Abstract
Understanding environmental controls on vegetation spring onset (SO) in the Tibetan Plateau (TP) is crucial to diagnosing regional ecosystem responses to climate change. We investigated environmental controls on the SO of the TP grasslands using satellite vegetation index (VI) from the 3rd Global Inventory Modeling and Mapping Studies (GIMMS3g) product, with in situ air temperature (Ta) and precipitation (Prcp) measurement records from 1982 to 2008. The SO was determined using a dynamic threshold method based on a 25% threshold of seasonal VI amplitude. We find that SO shows overall close associations with spring Ta, but is also subject to regulation from spring precipitation. In relatively dry but increasingly wetting (0.50 mm·year−1, p < 0.10) grasslands (mean spring Prcp = 22.8 mm; Ta = −3.27 °C), more precipitation tends to advance SO (−0.146 day·mm−1, p = 0.150) before the mid-1990s, but delays SO (0.110 day·mm−1, p = 0.108) over the latter record attributed to lower solar radiation and cooler temperatures associated with Prcp increases in recent years. In contrast, in relatively humid TP grasslands (73.0 mm; −3.51 °C), more precipitation delays SO (0.036 day·mm−1, p = 0.165) despite regional warming (0.045 °C·year−1, p < 0.05); the SO also shows a delaying response to a standardized drought index (mean R = 0.266), indicating a low energy constraint to vegetation onset. Our results highlight the importance of surface moisture status in regulating the phenological response of alpine grasslands to climate warming.
1. Introduction
The Tibetan Plateau (TP) has been experiencing intensive climate changes during the last half century [1,2], which have exerted significant influences on local ecosystems [3,4,5], and interactive with regional and continental climate feedbacks [6]. Vegetation phenology is regarded as a sensitive climate change indicator [4,7,8,9,10,11,12]. Understanding spatial and temporal variations of vegetation spring onset (SO) may reveal underlying mechanisms driving regional phenological responses to ongoing climate change. Better knowledge of environmental controls on vegetation phenology over the TP is crucial for projecting regional ecosystem responses to future climate conditions and potential feedbacks.
With a mean elevation of approximately 4000 m above sea level, the TP ecosystems show characteristically different phenological responses to climate change compared with other temperate and boreal ecosystems [6,8,10,13,14,15]. Spring phenology in the TP grasslands is strongly responsive to temperature changes, especially at higher elevations [16]. The local surrounding mountains inhibit oceanic air masses from reaching the TP hinterland [2]. Therefore, most TP areas have a characteristic cold and dry climate [6,17], and the TP grasslands are exposed to climatic extremes involving both temperature and water stresses. Because of the closely coupled surface processes of heat and water exchanges, warming may have diverse effects on the TP ecosystems [13]. Warming air temperatures may not only relieve cold temperature constraints to vegetation activity in spring [5,18], but also advance surface soil thawing [19,20,21], which may exacerbate soil water deficits and drought stress due to increasing water loss through evapotranspiration [22]. Therefore, environmental variables for air temperature and precipitation are interactive in affecting the spring phenology of the TP ecosystems [8,13,16,18,23] and should be studied together when investigating underlying mechanisms controlling climatic responses of the TP grasslands.
Understanding how environmental factors regulate spring phenology of the TP grasslands and how spring phenology, in turn, responds to climate change is still limited. There has been extensive debate on whether climate warming has advanced or delayed the spring onset of the TP grasslands during the past several decades based on satellite observations (e.g., [3,4,5,8,13,15,16]). Spring warming is widely regarded as the main driver of spring phenology changes over the TP grasslands [3,5,15,16,23,24]. The green-up of the TP grasslands is reported to advance at the rate of 5 days per 1 °C rise in air temperature [16], more intensively than European ecosystems have responded [10]. However, the available satellite records do not show a consistent advancing trend in spring onset despite continuous warming [5,13,25], which may reflect additional environmental factors (such as precipitation) affecting vegetation green-up [13,26].
Precipitation has been identified as a potential regulating factor on spring phenology of the TP ecosystems [15,27], but a detailed investigation of precipitation effects on the TP grasslands is still absent. More recently, precipitation was found to regulate the temperature sensitivity of spring phenology in the TP grasslands from 2000 to 2012 [26]. However, phenology observations in the TP grasslands indicate a temporal shift around the mid-1990s [23,28] leading to questions regarding how the environmental controls on spring phenology may vary with changing climate trends. A general delay in spring onset from the mid-1990s into the current decade is likely caused by a cooling trend in spring air temperature [23,29]. Therefore, in this study we used satellite-based vegetation greenness observations with in situ meteorological station measurements to explore co-variations between vegetation green-up and environmental variables over the TP grasslands during the past three decades. Due to inconsistencies in spring onset trends derived from the different satellite vegetation index (VI) datasets (e.g., [5,15,20]), we focused on analyzing inter-annual variations of SO and underlying environmental controls, which have larger characteristic variability and signal-to-noise, relative to long-term SO trends that are subject to larger uncertainty. Our main objectives were to (1) identify and investigate the predominant environmental controls affecting spring phenology of the TP grasslands from 1982 to 2008 using satellite observations and in situ meteorological measurements, and (2) quantify the spatial and temporal variations in vegetation spring phenology in response to varying climate trends.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Tibetan Plateau extends from 26.5–39.5°N and 78.5–103.0°E in Southwest China at an average elevation of approximately 4000 m above sea level (Figure 1a), and is characterized by a cold and dry climate [1,21]. The monthly mean air temperature over most TP regions varies between −10 °C and 10 °C [1,30], while the regional precipitation regime follows a northwesterly gradient of declining precipitation mainly affected by the Indian Ocean Monsoon [1,2]. The TP interior is dominated by alpine meadow, steppe and desert grasslands depending on local temperature and moisture conditions [30], while alpine forests and shrublands are found in surrounding mountains with more abundant precipitation [24,31,32].
As the spring onset of grasslands is more sensitive to climate change than that of forests and shrubs in the TP [33], we chose the Tibetan grasslands as our study area as delineated according to the China Vegetation Map [34] (Figure 1b). Over 80% of the study area (4592 ± 510 m) ranges between 4300 and 5000 m in elevation, and ecosystems within this elevation zone likely experience an earlier green-up of 6–8 days in response to a 1 °C rise in May air temperatures [16]. In-situ observations have documented different spring leaf-out dates between the TP meadow and steppe grasslands [35], so we divided the study domain into three sub-areas based on regional eco-geographic attributes [30]. Among the three eco-zones examined, Zone-3 is the warmest with a mean annual air temperature (Ta) of −1.07 °C, followed by Zone-2 (−3.83 °C) and Zone-1 (−4.67 °C). Zone-2 has the largest annual precipitation (483 mm) followed by Zone-3 (254 mm) and Zone-1 (206 mm). Therefore, we also analyzed how precipitation may influence the temperature sensitivity of spring phenology by comparing the effects of precipitation on SO in different eco-zones. Zone-1 is dominated by alpine steppe, while alpine meadow is mainly distributed in the relatively humid Zone-2 area (Figure 1b and Table 1). Zone-3 is covered by both alpine meadow and steppe dependent on local soil water conditions. With extremely high elevation (5000 m on average) and low precipitation (125 mm·year−1), the northwest area of Zone-1 is very cold and dry, and mainly covered by alpine desert with sparse vegetation. Grid cells with mean satellite observation based Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) values during the active season (from June to September) lower than 0.10 were screened to exclude barren and sparsely vegetated areas from the analysis.

