A Weighted Algorithm Based on Normalized Mutual Information for Estimating the Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Inland Waters Using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
2.2. In Situ Data
2.2.1. Samples Collection and Datasets Used
2.2.2. Reflectance Measurements
2.2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Satellite Data
| Band | Central Wavelength (nm) | Band Width (nm) | SNR | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 412 | 20 | 1000 | Visible |
| 2 | 443 | 20 | 1090 | Visible |
| 3 | 490 | 20 | 1170 | Visible |
| 4 | 555 | 20 | 1070 | Visible |
| 5 | 660 | 20 | 1010 | Visible |
| 6 | 680 | 10 | 870 | Visible |
| 7 | 745 | 20 | 860 | NIR |
| 8 | 865 | 40 | 750 | NIR |
3. Methods

3.1. Pre-Treatment of Data
3.1.1. Pre-Treatment of the In Situ Spectral Data
3.1.2. Pre-Treatment of the GOCI Data
3.2. Spectra Classification and Matching Based on the NMI Algorithm
3.2.1. Normalized Mutual Information Theory
3.2.2. Classification and Matching Algorithms
3.3. NMI Weighted Algorithms for Chl-a Estimation
3.4. Accuracy Assessment
4. Results
4.1. Variations in the Optical Properties of Each Water Type
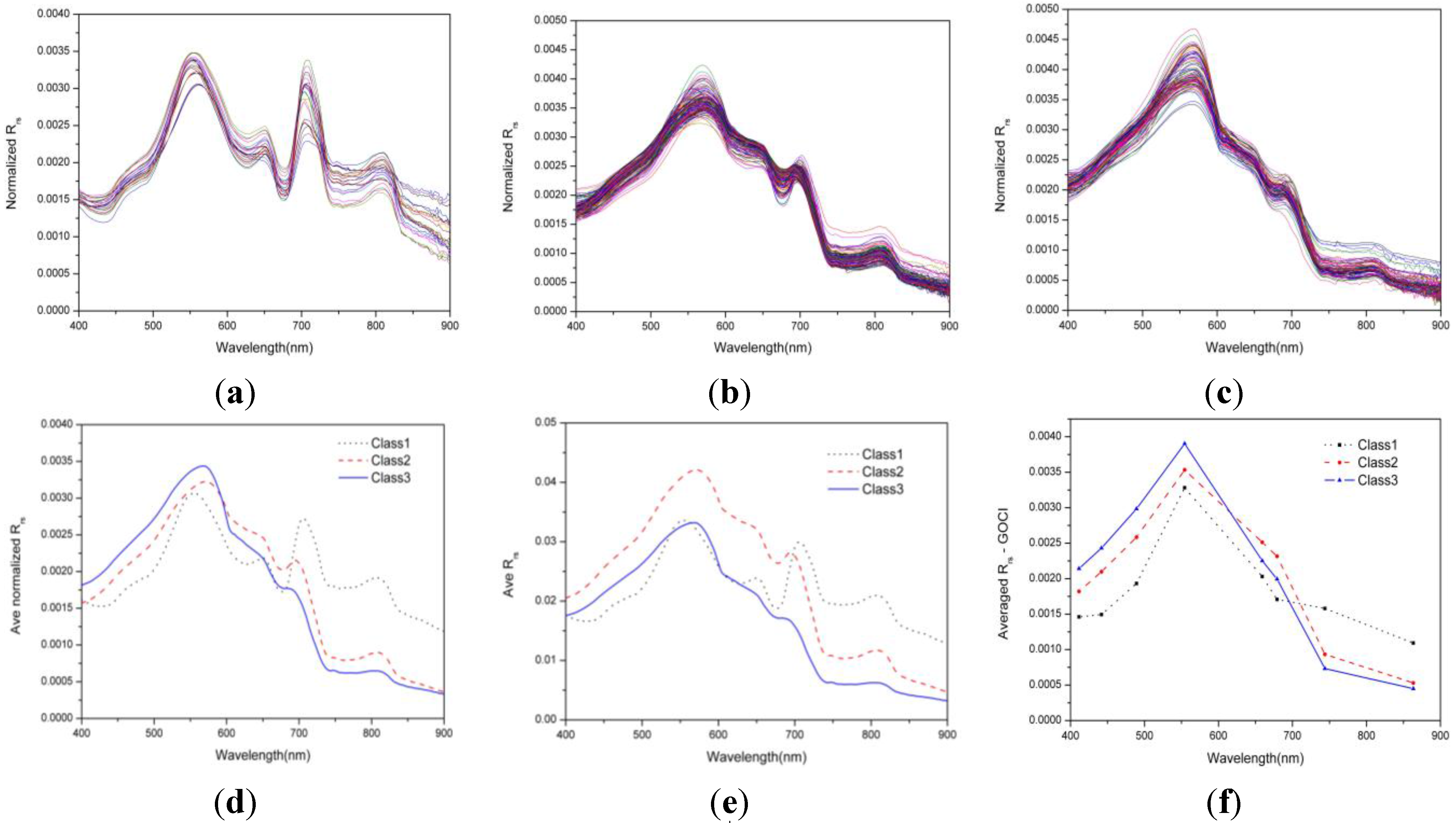
| Water Type | Parameter | Min | Max | Mean | S.D. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Chl-a(mg/m3) TSM(mg/L) ISM(mg/L) aCDOM(440)(m−1) Chl-a:TSM | 21.31 10.50 5.99 0.13 0.46 | 201.30 86.76 67.31 1.45 6.35 | 81.63 42.72 19.59 0.61 1.95 | 42.81 21.09 15.91 0.44 1.66 |
| Class 2 | Chl-a(mg/m3) TSM(mg/L) ISM(mg/L) aCDOM(440)(m−1) Chl-a:TSM | 4.99 12.15 9.00 0.17 0.07 | 82.65 116.12 106.12 1.89 1.86 | 22.61 36.31 29.64 0.51 0.86 | 13.60 18.90 17.29 0.34 0.41 |
| Class 3 | Chl-a(mg/m3) TSM(mg/L) ISM(mg/L) aCDOM(440)(m−1) Chl-a:TSM | 5.29 4.63 2.13 0.16 0.22 | 36.45 40.34 30.46 1.54 2.57 | 12.22 8.54 4.67 0.46 1.22 | 4.71 5.86 3.42 0.38 0.62 |
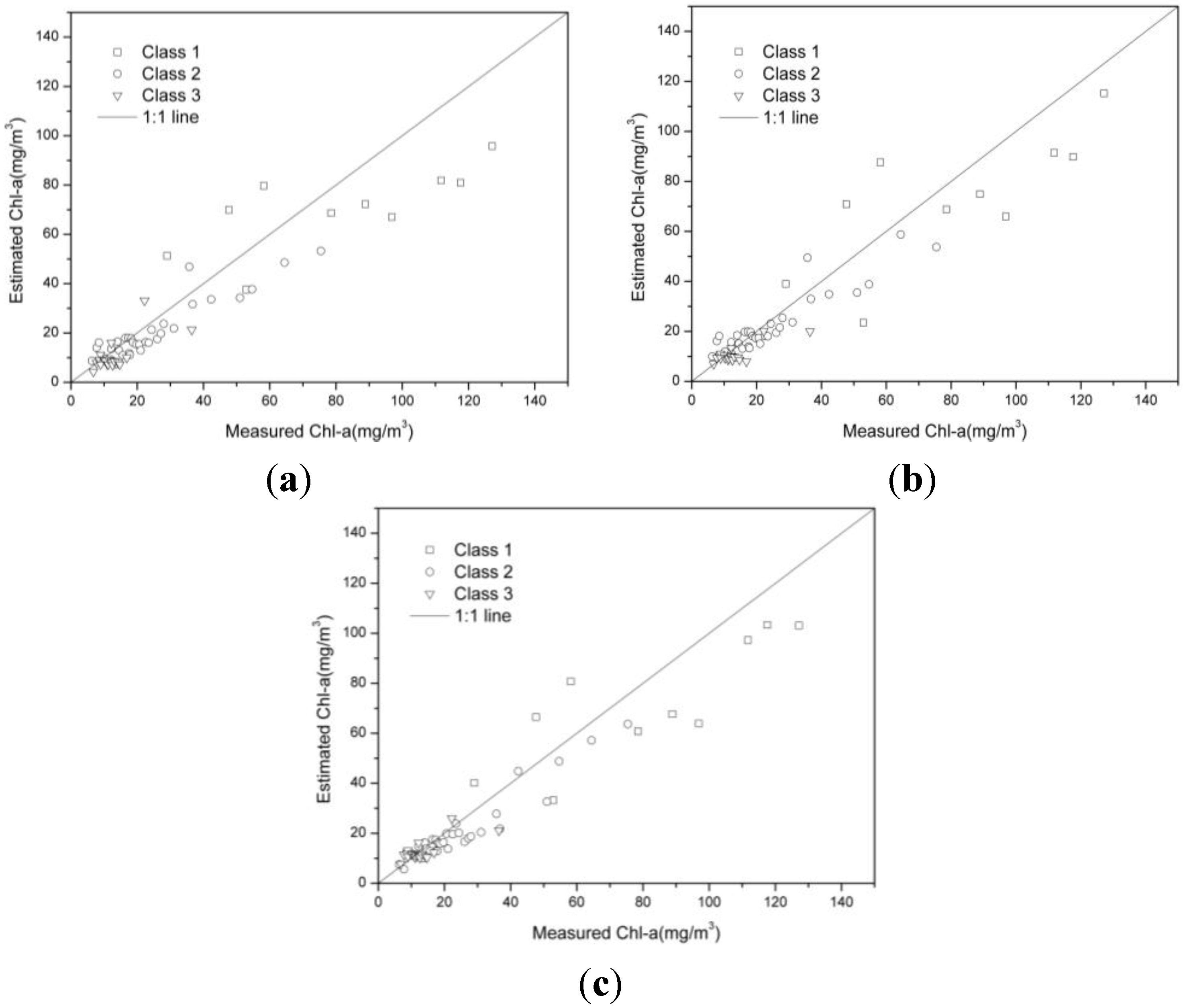
4.2. Estimation of Chl-a Using the NMI Weighted Algorithm
4.3. Validation of the NMI Weighted Algorithm


| GOCI Type | Index | Non-Classification Algorithm | Hard-Classification Algorithm | NMI Weighted Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | MAE RMSE(mg/m3) | 33.4% 28.83 | 30.06% 25.40 | 27.28% 22.52 |
| Class 2 | MAE RMSE(mg/m3) | 28.40% 8.15 | 25.77% 7.34 | 21.56% 6.64 |
| Class 3 | MAE RMSE(mg/m3) | 30.89% 6.67 | 22.45% 5.98 | 21.69% 4.37 |
| All validation data | MAE RMSE(mg/m3) | 31.09% 12.76 | 26.23% 11.02 | 22.63% 9.41 |
5. Discussion
