Abstract
In this study, to discover how the growth of digital agriculture has impacted agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP), we take panel data from 2011 to 2019 for 30 Chinese provinces as the research object, measure the growth of AGTFP and digital agriculture development using the SBM-ML and entropy method, and use a fixed effect model to analyze the effects of digital agriculture development on AGTFP. The results demonstrate that (1) from the time-series characteristics, digital agriculture presented a steady growth state from 2011 to 2019; (2) during the study period, the technical efficiency index was slightly lower than the technological progress index in the AGTFP index, meaning that there is room for further development; (3) the relationship between the growth of digital agriculture and AGTFP presents an inverted U-shaped curve, with human capital playing a moderating role. Finally, corresponding countermeasures are proposed in four aspects: strengthening the construction of organizational mechanisms, building a standardized base for digital agriculture output, enhancing the traceability and certification of agricultural products, and improving social services in the agricultural industry.
1. Introduction
As a new direction for agricultural development, digital farming plays an essential role in enhancing industrial integration and innovation, encouraging the growth of high-quality agriculture and rural revitalization [,,,]. According to the 2021 white paper for the growth of China’s digital economy, China’s agricultural digitization level is only 7.3%, and the lagging development of the digital agricultural infrastructure and the lack of digital talents have caused the overall digitization process of rural regions and farming to lag []. To improve the digitalization level of rural agriculture, accelerate the layout of farming and rural informatization, and encourage the green transformation of agriculture, the 2018 Central Government No. 1 document proposed the “Digital Countryside Development Strategy”. Successive documents were issued, such as the “Outline of the Digital Countryside Development Strategy” and the “Action Plan for Digital Countryside Development (2022–2025)”. With the No. 1 document of the Central Government in 2020 and 2021, China’s digital agriculture has been moving from top-level planning to practical implementation. The 2022 No. 1 document of the Central Government proposed to “vigorously encourage the construction of digital villages, empower rural public services with digital technology, and encourage the green development of rural regions and farming” [].
The 19th party congress report pointed out that China’s economy has shifted from a high growth stage to a higher-quality development stage, and it indicated the urgency of the need to increase TFP at this stage []. To build a modern socialist country in an all-round way, we must first pursue high-quality development. To boost the growth of China’s farming sector in a high-quality manner, the AGTFP provides practical guidance and significance for China to build a moderately prosperous society and start a new journey toward building a modern socialist country. To build a socialist country in an all-round way, we must take the people as the center of development thinking, accelerate the transformation of the development mode, rely more on innovation drive, promote quality change, efficiency change, power change, and strive to improve the quality and level of development []. At the same time, the Central Government’s No. 1 document proposes to vigorously promote the creation of digital rural and the green growth of agrarian and rural areas. Digital agriculture development, as a booster of green agricultural development, has become a new driving force for green agricultural development []. Therefore, the development of digital agriculture is of tremendous practical value for enhancing the AGTFP and realizing rural revitalization.
However, various questions arise in this context, such as the following: Has digital agriculture development increased AGTFP? How has digital agricultural development empowered AGTFP? What is the underlying logic of empowerment? What is the mechanism by which digital agricultural development acts on AGTFP? What is the current trend of development between the two? How does the development of digital agriculture impact AGTFP? At present, these is no extensive research on this topic available in the literature. In this paper, we measure the state of digital agriculture development and AGTFP, respectively, analyze the difference status of the two and make a judgment on their development trends, and analyze how the growth of digital farming has affected the AGTFP, in order to present concrete solutions and recommendations for rural revitalization, as well as some academic direction and empirical evidence for enhancing AGTFP.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review
The notion of digital agriculture was officially introduced in 1997, referring to intensive and informative agricultural technology supported by geospatial and information technology []. Digital agriculture is supported by digital technology and digital resources, and it places greater emphasis on digital features and the role of digital technology in all processes to achieve increased efficiency in agriculture, increased income for farmers, and increased competitiveness of agricultural products. With the development of society, digital agriculture is also known as precision or intelligent farming [], which was initially developed for crop production in the 1990s []. Precision agriculture is created through the use of various sensing technologies, such as proximity sensing and remote sensing []. It synthesizes the current mobile connectivity, digital governance, and data valorization technologies combined with the characteristics of rural agricultural development [,]. At present, research on digital agriculture in some developed countries is focused on the precise control of agricultural production tools, accurate distribution of agricultural production components, and integrated management of agricultural production data []. IoT devices such as sensors are entering full commercialization in developed countries [], providing information and technical support to farmers in a networked manner. Farmers can use the Internet and other forms of networking to share information resources such as agricultural production and operations, thus improving the level of refinement and management of the agricultural output. Some even believe that, in the future, farmers can decide the day of sowing through the use of electronic devices []. Compared with developed nations, the progress of digitized farming in China started late and has been put forth within a short amount of time. Regarding digitized agriculture, a consensus has not yet been formed, and some scholars have defined it conceptually, according to the different focus of their understanding [,,]. In the last few years, academics have gradually attached importance to the study of digital agriculture, focusing on several aspects such as digital infrastructure construction [], digitalization of agriculture [,], and digital industrialization []. Regarding the quantification of digital agriculture, most scholars mainly construct evaluation index systems in terms of agricultural informatization [] and high-quality agricultural development []. In general, China’s research on digital agriculture is still at the stage of continuous catching-up.
Improving AGTFP is the main path to advance the sustainable and environmentally friendly development of agriculture and is one of the main ways to realize the rural revitalization strategy []. Through a review of the relevant literature, the current academic research on AGTFP mainly involves approaches for measuring AGTFP, its influencing factors, and different research perspectives affecting it. In terms of measurement methods, most domestic scholars have used the SBM-GML [] and SBM-ML [] indices, combined with the entropy method or Tobit model, to measure AGTFP with provincial- and county-level panel data in China. Foreign scholars have also used the growth accounting method [], the transcendental logarithm function combined with the Malmquist index [], and the growth accounting method [] to measure agricultural TFP in various study periods. From the perspective of influencing factors, domestic and international academic research has mainly focused on the study of the influences of R&D innovation behavior and technological progress [], environmental regulation [], human capital and urbanization [,], technical efficiency [], resource allocation [,], internal restructuring of agriculture [], agricultural insurance [], agricultural trade [], operation scale and financial support [], agricultural socialization services [], and agricultural mechanization [] on AGTFP. In terms of research perspectives, more relevant studies have been conducted from a technological innovation perspective, pastoral finance perspective and spatial heterogeneity perspective as entry points []. However, there are few studies focused on the effects of digital agriculture development on AGTFP.