Figure 1.
Terrain (a) and vegetation cover (b) of the Tibetan Plateau. Black points in panel (a) denote weather stations used in the study (Zones 1, 2 and 3). The dashed gray line indicates the boundary of the study area, which is divided into three regions based on Zheng et al. [30] and the China Vegetation Map [34]. The black triangles denote the locations of two weather stations used for detailed analysis of co-variation between climate variables and spring onset in this study.

Table 1.
Multi-year means and trends of spring (MAM) environmental variables in the TP grasslands for the 1982–2008 record and two sub-periods (1982–1995 and 1996–2008). Environmental variables include spring air temperature (Ta), precipitation (Prcp), Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI).
| Region | Period | Ta | Prcp | SPEI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (°C) | Trend (°C·year−1) | Mean ± SD (mm) | Trend (mm·year−1) | Mean ± SD | Trend (year−1) | ||
| Zone-1 | 1982–2008 | −3.27 ± 0.87 | 0.047 ** | 22.8 ± 11.1 | 0.50 * | 0.035 ± 0.486 | −0.003 * |
| 1982–1995 | −3.49 ± 0.82 | 0.066 ** | 18.4 ± 8.9 | −0.68 * | −0.004 ± 0.476 | −0.057 ** | |
| 1996–2008 | −2.96 ± 0.81 | 0.038 * | 27.4 ± 11.3 | 1.01 ** | 0.077 ± 0.494 | 0.001 ** | |
| Zone-2 | 1982–2008 | −3.51 ± 0.77 | 0.045 ** | 73.0 ± 11.5 | −0.06 | 0.081 ± 0.426 | −0.016 * |
| 1982–1995 | −3.80 ± 0.64 | 0.054 * | 71.9 ± 2.6 | −0.79 * | 0.128 ± 0.405 | −0.037 ** | |
| 1996–2008 | −3.16 ± 0.77 | 0.039 | 73.8 ± 10.1 | −0.67 | 0.022 ± 0.441 | −0.049 * | |
| Zone-3 | 1982–2008 | −2.18 ± 0.80 | 0.073 ** | 69.6 ± 16.7 | −0.92 ** | 0.065 ± 0.475 | −0.039 ** |
| 1982–1995 | −2.61 ± 0.63 | 0.062 ** | 74.6 ± 17.2 | −2.08 ** | 0.280 ± 0.412 | −0.058 ** | |
| 1996–2008 | −1.61 ± 0.58 | 0.035 | 65.1 ± 14.9 | −1.23 | −0.167 ± 0.431 | −0.056 * | |
Note: Trend significance denoted at * p < 0.10 and ** p < 0.05; SD is the standard deviation.
2.2. Datasets
We mainly used satellite NDVI records from the third generation Global Inventory Modeling and Mapping Studies (GIMMS3g) dataset for detecting vegetation spring onset from 1982 to 2008. The NDVI is sensitive to the cover density of green vegetation due to the differences in reflectance sensitivity to chlorophyll between near-infrared and red spectra [36]. Therefore, NDVI time series have been widely used to characterize vegetation development at different stages, including onset, peak and offset of the growing season [4,37,38,39]. The GIMMS3g dataset was assembled from different NOAA Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) records accounting for various deleterious effects including calibration loss, orbital drift, inter-sensor inconsistency and volcanic eruptions [40]. Although there may still exist uncertainties in this long-term NDVI dataset [41], the GIMMS3g dataset has been successfully used to analyze vegetation spring phenology over large regions [42,43]. The GIMMS3g product has a spatial resolution of 8 km and 15-day temporal fidelity. The TP has limited snowfall during winter and spring in most areas [44], so the NDVI time series are less influenced by snow cover than the northern high latitudes [45].
To examine the trends and variability of environmental conditions affecting spring onset over the TP grasslands, we used both in situ and gridded meteorological data from the China Meteorology Administration [46]. The gridded dataset is derived at half-degree resolution by interpolating in situ air temperature and precipitation observations using the thin plate spline method [46]. As it utilizes the most extensive weather stations currently available over China, at both national (756 sites) and regional (1691 sites) levels, this dataset provides the best estimation of climate available over the TP despite remaining uncertainty due to sparse weather stations (Figure 1a; [46]). Therefore, the northwest TP was completely excluded from our study domain due to extremely sparse in situ meteorological observations in this area. We also used the in situ weather station observations to examine climatic controls on spring onset at the local site level. As soil water conditions likely regulate vegetation green-up in the Tibetan Plateau [26], we used the difference between in situ surface ground (0 cm) and air temperature measurements (T-diff) at the weather stations as an indicator of soil water conditions [47], and investigated the co-variation of this variable with spring onset defined from collocated satellite NDVI observations. Surface temperature (0 cm) at the weather stations is measured using an earth thermometer with each half of its bulb located in air and below the soil surface in an area with bare, loose soil not covered by vegetation [46].
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Satellite Data Analysis
Vegetation spring onset over the TP grasslands was detected from the satellite NDVI data using a dynamic threshold method. We examined spring onset using different thresholds of 15%, 20%, 25%, 30% and 40% of the seasonal NDVI amplitude averaged for the whole study period based on a pixel-wise analysis [15,48], and the results indicated negligible differences in correlations between the environmental variables and the spring onset derived using different thresholds. This is consistent with previous studies indicating that the discrepancies in spring onset are mainly due to sensor differences rather than data extraction methods (e.g., [5,15]). Therefore, we selected a single consistent 25% threshold of the multi-year averaged seasonal NDVI amplitude to define the spring onset in our analysis. Before onset detection, the NDVI time series were filtered using the double logistic method to remove outliers and fill data gaps [48]. In addition, pixels with spring onset dates occurring beyond the May–June period were excluded to limit the influence of data uncertainty on the phenology analyses. About 45% of grid cells in the study area were screened out during the analysis; these areas were predominantly located in the northwest TP, with annual precipitation below 100 mm [30].
Although the GIMMS3g NDVI record has been widely used for detecting long-term vegetation changes (e.g., [13,40,49]), large uncertainties may still remain in this dataset (e.g., [3,5]). Therefore, we compared alternative spring onset series derived from GIMMS3g and two other widely-used satellite NDVI datasets, including the Systeme Pour l’observation de la Terre (SPOT) sensor record extending from 1998 to 2012 [50] and Moderate resolution Imaging Spectrotradiometer (MODIS) record extending from 2000 to 2012 [51]. The three NDVI datasets produced generally consistent inter-annual variations in vegetation spring onset over the TP grasslands, despite differences in spring onset trends for the overlapping record (2000–2008). The inter-annual variations in spring onset series derived from the three NDVI datasets were favorably correlated (R > 0.53) over most (>80%) of the study domain. Moreover, the three NDVI datasets showed similar correlation patterns between spring onset and the environmental variables. Therefore, we used the GIMMS3g NDVI dataset to investigate inter-annual variations in vegetation green-up and linkages with underlying environmental control factors instead of evaluating long-term temporal trends in these data. A sharp rise in the NDVI record was observed over the TP in the latter portion (2009 to 2011) of the GIMMS3g record, which has been reported in previous studies [13,15] and may reflect greater uncertainty in the recent NDVI record. We therefore excluded the GIMMS3g data for this period and limited our analysis to the 1982–2008 record.