5.1. Assessment of Water Classification
5.2. Application of the NMI Weighted Algorithm to GOCI Images

5.2.1. Assessment of Atmospheric Correction
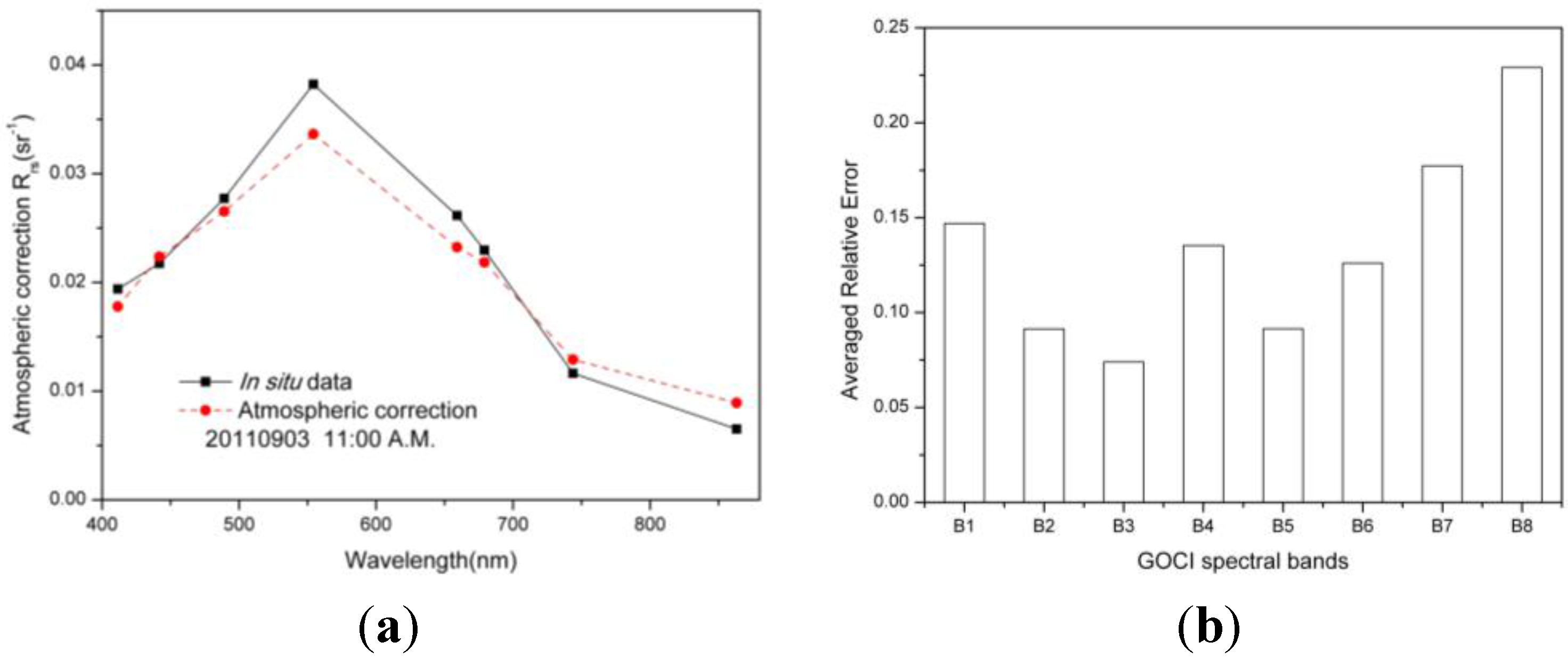
5.2.2. Effect of Fuzzy Boundaries of Water Types in a GOCI Image

5.2.3. Spatial-Diurnal Distribution of Chl-a in Taihu Lake

6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Chen, J.; Fukushima, T. Estimating constituent concentrations in case II waters from MERIS satellite data by semi-analytical model optimizing and look-up tables. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Hu, C. Evaluation of remote sensing algorithms for cyanobacterial pigment retrievals during spring bloom formation in several lakes of East China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 126, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T. Quantitative detection of chlorophyll in cyanobacterial blooms by satellite remote sensing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, H.; Song, K.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z. Remote chlorophyll-a estimates for inland waters based on a cluster-based classification. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhao, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C. Estimation of chlorophyll a concentration using NIR/red bands of MERIS and classification procedure in inland turbid water. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Li, L.; Tedesco, L.P.; Li, S.; Duan, H.; Liu, D.; Hall, B.E.; Du, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, K.; et al. Remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in turbid inland waters: Three-band model versus GA-PLS model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Li, R.; Oyama, Y.; Fukushima, T. Remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in inland waters by a NIR-red-based algorithm: Validation in Asian Lakes. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3492–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zou, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Shi, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Chena, X.; Zheng, F. Assessment of NIR-red algorithms for observation of chlorophyll-a in highly turbid inland waters in China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A.; Rundquist, D.C.; Leavitt, B.; Barrow, T.; Holz, J.C. Assessing the potential of SeaWiFS and MODIS for estimating chlorophyll concentration in turbid productive waters using red and near-infrared bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Povazhnyy, V. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in case II waters using MODIS and MERIS data—Successes and challenges. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Hu, C.; Cannizzaro, J.; English, D.; Muller-Karger, F.; Lee, Z. Evaluation of chlorophyll-a remote sensing algorithms for an optically complex estuary. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Gitelson, A.A. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in estuarine waters: Case study of the Pearl River estuary, South China Sea. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantrepotte, V.; Loisel, H.; Dessailly, D.; Meriaux, X. Optical classification of contrasted coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 306–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Alem, A.; Chokmani, K.; Laurion, I.; El-Adloini, S.E. An adaptive model to monitor chlorophyll-a in inland waters in southern Quebec using downscaled MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6446–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.S.; Dowell, M.D.; Bradt, S.; Verdu, A.R. An optical water type framework for selecting and blending retrievals from bio-optical algorithms in lakes and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, T.S.; Campbell, J.W.; Feng, H. A fuzzy logic classification scheme for selecting and blending satellite ocean color algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zha, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Developing a two-step retrieval method for estimating total suspended solid concentration in Chinese turbid inland lakes using Geostationary Ocean Colour Imager (GOCI) imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 1385–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.F.; Li, Y.; Zha, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H. Remote estimation of chlorophyll a in optically complex waters based on optical classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubac, B.; Loisel, H. Variability and classification of remote sensing reflectance spectra in the eastern English Channel and southern North Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Lu, Z. Algorithms and schemes for chlorophyll a estimation by remote sensing and optical classification for Turbid Lake Taihu, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Usó, A.; Pla, F.; Sotoca, J.M.; Garcia-Sevilla, P. Clustering-based