Abstract
Snow is a water resource and plays a significant role in the water cycle. However, traditional ground techniques for snow monitoring have many limitations, e.g., high-cost and low resolution. Recently, the new Global Positioning System-Reflectometry (GPS-R) technique has been developed and applied for snow sensing. However, most previous studies mainly used GPS L1C/A and L2C Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) data to retrieve snow depth. In this paper, snow depth variations are retrieved from new weak GPS L2P SNR data at three stations in Alaska and evaluated by comparing with in situ measurements. The correlation coefficients for the three stations are 0.79, 0.88 and 0.98, respectively. The GPS-estimated snow depths from the L2P SNR data are further compared with L1C/A results at three stations, showing a high correlation of 0.94, 0.93 and 0.95, respectively. These results indicate that geodetic GPS observations with SNR L2P data can well estimate snow depths. The samplings of 15 s or 30 s have no obvious effect on snow depth estimation using GPS SNR L2P measurements, while the range of 5°–35°elevation angles has effects on results with a decreasing correlation of 0.96 and RMSE of 0.04 m when compared to the range of 5°–30° with correlation of 0.98 and RMSE of 0.03 m. GPS SNR data below 30° elevation angle are better to estimate snow depth.
1. Introduction
Snow is one of the most important components in the hydrological system, which impacts the water cycle and atmospheric circulation [1,2,3]. Water runoff from snowmelt is an important water resource feeding one sixth of the world population [4]. Through mentoring the snow status, we can know how much fresh water is stored by the snow. However, it is difficult to monitor snow variations because of high spatial and temporal variability. Manual and automated techniques are the main ground-based measurement [5]. Manual measurements, including snow depth and density observations, have high precision, but low temporal resolution. Compared to manual measurements, the automated techniques, e.g., sonic depth measurements, snow pillows and gamma radiation measurements, have a higher temporal resolution, but miss the information of the spatial variations on-site [5]. Due to physical reflectivity and polarization characteristics of snow surfaces with GPS-reflected signals [6,7], GPS-Reflectometry (GPS-R) can be used to monitor snow depth variations [8,9,10]. One of the benefits is that GPS-R has a high temporal and spatial resolution, and GPS observations from IGS network are permanent, continuous and freely available. Concerning the spatial resolution, the sensing footprint of the GPS-R has an area about 1000 m2 [11]. Most importantly, the current GPS network covers a large area of the world [12], which can be directly used without additional cost for snow sensing. Because of these benefits, the GPS-R will complement the traditional snow measurements [9].
GPS-R theories and models have been investigated and discussed and geophysical parameters can be estimated using unique GPS receivers with two antennas: one to receive direct signal and the other to receive reflected signal [13,14], which employied the GPS reflected signal for the ocean remote sensing based on the waveform correlation. Then, the method is extended to land applications including the soil moisture and vegetation growth retrieval. Larson et al. [15] first demonstrated that the snow depth retrieved from traditional geodetic-GPS receivers has a good agreement with in situ depth measurements, indicating that geodetic-GPS receivers can be used to estimate snow depth. Later, GPS-R based on the signal noise ratio (SNR) data from GPS L2C signal was developed and applied for snow depth retrieval [5,16]. The method employs the multipath SNR data caused by the interference between direct and reflected signals. The frequency of multipath oscillations is changing with the antenna height variations, so the snow depth can be estimated based on this relationship. Based on the method presented by Larson and Nievinski [16] and Chen et al. [17] evaluated the snow depth sensing results using the GPS L2C signal with a dipole antenna, which showed an improvement for snow depth estimation compared with the typical geodetic equipment. Recently, Tabibi et al. [18] assessed the modernized GPS L5 SNR for snow depth and soil moisture retrieval, which was comparable to those from L2C.
Because GPS L2C signal has a higher SNR strength when compared to L1C/A and L2P signals, previous studies, e.g., Larson et al. [15] and Larson and Nievinski [16], mainly used L2C SNR data to retrieve snow depth but did not evaluate and validate the estimations from the L2P signal. Although Hefty and Gerhatova [19] compared three different snow depth results from L1C/A and L2P SNR and GPS L4 combinations (the geometry-free linear combination of carrier phases) based on the GPS-R theory, they did not systematically evaluate the GPS L2P results and only used one GPS satellite to estimate snow depth. In addition, the first Block IIR-M GPS satellite with broadcasting L2C signal was launched in 2005, while the first new Block IIF satellite with broadcasting L5 and L2C signal was launched in 2010. Because of short operational time, the old-configuration GPS receivers cannot track the L2C or L5 signal and also GPS observations before 2005 did not provide the L2C or L5 SNR data, so only L2P or L1C/A SNR data are avaliable at some GPS sites.
This paper aims to overcome the above limitations with the new L2P SNR data, which are used to retrieve snow depth. Snow depth estimations from L2P SNR are evaluated and validated by in situ snow depths. Theoretical simulations are employed to evaluate the effect of snow parameters (density and snow depth) and surface roughness on SNR observations. Furthermore, the L2P results are compared to L1C/A. Finally, the effect of different sampling rates on snow depth estimations is discussed as well as the elevation angles.
2. GPS Observations and Climate Data
2.1. GPS Observations
Plate Boundary Observatory (PBO) operated by the Earthscope network aims to monitor the boundary plate deformation, which has hundreds of permanent GPS stations. Here only three stations in Alaska State are chosen with available co-located in situ snow measurements (Figure 1): SG27 (latitude: 71.32°, longitude: −156.61°, elevation: 9.4 m), AB39 (latitude: 66.56°, longitude: −145.21°, elevation: 147.7 m) and AB33 (latitude: 67.25°, longitude: −150.17°, elevation: 334.8 m). The sampling rate of the L2P SNR data is 15 s, but 1 s rate is also available at some stations. The GPS data at SG27 and AB39 stations cover from June 2008 to July 2010 and June 2009 to July 2011, respectively. The data at AB33 station only cover from July 2010 to May 2011. Figure 2 shows the three GPS stations location with a TRMNETRS receiver (antenna model: TRM29659).
Figure 1.
Location of GPS stations in Alaska.

Figure 2.
Antenna of three GPS stations SG27 (a); AB39 (b) and AB33 (c).
2.2. Climate Data
The in situ snow depth data are obtained from the National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) and the National Water and Climate Center (NWCC). The co-located climate station of SG27 is BARRROW (latitude: 71.28°, longitude: −156.78°, elevation: 9.4 m). The average daily snow depth measurements are provided by National Climatic Data Center (NCDC). The Fort Yukon (latitude: 66.57°, longitude: −145.25°, elevation: 131.1 m) and Coldfoot (latitude: 67.25°, longitude: −150.18°, elevation: 317.0 m) from the Snowpack Telemetry (SNOTEL) network, are the co-located climate stations of AB39 and AB33, respectively. Their daily averages of snow depths are provided by the National Water and Climate Center (NWCC).
