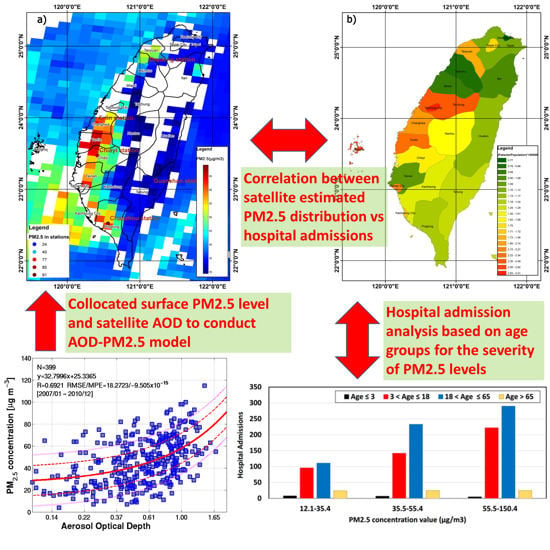
Spatial Correlation of Satellite-Derived PM2.5 with Hospital Admissions for Respiratory Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Ground In Situ PM2.5 Data
2.4. Hospital Admission Data
3. Preliminary Results
3.1. AOD-PM2.5 Model
3.2. Satellite-Derived PM2.5 and Hospital Admissions for Allergic Rhinitis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lipsett, M.; Hurley, S.; Ostro, B. Air pollution and emergency room visits for asthma in Santa Clara County, California. Environ. Health Perspect. 1997, 105, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilabaca, M.; Olaeta, I.; Campos, E.; Villaire, J.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Romieu, I. Association between levels of fine particulate and emergency visits for pneumonia and other respiratory illnesses among children in Santiago, Chile. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1999, 49, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaughter, J.C.; Kim, E.; Sheppard, L.; Sullivan, J.H.; Larson, T.V.; Claiborn, C. Association between particulate matter and emergency room visits, hospital admissions and mortality in Spokane, Washington. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2005, 15, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.; Ebisu, K.; Peng, R. Community-level spatial heterogeneity of chemical constituent levels of fine particulates and implications for epidemiological research. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, F.; Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L.; Pham, L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M. Fine particulate air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2006, 295, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, S.; Castro, R.; Pan, X. PM2.5 monitoring and mitigation in the cities of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3627–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, L.; Grize, L.; Infanger, D.; Künzli, N.; Sommer, H.; Alt, G.M.; Schindler, C. Associations of daily levels of PM10 and NO2 with emergency hospital admissions and mortality in Switzerland: Trends and missed prevention potential over the last decade. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, T.; Su, C.C.; Siringan, F.; Amano, A.; Onodera, S.I. Effects of environmental regulations on heavy metal pollution decline in core sediments from Manila Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, R.M.; Christopher, S.A. Remote sensing of particulate pollution from space: Have we reached the promised land? J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.; Kaufman, Y.; Zibordi, G.; Chern, J.; Mao, J.; Li, C.; Holben, B. Global Monitoring of Air Pollution Over Land from the Earth Observing System-Terra Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Liang, D.; Comellas, A.; Chu, A.; Abrams, T. Satellite-Based PM Concentrations and Their Application to Copd in Cleveland, OH. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 in China Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7436–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.; Ferrare, R.; Szykman, J.; Lewis, J.; Scarino, A.; Hains, J.; Burton, S.; Chen, G.; Tsai, T.; Hostetler, C.; et al. Regional Characteristics of the Relationship Between Columnar AOD and Surface PM2.5: Application of Lidar Aerosol Extinction Profiles Over Baltimore-Washington Corridor during Discover-AQ. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Liu, S.C.; Chou, C.C.-K.; Liu, T.H.; Lee, C.-T.; Yuan, C.-S.; Shiu, C.-J.; Young, C.-Y. Long-Range Transport of Asian Dust and Air Pollutants to Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2004, 15, 759–784. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Kuo, S.-Z.; Lim, A.H.N.; Hsu, S.-C.; Tseng, K.-H.; Yeh, N.-C.; Yang, Y.-C. Optimal Use of Space-Borne Advanced Infrared and Microwave Soundings for Regional Numerical Prediction. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-L.; Schmit, T.J.; Wu, X.; Menzel, W.P.; Gurka, J.J. Optimal Cloud-Clearing for AIRS Radiances Using MODIS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Li, J.; Weisz, E.; Schmit, T.J.; Ackerman, S.A.; Huang, H.-L. Synergistic use of AIRS and MODIS radiance measurements for atmospheric profiling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L21802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, C.-Y.; Zhang, P.; Schmit, T.J. Applications of Full Spatial Resolution Space-Based Advanced Infrared Soundings in the Preconvection Environment. Weather Forecast. 2012, 27, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Li, J.; Ho, S.-P.; Liu, G.-R.; Lin, T.-H.; Young, C.-C. Retrieval of Atmospheric Thermodynamic State from Synergistic Use of Radio Occultation and Hyperspectral Infrared Radiances Observations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.C.; Jeng, Y.J.; Chu, D.A.; Chen, J.P.; Chang, S.C. Analysis of the relationship between MODIS aerosol optical depth and particulate matter from 2006 to 2008. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4777–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Injuries, and Causes of Death, 9th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Fuertes, E.; Brauer, M.; MacIntyre, E.; Bauer, M.; Bellander, T.; von Berg, A.; Berdel, D.; Brunekreef, B.; Chan-Yeung, M.; Gehring, U.; et al. Childhood allergic rhinitis, traffic-related air pollution, and variability in the GSTP1, TNF, TLR2, and TLR4 genes: Results from the TAG Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Qiu, Z.; Chung, K.F.; Huang, S.-K. Link between environmental air pollution and allergic asthma: East meets West. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Liu, G.-R.; Lin, T.-H.; Liu, C.-C.; Ren, H.; Young, C.-C. Using Surface Stations to Improve Sounding Retrievals from Hyperspectral Infrared Instruments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6957–6963. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lau, A.; Mao, J.; Chu, D. Retrieval, Validation, and Application of the 1-km Aerosol Optical Depth from MODIS Measurements over Hong Kong. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Chudnovsky, A.A.; Kostinski, A.; Lyapustin, A.; Koutrakis, P. Spatial scales of pollution from variable resolution satellite imaging. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Franklin, M.; Kahn, R.; Koutrakis, P. Using aerosol optical thickness to predict ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the St. Louis area: A comparison between MISR and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sarnat, J.A.; Kilaru, V.; Jacob, D.J.; Koutrakis, P. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 in the eastern United States using satellite remote sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3269–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, L.; Malakar, N.; Wu, Y.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F. Assessing surface PM2.5 estimates using data fusion of active and passive remote sensing methods. Br. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 547–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A. Particulate matter air quality assessment using integrated surface, satellite, and meteorological products: Multiple regression approach. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D14205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Variable | Mean ± Std. Dev. | Percentile | IQR/(Max-Min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (25th) | Q2 (50th) | Q3 (75th) | |||
| Satellite-derived AOD | 0.6029 ± 0.3195 | 0.378 | 0.581 | 0.842 | 27.7% |
| Observed PM2.5 (µg·m−3) | 45.1108 ± 21.4385 | 27.0 | 44.0 | 62.0 | 23.8% |
| Estimated PM2.5 (µg·m−3) | 44.9092 ± 10.4801 | 37.7 | 44.4 | 53.0 | 27.1% |
| City | Area (km2) | Population (Thousand) | Temperature (°C) (Spring/Fall) | RH (%) (Spring/Fall) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taoyuan | 1221 | 2106 | 19.9/24.1 | 81.1/76.7 |
| Taichung | 2215 | 2744 | 21.5/24.8 | 77.0/73.7 |
| Tainan | 2192 | 1885 | 22.9/25.7 | 77.0/76.3 |
| PM2.5 Concentration (µg·m−3) | Air Quality Scenarios | Health Advisory |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0~12.0 | Good | None |
| 12.1~35.4 | Moderate | Unusually sensitive people should consider reducing prolonged or heavy exertion |
| 35.5~55.4 | Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups | People with heart or lung disease, older adults, and children should reduce prolonged or heavy exertion |
| 55.5~150.4 | Unhealthy | People with heart or lung disease, older adults, and children should avoid prolonged or heavy exertion. Everyone else should reduce prolonged or heavy exertion. |
| 150.5~500.0 | Very Unhealthy | People with heart or lung disease, older adults, and children should avoid physical activity outdoors. Everyone else avoid prolonged or heavy exertion. |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-J.; Liu, C.-Y.; Mong, N.T.; Chou, C.C.K. Spatial Correlation of Satellite-Derived PM2.5 with Hospital Admissions for Respiratory Diseases. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110914
Liu C-J, Liu C-Y, Mong NT, Chou CCK. Spatial Correlation of Satellite-Derived PM2.5 with Hospital Admissions for Respiratory Diseases. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(11):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110914
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ching-Ju, Chian-Yi Liu, Ngoc Thi Mong, and Charles C. K. Chou. 2016. "Spatial Correlation of Satellite-Derived PM2.5 with Hospital Admissions for Respiratory Diseases" Remote Sensing 8, no. 11: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110914
APA StyleLiu, C.-J., Liu, C.-Y., Mong, N. T., & Chou, C. C. K. (2016). Spatial Correlation of Satellite-Derived PM2.5 with Hospital Admissions for Respiratory Diseases. Remote Sensing, 8(11), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110914