Monitoring House Vacancy Dynamics in The Pearl River Delta Region: A Method Based on NPP-VIIRS Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.2.1. Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Images
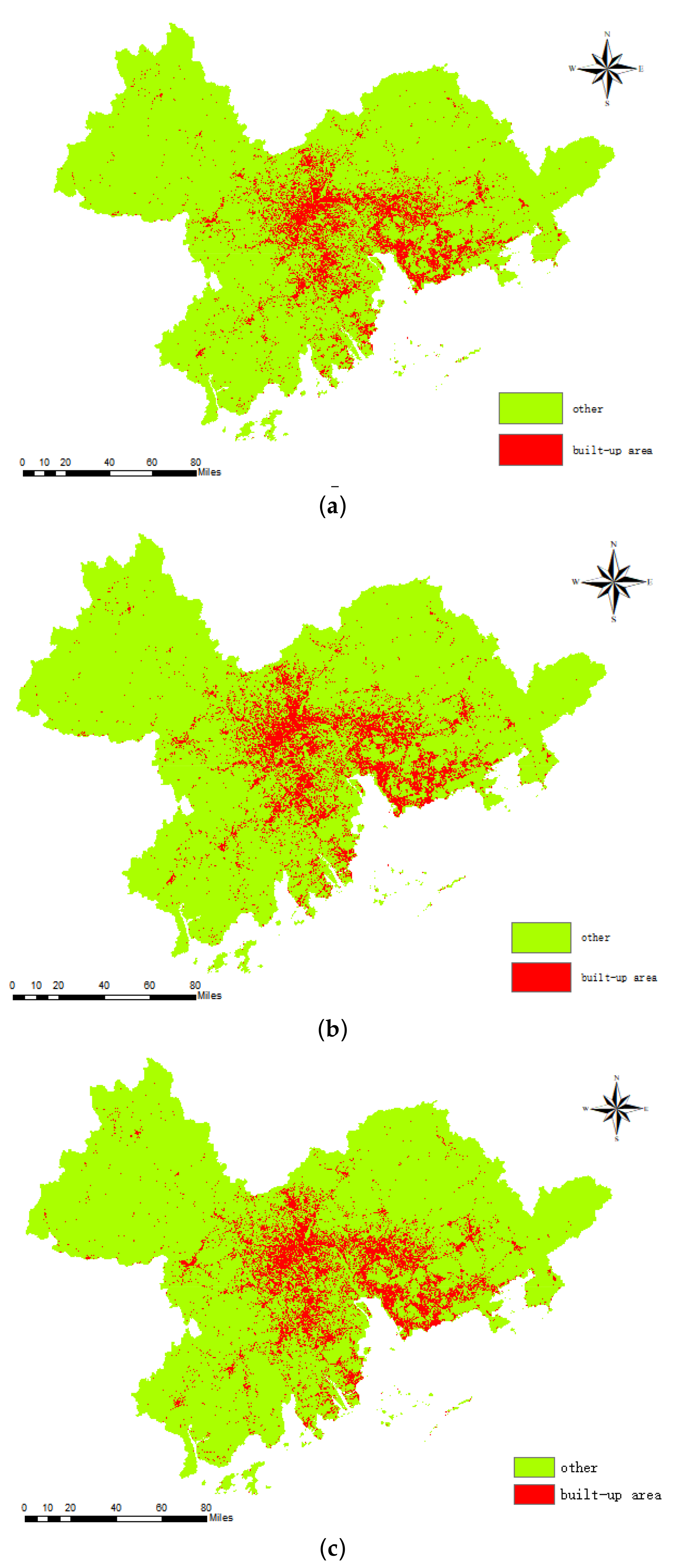
2.2.2. Urban Built-Up Area Data
2.2.3. Housing Rent/Sale Data
2.3. Data Processing
2.3.1. Workflow
2.3.2. Pre-Processing NTL Data
2.3.3. Pre-Processing Landsat 8 OLI Data
2.3.4. Removing Non-Residential Lights
2.4. House Vacancy Rate Estimation
2.4.1. Estimating Light Intensity in the Urban Built-Up Area
2.4.2. Estimating HVR
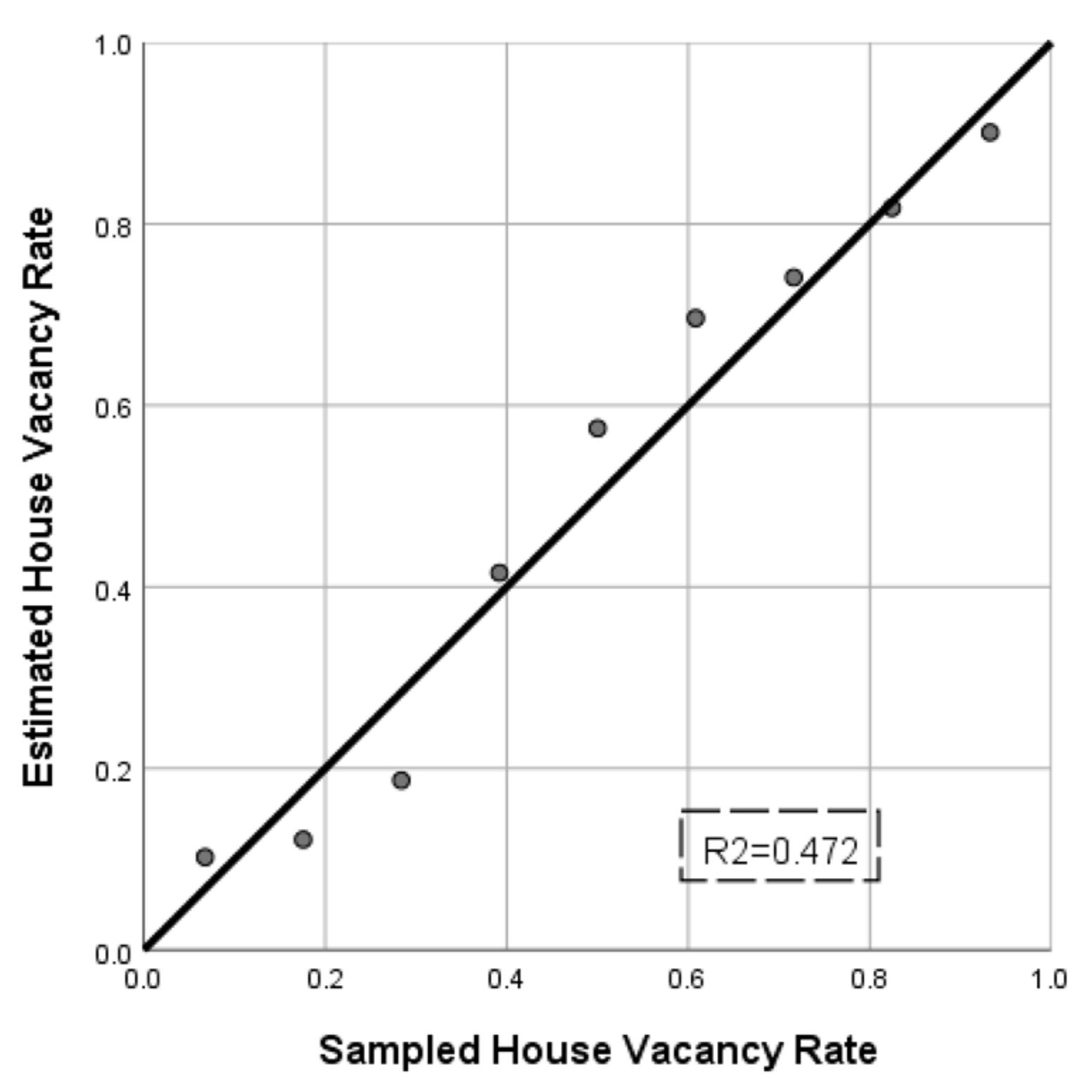
2.5. Verification
3. Results
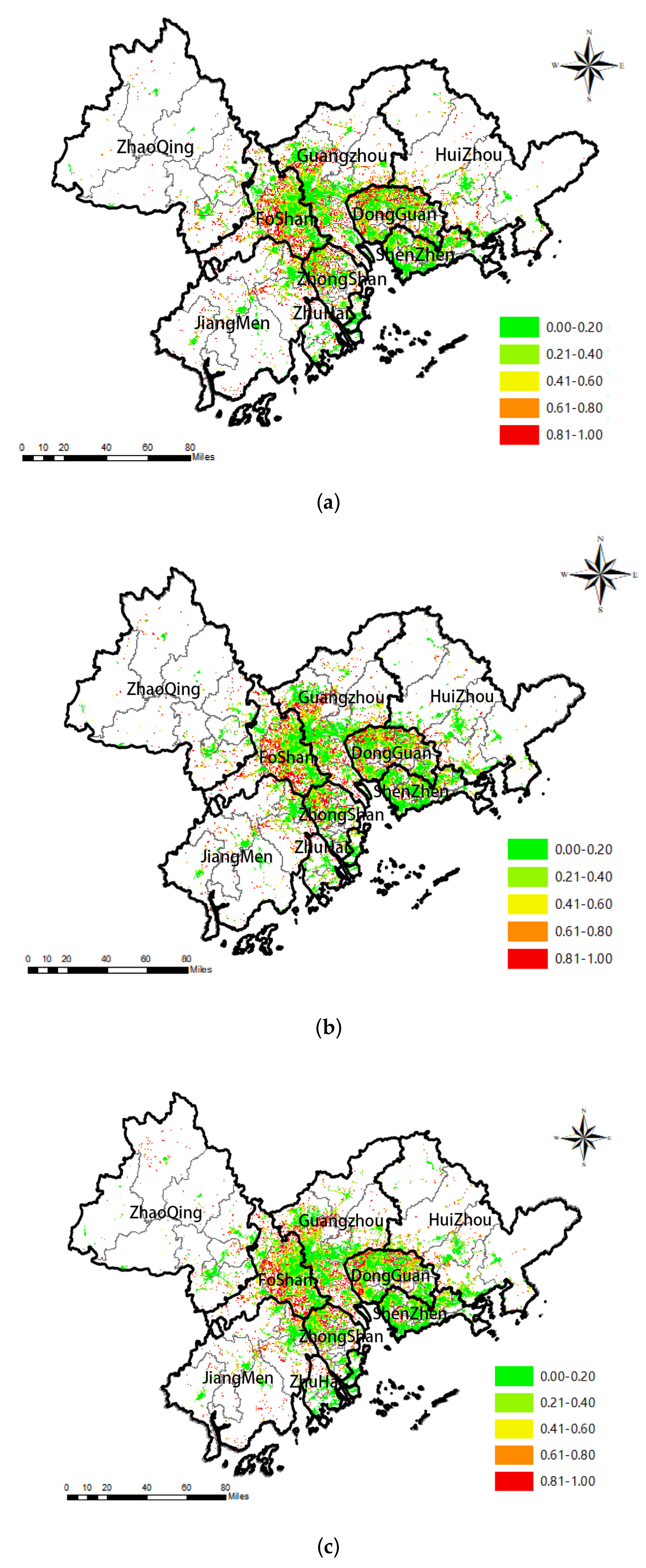
3.1. Overall Decreasing HVRs in the PRD
3.2. Dynamics of HVRs at the District Scale
3.3. Spatial Differentiation of HVRs Changes
3.4. Potential Risk: Increasing Vacant Pixels in the PRD
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glaeser, E.; Huang, W.; Ma, Y.; Shleifer, A. A real estate boom with Chinese characteristics. J. Econ. Perspect. 2017, 31, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, G.; Lee, R.J.; Gu, D.; Park, Y.; Saginor, J.; Van Zandt, S.; Li, W. Evaluating drivers of housing vacancy: A longitudinal analysis of large U.S. cities from 1960 to 2010. J. Hous. Built Environ. 2019, 34, 807–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Jia, S.; Yang, R. Housing affordability and housing vacancy in China: The role of income inequality. J. Hous. Econ. 2016, 33, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, M.; Blackwell, C. The information age: Economy, society and culture. Volume 1. The rise of the network society. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 1998, 25, 631–636. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-López, M.À.; Muñiz, I. Urban spatial structure, agglomeration economies, and economic growth in Barcelona: An intra-metropolitan perspective. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2013, 92, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limtanakool, N.; Schwanen, T.; Dijst, M. Ranking functional urban regions: A comparison of interaction and node attribute data. Cities 2007, 24, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Chen, M.; Duan, J.; Yang, D. Uneven development, urbanization and production of space in the middle-scale region based on the case of Jiangsu province, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 66, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wurm, M.; Huang, X.; Zhong, T.; Leichtle, T.; Taubenböck, H. Estimating housing vacancy rates at block level: The example of Guiyang, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 224, 104431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Liu, B.; Jia, K.; Cai, Z.; Cheng, H. Application of Power Big Data in Power Acquisition System—The vacancy rate of residential housing based on power data. Agric. Electr. Manag. 2021, 02, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, G.; Soebarto, V.; Zuo, J. Vacancy visual analytics method: Evaluating adaptive reuse as an urban regeneration strategy through understanding vacancy. Cities 2021, 115, 103220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, P. Empty dwellings: The use of council-tax records in identifying and monitoring vacant private housing in England. Environ. Plan. A 2008, 40, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, J.L. Viviendas Vacías: Un Universo Complejo; Su Vivienda, El Mundo: Medellín, Colombia, 2004; p. 369. [Google Scholar]
- Gentili, M.; Hoekstra, J. Houses without people and people without houses: A cultural and institutional exploration of an Italian paradox. Hous. Stud. 2019, 34, 425–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, E.L.; Blanco, Z.G. Ghost cities and empty houses: Wasted prosperity. Am. Int. J. Soc. Sci. 2014, 3, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal dynamics of electricity consumption in China. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2019, 12, 395–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS night-time light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Hu, Y. Spatial identification of multi-dimensional poverty in rural China: A perspective of nighttime-light remote sensing data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 1093–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Shi, K.; Wu, J. Estimating house vacancy rate