3. Theory and Methods
3.1. Data and Methods
For traditional GPS applications, multipath is regarded as an error source. When direct and reflected signals are received at the same time by GPS receivers, they will interference in the antenna and cause multipath errors, which will degrade the observation accuracy in typical positioning and surveying applications. Although the reflected signal can be suppressed by the antenna gain of geodetic-quality GPS receivers, it still exists, particularly at low satellite elevation angles (5°–25°). Due to multipath effects, oscillations will appear in GPS observations (Figure 3a). The Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is one of the GPS observables, which has been used to assess the signal quality and noise characteristics of typical GPS surveying [20]. SNR can be calculated using the ratio of the signal power to the measurement noise. In GPS RINEX files, SNR measurements are usually denoted as S1/S2 in decibel (dB) units. It is convenient to extract the multipath effect by the SNR observable from GPS observations when compared to carrier-phase and pseudorange observables.
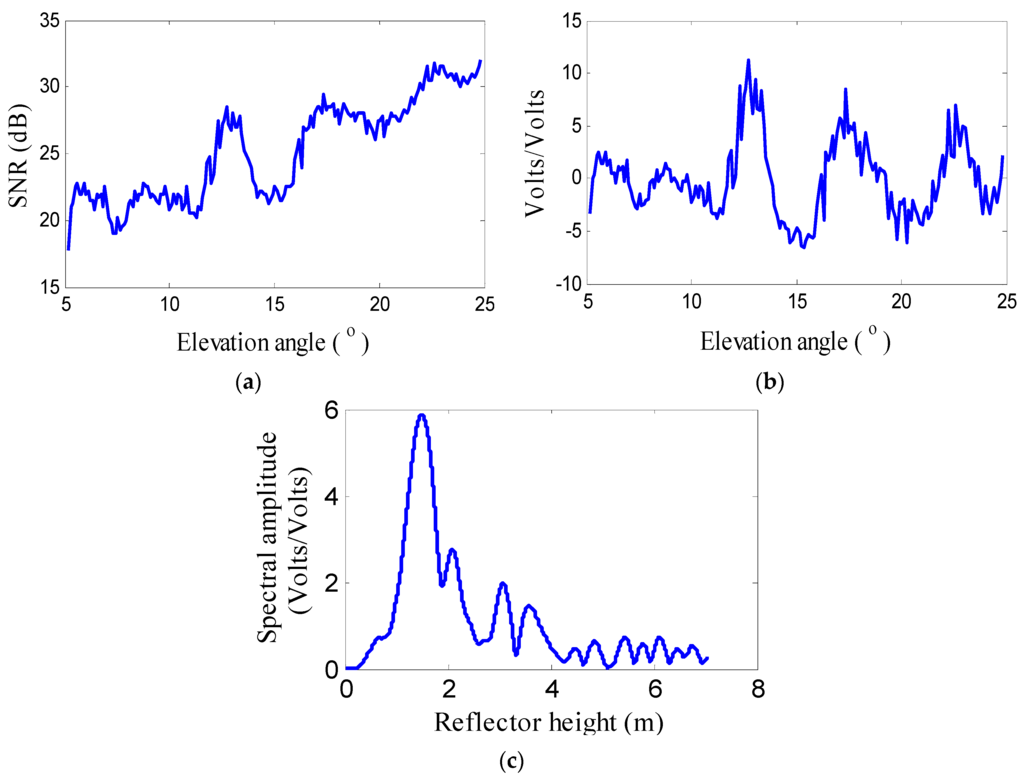
Figure 3.
L2P SNR data, multipath modulations and Lomb–Scargle periodogram of multipath pattern at AB33. (a) L2P SNR data from satellite PRN10; (b) Multipath modulations; (c) Lomb-Scargle periodogram of multipath pattern.
According to the method presented by Larson and Nievinski [16], we know:
where Pd is the direct power, Pr is the reflected power and ϕ is the interference phase. SNR measurements will smoothly rise from 16 dB to 33 dB at a low elevation angle without multipath effect (Figure 3a). However, due to the multipath effect or the interferences, several oscillations appear in SNR measurements at low satellite elevation angles. In GPS multipath reflectometry, the direct trends Pd and Pr are not required and should be removed. After removing the direct trend, we can obtain the multipath pattern (Figure 3b) described simply as followings [16]:
where dSNR is the detrended SNR, A is the amplitude, H is the reflector height, λ is the GPS carrier wavelength, e is the satellite elevation angle and φ is the phase. In order to remove the direct trend, a low-order polynomial is used to fit the SNR measurements. Before fitting the measurements, we convert the dB scale into a linear scale, such as volts for the reason of linearity, using the equation: . From Figure 3b, we can clearly see the modulations in the SNR time series. The detrended SNR signal can be modeled following Equation (2). This equation provides the multipath modulation frequency at a constant of sinus of elevation angle e. Through Equation (2), we can derive the relation between the reflector height and the multipath modulation frequency
When retrieving the frequency f, we can derive the reflector height and the snow depth. In order to obtain the frequency of the modulations, we use the Lomb-Scargle periodogram (Figure 3c).
The main procedures of retrieving snow depth from GPS SNR data can be summarized as follow:
- (1)
- Using low-order polynomial function to fit GPS SNR time series and remove the direct trend, the multipath oscillations are obtained.
- (2)
- The domain frequency of multipath oscillations is obtained using the Lomb–Scargle periodogram.
- (3)
- The domain frequency is converted to the reflector height.
3.2. Theoretical Simulation
Based on the multipath simulator presented by Nievinski and Larson [21], we evaluate the modeled L1C/A and L2P SNR observables. The multipath simulator considers the coherence between the direct and reflected signals, and the combinations of antenna and surface responses. In order to know the differences between L1C/A and L2P signals, their modulations are compared in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of L1C/A and L2P signals.
| GPS Signal | Wavelength (cm) | Frequency (MHz) | Chipping Rate (Mchip/s) | Code Length (Chip) | Min Received Power (dBW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1C/A | 19.0 | 154 × 10.23 | 1.023 | 1023 | −158.5 |
| L2P | 24.4 | 120 × 10.23 | 10.23 | 6.187 × 1012 | −164.5 |
The SNR is the ratio of the signal power to the noise power, so the minimum power is the most important difference. The received low minimum power causes a weak strength of the L2P SNR measurements. During the process, we suppose that the land surface is the dry snow with a density of 0.5 g/cm2 and small roughness. The L2P SNR is about 15 dB weaker than the L1C/A. Despite of the weak strength, oscillations still exist in L2P SNR measurements. These oscillations are shown in Figure 4a. After removing the direct trend, low amplitude modulations still can be clearly seen in Figure 4b. From Figure 4c, we can see no significant difference for the reflector height from the frequency of modulations, except from the amplitude due to the weak strength of L2P signal. For example, Figure 5 shows the comparison of L1C/A and L2P SNR measurements from satellite PRN10 at AB33.