As vegetation green-up trends derived from different satellite NDVI datasets may be inconsistent [3,13,18,27] and even contradictory [5,25], we detrended all data time series prior to the correlation analysis to mitigate potential impacts from inconsistent temporal trends. For each time series, we first estimated the temporal trend (from 1982 to 2008) using linear regression analysis. Significance of the trends was tested using a non-parametric Mann-Kendall trend detection method, and significant (p < 0.1) trends were removed from the raw time series prior to the correlation analysis. In addition, in situ climate and phenology conditions over the TP areas were reported to experience a temporal shift in the mid-1990s [23,28], and our analysis of the correlations between spring onset and environmental variables using an 11-year moving-window also indicated a temporal shift of the apparent air temperature control on spring onset after the mid-1990s. The surface temperature observations showed a strong warming trend (>0.054 °C·year−1, p < 0.10) before 1995, with a weaker trend over the more recent record (<0.039 °C·year−1). Therefore, we analyzed the climatic control on spring phenology during two sub-periods reflecting earlier (1982–1995) and latter (1996–2008) portions of the study record to investigate potential shifts in relative climatic control factors influencing spring phenology due to changing climate trends.
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
We analyzed correlations between satellite-derived spring onset and selected environmental indicators, including surface air temperature, precipitation and a standardized precipitation and evapotranspiration index (SPEI) in spring (from March to May, MAM). The SPEI is derived as the difference between total precipitation and potential evapotranspiration (PET), where smaller SPEI values denote stronger soil water deficits, which could reflect variations in surface moisture status induced by both changes in precipitation and air temperature [52]. The advantage of the SPEI over most widely used moisture indices is that it can identify surface water conditions of different durations due to its varying temporal scale characteristics [52]. Following Vicente-Serrano et al. (2009), we used the Thornthwaite approach to calculate the PET component of the SPEI. The Thornthwaite approach uses day length and mean air temperature data to calculate PET [53]. This approach is relatively flexible [52,53] with fewer data requirements than other PET estimation approaches, which provides advantages in the Tibetan Plateau which has very limited in situ surface meteorology observations. As the growing season of the TP grasslands generally starts around May [5,25,35,54], we used the period from March to May to represent pre-season climate conditions for spring onset. The use of partial correlation analysis allows for distinguishing phenological effects from individual environmental variables while accounting for the interactive effects of other contributing variables. Therefore, partial correlation analysis was used to evaluate the link between spring onset and air temperature (or precipitation) while accounting for co-variation among these climate variables. Pearson correlation analysis was also used to examine relationships between spring onset and the SPEI.
We conducted a grid cell-wise analysis and then averaged the resulting statistics across all grid cells within each TP zone. To detect temporal variations in climatic controls on spring phenology at the site level, we used an 11-year moving-window to detect potential temporal shifts among the correlations between vegetation spring onset from the satellite NDVI observations and collocated environmental factors defined from in situ observations from 1982 to 2008 at two selected weather stations, i.e., Shenzha (Zone-1, steppe) and Qumarleb (Zone-2, meadow), as shown in Figure 1a. Shenzha (−0.05 ± 0.85 °C) and Qumarleb (−0.98 ± 0.91 °C) sites have similar spring air temperatures but contrasting precipitation regimes (24.9 ± 16.7 mm and 56.5 ± 17.1 mm, respectively).
3. Results
3.1. Variations in Environmental Indicators
The in situ climate observations indicated distinct changes in both air temperature and precipitation over the TP grasslands from 1982 to 2008. Strong spring warming (0.045 °C·year−1, p < 0.05) was observed over almost the entire study domain (Table 1), while Zone-3 and western Zone-1 areas showed particularly intensive warming (0.056 °C·year−1, p < 0.05). At the same time, the TP experienced a spatially varying trend in spring precipitation (Table 1), including strong increases in southeast Zone-1 and western Zone-2 areas (>0.80 mm·year−1, p < 0.10), and distinct decreases in northwest Zone-2 and eastern Zone-3 areas (<−1.00 mm·year−1, p < 0.10). In response to changes in air temperature and precipitation, the SPEI showed a general decrease in most areas of the domain (Table 1), especially in northeast Zone-2 and eastern Zone-3 areas (−0.042 year−1, p < 0.10), except for a slight increase (0.01 year−1, p < 0.10) in the southeast of Zone-1. These results reflect a general increase in the spring water deficit in most areas of the study domain (except for the southeast Zone-1) mainly due to a precipitation decrease.
The in situ observations also showed a significant temporal shift in spring air temperature and precipitation trends in the mid-1990s (Figure 2 and Table 1). Generally, the study area experienced a spatially uniform spring warming trend (Figure 2a: 0.060 °C·year−1, p < 0.10) during the initial sub-period (1982–1995), but reduced warming (Figure 2b: 0.035 °C·year−1, p = 0.11) during the later sub-period (1996–2008) except for eastern Zone-1 and southwest Zone-2 areas (Figure 2b). Similarly, almost the entire study area showed a declining trend in spring precipitation during the initial sub-period (−0.70 mm·year−1, p < 0.10) (Figure 2c and Table 1), while during the later sub-period the precipitation trend varied spatially (Figure 2d and Table 1), including a strong wetting trend in Zone-1 (1.01 mm·year−1, p < 0.05) and a drying trend in Zone-3 (−1.23 mm·year−1, p < 0.05). Generally, the SPEI trend followed the spatial patterns of spring precipitation throughout the study period (Figure 2e,f). In the areas with increasing pre-season precipitation and spring warming (e.g., in Zone 1), the SPEI result indicated less water stress in the later sub-period, while in the areas with a strong warming trend but no significant precipitation increase (e.g., in Zones 2 and 3), a strong declining trend in SPEI indicated an increasing water deficit over the study period.
