Development of Dense Time Series 30-m Image Products from the Chinese HJ-1A/B Constellation: A Case Study in Zoige Plateau, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area

2.2. HJ-1A/B Overview
2.2.1. Sensors
| -- | HJ-1A/B CCD | Landsat TM/ETM |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial resolution (m) | 30 | 30 |
| Spectral bands | 4 | 7 |
| Revisiting period (days) | 2 | 16 |
| Central wavelength (nm) | 475; 560; 660; 830 | 485; 565; 665; 820; 1650; 2190; 11,400 |
| Field of view (km) | 360 (700 for 2 CCD) | 180 |
| Launch date | 2008 | 1984 Landsat 5; 1999 Landsat 7 |

2.2.2. Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Pre-Processing
3.2. Compositing Method
3.2.1. Tiling

3.2.2. Image Composition Algorithm
3.3. Quality Assessment
3.3.1. Comparison between HJ Composites and WELD Products
3.3.2. Comparison between HJ Composites and MODIS Products
3.3.3. Agreement Measures
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Performance of the Composites for Reducing Cloud Contamination
4.1.1. Statistics of the Cloud Cover Percentage

4.1.2. Visual Assessment of 8-Day, 16-Day and Monthly Composites

4.2. Consistency Assessment with WELD Products
4.2.1. Visual Assessment
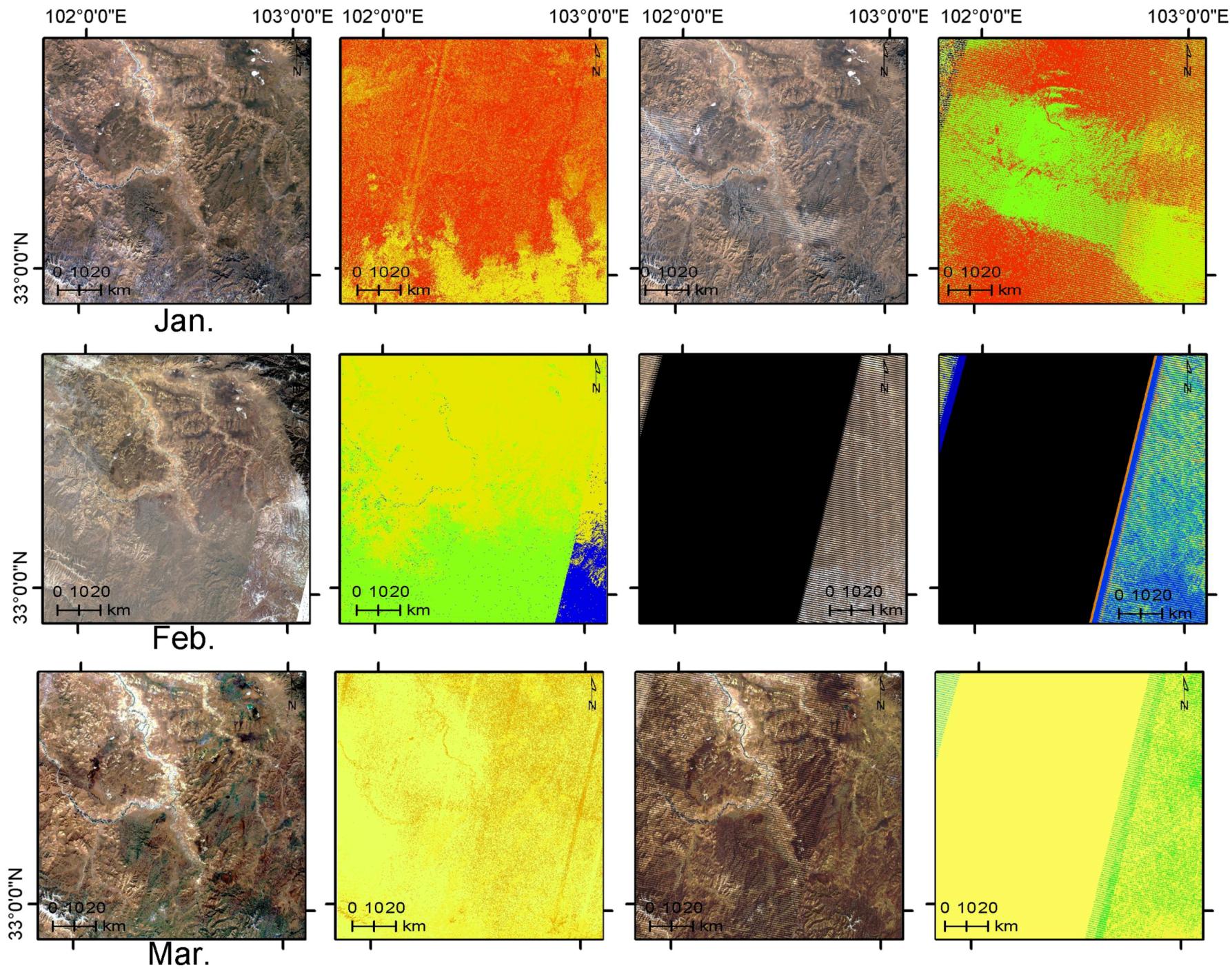


4.2.2. Radiometric Consistency Assessment

| Month | Slope | Intercept | R2 | RMSE | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | |
| January | 0.9329 | 0.9263 | 0.9274 | 1.0190 | −0.0128 | −0.0012 | −0.0039 | −0.0104 | 0.6956 | 0.7951 | 0.8173 | 0.8068 | 0.0227 | 0.0134 | 0.0196 | 0.0228 |
| February | 0.9595 | 0.9867 | 0.9503 | 1.0531 | −0.0001 | 0.0031 | 0.0059 | 0.0027 | 0.4972 | 0.6330 | 0.7267 | 0.7821 | 0.0114 | 0.0097 | 0.0113 | 0.0166 |
