Generation of a Zebrafish Knock-In Model Recapitulating Childhood ETV6::RUNX1-Positive B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Donor Plasmid Construction
2.2. In Vitro Transcription of sgRNAs and Cas9 mRNA
2.3. Generation of the Transgenic and Mutant Zebrafish Lines
2.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.5. Giemsa Staining of Peripheral Blood Smears of Adult Zebrafish
2.6. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining on Paraffin Sections of Whole Adult Zebrafish
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Isolation of Total RNA from Whole Zebrafish and Kidney Tissue
2.9. Statistics and Language Editing
2.10. Zebrafish Maintenance
2.11. RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Generation of the ETV6::RUNX1 Zebrafish Model
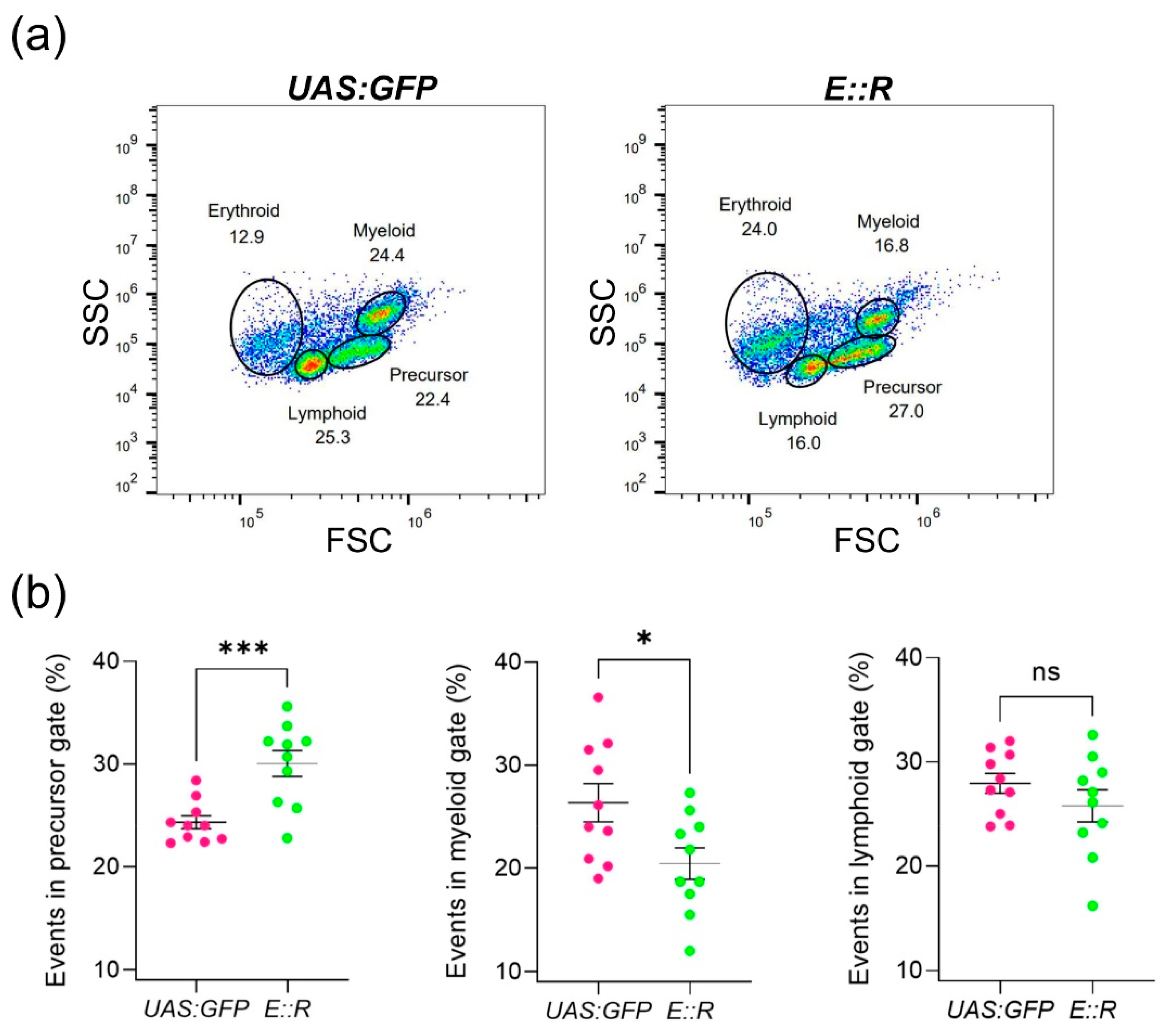
3.2. ETV6::RUNX1 Zebrafish Have an Expansion of the Precursor Cell Pool and a Low Incidence of Leukemia
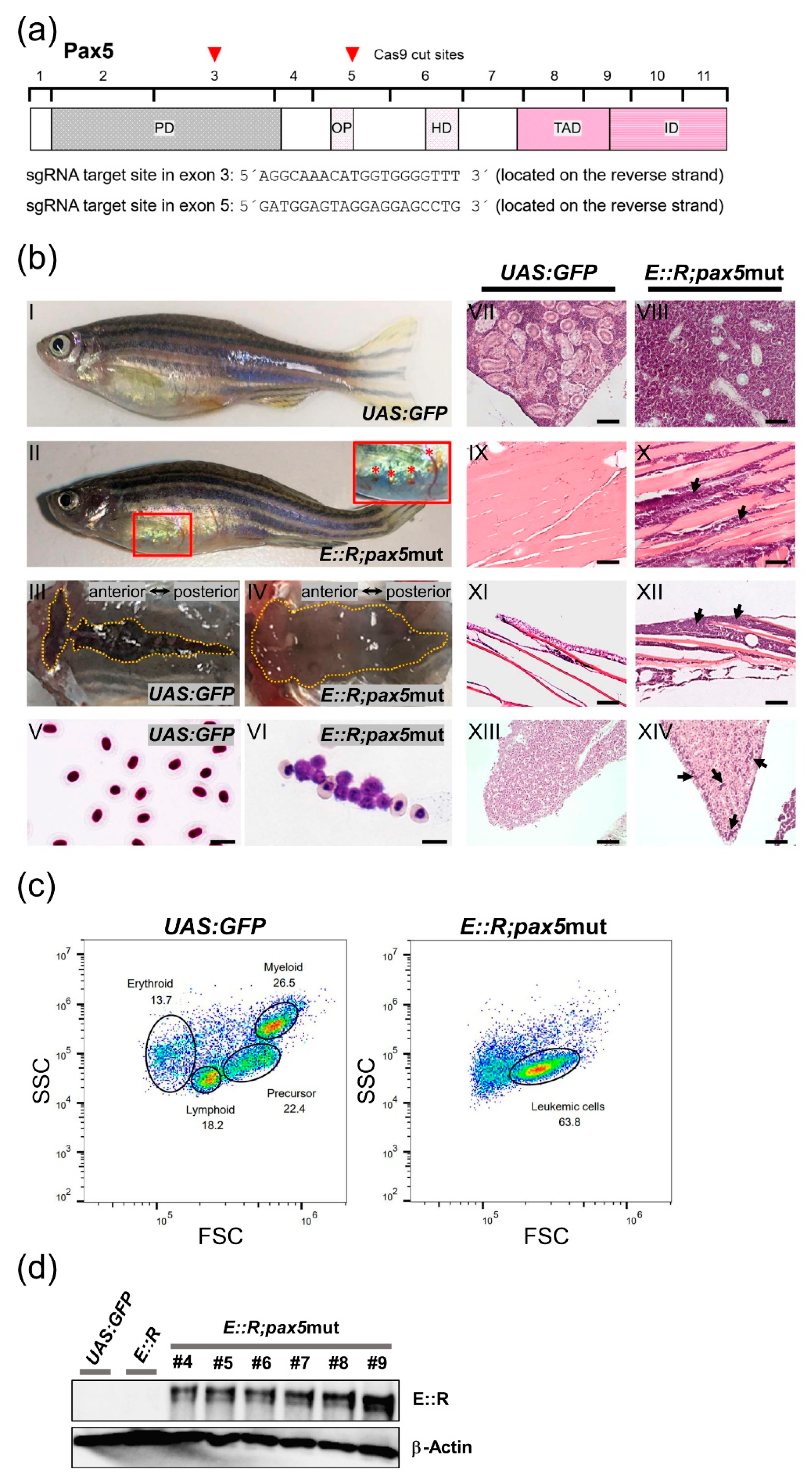
3.3. CRISPR/Cas9-Induced Mutations in pax5 Increase Leukemia Incidence in the ETV6::RUNX1 Zebrafish Model
3.4. A Frameshift Mutation in cdkn2a/b Increases Leukemia Incidence in the ETV6::RUNX1 Zebrafish Model
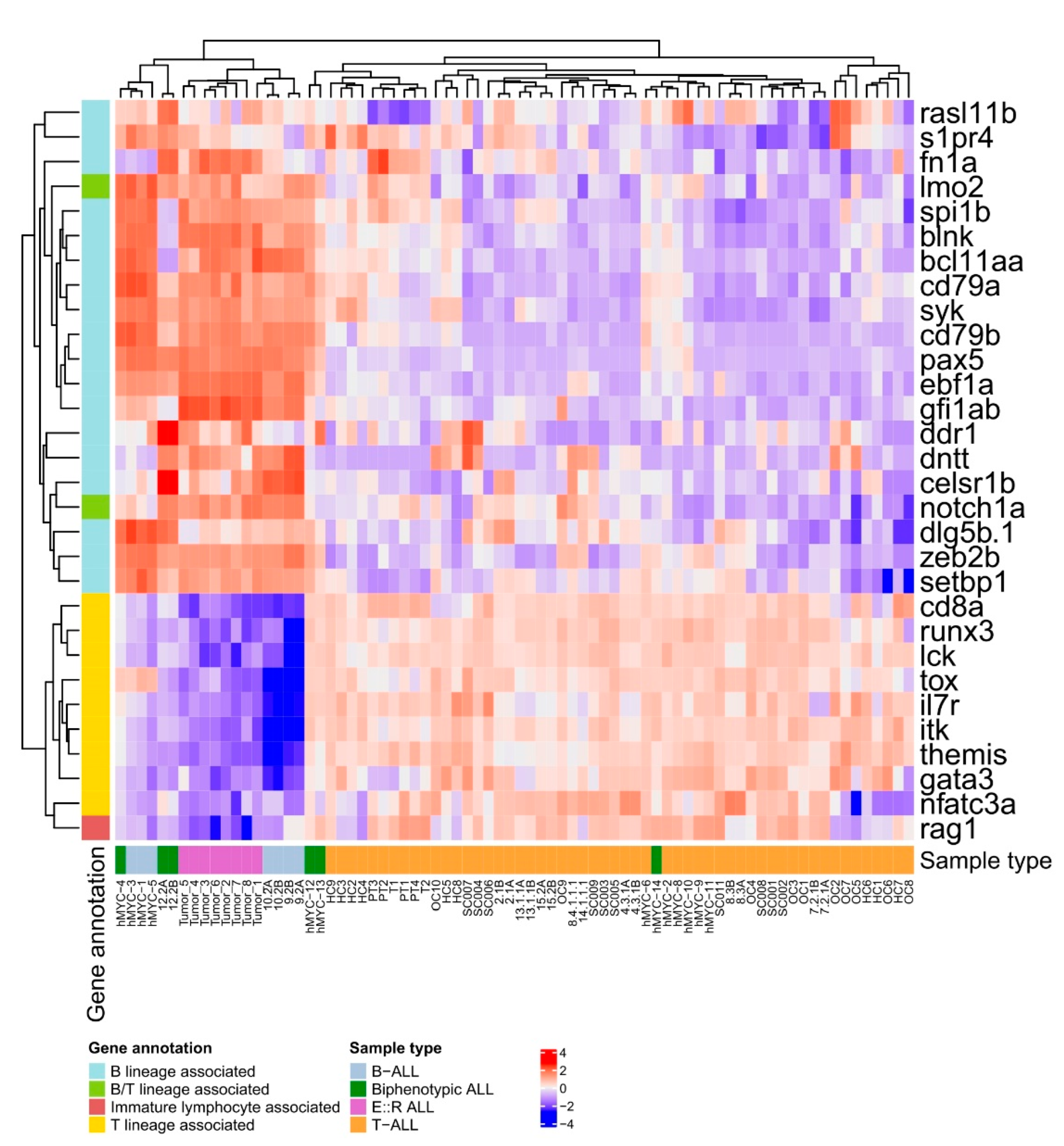
3.5. Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal That E::R;pax5mut Zebrafish Develop B-Lineage ALL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowley, J.D. The Role of Chromosome Translocations in Leukemogenesis. Semin. Hematol. 1999, 36, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romana, S.P.; Le Coniat, M.; Berger, R. T(12;21): A New Recurrent Translocation in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 1994, 9, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurtleff, S.A.; Buijs, A.; Behm, F.G.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hancock, M.L.; Chan, G.C.; Pui, C.H.; Grosveld, G.; Downing, J.R. TEL/AML1 Fusion Resulting from a Cryptic t(12;21) Is the Most Common Genetic Lesion in Pediatric ALL and Defines a Subgroup of Patients with an Excellent Prognosis. Leukemia 1995, 9, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golub, T.R.; Barker, G.F.; Bohlander, S.K.; Hiebert, S.W.; Ward, D.C.; Bray-Ward, P.; Morgan, E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Rowley, J.D.; Gilliland, D.G. Fusion of the TEL Gene on 12p13 to the AML1 Gene on 21q22 in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4917–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romana, S.P.; Mauchauffé, M.; Le Coniat, M.; Chumakov, I.; Le Paslier, D.; Berger, R.; Bernard, O.A. The t(12;21) of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Results in a Tel-AML1 Gene Fusion. Blood 1995, 85, 3662–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Colman, S.M.; Xiao, Z.; Ford, A.M.; Healy, L.E.; Donaldson, C.; Hows, J.M.; Navarrete, C.; Greaves, M. Chromosome Translocations and Covert Leukemic Clones Are Generated during Normal