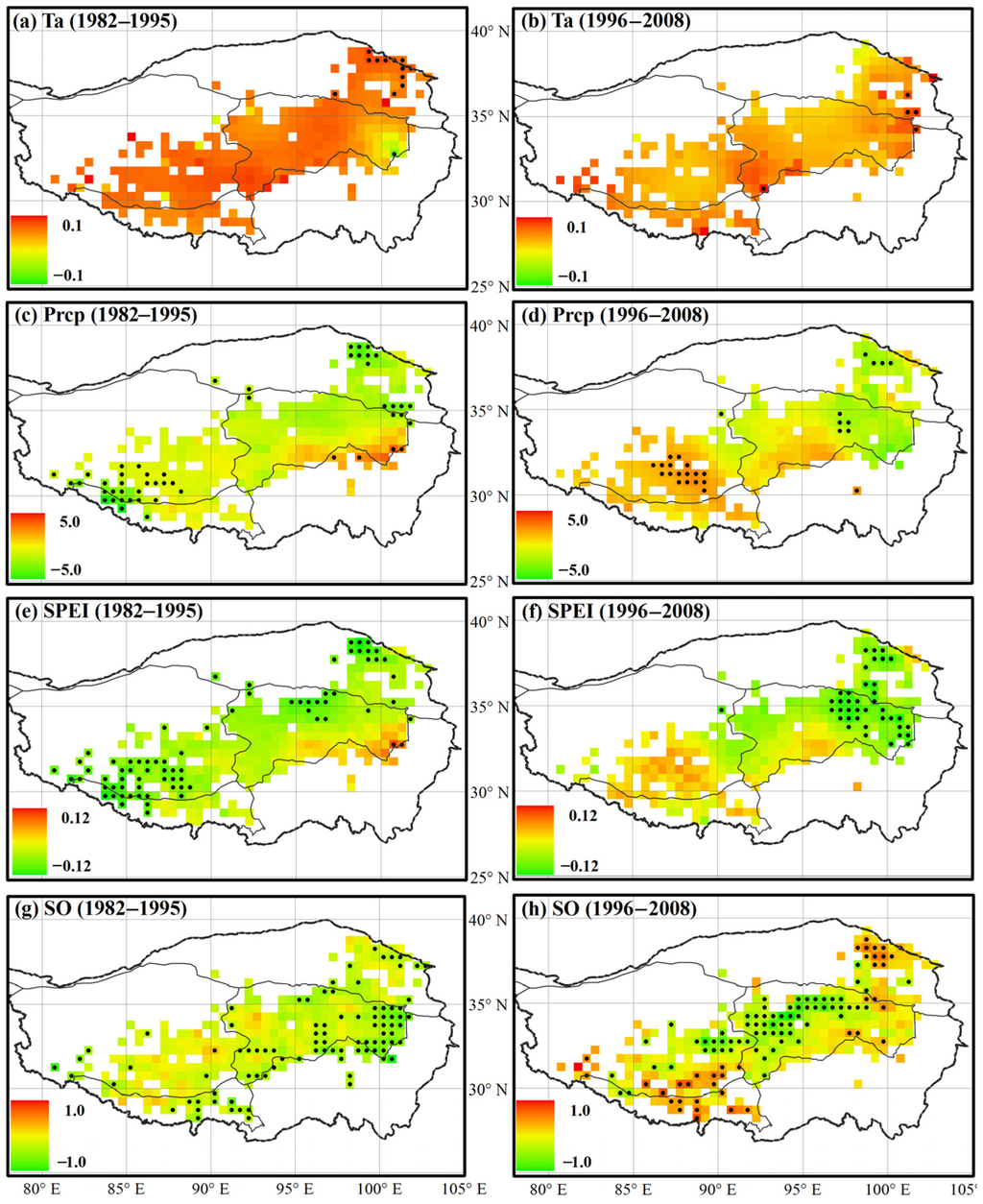
Figure 2.
Trends in spring (MAM) air temperature (Ta, °C·year−1; (a,b)), precipitation (Prcp, mm·year−1; (c,d)), SPEI (year−1; (e,f)) and GIMMS3g NDVI-derived spring onset (SO, day·year−1; (g,h)) during the two sub-periods, respectively. Grid cells with black dots denote trends at the 90% (p < 0.1) significance level, while cells without black dots have non-significant trends (p > 0.1).
The in situ observations at the weather stations showed a general increase in the temperature difference between surface ground (0 cm) and air in spring (Figure 3a,c). Consistent with an increasing water deficit indicated by the spring SPEI trend in most areas of Zone-2 and 3 (Figure 2e,f), we observed an overall increasing trend (0.034 °C·year−1, p < 0.05) in the difference between in-situ surface ground and air temperatures in spring during the 1996–2008 sub-period (Figure 3c). The increasing T-diff trend is likely caused by increasing evaporative water loss due to spring warming, since most of the study domain has a monsoon climate with precipitation mainly falling during summer [2] and almost no continuous snow cover during the dormant season [55]. These results indicate an increasing topsoil water deficit in this region especially during the later sub-period.

Figure 3.
Trends (°C·year−1) of the vertical temperature difference (T-diff) between spring (MAM) surface ground (0 cm) and air temperatures at in-situ weather stations, and correlations of GIMMS3g NDVI-derived SO versus T-diff respectively during the sub-periods of (a,b) 1982–1995 and (c,d) 1996–2008. In panels (a) and (c), the large colored dots indicate stations with increasing (in red) or decreasing (in blue) T-diff trends (p < 0.1), while small black dots denote non-significant trends. In panels (b) and (d), the red (blue) dots indicate weather stations with positive (negative) correlations between SO and T-diff, with correlation magnitude proportional to symbol size. Correlations were not computed for weather station locations that were sparsely vegetated or had a SO date beyond the May-June period (grey dots).
3.2. Variations in Spring Onset and Associated Climate Controls
Our results indicate an overall advancing effect of spring air temperature on vegetation spring onset from 1982 to 2008 over the TP grasslands, while spring precipitation showed an overall delaying influence on vegetation green-up except in Zone-3 (Table 2). However, in contrast to previous studies [5,15,16,18,44], our results show strong spatial and temporal heterogeneity in environmental controls on vegetation green-up of the TP grasslands, with a temporal shift in the environmental controls on SO after the mid-1990s in response to recent climate variability (Figure 4 and Figure 5). In the dry (mean spring Prcp = 22.8 mm) but increasingly wetting (0.50 mm·year−1, p < 0.10) Zone-1 grasslands, spring air temperature showed slightly (−0.043 day·°C−1, p > 0.10) and strongly (−0.967 day·°C−1, p < 0.10) advancing effects on vegetation green-up during the initial (Figure 4a) and later sub-periods (Figure 4b) respectively, while more spring precipitation tends to advance spring onset (−0.146 day·mm−1, p = 0.150) during the initial sub-period, but has a delaying effect on SO in the later sub-period likely due to lower solar radiation and cooler temperatures coinciding with recent precipitation increases (1.01 mm·year−1, p < 0.05; Figure 4c,d). In response to the increasing spring precipitation, the SPEI also showed a delaying influence on SO in the increasingly wetting Zone-1, especially during the later sub-period (Figure 4e,f). The frequency distributions of correlations between SO and the environmental variables (Figure 5) indicate changing climatic controls on spring phenology between the two sub-periods in the Zone-1 grasslands. In contrast, in the relatively humid (mean spring Prcp = 73.0 mm) Zone-2 (Table 1), spring precipitation showed a consistent delaying effect on SO (0.036 day·mm−1, p = 0.165) throughout the study period due to relatively abundant precipitation (Figure 4c,d). In this humid region, the SPEI showed a similar delaying impact on SO as precipitation (mean R = 0.266; Figure 4e,f). In the Zone-3 grasslands, a decreasing trend in spring precipitation (0.92 mm·year−1, p < 0.05) and the strong warming (0.073 °C·year−1, p < 0.05) resulted in a SO delay (0.119 day·year−1, p < 0.05) during the later sub-period.