In view of this, based on panel data from 30 Chinese provinces (autonomous regions/municipalities, hereafter referred to as provinces) through 2011–2019, we examined the effect of digital agriculture development on AGTFP through a fixed effect model, using the entropy value method and the SBM-ML index, on the basis of measuring the stage of digital agriculture advancement and AGTFP, respectively, in order to provide empirical support for further promoting digital agriculture advancement and improving AGTFP in the context of the comprehensive promotion of rural revitalization.
2.2. Theoretical Analysis and Hypothesis
There is an inextricable link between digital agriculture development and AGTFP. Based on the logic of conceptual empowerment, technological empowerment, and value empowerment, this paper provides a theoretical explanation for how digital agriculture can improve AGTFP; that is, digital agriculture takes information as a production component; utilizes contemporary information technology and digital means to visualize and express, digitally design, and informally direct agricultural objects, the environment, and the entire procedure; and transforms agricultural production methods by transforming traditional agriculture. It will form a path to improve AGTFP, realize the judicious use of agricultural resources, lower production costs, promote output quality, and improve the environment, thereby enhancing the competitiveness, premium capacity, and added value of agricultural products [,,].
2.2.1. Enabling Logic of Digital Agricultural Development for Green Total Factor Productivity in Agriculture
- (1)
- Concept Empowerment Logic
Digital agriculture development embraces the concepts of green, efficient, high quality, and sustainable development [,]. Digital agriculture is a new type of modern agriculture that realizes high efficiency, regulation, and quality of agricultural products through agricultural technology, forming a continuous virtuous cycle with ecosystems and beautiful landscapes. Therefore, the advancement of digital agriculture adheres strictly to the scientific connotations of high effectiveness, green development, and green transformation, reflecting the concept of sustainable agricultural development. If digital agriculture is developed and industrialization practices are implemented, embedding of the sustainable development concept can provide guidance for the transformation of traditional agricultural development methods. At a micro level, under the new development pattern of green transformation, the concepts of intelligent management, refined production, and full-quality traceability in digital agriculture and industrialization can enable agricultural operators to change from the crude agricultural production and management methods they once adhered to, in order to focus more on using new production concepts to guide agricultural production and management [,]. Once this transformation has matured, become established, and is internalized in the minds of agricultural operators, thus forming a green and efficient production consciousness and green and efficient production behavior, the impact of digital agricultural industrialization on agricultural operators is manifested externally, in the form of green and low-carbon changes, quality changes, efficiency changes, and dynamic changes in the process of farming production. This assists in lowering the price of agricultural produce and enhancing agricultural business incomes. Therefore, the development of digital agriculture requires not only advanced concepts, but also a key emphasis on its essential empowerment.
- (2)
- Technology Empowerment Logic
The development of digital agriculture industrialization cannot be achieved without strong technical support []. To date, the digital agriculture technology system has gradually matured and improved and started to explore industrialization, which can well-support the development of agriculture and its industrialization practice. Digital agricultural development is a revolution of the agricultural technology system []. In agricultural production and operation, the agricultural technology system can replace and update the old agricultural output technology, realizing the enhancement in agricultural productivity, quality, and standard of living for farmers []. In the area of agricultural processing, the advanced technology of digital agricultural industrialization can realize the deep processing of primary agricultural products; extract beneficial elements or nutrients from them; produce products with high quality and processed products; expand the product system of agricultural industrialization; develop nutritious food, healthcare products, cosmetics, and drugs; and realize the value-added of digital agricultural industry.
In terms of ecological protection technology empowerment, the state of agricultural land and the effect of breeding selection can be improved in the upstream through scientific and technological forces. First, the conservation of arable land quality should be realized, specifically through fertilizing the soil according to soil formulas and increasing the application of micronutrient fertilizers to improve soil fertility and thus land productivity [,]; second, a standardized basis for digital agricultural breeding should be developed, specifically by selecting seedlings with regional characteristics, good tolerance performance, and high economic value, as well as adopting standardized agronomy practices for planting management, in order to improve land productivity. Through a series of strengthening technologies such as microorganisms, breeding, and agronomy, we can address the problem of low land productivity caused by the poor ecological environment of farmland and the rough land management operation mode of the past. Next, in terms of financial technology empowerment, in the midstream agricultural product industrial parks should be established; support should be strengthened through digital technology innovation and financial poverty alleviation policies to achieve information sharing; deep processing should be developed to provide safe, nutritious, and healthy agricultural products; and industrial production efficiency should be improved []. Through production technology innovation, the production process-related redundant expenditures can be reduced, with the help of financial support, the production and operation capacity of the industry and farmers can be driven, in order to enhance work efficiency through production technology training of farmers, thus increasing the industry’s overall production effectiveness. Third, in terms of certification technology empowerment, the added value of products can be enhanced in the downstream through agricultural product cognition. According to the requirements of the relevant legal departments to submit for approval of certification, branding creation can center around improved product quality certification, helping to form a differentiation strategy and improving the added value of products.
- (3)
- Value Empowerment Logic
The digital agriculture’s growth releases digital dividends and enhances the value of the agricultural industry []. Digital agriculture is clearly different from traditional agriculture. For example, digital agriculture promotes agricultural products through Internet technology, such as WeChat, apps, websites, TikTok, and other kinds of communication channels, thus expanding the publicity channels for agricultural products, realizing interactions between consumers and products, and through real-time feedback of information, better grasping the needs of consumers. This forces the standardized, high-quality, and personalized production of agricultural products, and helps to guide producers to produce on demand and realize accurate production and delivery, thus increasing revenue []. Secondly, digital agriculture can help to improve product awareness and create brands for agricultural products with the help of various channels, such as the Internet and social media, better realizing both online sales and offline transactions. This dramatically reduces the cost of sales and adds value to agricultural products.
