An Assessment of HIRS Surface Air Temperature with USCRN Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Retrieval Algorithm
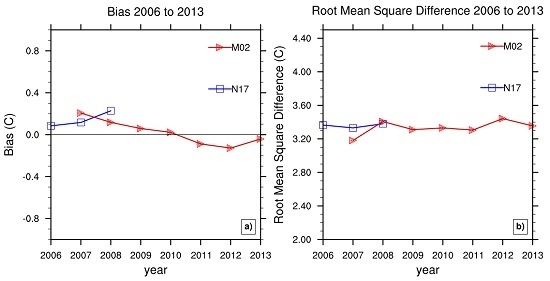
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HIRS | High Resolution Infrared Radiation Sounder |
| USCRN | U.S. Climate Reference Network |
| RCRN | Regional Climate Reference Network |
| RMSD | root mean square difference |
| SAT | surface air temperature |
| CDR | climate data record |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| Metop | Meteorological Operational satellite program |
| EUMETSAT | European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites |
| AVHRR | Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer |
| PATMOS-x | Pathfinder Atmospheres-Extended |
| N17 | NOAA-17 |
| M02 | Metop-A |
| UTC | Coordinated Universal Time |
| AIRS | Atmospheric Infrared Sounder |
| TOVS | TIROS Operational Vertical Sounder |
| TIROS | Television Infrared Observation Satellite |
References
- Rennie, J.J.; Lawrimore, J.H.; Gleason, B.E.; Thorne, P.W.; Morice, C.P.; Menne, M.J.; Williams, C.N.; De Almeida, W.G.; Christy, J.R.; Flannery, M.; et al. The International Surface Temperature Initiative Global Land Surface Databank: Monthly Temperature Data Release Description and Methods. Geosci. Data J. 2014, 1, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Key, J.R.; Schweiger, A.; Francis, J. Characteristics of Satellite-Derived Clear-Sky Atmospheric Temperature Inversion Strength in the Arctic 1980–1996. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4902–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, E. Daily Minimum and Maximum Surface Air Temperatures from Geostationary Satellite Data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2306–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilibarda, M.; Hengl, T.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Gräler, B.; Pebesma, E.; Tadić, M.P.; Bajat, B. Spatio-Temporal Interpolation of Daily Temperatures for Global Land Ares at 1 km Resolution. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 2294–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, A.; Carvalho, A.C.; Nunes, J.P.; Carvalhais, N.; Santos, A. Estimating Air Surface Temperature in Portugal using MODIS LST Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, B.; McGill, B.J.; Wilson, A.M.; Regetz, J.; Jetz, W.; Guralnick, R.; Tuanmu, M.-N.; Schildhauer, M. Using Multi-Timescale Methods and Satellite-Derived Land Surface Temperature for the Interpolation of Daily Maximum Air Temperature in Oregon. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3862–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Bates, J.J.; Cao, C. Scene Radiance—Dependent Intersatellite Biases of HIRS Longwave Channels. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Matthews, J.; Ho, S.-P.; Yang, Q.; Bates, J. Algorithm development of temperature and humidity profile retrievals for long-term HIRS observations. Remote Sens. Basel 2016, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, G.; Siemann, A.L.; Pan, M.; Wood, E.F. Creating consistent datasets by combining remotely-sensed data and land surface model estimates through Bayesian uncertainty post-processing: The case of Land Surface Temperature from HIRS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.L.; Wylie, D.P.; Bates, J.J. The HIRS pathfinder radiance data set (1979–2001). In Proceedings of the 12th Conference on Satellite Meteorology and Oceanography, American Meteorological Society, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–13 February 2003.
- Shi, L. Intersatellite differences of HIRS longwave channels between noaa-14 and noaa-15 and between noaa-17 and metop-a. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B.; Garder, L.C. Cloud detection using satellite measurements of infrared and visible radiances for ISCCP. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 2341–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, A.K.; Foster, M.J.; Walther, A.; Zhao, X. The Pathfinder Atmospheres Extended (PATMOS-x) AVHRR Climate Data Set. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, H.J.; Karl, T.R.; Palecki, M.A.; Baker, C.B.; Bell, J.E.; Leeper, R.D.; Easterling, D.R.; Lawrimoer, J.H.; Meyers, T.P.; Helfert, M.R.; et al. U.S. Climate Reference Network after One Decade of Operations, Status and Assessment. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2013, 94, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Baker, C.B.; Karl, T.R.; Gifford, M.D. A Comparative Study of ASOS and USCRN Temperature Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, K.G.; Lin, X.; Baker, C.B.; Sun, B. Air Temperature Comparison between the MMTS and the USCRN Temperature Systems. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otkin, J.A.; Anderson, M.C.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Diak, G.R. Validation of GOES-Based Insolation Estimates using Data from the U.S. Climate Reference Network. J. Hydrometeor. 2005, 6, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.E.; Palecki, M.A.; Baker, C.B.; Collins, W.G.; Lawrimore, J.H.; Leeper, T.D.; Hall, M.E.; Kochendorger, J.; Meyers, T.P.; Wilson, T.; et al. U.S. Climate Reference Network Soil Moisture and Temperature Observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Shi, L.; Stegall, S.T.; Matthwes, J.L.; Fairall, C.W. An evaluation of HIRS near-surface air temperature product in the arctic with sheba data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.L.; Soden, B.J. Detection and correction of diurnal sampling bias in HIRS/2 brightness temperatures. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.; Matricardi, M.; Brunel, P. An improved fast radiative transfer model for assimilation of satellite radiance observations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 1407–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, F. Sampled Databases of 60-Level Atmospheric Profiles from the ECMWF Analyses; Research Report No. 4; EUMETSAT/ECMWF SAF Programme 2001. Available online: http://nwpsaf.eu/downloads/profiles/profiles_60L.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Gao, W.; Zhao, F.; Xu, Y.; Feng, X. Validation of the Surface Air Temperature Products Retrieved from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder over China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, V.; Czajkowski, K.; Dubayah, R.; Susskind, J. Land Surface Air Temperature Mapping Using TOVS and AVHRR. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stegall, S.T.; Shi, L. An Assessment of HIRS Surface Air Temperature with USCRN Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060485
Stegall ST, Shi L. An Assessment of HIRS Surface Air Temperature with USCRN Data. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(6):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060485
Chicago/Turabian StyleStegall, Steve T., and Lei Shi. 2016. "An Assessment of HIRS Surface Air Temperature with USCRN Data" Remote Sensing 8, no. 6: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060485
APA StyleStegall, S. T., & Shi, L. (2016). An Assessment of HIRS Surface Air Temperature with USCRN Data. Remote Sensing, 8(6), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060485