Table 2.
Multi-year means of vegetation spring onset and associated correlations with the spring (MAM) environmental variables. The correlations are derived from regional means, and thus the statistical significance was not tested. All data series were detrended prior to the correlation analyses.
| Region | Period | Spring Onset | Mean Correlation with Spring Onset | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD (day of year) | Trend (day·year−1) | Ta Mean ± SD | Prcp Mean ± SD | SPEI Mean ± SD | ||
| Zone-1 | 1982–2008 | 141.6 ± 2.1 | −0.187 ** | −0.121 ± 0.206 | 0.044 ± 0.203 | 0.185 ± 0.207 |
| 1982–1995 | 143.0 ± 1.0 | −0.121 ** | −0.027 ± 0.287 | −0.085 ± 0.283 | 0.016 ± 0.345 | |
| 1996–2008 | 140.1 ± 1.7 | −0.015 * | −0.300 ± 0.294 | 0.157 ± 0.299 | 0.403 ± 0.190 | |
| Zone-2 | 1982–2008 | 139.6 ± 2.5 | −0.257 ** | −0.268 ± 0.218 | 0.149 ± 0.259 | 0.266 ± 0.234 |
| 1982–1995 | 141.3 ± 2.0 | −0.274 ** | −0.275 ± 0.263 | 0.211 ± 0.432 | 0.333 ± 0.362 | |
| 1996–2008 | 137.8 ± 1.5 | −0.207 * | −0.254 ± 0.377 | 0.125 ± 0.312 | 0.262 ± 0.348 | |
| Zone-3 | 1982–2008 | 140.4 ± 1.9 | −0.123 ** | −0.166 ± 0.163 | −0.099 ± 0.261 | −0.109 ± 0.248 |
| 1982–1995 | 141.2 ± 1.8 | −0.211 ** | −0.054 ± 0.264 | −0.181 ± 0.317 | −0.076 ± 0.298 | |
| 1996–2008 | 139.4 ± 1.2 | 0.119 ** | −0.190 ± 0.319 | −0.050 ± 0.350 | −0.101 ± 0.329 | |
Note: Trend significance denoted at * p < 0.10 and ** p < 0.05; SD is the standard deviation.

Figure 4.
The correlations between GIMMS3g NDVI-derived vegetation spring onset (SO) and spring (MAM) air temperature (a,b), precipitation (c,d) and SPEI (e,f) during the two sub-periods. Inset panels show corresponding correlation differences between the two sub-periods of 1982–1995 and 1996–2008.
Our site level analysis at the individual weather station locations are generally consistent with the above analysis indicating that the environmental controls on spring onset of the TP grasslands vary temporally and spatially due to varying climate conditions and trends. The two selected sites in Zone-1 (Shenzha) and Zone-2 (Qumarleb) both show non-significant spring warming trends during the study period (p > 0.10), while the Shenzha site experienced increasing spring precipitation, especially during the later sub-period (2.72 mm·year−1, p < 0.05). Correspondingly, the SPEI at Shenzha showed a significant increase (0.135 year−1, p < 0.10) indicating relaxing spring water stress in response to increasing precipitation. Our correlation analyses using an 11-year moving-window at the two selected sites indicates that the SO response to environmental factors varies with changing local climate characteristics and trends (Figure 6). Our results also show a temporal shift in the environmental controls on spring onset after the mid-1990s in response to recent climate variability at these two sites, and consistent with the larger regional analysis. At Shenzha (steppe, Zone-1), spring precipitation shows a stronger control on SO than air temperature, and the effect of precipitation shifts from advancing to delaying on spring onset due to a continuing increasing precipitation trend, while the effects of precipitation on SO at the Qumarleb site (meadow, Zone-2) are reversed, likely due to the slight but continuous decrease in precipitation (−0.36 mm·year−1, p = 0.19). The SPEI shows similar effects on SO as precipitation, which indicates less impact of the temperature trends on SO, but stronger regulation of spring precipitation on SO at these two sites.
The surface ground-air temperature gradient at most of the weather stations in the study domain, is strongly correlated with SO as shown in Figure 3b,d, whereby a larger (smaller) T-diff gradient in spring corresponds with a general delay (advance) in vegetation green-up in most TP grassland areas (especially Zone-2 and 3). An increasing T-diff gradient generally coincides with a SO delay in areas with strong warming accompanied by decreasing or negligible precipitation changes. The results of the T-diff and SO correlation analysis are consistent with above analyses indicating that an increasing surface water deficit associated with a stronger surface-air vertical temperature gradient due to spring warming promotes a general SO delay over the TP grasslands.
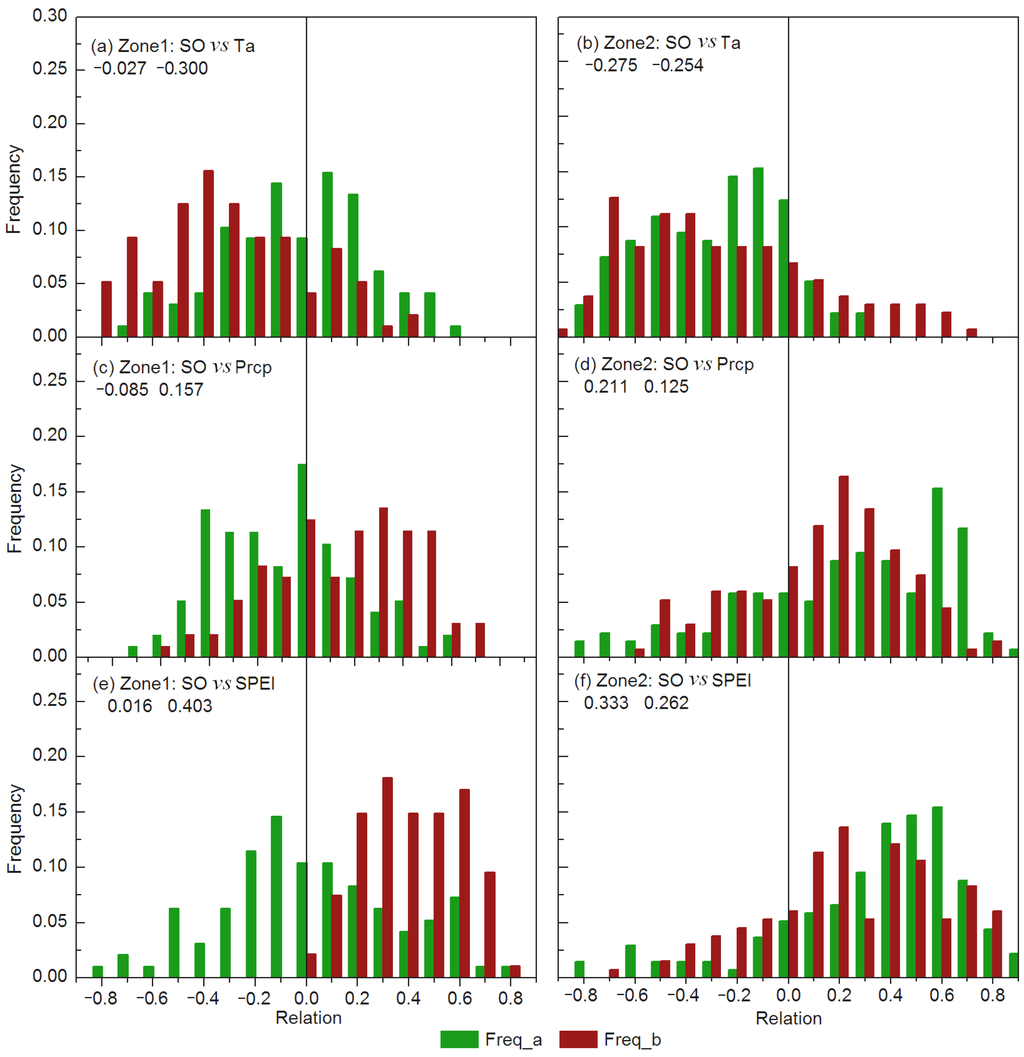
Figure 5.