2.2.2. Mechanism of the Role of Digital Agriculture Development in Improving AGTFP
- (1)
- Promoting the Technology of Agricultural Industry
To improve AGTFP, it is necessary to vigorously promote the scientific and technological aspects of digital agriculture industry, strengthen the quality conservation of farmland, and establish a digital agriculture standardization base []. First, scientific and technical cultivated land quality conservation must be upgraded. The growth and development of a seed cannot be separated from the soil, and the soil is the fundamental guarantee of agricultural industrialization. If the soil quality is damaged or the soil lacks the micronutrients needed in the process of plant growth and development—or if the soil contains some factors that inhibit the absorption of plant micronutrients—then the growth of plants will be affected. For example, plant seeds usually contain phytic acid, which can effectively store the phosphorus needed for plant growth, but can also inhibit the absorption of calcium, iron, magnesium, zinc, and other elements, eventually leading to a lack of minerals in the grown crops. At the same time, phytic acid can also pollute the soil to a certain extent. As the content of antinutrients such as phytic acid varies in various plant seeds, we can use molecular biotechnology to control its content in plants and reduce its inhibitory effect on micronutrients through the use of technology. Second, the standardization of digital agriculture in the cultivation process should be promoted through science and technology. We strive to create a digital agriculture “seed-feeding” cycle model, combining manure from livestock and poultry breeding with scientific technology, and applying it for soil maintenance and plant cultivation through safe treatment, thus reducing intensive fertilizer application and taking the path of the ecological recycling economy. By creating a standardized economy of “planting-farming”, one can effectively prevent the deterioration of the ecological environment and enhance the soil environment’s quality; secondly, the reuse of animal and poultry manure can significantly reduce the waste of resources, such that both ecological and economic benefits can be significantly enhanced [].
- (2)
- Encourage the agricultural industry’s intelligence
We should encourage the intelligence of the agricultural industry, mainly focusing on the study of agricultural products and industrial parks regarding the processes of cleaning, extraction, processing, packaging, transportation, and so on, through the combination of relevant production management software and hardware; timely, rapid, and accurate access to the process of feedback information; and processing and applications supplemented by quality control system, based on the production of “source control, process tracking, product feedback”. This serves to form a traceability system based on “source control, process tracking and product feedback”, thus realizing intelligent management of the industrial park, improving industrial output efficiency, and increasing the overall efficiency of enterprises. First, in the process of automatic sorting of agricultural products, image processing technology may be used to quickly and accurately sort agricultural products. The specific process selects the agricultural products according to pre-set corresponding standards through the modules of conveyor belts, video image acquisition and processing, logical operations, and automation []. Second, in the production management process of agricultural products, the information generated by the production process can be summarized, analyzed, and processed in the form of data from sensors, then optimized to form standardized production processes and operating procedures, consequently promoting the transmission and optimization of experience and knowledge in the production process, in turn actualizing the agricultural sector’s intelligent management and increasing the effectiveness of enterprise output. Third, the establishment of agricultural quality traceability systems must be promoted. Specifically, through a series of information on production links, processing links, transportation links, inspection and quarantine, and product quality and safety certifications, the information can be intelligently processed in the form of digital information through a big data platform utilizing cutting-edge computer technologies such as cloud computing, big data, and artificial intelligence, which can enable consumers to achieve information traceability across time, space, regions, and subjects. This can aid farmers in promptly modifying their production schedules and product architectures in response to shifts in market demand [], thus solving the problem of the “lemon market” caused by asymmetric market information at the consumer level [].
- (3)
- Promote multi-functionalization of agricultural industry
The multi-functionalization of digital agriculture, as well as deep integration within the digital agriculture industry and between the digital agriculture industry and other industries, should be promoted. For this, market demand should be taken as the guide, digital agriculture museums and science and technology museums should be created, and the development of “digital agriculture +” and other related forms and modes should be promoted, in order to develop diversified, characteristic, personalized, and customized functions of the digital agriculture industry (e.g., food and medicine supply, breeding experience, entertainment and leisure, tourism and sightseeing, cultural heritage, education and science popularization, and recreation experiences), improve the supply capacity and quality of products and services of the digital agriculture industry, and extend the digital agriculture value, industrial, and spatial chains while fully utilizing its driving force [,,].
- (4)
- Promote the AGTFP and realize the conversion of old and new dynamics of agricultural development
Promoting agricultural industrialization is an excellent choice for promoting the green transformation and upgrading of agricultural production while realizing the change from old to new dynamics in agricultural development. In order to advance the supply-side structural change in agriculture, digital agriculture must break the original disciplinary boundaries; allow for unity across regions, departments, and disciplines; change the traditional old mode of agricultural production; promote the green transformation of farming output methods; constantly speed up the conversion of technical innovation and agriculture science and technology breakthroughs []; and, in the areas of arable land quality maintenance, promote the selection and breeding of good seeds, the application of green production technology, green product output, and nutritional enhancement of agricultural products, among other aspects. By getting rid of the development dilemma of the “ceiling” of agricultural prices and high production costs, we can improve the added value of agricultural products, in order to actively promote the transformation of old and new dynamics of agricultural development.
2.2.3. Theoretical Hypothesis
- (1)
- Measurement of digital agriculture development level
Drawing on the relevant literature, and based on the concepts of objectivity, operability and systematization, we developed a comprehensive evaluation system for the growth of digital agriculture at the macro level. On the basis of relevant studies by scholars such as Jiang S et al. [] and Cui K et al. [], combined with the actual situation and data accessibility, 13 specific indicators were selected to build the digital agriculture development evaluation index system, as shown in Table 1. These include the length of optical fiber cables, cell phone penetration rate, internet penetration rate, digital financial breadth and depth, and so on.

Table 1.
Digital agriculture development measurement indicators.
Evaluation methods regarding digital agriculture have gradually transformed from mainly single-indicator measures to comprehensive indicator measures. The evaluation of digital agriculture development in foreign countries has mainly focused on constructing assessment frameworks based on theoretical models or measuring a particular aspect of technical measures, such as Li’s construction of an intelligent agricultural sustainability analysis model, which has been used to study and analyze sustainable agricultural development and explore intelligent paths for sustainable agricultural development []. Based on the idea of “experimental digital experimental farm”, Solodovnik et al. [] have proposed that the objective evaluation of digital efficiency at the level of specific farms helps to select differentiated digital transformation strategies for agricultural enterprises. Domestic scholars have mainly focused on the entropy method [], entropy method and Moran index [], and entropy method and topsis [] among other methods. From the relevant literature, it was determined that the entropy value method is generally used as the primary measure of digital agriculture development, in order to determine the appropriate weights and to evaluate them. Therefore, in this paper, the comprehensive index of digital agriculture advancement in various years and areas was measured using the entropy value approach. The specific method is as follows:
First, standardization of indicator data is carried out to eliminate the interference of their outline quantities. The standardization method is as follows:
First, positive indicators:
Second, negative indicators:
where is the original indicator value, represents the region, represents the indicator, and is the normalized indicator value, represents the number of indicators, and represents the number of samples.