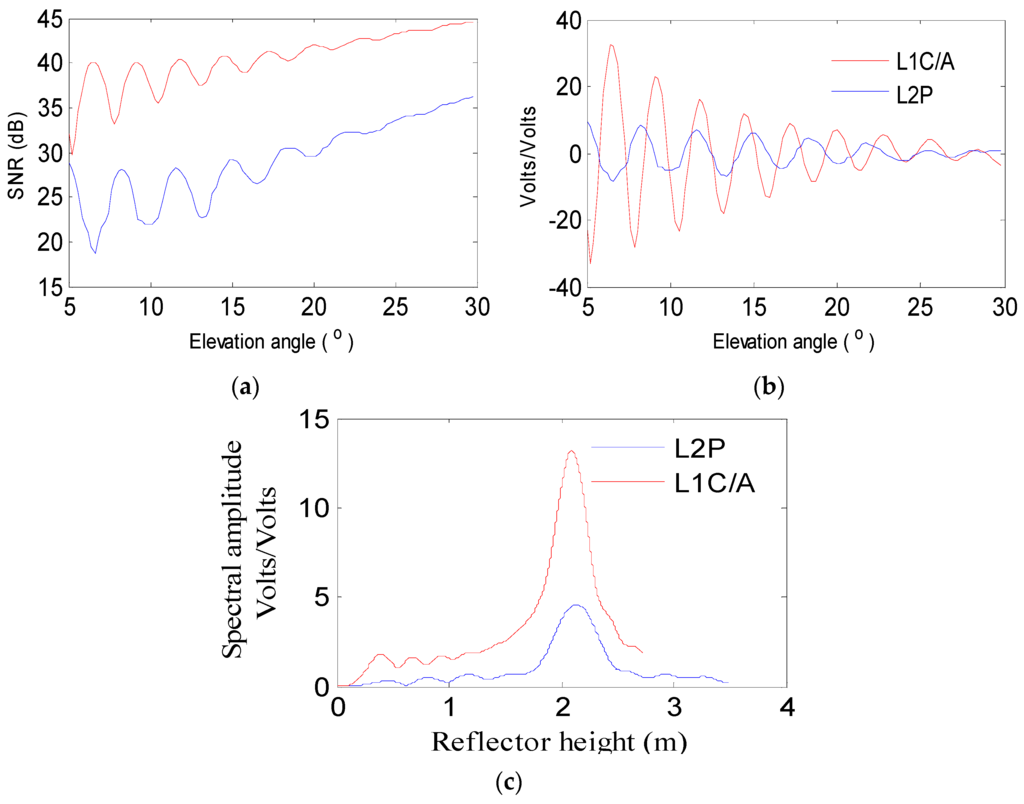
Figure 4.
Comparison of simulated L1C/A and L2P SNR observables. (a) Simulated L1C/A and L2P SNR; (b) Multipath modulations; (c) Lomb–Scargle periodogram of multipath pattern.
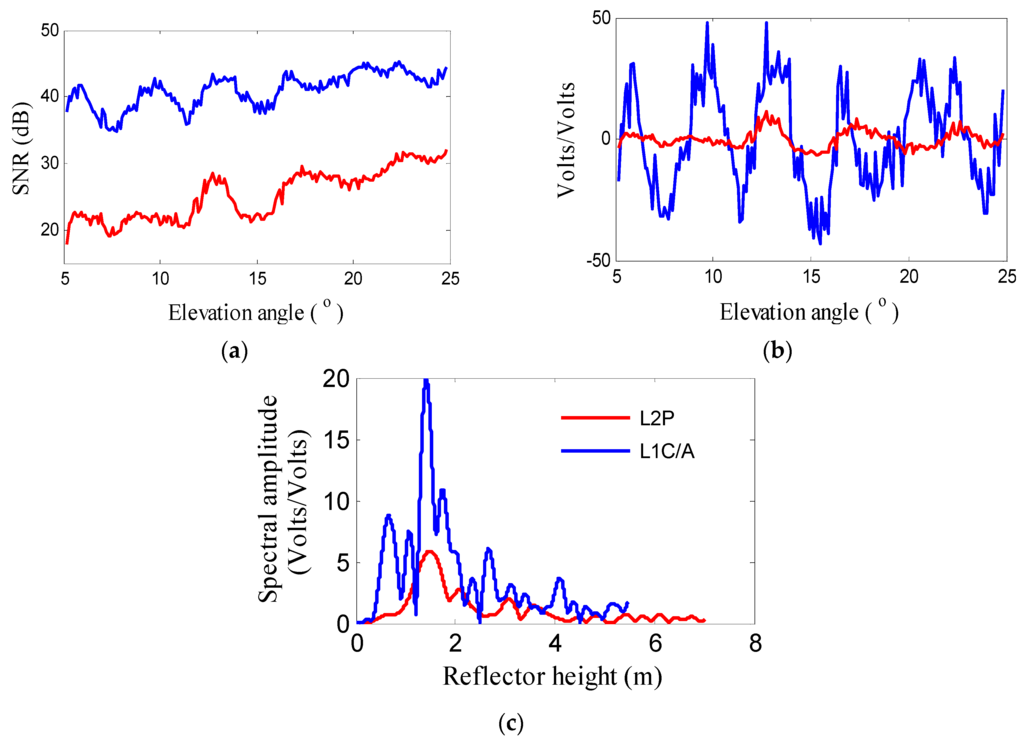
Figure 5.
Comparison of L1C/A and L2P SNR data, multipath modulations and Lomb–Scargle periodogram of multipath pattern at AB33. (a) L1C/A and L2P SNR from satellite PRN10; (b) Multipath modulations; (c) Lomb–Scargle periodogram of multipath pattern.
Snow density is one of the most important parameters for snow monitoring. The values can vary from 0.2 g/cm2 (new snow) to 0.9 g/cm2 (ice). In addition, the snow density is different in different stages of accumulation or melting, meaning that the composition of snow is changing. The composition will have an impact on the reflected signal and we should evaluate effects caused by the changes in snow density. When the GPS Right Hand Circular Polarized (RHCP) signal reflects from the surface, it will be changed into the Left Hand Circular Polarization (LHCP) because of the reflecting surface and geometry [9]. Therefore, the simulator presented by Nievinski and Larson [22] considers the surface reflection characteristics. The dielectric model used in the simulator is related to the density, so the coherent scattering coefficients of different snow densities at linear and circular polarizations are computed (Figure 6). In Figure 6, the VV denotes the coherent scattering coefficient with vertical transmitting and vertical receiving and the HH shows horizontal transmitting and horizontal receiving. The RR is the coherent scattering coefficient from RHCP to RHCP, which shows the RHCP signal does not change the polarization, while the RL is the scattering coefficient from RHCP to LHCP. From the simulations, the snow density has a dramatic impact on coherent scattering coefficient. With the increasing of snow density, the scattering coefficients also increase. Figure 7 presents the SNR modulations of different densities. The snow density does not affect the multipath frequency, while the amplitude has a dramatic change with different snow densities. When the density increases, the amplitude of the modulations also increases because of the increasing of the scattering coefficients.
