Adsorption Behavior of Cd2+ and Zn2+ onto Natural Egyptian Bentonitic Clay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorbent
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Application for Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.1.1. Specific Surface Area (SSA) and Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
3.1.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
3.1.3. FT-IR Analysis
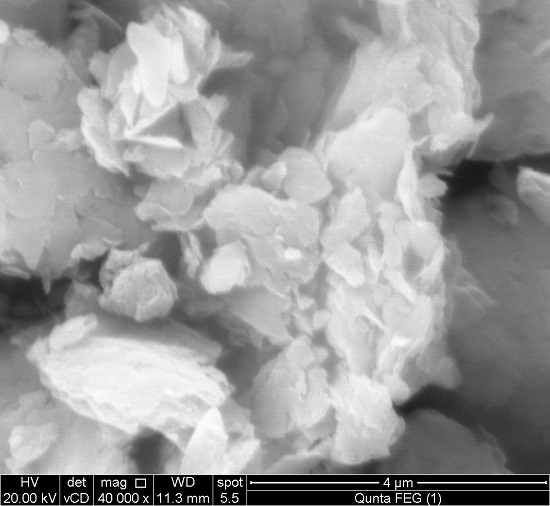
3.1.4. SEM-EDX Analysis
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
3.2.1. Effect of pH
3.2.2. Effect of Sorbent Dosage
3.2.3. Effect of Shaking Time
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
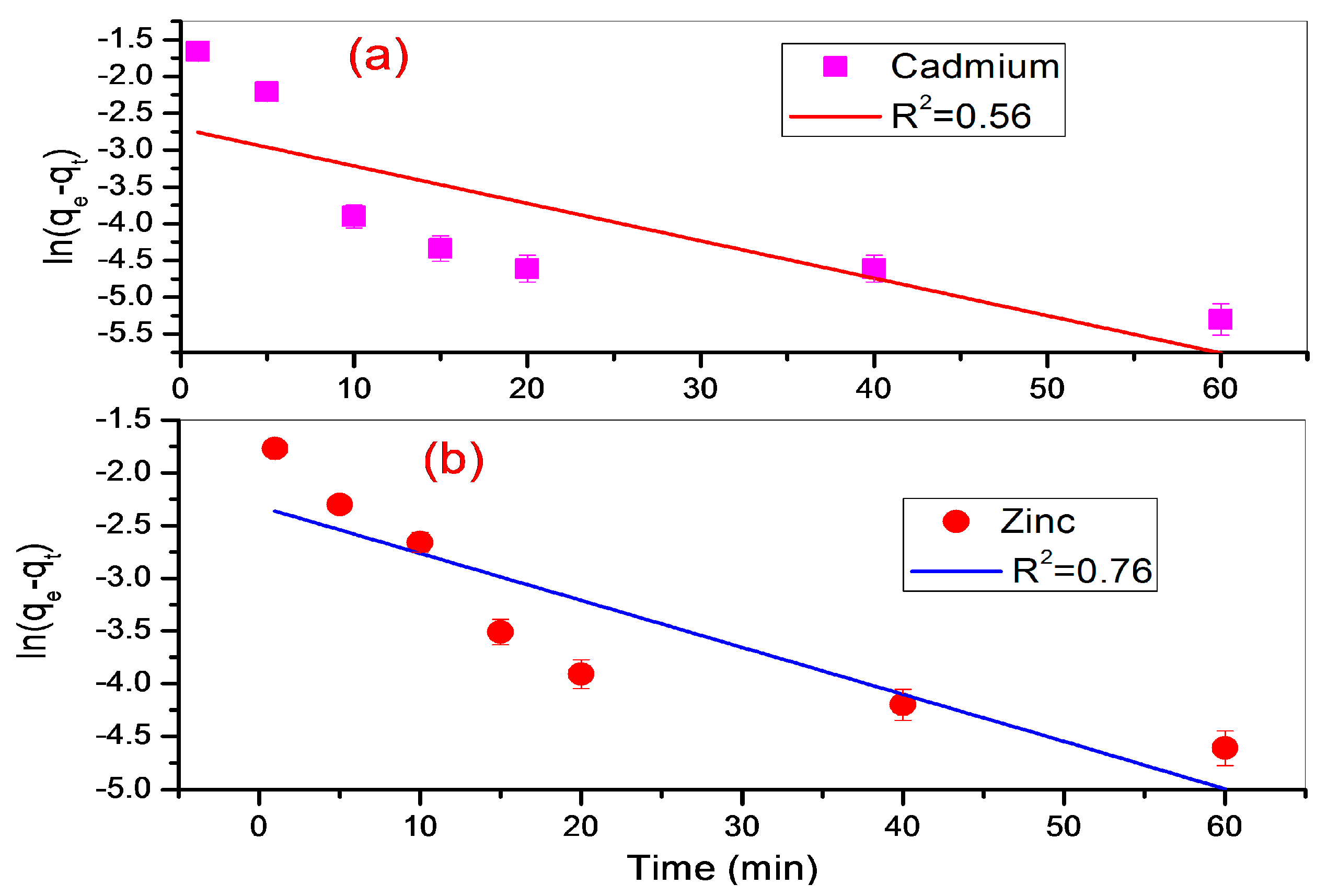
3.3.1. Pseudo-First Order Model
3.3.2. Pseudo-Second Order Model
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm
3.4.1. Langmuir Isotherm
3.4.2. Freundlich Isotherm
3.5. Application to Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nguyen, T.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Yue, Q.; Li, Q.; Nguyen, T. Applicability of agricultural waste and by-products for adsorptive removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.S.; Ramalingam, S.; Sathyaselvabala, V.; Kirupha, S.D.; Murugesan, A.; Sivanesan, S. Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solution by agricultural waste cashew nut shell. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 29, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbeiro, R.; Garcia, S.; Gaubeur, I. A green and efficient procedure for the preconcentration and determination of cadmium, nickel and zinc from freshwater, hemodialysis solutions and tuna fish samples by cloud point extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, M. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatstein, D.A.; Francisca, F.M. Influence of pH and ionic strength on Cd, Cu and Pb removal from water by adsorption in Na–Bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 118, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charerntanyarak, L. Heavy metals removal by chemical coagulation and precipitation. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Younesi, H.; Bahramifar, N. Statistical modeling and optimization of the cadmium biosorption process in an aqueous solution using Aspergillus niger. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 337, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qdais, H.A.; Moussa, H. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater by membrane processes: A comparative study. Desalination 2004, 164, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyüz, B.; Veli, S. Kinetics and equilibrium studies for the removal of nickel and zinc from aqueous solutions by ion exchange resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahluwalia, S.S.; Goyal, D. Microbial and plant derived biomass for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurko, S.V.; Matović, L.L. Simultaneous removal of Pb2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ from highly acidic solutions using mechanochemically synthesized montmorillonite–kaolinite/TiO2 composite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 103, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 140, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaedi, M.; Shokrollahi, A.; Kianfar, A.; Pourfarokhi, A.; Khanjari, N.; Mirsadeghi, A.; Soylak, M. Preconcentration and separation of trace amount of heavy metal ions on bis (2-hydroxy acetophenone) ethylendiimine loaded on activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sahu, J.N.; Sengupta, B. Remediation technologies for heavy metal contaminated groundwater. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2355–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, L.C.; Rios, R.V.; Fabris, J.D.; Sapag, K.; Garg, V.K.; Lago, R.M. Clay–iron oxide magnetic composites for the adsorption of contaminants in water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2003, 22, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burham, N.; Abdel-Azeem, S.; El-Shahat, M. Separation and determination of trace amounts of zinc, lead, cadmium and mercury in tap and Qaroun lake water using polyurethane foam functionalized with 4-hydroxytoluene and 4-hydroxyacetophenone. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 579, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitko, R.; Zawisza, B.; Malicka, E. Modification of carbon nanotubes for preconcentration, separation and determination of trace-metal ions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, T.K.; Gomez, D. Adsorption of zinc (Zn2+) from aqueous solution on natural bentonite. Desalination 2011, 267, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, D.; Mello, I.; Resende, R.; Silva, R. Application as absorbents of natural and functionalized Brazilian bentonite in Pb2+ adsorption: Equilibrium, kinetic, pH, and thermodynamic effects. Water Resour. Ind. 2013, 4, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-G.; Ye, W.-M.; Yang, X.-M.; Deng, F.-Y.; He, Y. Effect of contact time, pH, and ionic strength on Cd (II) adsorption from aqueous solution onto bentonite from Gaomiaozi, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdiri, A.; Higashi, T.; Hatta, T.; Jamoussi, F.; Tase, N. Evaluating the adsorptive capacity of montmorillonitic and calcareous clays on the removal of several heavy metals in aqueous systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, M.A.; Ferrell, R.E.; Hart, G.F.; El Ghar, M.S.A.; Abdel-Motelib, A. Mineralogy of Egyptian Bentonitic Clays II: Geologic Origin. Clays Clay Miner. 2013, 61, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.A.; Silva-Valenzuela, M.G.; Ehsan, A.M.; Díaz, F.R.V.; Khattak, N.S. Characterization of Pakistani purified bentonite suitable for possible pharmaceutical application. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 83, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birand, A.; Cokca, E. Determination of cation exchange capacity of clayey soils by the methylene blue test. Geotech. Test. J. 1993, 16, 518–524. [Google Scholar]
- Yukselen, Y.; Kaya, A. Suitability of the methylene blue test for surface area, cation exchange capacity and swell potential determination of clayey soils. Eng. Geol. 2008, 102, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed-Azizi, F.; Dib, S.; Boufatit, M. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by Algerian bentonite. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 4447–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdiri, A.; Khairy, M.; Bouaziz, S.; El-Safty, S. A natural clayey adsorbent for selective removal of lead from aqueous solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 126, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.; Khattak, N.; Silva-Valenzuela, M.G.; Manan, A.; Díaz, F.V. Preparation and characterization of purified Na-activated bentonite from Karak (Pakistan) for pharmaceutical use. Clay Miner. 