Structural Characterization of the Body Frame and Spicules of a Glass Sponge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. TG-DTA
2.3. NMR Spectroscopy
2.4. Raman and Infrared Spectroscopy
2.5. XRD Analysis
3. Results
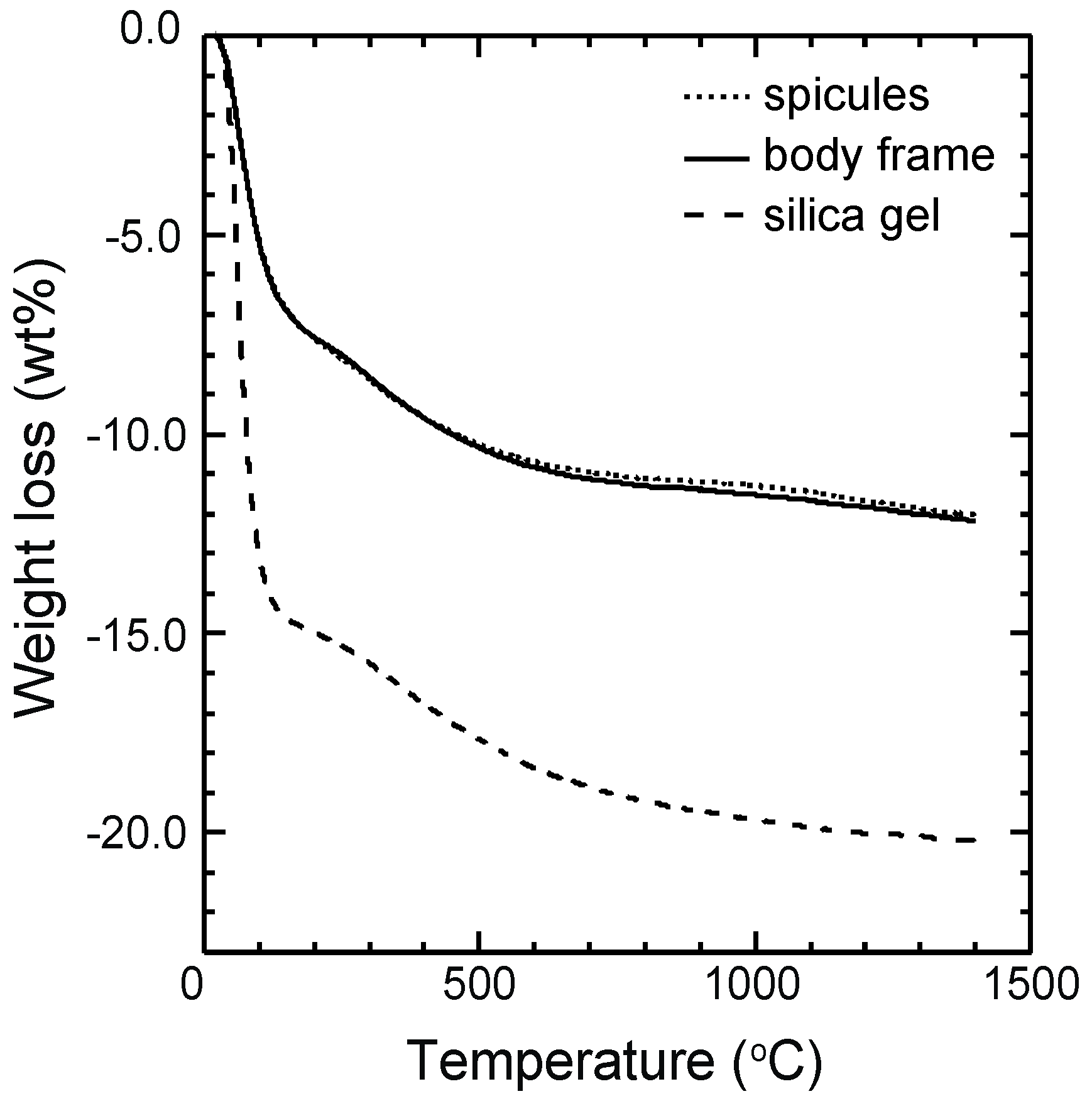
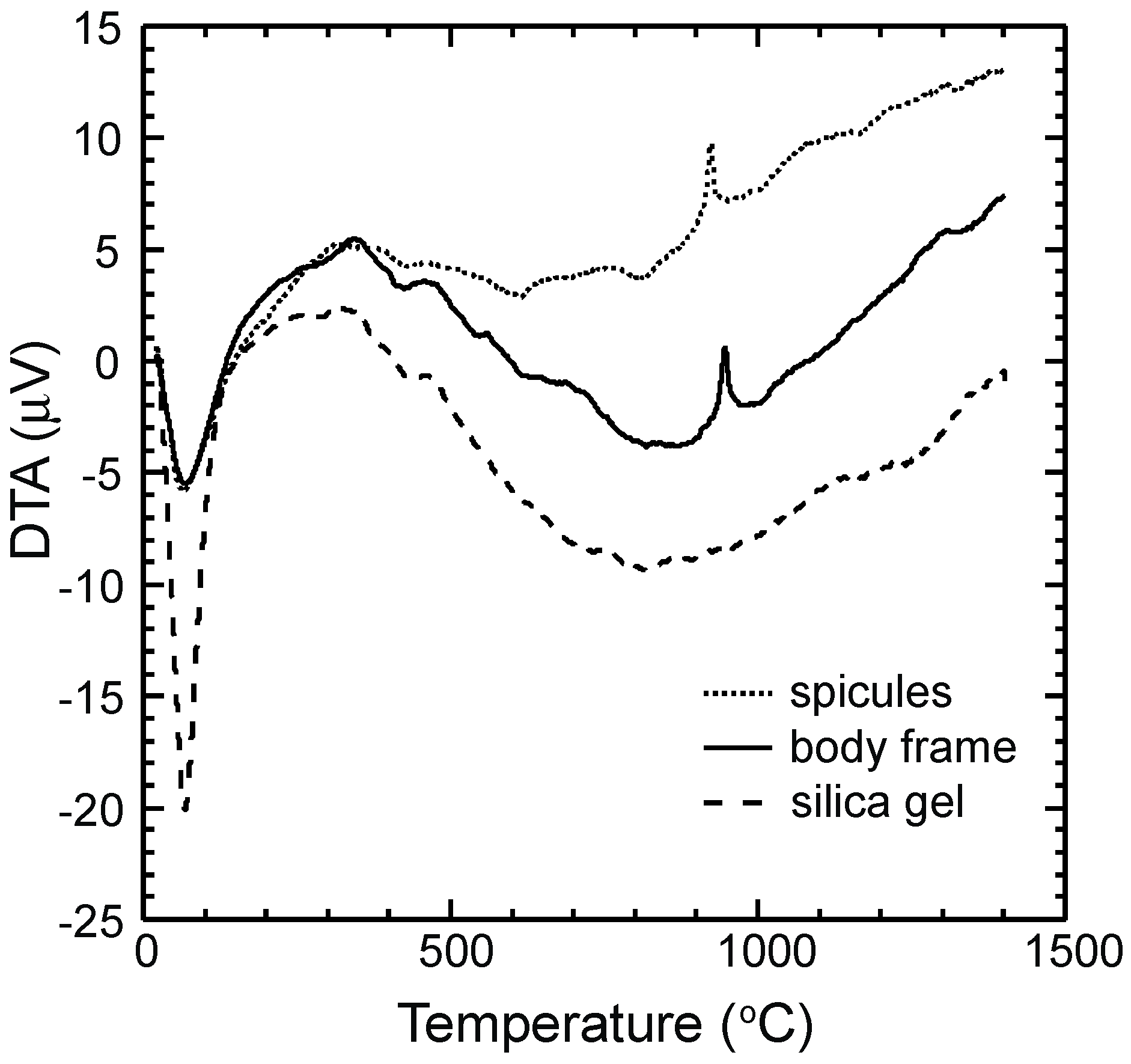
3.1. TG-DTA Curves
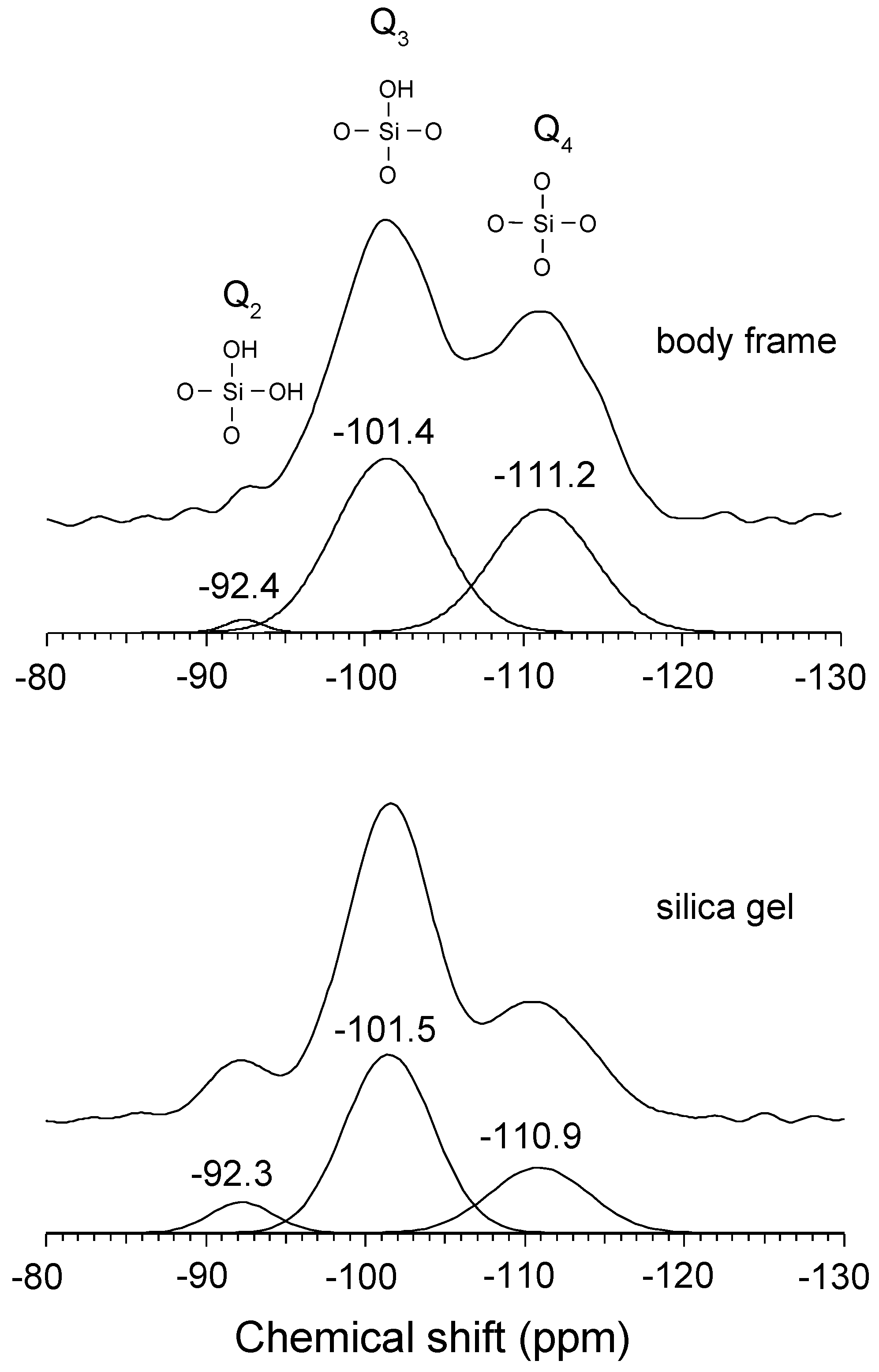
3.2. 1H Static and 29Si {1H} CP-MAS NMR Spectra
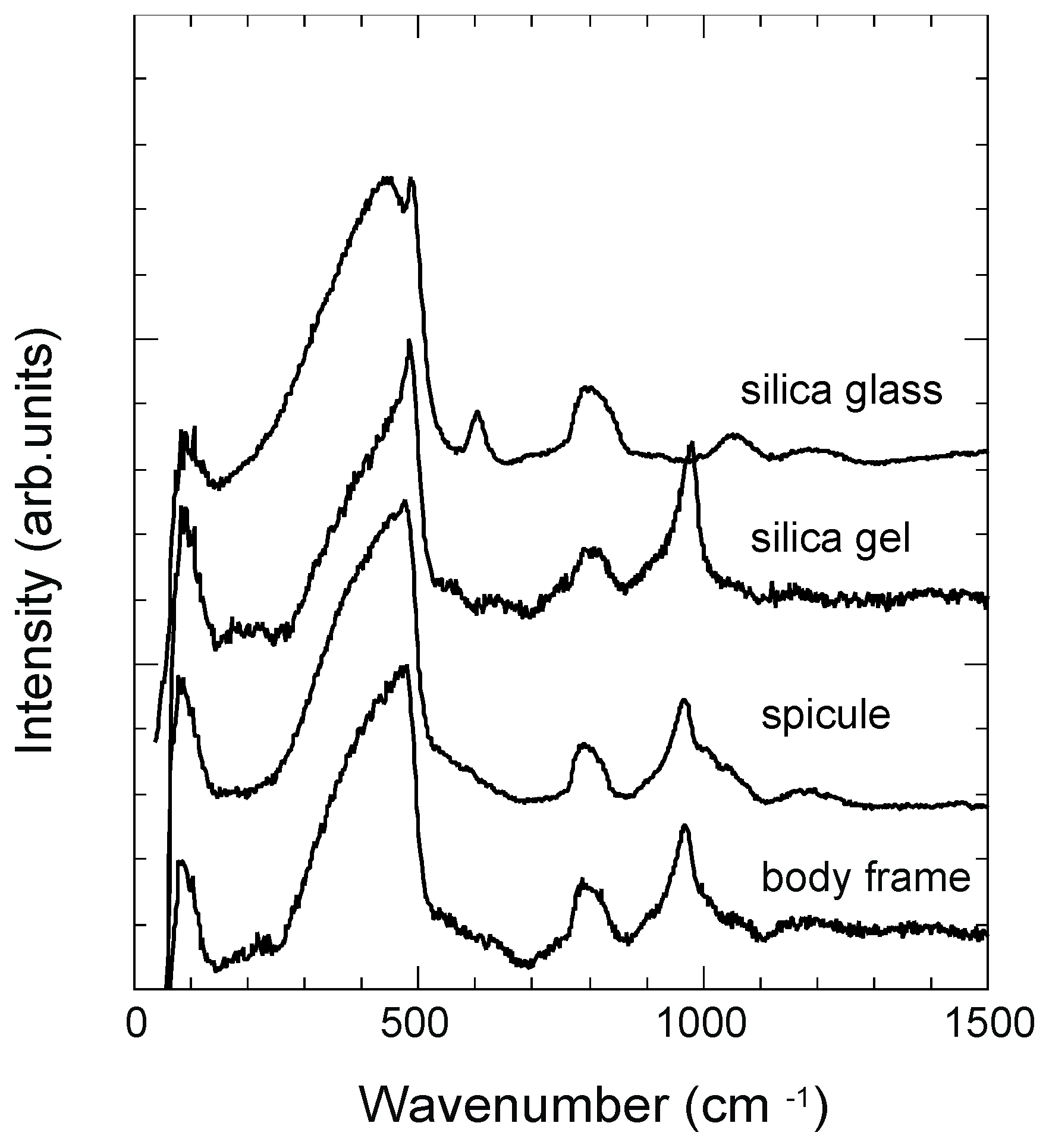
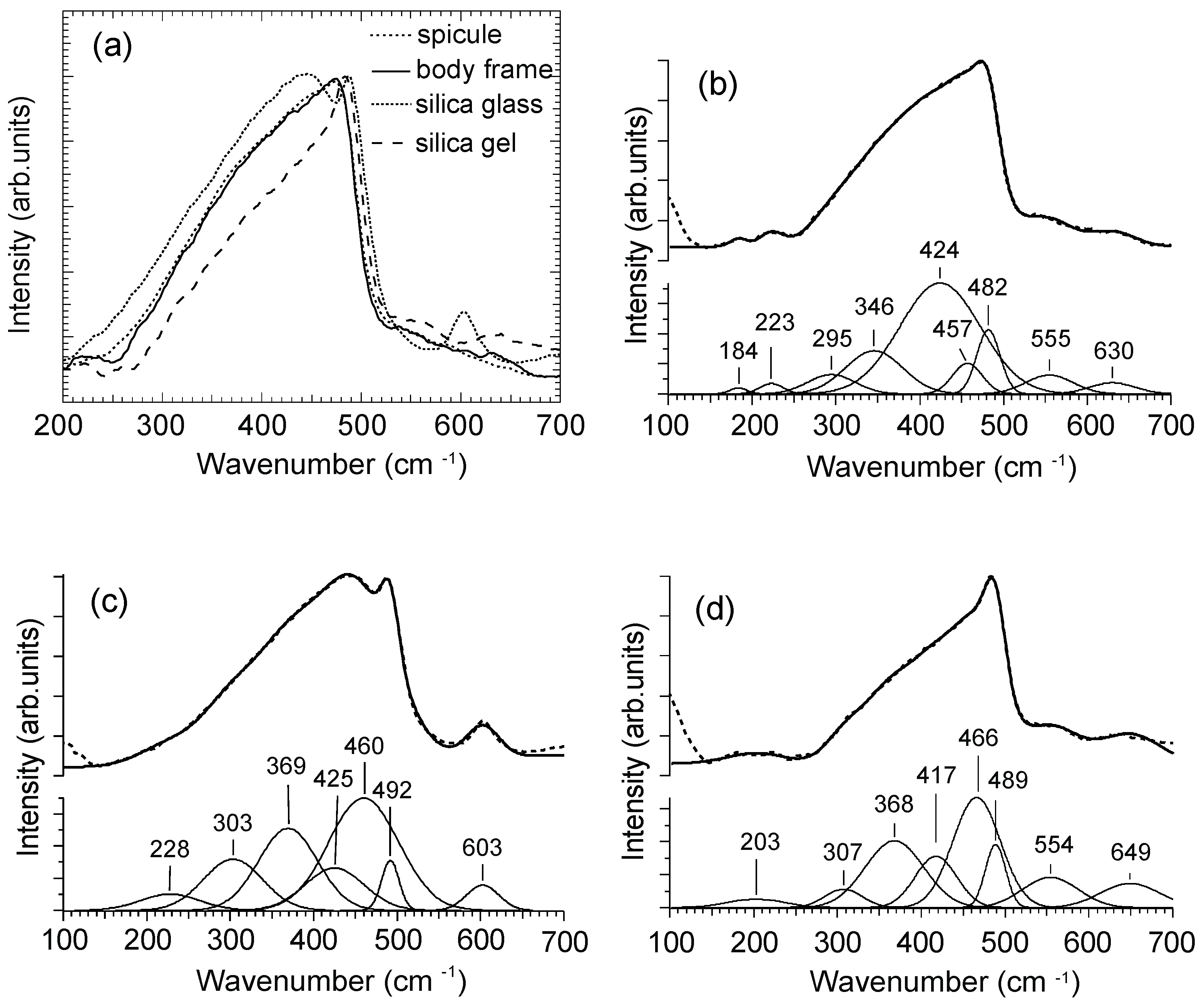
3.3. Raman Spectra
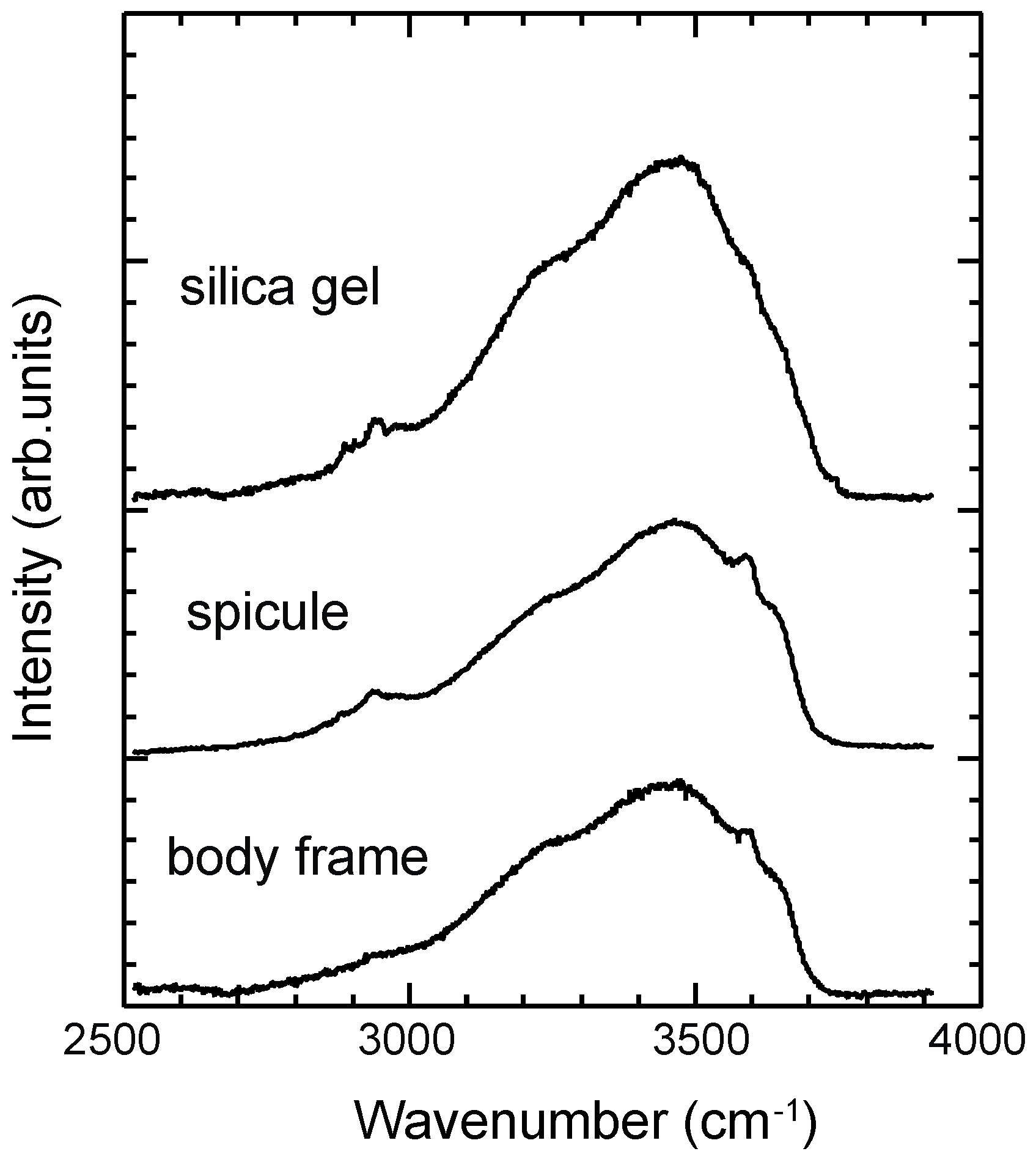
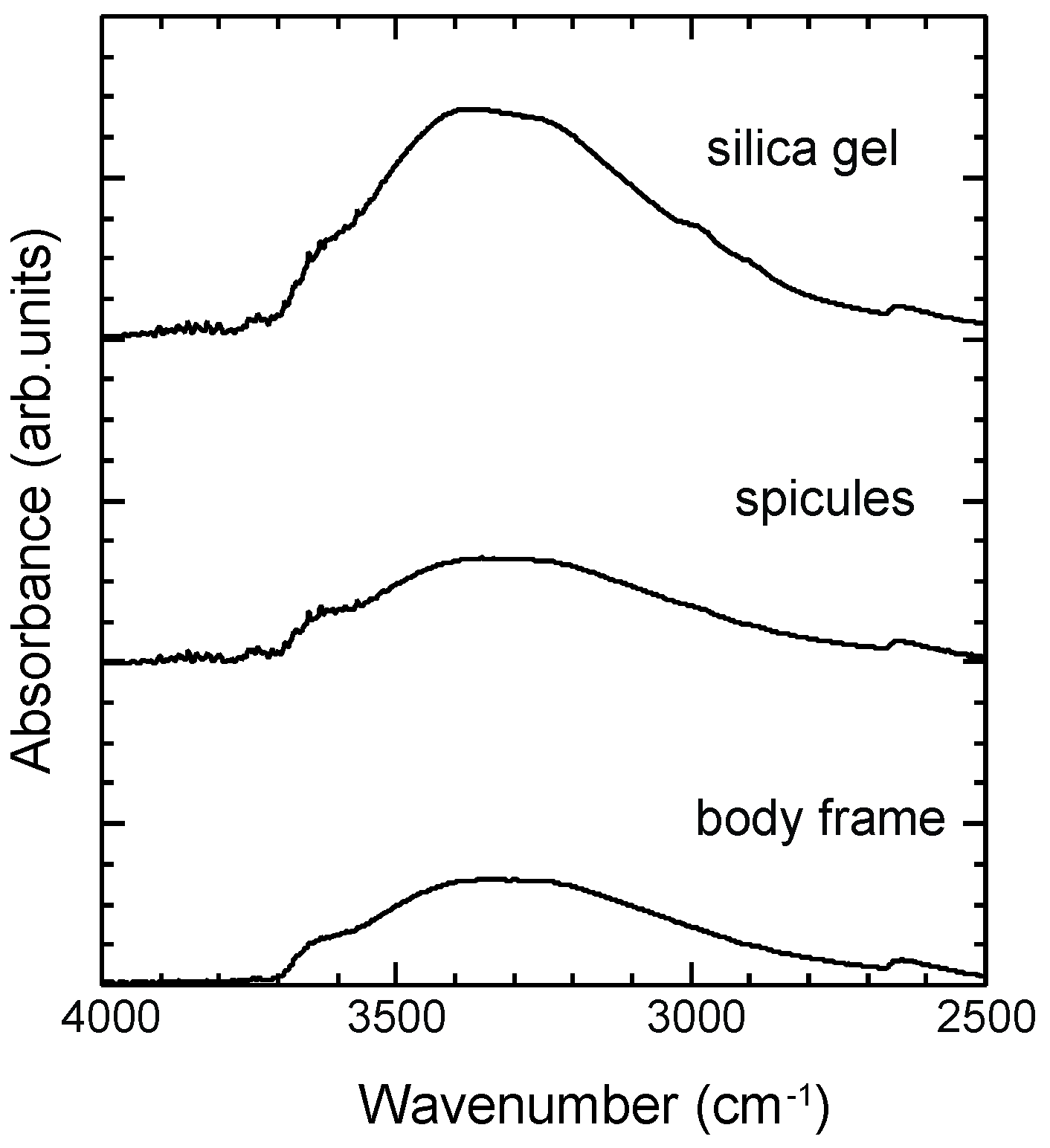
3.4. ATR-IR Spectra
3.5. XRD Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Content and Water Species in Sponge Samples
4.2. Nano-Structure of Spicules and Body Frame of Glass Sponges
5. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Müller, W.E.G.; Wang, X.; Belikov, S.I.; Tremel, W.; Schloßmacher, U.; Natoli, A.; Brandt, D.; Boreiko, A.; Tahir, M.N.; Müller, I.M.; et al. Formation of Siliceous Spicules in Demosponges: Example Suberites domuncula. In Handbook of Biomineralization Biological Aspects and Structure Formation; Bäuerlein, E., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 59–82. ISBN 978-3-527-31804-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, H.; Worch, W. Collagen: A huge matrix in glass sponge flexible spicules of the meter-long Hyalonema sieboldi. In Handbook of Biomineralization Biological Aspects and Structure Formation; Bäuerlein, E., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 23–41. ISBN 978-3-527-31804-9. [Google Scholar]