Fetal Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8242–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemels, J.L.; Ford, A.M.; Van Wering, E.R.; Postma, A.; Greaves, M. Protracted and Variable Latency of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia after TEL-AML1 Gene Fusion in Utero. Blood 1999, 94, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuffel, O.; Betts, D.R.; Dettling, M.; Schaub, R.; Schäfer, B.W.; Niggli, F.K. Prenatal Origin of Separate Evolution of Leukemia in Identical Twins. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, D.; Olsen, M.; Lähnemann, D.; Stanulla, M.; Slany, R.; Schmiegelow, K.; Borkhardt, A.; Fischer, U. Five Percent of Healthy Newborns Have an ETV6-RUNX1 Fusion as Revealed by DNA-Based GIPFEL Screening. Blood 2018, 131, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuna, J.; Madzo, J.; Krejci, O.; Zemanova, Z.; Kalinova, M.; Muzikova, K.; Zapotocky, M.; Starkova, J.; Hrusak, O.; Horak, J.; et al. ETV6/RUNX1 (TEL/AML1) Is a Frequent Prenatal First Hit in Childhood Leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 368–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, A.T.; Koechling, J.; Corbett, R.; Metzler, M.; Wiemels, J.L.; Greaves, M. Protracted Postnatal Natural Histories in Childhood Leukemia. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2004, 39, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, J.W.; Van Buren, D.; Foudi, A.; Krejci, O.; Qin, J.; Orkin, S.H.; Hock, H. TEL-AML1 Corrupts Hematopoietic Stem Cells to Persist in the Bone Marrow and Initiate Leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Weyden, L.; Giotopoulos, G.; Rust, A.G.; Matheson, L.S.; van Delft, F.W.; Kong, J.; Corcoran, A.E.; Greaves, M.F.; Mullighan, C.G.; Huntly, B.J.; et al. Modeling the Evolution of ETV6-RUNX1-Induced B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Mice. Blood 2011, 118, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, G.; Casado-García, A.; Isidro-Hernández, M.; Picard, D.; Raboso-Gallego, J.; Alemán-Arteaga, S.; Orfao, A.; Blanco, O.; Riesco, S.; Prieto-Matos, P.; et al. The Second Oncogenic Hit Determines the Cell Fate of ETV6-RUNX1 Positive Leukemia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 704591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Chang, L.; Zhu, X. Pathogenesis of ETV6/RUNX1-Positive Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Mechanisms Underlying Its Relapse. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 35445–35459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarska, A.; Derebas, J.; Pinkosz, M.; Niedźwiecki, M.; Lejman, M. The Landscape of Secondary Genetic Rearrangements in Pediatric Patients with B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with t(12;21). Cells 2023, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, M.L.; Goldwasser, M.A.; Silverman, L.B.; Poon, W.