Third, the information entropy of the th indicator:
Fourth, the weight of the th indicator:
Finally, the combined score levels are calculated as:
- (2)
- Green total factor productivity measurement in agriculture
In this paper, the AGTFP in 30 provinces was measured using the SBM-ML index (Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan, and Xizang were excluded due to incomplete data) from 2011 to 2019, drawing on the existing literature to measure input indicators in terms of both intended and unwanted outputs. The input indicators included the quantity of individuals employed in the primary sector, pesticide use, total mechanized agricultural power, fertilizer application, agricultural sown area, effective irrigated area, and plastic film use. Total primary sector production value represents the intended output, while total agriculture carbon emissions represent the unwanted output. Drawing on related studies [], agricultural carbon emissions were measured using the equation:
Where and , respectively, represent the total agricultural carbon emissions and the carbon emissions caused by various carbon sources, and represents the specific number of various carbon sources and their corresponding carbon emission coefficients.
We referring to the agricultural carbon source and carbon emission coefficient provided by Min et al. [], IPCC [], Tian et al. []. Accounting for carbon emissions, including fertilizer, pesticide, agricultural film, diesel, irrigation and so on. To reduce the impact of price factors on the total output value of the primary industry, the base period of 2011 was used, and the expected output was deflated with the help of the price index of the total output value of the primary industry.
Second, the ML index can be decomposed into EC (technical efficiency change) and TC (technical progress change), where technical efficiency reflects the situation that the decision-making unit causes the production efficiency to change toward the frontier side through management changes and other means, while technological progress directly expresses the frontier-side change situation. This paper uses Matlab software to calculate the SBM-ML index of non-expected output super-efficiency under CRS conditions.
- (3)
- Analysis of the effect of digital agriculture development on AGTFP
Some foreign studies have regarded the development of digital agriculture as an essential direction to improve agricultural production efficiency, and the authors believed that digital agriculture is gradually changing agricultural production methods to achieve further sustainable advancement of farming [,,,,]. From an empowerment perspective, the empowerment of digital agriculture can encourage the development of a greener transformation at a greater level in agriculture. Digital agriculture integrates modern technological tools with lower environmental impact and a higher degree of informatization, which can reduce the dependence on material resources based on the continuous improvement of agricultural production efficiency and (directly or indirectly) improve the environmental and economic benefits of modern agriculture. Evidence has been shown by the development experience of developed countries, which based on the use of digital information technology and management models, encourage the development of a greener transformation at a greater level in agriculture (i.e., effectively achieving carbon emissions reductions by reducing fertilizer and pesticide inputs and fossil energy consumption). This can significantly contribute to the development of the green agricultural transition []. This view is confirmed by the development experience in China, where digital agriculture has led to saved water resources, reduced fertilizer and pesticide use, and significantly reduced labor use []. However, the role of digital agriculture empowerment in enhancing the state of green transformation advancement in farming is conditional, and there is some logic or mechanism underlying it. Studies have shown that the level of digitalization has a positive contribution to total factor productivity in agriculture []. Furthermore, combined with human capital, it is an endogenous force that promotes economic growth. Ding et al. [] have used educational attainment to measure human capital, and Wang et al. [] have verified that human capital promotes the green development of the economy. It has also been suggested that there is a double threshold effect between AGTFP and human capital []. For this reason, studies have shown that research on digital agriculture on AGTFP is involved but still needs to be improved, with few logical and empirical studies.
The following two research hypotheses are put forth in this work, based on the analyses described above:
H1.
The association between the growth of digital agriculture and AGTFP is an inverted U-shaped curve.
H2.
Human capital plays a moderating role between digital agriculture development and AGTFP.
2.3. Model Setting
2.3.1. Benchmark Regression Model
To explore the effect of digital agriculture development on AGTFP, and to test hypothesis 1 (H1), we established a fixed effect model, as follows:
2.3.2. Moderating Effect Model
To examine the role of human capital in moderating between digital agriculture development and AGTFP, hypothesis 2 (H2) was tested, and the specific model was constructed as follows:
2.3.3. Variable Description
The explained variable was agricultural green total factor productivity (AGTFP), and the core explanatory variable was the level of digital agriculture development (DIG). The control variables (Z) included level of foreign investment (FDI), as the ratio of foreign direct investment to GDP; degree of government intervention (GOV), as the proportion of local fiscal expenditure to regional GDP; human capital (HC), as the number of people educated in primary school × 6 + number of people educated in junior high school × 9 + number of people educated in senior high school × 12 + number of people educated in college and above × 16, divided by the total number of people aged six and above; and financial support to agriculture (FINA), as the ratio of spending on forestry, agriculture, and water to overall fiscal spending.
2.4. Data Collection
In view of the availability and objectivity of data, panel data from 30 Chinese provinces (excluding Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan, and Tibet) from 2011 to 2019 were taken as research samples. The data were gleaned from the Tertiary Industry Statistical Yearbook, China Statistical Yearbook, Information Industry Yearbook, China Agricultural Statistics, China Animal Husbandry Yearbook, China Rural Statistical Yearbook, China Agricultural Mechanization Industry Statistical Yearbook, National Bureau of Statistics, Peking University Digital Inclusive Finance Index, provincial statistical yearbooks, and Mark Data Network for 2011 to 2019. Missing values in the data were filled in by interpolation and the mean value method.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the State of Growth of Digital Agriculture
The digital agriculture development of each province was measured from 2011 to 2019, and we calculated the comprehensive index of digital agriculture advancement and the average values for the eastern, central, and western regions. According to the regional economic advancement level, we divided the provinces into three regions: east, middle, and west. There were 11 eastern provinces, including Tianjin, Beijing, Liaoning, Hebei, Fujian, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Shandong, Zhejiang, Hainan, and Guangdong; the central region covered eight provinces, including Shanxi, Henan, Anhui, Jiangxi, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Hunan, and Hubei; and the western part covered 11 provinces, including Inner Mongolia, Yunnan, Gansu, Shanxi, Guangxi Sichuan, Qinghai, Ningxia, Chongqing, Guizhou, and Xinjiang. The specific composite indices for each province and distribution area are provided in the following Table 2.

Table 2.
Comprehensive indices of digital agriculture development for 30 provinces of China, 2011–2019.
According to the results of the comprehensive index of digital agriculture development level combined with Figure 1, it was found that, from 2011 to 2019, each province in China had a large increase in average digital agriculture value, indicating that the sector’s degree of development has been steadily rising and the overall trend is positive. Since 2018, all provinces in China have issued documents on “digital agriculture” and “digital countryside” strategies. In response to the national policy, Figure 1 demonstrates that, since 2018, the growth of digital agriculture has been steadily increasing. From the average value of each province, Jiangsu topped the list, with an average value of 0.1811, followed by Guangdong with 0.1759; meanwhile, the bottom two were Qinghai and Ningxia, with average values of 0.0299 and 0.0294, respectively. The top four provinces in China, in terms of digital agriculture development, were Jiangsu, Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Beijing, which are all eastern areas. This phenomenon may be due to the geographical advantages of eastern regions, considering that their more developed economies provide convenient conditions for the growth of local digital farming.