Frequency distributions of correlations between vegetation spring onset (SO) and spring (MAM) air temperature (a,b), precipitation (c,d) and SPEI (e,f) during the two sub-periods in Zone-1 and Zone-2, respectively. All data series were detrended prior to the analysis. Freq_a and Freq_b indicate corresponding frequency distributions of correlations during the two sub-periods. Numbers in the panels denote the regional mean correlations during the two sub-periods.
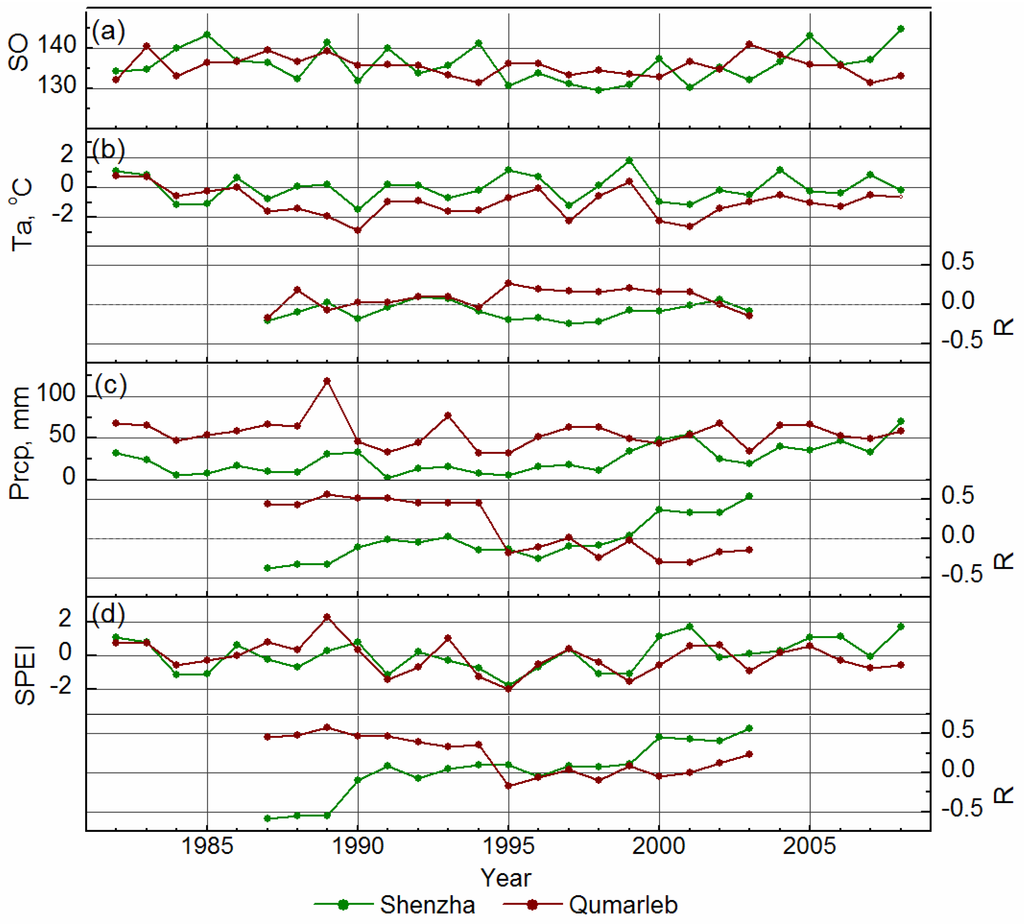
Figure 6.
Time series of GIMMS3g NDVI-derived spring onset (SO, (a)), in-situ spring air temperature (Ta, (b)), precipitation (Prcp, (c)) and SPEI (d) from 1982 to 2008 at two respective weather station locations in Zone-1 (Shenzha) and Zone-2 (Qumarleb) of the TP domain. The partial correlation of SO with Ta (or Prcp), while accounting for the influence of Prcp (or Ta) was based on an 11-year moving-window analysis, while the correlation of SO with SPEI was calculated using a Pearson correlation also based on the 11-year moving-window analysis.
4. Discussion
We investigated the co-variation between satellite NDVI derived spring onset and environmental variables during the past three decades (1982–2008) to explore how climate variations regulate seasonal green-up over the TP grasslands. Our study shows that the spring onset of the TP grasslands is strongly sensitive to recent regional climate change, while the green-up response is spatially and temporally complex over the region.
Our results indicate that spring air temperature is the overall dominant control factor regulating the spring onset over the TP grasslands, which is generally consistent with previous studies [5,13,15,18,56]. However, the temperature response of spring phenology is subject to strong control of pre-season precipitation or moisture conditions [26]. Though spring warming was generally spatially homogeneous and temporally continuous over the TP domain and study period, the effects of warming on spring onset were more spatially and temporally variable depending on the local water balance. The SO trend in Zone-1 shifted from a general delaying trend in the early portion of the study record to an advancing trend after the mid-1990s (Figure 4a); this implies that there are other environmental factors than air temperature affecting spring greening over the TP grasslands. Our results indicate strong precipitation regulation of the SO response to air temperature, especially over relatively drier TP climate sub-zones. Our finding of a strong moisture control affecting the spring phenology response to air temperature for the TP alpine grasslands is supported by evidence from regional field studies [24] indicating a delaying effect of warming on the reproductive phenology of shallow-rooted Kobresia pygmaea C. B. Clarke due to the constraint of topsoil moisture availability. In addition, Cong et al. [13] indicate that the ecological control of air temperature would become stronger if soil water constraints were relieved.
Our findings that the environmental controls on spring onset of the TP grasslands vary spatially and temporally with large regional climate variability, may explain the recent debate and discrepancy regarding the TP grassland response to climate warming [3,5,15,25,33]. This debate partially reflects inconsistencies in the spatial extent and temporal duration of various studies, as indicated by the contrasting environmental trends and vegetation green-up responses during the two sub-periods in our study results. For example, the correlations between spring onset and air temperature in the TP grasslands estimated in this study are relatively low compared with some prior studies [5] due to differences in the study domain, study duration and satellite NDVI datasets used. Zhang et al. [5] examined the correlations between spring onset and air temperature averaged over selected weather station locations for the 1982–2011 period using a combined NDVI record from GIMMS (1982–2000) and SPOT (2001–2011) datasets, while the current study reflects sub-regional average correlations within a 1982-2008 record using the latest generation GIMMS3g NDVI dataset.