- Uriz, M.J.; Turon, X.; Becerro, G.; Ageli, G. Siliceous spicules and skeleton frameworks in sponges: Origin, diversity, ultrastructural patterns, and biological functions. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 32, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizenberg, J.; Weaver, J.C.; Thanawala, M.S.; Sundar, V.C.; Morse, D.E.; Fratzl, P. Skeleton of Euplectella sp.: Structural hierarchy from the nanoscale to the macroscale. Science 2005, 309, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woesz, A.; Weaver, J.C.; Kazanci, M.; Dauphin, Y.; Aizenberg, J.; Morse, D.E.; Fratzl, P. Micromechanical properties of biological silica in skeletons of deep-sea sponges. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 2068–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.C.; Aizenberg, J.; Fantner, G.E.; Kisailus, D.; Woesz, A.; Allen, P.; Fields, K.; Porter, M.J.; Zok, F.W.; Hansma, P.K.; et al. Hierarchical assembly of the siliceous skeletal lattice of the hexactinellid sponge Euplectella aspergillum. J. Struct. Biol. 2007, 158, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendron-Badou, A.; Coradin, T.; Maquet, J.; Frohlich, F.; Livage, J. Spectroscopic characterization of biogenic silica. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 316, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.N.; Shimizu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Christiansen, S.C.