| March | 1.0314 | 1.0180 | 1.0737 | 1.1457 | −0.0185 | −0.0126 | −0.0184 | −0.0190 | 0.7040 | 0.7677 | 0.8254 | 0.8385 | 0.0173 | 0.0130 | 0.0135 | 0.0149 |
| April | 1.0246 | 1.0526 | 1.0289 | 1.0980 | −0.0134 | −0.0135 | −0.0018 | 0.0020 | 0.6168 | 0.6597 | 0.6745 | 0.7904 | 0.0304 | 0.0307 | 0.0309 | 0.0350 |
| May | 0.7735 | 0.9091 | 0.8788 | 1.0722 | 0.0336 | 0.0143 | 0.0195 | 0.0100 | 0.2663 | 0.3191 | 0.3759 | 0.4892 | 0.0179 | 0.0191 | 0.0393 | 0.0313 |
| June | 0.6218 | 0.5322 | 0.7231 | 1.1764 | 0.0323 | 0.0365 | 0.0123 | −0.0895 | 0.0614 | 0.0931 | 0.0593 | 0.2739 | 0.0245 | 0.0247 | 0.0462 | 0.0986 |
| July | 1.4133 | 1.2928 | 1.1291 | 1.3420 | −0.0199 | −0.0093 | −0.0004 | −0.0182 | 0.1611 | 0.2501 | 0.3141 | 0.6871 | 0.0144 | 0.0185 | 0.0153 | 0.0736 |
| August | 1.1458 | 1.2125 | 0.9821 | 1.2190 | −0.0148 | −0.0121 | −0.0102 | −0.0146 | 0.1663 | 0.2453 | 0.3638 | 0.6977 | 0.0130 | 0.0147 | 0.0139 | 0.0554 |
| September | 1.1714 | 1.1486 | 1.1628 | 1.2810 | −0.0005 | 0.0042 | −0.0005 | −0.0181 | 0.4329 | 0.6105 | 0.7026 | 0.7141 | 0.0105 | 0.0167 | 0.0117 | 0.0534 |
| October | 1.0268 | 1.0163 | 1.1754 | 1.1680 | −0.0006 | 0.0053 | −0.0021 | −0.0201 | 0.4105 | 0.6392 | 0.6733 | 0.7433 | 0.0176 | 0.0199 | 0.0239 | 0.0362 |
| November | 0.8766 | 0.8358 | 1.0236 | 1.0781 | 0.0039 | 0.0145 | −0.0017 | −0.0056 | 0.4983 | 0.5373 | 0.6724 | 0.6993 | 0.0156 | 0.0159 | 0.0182 | 0.0260 |
| December | 0.7742 | 0.9038 | 0.9221 | 1.0665 | 0.0044 | −0.0081 | 0.0002 | −0.0100 | 0.5759 | 0.7131 | 0.7963 | 0.7984 | 0.0292 | 0.0227 | 0.0175 | 0.0137 |
| Mean | 0.9793 | 0.9862 | 0.9981 | 1.1433 | −0.0005 | 0.0018 | −0.0001 | −0.0159 | 0.4239 | 0.5219 | 0.5835 | 0.6934 | 0.0187 | 0.0183 | 0.0218 | 0.0398 |