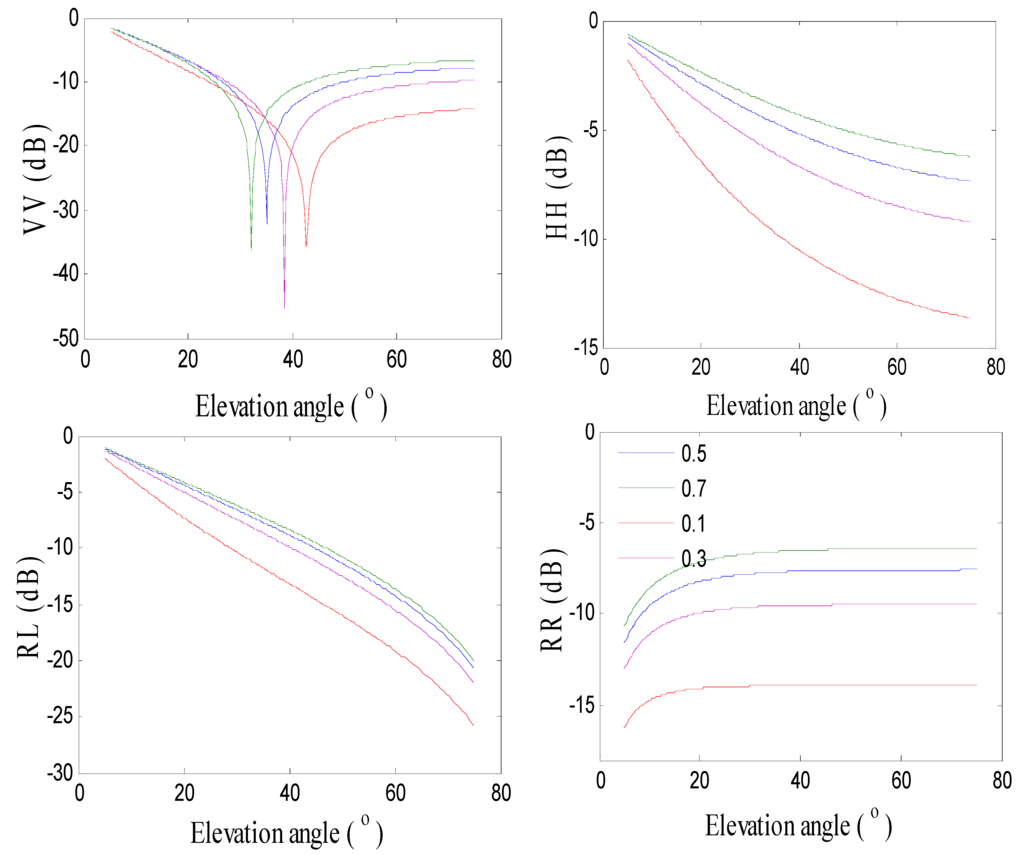
Figure 6.
Coherent scattering coefficients of different snow densities (g/cm2) at linear (VV and HH) and circular polarizations (RR and LR).
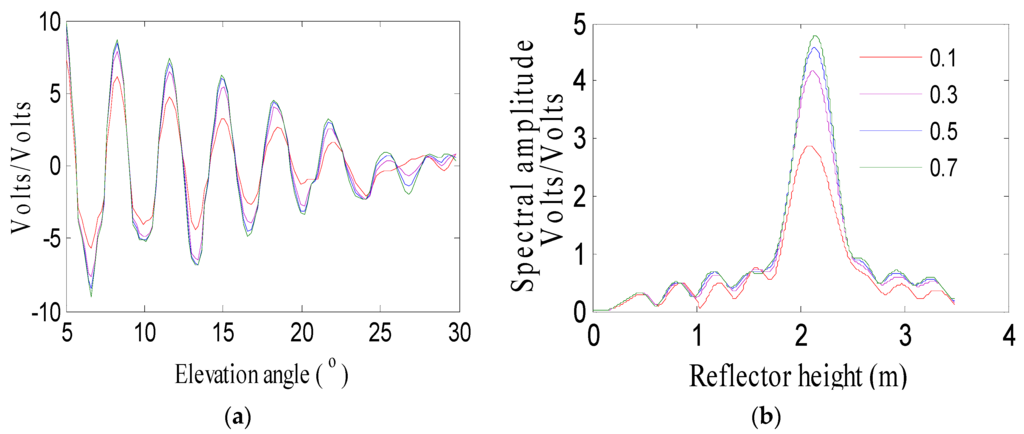
Figure 7.
Simulated Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) modulations of different snow densities (g/cm2). (a) SNR modulations after removing the direct trend; (b) Lomb–Scargle periodogram of multipath pattern.
For multipath reflectometry, the planer surface should be smoother, which is beneficial for the coherent reflection. In the multipath simulator, the surface roughness is formulated by the roughness factor [22]:
where k is the wave number, s is the RMS height (the standard deviation of surface heights), and θ is the angle of incidence. Setting the RMS height s at 5 cm, 15 cm and 25 cm, we compare the SNR modulations (Figure 8). We can see that the SNR modulations are not so obvious with the increasing of the RMS height (Figure 8a). In the frequency domain, the peak amplitude disappears when the RMS height is about 25 cm. The strong mirror reflection is getting weaker with the increasing of the RMS height. The reason is that the diffuse scatter plays a domain role when the RMS height increases.
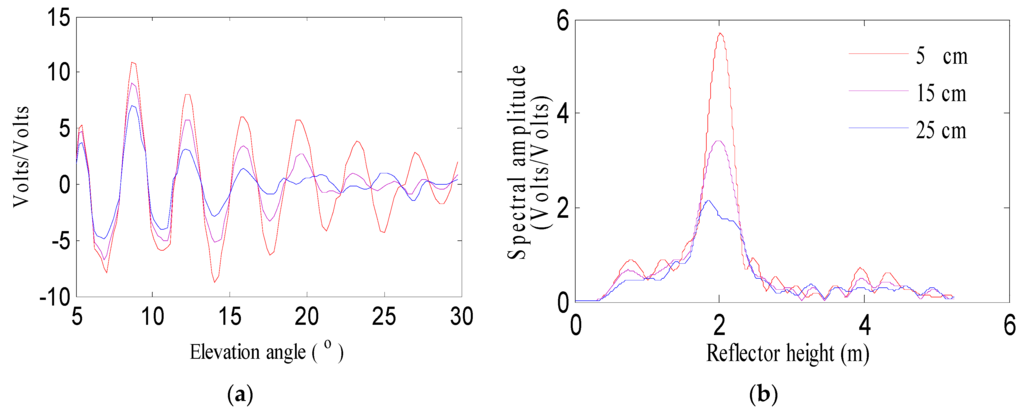
Figure 8.
Comparison of simulated L2P SNR modulations at different surface roughness. (a) Multipath modulations with different surface roughness; (b) Lomb–Scargle periodogram of multipath pattern.
