Runoff and Sediment Deposition Characteristics of Gravel-Mulched Land: An Experimental Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
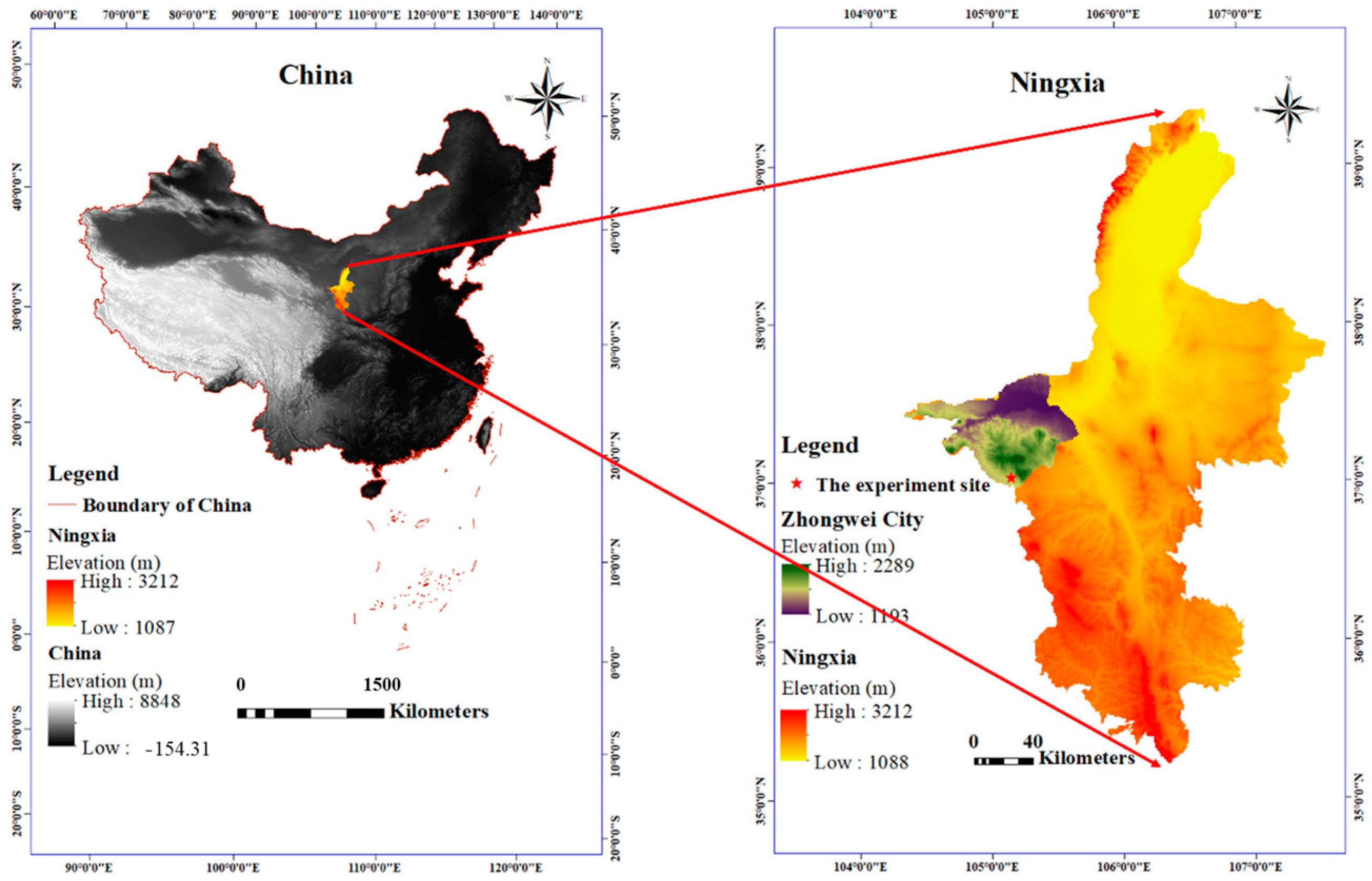
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Control Variables
2.2. Gravel and Soil
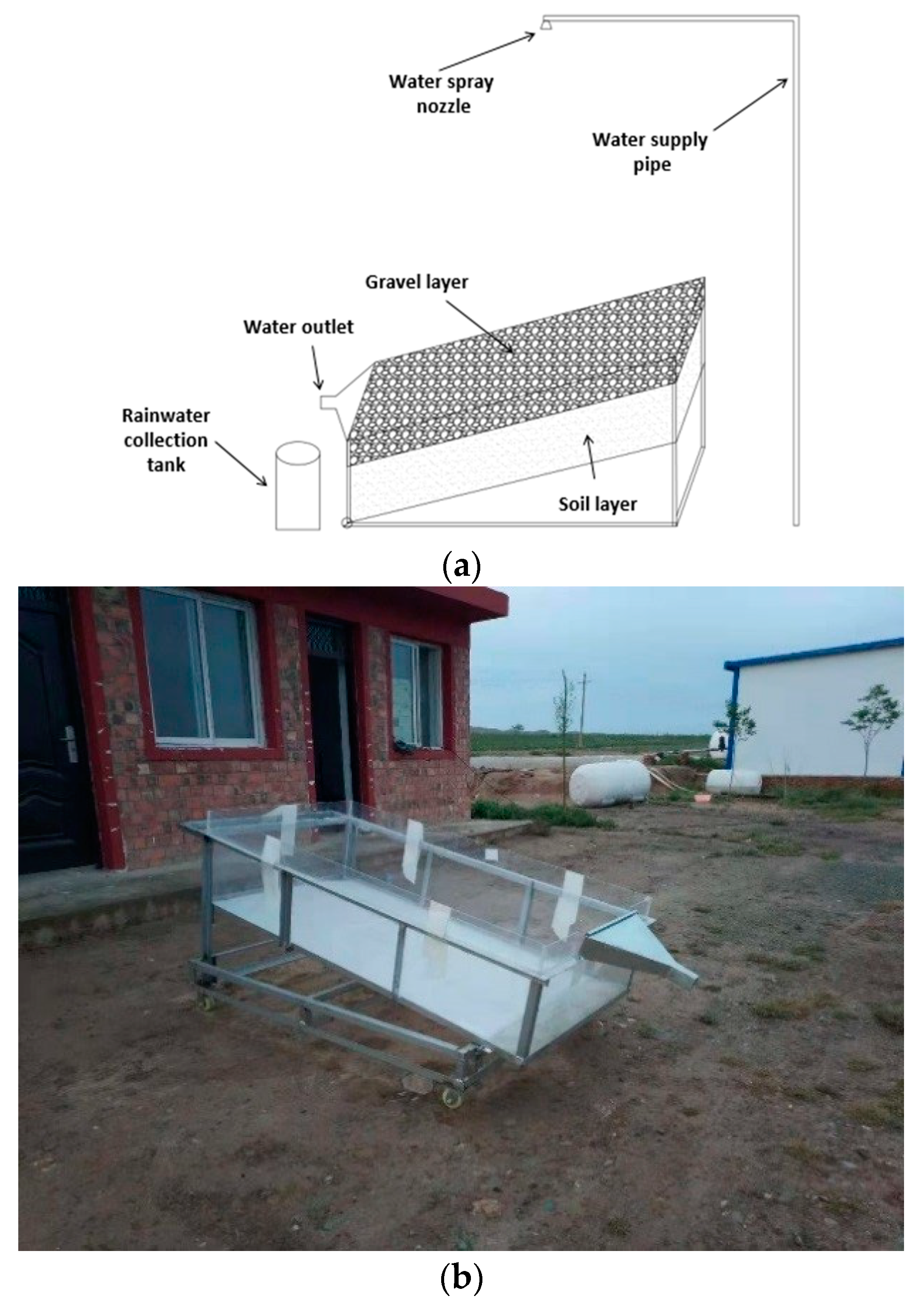
2.3. Experimental Device
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.5. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Runoff Start Time
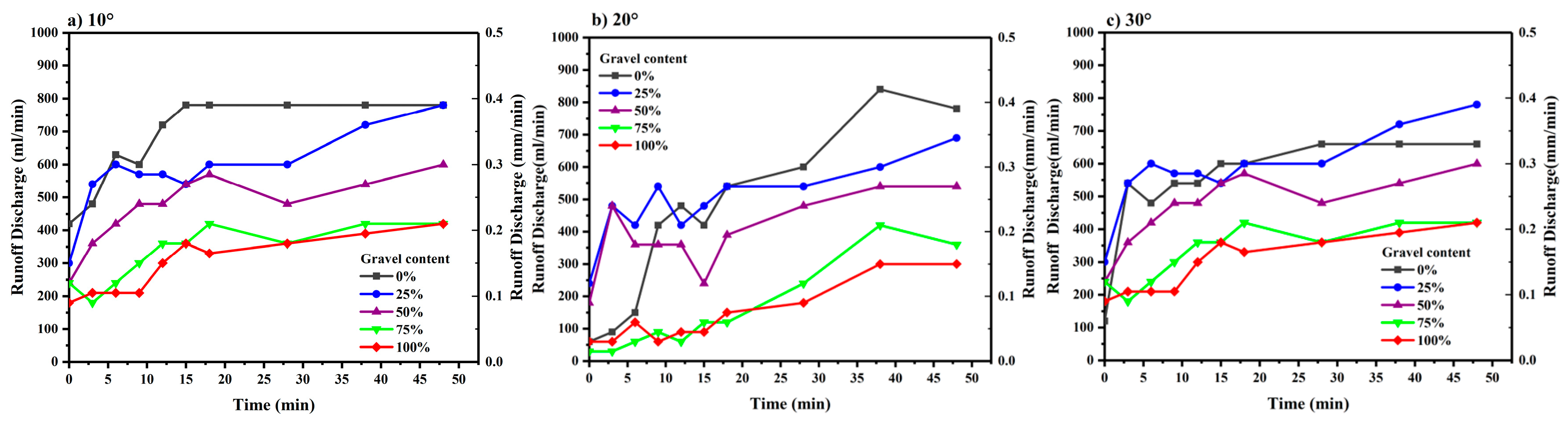
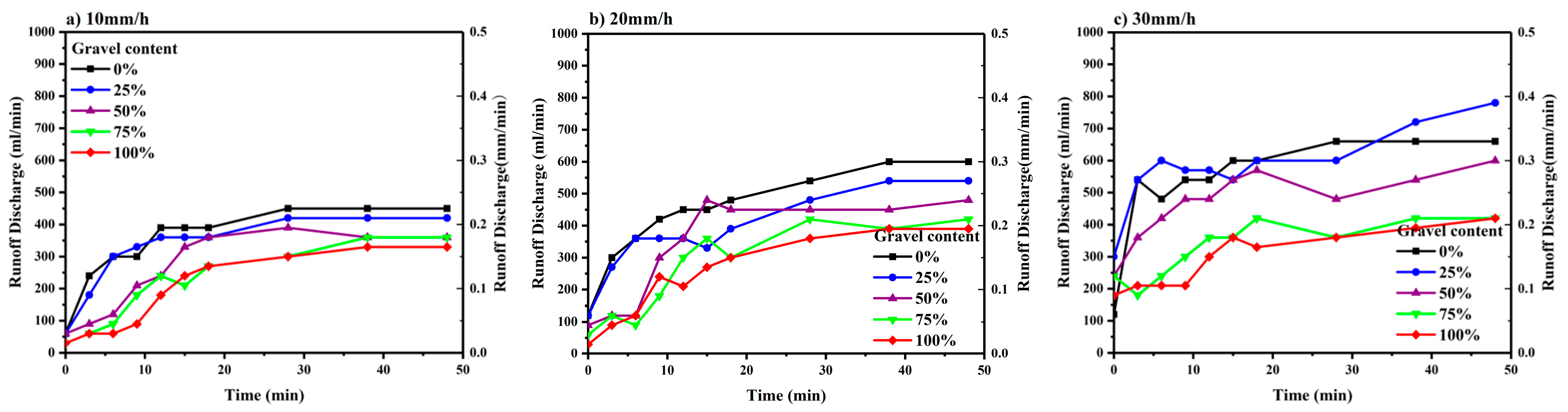
3.2. Runoff Discharge and Total Runoff
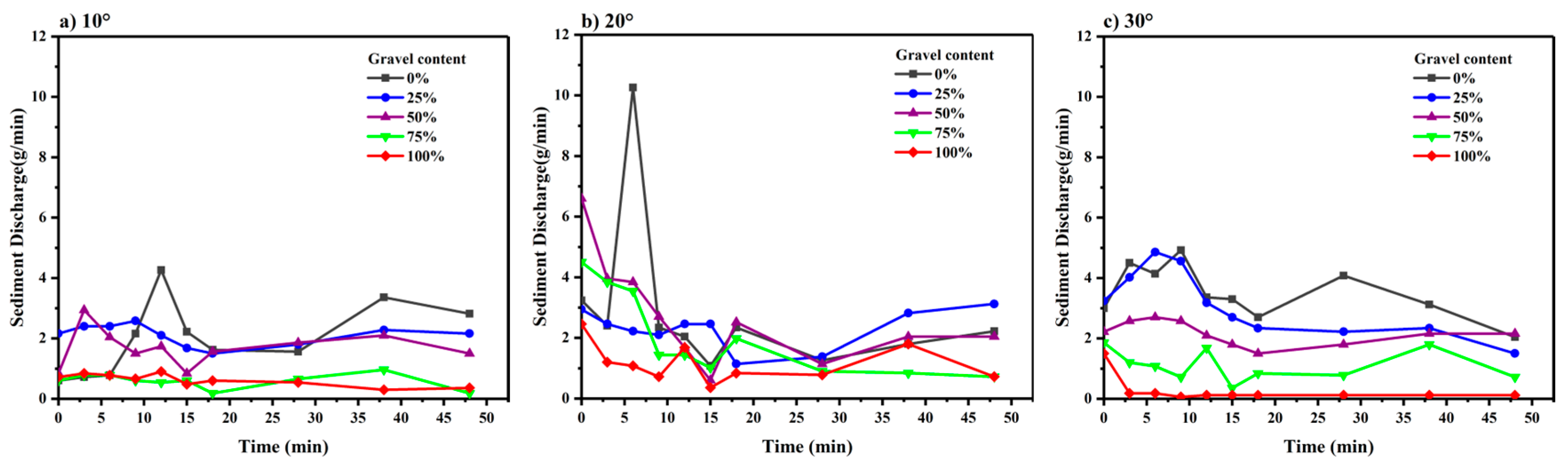
3.3. Sediment Transport Rate and Soil Loss
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Gravel Content on Runoff and Sediment
4.2. Influence of Rainfall Intensity on Runoff and Sediment
4.3. Influence of Slope Change on Runoff and Sediment
4.4. Analysis of Runoff Erosion Process
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poesen, J.; Ingelmo-Sanchez, F.; Mucher, H. The hydrological response of soil surfaces to rainfall as affected by cover and position of rock fragments in the top layer. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 15, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinoga, J.D.R.; Murillo, J.F.M. Effects of soil surface components on soil hydrological behaviour in a dry Mediterranean environment (Southern Spain). Geomorphology 2009, 108, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotterweich, M.; Stankoviansky, M.; Minár, J.; Koco, Š.; Papčo, P. Human induced soil erosion and gully system development in the Late Holocene and future perspectives on landscape evolution: The Myjava Hill Land, Slovakia. Geomorphology 2013, 201, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, M.; Errea, M.-P.; Beguería, S.; Arnáez, J.; Martí, C.; García-Ruiz, J.M. Catchment soil moisture and rainfall characteristics as determinant factors for discharge/suspended sediment hysteretic loops in a small headwater catchment in the Spanish pyrenees. J. Hydrol. 2004, 288, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources and Agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Dou, S.; Deng, X.; Xue, X.; Wang, T. Assessment of wind and water erosion risk in the watershed of the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia Reach of the Yellow River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. Improved interrill erosion prediction by considering the impact of the near-surface hydraulic gradient. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 203, 104687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Shun, D.; Fan, Z.; Dong, Y.; Shen, Y. Evolution in sandstone pore structures with freeze-thaw cycling and interpretation of damage mechanisms in saturated porous rocks. Catena 2020, 195, 104915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jia, H.; Sun, Q.; Tan, X.; Tang, L. Effects of thawing-induced softening on fracture behaviors of frozen rock. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, M.; Luo, P.; Duan, W.; Hu, M. Quantitative Model Construction for Sustainable Security Patterns in Social–Ecological Links Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Chao, L.; Chen, G.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, C. Investigating the feasibility of using satellite rainfall for the integrated prediction of flood and landslide hazards over Shaanxi Province in northwest China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Arrúe, J.L.; López, M.V.; Sterk, G.; Richard, D.; Gracia, R.; Sabre, M.; Gaudichet, A.; Frangi, J.P. Wind erosion in a semiarid agricultural area of Spain: The WELSONS project. CATENA 2003, 52, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, M.; Puigdefábregas, J. Effects of spatially structured vegetation patterns on hillslope erosion in a semiarid Mediterranean environment: A simulation study. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 30, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzet, A.V.; Boiffin, J.; Ludwig, B. Concentrated flow erosion in cultivated catchments: Influence of soil surface state. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1995, 20, 759–767. [Google Scholar]
- You, Z.; Li, Z.B. Mechanism and experiment of vegetation on slope to reduce runoff and sediment. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 3, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Rmkens, M.J.M.; Helming, K.; Prasad, S.N. Soil Erosion under Different Rainfall Intensities, Surface Roughness, and Soil Water Regimes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Taguas, E.V.; Arroyo, C.; Lora, A.; Guzmán, G.; Vanderlinden, K.; Gómez, J.A. Exploring the linkage between spontaneous grass cover biodiversity and soil degradation in two olive orchard microcatchments with contrasting environmental and management conditions. SOIL Discuss. 2015, 2, 233–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, B.K.; Lal, R. Soil and carbon losses from five different land management areas under simulated rainfall. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beullens, J.V.; van deNyssen, D.; Nyssen, J. Impact of slope aspect on hydrological rainfall and on the magnitude of rill erosion in Belgium and northern France. Catena Interdiscip. J. Soil Sci. Hydrol. Geomorphol. Focus. Geoecol. Landsc. Evol. 2014, 114, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigua, G.; Coleman, S. Spatial distribution of soil carbon in pastures with cow-calf operation: Effects of slope aspect and slope position. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzen, M.; Iserloh, T.; Casper, M.C.; Ries, J.B. Quantification of particle detachment by rain splash and wind-driven rain splash. Catena Interdiscip. J. Soil Sci. Hydrol. Geomorphol. Focus. Geoecol. Landsc. Evol. 2015, 127, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kateb, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Mosandl, R. Soil erosion and surface runoff on different vegetation covers and slope gradients: A field experiment in Southern Shaanxi Province, China. Catena 2013, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Jordán, A.; Tarolli, P.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. The immediate effectiveness of barley straw mulch in reducing soil erodibility and surface runoff generation in Mediterranean vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Lv, C. Effects of vegetation on runoff and soil erosion on reclaimed land in an opencast coal-mine dump in a loess area. Catena 2015, 128, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahddou, S.; Otten, W.; Whalley, W.R.; Shin, H.-C.; El Gharous, M.; Rickson, R.J. Changes in soil surface properties under simulated rainfall and the effect of surface roughness on runoff, infiltration and soil loss. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombini, A.; Amanian, N.; Talebi, A.; Kiani-Harchegani, M.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Surface roughness effects on soil loss rate in complex hillslopes under laboratory conditions. Catena 2021, 206, 105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.; Yang, Y.; Long, Y.; Lei, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z. Effects of rainfall pattern and soil surface roughness on surface–subsurface hydrological response and particle size distribution of red soil slope. Catena 2023, 232, 107422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Nie, X. Complex vegetation patterns improve soil nutrients and maintain stoichiometric balance of terrace wall aggregates over long periods of vegetation recovery. Catena 2023, 227, 107141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizkar, M.; Shabanpour, M.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Zema, D.A.; Li, S.; Tanaka, N.; Cerda, A. Effects of length and application rate of rice straw mulch on surface runoff and soil loss under laboratory simulated rainfall. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtergaele, J.; Poesen, J.; Van Wesemael, B. Gravel mulching in vineyards of southern Switzerland. Soil Tillage Res. 1998, 46, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Tang, S.; Lu, K.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Gao, H.; Zhao, B. Runoff and sediment yield under simulated rainfall on sand-covered slopes in a region subject to wind–water erosion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, Z.; Fan, Y.; Cao, Q. Predicting spatial variability of soil bulk density in gravel-mulched fields. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2018, 23, 04018022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Liu, L.-Y. Effect of gravel mulch on aeolian dust accumulation in the semiarid region of northwest China. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 70, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, C.; Casenave, A. Infiltration into sealed soils as influenced by gravel cover. SSSAJ 1992, 56, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, G.; Van Rompaey, A.; Poesen, J.; Van Oost, K.; Govers, G. Evaluating the impact of watershed management scenarios on changes in sediment delivery to rivers? In Proceedings of the Interactions between Sediments and Water: Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on the Interactions between Sediments and Water, Banff, AB, Canada, 5–10 May 2002; pp. 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, S.; Sharma, E. Comparative assessment of runoff characteristics under different land use patterns within a Himalayan watershed. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 2235–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wesemael, B.; Poesen, J.; de Figueiredo, T.; Govers, G. Surface roughness evolution of soils containing rock fragments. ESPL 1996, 21, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liang, X.; Wu, F. Soil surface roughness change and its effect on runoff and erosion on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Arid. Land 2014, 6, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Lavee, H. Rock fragments in top soils: Significance and processes. Catena 1994, 23, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, A.D.; Li, G.; Krishnan, C.; Atkinson, J.F. A sediment transport equation for interrill overland flow on rough surfaces. ESPL 2001, 26, 1443–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, T.; Rees, H. Effects of coarse-fragment content and size on soil erosion under simulated rainfall. CaJSS 1995, 75, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; He, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, C.; Wang, R. Effects of gravel on infiltration, runoff, and sediment yield in landslide deposit slope in Wenchuan earthquake area, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12075–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Zhuang, J. Effect of surface stone cover on sediment and solute transport on the slope of fallow land in the semi-arid loess region of northwestern China. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, V.H.D.; Pleguezuelo, C.R.R. Soil-erosion and runoff prevention by plant covers. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y. Effects of gravel-sand mulch on the runoff, erosion, and nutrient losses in the Loess Plateau of north-western China under simulated rainfall. Soil Water Res. 2021, 16, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-C.; He, S.-Q.; Wu, F.-Q. Changes of soil surface roughness under water erosion process. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 3919–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehuys, G.R.; Stolzy, L.H.; Letey, J. Effect of Stones on the Hydraulic Conductivity of Relatively Dry Desert Soil. SSSAJ 1975, 39, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravina, I.; Magier, J. Hydraulic Conductivity and Water Retention of Clay Soils Containing Coarse Fragments. J. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 1984, 48, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, T.J.; Logsdon, S.D. Hydraulic and Physical Properties of Stone Soils in a Small Watershed. SSSAJ 2002, 66, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Zavala, L.; Jordán, A. Effect of rock fragment cover on interrill soil erosion from bare soils in Western Andalusia, Spain. Soil Use Manag. 2010, 24, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, S.; Barry, D.A.; Brovelli, A.; Heng, B.C.P.; Sander, G.C.; Parlange, J.Y.; Rose, C.W. Rain splash soil erosion estimation in the presence of rock fragments. Catena Interdiscip. J. Soil Sci. Hydrol.-Geomorphol. Focus. Geoecol. Landsc. Evol. 2012, 92, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, S.; Barry, D.A.; Heng, B.C.P.; Brovelli, A.; Sander, G.C.; Parlange, J.Y. Effect of antecedent conditions and fixed rock fragment coverage on soil erosion dynamics through multiple rainfall events. J. Hydrol. 2013, 484, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, S.; Barry, D.A.; Heng, B.C.P.; Brovelli, A.; Sander, G.C.; Parlange, J.Y. Influence of rock fragment coverage on soil erosion and hydrological response: Laboratory flume experiments and modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Cai, C.; Shi, Z.; Xu, Q.; Fu, Z.; Guo, Z. Effects of rock fragment cover on hydrological response and soil loss from Regosols in a semi-humid environment in South-West China. Geomorphology 2012, 151–152, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, Z.; Tianyu, L.; Jia, L. Effect of Upslope Runoff on Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss in Slope Cropland of Purple Soil. J. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 34, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, N. Study on the Influence of Soil sand Covering on Soil Erosion in Xiangshan Area of Ningxia. Master’s Thesis, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kibet, L.C.; Saporito, L.S.; Allen, A.L.; May, E.B.; Bryant, R.B. A Protocol for Conducting Rainfall Simulation to Study Soil Runoff. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 86, 51664. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Ma, B. Technical standards for construction of sand-pressed land in the arid zone of central Ningxia. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual Conference of China Hydraulic Engineering Society, Guiyang, China, 24 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sobol, N.; Gabbasova, I.; Komissarov, M. Effect of rainfall intensity and slope steepness on the development of soil erosion in the Southern Cis-Ural region (A model experiment). Eurasian Soil Sci. 2017, 50, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Shi, D.; Jiang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. Runoff erosion process on different underlying surfaces from disturbed soils in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Catena Interdiscip. J. Soil Sci. Hydrol. Geomorphol. Focus. Geoecol. Landsc. Evol. 2014, 123, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yan, G. Summary on influencing factors of soil surface crust or seal. Arid. Land Geogr. 2009, 32, 662–668. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Yu, X.; Fan, D.; Huang, C. Hydrological and erosive response of soil surfaces to rainfall intensity as affected by gravel fragment coverage. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavee, H.; Imeson, A.C.; Sarah, P. The impact of climate change on geomorphology and desertification along a Mediterranean-arid transect. LDD 2015, 9, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieke-Zapp, D.; Poesen, J.; Nearing, M. Effects of rock fragments incorporated in the soil matrix on concentrated flow hydraulics and erosion. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Group 2007, 32, 1063–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Huang, P.; Guo, M.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y. Experimental study of runoff velocity and sediment yield affected by gravels of engineering deposits in loess area. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2015, 9, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Xie, Y.; Tian, F.; Jing, M. Study on runoff and sediment yield of spoil-banks with different ratios of soil to rock under simulated rainfall condition. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 3, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; Yan, P.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, J.; He, B.; Duan, W.; Wang, S.; Zha, X. Historical and comparative overview of sponge campus construction and future challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Mohd, M.; Duan, W.; Hu, M.; Guo, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Nover, D. Future Land Use and Flood Risk Assessment in the Guanzhong Plain, China: Scenario Analysis and the Impact of Climate Change. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, B.; Fouché, O.; Torri, D. Coupling published pedotransfer functions for the estimation of bulk density and saturated hydraulic conductivity in stony soils. Catena 2015, 131, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shao, M. Processes of rainfall infiltration and sediment yield in soils containing different rock fragment contents. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng 2006, 22, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Rong, Y.; Lv, J.; Xie, Y. Runoff erosion processes on artificially constructed conically-shaped overburdened stockpiles with different gravel contents: Laboratory experiments with simulated rainfall. Catena 2019, 175, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, L.; Vignozzi, N.; Miralles, I.; Solé-Benet, A. Organic amendments and mulches modify soil porosity and infiltration in semiarid mine soils. LDD 2018, 29, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Wang, W.; Xue, Z.; Guo, M.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of gravel on runoff and erosion characteristics on engineering accumulation slope in windy and sandy area, northern China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.-W.; Cai, C.; Xie, D. Processes of rainfall infiltration, runoff and sediment yield on purple soil slope containing rock fragments. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce-Okine, E.; Lal, R. Soil erodibility as determined by raindrop technique. Soil Sci. 1975, 119, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J. Mechanisms of Overland Flow Generation and Sediment Production on Loamy and Sandy Soils with and without Rock Fragments; ULC Press: London, UK, 1992; pp. 275–305. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, F.; Li, G.; Bian, F.; An, J. The effects of raindrop impact and runoff detachment on hillslope soil erosion and soil aggregate loss in the Mollisol region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 161, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, A.R.; Ahmadi, M.; Cerdà, A. Contribution of raindrop impact to the change of soil physical properties and water erosion under semi-arid rainfalls. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poesen, J.; Lavee, H. Effects of size and incorporation of synthetic mulch on runoff and sediment yield from interrils in a laboratory study with simulated rainfall. Soil Tillage Res. 1991, 21, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Field measurements of interrill erosion under different slopes and plot sizes. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Group 2000, 25, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, P.; Xu, C.; Zhu, W.; Cao, Z.; Ly, S. Reconstruction of Historical Land Use and Urban Flood Simulation in Xi’an, Shannxi, China. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Cao, Z.; Luo, P.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; He, B. Urban Flood-Related Remote Sensing: Research Trends, Gaps and Opportunities. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Soil mineralogy effects on seal formation, runoff and soil loss. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 24, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.-H.; Yan, F.-L.; Li, L.; Li, Z.-X.; Cai, C.-F. Interrill erosion from disturbed and undisturbed samples in relation to topsoil aggregate stability in red soils from subtropical China. Catena 2010, 81, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P. Raindrop-impact-induced erosion processes and prediction: A review. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2005, 19, 2815–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Ben-Hur, M. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on the dynamics of interrill erosion during soil surface sealing. Catena 2006, 66, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jin, J. Temporal stability and variability of soil-water content in a gravel-mulched field in northwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Rainfall Intensity/mm·h−1 | Slope/° | Soil Surface Gravel Content/% |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 30 | 0% |
| 25% | ||
| 50% | ||
| 75% | ||
| 100% | ||
| 20 | 30 | 0% |
| 25% | ||
| 50% | ||
| 75% | ||
| 100% | ||
| 30 | 10 | 0% |
| 25% | ||
| 50% | ||
| 75% | ||
| 100% | ||
| 20 | 0% | |
| 25% | ||
| 50% | ||
| 75% | ||
| 100% | ||
| 30 | 0% | |
| 25% | ||
| 50% | ||
| 75% | ||
| 100% |
| Rainfall Intensity | Gradient | Runoff Start Time for Different Gravel Contents (min) | R | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25% | 50% | 75% | 100% | ||||
| 10 mm/h | 30° | 14.58 | 14.95 | 15.52 | 15.77 | 16.87 | 0.97 | 0.0059 |
| 20 mm/h | 30° | 8.28 | 8.78 | 9.42 | 12.82 | 13.48 | 0.95 | 0.0149 |
| 30 mm/h | 10° | 15.58 | 15.78 | 16.5 | 17.61 | 20.7 | 0.91 | 0.0057 |
| 20° | 13.58 | 14.7 | 16.4 | 17.55 | 18.87 | 0.99 | 0.0001 | |
| 30° | 5.7 | 6.6 | 7.47 | 9.53 | 9.88 | 0.98 | 0.0033 | |
| Indicators | Rainfall Intensity (mm/h) | Gravel Content/% | R | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | ||||
| The total sediment/g | 10 | 53.28 | 47.39 | 32.24 | 18.89 | 9.58 | −0.99 | 0.0007 |
| 20 | 72.65 | 70.91 | 42.58 | 32.55 | 13.23 | −0.98 | 0.0045 | |
| 30 | 107.23 | 98.72 | 52.59 | 39.24 | 16.55 | −0.98 | 0.0038 | |
| The total runoff/mm | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 6 | −0.97 | 0.0062 |
| 20 | 12 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 8 | −0.93 | 0.0182 | |
| 30 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | −0.98 | 0.0031 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Luo, P.; Li, W.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M. Runoff and Sediment Deposition Characteristics of Gravel-Mulched Land: An Experimental Study. Land 2024, 13, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040445
Wang S, Luo P, Li W, Lyu J, Zhou M. Runoff and Sediment Deposition Characteristics of Gravel-Mulched Land: An Experimental Study. Land. 2024; 13(4):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040445
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuangtao, Pingping Luo, Wangcheng Li, Jiqiang Lyu, and Meimei Zhou. 2024. "Runoff and Sediment Deposition Characteristics of Gravel-Mulched Land: An Experimental Study" Land 13, no. 4: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13040445