hyperspectral band selection using information measures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4158–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Tian, Q.; Chen, M.; Lin, H. An automatic extraction method for individual tree crowns based on self-adaptive mutual information and tile computing. Int. J. Digital Earth 2015, 8, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Moral, F.G.; Guillen, A.; Del Moral, L.G.; O’Valle, F.; Martinez, L.; Del Moral, R.G. Duroc and Iberian pork neural network classification by visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.X.; Li, H.D.; Fan, W.; Xu, Q.S.; Liang, Y.Z. A model population analysis method for variable selection based on mutual information. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2012, 121, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Dai, J. Investigation of chlorophyll-a and total suspended matter concentrations using Landsat ETM and field spectral measurement in Taihu Lake, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2779–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, W.; An, S. Estimation of water clarity in Taihu Lake and surrounding rivers using Landsat imagery. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.B.; Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.M.; Wei, Y.C.; huang, J.Z. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in Lake Tai, China using in situ hyperspectral data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4267–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.W.; Tian, G.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Song, Q.J. Methods of water spectra measurement and analysis I: Above-water method. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzen, C. Determination of chlorophyll and pheo-pigments: Spectrophotometric equations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1967, 2, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Saprygin, V.; Povazhnyi, V. Operational MERIS-based NIR-red algorithms for estimating chlorophyll-a concentrations in coastal waters—The Azov Sea case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Mechanisms of remote-sensing reflectance variability and its relation to bio-optical processes in a highly turbid eutrophic lake: Lake Taihu (China). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Ocean Satellite Center (KOSC). Available online: http://kosc.kordi.re.kr/ (accessed on 10 September 2015).
