The Fate of Trace Elements in Yanshan Coal during Fast Pyrolysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Samples
2.2. Pyrolysis Procedure
2.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.5. TE Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
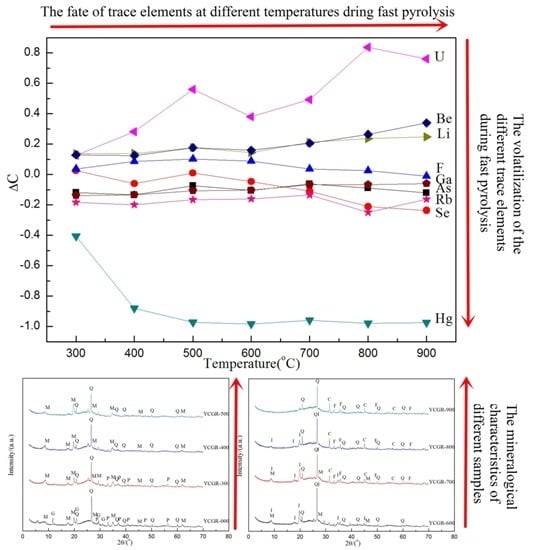
3.1. Effect of Temperature on TE Concentration During Pyrolysis
3.2. Effect of Temperature on Functional Groups During Pyrolysis
3.3. Effect of Temperature on Mineralogical Characteristics During Pyrolysis
4. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Chou, C.L.; Finkelman, R.B.; Seredin, V.V.; Zhou, Y.P. Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: A review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z. Some recent advances in the understanding of the pyrolysis and gasification behavior of Victorian brown coal. Fuel 2007, 86, 1664–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaine, D.J. Why trace elements are important. Fuel Process. Technol. 2000, 65, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, K.W.; French, D.H.; Farrel, O.P.; Wood, R.A.; Huggins, F.E. Modes of occurrence of trace and minor elements in some Australian coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Ma, S.M. The cause of endemic fluorosis in western Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Fuel 2004, 83, 2095–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, S.F.; Goldhaber, M.B.; Koening, A.E.; Lowers, H.A.; Ruppert, L.F. Distribution of arsenic, selenium, and other trace elements in high pyrite Appalachian coals: Evidence for multiple episodes of pyrite formation. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 94, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ward, C.R.; French, D.; Graham, I.T. Major and trace element geochemistry of coals and intra-seam claystones from the Songzao Coalfield, SW China. Minerals 2015, 5, 870–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, R.B. Modes of occurrence of potentially hazardous elements in coal: Levels of confidence. Fuel Process. Technol. 1994, 39, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Wang, R.X.; Wei, Q.; Wang, P.P.; Wei, J.P. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of Late Permian coals from the Mahe Mine, Zhaotong Coalfield, Northeastern Yunnan, China. Minerals 2015, 5, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejahati, F.; Xu, Z.H.; Gupta, R. Trace elements in coal: Associations with coal and minerals and their behavior during coal utilization—A review. Fuel 2010, 89, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Luo, Y.B.; Seredin, V.V.; Ward, C.R.; Hower, J.C.; Zhao, L.; Liu, S.D.; Zhao, C.L.; Tian, H.M.; Zou, J.H. Revisiting the Late Permian coal from the Huayingshan, Sichuan, Southestern China: Enrichment and occurrence modes of minerals and trace elements. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 122, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Yang, Z.; Yan, X.Y.; Ji, D.P.; Yang, Y.C.; Hu, L.C. Modes of occurrence of highly-elevated trace elements in superhigh-organic-sulfur coals. Fuel 2015, 156, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.H.; Yan, R.; Zheng, C.G.; Qiao, Y.; Han, J.; Sheng, C.D. Status of trace element emission in a coal combustion process: A review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2003, 85, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.M.; Luo, Z.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.C. Modes of occurrence of fluorine by extraction and SEM method in a coal-fired power plant from Inner Mongolia, China. Minerals 2015, 5, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, S.M.; Engle, M.A.; Ruppert, L.F.; Affolter, R.H.; Jones, K.B. Partitioning of selected trace elements in coal combustion products from two coal-burning power plants in the United States. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2013, 113, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Liu, G.J.; Zhou, C.C.; Sun, R.Y. Distribution of trace elements in feed coal and combustion residues from two coal-fired power plants at Huainan, Anhui, China. Fuel 2013, 107, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Choo, W.L.; Bhattacharya, S. Prediction of distribution of trace elements under oxy-fuel combustion condition using Victorian brown coals. Fuel 2013, 114, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboirien, B.O.; Thulari, V.; North, B.C. Major and trace elements in coal bottom ash at different oxy coal combustion conditions. Appl. Energy 2014, 129, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.W.