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D.; Morse, D.E. Silicatein filaments and subunits from a marine sponge direct the polymerization of silica and silicones in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Amano, T.; Bari, M.R.; Weaver, J.C.; Arima, J.; Mori, N. Glassin, a histidine-rich protein from the siliceous skeletal system of the marine sponge Euplectella, directs silica polycondensation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11449–11454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, I.; Aluma, Y.; Ilan, M.; Mastai, Y. Induced crystallization of amorphous biosilica to cristobalite by silicatein. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 2014–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamiya, K.; Nasu, H. Structure and thermal change of alkoxyderived silica gel fibers and films. Ceram. Trans. 1998, 81, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquarello, A.; Roberto, C. Identification of Raman defect Lines as signatures of ring structures in vitreous silica. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 5145–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Okuno, M.; Syono, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Fukuoka, K.; Ishizawa, N. An X-ray diffraction study of shock-wave-densified SiO2 glasses. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2002, 29, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Kieffer, J. Amorphous-amorphous transitions in silica glass. I. Reversible transitions and thermomechanical anomalies. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 224203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerette, M.; Ackerson, M.R.; Thomas, J.; Yuan, F.; Watson, E.B.; Walker, D.; Huang, L. Structure and properties of silica glass densified in cold compression and hot compression. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arasuna, A.; Okuno, M.; Chen, L.; Mashimo, T.; Okudera, H.; Mizukami, T.; Arai, S. Shock-wave compression of silica gel as a model material for comets. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2016, 43, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, M.; Reynard, B.; Shimada, Y.; Syono, Y.; Willaime, C. A Raman spectroscopic study of shock-wave densification of vitreous silica. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1999, 26, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, Y. Structural Changes of Glass Sponge by Heat-Treatment and Compression. Master’s Thesis, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, A.E.; Rienstra, C.M.; Auger, M.; Lakshmi, K.V.; Griffin, R.G. Heteronuclear decoupling in rotating solids. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronnimann, C.E.; Zeigler, R.C.; Maciel, G.E. Proton NMR Study of Dehydration of the Silica Gel Surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 2023–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, H.; Yesinowski, J.P.; Silver, L.A.; Stolper, E.M. Water in silicate glasses: Quantitation and structural studies by 1H Solid echo and MAS-NMR Methods. J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, D.R.; Chuang, I.-S.; Marciel, G.E. Water and the silica surface as studied by variable-temperature High-Resolution 1H NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 6786–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeener, F.L. Planar rings in vitreous silica. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1982, 49, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeener, F.L. Planar rings in glasses. Solid State Commun. 