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Loiselle, S.A.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, L.; Shang, L. A new three-band algorithm for estimating chlorophyll concentrations in turbid inland lakes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L. Atmospheric correction using near-infrared bands for satellite ocean color data processing in the turbid western Pacific region. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, L.; Pu, R.; Loraamm, R.W.; Yang, G.; Wang, J. Comparison between wavelet spectral features and conventional spectral features in detecting yellow rust for winter wheat. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 100, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, S.C.; Lin, I.I.; Kwoh, L.K.; Holmes, M.; Teo, S.; Gin, K.; Lim, H. Spectral Reflectance Signatures of Case II Waters: Potential for Tropical Algal Bloom Monitoring Using Satellite Ocean Color Sensors. In Proceddings of 10th JSPS/VCC Joint Seminar on Marine and Fisheries Sciences, Melaka, Malaysia, 29 November–1 December 1999.
- Liang, L.; Wang, B.; Guo, Y.; Ni, H.; Ren, Y. A support vector machine-based analysis method with wavelet denoised near-infrared spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2009, 49, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Normalized spectral mixture analysis for monitoring urban composition using ETM+ imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Moses, W.; Rundquist, D.C.; Barrow, T.; Fisher, T.R.; Gurlin, D.; Holz, J. A simple semi-analytical model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in turbid waters: Validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3582–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A. The peak near 700 nm on radiance spectra of algae and water: Relationships of its magnitude and position with chlorophyll concentration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; Gons, H.J.; Rijkeboer, M.; Tilstone, G. Optical remote sensing of chlorophyll a in case 2 waters by use of an adaptive two-band algorithm with optimal error properties. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 3575–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraçli, S.; Doğan, N.; Doğan, I. Comparison of hierarchical cluster analysis methods by cophenetic correlation. J. Inequal. Appl. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Liu, M.L. Temporal-spatial variations of chlorophyll a and primary production in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu, China from 1995 to 2003. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Hu, C. Diurnal changes of a harmful algal bloom in the East China Sea: Observations from GOCI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Walsby, A.E. Water blooms. Biol. Rev. 1975, 50, 437–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Lu, G. The diurnal rhythm of phytoplankton in an eutrophic lake-West Lake, Hangzhou. Acta Hydrob. Sin. 1992, 16, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized difference chlorophyll index: A novel model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Zhu, W.; Suhyb Salama, M. Medium resolution imaging spectrometer (MERIS) estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in the turbid sediment-laden waters of the Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuary. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4635–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, Y.; Tian, Q.; Chen, M. A Weighted Algorithm Based on Normalized Mutual Information for Estimating the Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Inland Waters Using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11731-11752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70911731
Bao Y, Tian Q, Chen M. A Weighted Algorithm Based on Normalized Mutual Information for Estimating the Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Inland Waters Using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Data. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(9):11731-11752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70911731
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Ying, Qingjiu Tian, and Min Chen. 2015. "A Weighted Algorithm Based on Normalized Mutual Information for Estimating the Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Inland Waters Using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Data" Remote Sensing 7, no. 9: 11731-11752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70911731
APA StyleBao, Y., Tian, Q., & Chen, M. (2015). A Weighted Algorithm Based on Normalized Mutual Information for Estimating the Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Inland Waters Using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Data. Remote Sensing, 7(9), 11731-11752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70911731