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Benson, S.A.; Seames, W.S. Modeling trace elements partitioning during coal combustion. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 126, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, W.J.; Irons, R.M.A. Trace element partitioning during the firing of washed and untreated power station coals. Fuel 2002, 81, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.H.; Hao, J.M.; Duan, L.; Tang, X.L.; Ning, P.; Li, X.H. Fine particle and trace elements emissions from an anthracite coal-fired power plant equipped with a bag-house in China. Fuel 2008, 87, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, L.B. The fate of trace elements during coal combustion and gasification: An overview. Fuel 1993, 72, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, J.R.; Waanders, F.B. Trace element behavior in the Sasol-Lurgi MK IV FBDB gasifier. Part 1—The volatile elements: Hg, As, Se, Cd and Pb. Fuel 2008, 87, 2374–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunt, J.R.; Waanders, F.B. Trace element behavior in the Sasol-Lurgi MK IV FBDB gasifier. Part 2—The semi-volatile elements: Cu, Mo Ni and Zn. Fuel 2009, 88, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Jin, B.S.; Zhong, Z.P.; Rui, X.; Zhou, H.C. The relationship between occurrence of trace elements and gasification temperature. Proc. CSEE 2006, 26, 10–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Q.; Wang, Y.T.; Yu, L.; Oakey, J. Volatilization of mercury, arsenic and selenium during underground coal gasification. Fuel 2006, 85, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiie, R.; Taya, Y.; Ichiyanagi, T.; Ueki, Y.; Naruse, I. Emissions of particles and trace elements from coal gasification. Fuel 2013, 108, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Wang, Y.T.; Yu, L.; Oakey, J. Thermodynamic equilibrium study of trace element transformation during underground coal gasification. Fuel Process. Technol. 2006, 87, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, M.A.; Hall, A.D.; Hughes, R.W.; Mccalden, D.J.; Anthony, E.J.; Macchi, A. Fate of inorganic matter in entrained-flow slagging gasifiers: Fuel characterization. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 118, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, B.M.; Thompson, D.; Argent, B.B. A thermodynamic equilibrium comparison of the mobilities of trace elements when washed and unwashed coals are burnt under Pffiring conditions. Fuel 2004, 83, 2271–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Somoano, M.; Martinez-Tarazona, M.R. Trace element evaporation during coal gasification based on a thermodynamic equilibrium calculation approach. Fuel 2003, 82, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, R.X.; Yang, J.L.; Liu, D.Y.; Liu, Z.Y. Transformation behavior of trace elements during coal pyrolysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2002, 77, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.X.; Yang, J.L.; Liu, D.Y.; Liu, Z.Y. The fate of As, Pb, Cd, Cr and Mn in a coal during pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2003, 70, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.X.; Yang, J.L.; Liu, Z.Y. Behavior of trace elements during pyrolysis of coal in a simulated drop-tube reactor. Fuel 2004, 83, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Wang, X.B.; Chen, W.M.; Li, D.H.; Chou, C.L.; Zhou, Y.P.; Zhu, C.S.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.W.; Xing, Y.W.; et al. A high-pyrite semianthracite of Late Permian age in the Songzao Coalfield, Southwestern China: Mineralogical and geochemical relations with underlying mafic tuffs. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2010, 83, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Method for Preparation of Coal Sample; Chinese Stand GB/T 474-2008; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Proximate Analysis of Coal; Chinese Stand GB/T 212-2008; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- Hower, J.C.; Eble, C.F.; O’Keefe, J.M.; Dai, S.F.; Wang, P.P.; Xie, P.P.; Liu, J.J.; Ward, C.R.; French, D. Petrology, palynology, and geochemistry of Gray Hawk Coal (Early Pennsylvanian, Langsettian) in Eastern Kentucky, USA. Minerals 2015, 5, 592–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Liang, D.C.; Tian, M.; Dang, J.T.; Liu, J.C.; Yang, M.S. Influence of heating rate on structure of chars derived from pyrolysis of Shenmu coal. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2015, 43, 798–908. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.F.; Wang, X.B.; Zhou, Y.P.; Hower, J.C.; Li, D.H.; Chen, W.M.; Zhu, X.W.; Zou, J.H. Chemical and mineralogical compositions of silicic, mafic, and alkali tonsteins in the Late Permian coals from the Songzao Coalfield, Chongqing, Southwest China. Chem. Geol. 2011, 282, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Dai, S.F.; Sun, Y.Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.G.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.B. Modes of occurrence of fluorine in the Late Paleozoic No.6 coal from the Haerwsu Surface Mine, Inner Mongolia, China. Fuel 2011, 90, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolo, G.N.; Neomagus, H.W.; Everson, R.C.; Roberts, M.J.; Bunt, J.R.; Sakurovs, R.; Mathews, J.P. Chemical-structural properties of South African bituminous coals: Insights from wide angle XRD-carbon fraction analysis, ATR-FTIR, solid state 13C NMR, and HRTEM techniques. Fuel 2015, 158, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.H.; Chen, H.; Yan, Y.J.; Li, C.S.; Rong, L.M.; Yang, X.Q. FTIR quantitative analysis upon solubility of carbon disulfide/N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone mixed solvent to coal petrographic constituents. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 133, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.C.; Gupta, R. Understanding of mineralogy and residence of trace elements in coals via a novel method combining low temperature ashing and float-sink technique. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 13, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, F.E.; Huffman, G.P. Modes of occurrence of trace elements in coal from XAFS spectroscopy. Int. J. Coal Geol. 1996, 32, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.F.; Zeng, R.S.; Sun, Y.Z. Enrichment of arsenic, antimony, mercury, and thallium in a Late Permian anthracite from Xingren, Guizhou, Southwest China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2006, 66, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeva, A.A.; Dongari, N.; Artemyeva, A.A.; Kozliak, E.I.; Pierce, D.T.; Seames, W.S. Experimental simulation of trace element evolution from the excluded mineral fraction during coal combustion using GFAAS and TGA-DSC. Fuel 2014, 124, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Proximate Analysis % | Ultimate Analysis % | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Ad | Vdaf | FCdaf | Cdaf | Hdaf | Odaf | Ndaf | St,daf | |
| Yanshan Coal | 3.32 | 40.98 | 17.32 | 82.68 | 77.97 | 3.25 | 1.72 | 1.08 | 15.98 |
| Sample | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | V2O5 | Fe2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass Percentage (%) | 0.36 | 1.60 | 26.98 | 54.43 | 4.15 | 3.41 | 3.34 | 0.78 | 0.15 | 4.60 |
| Sample | YCGR-300 | YCGR-400 | YCGR-500 | YCGR-600 | YCGR-700 | YCGR-800 | YCGR-900 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Char Yield (%) | 98.41 | 97.62 | 93.25 | 91.95 | 89.40 | 87.31 | 86.58 |
| Sample | As (μg/g) | Be (μg/g) | F (μg/g) | Ga (μg/g) | Hg (μg/kg) | Li (μg/g) | Rb (μg/g) | Se (μg/g) | U (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YCGR-000 | 13.3 | 1.73 | 1153 | 16.1 | 165 | 55.9 | 34.8 | 25.7 | 67.6 |
| YCGR-300 | 11.7 | 1.95 | 1194 | 13.9 | 98.0 | 63.6 | 28.4 | 26.4 | 76.2 |
| YCGR-400 | 11.5 | 1.95 | 1252 | 14.0 | 19.7 | 63.7 | 27.9 | 24.2 | 86.6 |
| YCGR-500 | 12.3 | 2.04 | 1270 | 14.4 | 4.60 | 65.8 | 29.0 | 26.0 | 105 |
| YCGR-600 | 11.9 | 2.01 | 1254 | 14.4 | 2.87 | 64.0 | 29.2 | 24.5 | 93.3 |
| YCGR-700 | 12.5 | 2.09 | 1195 | 15.0 | 6.84 | 67.8 | 30.1 | 22.9 | 101 |
| YCGR-800 | 12.1 | 2.19 | 1183 | 15.0 | 3.31 | 69.1 | 26.1 | 20.3 | 124 |
| YCGR-900 | 11.7 | 2.32 | 1141 | 15.2 | 4.09 | 69.8 | 29.1 | 19.6 | 119 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dang, J.; Xie, Q.; Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Dong, H.; Cao, J. The Fate of Trace Elements in Yanshan Coal during Fast Pyrolysis. Minerals 2016, 6, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020035
Dang J, Xie Q, Liang D, Wang X, Dong H, Cao J. The Fate of Trace Elements in Yanshan Coal during Fast Pyrolysis. Minerals. 2016; 6(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleDang, Jiatao, Qiang Xie, Dingcheng Liang, Xin Wang, He Dong, and Junya Cao. 2016. "The Fate of Trace Elements in Yanshan Coal during Fast Pyrolysis" Minerals 6, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020035
APA StyleDang, J., Xie, Q., Liang, D., Wang, X., Dong, H., & Cao, J. (2016). The Fate of Trace Elements in Yanshan Coal during Fast Pyrolysis. Minerals, 6(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6020035