in metropolitan areas using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2188–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y. An estimation of housing vacancy rate using NPP-VIIRS night-time light data and OpenStreetMap data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 8566–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, D.; Zhou, L.; Huang, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y. High precision space estimation of housing vacancy rate using high resolution image and Luojia-1. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2021, 1, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Pan, J. Estimating Housing Vacancy Rate Using Nightlight and POI: A Case Study of Main Urban Area of Xi’an City, China. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. Estimation of Urban Housing Vacancy Based on Daytime Housing Exterior Images—A Case Study of Guangzhou in China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; An, W. The Generation and Development of the Urban Agglomeration in the Pearl River Delta. J. Tongji Univ. Soc. Sci. Sect. 2004, 5, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, B.H.; He, Q.Y. Study on evolution of spatial structure of Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration and its effects. Econ. Geogr. 2011, 31, 404–408. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS night-time light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dou, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H. Urban land extraction using VIIRS nighttime light data: An evaluation of three popular methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, C.; De Luccia, F.J.; Xiong, X.; Wolfe, R.; Weng, F. Early on-orbit performance of the visible infrared imaging radiometer suite onboard the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (S-NPP) satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López, R.; Valdés, A. Fighting rural poverty in Latin America: New evidence of the effects of education, demographics, and access to land. Econ. Dev. Cult. Chang. 