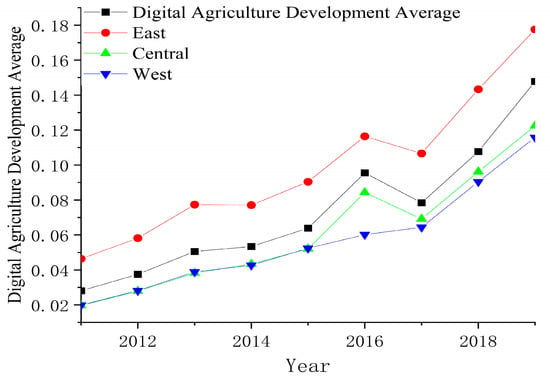
Figure 1.
Trends in the mean value of digital agriculture development in China, 2011–2019.
Analyzing the east, middle, and west regions, the overall development trend showed the trend of eastern > central > western, with average values of 0.0993 > 0.0615 > 0.0570, respectively. The gap between the development of digital agriculture in the eastern provinces was large, and the distribution was uneven. As can be seen from Figure 1, compared to the national average, the east had a higher level of digital agriculture development. At the same time, digital agriculture development was less advanced in the central and western regions than it is nationwide. On the whole, first, from the standpoint of investment, the eastern region has a geographical advantage since the majority of its provinces are coastal, which helps to draw investment, spur local economic growth, and so advance the state of local digital agriculture. Second, from the standpoint of learning capacity, there are some variations in the level of digital literacy among farmers in various regions, which results in varying degrees of farmers’ access to agricultural information and digital agricultural technology during the process of developing digital agriculture, so that the application and promotion of digital agricultural technology are hindered to varying degrees, leading to the uneven development of eastern > central > western. Third, from a financial standpoint, the promotion of agricultural marketization and large-scale promotion in the central region would aid in generating economies of scale, offset the high cost of digital agriculture, and further promote the sustainable development of digital agriculture; however, the farmers in the west are dispersed and the cost of digital agriculture is high, making it difficult to promote digital agriculture in this area. Specifically, Jiangxi and Heilongjiang, located in the central region, had digital agriculture development values that were 0.0495 and 0.0460 below the national central average, respectively. Meanwhile, Henan’s comprehensive index was 0.0746, lying between the national and eastern average values. The reason for the relatively high level of digital agriculture in Henan is that Henan itself is a predominantly agricultural province located on a plain, with a warm and humid climate, making it suitable for agricultural development. The higher overall index of digital agriculture in Inner Mongolia among the western regions is mainly due to its good climatic conditions and geographical advantages. Various government departments regard the creation of the green food industry as an advantageous critical industry to be cultivated in the western region, thus promoting the growth of digital farming in the area with the impetus of capital, policies, and location advantages. Xinjiang, Qinghai, and Ningxia are still in the preliminary development stage of digital agriculture, due to their relatively remote locations, droughts and water shortages, and rather harsh natural environments, resulting in a relatively low level of digital agriculture development.
3.2. Green Total Factor Productivity Index Analysis for Agriculture
From Figure 2, we can see that, during the research period, China’s AGTFP index showed an overall steady growth, with an overall average value greater than one and a yearly growth rate of about 2.05% on average. From the figure, it can be seen that the general trend fluctuated up and down from 2012 to 2016, with an upward trend after 2016. The reason may be that the concept of green production in agriculture during the study period was still in the primary stage while, since 2016, the relevant guidance programs and agricultural green ecological subsidy policies such as “Zero Growth Use Program of Fertilizer Use by 2020” and “Zero Growth Use Program of Pesticide Use by 2020” were introduced to encourage localities to advocate green and environmentally friendly production patterns.
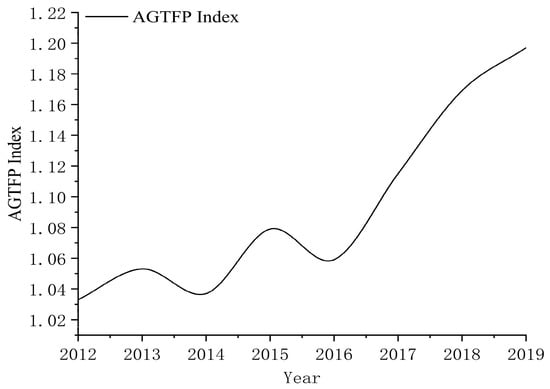
Figure 2.
China’s AGTFP index.
Secondly, from Table 3, we can find that the AGTFP index was only 0.94 in Shanghai, which is lower than 1, while the AGTFP indices in other areas from 2011 to 2019 were above 1. Meanwhile, from the decomposition index, the technical progress indices were all above 1, while the technical efficiency index was below 1 in 12 provinces, indicating that technological progress significantly contributes to the improvement of AGTFP. In contrast, technical efficiency should be further improved.

Table 3.
The average AGTFP index and decomposition index in 30 provinces of China, 2011–2019.
3.3. Analysis of the Effect of Digital Agriculture Development on AGTFP
3.3.1. Benchmark Regression test
Model (1) denotes a random effect without the inclusion of the squared term of the independent variable; model (2) denotes the inclusion of the squared term of the independent variable; and model (3) denotes a fixed effect model.
Regarding the effect of digital agriculture development on AGTFP, Table 4 displays the results of the regression analysis: model (1) is a least squares regression of digital agriculture development on AGTFP, and model (2) introduces the DIG2 on the basis of model (1), in order to examine whether there is a non-linear effect of digital agriculture development level on AGTFP. The Hausman test p-value was 0.0011—that is, noteworthy at the 5% level—thus rejecting the random effect model. Therefore, the test using models (2) and (3) revealed that DIG and DIG2 regression coefficients were significant at 1%. Thus, digital agriculture development positively contributes to AGTFP, and there is an inverted U-shaped curve relationship.

Table 4.
Test results for the correlation between digital agriculture development and total factor productivity in agriculture.
3.3.2. Moderating Effect Test
Based on the regression model shown in Table 5, the regression coefficient of the interaction term (C_interact = HC × DIG) between the moderating variable and the core variable after centering was −0.435, which was significant at the 1% level, meaning that human capital moderates the impact of digital agriculture development on AGTFP.

Table 5.
Test results of moderating effect of digital agriculture development on AGTFP.