Spring precipitation has different effects on vegetation green-up in different climate zones because of the close association of the energy and water balance in the study domain. In relatively dry TP grasslands (mean spring Prcp = 22.8 mm), whether warming will advance or delay vegetation green-up largely depends on changes in spring precipitation, due to the strong control of surface moisture on the grassland phenology. For example, in Zone-1, the increase in spring precipitation during the later sub-period gradually relieved the topsoil water deficit (Figure 5c), but may also promote a delaying effect on spring onset due to lower solar irradiance and more evaporation-caused heat loss [1]. On the other hand, a declining spring precipitation trend (−0.92 mm·year−1, p < 0.05) with intensive warming in Zone-3 (0.073 °C·year−1, p < 0.05) likely promoted a stronger moisture constraint on vegetation green-up. However, in the relatively humid Zone-2 sub-region (mean spring Prcp = 73.0 mm), a persistent spring warming trend accompanied with a slight precipitation decline may relieve the low temperature constraint while still maintaining adequate moisture to support vegetation growth, so the delaying influence of spring precipitation on SO appears to be weakened (Figure 4c,d and Figure 6c). Thus the potential effects of climate warming on the spring green-up of the TP grasslands strongly depend on topsoil moisture conditions that are influenced by spring precipitation and warming-induced changes in evaporation [15,18]. Spring warming trends accompanied by a relatively weak increase (or even decrease) in precipitation observed in some TP areas (e.g., in Zone-3) coincide with an increasing trend in ground-air temperature vertical gradients (Figure 5a), which may promote greater evaporative water losses and drier topsoil conditions. Future warming may potentially delay vegetation green-up of some TP grasslands if spring precipitation does not increase sufficiently to compensate for warming-enhanced evaporation.
The above results distinguish the current study from previous investigations, which have focused more on evaluating long-term SO trends and associated environmental controls. Our investigation focused on evaluating the larger inter-annual variability in SO and its co-variation with underlying environmental control factors. In this way, we mitigated the potential impacts from inconsistent temporal trends of satellite vegetation index datasets. In addition, we included an additional water stress index to include effects of both changing precipitation and temperature on the variability of SO. The general consistency between SPEI and precipitation effects on SO support our conclusion that precipitation is an important control on the spring phenology of the Tibetan grasslands. Previous studies have attempted to pinpoint a consistent relationship between climate variables (either temperature or precipitation) and spring phenology trends in the Tibetan Plateau, while our analysis indicates both temporally and spatially varying environmental controls on spring phenology with changing climate conditions. These results indicate that the dominant environmental controls on spring phenology of the Tibetan vegetation changes with changing climate conditions.
Several limitations of this study stem from the satellite observational constraints and sparse in situ observations in the Tibetan Plateau. Previous investigations [3,5,13,15] and the current study highlight the uncertainties in satellite NDVI datasets used to infer spring green-up. In this investigation, we emphasized the analysis of inter-annual variations in SO using a detrended satellite NDVI time series from the latest generation GIMMS3g record. The detrended NDVI and SO annual anomalies have generally larger signal-to-noise and are expected to be more reliable than the subtle and variable long-term trends indicated from the range of available satellite NDVI records. Apart from uncertainties in the satellite NDVI record, the sparse weather-station network in most TP areas introduces additional uncertainties into our analysis due to strong heterogeneity in regional precipitation, despite screening out the northwest TP from our analysis due to extremely sparse station observations in this area. Exploiting new satellite observations, including surface soil moisture retrievals from next generation microwave sensors [57], may provide a more direct measure of plant-available moisture controls. Increasing the density of regional ground observations would also help reduce uncertainties and thus further advance our understanding of climate controls on the TP ecosystems.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we investigated interactive environmental controls on spring onset of the TP grasslands using a satellite vegetation index (NDVI) record and in-situ weather station observations over the past three decades. Our results show that air temperature has an overall dominant control on vegetation spring onset (SO), though the phenology response to air temperature is regulated by precipitation. In relatively dry (mean spring Prcp = 22.8 mm; mean spring Ta = −3.27 °C) but increasingly wetting (0.50 mm·year−1, p < 0.10) TP grasslands (e.g., Zone-1), more precipitation tends to advance spring onset (−0.146 day·mm−1, p = 0.150) in the early portion of the study record, but with a contrasting SO delay response (0.110 day·mm−1, p = 0.108) after the mid-1990s due to the increasing effect of lower solar radiation and cooler temperatures with continuing precipitation increases (1.01 mm·year−1, p < 0.05). A positive correlation between SO and a standardized drought index (SPEI; mean R= 0.403 ± 0.190) also indicates a delaying effect of increasing spring precipitation on SO after the mid-1990s (Zone-1). In relatively humid TP grassland sub-regions (Zone-2; mean spring Prcp = 73.0 mm; mean spring Ta = −3.51 °C) annual precipitation increases also coincide with a delayed, but insignificant SO response (0.036 day·mm−1, p = 0.165) due to relatively abundant precipitation and lower water stress. The mean correlation between SO and temperature in the humid Zone-2 area reduced from 0.333 ± 0.362 during the initial sub-period of 1982–1995 to 0.262 ± 0.348 afterwards, indicating weakening cold temperature constraints to SO and associated vegetation activity with continued warming. We also find a larger surface ground-air temperature gradient generally associated with SO delay in areas experiencing drying trends. Consequently, continuing warming of the region may not necessarily promote further SO advancement in the TP grasslands due to the interactive effects of both plant-available moisture and temperature constraints to grassland phenology. Our results highlight the importance of surface moisture status in affecting the response of alpine grasslands to climate warming, and the necessity of considering both water supply and thermal constraints when projecting ecosystem responses to future climate change in the Tibetan Plateau.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Fund of China (41471084) and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Earth Sciences program (NNX15AB59G).
