Tungsten Recovery from Spent SCR Catalyst Using Alkaline Leaching and Ion Exchange
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Leaching Experiments
2.3. Column Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Leaching of V and W
3.1.1. Effects of NaOH Concentration
3.1.2. Effects of Pulp Density
3.1.3. Effects of Temperature
3.1.4. Effects of Particle Size
3.1.5. Effects of Leaching Time
3.2. Ion Exchange Separation of W
3.2.1. Effects of the Effluent Volume
3.2.2. Effects of pH on Adsorption
3.2.3. Column Tests
Loading Test
Stripping Test
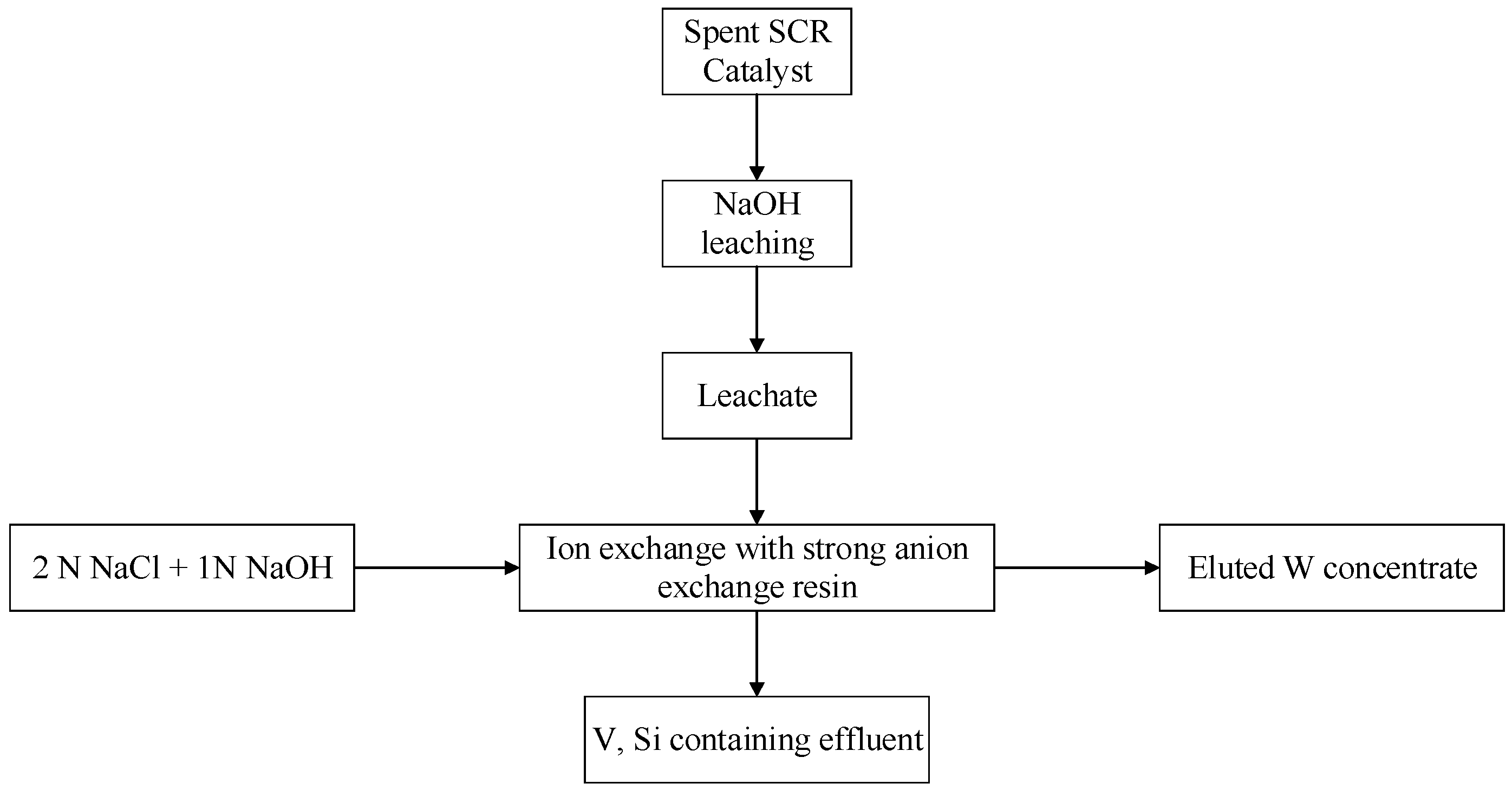
3.3. Recycling Process of W from Spent SCR Catalyst
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Busca, G.; Lietti, L.; Ramis, G.; Berti, F. Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia over oxide catalysts: A review. Appl. Catal. B 1998, 18, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Chang, H.Z.; Ma, L.; Hao, J.M.; Yang, R.T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts—A review. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietti, L.; Alemany, J.L.; Forzatti, P.; Busca, G.; Ramis, G.; Giamello, E.; Bregani, F. Reactivity of V2O5/WO3/TiO2 catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by ammonia. Catal. Today 1996, 29, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshneva, V.I.; Slavinskaya, E.M.; Kalinkina, O.V.; Odegova, G.V.; Moroz, E.M.; Lavrova, G.V.; Salanov, A.N. Reactivity and physicochemical characterization of V2O5/WO3/TiO2 De-NOx catalysts. J. Catal. 1995, 155, 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, M.; Sheppard, P.; Witten, B. Tungsten toxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2012, 196, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imtiaz, M.; Rizwan, M.S.; Xiong, S.L.; Li, H.L.; Ashraf, M.; Shahzad, S.; Shahzad, M.; Rizwan, M.M.; Tu, S.X. Vanadium recent advancements and research prospects: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Industrial Waste Report and Management System. Available online: http://www.waste.epa.gov.tw/prog/IndexFrame.asp (accessed on 15 August 2015).