3.3.3. Robustness Tests
Robustness analysis of the regression results was performed by subjecting the results to robustness tests, mainly through replacing explanatory variables and panel quantile regressions. First, panel quantile regression analysis was conducted (as shown in Table 6), and the results were the same as in model (1); second, considering that digital agriculture development and AGTFP may have an inverse causal relationship, to solve the endogeneity problem, the level of digital agriculture development lagged by one period was brought into the regression as an instrumental variable. The F value was 59.2282 > 10 (p = 0.0000), and the findings indicated that the explanatory factors were still important. The results were as in model (2). Furthermore, these results indicate that the empirical results were robust.

Table 6.
Robustness test results of digital agriculture development on AGTFP.
3.3.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
Considering that digital agriculture development can be affected by regional differences, which may lead to differences in the research results, we attempted to analyze whether the extent of digital agriculture advancement in various locations had similar or different impacts on AGTFP. Table 7 presents the outcomes. Columns (1)–(3) of Table 7 demonstrate that the impact of digital agriculture development level on AGTFP in the western region was not significant, while the impact of the digital agriculture advancement level on AGTFP in the eastern and central areas was significant. It presented an inverted U-shaped curve, and the center and eastern areas showed DIG and DIG2 significance at the 10% level. The main reasons for this may be as follows: first, the location advantage and economic development level in the east make it easier to promote agricultural technology innovation and improve the optimization of resource allocation, thus helping to improve AGTFP; second, the central region has higher marketization and scale of agriculture, as well as better adoption of agricultural mechanization, therefore promoting production efficiency, which leads to the improvement in AGTFP level; third, due to its remote location, harsh climatic environment, lagging infrastructure construction, and backward agricultural science and technology, the western region is not conducive to introducing external funds, such that the advancement of digital agriculture presented no significant effect on AGTFP.

Table 7.
Analysis of heterogeneity results of digital agriculture development on total factor productivity in agriculture.
4. Conclusions and Policy Implications
4.1. Conclusions
In this paper, we constructed an index system for digital agriculture development and AGTFP. First, the entropy value method and SBM-ML index model were used to evaluate the state of digital agriculture advancement and AGTFP in 30 provinces of China from 2011–2019, respectively; then, a fixed effect model and a moderating effect model were constructed to examine the impact of digital agriculture development on AGTFP. The following study findings were deduced: First, the growth level of digital agriculture was positive during the study period, while technical efficiency in the AGTFP decomposition index presented some room for improvement. Second, we confirmed that there is an inverse U-shaped association between AGTFP and the advancement of digital agriculture. This suggests that, to a certain extent, the advancement of digital agriculture will impede the advancement of AGTFP. Third, we verified the moderating effect of human capital between digital agriculture development and AGTFP.
4.2. Policy Implications
4.2.1. Strengthen the Construction of an Organizational Mechanism
A whole organizational system to fortify the growth of the digital farming sector’s organizational structures and creating a working path of “government–industry organization–lead enterprises–cooperatives–grassroots party organizations–farmers” should be built in order to realize the sustainable promotion of digital agriculture industrialization. First, the government must take the lead in promoting the process of digital agriculture industrialization, actively cultivate leading enterprises, and implement leading enterprises to drive local cooperatives. Second, the establishment of industry organizations, as well as close contact and integration between the government, enterprises, and various resources from industries, academia, and research to serve as a link and a bridge. Third, grassroots party organizations should be utilized as a grip to build a linkage and integration platform for cooperatives and local farmers, reach out to farmer groups, and encourage farmers to participate through a series of measures such as active guidance, support, and incentives promoting their participation in the development of digital agriculture industry.
4.2.2. Construction of Digital Agricultural Production Standardization Base
The construction of standardized production bases for digital agriculture should be vigorously strengthened. The standardization system may be formulated in three aspects—natural conditions of the base, production process, and final agricultural products—which help to facilitate the production of agricultural products and processed products with high quality, high standards, and high added value to adequately meet market demands. First, to improve the natural conditions of the base, matched with the actual soil conditions in the area, we should choose high-quality soil rich in minerals and trace elements which, according to regional soil differences and crop types, may be supplemented through scientific fertilization improvement technology and/or the comprehensive use of planting waste, in an effort to achieve the sustainable cycle of planting and raising while improving the overall fertility of the soil. Second, the production process relies on scientific research institutes to transform the results of scientific and technological practice, strengthen deep processing technology, constantly improve key production technology, and optimize the production process to increase the productivity of business output. Finally, concerning the finished agricultural products, the vigorous development of multi-functional fruits, drinks, healthcare products, and skin care products can be achieved, realizing the diversification, serialization, and high added value of agricultural products. In addition, refrigeration and preservation, packaging, logistics, and distribution technologies must be further developed, in order to create a standardized base for digital agricultural production, thus continuously improving the comprehensive benefits.
4.2.3. Strengthen the Certification and Traceability of Digital Agricultural Products
There is no national certification for digital agricultural products at present. It is essential to further lead the development of digital farm product certification with an innovation drive, in order to carry out digital agricultural food safety management system and good manufacturing practice (GMP) certifications according to the breeding environment, production links, and circulation links in agriculture. Products certified for agricultural product quality and safety, under the food safety law of the People’s Republic of China, promote the high quality and safety of farm products and further enhance their credibility among the public. Certification raises the threshold effect and reflects the difference and uniqueness of digital agricultural products, thus enhancing competitiveness in the product market. Additionally, certified digital agricultural products can be quality-traced. Through traceability platforms, information on the original environment, production, processing, and other aspects of agricultural products can be traced, thus further increasing the informational transparency of farm products and dissolving information asymmetry.
