NF-κB Dependent Chemokine Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. NF-κB Signaling in PDAC
3. Chemokines and Their Receptors
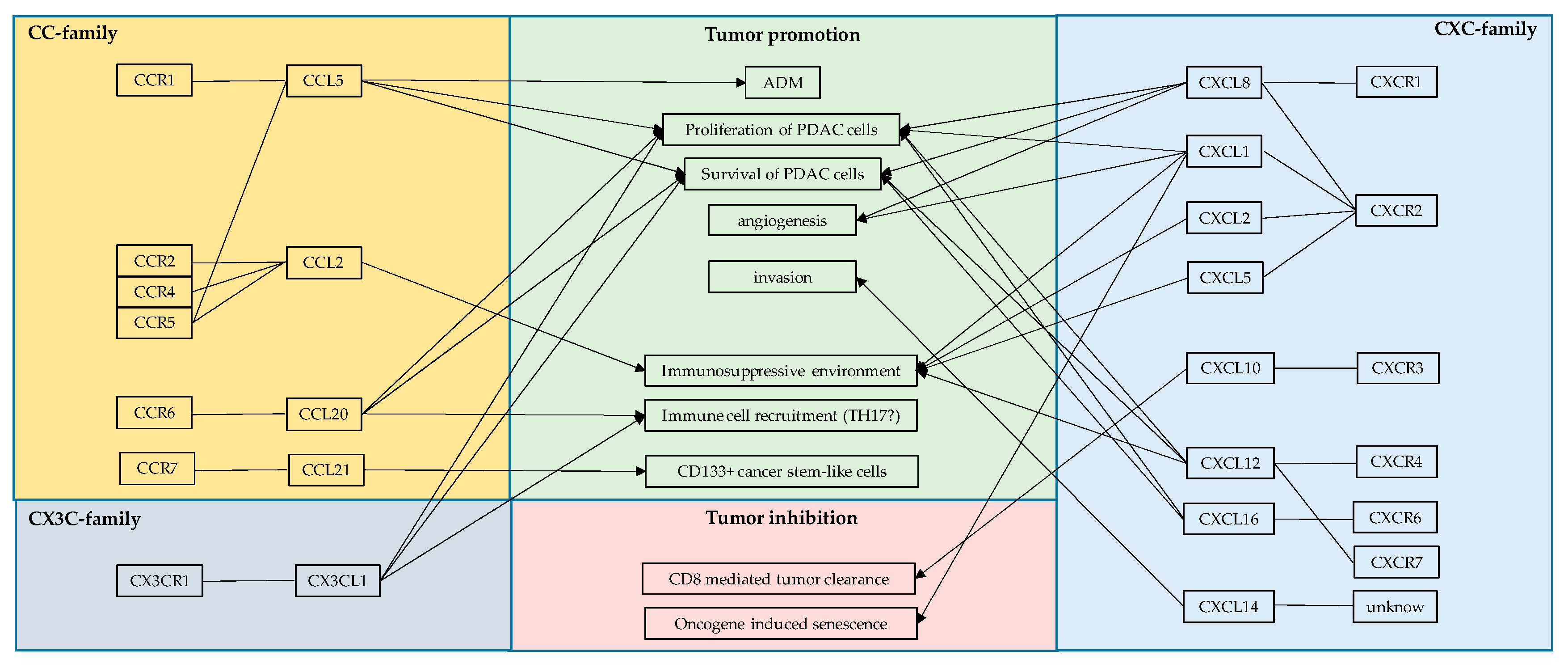
4. NF-κB Interacting Chemokines in PDAC
4.1. CCL2
4.2. CCL5
4.3. CCL20
4.4. CCL21
4.5. CXCL1
4.6. CXCL5
4.7. CXCL8
4.8. CXCL10
4.9. CXCL12
4.10. CXCL14
4.11. CXCL16
4.12. CX3CL1
5. Discussion
Anti-Tumor Effects of NF-κB/Chemokine Interactions—A Double Edged Sword
6. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aichler, M.; Seiler, C.; Tost, M.; Siveke, J.; Mazur, P.K.; Da Silva-Buttkus, P.; Bartsch, D.K.; Langer, P.; Chiblak, S.; Durr, A.; et al. Origin of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from atypical flat lesions: A comparative study in transgenic mice and human tissues. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Palmer, D.H.; Ghaneh, P.; Psarelli, E.E.; Valle, J.W.; Halloran, C.M.; Faluyi, O.; O’Reilly, D.A.; Cunningham, D.; Wadsley, J.; et al. Comparison of adjuvant gemcitabine and capecitabine with gemcitabine monotherapy in patients with resected pancreatic cancer (ESPAC-4): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chiaro, M.; Valente, R.; Arnelo, U. Neoadjuvant treatment in locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer vs. primary resectable pancreatic cancer. JAMA Surg. 2017, 152, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabar, C.S.; Winter, J.M. Pancreatic cancer: A review. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 45, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neesse, A.; Algul, H.; Tuveson, D.A.; Gress, T.M. Stromal biology and therapy in pancreatic cancer: A changing paradigm. Gut 2015, 64, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Laguna, I.; Hidalgo, M. Pancreatic cancer: From state-of-the-art treatments to promising novel therapies. Nat. Rev. 2015, 12, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlt, A.; Schafer, H.; Kalthoff, H. The ‘N-factors’ in pancreatic cancer: Functional relevance of NF-kappaB, NFAT and Nrf2 in pancreatic cancer. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormann, S.M.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Lesina, M.; Algul, H. The immune network in pancreatic cancer development and progression. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2956–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neesse, A.; Bauer, C.A.; Ohlund, D.; Lauth, M.; Buchholz, M.; Michl, P.; Tuveson, D.A.; Gress, T.M. Stromal biology and therapy in pancreatic cancer: Ready for clinical translation? Gut 2019, 68, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromnes, I.M.; Brockenbrough, J.S.; Izeradjene, K.; Carlson, M.A.; Cuevas, C.; Simmons, R.M.; Greenberg, P.D.; Hingorani, S.R. Targeted depletion of an MDSC subset unmasks pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma to adaptive immunity. Gut 2014, 63, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arlt, A.; Muerkoster, S.S.; Schafer, H. Targeting apoptosis pathways in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geismann, C.; Grohmann, F.; Sebens, S.; Wirths, G.; Dreher, A.; Hasler, R.; Rosenstiel, P.; Hauser, C.; Egberts, J.H.; Trauzold, A.; et al. c-Rel is a critical mediator of NF-kappaB-dependent TRAIL resistance of pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabacaoglu, D.; Ruess, D.A.; Ai, J.; Algul, H. NF-kappaB/Rel transcription factors in pancreatic cancer: Focusing on RelA, c-Rel, and RelB. Cancers 2019, 11, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muerkoster, S.; Arlt, A.; Witt, M.; Gehrz, A.; Haye, S.; March, C.; Grohmann, F.; Wegehenkel, K.; Kalthoff, H.; Folsch, U.R.; et al. Usage of the NF-kappaB inhibitor sulfasalazine as sensitizing agent in combined chemotherapy of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 104, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlt, A.; Gehrz, A.; Muerkoster, S.; Vorndamm, J.; Kruse, M.L.; Folsch, U.R.; Schafer, H. Role of NF-kappaB and Akt/PI3K in the resistance of pancreatic carcinoma cell lines against gemcitabine-induced cell death. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3243–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlt, A.; Vorndamm, J.; Breitenbroich, M.; Folsch, U.R.; Kalthoff, H.; Schmidt, W.E.; Schafer, H. Inhibition of NF-kappaB sensitizes human pancreatic carcinoma cells to apoptosis induced by etoposide (VP16) or doxorubicin. Oncogene 2001, 20, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kober-Hasslacher, M.; Schmidt-Supprian, M. The unsolved puzzle of c-Rel in B cell lymphoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltschmidt, C.; Banz-Jansen, C.; Benhidjeb, T.; Beshay, M.; Forster, C.; Greiner, J.; Hamelmann, E.; Jorch, N.; Mertzlufft, F.; Pfitzenmaier, J.; et al. A role for NF-kappaB in organ specific cancer and cancer stem cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czauderna, C.; Castven, D.; Mahn, F.L.; Marquardt, J.U. Context-dependent role of NF-kappaB signaling in primary liver cancer-from tumor development to therapeutic implications. Cancers 2019, 11, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, L.; Mundade, R.; Korc, M.; Loehrer, P.J.; Lu, T. Critical role of NF-kappaB in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 10969–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauzold, A.; Roder, C.; Sipos, B.; Karsten, K.; Arlt, A.; Jiang, P.; Martin-Subero, J.I.; Siegmund, D.; Muerkoster, S.; Pagerols-Raluy, L.; et al. CD95 and TRAF2 promote invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauzold, A.; Siegmund, D.; Schniewind, B.; Sipos, B.; Egberts, J.; Zorenkov, D.; Emme, D.; Roder, C.; Kalthoff, H.; Wajant, H. TRAIL promotes metastasis of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7434–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roder, C.; Trauzold, A.; Kalthoff, H. Impact of death receptor signaling on the malignancy of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, L.; Pan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Cao, G. Integrated analysis of mRNA and miRNA expression profiles in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2779–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimada, M.; Andoh, A.; Araki, Y.; Fujiyama, Y.; Bamba, T. Ligation of the Fas antigen stimulates chemokine secretion in pancreatic cancer cell line PANC-1. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 16, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaya, H.; Andoh, A.; Shimada, M.; Hata, K.; Fujiyama, Y.; Bamba, T. The expression of chemokine genes correlates with nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pancreas 2000, 21, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, G.Y.; Doppler, H.; Necela, B.; Krishna, M.; Crawford, H.C.; Raimondo, M.; Storz, P. Macrophage-secreted cytokines drive pancreatic acinar-to-ductal metaplasia through NF-kappaB and MMPs. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geismann, C.; Grohmann, F.; Dreher, A.; Hasler, R.; Rosenstiel, P.; Legler, K.; Hauser, C.; Egberts, J.H.; Sipos, B.; Schreiber, S.; et al. Role of CCL20 mediated immune cell recruitment in NF-kappaB mediated TRAIL resistance of pancreatic cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Das, S.; Rachagani, S.; Kaur, S.; Joshi, S.; Johansson, S.L.