4. Results and Validation
Following the procedure presented by Larson and Nievinski [16], we process the SNR data. For each day, we divided the SNR data into two portions according to the ascending and descending GPS satellite tracks. Not all tracks are useful, and only these peak amplitudes with over four times of the background noise are kept. Then, each ascending or descending SNR trace is computed using the LSP method to obtain the reflector height. Reflector heights among summer days are used to estimate the free-snow ground height. The daily snow depth is the average of all depths from each valid GPS track. Figure 9 shows the comparison of GPS-estimated snow depths from L2P SNR data and in situ measurements at AB33, AB39 and SG27.
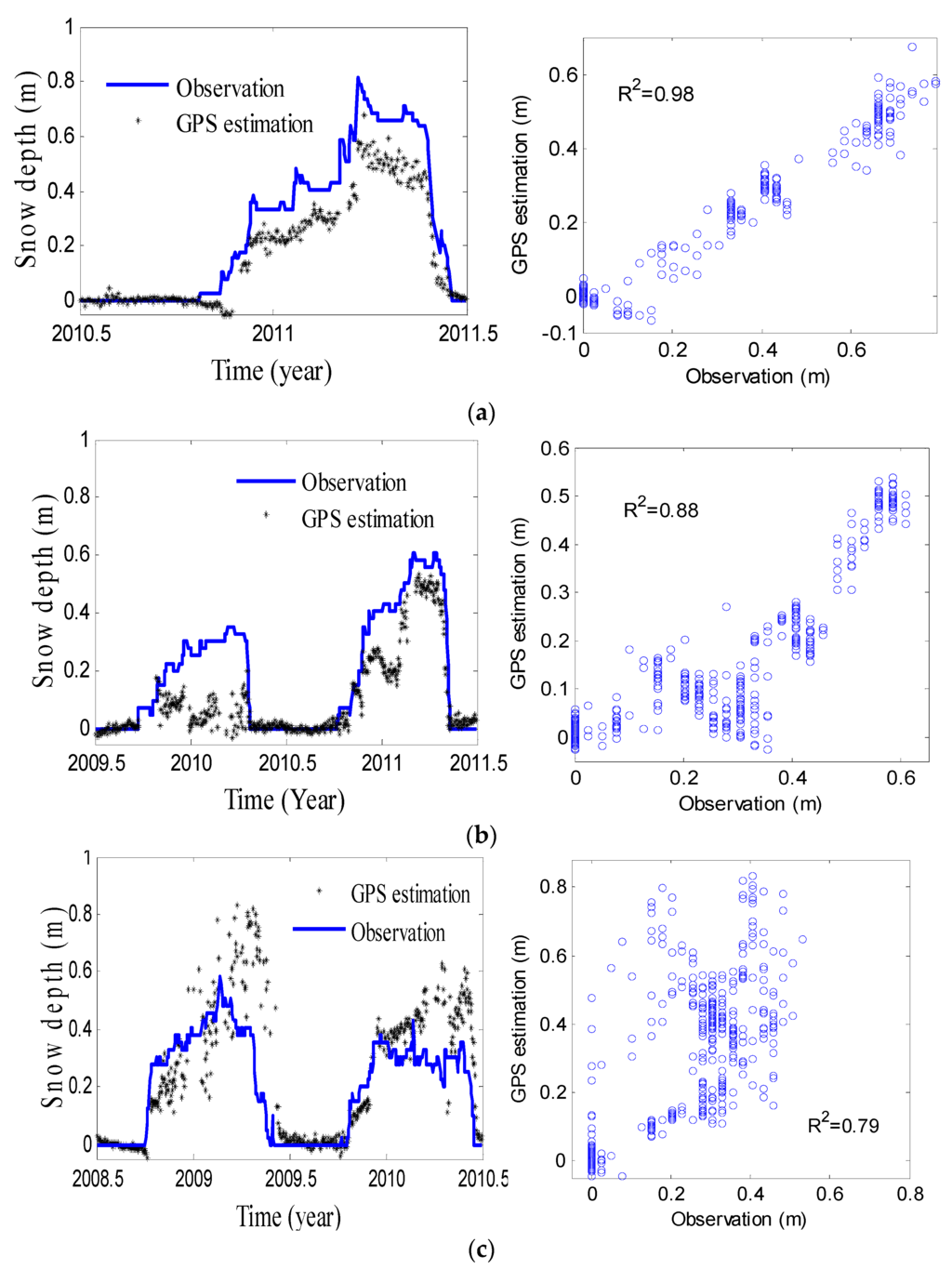
Figure 9.
Comparison of GPS and in situ snow depth at AB33, AB39 and SG27. (a) AB33; (b) AB39; (c) SG27.
At AB33, the in situ snow depth is slightly higher than the GPS estimation in the winter of 2011, but has the same variation and trend (Figure 9a). Meanwhile, there are the same changes in snow depths between GPS and in situ measurements, and both have a peak height in the spring of 2011. After that, the snow is increasingly melting. Both have a good correlation coefficient of 0.98, so the GPS estimations show a good agreement with in situ measurements. Figure 9b shows the GPS snow depth estimation from L2P SNR data at AB39. The GPS snow depth is a little lower than in situ measurements in the winter of 2009 and the spring of 2010, and also GPS estimations have a temporal variation with different trends. After that, they have the same change in the winter of 2011 and both have a correlation of 0.88 and a RMSE of 0.12 m between GPS estimation and in situ measurements. The differences in snow depth estimation may be affected by other factors, like the wind causing variations. Figure 9c is the comparison of GPS and in situ results at SG27 from L2P SNR data. In the spring of 2009, GPS estimations are higher than in situ measurements with a significant temporal variation. The correlation coefficient and RMSE between GPS and in situ measurements are 0.79 and 0.14 m, respectively (Table 2). Although the correlation coefficient is smaller than AB33 and AB39, GPS and in situ measurements almost agree each other.

Table 2.
Comparison of snow estimates from L2P SNR and in situ depths.
| Locations | Years | Correlation Coefficient | RMSE (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AB33 | May 2010–May 2011 | 0.98 | 0.12 |
| AB39 | May 2009–May 2011 | 0.88 | 0.12 |
| SG27 | May 2008–May 2010 | 0.79 | 0.14 |
5. Discussion and Effects
5.1. Comparison of L1 C/A and L2P
Through above analysis and validations, L2P SNR data can be well used to retrieve snow depth with a good agreement with in situ measurements. Since the L1C/A signal is 15 dB higher than the L2P signal, modulations in L1C/A SNR observations are clearer. We further evaluate the snow depth from L2P SNR data by using L1C/A SNR data.
Figure 10a shows the estimations from L1C/A SNR data at AB33 with a good agreement with the in situ depths. The correlation coefficient is about 0.98. In the winter of 2011, the trend is almost the same and both have a peak height in March 2011. The estimations from L1C/A is slightly higher than the L2P, but both have the same change at the same times (Figure 10b). The correlation coefficient is about 0.97 with a RMSE of 0.07 m, which means that there are no significant differences between L1C/A and L2P estimations. Figure 11 shows the comparison of L1C/A and L2P results at AB39. The L1C/A estimation has a correlation of 0.94 with in situ data, indicating a good agreement. The correlation of L1C/A and L2P results is 0.93. Figure 12 show the comparison of L1C/A and L2P results at SG27, which has a correlation of 0.94 and a RMSE of 0.11 m.