2000, 49, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory, 2nd ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; He, C.; Liu, Z.; Dou, Y. How did urban land expand in China between 1992 and 2015? A multi-scale landscape analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Hara, M.; Yagi, H.; Naoki, K.; Tana, G.; Nishio, F.; Shuhei, O. Estimating energy consumption from night-time DMPS/OLS imagery after correcting for sat-uration effects. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4443–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Pan, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W. Spatial difference pattern of house vacancy in China from nighttime light view. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Shi, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. Generating 2m fine-scale urban tree cover product over 34 metropolises in China based on deep context-aware sub-pixel mapping network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 106, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Shi, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Xia, G.; Zhang, L. Generating annual high resolution land cover products for 28 metropolises in China based on a deep super-resolution mapping network using Landsat imagery. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 2036–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| District | Number of Sampled Projects | Number of Total Housing Units | Number of Units on Sale or for Rent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nansha | 89 | 152,214 | 7686 |
| Tianhe | 549 | 440,390 | 17,572 |
| Haizhu | 455 | 519,167 | 15,204 |
| Panyu | 458 | 480,830 | 22,832 |
| Baiyun | 285 | 347,703 | 14,280 |
| Huadu | 178 | 238,088 | 11,698 |
| Liwan | 223 | 307,323 | 8788 |
| Yuexiu | 334 | 408,106 | 10,918 |
| Huangpu | 144 | 247,643 | 8754 |
| Type | Sample | Number |
|---|---|---|
| Water |  | 34 |
| Urban |  | 40 |
| Forest |  | 32 |
| Grassland |  | 36 |
| Mountain |  | 34 |
| Cropland |  | 31 |
| District | Estimated House Vacancy Rate | Sampled House Vacancy Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Nansha | 49.85% | 5.51% |
| Tianhe | 19.40% | 4.65% |
| Haizhu | 27.76% | 3.61% |
| Panyu | 39.45% | 5.54% |
| Baiyun | 43.16% | 5.45% |
| Huadu | 28.70% | 5.99% |
| Liwan | 30.47% | 3.47% |