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Jain, M.; Batra, S.K. NCOA3-mediated upregulation of mucin expression via transcriptional and post-translational changes during the development of pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4879–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; et al. CCL21/CCR7 Axis contributed to CD133+ pancreatic cancer stem-like cell metastasis via EMT and Erk/NF-kappaB pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharry, C.E.; Haines, K.M.; Carroll, R.G.; May, M.J. Constitutive non-canonical NFkappaB signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesina, M.; Wormann, S.M.; Morton, J.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Korneeva, O.; Wimmer, M.; Einwachter, H.; Sperveslage, J.; Demir, I.E.; Kehl, T.; et al. RelA regulates CXCL1/CXCR2-dependent oncogene-induced senescence in murine Kras-driven pancreatic carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2919–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosoi, F.; Izumi, H.; Kawahara, A.; Murakami, Y.; Kinoshita, H.; Kage, M.; Nishio, K.; Kohno, K.; Kuwano, M.; Ono, M. N-myc downstream regulated gene 1/Cap43 suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer through attenuation of inhibitor of kappaB kinase beta expression. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4983–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, T.; Furth, E.E.; Vonderheide, R.H. CXCR2-dependent accumulation of tumor-associated neutrophils regulates T-cell immunity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 968–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Hosoi, F.; Izumi, H.; Maruyama, Y.; Ureshino, H.; Watari, K.; Kohno, K.; Kuwano, M.; Ono, M. Identification of sites subjected to serine/threonine phosphorylation by SGK1 affecting N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 (NDRG1)/Cap43-dependent suppression of angiogenic CXC chemokine expression in human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Ding, G.; Zhou, L.; Shen, T.; Xu, X.; Zhao, T.; Jia, S.; Cao, L. Interferon gamma inhibits CXCL8-induced proliferation and migration of pancreatic cancer BxPC-3 cell line via a RhoGDI2/Rac1/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2018, 38, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Imafuji, H.; Okubo, T.; Maeda, Y.; Sato, T.; Shamoto, T.; Tsuboi, K.; Morimoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Xanthohumol inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing nuclear factor-kappaB activation in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legler, K.; Hauser, C.; Egberts, J.H.; Willms, A.; Heneweer, C.; Boretius, S.; Rocken, C.; Gluer, C.C.; Becker, T.; Kluge, M.; et al. The novel TRAIL-receptor agonist APG350 exerts superior therapeutic activity in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Baba, T.; Li, Y.Y.; Furukawa, K.; Tanabe, Y.; Matsugo, S.; Sasaki, S.; Mukaida, N. Gemcitabine-induced CXCL8 expression counteracts its actions by inducing tumor neovascularization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, K.; Uwagawa, T.; Haruki, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Iida, T.; Shiba, H.; Misawa, T.; Ohashi, T.; Yanaga, K. Nuclear factor kappaB activity correlates with the progression and prognosis of pancreatic cancer in a mouse model. Surg. Today 2013, 43, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, A.; Multhoff, G.; Radons, J. Interleukin-33 acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine and modulates its receptor gene expression in highly metastatic human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cytokine 2012, 60, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.J.; Sun, B.; Cheng, Z.X.; Zhou, H.X.; Gao, Y.; Kong, R.; Chen, H.; Jiang, H.C.; Pan, S.H.; Xue, D.B.; et al. Dihydroartemisinin inhibits angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer by targeting the NF-kappaB pathway. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 68, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasramka, M.A.; Gupta, S.V. Garcinol inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurbitz, C.; Heise, D.; Redmer, T.; Goumas, F.; Arlt, A.; Lemke, J.; Rimbach, G.; Kalthoff, H.; Trauzold, A. Epicatechin gallate and catechin gallate are superior to epigallocatechin gallate in growth suppression and anti-inflammatory activities in pancreatic tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Haruki, K.; Shimada, Y.; Iida, T.; Shiba, H.; Uwagawa, T.; Ohashi, T.; Yanaga, K. Nafamostat mesilate can prevent adhesion, invasion and peritoneal dissemination of pancreatic cancer thorough nuclear factor kappa-B inhibition. J. Hepato Biliary Pancreat. Sci. 2011, 18, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Sawai, H.; Ochi, N.; Yasuda, A.; Sakamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Funahashi, H.; Takeyama, H.; Guha, S. Proteasome inhibitor MG132 inhibits angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer by blocking NF-kappaB activity. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, C.M.; Mathew, L.; Mosley, S.A.; Kurzrock, R.; Smith, J.A. Determination of minimum effective dose and optimal dosing schedule for liposomal curcumin in a xenograft human pancreatic cancer model. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 1895–1899. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.H.; Trauzold, A.; Roder, C.; Pan, G.; Zheng, C.; Kalthoff, H. The potential molecular mechanism of overexpression of uPA, IL-8, MMP-7 and MMP-9 induced by TRAIL in pancreatic cancer cell. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2008, 7, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, N.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Newman, R.A.; Wolff, R.A.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Ng, C.S.; Badmaev, V.; Kurzrock, R. Phase II trial of curcumin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4491–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamohara, H.; Takahashi, M.; Ishiko, T.; Ogawa, M.; Baba, H. Induction of interleukin-8 (CXCL-8) by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and leukemia inhibitory factor in pancreatic carcinoma cells: Impact of CXCL-8 as an autocrine growth factor. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 31, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farrow, B.; Sugiyama, Y.; Chen, A.; Uffort, E.; Nealon, W.; Mark Evers, B. Inflammatory mechanisms contributing to pancreatic cancer development. Ann. Surg. 2004, 239, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, J.A., 2nd; Barve, S.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Talwalker, R.; Gates, L.K., Jr. Antioxidants inhibit cytokine production and suppress NF-kappaB activation in CAPAN-1 and CAPAN-2 cell lines. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2001, 46, 2768–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andoh, A.; Shimada, M.; Takaya, H.; Hata, K.; Fujiyama, Y.; Bamba, T. Transforming growth factor-beta1 acts as a potent inhibitor of complement C3 biosynthesis in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pancreas 2000, 20, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.A.; Kawahara, T.L.; Sutphin, P.D.; Chang, H.Y.; Chi, J.T.; Giaccia, A.J. Tumor vasculature is regulated by PHD2-mediated angiogenesis and bone marrow-derived cell recruitment. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnemuth, B.; Muhlberg, L.; Schipper, M.; Griesmann, H.; Neesse, A.; Milosevic, N.; Wissniowski, T.; Buchholz, M.; Gress, T.M.; Michl, P. CUX1 modulates polarization of tumor-associated macrophages by antagonizing NF-kappaB signaling. Oncogene 2015, 34, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Cai, J.; Du, S.; Xin, B.; Wei, W.; Zhang, T.; Shen, X. Artemin regulates CXCR4 expression to induce migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells through activation of NF-kappaB signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 365, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, B.; Giri, B.; Modi, S.; Sethi, V.; Castro, I.; Umland, O.; Ban, Y.; Lavania, S.; Dawra, R.; Banerjee, S.; et al. NFkappaB in pancreatic stellate cells reduces infiltration of tumors by cytotoxic T cells and killing of cancer cells, via up-regulation of CXCL12. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Wu, P.; Tian, L.; Zhao, L.; Cai, B.; Yin, J.; Wu, Y.; Staveley-O’Carroll, K.F.; et al. Galectin-1-driven upregulation of SDF-1 in pancreatic stellate cells promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 397, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, S.; Srivastava, S.K.; McClellan, S.; Nirodi, C.S.; Piazza, G.A.; Grizzle, W.E.; Owen, L.B.; Singh, A.P. An undesired effect of chemotherapy: Gemcitabine promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness through reactive oxygen species-dependent, nuclear factor kappaB- and hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha-mediated up-regulation of CXCR4. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21197–21207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Arora, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Kadakia, M.P.; Wang, B.; Grizzle, W.E.; Owen, L.B.; Singh, S. CXCL12/CXCR4 protein signaling axis induces sonic hedgehog expression in pancreatic cancer cells via extracellular regulated kinase- and Akt kinase-mediated activation of nuclear factor kappaB: Implications for bidirectional tumor-stromal interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 39115–39124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Srivastava, S.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Owen, L.B.; Singh, A.P. CXCL12-CXCR4 signalling axis confers gemcitabine resistance to pancreatic cancer cells: A novel target for therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, A.W.; Hay, H.S.; Rajendran, P.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Li, F.; Bist, P.; Koay, E.S.; Lim, L.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G. Butein downregulates chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression and function through suppression of NF-kappaB activation in breast and pancreatic tumor cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wente, M.N.; Mayer, C.; Gaida, M.M.; Michalski, C.W.; Giese, T.; Bergmann, F.; Giese, N.A.; Buchler, M.W.; Friess, H. CXCL14 expression and potential function in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2008, 259, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalabi-Dchar, M.; Cassant-Sourdy, S.; Duluc, C.; Fanjul, M.; Lulka, H.; Samain, R.; Roche, C.; Breibach, F.; Delisle, M.B.; Poupot, M.; et al. Loss of somatostatin receptor subtype 2 promotes growth of KRAS-induced pancreatic tumors in mice by activating PI3K signaling and overexpression of CXCL16. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1452–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geismann, C.; Erhart, W.; Grohmann, F.; Schreiber, S.; Schneider, G.; Schafer, H.; Arlt, A. TRAIL/NF-kappaB/CX3CL1 mediated onco-immuno crosstalk leading to trail resistance of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cai, J.; Du, S.; Guo, Z.; Xin, B.; Wang, J.; Wei, W.; Shen, X. Fractalkine/CX3CR1 induces apoptosis resistance and proliferation through the activation of the AKT/NF-kappaB cascade in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2017, 35, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimsey, T.F.; Campbell, A.S.; Albo, D.; Wilson, M.; Wang, T.N. Co-localization of macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha (Mip-3alpha) and its receptor, CCR6, promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasion. Cancer J. 2004, 10, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Phan, T.K.; Hulett, M.D.; Korner, H. The relationship between CCR6 and its binding partners: Does the CCR6-CCL20 axis have to be extended? Cytokine 2015, 72, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Yang, X.O.; Chung, Y.; Fukunaga, A.; Nurieva, R.; Pappu, B.; Martin-Orozco, N.; Kang, H.S.; Ma, L.; Panopoulos, A.D.; et al. CCR6 regulates the migration of inflammatory and regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8391–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.S.; Albo, D.; Kimsey, T.F.; White, S.L.; Wang, T.N. Macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasion. J. Surg. Res. 2005, 123, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, D. TRAIL receptor mediates inflammatory cytokine release in an NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Lv, H.; Jia, X.; Liu, G.; Li, T.; Xu, Z.; Li, J. CC chemokine receptor 6 expression predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 110, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ke, F.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yan, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. CCR6 is a prognostic marker for overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer, and its overexpression enhances metastasis in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, B.; Pai, C.; Huang, Q.; Prabhala, R.H.; Munshi, N.C.; Gold, J.S. CCR6, the sole receptor for the chemokine CCL20, promotes spontaneous intestinal tumorigenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, S.T.; Faulkner, J.W.; McColl, S.R.; Kochetkova, M. The chemokine receptor CCR6 facilitates the onset of mammary neoplasia in the MMTV-PyMT mouse model via recruitment of tumor-promoting macrophages. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, C.; Dommisch, H.; Goke, F.; Kreppel, M.; Jepsen, S.; Rolf, F.; Dommisch, K.; Perner, S.; Standop, J. Expression profiles for 14-3-3 zeta and CCL20 in pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubie, C.; Frick, V.O.; Ghadjar, P.; Wagner, M.; Grimm, H.; Vicinus, B.; Justinger, C.; Graeber, S.; Schilling, M.K. CCL20/CCR6 expression profile in pancreatic cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Wu, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. CrkL meditates CCL20/CCR6-induced EMT in gastric cancer. Cytokine 2015, 76, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.C.; Chen, C.N.; Kuo, H.C.; Shi, C.S.; Hsieh, M.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Tung, S.Y.; Lee, K.F.; Huang, W.S. Interleukin-17 induces CC chemokine receptor 6 expression and cell migration in colorectal cancer cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2015, 230, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Pan, K.; Zheng, H.X.; Li, J.J.; Qiu, H.J.; Zhao, J.J.; Weng, D.S.; Pan, Q.Z.; Wang, D.D.; Jiang, S.S.; et al. IL-17A promotes immune cell recruitment in human esophageal cancers and the infiltrating dendritic cells represent a positive prognostic marker for patient survival. J. Immunother. 