Although the strength of L1C/A is higher than L2P, the mean bias between L1C/A and L2P results are 0.07 m, 0.09 m and 0.11 m at AB33, AB39 and SG27, respectively, showing no significant differences. Therefore, L2P signals are able to well retrieve the snow depth using older SNR antennas. In this paper, three stations have no L2C records, but snow depth variations can be estimated using L1C/A or L2P SNR data.
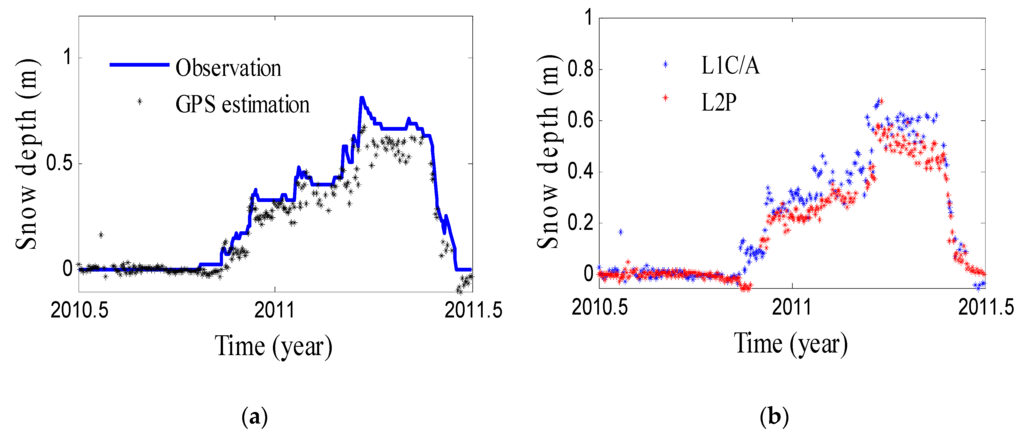
Figure 10.
Comparison of L1C/A and L2P results at AB33. (a) Snow depth estimation from L1C/A; (b) Snow depth estimation from L1C/A and L2P.
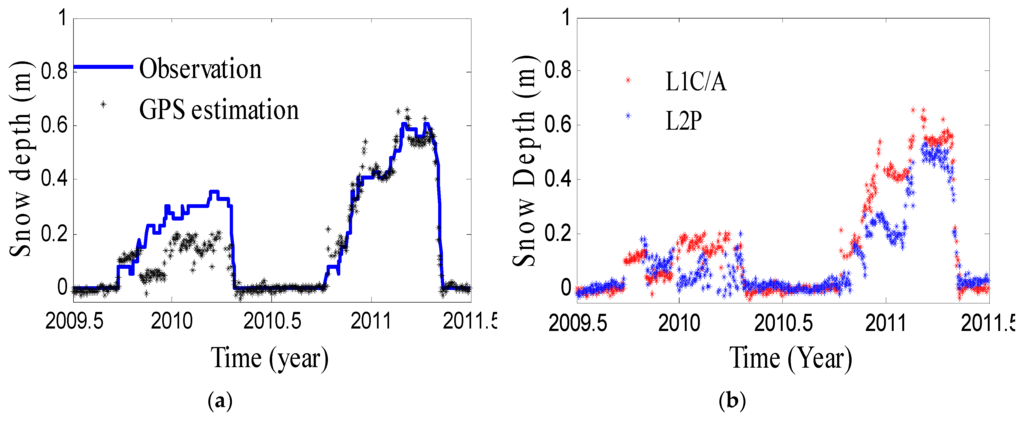
Figure 11.
Comparison of L1C/A and L2P results at AB39. (a) Snow depth estimation from L1C/A; (b) Snow depth estimation from L1C/A and L2P.
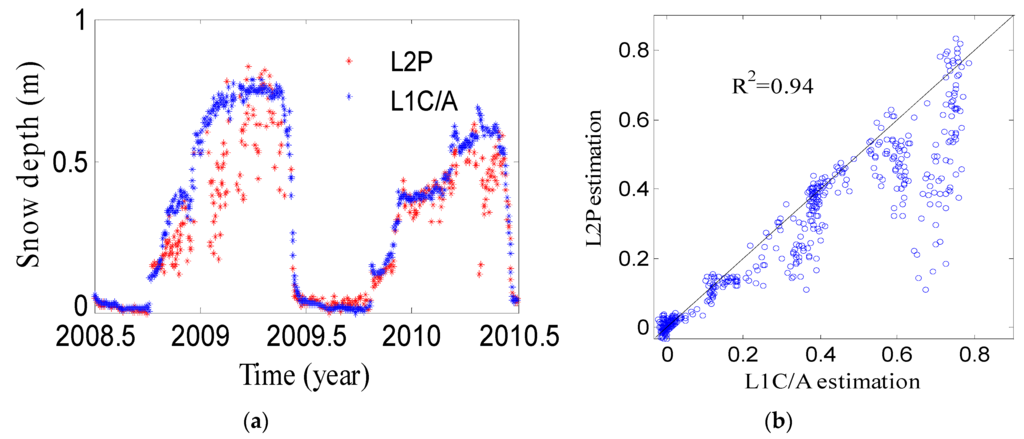
Figure 12.
Comparison of L1C/A and L2P results at SG27. (a) Snow depth estimation from L1C/A and L2P; (b) Correlation between L1C/A and L2P.
5.2. Satellite Elevation Effects
The reflected signal is mainly from the First Fresnel zone at a certain elevation angle. For a planner surface, the First Fresnel zone can be described as an ellipse:
where e is satellite elevation angle, h is antenna height and λ is carrier wavelength [23]. For a given SNR trace, the sensing footprint is the total area of First Fresnel zones at different elevation angles. The First Fresnel zone is related to the satellite elevation angle e, so the First Fresnel zone changes with the elevation angle e (Figure 13). With the ascending of the satellite, the zone becomes smaller and closer to the antenna.
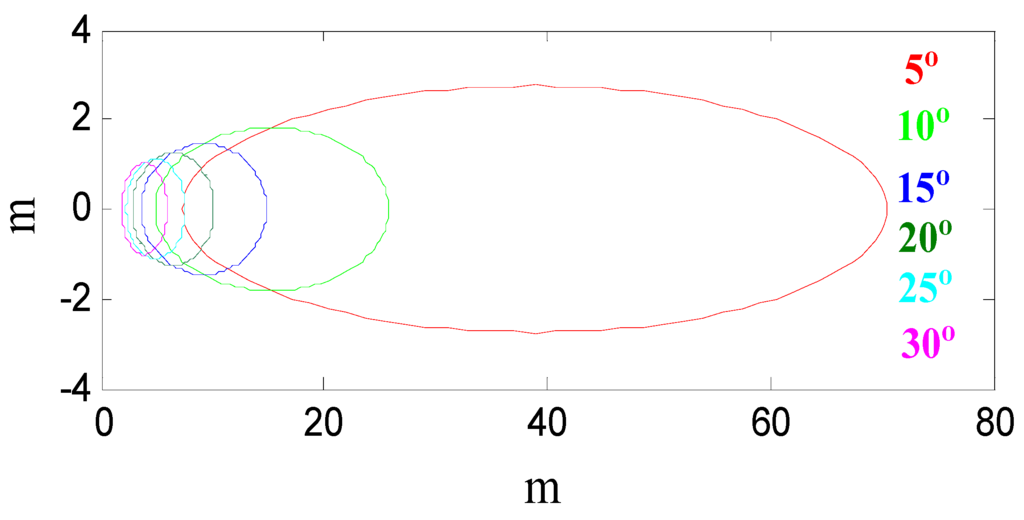
Figure 13.