1982, 44, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeener, F.L.; Geissberger, A.E. Vibrational dynamics in 30Sisubstituted vitreous SiO2. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 6199–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Matson, D.W.; Philpotts, J.A.; Roush, T.L. Raman study of the structure of glasses along the join SiO2-GeO2. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1984, 68, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolen, R.H.; Walrafen, G.E. Water and its relation to broken bond defects in fused silica. J. Chem. Phys. 1976, 64, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.A.; Greytak, T.J. Intrinsic surface phonons in amorphous silica. Phys. Rev. B 1979, 20, 3368–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, P. Structural studies of silicate glasses and melts-applications and limitations of Raman spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 1984, 69, 622–644. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K.M.; Tomozawa, M. An infrared spectroscopic study of water-related species in silica glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1996, 201, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anedda, A.; Carbonaro, C.M.; Clemente, F.; Corda, L.; Corpino, R.; Ricci, P.C. Surface hydroxyls in porous silica: A Raman spectroscopy study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2003, 23, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergna, H.E. Colloid chemistry of silica: An overview. In Colloidal Silica: Fundamentals and Applications; Bergna, H.E., Roberts, W.O., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 9–35. ISBN 0-8247-0967-5. [Google Scholar]
- Handke, M.; Mozgawa, W. Vibrational spectroscopy of the amorphous silicates. Vib. Spectrosc. 1993, 5, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, K.; Oka, A.; Nasu, H.; Hashimoto, T. Comparative study of structure of silica gels from different sources. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2000, 19, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesi, H.A.; Jones, A.C. An infrared study of the water-silica gel system. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.S. Surface functionality of amorphous silica by infrared spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. 1958, 62, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orcel, G.; Phalippou, J.; Hench, L.L. Structural changes of silica xerogels during low temperature dehydration. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1986, 88, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graetsch, H.; Flörke, O.W.; Miehe, G. The nature of water in chalcedony and opal-C from Brazilian agate geodes. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1985, 12, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.R. Medium-range structural order in covalent amorphous solids. Nature 1991, 354, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Mammone, J.F.; Nicol, M.F. Raman investigations of ring configurations in vitreous silica. Nature 1981, 292, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, K.J.; Hemley, R.J. Raman spectroscopic study of microcrystalline silica. Am. Mineral. 