Author Contributions
Wenjiang Zhang and Yonghong Yi designed this study, and Wenjiang Zhang wrote this manuscript including the figures and tables. John S. Kimball, Youngwook Kim and Kechao Song contributed significantly to the discussion of results.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, K.; Wu, H.; Qin, J.; Lin, C.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 112, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Gao, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Risi, C.; Sturm, C.; Werner, M.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; et al. A review of climatic controls on δ18o in precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau: Observations and simulations. Rev. Geophys. 2013, 51, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.A.; Hopping, K.A.; Yeh, E.T.; Nyima, Y.; Boone, R.B.; Galvin, K.A. Unexpected climate impacts on the Tibetan Plateau: Local and scientific knowledge in findings of delayed summer. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 28, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Green-up dates in the Tibetan Plateau have continuously advanced from 1982 to 2011. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4309–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Nelson, F.E.; Shiklomanov, N.I.; Guo, D.; Wan, G. Permafrost degradation and its environmental effects on the Tibetan Plateau: A review of recent research. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 103, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henebry, G.; de Beurs, K. Remote sensing of land surface phenology: A prospectus. In Phenology: An Integrative Environmental Science; Schwartz, M.D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 385–411. [Google Scholar]
- Inouye, D.; Wielgolaski, F. Phenology at high altitudes. In Phenology: An Integrative Environmental Science; Schwartz, M.D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 249–272. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, A.D.; Keenan, T.F.; Migliavacca, M.; Ryu, Y.; Sonnentag, O.; Toomey, M. Climate change, phenology, and phenological control of vegetation feedbacks to the climate system. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 169, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, A.; Sparks, T.H.; Estrella, N.; Koch, E.; Aasa, A.; Ahas, R.; Alm-KÜBler, K.; Bissolli, P.; BraslavskÁ, O.G.; Briede, A.; et al. European phenological response to climate change matches the warming pattern. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Dash, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Intercomparison of satellite sensor land surface phenology and ground phenology in Europe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, A.; Jones, M.; Sweeney, J. A review of indicators of climate change for use in Ireland. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2004, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, N.; Wang, T.; Nan, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Myneni, R.B.; Piao, S. Changes in satellite-derived spring vegetation green-up date and its linkage to climate in China from 1982 to 2010: A multimethod analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beurs, K.; Henebry, G. Vegetation phenology in global change studies. In Phenology: An Integrative Environmental Science; Schwartz, M.D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 483–502. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, G.; Cong, N.; Wang, S.; Kong, W.; Piao, S. Increasing altitudinal gradient of spring vegetation phenology during the last decade on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Liang, L.; Donnelly, A.; Park, I.; Schwartz, M. Effects of elevation on spring phenological sensitivity to temperature in Tibetan Plateau grasslands. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 4856–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, K.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, H. Consistent shifts in spring vegetation green-up date across temperate biomes in China, 1982–2006. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Wu, T. Responses of permafrost to climate change and their environmental significance, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, R.; Pan, X.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J. Changes in the near-surface soil freeze-thaw cycle on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 17, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y. Permafrost temperatures and thickness on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 72, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Guangsheng, L.; Chunjie, L.; Yan, Y. The variability of soil thermal and hydrological dynamics with vegetation cover in a permafrost region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 162, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.; Cui, M.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y. Altitude and temperature dependence of change in the spring vegetation green-up date from 1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, T.; Totland, Ø.; Moe, S.R.; Hopping, K.A.; Pan, J.; Klein, J.A. Plant functional traits mediate reproductive phenology and success in response to experimental warming and snow addition in Tibet. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Luedeling, E.; Xu, J. Winter and spring warming result in delayed spring phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22151–22156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Piao, S.; Cong, N.; Zhang, G.; Jassens, I.A. Precipitation impacts on vegetation spring phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Duan, J.; Zhu, X.; Xu, G.; Luo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, F.; Li, Y.; Du, M. Timing and duration of phenological sequences of alpine plants along an elevation gradient on the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, M.; Chen, B.; Innes, J.L.; Wang, G.; Dou, X.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Xu, G.; Zhao, H. Spatial and temporal variations in the end date of the vegetation growing season throughout the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2011. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M. Spring phenology was not consistently related to winter warming on the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E91–E92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D. The Zoning of Ecographical Systems in China; The Commercial Press: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; An, S.; Inouye, D.; Schwartz, M. Temperature and snowfall trigger alpine vegetation green-up on the world’s roof. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Xiong, D.; Su, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Shi, L.; Liu, G. The distribution of and factors influencing the vegetation in a gully in the dry-hot valley of Southwest China. CATENA 2014, 116, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, C.; Ji, L.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Dai, L. The long-term trends (1982–2006) in vegetation greenness of the alpine ecosystem in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Vegetation Map of the People's Republic of China (1:1,000,000); China Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. (in Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.K.; Yao, B.Q.; Xu, W.X.; Ye, X.; Fu, J.J.; Jin, Y.X.; Zhao, X.Q. Field evidence for earlier leaf-out dates in alpine grassland on the eastern Tibetan Plateau from 1990 to 2006. Biol. Lett. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buermann, W.; Parida, B.; Jung, M.; MacDonald, G.M.; Tucker, C.J.; Reichstein, M. Recent shift in Eurasian boreal forest greening response may be associated with warmer and drier summers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.; Salick, J.; Ranjitkar, S.; Xu, J. Herbarium specimens show contrasting phenological responses to Himalayan climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10615–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, Y.; Sobrino, J.A. Global land surface phenology trends from GIMMS database. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3495–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzon, J.; Tucker, C. A non-stationary 1981–2012 AVHRR NDVI3g time series. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6929–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Evaluation of earth observation based global long term vegetation trends—Comparing GIMMS and MODIS global NDVI time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.; Sangermano, F.; Machado, E.; Rogan, J.; Anyamba, A. Global trends in seasonality of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), 1982–2011. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzberger, C.; Klisch, A.; Mattiuzzi, M.; Vuolo, F. Phenological metrics derived over the european continent from NDVI 3g data and MODIS time series. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Sun, P.; Liu, W.; Hartley, D.S. Effects of seasonal snow on the growing season of temperate vegetation in China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2182–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbart, N.; Kergoat, L.; Le Toan, T.; Lhermitte, J.; Picard, G. Determination of phenological dates in boreal regions using normalized difference water index. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Meteorological Administration. China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System. Available online: http://cdc.nmic.cn/home.do (accessed on 15 March 2014). (In Chinese)
- Majorowicz, J.A.; Skinner, W.R. Potential causes of differences between ground and surface air temperature warming across different ecozones in Alberta, Canada. Glob. Planet. Chang. 1997, 15, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, A.M.; Eklundh, L.; Hellström, M.; Bärring, L.; Jönsson, P. Annual changes in MODIS vegetation indices of swedish coniferous forests in relation to snow dynamics and tree phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2719–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Kimball, J.S.; Reichle, R.H. Spring hydrology determines summer net carbon uptake in northern ecosystems. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 064003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioubimtseva, E.; Milanova, E.V.; Tcherkashin, P.; Solntsev, V.N. VEGETATION/SPOT4 applications for macro-regional landscape mapping. In Proceedings of VEGETATION 2000 Conference, Belgirate, Italy, 3–6 April 2000.
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; van Leeuwen, W.; Miura, T.; Glenn, E. MODIS vegetation indices. In Land Remote Sensing and Global Environmental Change; Ramachandran, B., Justice, C.O., Abrams, M.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 11, pp. 579–602. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J. Clim. 2009, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornthwaite, C.W. An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geogr. Rev. 1948, 38, 55–94. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X. East Asia. In Phenology: An Integrative Environmental Science; Schwartz, M.D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Fang, J.; Wang, X. Change in winter snow depth and its impacts on vegetation in China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 3004–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Qiu, Y.; Sun, Z. Assessing phenological change and climatic control of alpine grasslands in the Tibetan Plateau with MODIS time series. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 59, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The soil moisture active and passive (SMAP) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).