4.2.4. Improve the Social Services of the Agricultural Industry
In the stage of rural revitalization, in order to improve AGTFP, we must constantly improve the social service system underlying the agricultural industry. First, we should take government support as the guide, supplemented by market demand-oriented supply, and continuously improve and perfect digital agriculture market system construction. Secondly, digital agriculture production services must be strengthened by combining the actual development of digital agriculture in different regions; screening excellent varieties suitable for development; enhancing technologies related to microorganism monitoring, breeding, agronomy, deep processing, and waste recycling processes; and strictly controlling the quality of nutritional safety through monitoring information feedback. Again, we must strengthen digital agriculture financial services, reduce taxes and fees, and set up special risk funds. Through the mode of “digital agriculture +”, we can continue to make up for the shortage of funds needed for developing digital agriculture. Finally, the quality of digital agriculture information services should be improved, by strengthening the construction of agricultural network facilities in various regions, building a digital agriculture market information service platform, at the same time, conducting multifaceted publicity and building a technical training platform to promote the growth of digital farming and improve economic benefits in an ongoing manner.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z., T.C. and B.Z.; methodology, X.Z.; software, X.Z.; validation, X.Z.; formal analysis, X.Z., T.C. and B.Z.; investigation, X.Z.; resources, X.Z.; data curation, X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.Z.; visualization, X.Z.; supervision, X.Z.; project administration, B.Z.; funding acquisition, B.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Social Science Foundation Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region in China (grant number 21BGL099).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Leng, X.C.; Tong, G.J. The Digital Economy Empowers the Sustainable Development of China’s Agriculture-Related Industries. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klerkx, L.; Jakku, E.; Labarthe, P. A review of social science on digital agriculture, smart farming and agriculture 4.0: New contributions and a future research agenda. NJAS-Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2019, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runck, B.C.; Joglekar, A.; Silverstein, K.A.T.; Chan-Kang, C.; Pardey, P.G.; Wilgenbusch, J.C. Digital agriculture platforms: Driving data-enabled agricultural innovation in a world fraught with privacy and security concerns. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Piao, H.L. Does Agricultural Mechanization Improve the Green Total Factor Productivity of China’s Planting Industry? Energies 2022, 15, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.R.; Li, Z. Measurement of high-quality development level of China’s digital agriculture in the context of rural revitalization—Based on the analysis of data of 31 provinces and cities nationwide from 2015 to 2019. J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2021, 50, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, Y.J.; Liu, N.X.; Zheng, T.Y. Accelerate the exploration of agricultural digitalization to promote rural revitalization in an all-round way—Interpretation of the contents of “digitalization” in the No. 1 central document from 2004 to 2022. Globalization 2022, 6, 102–112, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. China’s agricultural green total factor productivity based on carbon emission: An analysis of evolution trend and influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 278, 123692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. The next five years will be a critical period for building a socialist modern country in an all-round way—Learning from the report of the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China. China Bus. Mark. 2022, 36, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Cheng, C.M.; Sun, G.L.; Li, J.F. The Impact of Digital Inclusive Finance on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity: Evidence from China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 905644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.P.; Mei, S.; Zhang, W.C. The development path of digital agriculture in less developed regions: An example of developing digital agriculture in Huanggang City. Decis. Inf. 2021, 2, 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Subaeva, A.K.; Nizamutdinov, M.M.; Mavlieva, L.M. Changes of the agricultural staff potential in the transition to digital agriculture. BIO Web Conf. 2020, 17, 00178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.Q.; Wang, M.H.; Wang, N. Precision agriculture—A worldwide overview. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 36, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birner, R.; Daum, T.; Pray, C. Who drives the digital revolution in agriculture? A review of supply-side trends, players and challenges. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2021, 43, 1260–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.H.; Liu, T.J.; Feng, X.C.; Qiao, Z.; Huo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, X. Digital agriculture operation management: Key issues, theoretical approaches and demonstration projects. Manag. World 2020, 36, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.W.; Song, Y.X.; Lin, X.Z.; Fu, C. Some problems of digital village construction in China. China Rural Econ. 2021, 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.W. Development of digital agriculture at home and abroad and experiences. Yunnan Agric. 2019, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, A. How will digitalization change agriculture? Int. Trade Forum 2016, 2016, 28–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackfort, S. Patterns of Inequalities in Digital Agriculture: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lu, X.S.; Zhang, D.G.; Liang, F.; Ren, Z.B. Study on the framework system of digital agriculture. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2003, 13, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.A.; Buttel, F.H. The Political Economy of Precision Farming. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1996, 78, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, A. Digital from farm to fork: Infrastructures of quality and control in food supply chains. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 91, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, J.; Voglhuber-Slavinsky, A.; Olbrisch, M.; Schobel, P.; Donitz, E.; Mouratiadou, I.; Helming, K. Future agricultural systems and the role of digitalization for achieving sustainability goals. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garske, B.; Bau, A.; Ekardt, F. Digitalization and AI in European Agriculture: A Strategy for Achieving Climate and Biodiversity Targets? Sustainability 2021, 13, 4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C. Digital Development Strategy of Agricultural Planting and Breeding Enterprises Based on Intelligent Sensors. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 6495191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, J.; Wang, D.Y. Optimal evaluation index system and benefit evaluation model for agricultural informatization in Beijing. Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2018, 33, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Han, Z.Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.K.; Guo, C. High-Quality Development of Chinese Agriculture under Factor Misallocation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zhao, J.; Di, J.; Zhang, L.J. Spatial correlations and driving mechanisms of low-carbon agricultural development in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Hu, R.; Mao, H.; Chen, S. How crop insurance influences agricultural green total factor productivity: Evidence from Chinese farmers. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Fu, W.W.; Wang, J.Y. Evaluation and Influencing Factors of China’s Agricultural Productivity from the Perspective of Environmental Constraints. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akroush, S.N.; Dhehibi, B.; Aw-Hassan, A. Agricultural Growth Accounting and Total Factor Productivity in Jordan Trends determinants and future challenges. Int. J. Product. Manag. Assess. Technol. 2016, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, R.K.; Rezek, J.P. Environmentally Adjusted Agricultural Productivity in the Great Plains. West. J. Agric. Econ. 2004, 29, 346–369. [Google Scholar]