2013, 36, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadjar, P.; Rubie, C.; Aebersold, D.M.; Keilholz, U. The chemokine CCL20 and its receptor CCR6 in human malignancy with focus on colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, S.; Olszak, T.; Beigel, F.; Diebold, J.; Otte, J.M.; Eichhorst, S.T.; Goke, B.; Dambacher, J. Cell differentiation dependent expressed CCR6 mediates ERK-1/2, SAPK/JNK, and Akt signaling resulting in proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2006, 97, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neesse, A.; Ellenrieder, V. NEMO-CXCL12/CXCR4 axis: A novel vantage point for antifibrotic therapies in chronic pancreatitis? Gut 2017, 66, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarsheth, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Zou, W. Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Argentiero, A.; De Summa, S.; Di Fonte, R.; Iacobazzi, R.M.; Porcelli, L.; Da Via, M.; Brunetti, O.; Azzariti, A.; Silvestris, N.; Solimando, A.G. Gene expression comparison between the lymph node-positive and -negative reveals a peculiar immune microenvironment signature and a theranostic role for WNT targeting in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A pilot study. Cancers 2019, 11, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Liao, Q.; Niu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Y. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Future Oncol. 2015, 11, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, L.; Iacobazzi, R.M.; Di Fonte, R.; Serrati, S.; Intini, A.; Solimando, A.G.; Brunetti, O.; Calabrese, A.; Leonetti, F.; Azzariti, A.; et al. CAFs and TGF-beta signaling activation by mast cells contribute to resistance to gemcitabine/nabpaclitaxel in pancreatic cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoberg, E.; Meyrath, M.; Milde, L.; Herrera, M.; Lovrot, J.; Hagerstrand, D.; Frings, O.; Bartish, M.; Rolny, C.; Sonnhammer, E.; et al. A novel ACKR2-dependent role of fibroblast-derived CXCL14 in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3702–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessmann, E.; Patzak, M.S.; Klein, L.; Chen, N.; Kari, V.; Ramu, I.; Bapiro, T.E.; Frese, K.K.; Gopinathan, A.; Richards, F.M.; et al. Fibroblast drug scavenging increases intratumoural gemcitabine accumulation in murine pancreas cancer. Gut 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Bosch, N.; Vinaixa, J.; Navarro, P. Immune evasion in pancreatic cancer: From mechanisms to therapy. Cancers 2018, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.F.; Qi, W.X.; Liu, M.Y.; Li, Y. The combination of NK and CD8+T cells with CCL20/IL15-armed oncolytic adenoviruses enhances the growth suppression of TERT-positive tumor cells. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 318, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.H.; Hwang-Verslues, W.W.; Lee, W.H.; Huang, C.K.; Wei, P.C.; Chen, C.L.; Shew, J.Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Jeng, Y.M.; Tien, Y.W.; et al. Targeting IL-17B-IL-17RB signaling with an anti-IL-17RB antibody blocks pancreatic cancer metastasis by silencing multiple chemokines. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Family | Name | Alternative Name | Receptor |
|---|---|---|---|
| CC | CCL1 | I-309, TCA-3 | CCR8 |
| CCL2 | MCP-1 | CCR2/4/5 | |
| CCL3 | MIP-1α | CCR1/5 | |
| CCL4 | MIP-1ß | CCR5 | |
| CCL5 | RANTES | CCR1/3/5 | |