The First Fresnel zone for a typical 2 m antenna height with different elevation angles.
As described in Section 3.1, multipath modulations only exist at low elevation angles, such as 5°–25°. The sensing footprint becomes smaller with the rising of the elevation angles, which means that the received reflected signal will be smaller in the amplitude. In order to know the impact on snow depth retrieval, we compare the snow depth derived from different ranges of elevation angles (5°–30°, 5°–35° and 5°–25°) at AB39 (Figure 14). The snow depth derived from 5°–25° and 5°–30° has little differences, with a correlation of 0.98 and a RMSE of 0.03 m. While the results of 5°–35°are not as good as 5°–30°, which has a decreasing correlation of 0.96 and RMSE of 0.04 m. It indicates that snow depth estimations will be affected when the range of elevation angles is higher. Therefore, using GPS SNR data below 30° is better to retrieve the snow depth.
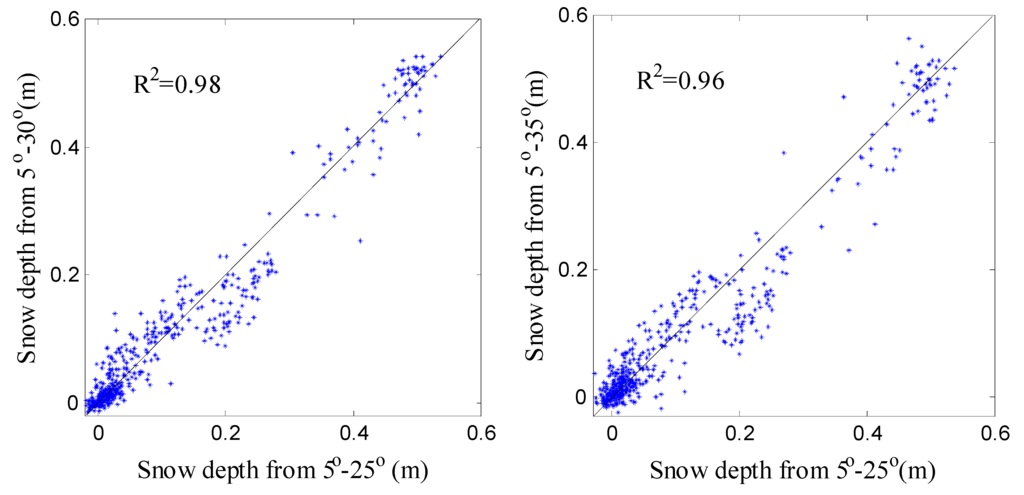
Figure 14.
Comparison of snow depth estimations from different ranges of 5°–25°, 5°–30°and 5°–35° elevation angles at AB39.
5.3. Effect of the Data Sampling Rate
With the increasing the sampling rate of GPS observations, the number of observations is reducing, meaning that the multipath modulations will become smoother. The smoothing modulations will lose some information in high frequency variations. Therefore, the data sampling rate may affect snow depth estimation. The SNR data used in previous studies of Larson and Nievinski [16] are 1 s sampling rate, because they thought that 1 s sampling would reduce the effect of high frequency noise. However, most of the IGS stations and other GPS stations are typically with a 15 s or 30 s sampling rate. Figure 15 shows comparison of 15 s and 60 s sampling multipath patterns and Lomb Scargle Periodograms at AB39. The multipath pattern becomes smoother when the sampling rate is 60 s, which indicates that some high frequency information is lost. After converted into the Lomb Scargle Periodogram, the peak height also has some differences. In order to find out the effect of the sampling rate on results, we compare the different sampling rate results (30 s and 60 s) with a sampling rate of 15 s (Figure 16). The result derived from 30 s sampling has little differences with respect to 15 s, showing a correlation coefficient of 0.99 and a RMSE of 0.02 m, while the correlation of GPS estimations from 60 s is 0.98 and the RMSE is 0.04 m. When the sampling rate is 60 s, one SNR trace for a ascending or descending track has less observations. These fewer observations will have an impact on retrieving the frequency of modulations. The sampling rate for most IGS stations or other GPS networks is normally 30 s. Based on the above analysis, the 30 s of data can be used to retrieve accurate snow depths. More important, the results have fewer differences with respect to results from a low sampling rate.
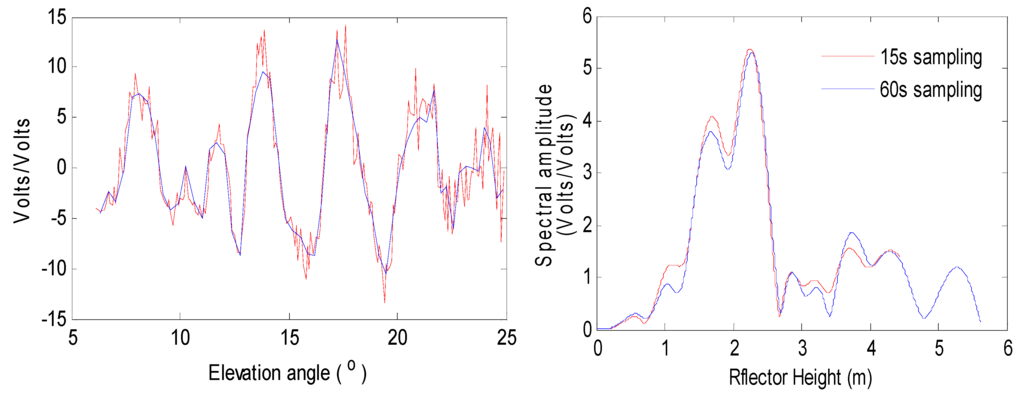
Figure 15.
Comparison of 15 s and 60 s sampling multipath patterns and Lomb Scargle Periodograms at AB39.