- Baráth, L.; Fert, I. Accounting for TFP Growth in Global Agriculture—A Common-Factor-Approach-Based TFP Estimation. AGRIS on-line Pap. Econ. Inform. 2020, 12, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.C.; Li, E.L.; Cui, Z.Z. Evaluation and Influence Factor of Green Efficiency of China’s Agricultural Innovation from the Perspective of Technical Transformation. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusiawan, W.; Tjiptoherijanto, P.; Suganda, E.; Darmajanti, L. Assessment of Green Total Factor Productivity Impact on Sustainable Indonesia Productivity Growth. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barro, R.J.; Lee, J.W. A new data set of educational attainment in the world, 1950–2010. J. Dev. Econ. 2013, 104, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Han, D.R.; Ding, Y.Y.; Shi, Z.Y. How Does the Development of the Internet Affect Green Total Factor Productivity? Evidence From China. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 216477–216490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, F.; Kerstens, P.J. Decomposing the Luenberger-Hicks-Moorsteen Total Factor Productivity indicator: An application to US agriculture. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 260, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syverson, C. What Determines Productivity? J. Econ. Lit. 2011, 49, 326–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q.H. Factor allocation structure and green-biased technological progress in Chinese agriculture. Econ. Res. Ekon. Istraživanja 2021, 34, 2034–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.Y.; Tian, M.J.; Wang, J. Digital Inclusive Finance, Agricultural Industrial Structure Optimization and Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Hamid, Z.; Mahboob, F.; Rehman, K.U.; Ali, M.S.E.; Senkus, P.; Wysokinska-Senkus, A.; Sieminski, P.; Skrzypek, A. Causal Linkage among Agricultural Insurance, Air Pollution, and Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in United States: Pairwise Granger Causality Approach. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, J.Y.; Tang, M.Q.; Su, M.Y.; Guo, L.L. Scale of Operation, Financial Support, and Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity: Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heath 2022, 19, 9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.H.; Zhu, P.X.; Tang, L. Agricultural Services: Another Way of Farmland Utilization and Its Effect on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in China. Land 2022, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.P.; Shi, R.; Mi, L.C.; Liu, P.; Wang, G.F. Spatial Distribution and Convergence of Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heath 2022, 19, 8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pylianidis, C.; Osinga, S.; Athanasiadis, I.N. Introducing digital twins to agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 184, 105942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namani, S.; Gonen, B. Smart Agriculture Based on IoT and Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies (ICICT), San Jose, CA, USA, 9–12 March 2020; pp. 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.B.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Wen, C.C.; Sun, H.G. Agricultural environmental total factor productivity in China under technological heterogeneity: Characteristics and determinants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32096–32111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.Y.; Jing, X.N.; Shen, Z.Y. Internet technology and green productivity in agriculture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 81441–81451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, D.S.; Tyagi, S.; Soni, S.K. A techno-economic analysis of digital agriculture services: An ecological approach toward green growth. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 3859–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.; Robert, F.; Huber, R.; Buchmann, N. Smart farming is key to developing sustainable agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6148–6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lu, X.S.; Zhang, D.G.; Liang, F. The main content, technical support and enforcement strategy of digital agriculture. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 5, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, M.; Turner, J.A.; Small, B.; Wheeler, D. Priorities for science to overcome hurdles thwarting the full promise of the ‘digital agriculture’ revolution. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 5083–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sott, M.K.; Nascimento, L.S.; Foguesatto, C.R.; Furstenau, L.B.; Faccin, K.; Zawislak, P.A.; Mellado, B.; Kong, J.D.; Bragazzi, N.L. Agriculture 4.0 and Smart Sensors. The Scientific Evolution of Digital Agriculture: Challenges and Opportunities. Sensors 2021. preprints. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.A.; Ilango, P. The Impact of Wireless Sensor Network in the Field of Precision Agriculture: A Review. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 98, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, J. Precision agriculture: Introduction to the spatial and temporal variability of environmental quality. In Ciba Foundation Symposium 210-Precision Agriculture: Spatial and Temporal Variability of Environmental Quality: Precision Agriculture: Spatial and Temporal Variability of Environmental Quality: Ciba Foundation Symposium 210; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1997; pp. 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshari, M.; Almunawar, M.N.; Masri, M.; Hamdan, M. Digital Marketplace and FinTech to Support Agriculture Sustainability. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Power and Energy Systems Engineering (CPESE), Nagoya, Japan, 19–21 September 2018; pp. 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, W.; Tao, Y.D. Reverse integration and optimisation of agricultural products E-commerce omnichannel supply chain under Internet technology. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2021, 71, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.P.; Su, Z.X.; Yang, X.; Xu, S.; Pan, H. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Beef Cattle Breeding Based on the Ecological Cycle Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heath 2022, 19, 9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, H. Actuators and Sensors for Application in Agricultural Robots: A Review. Machines 2022, 10, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.Q.; Zhang, R.W. Can Digitalization Levels Affect Agricultural Total Factor Productivity? Evidence From China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 860780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q. Quality information disclosure, signaling and certification of agricultural products: A comparative analysis based on meat and vegetable industries. Agric. Econ. Issues 2020, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Yan, Z.; Seah, H.S.; Feng, T.; Yan, X. Plant Modeling and Its Application in Digital Agriculture Museum; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergvinson, D. Unlocking the power of digital agriculture. In Proceedings of the 2017: Transforming Lives and Livelihoods: The Digital Revolution in Agriculture, Canberra, Australia, 7–8 August 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, S. Digital Agriculture and Urbanization: Mechanism and Empirical Research. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 180, 121724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Feng, X. Research on the indicator system design for rural digital economy from the perspective of digital village construction. Res. Agric. Mod. 2020, 41, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.K. Application of artificial intelligence and machine learning based on big data analysis in sustainable agriculture. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2021, 71, 956–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodovnik, A.I.; Gulyaeva, T.I. Evaluation methodology of the potential of agricultural universities in the “experimental digital pilot farm” project. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 422, 012096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.S. Comprehensive evaluation of the development level of digital agriculture in China’s provincial areas and analysis of influencing factors. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia University of Finance and Economics, Hohhot, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhao, D.D. Evaluation of the high-quality development of digital agriculture in Hebei Province. Agric. Technol. 2022, 42, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.B. Research on the equity of agricultural carbon emissions in China’s provincial regions. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2013, 23, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Min, J.S.; Hu, H. Measurement of greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural production in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kozina, A.M.; Semkiv, L.P. Sustainable development of dairy farming through the use of digital technologies. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 613, 012061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyinbo, O.; Chamberlin, J.; Maertens, M. Design of Digital Agricultural Extension Tools: Perspectives from Extension Agents in Nigeria. J. Agric. Econ. 2020, 71, 798–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, S.; Jackson, E.L.; Fisher, M.J.; Baker, D.; Diepeveen, D. Embedding digital agriculture into sustainable Australian food systems: Pathways and pitfalls to value creation. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2022, 20, 346–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountas, S.; Espejo-Garcia, B.; Kasimati, A.; Mylonas, N.; Darra, N. The Future of Digital Agriculture: Technologies and Opportunities. IT Prof. 2020, 22, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, S.; Duncan, E.; Small, M.; Botschner, J.; Dara, R.; Mosby, I.; Reed, M.; Fraser, E.D.G. The Politics of Digital Agricultural Technologies: A Preliminary Review. Sociol. Rural. 2019, 59, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhu, R.B. Digital agriculture development: International experience, emission reduction effect and financial support—A case study based on Chengdu. Southwest Financ. 2022, 1, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Q.C.; Zhang, H. Feasibility, problems and suggestions of digital agriculture development in China. Econ. Res. Ref. 2022, 2, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Huang, Y.; Gao, W.; Min, W. A Comparative Study of the Impacts of Human Capital and Physical Capital on Building Sustainable Economies at Different Stages of Economic Development. Energies 2021, 14, 6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, R.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y. Impact of human capital on the green economy: Empirical evidence from 30 Chinese provinces. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lv, N. The threshold effect test of human capital on the growth of agricultural green total factor productivity: Evidence from China. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Educ. 2021, 002072092110032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).