4.2.3. Temporal Profile

4.3. Consistency Assessment with MODIS Products
4.3.1. Comparison with 8-Day MODIS Reflectance Product

4.3.2. Comparison with 16-Day MODIS NDVI Product

5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Justice, C.O.; Vermote, E.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Defries, R.; Roy, D.P.; Hall, D.K.; Salomonson, V.V.; Privette, J.L.; Riggs, G.; Strahler, A.; et al. The moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS): Land remote sensing for global change research. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1228–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanre, D.; Holben, B.N.; Kaufman, Y.J. Atmospheric correction against algorithm for NOAA-AVHRR products: Theory and application. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, A.; Bian, J.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Z. A synergetic algorithm for mid-morning land surface soil and vegetation temperatures estimation using MSG-SEVIRI products and TERRA-MODIS products. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2213–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, X.; Masek, J.G. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions. Remote Sens Environ. 2010, 114, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Q.; Coward, S.N.; Masek, J.G.; Thomas, N.; Zhu, Z.L.; Vogelmann, J.E. An automated approach for reconstructing recent forest disturbance history using dense Landsat time series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Huang, C.; Sun, G.; Shi, H.; Toney, C.; Zhu, Z.L.; Rollins, M.; Goward, S.; Masek, J. Modeling the height of young forests regenerating from recent disturbances in Mississippi using Landsat and ICESat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, J.O.; Song, X.-P.; Feng, M.; Noojipady, P.; Anand, A.; Huang, C.; Kim, D.-H.; Collins, K.M.; Channan, S.; DiMiceli, C. Global, 30-m resolution continuous fields of tree cover: Landsat-based rescaling of MODIS vegetation continuous fields with Lidar-based estimates of error. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 427–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, E.A.; Wallace, J.F.; Caccetta, P.A.; Furby, S.L.; Zdunic, K. Forest cover trends from time series Landsat data for the Australian continent. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. 2013, 21, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Lei, G.; Zhang, Z.; Bian, J.; Deng, W. China land cover monitoring in mountainous regions by remote sensing technology—Taking the southwestern China as a case. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2014), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 4216–4219.
- Townshend, J.R.G.; Justice, C.O. Selecting the spatial-resolution of satellite sensors required for global monitoring of land transformations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 187–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Hobart, G.W.; Luther, J.E.; Hermosilla, T.; Griffiths, P.; Coops, N.C.; Hall, R.J.; Hostert, P.; Dyk, A.; et al. Pixel-based image compositing for large-area dense time series applications and science. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Trishchenko, A.P.; Khlopenkov, K.V. Developing clear-sky, cloud and cloud shadow mask for producing clear-sky composites at 250-meter spatial resolution for the seven MODIS land bands over Canada and north America. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4167–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, Q.; Zheng, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. Missing information reconstruction of remote sensing data: A technical review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.C.; Kline, K.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Kovalskyy, V.; Hansen, M.; Loveland, T.R.; Vermote, E.; Zhang, C.S. Web-Enabled Landsat Data (WELD): Landsat ETM plus composited mosaics of the conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.V.; Turubanova, S.A.; Hansen, M.C.; Adusei, B.; Broich, M.; Altstatt, A.; Mane, L.; Justice, C.O. Quantifying forest cover loss in democratic republic of the congo, 2000–2010, with Landsat ETM plus data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, N. Seasonal composite Landsat TM/ETM plus images using the medoid (a multi-dimensional median). Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6481–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalskyy, V.; Roy, D.P. The global availability of Landsat 5 TM and Landsat 7 ETM+ land surface observations and implications for global 30m Landsat data product generation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; van der Linden, S.; Kuemmerle, T.; Hostert, P. Pixel-based Landsat compositing algorithm for large area land cover mapping. IEEE J-STARS 2013, 6, 2088–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Roy, D. Automated crop field extraction from multi-temporal web enabled Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 42–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Egorov, A.; Potapov, P.V.; Stehman, S.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Turubanova, S.A.; Roy, D.P.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; Ju, J.; et al. Monitoring conterminous United States (CONUS) land cover change with web-enabled Landsat data (WELD). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Roy, D.P. Improved time series land cover classification by missing-observation-adaptive nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, B. Aerosol optical depth retrieval by HJ-1/CCD supported by MODIS surface reflectance data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Qiu, F.; Zhao, X. Atmospheric correction of HJ-1A/B CCD images over Chinese coastal waters using MODIS-TERRA aerosol data. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Li, Q.; Li, J. Chinese HJ-1A/B satellites and data characteristics. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Jin, H.; Lei, G.; Huang, C.; Li, M. Auto-registration and orthorectification algorithm for the time series HJ-1A/B CCD images. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 754–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cui, T.W.; Qiu, Z.F.; Lin, C.S. A three-band semi-analytical model for deriving total suspended sediment concentration from HJ-1A/CCD data in turbid coastal waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Jin, H.; Zhao, W.; Lei, G.; Huang, C. Multi-temporal cloud and snow detection algorithm for the HJ-1A/B CCD imagery of China. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2014), Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 501–504.
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Deng, W. Estimation and analysis of net primary productivity of Ruoergai wetland in China for the recent 10 years based on remote sensing. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z.C.; Zhao, W.W. Holocene vegetation and climate histories in the eastern Tibetan plateau: Controls by insolation-driven temperature or monsoon-derived precipitation changes? Quat. Sci. Rev. 2011, 30, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Bian, J.; Lei, G.; Huang, C. Estimating the maximal light use efficiency for different vegetation through CASA model combined with time-series remote sensing data and ground measurements. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3857–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.L.; Wu, B.F.; Yan, N.N.; Wang, H. Water body mapping method with hj-1a/b satellite imagery. Int. J. Earth Obs. 2011, 13, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Centre for Resources Satellite Data and Application. Available online: http://www.Cresda.Com/site2/satellite/7117.Shtml (accessed on 1 September 2015).
- Zhao, Z.; Li, A.; Bian, J.; Huang, C. An improved ddv method to retrieve aot for HJ CCD image in typical mountainous areas. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2015, 35, 1479–1487. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, R.E.; Nishihama, M.; Fleig, A.J.; Kuyper, J.A.; Roy, D.P.; Storey, J.C.; Patt, F.S. Achieving sub-pixel geolocation accuracy in support of MODIS land science. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, G.; Huang, C.Q.; Chander, G.; Noojipady, P.; Masek, J.G. Assessment of the NASA-USGS Global Land Survey (GLS) datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, A.; Huang, C. Cloud and snow discrimination for CCD images of HJ-1A/B constellation based on spectral signature and spatio-temporal context. Remote Sens. 2015. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Chova, L.; Camps-Valls, G.; Calpe-Maravilla, J.; Guanter, L.; Moreno, J. Cloud-screening algorithm for envisat/meris multispectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2007, 45, 4105–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guindon, B.; Cihlar, J. An image transform to characterize and compensate for spatial variations in thin cloud contamination of landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, L.J.; Jackson, A.A.; Zook, H.A.; Kessler, D.J. Analysis of orbital perturbations acting on objects in orbits near geosynchronous earth orbit. J. Geophys. Res. Planet 1992, 97, 3845–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Bai, Z.; Tang, T.; Yu, G. Orbit maintenance technology and implement for HJ-1A/B constellation. Chinese Space Science and Technology 2012, 5, 69–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Van Leeuwen, W.J.D.; Huete, A.R.; Laing, T.W. MODIS vegetation index compositing approach: A prototype with AVHRR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 69, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walthall, C.L.; Norman, J.M.; Welles, J.M.; Campbell, G.; Blad, B.L. Simple equation to approximate the bidirectional reflectance from vegetative canopies and bare soil surfaces. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USGS National Center for Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS). Available online: http://globalweld.cr.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 1 September 2015).
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D. Atmospherically Resistant Vegetation Index (ARVI) for EOS-MODIS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Sexton, J.O.; Huang, C.; Masek, J.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Gao, F.; Narasimhan, R.; Channan, S.; Wolfe, R.E.; Townshend, J.R. Global surface reflectance products from Landsat: Assessment using coincident MODIS observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, X.L.; Vogelmann, J.E.; Gao, F.; Jin, S.M. A simple and effective method for filling gaps in Landsat ETM plus SLC-off images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psomas, A.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Kneubühler, M.; Kellenberger, T.; Itten, A.K. Seasonal variability in spectral reflectance for discriminating grasslands along a dry-mesic gradient in Switzerland. In Proceedings of the 4th EARSEL Workshop on Imaging Spectroscopy, Warsaw, Poland; 2005; pp. 709–722. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.P.; Qin, Y.; Kovalskyy, V.; Vermote, E.F.; Ju, J.; Egorov, A.; Hansen, M.C.; Kommareddy, I.; Yan, L. Conterminous united states demonstration and characterization of MODIS-based Landsat ETM+ atmospheric correction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trishchenko, A.P.; Cihlar, J.; Li, Z.Q. Effects of spectral response function on surface reflectance and NDVI measured with moderate resolution satellite sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsamo, A.; Chen, J.M. Spectral response function comparability among 21 satellite sensors for vegetation monitoring. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1319–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagolle, O.; Lobo, A.; Maisongrande, P.; Cabot, F.; Duchemin, B.; De Pereyra, A. Quality assessment and improvement of temporally composited products of remotely sensed imagery by combination of vegetation 1 and 2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Jupp, D.L.; Thankappan, M.; Lymburner, L.; Mueller, N.; Lewis, A.; Held, A. A physics-based atmospheric and BRDF correction for Landsat data over mountainous terrain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 756–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, N. Testing the local applicability of MODIS BRDF parameters for correcting landsat TM imagery. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, Q.; Bian, J.; Lei, G. An improved physics-based model for topographic correction of Landsat TM images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6296–6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, A.; Bian, J.; Guo, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, W.; Huang, C. Automatic detection of the DDV pixels from VIS-NIR images in typical mountainous areas. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2015, 30, 58–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Liang, S.; Townshend, J.R.; Dodson, Z.M. Assessment of the radiometric performance of Chinese HJ-1 satellite ccd instruments. IEEE J-STARS 2013, 6, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, G.; Kang, Q.; Wu, D. Radioactive quality evaluation and cross validation of data from the HJ-1A/B satellites’ CCD sensors. Sensors 2013, 13, 8564–8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Tian, L.; Feng, L. Tracking radiometric responsivity of optical sensors without on-board calibration systems-case of the Chinese HJ-1A/B CCD sensors. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 1829–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalskyy, V.; Roy, D.P.; Zhang, X.; Ju, J.C. The suitability of multi-temporal web-enabled landsat data NDVI for phenological monitoring—A comparison with flux tower and MODIS NDVI. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, T.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Hobart, G.W. Regional detection, characterization, and attribution of annual forest change from 1984 to 2012 using Landsat-derived time-series metrics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Baysal, O.; Kauffmann, P. Current status and future tendency of sensors in earth observing satellites. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.222.3589&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 1 September 2015).
- Sandau, R. Status and trends of small satellite missions for earth observation. Acta Astronaut. 2010, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalskyy, V.; Roy, D. A one year Landsat 8 conterminous United States study of cirrus and non-cirrus clouds. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Hilker, T.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Masek, J.G.; Pflugmacher, D.; Crevier, Y. Virtual constellations for global terrestrial monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanonckelen, S.; Lhermitte, S.; Van Rompaey, A. The effect of atmospheric and topographic correction on pixel-based image composites: Improved forest cover detection in mountain environments. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2015, 35, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, J.; Li, A.; Wang, Q.; Huang, C. Development of Dense Time Series 30-m Image Products from the Chinese HJ-1A/B Constellation: A Case Study in Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16647-16671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215846
Bian J, Li A, Wang Q, Huang C. Development of Dense Time Series 30-m Image Products from the Chinese HJ-1A/B Constellation: A Case Study in Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(12):16647-16671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215846
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Jinhu, Ainong Li, Qingfang Wang, and Chengquan Huang. 2015. "Development of Dense Time Series 30-m Image Products from the Chinese HJ-1A/B Constellation: A Case Study in Zoige Plateau, China" Remote Sensing 7, no. 12: 16647-16671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215846
APA StyleBian, J., Li, A., Wang, Q., & Huang, C. (2015). Development of Dense Time Series 30-m Image Products from the Chinese HJ-1A/B Constellation: A Case Study in Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sensing, 7(12), 16647-16671. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215846