| CCL6 | C10, MRP-2 | CCR1 | |
| CCL7 | MARC, MCP-3 | CCR1/2 | |
| CCL8 | MCP-2 | CCR8 | |
| CCL9/10 | MRP-2, CCF18 | CCR1 | |
| CCL11 | Eotaxin | CCR3 | |
| CCL12 | MCP-5 | CCR2 | |
| CCL13 | MCP-4, NCC-1, Ckß10 | CCR1/2 | |
| CCL14 | HCC-1, MCIF, Ckß1, NCC-2, CCL | CCR1 | |
| CCL15 | Leukotactin-1, MIP-5, HCC-2, NCC-3 | CCR1/3 | |
| CCL16 | LEC, NCC-4, LMC, Ckß12 | CCR1/3 | |
| CCL17 | TARC, dendrokine, ABCD-2 | CCR4 | |
| CCL18 | PARC, DC-CK1, AMAC-1, Ckß7, MIP-4 | CCR8/GPR30 | |
| CCL19 | ELC, Exodus-3, Ckß11 | CCR7 | |
| CCL20 | LARC, Exodus-1, Ckß4 | CCR6 | |
| CCL21 | SLC, 6Ckine, Exodus-2, Ckß9, TCA-4 | CCR7 | |
| CCL22 | MDC, DC/ß-CK | CCR4 | |
| CCL23 | MPIF-1, Ckß8, MIP-3, MPIF-1 | unknown | |
| CCL24 | Eotaxin-2, MPIF-2, Ckß6 | CCR3 | |
| CCL25 | TECK, Ckß15 | CCR9 | |
| CCL26 | Eotaxin-3, MIP-4α, IMAC, TSC-1 | CCR3 | |
| CCL27 | CTACK, ILC, Eskine, PESKY, skinkine | CCR10 | |
| CCL28 | MEC | CCR10 | |
| CXC | CXCL1 | Gro-α, GRO1, NAP-3 | CXCR2 |
| CXCL2 | Gro-ß, GRO2, MIP-2a | CXCR2 | |
| CXCL3 | Gro-γ GRO3, MIP-2ß | CXCR2 | |
| CXCL4 | PF-4 | unknown | |
| CXCL5 | ENA-78 | CXCR2 | |
| CXCL6 | GCP-2 | CXCR1/2 | |
| CXCL7 | NAP-2, CTAPIII, ß-Ta, PEP | CXCR2 | |
| CXCL8 | IL-8, NAP-1, MDNCF, GCP-1 | CXCR1/2 | |
| CXCL9 | MIG, CRG-10 | CXCR3 | |
| CXCL10 | IP-10, CRG-2 | CXCR3 | |
| CXCL11 | I-TAC, ß-R1, IP-9 | CXCR3 | |
| CXCL12 | SDF-1, PBSF | CXCR4/7 | |
| CXCL13 | BCA-1, BLC | CXCR5 | |
| CXCL14 | BRAK, bolekine | unknown | |
| CXCL15 | Lungkine, WECHE | unknown | |
| CXCL16 | SRPSOX | CXCR6 | |
| CXCL17 | DMC, VCC-1 | unknown | |
| C | XCL1 | Lymphotactin α, SCM-1α, ATAC | XCR1 |
| XCL2 | Lymphotactin ß, SCM-1ß | XCR1 | |
| CX3C | CX3CL1 | Fractalkine, Neurotactin, ABCD-3 | CX3CR1 |
| Family | Name | Alternative Name | Receptor | PDAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | CCL2 | MCP-1 | CCR2/4/5 | [25,26,27] |
| CCL5 | RANTES | CCR1/3/5 | [27,28] | |
| CCL20 | LARC, Exodus-1, Ckß4 | CCR6 | [29,30] | |
| CCL21 | SLC, 6Ckine, Exodus-2, Ckß9, TCA-4 | CCR7 | [31,32] | |
| CXC | CXCL1 | Gro-α, GRO1, NAP-3 | CXCR2 | [30,32,33,34] |
| CXCL2 | Gro-ß, GRO2, MIP-2a | CXCR2 | [35] | |
| CXCL5 | ENA-78 | CXCR2 | [34,35,36] | |
| CXCL8 | IL-8, NAP-1, MDNCF, GCP-1 | CXCR1/2 | [22,27,34,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55] | |
| CXCL10 | IP-10, CRG-2 | CXCR3 | [56] | |
| CXCL12 | SDF-1, PBSF | CXCR4/7 | [32,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] | |
| CXCL14 | BRAK, bolekine | unknown | [64] | |
| CXCL16 | SRPSOX | CXCR6 | [65] | |
| CX3C | CX3CL1 | Fractalkine, Neurotactin, ABCD-3 | CX3CR1 | [66,67] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geismann, C.; Schäfer, H.; Gundlach, J.-P.; Hauser, C.; Egberts, J.-H.; Schneider, G.; Arlt, A. NF-κB Dependent Chemokine Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101445
Geismann C, Schäfer H, Gundlach J-P, Hauser C, Egberts J-H, Schneider G, Arlt A. NF-κB Dependent Chemokine Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2019; 11(10):1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101445
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeismann, Claudia, Heiner Schäfer, Jan-Paul Gundlach, Charlotte Hauser, Jan-Hendrik Egberts, Günter Schneider, and Alexander Arlt. 2019. "NF-κB Dependent Chemokine Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 11, no. 10: 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101445
APA StyleGeismann, C., Schäfer, H., Gundlach, J.-P., Hauser, C., Egberts, J.-H., Schneider, G., & Arlt, A. (2019). NF-κB Dependent Chemokine Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 11(10), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101445