-M.; Vattikuti, S.; Cardoso, A.; Neuberg, D.S.; Shannon, K.M.; Sallan, S.E.; Gilliland, D.G. Prospective Analysis of TEL/AML1-Positive Patients Treated on Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Consortium Protocol 95-01. Blood 2006, 107, 4508–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestier, E.; Heyman, M.; Andersen, M.K.; Autio, K.; Blennow, E.; Borgström, G.; Golovleva, I.; Heim, S.; Heinonen, K.; Hovland, R.; et al. Outcome of ETV6/RUNX1-Positive Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia in the NOPHO-ALL-1992 Protocol: Frequent Late Relapses but Good Overall Survival. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 140, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubnitz, J.E.; Wichlan, D.; Devidas, M.; Shuster, J.; Linda, S.B.; Kurtzberg, J.; Bell, B.; Hunger, S.P.; Chauvenet, A.; Pui, C.-H.; et al. Prospective Analysis of TEL Gene Rearrangements in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Children’s Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2186–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojwani, D.; Pei, D.; Sandlund, J.T.; Jeha, S.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Shurtleff, S.; Onciu, M.; Cheng, C.; et al. ETV6-RUNX1-Positive Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Improved Outcome with Contemporary Therapy. Leukemia 2012, 26, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeghs, E.M.P.; Boer, J.M.; Hoogkamer, A.Q.; Boeree, A.; de Haas, V.; de Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; Horstmann, M.A.; Escherich, G.; Pieters, R.; den Boer, M.L. Copy Number Alterations in B-Cell Development Genes, Drug Resistance, and Clinical Outcome in Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokemeyer, A.; Eckert, C.; Meyr, F.; Koerner, G.; von Stackelberg, A.; Ullmann, R.; Türkmen, S.; Henze, G.; Seeger, K. Copy Number Genome Alterations Are Associated with Treatment Response and Outcome in Relapsed Childhood ETV6/RUNX1-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2014, 99, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.C.; MacRae, C.A. The Zebrafish: Scalable in Vivo Modeling for Systems Biology. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2011, 3, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhish, M.; Manjubala, I. Effectiveness of Zebrafish Models in Understanding Human Diseases-A Review of Models. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohi, O.; Parikka, M.; Rämet, M. The Zebrafish as a Model for Paediatric Diseases. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raby, L.; Völkel, P.; Le Bourhis, X.; Angrand, P.