2013, 48, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H. Magnetized bentonite by Fe3O4 nanoparticles treated as adsorbent for methylene blue removal from aqueous solution: Synthesis, characterization, mechanism, kinetics and regeneration. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 49, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Chen, D.; Frost, R.L. An insight into the removal of Pb (II), Cu (II), Co (II), Cd (II), Zn (II), Ag (I), Hg (I), Cr (VI) by Na (I)-montmorillonite and Ca (II)-montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 118, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izidoro, J.D.C.; Fungaro, D.A.; Abbott, J.E.; Wang, S. Synthesis of zeolites X and A from fly ashes for cadmium and zinc removal from aqueous solutions in single and binary ion systems. Fuel 2013, 103, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hicher, P.; Muresan, B.; Saiyouri, N.; Hicher, P.-Y. Heavy metal retention properties of kaolin and bentonite in a wide range of concentration and different pH conditions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, M.; Fotoohi, B.; Amamo, Y.; Mercier, L. Cadmium (II) and lead (II) adsorption onto hetero-atom functional mesoporous silica and activated carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7389–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamis, S.; Katsou, E. A review on zinc and nickel adsorption on natural and modified zeolite, bentonite and vermiculite: Examination of process parameters, kinetics and isotherms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252, 428–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Sun, B.; Luo, T.; Meng, F.; Jin, Z.; Lin, D.; Shen, W. Enhanced adsorption of cadmium ions by 3D sulfonated reduced graphene oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellir, K.; Lehocine, M.B.; Meniai, A.-H. Zinc removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto bentonite. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 5035–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdiri, A.; Higashi, T.; Chaabouni, R.; Jamoussi, F. Competitive removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by montmorillonitic and calcareous clays. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-J.; Lee, C.-S.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Chang, Y.-S. Hierarchically structured manganese oxide-coated magnetic nanocomposites for the efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9628–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, K.; Hameed, B. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shahrani, S. Treatment of wastewater contaminated with cobalt using Saudi activated bentonite. Alex. Eng. J. 2014, 53, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, F.H.; de Souza Costa, D.M.; Masini, J.C. Evaluation of thiol-modified vermiculite for removal of Hg (II) from aqueous solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 124, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, E.; Tabak, A.; Eren, B. Performance of magnesium oxide-coated bentonite in removal process of copper ions from aqueous solution. Desalination 2010, 257, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaoba, S. Comparison of Amberlite IR 120 and dolomite’s performances for removal of heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantawong, V.; Harvey, N.; Bashkin, V. Comparison of heavy metal adsorptions by Thai kaolin and ballclay. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 148, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Jain, C.; Ali, I.; Sharma, M.; Saini, V. Removal of cadmium and nickel from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—A sugar industry waste. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4038–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, S.A.; Attaf, S.M.; El-Shahat, M. Acetylacetone phenylhydrazone functionalized polyurethane foam: Determination of copper, zinc and manganese in environmental samples and pharmaceutics using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Element | Wt % |
|---|---|
| C | 2.32 |
| O | 38.79 |
| Na | 1.36 |
| Mg | 1.25 |
| Al | 13.26 |
| Si | 26.50 |
| K | 0.88 |
| Fe | 4.79 |
| Metal Ion | qe exp. | Pseudo-First Order Parameters | Pseudo-Second Order Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| k1 = 0.0445 min−1 | k2 = 1.77 g·mg−1·min−1 | ||
| Zn (II) | 0.97 mg/g | qe = 0.099 mg/g | qe = 0.98 mg/g |
| R2 = 0.76 | R2 = 0.9994 | ||
| k1 = 0.0508 min−1 | k2 = 2.83 g·mg−1·min−1 | ||
| Cd (II) | 0.935 mg/g | qe = 0.066 mg/g | qe = 0.94 mg/g |
| R2 = 0.56 | R2 = 0.9997 |
| Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | |
|---|---|---|
| Cd (II) | R2 = 0.72 qm = 8.2 mg/g KL = 1.83 L/mg | R2 = 0.89 0.38 = 5.09 mg/g |
| Zn (II) | R2 = 0.79 qm = 9.45 mg/g KL = 1.79 L/mg | R2 = 0.9 = 5.89 mg/g |
| Adsorbent | Metal Ion | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na–Bentonite | Cd2+ | 8.20 | This study |
| Na–Bentonite | Zn2+ | 9.45 | This study |
| Amberlite | Cd2+ | 0.640 | [44] |
| Kaolinite | Cd2+ | 0.750 | [45] |
| Kaolinite | Zn2+ | 1.80 | [45] |
| Bagasse fly ash | Cd2+ | 2.00 | [46] |
| Acetylacetone phenylhydrazone-PUF | Zn2+ | 0.490 | [47] |
| Metal Ion | Sample | Added (μg/L) | Found (μg/L) | Recovery % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd2+ | Qaroun lake water | 0 | 41 | - |
| 50 | 80 | 88.0 | ||
| 200 | 225 | 93.4 | ||
| Nile river water | 0 | 18 | - | |
| 50 | 62 | 91.2 | ||
| 200 | 203 | 93.1 | ||
| Zn2+ | Qaroun lake water | 0 | 153 | - |
| 50 | 194 | 95.5 | ||
| 200 | 343 | 97.0 | ||
| Nile river water | 0 | 209 | - | |
| 50 | 246 | 95.0 | ||
| 200 | 400 | 97.8 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burham, N.; Sayed, M. Adsorption Behavior of Cd2+ and Zn2+ onto Natural Egyptian Bentonitic Clay. Minerals 2016, 6, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040129
Burham N, Sayed M. Adsorption Behavior of Cd2+ and Zn2+ onto Natural Egyptian Bentonitic Clay. Minerals. 2016; 6(4):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040129
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurham, Nagwa, and Mahmoud Sayed. 2016. "Adsorption Behavior of Cd2+ and Zn2+ onto Natural Egyptian Bentonitic Clay" Minerals 6, no. 4: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040129
APA StyleBurham, N., & Sayed, M. (2016). Adsorption Behavior of Cd2+ and Zn2+ onto Natural Egyptian Bentonitic Clay. Minerals, 6(4), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/min6040129