- Lin, Y.C.; Bai, H. Evaluation of the economic instruments on nitrogen oxides removals: An example of the implementation of the selective catalytic reduction process. J. Chin. Inst. Environ. Eng. 2002, 12, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Marafi, M.; Stanislaus, A. Options and processes for spent catalyst handling and utilization. J. Hazard. Mater. B 2003, 101, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, B.B.; Murthy, B.V.R.; Misra, V.N. Extraction of molybdenum from spent catalyst by salt-roasting. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2005, 76, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Reddy, B.R.; Mohaparea, D. Hydrometallurgical processing and recovery of molybdenum trioxide from spent catalyst. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 80, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognyanova, A.; Ozturk, A.T.; Michelis, I.D.; Ferella, F.; Taglieri, G.; Akcil, A.; Veglio, F. Metal extraction from spent sulfuric acid catalyst through alkaline and acidic leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 10, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.Z.; Hao, X.C. Study on recovery of vanadium from waste catalyst containing vanadium. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2010, 42, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Kejun, L.; Shibayama, A.; Yen, W.; Fujita, T.; Shindo, O.; Katai, A. Recovery of tungsten and vanadium from tungsten alloy scrap. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 72, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cao, C.; Chen, X.; Huo, G. Separation of macro amounts of tungsten and molybdenum by selective precipitation. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, M.S. Separation of vanadium and tungsten from sodium molybdate solution by solvent extraction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8608–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y. Selective extraction and deep removal of tungsten from sodium molybdate solution by primary amine N1923. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 70, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, X.W.; Xiao, L.S.; Song, S.R.; Zhang, B.Q. Removal of vanadium(V) from molybdate solution by ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.G.; Zeng, L.; Xiao, L.S.; Yang, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.X. Completely removing vanadium(V) from ammonium molybdate solution using chelating ion exchange resins. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Chaudhury, G.R.; Kim, D.J. Recovery of metal values from spent petroleum catalyst using leaching-solvent extraction technique. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 101, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litz, J.E. Solvent extraction of W, Mo and V: Similarities and contrasts. In Extractive Metallurgy of Refractory Metals; The Metallurgical Society of AIME: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Moskalyk, R.R.; Alfantazi, A.M. Processing of vanadium: A review. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekesi, T.; Torok, T.I.; Isshiki, M. Anion exchange of chromium, molybdenum and tungsten species of various oxidation states, providing the basis for separation and purification in HCl solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 77, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J. Leaching of vanadium and tungsten from spent SCR catalysts for De-NOx by soda roasting and water leaching method. J. Korean Inst. Resour. Recycl. 2012, 21, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Component | Ti | Si | W | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt % | 33.40 | 2.81 | 6.37 | 1.57 |
| Volume Passed Through Column (BV) | W Adsorbed (%) | V Adsorbed (%) | Si Adsorbed (%) | Adsorbed W/V Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 99.36 | 10.68 | 0.24 | 40 |
| 31 | 84.57 | 6.15 | 3.84 | 59 |
| 43 | 58.85 | 4.28 | 7.25 | 59 |
| 51 | 44.30 | 3.16 | 9.17 | 60 |
| 71 | 40.61 | 2.96 | 5.54 | 60 |
| 86 | 26.25 | 2.28 | 8.72 | 50 |
| pH | W Adsorbed (%) | V Adsorbed (%) | Adsorbed W/V Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12.9 | 98.01 | 81.39 | 4 |
| 13.5 | 97.64 | 13.78 | 28 |
| 13.8 | 93.80 | 8.24 | 52 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.-C.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Shen, Y.-H. Tungsten Recovery from Spent SCR Catalyst Using Alkaline Leaching and Ion Exchange. Minerals 2016, 6, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040107
Wu W-C, Tsai T-Y, Shen Y-H. Tungsten Recovery from Spent SCR Catalyst Using Alkaline Leaching and Ion Exchange. Minerals. 2016; 6(4):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040107
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wen-Cheng, Tang-Yi Tsai, and Yun-Hwei Shen. 2016. "Tungsten Recovery from Spent SCR Catalyst Using Alkaline Leaching and Ion Exchange" Minerals 6, no. 4: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040107
APA StyleWu, W.-C., Tsai, T.-Y., & Shen, Y.-H. (2016). Tungsten Recovery from Spent SCR Catalyst Using Alkaline Leaching and Ion Exchange. Minerals, 6(4), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040107