-O. Genetic Engineering of Zebrafish in Cancer Research. Cancers 2020, 12, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.M.; Kanki, J.P.; Rhodes, J.; Liu, T.X.; Paw, B.H.; Kieran, M.W.; Langenau, D.M.; Delahaye-Brown, A.; Zon, L.I.; Fleming, M.D.; et al. Myelopoiesis in the Zebrafish, Danio Rerio. Blood 2001, 98, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zon, L.I. Developmental Biology of Hematopoiesis. Blood 1995, 86, 2876–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenau, D.M.; Traver, D.; Ferrando, A.A.; Kutok, J.L.; Aster, J.C.; Kanki, J.P.; Lin, S.; Prochownik, E.; Trede, N.S.; Zon, L.I.; et al. Myc-Induced T Cell Leukemia in Transgenic Zebrafish. Science 2003, 299, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenau, D.M.; Feng, H.; Berghmans, S.; Kanki, J.P.; Kutok, J.L.; Look, A.T. Cre/Lox-Regulated Transgenic Zebrafish Model with Conditional Myc-Induced T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6068–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabaawy, H.E.; Azuma, M.; Embree, L.J.; Tsai, H.-J.; Starost, M.F.; Hickstein, D.D. TEL-AML1 Transgenic Zebrafish Model of Precursor B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15166–15171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, A.M.; Grabher, C.; McBride, E.R.; Boyd, E.R.; Vigerstad, M.H.; Edgar, A.; Kai, F.-B.; Da’as, S.I.; Payne, E.; Look, A.T.; et al. NUP98-HOXA9-Transgenic Zebrafish Develop a Myeloproliferative Neoplasm and Provide New Insight into Mechanisms of Myeloid Leukaemogenesis. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 155, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Ye, Y.; Ye, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, W. Human BCR/ABL1 Induces Chronic Myeloid Leukemia-like Disease in Zebrafish. Haematologica 2020, 105, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierson, W.A.; Welker, J.M.; Almeida, M.P.; Mann, C.M.; Webster, D.A.; Torrie, M.E.; Weiss, T.J.; Kambakam, S.; Vollbrecht, M.K.; Lan, M.; et al. Efficient Targeted Integration Directed by Short Homology in Zebrafish and Mammalian Cells. Elife 2020, 9, e53968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, J.M.; Wierson, W.A.; Almeida, M.P.; Mann, C.M.; Torrie, M.E.; Ming, Z.; Ekker, S.C.; Clark, K.J.; Dobbs, D.L.; Essner, J.J.; et al. GeneWeld: Efficient Targeted Integration Directed by Short Homology in Zebrafish. Bio Protoc. 2021, 11, e4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, K.M.; Fujimoto, E.; Grabher, C.; Mangum, B.D.; Hardy, M.E.; Campbell, D.S.; Parant, J.M.; Yost, H.J.; Kanki, J.P.; Chien, C.-B. The Tol2kit: A Multisite Gateway-Based Construction Kit for Tol2 Transposon Transgenesis Constructs. Dev. Dyn. 2007, 236, 3088–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.J.; Balciunas, D.; Pogoda, H.-M.; Ding, Y.; Westcot, S.E.; Bedell, V.M.; Greenwood, T.M.; Urban, M.D.; Skuster, K.J.; Petzold, A.M.; et al. In Vivo Protein Trapping Produces a Functional Expression Codex of the Vertebrate Proteome. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Mateos, M.A.; Vejnar, C.E.; Beaudoin, J.-D.; Fernandez, J.P.; Mis, E.K.; Khokha, M.K.; Giraldez, A.J. CRISPRscan: Designing Highly Efficient sgRNAs for CRISPR-Cas9 Targeting in Vivo. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, G.K.; Pei, W.; LaFave, M.C.; Idol, J.; Xu, L.; Gallardo, V.; Carrington, B.; Bishop, K.; Jones, M.; Li, M.; et al. High-Throughput Gene Targeting and Phenotyping in Zebrafish Using CRISPR/Cas9. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, L.-E.; Wente, S.R.; Chen, W. Efficient Multiplex Biallelic Zebrafish Genome Editing Using a CRISPR Nuclease System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13904–13909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.C.; Cheong, W.C.; Lim, L.S.; Li, M.-H. A Simple, High Sensitivity Mutation Screening Using Ampligase Mediated T7 Endonuclease I and Surveyor Nuclease with Microfluidic Capillary Electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.M.; Fero, K.; Arrenberg, A.B.; Bergeron, S.A.; Driever, W.; Burgess, H.A. Deep Brain Photoreceptors Control Light-Seeking Behavior in Zebrafish Larvae. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasighaemi, P.; Onnebo, S.M.N.; Liongue, C.; Ward, A.C. ETV6 (TEL1) Regulates Embryonic Hematopoiesis in Zebrafish. Haematologica 2015, 100, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Page-McCaw, P.S.; Chen, W. Zebrafish Genome Engineering Using the CRISPR–Cas9 System. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traver, D.; Paw, B.H.; Poss, K.D.; Penberthy, W.T.; Lin, S.; Zon, L.I. Transplantation and in Vivo Imaging of Multilineage Engraftment in Zebrafish Bloodless Mutants. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, T.; Sacchini, S.; Paz, Y.; Rosales, R.S.; Câmara, N.; Andrada, M.; Arbelo, M.; Fernández, A. Comparison of Methods for the Histological Evaluation of Odontocete Spiral Ganglion Cells. Animals 2020, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of Embryonic Development of the Zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book; A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio); Zebrafish International Resource Center: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Loontiens, S.; Vanhauwaert, S.; Depestel, L.; Dewyn, G.; Van Loocke, W.; Moore, F.E.; Garcia, E.G.; Batchelor, L.; Borga, C.; Squiban, B.; et al. A Novel TLX1-Driven T-ALL Zebrafish Model: Comparative Genomic Analysis with Other Leukemia Models. Leukemia 2020, 34, 3398–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borga, C.; Foster, C.A.; Iyer, S.; Garcia, S.P.; Langenau, D.M.; Frazer, J.K. Molecularly Distinct Models of Zebrafish Myc-Induced B Cell Leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.G.; Iyer, S.; Garcia, S.P.; Loontiens, S.; Sadreyev, R.I.; Speleman, F.; Langenau, D.M. Cell of Origin Dictates Aggression and Stem Cell Number in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1860–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.A.; Peltzer, A.; Fillinger, S.; Patel, H.; Alneberg, J.; Wilm, A.; Garcia, M.U.; Di Tommaso, P.; Nahnsen, S. The Nf-Core Framework for Community-Curated Bioinformatics Pipelines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Galaxy Community. The Galaxy Platform for Accessible, Reproducible and Collaborative Biomedical Analyses: 2022 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W345–W351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An Efficient General Purpose Program for Assigning Sequence Reads to Genomic Features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene Ontology Analysis for RNA-Seq: Accounting for Selection Bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.