| Yuexiu | 11.41% | 3.26% |
| Huangpu | 18.43% | 3.32% |
| City | 2013–2016 | 2016–2019 | HVR (2019) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangzhou | −3.22% | −1.23% | 0.32 |
| Foshan | 3.02% | −0.90% | 0.44 |
| Zhaoqing | −2.91% | −7.65% | 0.33 |
| Shenzhen | −1.21% | −15.38% | 0.21 |
| Dongguan | −3.08% | −7.53% | 0.37 |
| Huizhou | −24.18% | 12.52% | 0.33 |
| Zhuhai | 2.21% | −21.50% | 0.27 |
| Zhongshan | −8.89% | 6.64% | 0.40 |
| Jiangmen | −3.22% | 5.71% | 0.40 |
| PRD | −4.99% | −2.39% | 0.35 |
| City | 2013 | 2016 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangzhou | 596 | 639 | 684 |
| Foshan | 938 | 854 | 906 |
| Zhaoqing | 9 | 24 | 45 |
| Shenzheng | 144 | 190 | 132 |
| Dongguan | 631 | 604 | 537 |
| Huizhou | 48 | 46 | 53 |
| Zhuhai | 153 | 131 | 140 |
| Zhongshan | 354 | 421 | 420 |
| Jiangmen | 107 | 122 | 159 |
| PRD | 2980 | 3031 | 3076 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Fu, X.; Yin, Z.; Liu, M.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Monitoring House Vacancy Dynamics in The Pearl River Delta Region: A Method Based on NPP-VIIRS Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Images. Land 2023, 12, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040831
Liu X, Li Z, Fu X, Yin Z, Liu M, Yin L, Zheng W. Monitoring House Vacancy Dynamics in The Pearl River Delta Region: A Method Based on NPP-VIIRS Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Images. Land. 2023; 12(4):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040831
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuan, Zehao Li, Xinyi Fu, Zhengtong Yin, Mingzhe Liu, Lirong Yin, and Wenfeng Zheng. 2023. "Monitoring House Vacancy Dynamics in The Pearl River Delta Region: A Method Based on NPP-VIIRS Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Images" Land 12, no. 4: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040831
APA StyleLiu, X., Li, Z., Fu, X., Yin, Z., Liu, M., Yin, L., & Zheng, W. (2023). Monitoring House Vacancy Dynamics in The Pearl River Delta Region: A Method Based on NPP-VIIRS Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Images. Land, 12(4), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040831













