rust | Healthy | Healthy | Rust | Healthy | Rust | |
| 1%–5% | 25 | 34 | 29 | 38 | 44 | 43 |
| 5%–10% | 12 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 11 | 19 |
| 10%–20% | 11 | 12 | 14 | 10 | 13 | 18 |
| 20%–30% | 15 | 10 | 17 | 14 | 17 | 15 |
| 30%–40% | 14 | 13 | 26 | 18 | 11 | 22 |
| 40%–50% | 25 | 21 | 26 | 28 | 21 | 28 |
| 50%–60% | 28 | 29 | 19 | 37 | 29 | 32 |
| 60%–70% | 31 | 37 | 44 | 36 | 34 | 47 |
| 70%–80% | 38 | 55 | 47 | 54 | 44 | 61 |
| >80% | 53 | 44 | 61 | 52 | 49 | 58 |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashourloo, D.; Mobasheri, M.R.; Huete, A. Developing Two Spectral Disease Indices for Detection of Wheat Leaf Rust (Pucciniatriticina). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4723-4740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6064723
Ashourloo D, Mobasheri MR, Huete A. Developing Two Spectral Disease Indices for Detection of Wheat Leaf Rust (Pucciniatriticina). Remote Sensing. 2014; 6(6):4723-4740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6064723
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshourloo, Davoud, Mohammad Reza Mobasheri, and Alfredo Huete. 2014. "Developing Two Spectral Disease Indices for Detection of Wheat Leaf Rust (Pucciniatriticina)" Remote Sensing 6, no. 6: 4723-4740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6064723
APA StyleAshourloo, D., Mobasheri, M. R., & Huete, A. (2014). Developing Two Spectral Disease Indices for Detection of Wheat Leaf Rust (Pucciniatriticina). Remote Sensing, 6(6), 4723-4740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6064723