-R.; Li, L.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, M.-K.; Shin, B.A.; Choi, S.-Y. High Cleavage Efficiency of a 2A Peptide Derived from Porcine Teschovirus-1 in Human Cell Lines, Zebrafish and Mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivasubbu, S.; Balciunas, D.; Davidson, A.E.; Pickart, M.A.; Hermanson, S.B.; Wangensteen, K.J.; Wolbrink, D.C.; Ekker, S.C. Gene-Breaking Transposon Mutagenesis Reveals an Essential Role for Histone H2afza in Zebrafish Larval Development. Mech. Dev. 2006, 123, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, P.D.; Schmale, M.C. GFP as a Genetic Marker Scorable Throughout the Life Cycle of Transgenic Zebra Fish. Mar. Biotechnol. 2000, 2, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattrus, S.J.; Zon, L.I. Stem Cell Safe Harbor: The Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niche in Zebrafish. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 3063–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, E.; Kissa, K.; Zapata, A.; Mordelet, E.; Briolat, V.; Lin, H.-F.; Handin, R.I.; Herbomel, P. Tracing Hematopoietic Precursor Migration to Successive Hematopoietic Organs during Zebrafish Development. Immunity 2006, 25, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.D. Cell Cycle and Developmental Control of Hematopoiesis by Runx1. J. Cell Physiol. 2009, 219, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Klemm, L.; Park, E.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Ford, A.; Kweon, S.-M.; Trageser, D.; Hasselfeld, B.; Henke, N.; Mooster, J.; et al. Mechanisms of Clonal Evolution in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, M. A Causal Mechanism for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, S.A.; Baron, C.S.; Corbin, A.F.; Yang, S.; Zon, L.I. Single-Cell Transcriptional Profiling of Zebrafish Hematopoiesis Offers Insight into Early Lymphocyte Development and Reveals Novel Immune Cell Populations. Blood 2021, 138, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.D.; Zapata, A.G. Lymphocyte Development in Fish and Amphibians. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittkopp, N.; Huntzinger, E.; Weiler, C.; Saulière, J.; Schmidt, S.; Sonawane, M.; Izaurralde, E. Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay Effectors Are Essential for Zebrafish Embryonic Development and Survival. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 3517–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, D.; Enshaei, A.; Bartram, J.; Hancock, J.; Harrison, C.J.; Hough, R.; Samarasinghe, S.; Schwab, C.; Vora, A.; Wade, R.; et al. Genotype-Specific Minimal Residual Disease Interpretation Improves Stratification in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchinskaya, E.; Heyman, M.; Nordgren, A.; Söderhäll, S.; Forestier, E.; Wehner, P.; Vettenranta, K.; Jonsson, O.; Wesenberg, F.; Sahlén, S.; et al. Interphase Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization Deletion Analysis of the 9p21 Region and Prognosis in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL): Results from a Prospective Analysis of 519 Nordic Patients Treated According to the NOPHO-ALL 2000 Protocol. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 152, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.-H.; Jeon, Y.; Kang, H.J.; Park, K.D.; Shin, H.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Cho, H.-I.; Ahn, H.S.; Lee, D.S. Native ETV6 Deletions Accompanied by ETV6-RUNX1 Rearrangements Are Associated with a Favourable Prognosis in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Candidate for Prognostic Marker. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 155, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.P.; Welker, J.M.; Siddiqui, S.; Luiken, J.; Ekker, S.C.; Clark, K.J.; Essner, J.J.; McGrail, M. Endogenous Zebrafish Proneural Cre Drivers Generated by CRISPR/Cas9 Short Homology Directed Targeted Integration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Kambakam, S.; Almeida, M.P.; Ming, Z.; Welker, J.M.; Wierson, W.A.; Schultz-Rogers, L.E.; Ekker, S.C.; Clark, K.J.; Essner, J.J.; et al. Cre/Lox Regulated Conditional Rescue and Inactivation with Zebrafish UFlip Alleles Generated by CRISPR-Cas9 Targeted Integration. eLife 2022, 11, e71478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichino, N.; Serres, M.R.; Urban, R.M.; Urban, M.D.; Treichel, A.J.; Schaefbauer, K.J.; Tallant, L.E.; Varshney, G.K.; Skuster, K.J.; McNulty, M.S.; et al. Building the Vertebrate Codex Using the Gene Breaking Protein Trap Library. Elife 2020, 9, e54572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balciunas, D.; Wangensteen, K.J.; Wilber, A.; Bell, J.; Geurts, A.; Sivasubbu, S.; Wang, X.; Hackett, P.B.; Largaespada, D.A.; McIvor, R.S.; et al. Harnessing a High Cargo-Capacity Transposon for Genetic Applications in Vertebrates. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botten, G.A.; Zhang, Y.; Dudnyk, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Liu, X.; Sanders, J.T.; Imanci, A.; Droin, N.; Cao, H.; Kaphle, P.; et al. Structural Variation Cooperates with Permissive Chromatin to Control Enhancer Hijacking–Mediated Oncogenic Transcription. Blood 2023, 142, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Song, F.; Lyu, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, Y.; Wang, X.; Luan, Y.; Jia, B.; et al. Subtype-Specific 3D Genome Alteration in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Nature 2022, 611, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, M.; Madsen, H.O.; Hjalgrim, H.; Gregers, J.; Rostgaard, K.; Schmiegelow, K. Preleukemic TEL-AML1-Positive Clones at Cell Level of 10(-3) to 10(-4) Do Not Persist into Adulthood. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2006, 28, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausten-Thomsen, U.; Madsen, H.O.; Vestergaard, T.R.; Hjalgrim, H.; Nersting, J.; Schmiegelow, K. Prevalence of t(12;21)[ETV6-RUNX1]-Positive Cells in Healthy Neonates. Blood 2011, 117, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, G.; Hauer, J.; Martín-Lorenzo, A.; Schäfer, D.; Bartenhagen, C.; García-Ramírez, I.; Auer, F.; González-Herrero, I.; Ruiz-Roca, L.; Gombert, M.; et al. Infection Exposure Promotes ETV6-RUNX1 Precursor B-Cell Leukemia via Impaired H3K4 Demethylases. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4365–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Gupta, R.; Ancliff, P.; Atzberger, A.; Brown, J.; Soneji, S.; Green, J.; Colman, S.; Piacibello, W.; Buckle, V.; et al. Initiating and Cancer-Propagating Cells in TEL-AML1-Associated Childhood Leukemia. Science 2008, 319, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weyden, L.; Giotopoulos, G.; Wong, K.; Rust, A.G.; Robles-Espinoza, C.D.; Osaki, H.; Huntly, B.J.; Adams, D.J. Somatic Drivers of B-ALL in a Model of ETV6-RUNX1; Pax5(+/−) Leukemia. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinäniemi, M.; Vuorenmaa, T.; Teppo, S.; Kaikkonen, M.U.; Bouvy-Liivrand, M.; Mehtonen, J.; Niskanen, H.; Zachariadis, V.; Laukkanen, S.; Liuksiala, T.; et al. Transcription-Coupled Genetic Instability Marks Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Structural Variation Hotspots. eLife 2016, 5, e13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardin, F.; Yang, Y.; Cleaves, R.; Zahurak, M.; Cheng, L.; Civin, C.I.; Friedman, A.D. TEL-AML1, Expressed from t(12;21) in Human Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia, Induces Acute Leukemia in Mice. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 3904–3908. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zapilko, V.; Moisio, S.; Parikka, M.; Heinäniemi, M.; Lohi, O. Generation of a Zebrafish Knock-In Model Recapitulating Childhood ETV6::RUNX1-Positive B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2023, 15, 5821. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245821
Zapilko V, Moisio S, Parikka M, Heinäniemi M, Lohi O. Generation of a Zebrafish Knock-In Model Recapitulating Childhood ETV6::RUNX1-Positive B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers. 2023; 15(24):5821. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245821
Chicago/Turabian StyleZapilko, Veronika, Sanni Moisio, Mataleena Parikka, Merja Heinäniemi, and Olli Lohi. 2023. "Generation of a Zebrafish Knock-In Model Recapitulating Childhood ETV6::RUNX1-Positive B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia" Cancers 15, no. 24: 5821. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15245821