1994, 79, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Innocenzi, P. Infrared spectroscopy of sol-gel derived silicabased films: A spectra-icrostructure orverview. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 316, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasuna, A.; Okuno, M.; Okudera, H.; Mizukami, T.; Arai, S.; Katayama, S.; Koyano, M.; Ito, N. Structural changes of synthetic opal by heat treatment. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2013, 40, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, F.M.; Grim, R.E.; Graf, R.B. Phase transformations in silica as examined by continuous X-ray diffraction. Am. Mineral. 1961, 46, 196–208. [Google Scholar]
- Sosman, R.B. The Properties of Silica; The Chemical Catalog Company Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1927; p. 856. [Google Scholar]
- Sosman, R.B. New and old phase of silica. Trans. Br. Ceram. Soc. 1955, 54, 655–670. [Google Scholar]
- Graetsch, H. Structural characteristics of opaline and microcrystalline silica minerals. Rev. Mineral. 1994, 29, 209–232. [Google Scholar]





| Samples | Element (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na2O | Al2O3 | SiO2 | SO3 | Cl | K2O | CaO | ZnO | PdO | |
| body frame | 0.31 | 0.02 | 99.20 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.02 | n.d. |
| spicules | 0.26 | 0.04 | 99.30 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.32 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.12 |
| silica glass | n.d. | 0.02 | 99.97 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Samples | Weight Loss Estimated from TG Results (wt %) | 1H NMR (wt %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-200 | 200–600 | 600–1400 | Total | ||
| body frame | 7.25 | 3.89 | 0.88 | 12.02 | 10.5 |
| spicules | 7.37 | 3.73 | 0.94 | 12.04 | - |
| silica gel | 14.84 | 4.34 | 1.03 | 20.21 | 17.2 |
| Samples | Relative Intensities (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q4 | Q3 | Q2 | Q4 / (Q2 + Q3) | |
| body frame | 40.9 | 57.1 | 2.0 | 0.7 |
| silica gel | 26.6 | 65.3 | 8.1 | 0.4 |
| Samples | Q (Å−1) |
|---|---|
| silica glass | 1.51 |
| silica gel | 1.63 |
| spicule | 1.60 |
| body frame | 1.61 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arasuna, A.; Kigawa, M.; Fujii, S.; Endo, T.; Takahashi, K.; Okuno, M. Structural Characterization of the Body Frame and Spicules of a Glass Sponge. Minerals 2018, 8, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8030088
Arasuna A, Kigawa M, Fujii S, Endo T, Takahashi K, Okuno M. Structural Characterization of the Body Frame and Spicules of a Glass Sponge. Minerals. 2018; 8(3):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8030088
Chicago/Turabian StyleArasuna, Akane, Masahito Kigawa, Shunsuke Fujii, Takatsugu Endo, Kenji Takahashi, and Masayuki Okuno. 2018. "Structural Characterization of the Body Frame and Spicules of a Glass Sponge" Minerals 8, no. 3: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8030088
APA StyleArasuna, A., Kigawa, M., Fujii, S., Endo, T., Takahashi, K., & Okuno, M. (2018). Structural Characterization of the Body Frame and Spicules of a Glass Sponge. Minerals, 8(3), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8030088