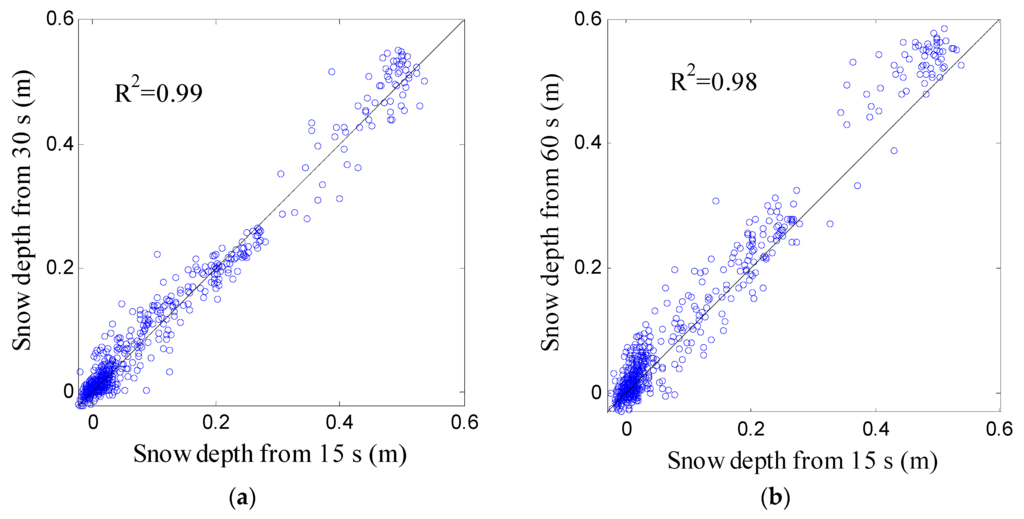
Figure 16.
Comparison of snow depth estimations from different sampling rates of 15 s, 30 s and 60 s at AB39. (a) Correlation between 15 s and 30 s; (b) Correlation between 15 s and 60 s.
6. Conclusions
Due to the interference between direct and reflected signals, multipath modulations appear in GPS measurements. The SNR data reflect multipath effects, which can be used to derive the frequency of modulations and the reflector height variations. In this paper, snow depth variations in Alaska are estimated from new GPS L2P SNR data at AB33, AB39 and SG27. The results from GPS L2P SNR data are compared with in situ snow depths from SNOTEL, showing a correlation of 0.98, 0.88 and 0.79 at AB33, AB39 and SG27, respectively. These results indicate that GPS L2P SNR data can be used to well retrieve snow depths from old antennas. Although the strength of L2P is lower than L1C/A, snow depth estimations from L1C/A and L2P have no significant differences with a correlation of 0.97, 0.93 and 0.94 at the AB33, AB39 and SG27 stations, respectively. When L2C SNR data are not available, old L1C/A or L2P SNR data also can be used to retrieve snow depths.
The sampling rate will affect the number of observations and the fitting of the direct trend for one SNR trace. The snow depths derived from 30 s and 60 s SNR data are comparable to 15 s sampling. The snow depth derived from 30 s sampling data has almost the same precision as 15 s sampling data with a correlation coefficient of 0.99 and a RMSE of 0.02 m. In addition, results from the range of 5°–30° elevation angles have less difference with respect to the range of 5°–25°, while the range of 5°–35°elevation angles has some differenc when compared to the range of 5°–30°. Therefore, SNR data below 30° elevation angle are better to estimate the snow depth. With the development of other GNSS systems like BeiDou, GLONASS and Galileo, it will provide more opportunity in the future.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Project (Grant Nos. 11173050 and 11373059) and Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Project (Grant No. 12DZ2273300). Great appreciation is extended to the PBO for providing the GPS data and as well as to the Scientific Research Project Office of Bulent Ecevit University for support.
Author Contributions
Shuanggen Jin and Xiaodong Qian wrote the main manuscript text and prepared the figures and tables. H. Kutoglu checked the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cohen, J.; Entekhabi, D. Eurasian snow cover variability and Northern Hemisphere climate predictability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.E. Snow cover and atmospheric variability: Changes in the snow covering the earth’s surface affect both daily weather and long-term climate. Am. Sci. 1984, 72, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Rott, H.; Yueh, S.H.; Cline, D.W.; Duguay, C.; Essery, R.; Haas, C.; Heliere, F.; Kern, M.; Macelloni, G.; Malnes, E.; et al. Cold Regions Hydrology High-Resolution Observatory for Snow and Cold Land Processes. IEEE Proc. 2010, 98, 752–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniston, M. Climatic change in mountain regions: A review of possible impacts. In Climate Variability and Change in High Elevation Regions: Past, Present & Future; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 5–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann, E.D.; Larson, K.M.; Williams, M.W.; Nievinski, F.G.; Zavorotny, V. Snow measurement by GPS interferometric reflectometry: An evaluation at Niwot Ridge, Colorado. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najibi, N.; Jin, S.G. Physical reflectivity and polarization characteristics for snow and ice-covered surfaces interacting with GPS signals. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4006–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najibi, N.; Jin, S.G.; Wu, X. Validating the variability of snow accumulating and melting from GPS reflected signals: Forward modeling. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 2646–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.G.; Feng, G.P.; Gleason, S. Remote sensing using GNSS signals: Current status and future directions. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.G.; Najibi, N. Sensing snow height and surface temperature variations in Greenland from GPS reflected signals. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.G.; Cardellach, E.; Xie, F. GNSS Remote Sensing: Theory, Methods and Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, K.M.; Braun, J.J.; Small, E.E.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Gutmann, E.D.; Bilich, A.L. GPS multipath and its relation to near-surface soil moisture content. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.G.; Occhipinti, G.; Jin, R. GNSS ionospheric seismology: Recent observation evidences and characteristics. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 147, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.U.; Voronovich, A.G. Scattering of GPS signals from the ocean with wind remote sensing application. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.U.; Larson, K.M.; Braun, J.J.; Small, E.E.; Gutmann, E.; Bilich, A. A physical model for GPS multipath caused by ground reflections: Toward bare soil moisture retrievals. IEEE-JSTARS 2010, 3, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, K.M.; Gutmann, E.D.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Braun, J.J.; Williams, M.W.; Nievinski, F.G. Can we measure snow depth with GPS receivers? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Nievinski, F.G. GPS snow sensing: Results from the EarthScope Plate Boundary Observatory. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Won, D.; Akos, D.M. Snow depth sensing using the GPS L2C signal with a dipole antenna. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibi, S.; Nievinski, F.G.; van Dam, T.; Monico, J.F.G. Assessment of modernized GPS L5 SNR for ground-based multipath reflectometry applications. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefty, J.; Gerhatova, L. Using GPS Multipath for Snow Depth Sensing-First Experience with Data from Permanent Stations in Slovakia. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2014, 11, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.G.; Wang, J.; Park, P.H. An improvement of GPS height estimates: Stochastic modeling. Earth Planets Space 2005, 57, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Nievinski, F.G.; Larson, K.M. An open source GPS multipath simulator in Matlab/Octave. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nievinski, F.G.; Larson, K.M. Inverse modeling of GPS multipath for snow depth estimation—Part I: Formulation and simulations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6555–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vey, S.; Guntner, A.; Wickert, J.; Blume, T.; Ramatschi, M. Long-term soil moisture dynamics derived from GNSS interferometric reflectometry: A case study for Sutherland, South Africa. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).